Apply Double-Angle and Half-Angle Formulas
|
|
|
- Dylan Hudson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 47 a2, 2A2A; P3A TEKS Apply Doble-Angle and Half-Angle Formlas Before Yo evalated expressions sing sm and difference formlas Now Yo will se doble-angle and half-angle formlas Why? So yo can find the distance an object travels, as in Example 4 Key Vocablary sine, p 852 cosine, p 852 tangent, p 852 In this lesson, yo will se formlas for doble angles (angles of measre 2a) and half angles angles of measre a 2 KEY CONCEPT For Yor Notebook Doble-Angle and Half-Angle Formlas Doble-Angle Formlas sin 2a 5 2 sin a cos a cos 2a sin 2 a tan 2a 5 2 tan a 2 tan 2 a cos 2a 5 2 cos 2 a 2 cos 2a 5 cos 2 a 2 sin 2 a Half-Angle Formlas sin a 56Î 2 cos a cos a 56Î cos a tan a 5 2 cos a sin a The signs of sin a and cos a depend on the tan a 5 sin a cos a qadrant in which a lies E XAMPLE Evalate trigonometric expressions Find the exact vale of (a) cos 658 and (b) tan p 2 a cos cos (3308) b tan p 2 5 tan p 6 2 CHOOSE SIGNS Becase 658 is in Qadrant II and the vale of cosine is negative in Qadrant II, the following formla is sed: cos a 52Î cos a 52Î 2 cos p cos sin p 6 52Î Ï 3 2 Ï Ï Ï Ï 3 47 Apply Doble-Angle and Half-Angle Formlas 955
2 E XAMPLE 2 Evalate trigonometric expressions Given cos a with 3p < a < 2p, find (a) sin 2a and (b) sin a Soltion MULTIPLY AN INEQUALITY In part (b), yo can mltiply throgh the ineqality 3p < a < 2π 2 by to get 3p < a < π So, a is in Qadrant II a Using a Pythagorean identity gives sin a sin 2a 5 2 sin a cos a b Becase a is in Qadrant II, sin a is positive 2 2 sin a 5 2 Î 2 2 cos a 5 2 Î Î Ï 3 3 E XAMPLE 3 TAKS PRACTICE: Mltiple Choice Which expression is eqivalent to 2 cos 2 sin 2? A cos B tan C cot D sin Soltion 2 cos ( 2 2 sin2 ) Use doble-angle formlas sin 2 2 sin cos 5 2 sin2 sin cos Simplify nmerator 5 sin cos Divide ot common factor 2 sin 5 tan Use tangent identity c The correct answer is B A B C D GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples, 2, and 3 Find the exact vale of the expression tan p 8 2 sin 5p 8 3 cos 58 4 Given sin a 5 Ï with 0 < a < p, find cos 2a and tan a 5 Given cos a with π < a < 3p, find sin 2a and sin a Simplify the expression 6 cos 2 sin cos 7 tan 2x tan x 8 sin 2x tan x 956 Chapter 4 Trigonometric Graphs, Identities, and Eqations
3 PATH OF A PROJECTILE The path traveled by an object that is projected at an initial height of h 0 feet, an initial speed of v feet per second, and an initial angle θ is given by y 52 6 v 2 cos 2 x2 (tan )x h 0 where x is the horizontal distance (in feet) and y is the vertical distance (in feet) (This model neglects air resistance) E XAMPLE 4 Derive a trigonometric model SOCCER Write an eqation for the horizontal distance traveled by a soccer ball kicked from grond level (h 0 5 0) at speed v and angle Soltion USE ZERO PRODUCT PROPERTY One soltion of this eqation is x 5 0, which corresponds to the point where the ball leaves the grond This soltion is ignored in later steps, becase the problem reqires finding where the ball lands 2 6 v 2 cos 2 x2 (tan )x Let h x 6 v 2 cos 2 x 2 tan Factor 6 x 2 tan 5 0 v 2 cos 2 Zero prodct property 6 x 5 tan v 2 cos 2 Add tan to each side x 5 6 v 2 cos 2 tan Mltiply each side by 6 v 2 cos 2 x 5 6 v 2 cos sin Use cos tan 5 sin x 5 32 v 2 (2 cos sin ) Rewrite 6 as 32 p 2 x 5 32 v 2 sin 2 Use a doble-angle formla GUIDED PRACTICE for Example 4 9 WHAT IF? Sppose yo kick a soccer ball from grond level with an initial speed of 70 feet per second Can yo make the ball travel 200 feet? 0 REASONING Use the eqation x 5 v 2 sin 2 to explain why the projection 32 angle that maximizes the distance a soccer ball travels is Apply Doble-Angle and Half-Angle Formlas 957
4 E XAMPLE 5 Verify a trigonometric identity Verify the identity cos 3x 5 4 cos 3 x 2 3 cos x cos 3x 5 cos (2x x) Rewrite cos 3x as cos (2x x) 5 cos 2x cos x 2 sin 2x sin x Use a sm formla 5 (2 cos 2 x 2 ) cos x 2 (2 sinx cos x) sin x Use doble-angle formlas 5 2 cos 3 x 2 cos x 2 2 sin 2 x cos x Mltiply 5 2 cos 3 x 2 cos x 2 2( 2 cos 2 x) cos x Use a Pythagorean identity 5 2 cos 3 x 2 cos x 2 2 cos x 2 cos 3 x Distribtive property 5 4 cos 3 x 2 3 cos x Combine like terms E XAMPLE 6 Solve a trigonometric eqation Solve sin 2x 2 cos x 5 0 for 0 x < 2p Soltion sin 2x 2 cos x 5 0 Write original eqation 2 sin x cos x 2 cos x 5 0 Use a doble-angle formla 2cosx (sin x ) 5 0 Factor Set each factor eqal to 0 and solve for x 2cosx 5 0 sin x 5 0 cos x 5 0 sin x 52 x 5 p, 3p x 5 3p CHECK Graph the fnction y 5 sin 2x 2 cos x on a graphing calclator Then se the zero featre to find the x-vales on the interval 0 x < 2π for which y 5 0 The two x-vales are: x 5 p ø 57 and x 5 3p ø 47 Zero X= Y=0 E XAMPLE 7 Find a general soltion Find the general soltion of 2 sin x 5 SOLVE EQUATIONS As seen in Example 7, some eqations that involve doble or half angles can be solved withot resorting to doble- or half-angle formlas 2 sin x 5 Write original eqation sin x 5 Divide each side by 2 x 5 p 6 2nπ or x 5 p 3 4nπ or 5p 6 2nπ General soltion for x 5p 3 4nπ General soltion for x 958 Chapter 4 Trigonometric Graphs, Identities, and Eqations
5 GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 5, 6, and 7 Verify the identity sin 3x 5 3 sin x 2 4 sin 3 x 2 cos 0x 5 2 cos 2 5x Solve the eqation 3 tan 2x tan x 5 0 for 0 x < 2π 4 2 cos x EXERCISES SKILL PRACTICE HOMEWORK KEY 5 WORKED-OUT SOLUTIONS on p WS for Exs 7, 3, and 53 5 TAKS PRACTICE AND REASONING Exs, 27, 54, 55, 57, and 58 VOCABULARY Copy and complete: sin 2a 5 2 sin a cos a is called the? formla for sine 2 WRITING Explain how to determine the sign of the answer when evalating a half-angle formla for sine or cosine EXAMPLE on p 955 for Exs 3 EVALUATING EXPRESSIONS Find the exact vale of the expression 3 sin tan tan (2658) 6 cos (2758) 7 cos p 8 8 sin 5p 2 9 tan 25p sin 2p 2 2 TAKS REASONING What is the exact vale of tan 58? A 2Ï 3 B 22 Ï 3 C Ï 3 D 2 Ï 3 EXAMPLE 2 on p 956 for Exs 2 20 HALF-ANGLE FORMULAS Find the exact vales of sin a, cos a, and tan a 2 cos a 5 4 5, 0 < a < p 3 cos a 5 3, 3p < a < 2π 4 sin a 5 2 3, p < a < π 5 sin a , π < a < 3p 6 ERROR ANALYSIS Describe and correct the error in finding the exact vale of sin a given that cos a with p < a < π sin a 2 52Î 2 cos a 52Î Î Ï 5 5 DOUBLE-ANGLE FORMULAS Find the exact vales of sin 2a, cos 2a, and tan 2a 7 tan a 5 2, π < a < 3p 8 tan a 52Ï 3, p < a < π 9 sin a , π < a < 3p 20 cos a 5 2 5, 2 p < a < 0 47 Apply Doble-Angle and Half-Angle Formlas 959
6 EXAMPLE 3 on p 956 for Exs 2 29 SIMPLIFYING EXPRESSIONS Rewrite the expression withot doble angles or half angles, given that 0 < < p Then simplify the expression 2 cos sin 2 22 sin 2 cos 23 ( 2 tan ) tan 2 24 cos 2 sin 2 cos 25 2tan csc 26 2 sin cos 27 TAKS REASONING Which expression is eqivalent to cot tan? A csc 2 B 2 csc 2 C sec 2 D 2 sec 2 ERROR ANALYSIS Describe and correct the error in simplifying the expression 28 cos 2x cos 2 x 5 cos2 x 2 sin 2 x cos 2 x 29 sin sin (458) 5 cos 2 x 5 sec 2 x 5 2 sin 458 cos Ï 2 Ï 2 5 EXAMPLE 5 on p 958 for Exs VERIFYING IDENTITIES Verify the identity 30 2 cos 2 5 cos 2 3 sin 3 5 sin (4 cos 2 2 ) 32 sin x 5 sin x cos x 33 2 sin 2 x tan x 5 2 sin x 2 sin 2x cos sin 2 csc 35 cos 4 5 cos sin 2 cos 2 sin 4 sin EXAMPLE 6 on p 958 for Exs 36 4 SOLVING EQUATIONS Solve the eqation for 0 x < 2p 36 sin x cos x tan x 2 tan 2x tan x Ï sin x 40 cos 2x 522 cos 2 x 4 2 sin 2x sin x 5 3 cos x EXAMPLE 7 on p 958 for Exs FINDING GENERAL SOLUTIONS Find the general soltion of the eqation 42 cos x 5 43 tan x 5 sin x 44 sin 2x 5 sin x 45 cos 2x cos x cos x sin x sin x cos x REASONING Show that the three doble-angle formlas for cosine are eqivalent 49 CHALLENGE Use the diagram shown at the right to derive the formlas for sin, cos, and tan when is an acte angle 2 cos sin WORKED-OUT SOLUTIONS 5 TAKS PRACTICE AND REASONING
7 PROBLEM SOLVING EXAMPLE 4 on p 957 for Exs GOLF Use the eqation x 5 32 v 2 sin 2 from Example 4 on page 957 to find the horizontal distance a golf ball will travel if it is hit at an initial speed of 50 feet per second and at an initial angle of SOCCER Sppose yo are attempting to kick a soccer ball from grond level Throgh what range of angles can yo kick the soccer ball with an initial speed of 80 feet per second to make it travel at least 50 feet? at classzonecom 52 MULTI-STEP PROBLEM At latitde L, the acceleration de to gravity g (in centimeters per second sqared) at sea level can be approximated by: g sin 2 L sin L cos L a Simplify the eqation above to show that g sin 2 L sin 2L b Graph the fnction from part (a) c Use the graph to approximate the acceleration de to gravity when the latitde is 458, 308, and 08 N Eqator S 45 latitde 30 latitde 0 latitde 53 MACH NUMBER An airplane s Mach nmber M is the ratio of its speed to the speed of sond When an airplane travels faster than the speed of sond, the sond waves form a cone behind the airplane The Mach nmber is related to the apex angle of the cone by the eqation sin 5 Find the angle 2 M that corresponds to a Mach nmber of TAKS REASONING AMercator projection is a map projection of the globe onto a plane that preserves angles On a globe with radis r, consider a point P that has latitde L and longitde T The coordinates (x, y) of the corresponding point P9 on the plane can be fond sing these eqations: P x 5 rt y 5 r lnftan p L P 9 2G y ΠΠ9 x a Use half-angle and sm formlas to show that the eqation for the y-coordinate can be written as y 5 r ln sin L cos L 2 b What is a reasonable domain for the eqation in part (a)? Explain 47 Apply Doble-Angle and Half-Angle Formlas 96
8 55 TAKS REASONING At a basketball game, a person has a chance to win million dollars by making a half cort shot The distance from half cort to the point below the 0-foot-high basketball rim is 475 feet a Write an eqation that models the path of the basketball if the person releases the ball 6 feet high with an initial speed of 40 feet per second b Simplify the eqation Use a calclator to find the angles at which the person can make the half cort shot c Assme the person releases the ball at one of the angles fond in part (b) What other assmption(s) mst yo make to say that the shot is made? 56 CHALLENGE A rectangle is inscribed in a semicircle with radis, as shown What vale of creates the rectangle with the largest area? y (cos, sin ) (cos, 0) x MIXED REVIEW FOR TAKS TAKS PRACTICE at classzonecom REVIEW Skills Review Handbook p 994; TAKS Workbook 57 TAKS PRACTICE MNO and PQR are spplementary angles Which of the following statements is tre? TAKS Obj 0 A MNO 5 PQR B MNO PQR C m MNO m PQR D m MNO m PQR REVIEW Lesson 32; TAKS Workbook 58 TAKS PRACTICE What is the approximate length of arc MN? TAKS Obj 8 F 305 ft G 330 ft P 4 ft 358 M H 396 ft J 550 ft N QUIZ for Lessons Find the exact vale of the expression (pp 949, 955) sin p 2 2 sin (22258) 3 tan (23458) 4 cos p 8 Solve the eqation for 0 x < 2p 5 sin x p sin x 2 p (p 949) 6 cos 2x 5 3 sin x 2 (p 955) Find the exact vales of sin a, cos a, and tan 2a (p 955) 7 tan a 5 3 5, 0 < a < p 8 cos a , π < a < 3p 9 FOOTBALL Use the formla x 5 32 v 2 sin 2 to find the horizontal distance x (in feet) that a football travels if it is kicked from grond level with an initial speed of 25 feet per second at an angle of 308 (p 955) 962 Chapter 4EXTRA PRACTICE for Lesson 47, p 023 ONLINE QUIZ at classzonecom
5-5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Identities
 Find the values of sin 2, cos 2, and tan 2 for the given value and interval. 1. cos =, (270, 360 ) Since on the interval (270, 360 ), one point on the terminal side of θ has x-coordinate 3 and a distance
Find the values of sin 2, cos 2, and tan 2 for the given value and interval. 1. cos =, (270, 360 ) Since on the interval (270, 360 ), one point on the terminal side of θ has x-coordinate 3 and a distance
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
Write Trigonometric Functions and Models
 .5 a.5, a.6, A..B; P..B TEKS Write Trigonometric Functions and Models Before You graphed sine and cosine functions. Now You will model data using sine and cosine functions. Why? So you can model the number
.5 a.5, a.6, A..B; P..B TEKS Write Trigonometric Functions and Models Before You graphed sine and cosine functions. Now You will model data using sine and cosine functions. Why? So you can model the number
Honors Algebra 2 w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals
 Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
5-5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Identities
 Find the values of sin 2, cos 2, tan 2 1 cos for the given value interval, (270, 360 ) Since on the interval (270, 360 ), one point on the terminal side of θ has x-coordinate 3 a distance of 5 units from
Find the values of sin 2, cos 2, tan 2 1 cos for the given value interval, (270, 360 ) Since on the interval (270, 360 ), one point on the terminal side of θ has x-coordinate 3 a distance of 5 units from
Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas
 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas MATH 160, Precalculus J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 011 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to: use multiple-angle formulas to rewrite
Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas MATH 160, Precalculus J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 011 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to: use multiple-angle formulas to rewrite
You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3)
 You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3) LEQ: How do we identify and use basic trigonometric identities to find trigonometric values & use basic trigonometric identities to simplify
You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3) LEQ: How do we identify and use basic trigonometric identities to find trigonometric values & use basic trigonometric identities to simplify
13-1 Practice. Trigonometric Identities. Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < 90. 1, find sin θ. 1. If cos θ = 1, find cot θ.
 1-1 Practice Trigonometric Identities Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < 90. 1. If cos θ = 5 1, find sin θ.. If cot θ = 1, find sin θ.. If tan θ = 4, find sec θ. 4. If tan θ =, find cot
1-1 Practice Trigonometric Identities Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < 90. 1. If cos θ = 5 1, find sin θ.. If cot θ = 1, find sin θ.. If tan θ = 4, find sec θ. 4. If tan θ =, find cot
Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet
 Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet In this unit, students will be able to: Convert angle measures from degrees to radians and radians to degrees. Find the measure of an angle given the lengths of the intercepted
Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet In this unit, students will be able to: Convert angle measures from degrees to radians and radians to degrees. Find the measure of an angle given the lengths of the intercepted
Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities
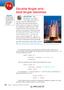 7-4 OBJECTIVE Use the doubleand half-angle identities for the sine, ine, and tangent functions. Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities ARCHITECTURE Mike MacDonald is an architect who designs water fountains.
7-4 OBJECTIVE Use the doubleand half-angle identities for the sine, ine, and tangent functions. Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities ARCHITECTURE Mike MacDonald is an architect who designs water fountains.
Chapter 1 and Section 2.1
 Chapter 1 and Section 2.1 Diana Pell Section 1.1: Angles, Degrees, and Special Triangles Angles Degree Measure Angles that measure 90 are called right angles. Angles that measure between 0 and 90 are called
Chapter 1 and Section 2.1 Diana Pell Section 1.1: Angles, Degrees, and Special Triangles Angles Degree Measure Angles that measure 90 are called right angles. Angles that measure between 0 and 90 are called
Sample Problems. Practice Problems
 Lectre Notes Trigonometric Integrals age Samle Problems Comte each of the following integrals.. sin Assme that a an b are ositive nmbers. 8. csc 5. sec ( ). 3. cos 5 cos sin 9.. sin sin 3 6. + cos. csc.
Lectre Notes Trigonometric Integrals age Samle Problems Comte each of the following integrals.. sin Assme that a an b are ositive nmbers. 8. csc 5. sec ( ). 3. cos 5 cos sin 9.. sin sin 3 6. + cos. csc.
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions. By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh
 Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I
 MAC 1114 Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize the fundamental identities: reciprocal identities, quotient identities,
MAC 1114 Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize the fundamental identities: reciprocal identities, quotient identities,
Math 1205 Trigonometry Review
 Math 105 Trigonometry Review We begin with the unit circle. The definition of a unit circle is: x + y =1 where the center is (0, 0) and the radius is 1. An angle of 1 radian is an angle at the center of
Math 105 Trigonometry Review We begin with the unit circle. The definition of a unit circle is: x + y =1 where the center is (0, 0) and the radius is 1. An angle of 1 radian is an angle at the center of
of the whole circumference.
 TRIGONOMETRY WEEK 13 ARC LENGTH AND AREAS OF SECTORS If the complete circumference of a circle can be calculated using C = 2πr then the length of an arc, (a portion of the circumference) can be found by
TRIGONOMETRY WEEK 13 ARC LENGTH AND AREAS OF SECTORS If the complete circumference of a circle can be calculated using C = 2πr then the length of an arc, (a portion of the circumference) can be found by
Unit 6 Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors
 Unit Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors Multiple Choice Portion SHOW ALL WORK! 1. How many radians are in 1800? 10 10π Name: Per: 180 180π 2. On the unit circle shown, which radian measure is located at ( 2,
Unit Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors Multiple Choice Portion SHOW ALL WORK! 1. How many radians are in 1800? 10 10π Name: Per: 180 180π 2. On the unit circle shown, which radian measure is located at ( 2,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 1203: Trigonometry Dr. Marcel B. Finan. Review Problems for Test #3
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 1203: Trigonometry Dr. Marcel B. Finan Review Problems for Test #3 Exercise 1 The following is one cycle of a trigonometric function. Find an equation of this graph. Exercise
Arkansas Tech University MATH 1203: Trigonometry Dr. Marcel B. Finan Review Problems for Test #3 Exercise 1 The following is one cycle of a trigonometric function. Find an equation of this graph. Exercise
Trigonometric identities
 Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions. The smallest number p with the above property is called the period of the function.
 Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
SECTION 1.5: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 SECTION.5: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS The Unit Circle The unit circle is the set of all points in the xy-plane for which x + y =. Def: A radian is a unit for measuring angles other than degrees and is measured
SECTION.5: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS The Unit Circle The unit circle is the set of all points in the xy-plane for which x + y =. Def: A radian is a unit for measuring angles other than degrees and is measured
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 14A Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 14-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary periodic function cycle period amplitude frequency
14A Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 14-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary periodic function cycle period amplitude frequency
Solutions to Exercises, Section 5.6
 Instructor s Solutions Manual, Section 5.6 Exercise 1 Solutions to Exercises, Section 5.6 1. For θ = 7, evaluate each of the following: (a) cos 2 θ (b) cos(θ 2 ) [Exercises 1 and 2 emphasize that cos 2
Instructor s Solutions Manual, Section 5.6 Exercise 1 Solutions to Exercises, Section 5.6 1. For θ = 7, evaluate each of the following: (a) cos 2 θ (b) cos(θ 2 ) [Exercises 1 and 2 emphasize that cos 2
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas
 Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Name Date Class. Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period
 Name Date Class 14-1 Practice A Graphs of Sine and Cosine Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period. 1.. Use f(x) = sinx or g(x) = cosx as a guide. Identify
Name Date Class 14-1 Practice A Graphs of Sine and Cosine Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period. 1.. Use f(x) = sinx or g(x) = cosx as a guide. Identify
WARM UP. 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) Factor the expression x 2 2x Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing.
 WARM UP Monday, December 8, 2014 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) 2 2. Factor the expression x 2 2x 8 3. Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Distinguish between
WARM UP Monday, December 8, 2014 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) 2 2. Factor the expression x 2 2x 8 3. Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Distinguish between
Trig Identities Packet
 Advanced Math Name Trig Identities Packet = = = = = = = = cos 2 θ + sin 2 θ = sin 2 θ = cos 2 θ cos 2 θ = sin 2 θ + tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ + cot 2 θ = csc 2 θ cot 2 θ = csc
Advanced Math Name Trig Identities Packet = = = = = = = = cos 2 θ + sin 2 θ = sin 2 θ = cos 2 θ cos 2 θ = sin 2 θ + tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ + cot 2 θ = csc 2 θ cot 2 θ = csc
13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions. Section 13.4
 13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 1 13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 2 Key Concept Section 13.4 3 Key Concept Section 13.4 4 Key Concept Section
13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 1 13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 2 Key Concept Section 13.4 3 Key Concept Section 13.4 4 Key Concept Section
Pythagorean Identity. Sum and Difference Identities. Double Angle Identities. Law of Sines. Law of Cosines
 Review for Math 111 Final Exam The final exam is worth 30% (150/500 points). It consists of 26 multiple choice questions, 4 graph matching questions, and 4 short answer questions. Partial credit will be
Review for Math 111 Final Exam The final exam is worth 30% (150/500 points). It consists of 26 multiple choice questions, 4 graph matching questions, and 4 short answer questions. Partial credit will be
Mathematics UNIT FIVE Trigonometry II. Unit. Student Workbook. Lesson 1: Trigonometric Equations Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days
 Mathematics 0- Student Workbook Unit 5 Lesson : Trigonometric Equations Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric Identities I Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric
Mathematics 0- Student Workbook Unit 5 Lesson : Trigonometric Equations Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric Identities I Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric
Trigonometric Graphs and Identities
 Trigonometric Graphs and Identities 1A Exploring Trigonometric Graphs 1-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine 1- Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions 1B Trigonometric Identities Lab Graph Trigonometric Identities
Trigonometric Graphs and Identities 1A Exploring Trigonometric Graphs 1-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine 1- Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions 1B Trigonometric Identities Lab Graph Trigonometric Identities
2. Be able to evaluate a trig function at a particular degree measure. Example: cos. again, just use the unit circle!
 Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
13-3The The Unit Unit Circle
 13-3The The Unit Unit Circle Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 2 Warm Up Find the measure of the reference angle for each given angle. 1. 120 60 2. 225 45 3. 150 30 4. 315 45 Find the exact value
13-3The The Unit Unit Circle Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 2 Warm Up Find the measure of the reference angle for each given angle. 1. 120 60 2. 225 45 3. 150 30 4. 315 45 Find the exact value
Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.
 MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
4-3 Trigonometric Functions on the Unit Circle
 Find the exact values of the five remaining trigonometric functions of θ. 33. tan θ = 2, where sin θ > 0 and cos θ > 0 To find the other function values, you must find the coordinates of a point on the
Find the exact values of the five remaining trigonometric functions of θ. 33. tan θ = 2, where sin θ > 0 and cos θ > 0 To find the other function values, you must find the coordinates of a point on the
# 1,5,9,13,...37 (hw link has all odds)
 February 8, 17 Goals: 1. Recognize trig functions and their integrals.. Learn trig identities useful for integration. 3. Understand which identities work and when. a) identities enable substitution by
February 8, 17 Goals: 1. Recognize trig functions and their integrals.. Learn trig identities useful for integration. 3. Understand which identities work and when. a) identities enable substitution by
Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes. Professor Miguel Ornelas
 Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes Professor Miguel Ornelas 1 M. Ornelas Math 180 Lecture Notes Section 6.1 Section 6.1 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Verify the identity. a. sin x + cos x cot x = csc
Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes Professor Miguel Ornelas 1 M. Ornelas Math 180 Lecture Notes Section 6.1 Section 6.1 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Verify the identity. a. sin x + cos x cot x = csc
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions
 Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
Section 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities
 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities 47 Section 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities Double-Angle Identities Half-Angle Identities This section develops another important set of identities
6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities 47 Section 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities Double-Angle Identities Half-Angle Identities This section develops another important set of identities
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide Section 8.2 and 8.3-1
 8.3-1 Transformation of sine and cosine functions Sections 8.2 and 8.3 Revisit: Page 142; chapter 4 Section 8.2 and 8.3 Graphs of Transformed Sine and Cosine Functions Graph transformations of y = sin
8.3-1 Transformation of sine and cosine functions Sections 8.2 and 8.3 Revisit: Page 142; chapter 4 Section 8.2 and 8.3 Graphs of Transformed Sine and Cosine Functions Graph transformations of y = sin
Name: Period: Date: Math Lab: Explore Transformations of Trig Functions
 Name: Period: Date: Math Lab: Explore Transformations of Trig Functions EXPLORE VERTICAL DISPLACEMENT 1] Graph 2] Explain what happens to the parent graph when a constant is added to the sine function.
Name: Period: Date: Math Lab: Explore Transformations of Trig Functions EXPLORE VERTICAL DISPLACEMENT 1] Graph 2] Explain what happens to the parent graph when a constant is added to the sine function.
Precalculus Second Semester Final Review
 Precalculus Second Semester Final Review This packet will prepare you for your second semester final exam. You will find a formula sheet on the back page; these are the same formulas you will receive for
Precalculus Second Semester Final Review This packet will prepare you for your second semester final exam. You will find a formula sheet on the back page; these are the same formulas you will receive for
Graphs of sin x and cos x
 Graphs of sin x and cos x One cycle of the graph of sin x, for values of x between 0 and 60, is given below. 1 0 90 180 270 60 1 It is this same shape that one gets between 60 and below). 720 and between
Graphs of sin x and cos x One cycle of the graph of sin x, for values of x between 0 and 60, is given below. 1 0 90 180 270 60 1 It is this same shape that one gets between 60 and below). 720 and between
Math 104 Final Exam Review
 Math 04 Final Exam Review. Find all six trigonometric functions of θ if (, 7) is on the terminal side of θ.. Find cosθ and sinθ if the terminal side of θ lies along the line y = x in quadrant IV.. Find
Math 04 Final Exam Review. Find all six trigonometric functions of θ if (, 7) is on the terminal side of θ.. Find cosθ and sinθ if the terminal side of θ lies along the line y = x in quadrant IV.. Find
3. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the cosine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians).
 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Desmos Activity 1. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the sine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians). sin 0 sin π 2 sin π
Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Desmos Activity 1. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the sine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians). sin 0 sin π 2 sin π
MATH Week 10. Ferenc Balogh Winter. Concordia University
 MATH 20 - Week 0 Ferenc Balogh Concordia University 2008 Winter Based on the textbook J. Stuart, L. Redlin, S. Watson, Precalculus - Mathematics for Calculus, 5th Edition, Thomson All figures and videos
MATH 20 - Week 0 Ferenc Balogh Concordia University 2008 Winter Based on the textbook J. Stuart, L. Redlin, S. Watson, Precalculus - Mathematics for Calculus, 5th Edition, Thomson All figures and videos
Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7
 A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Spring 2013 Eliminating Powers From Trig Functions
A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Spring 2013 Eliminating Powers From Trig Functions
The reciprocal identities are obvious from the definitions of the six trigonometric functions.
 The Fundamental Identities: (1) The reciprocal identities: csc = 1 sec = 1 (2) The tangent and cotangent identities: tan = cot = cot = 1 tan (3) The Pythagorean identities: sin 2 + cos 2 =1 1+ tan 2 =
The Fundamental Identities: (1) The reciprocal identities: csc = 1 sec = 1 (2) The tangent and cotangent identities: tan = cot = cot = 1 tan (3) The Pythagorean identities: sin 2 + cos 2 =1 1+ tan 2 =
Trigonometry Review Tutorial Shorter Version
 Author: Michael Migdail-Smith Originally developed: 007 Last updated: June 4, 0 Tutorial Shorter Version Avery Point Academic Center Trigonometric Functions The unit circle. Radians vs. Degrees Computing
Author: Michael Migdail-Smith Originally developed: 007 Last updated: June 4, 0 Tutorial Shorter Version Avery Point Academic Center Trigonometric Functions The unit circle. Radians vs. Degrees Computing
PreCalc: Chapter 6 Test Review
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A PreCalc: Chapter 6 Test Review Short Answer 1. Draw the angle. 135 2. Draw the angle. 3. Convert the angle to a decimal in degrees. Round the answer to two decimal places. 8. If
Name: Class: Date: ID: A PreCalc: Chapter 6 Test Review Short Answer 1. Draw the angle. 135 2. Draw the angle. 3. Convert the angle to a decimal in degrees. Round the answer to two decimal places. 8. If
( x "1) 2 = 25, x 3 " 2x 2 + 5x "12 " 0, 2sin" =1.
 Unit Analytical Trigonometry Classwork A) Verifying Trig Identities: Definitions to know: Equality: a statement that is always true. example:, + 7, 6 6, ( + ) 6 +0. Equation: a statement that is conditionally
Unit Analytical Trigonometry Classwork A) Verifying Trig Identities: Definitions to know: Equality: a statement that is always true. example:, + 7, 6 6, ( + ) 6 +0. Equation: a statement that is conditionally
1 Trigonometry. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 1 Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.2 Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Identify a unit circle and describe
1 Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.2 Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Identify a unit circle and describe
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Math 102 Key Ideas. 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry. 1. Consider the following right triangle: c b
 Math 10 Key Ideas 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry 1. Consider the following right triangle: A c b B θ C a sin θ = b length of side opposite angle θ = c length of hypotenuse cosθ = a length of side adjacent
Math 10 Key Ideas 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry 1. Consider the following right triangle: A c b B θ C a sin θ = b length of side opposite angle θ = c length of hypotenuse cosθ = a length of side adjacent
Right Triangle Trigonometry (Section 4-3)
 Right Triangle Trigonometry (Section 4-3) Essential Question: How does the Pythagorean Theorem apply to right triangle trigonometry? Students will write a summary describing the relationship between the
Right Triangle Trigonometry (Section 4-3) Essential Question: How does the Pythagorean Theorem apply to right triangle trigonometry? Students will write a summary describing the relationship between the
Section 7.6 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 4 Section 7. Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the sine and cosine function. The input values will be the angle in radians so we will be using x is
4 Section 7. Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the sine and cosine function. The input values will be the angle in radians so we will be using x is
13-1 Trigonometric Identities. Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. SOLUTION: 2. If, find cos θ.
 Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < 90 1. If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. 2. If, find cos θ. Since is in the first quadrant, is positive. Thus,. 3. If, find sin θ. Since is in the first quadrant,
Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < 90 1. If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. 2. If, find cos θ. Since is in the first quadrant, is positive. Thus,. 3. If, find sin θ. Since is in the first quadrant,
the input values of a function. These are the angle values for trig functions
 SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
Precalculus ~ Review Sheet
 Period: Date: Precalculus ~ Review Sheet 4.4-4.5 Multiple Choice 1. The screen below shows the graph of a sound recorded on an oscilloscope. What is the period and the amplitude? (Each unit on the t-axis
Period: Date: Precalculus ~ Review Sheet 4.4-4.5 Multiple Choice 1. The screen below shows the graph of a sound recorded on an oscilloscope. What is the period and the amplitude? (Each unit on the t-axis
PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW
 PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW Introduction This review sheet is a summary of most of the main topics that you should already be familiar with from your pre-calculus and trigonometry course(s), and which
PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW Introduction This review sheet is a summary of most of the main topics that you should already be familiar with from your pre-calculus and trigonometry course(s), and which
Unit 5. Algebra 2. Name:
 Unit 5 Algebra 2 Name: 12.1 Day 1: Trigonometric Functions in Right Triangles Vocabulary, Main Topics, and Questions Definitions, Diagrams and Examples Theta Opposite Side of an Angle Adjacent Side of
Unit 5 Algebra 2 Name: 12.1 Day 1: Trigonometric Functions in Right Triangles Vocabulary, Main Topics, and Questions Definitions, Diagrams and Examples Theta Opposite Side of an Angle Adjacent Side of
5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions.notebook. Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs
 Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2
Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2
Trigonometric Identities. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities Difference Identity for Cosine Sum Identity for Cosine Cofunction Identities Applications
5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities Difference Identity for Cosine Sum Identity for Cosine Cofunction Identities Applications
Chapter #2 test sinusoidal function
 Chapter #2 test sinusoidal function Sunday, October 07, 2012 11:23 AM Multiple Choice [ /10] Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. For the function y = sin x,
Chapter #2 test sinusoidal function Sunday, October 07, 2012 11:23 AM Multiple Choice [ /10] Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. For the function y = sin x,
Probability of Independent Events. If A and B are independent events, then the probability that both A and B occur is: P(A and B) 5 P(A) p P(B)
 10.5 a.1, a.5 TEKS Find Probabilities of Independent and Dependent Events Before You found probabilities of compound events. Now You will examine independent and dependent events. Why? So you can formulate
10.5 a.1, a.5 TEKS Find Probabilities of Independent and Dependent Events Before You found probabilities of compound events. Now You will examine independent and dependent events. Why? So you can formulate
Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations
 Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations Lesson Package MHF4U Chapter 4/5 Part 2 Outline Unit Goal: By the end of this unit, you will be able to solve trig equations and prove trig identities.
Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations Lesson Package MHF4U Chapter 4/5 Part 2 Outline Unit Goal: By the end of this unit, you will be able to solve trig equations and prove trig identities.
13-2 Angles of Rotation
 13-2 Angles of Rotation Objectives Draw angles in standard position. Determine the values of the trigonometric functions for an angle in standard position. Vocabulary standard position initial side terminal
13-2 Angles of Rotation Objectives Draw angles in standard position. Determine the values of the trigonometric functions for an angle in standard position. Vocabulary standard position initial side terminal
Year 10 Term 1 Homework
 Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 1 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 6 Year 10 Term 1 Week 6 Homework 1 6.1 Triangle trigonometry................................... 1 6.1.1 The
Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 1 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 6 Year 10 Term 1 Week 6 Homework 1 6.1 Triangle trigonometry................................... 1 6.1.1 The
13-1 Trigonometric Identities. Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. ANSWER: 2. If, find cos θ.
 Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < 90 1. If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. 8. CCSS PERSEVERANCE When unpolarized light passes through polarized sunglass lenses, the intensity of the light is cut
Find the exact value of each expression if 0 < θ < 90 1. If cot θ = 2, find tan θ. 8. CCSS PERSEVERANCE When unpolarized light passes through polarized sunglass lenses, the intensity of the light is cut
Trigonometry Review Page 1 of 14
 Trigonometry Review Page of 4 Appendix D has a trigonometric review. This material is meant to outline some of the proofs of identities, help you remember the values of the trig functions at special values,
Trigonometry Review Page of 4 Appendix D has a trigonometric review. This material is meant to outline some of the proofs of identities, help you remember the values of the trig functions at special values,
Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure. Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles?
 Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles? You re riding on a Ferris wheel and wonder how fast you are traveling. Before you got on the ride, the operator told you
Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles? You re riding on a Ferris wheel and wonder how fast you are traveling. Before you got on the ride, the operator told you
Math 10/11 Honors Section 3.6 Basic Trigonometric Identities
 Math 0/ Honors Section 3.6 Basic Trigonometric Identities 0-0 - SECTION 3.6 BASIC TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Copright all rights reserved to Homework Depot: www.bcmath.ca I) WHAT IS A TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITY?
Math 0/ Honors Section 3.6 Basic Trigonometric Identities 0-0 - SECTION 3.6 BASIC TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Copright all rights reserved to Homework Depot: www.bcmath.ca I) WHAT IS A TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITY?
GRAPHING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 GRAPHING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Section.6B Precalculus PreAP/Dual, Revised 7 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions REVIEW OF GRAPHS 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions A. Equation:
GRAPHING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Section.6B Precalculus PreAP/Dual, Revised 7 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions REVIEW OF GRAPHS 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions A. Equation:
In this section, you will learn the basic trigonometric identities and how to use them to prove other identities.
 4.6 Trigonometric Identities Solutions to equations that arise from real-world problems sometimes include trigonometric terms. One example is a trajectory problem. If a volleyball player serves a ball
4.6 Trigonometric Identities Solutions to equations that arise from real-world problems sometimes include trigonometric terms. One example is a trajectory problem. If a volleyball player serves a ball
cos sin sin 2 60 = 1.
 Name: Class: Date: Use the definitions to evaluate the six trigonometric functions of. In cases in which a radical occurs in a denominator, rationalize the denominator. Suppose that ABC is a right triangle
Name: Class: Date: Use the definitions to evaluate the six trigonometric functions of. In cases in which a radical occurs in a denominator, rationalize the denominator. Suppose that ABC is a right triangle
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions
 Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Section 8 Radian and Degree Measure Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Right Triangle Trigonometry
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Section 8 Radian and Degree Measure Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Right Triangle Trigonometry
1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Exercise 1 Sketch a graph of y = cos(t). Label the multiples of π 2 and π 4 on your plot, as well as the amplitude and the period of the function. (Feel free to sketch the unit
1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Exercise 1 Sketch a graph of y = cos(t). Label the multiples of π 2 and π 4 on your plot, as well as the amplitude and the period of the function. (Feel free to sketch the unit
Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs
 HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 3 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs (2) The Unit Circle (3) Displacement and Terminal Points (5) Significant t-values Coterminal Values of t (7) Reference
HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 3 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs (2) The Unit Circle (3) Displacement and Terminal Points (5) Significant t-values Coterminal Values of t (7) Reference
Algebra 2/Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & 2: Trigonometry Mega-Session. The Unit Circle
 Algebra /Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & : Trigonometry Mega-Session Trigonometry (Definition) - The branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles
Algebra /Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & : Trigonometry Mega-Session Trigonometry (Definition) - The branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles
Geometry Problem Solving Drill 11: Right Triangle
 Geometry Problem Solving Drill 11: Right Triangle Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following points lies on the unit circle? Question #01 A. (1/2, 1/2) B. (1/2, 2/2) C. ( 2/2, 2/2) D. ( 2/2, 3/2) The
Geometry Problem Solving Drill 11: Right Triangle Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following points lies on the unit circle? Question #01 A. (1/2, 1/2) B. (1/2, 2/2) C. ( 2/2, 2/2) D. ( 2/2, 3/2) The
Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions
 HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 5 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions This is a BASIC CALCULATORS ONLY unit. (2) Periodic Functions (3) Graph of the Sine Function (4) Graph of the Cosine Function
HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 5 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions This is a BASIC CALCULATORS ONLY unit. (2) Periodic Functions (3) Graph of the Sine Function (4) Graph of the Cosine Function
Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws
 Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws GRAPHING SINE AND COSINE Graph of sine function: Plotting every angle and its corresponding sine value, which is the y-coordinate, for different angles on the unit
Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws GRAPHING SINE AND COSINE Graph of sine function: Plotting every angle and its corresponding sine value, which is the y-coordinate, for different angles on the unit
Trigonometric Functions. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 1 Trigonometric Functions Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 1.4 Using the Definitions of the Trigonometric Functions Reciprocal Identities Signs and Ranges of Function Values Pythagorean
1 Trigonometric Functions Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 1.4 Using the Definitions of the Trigonometric Functions Reciprocal Identities Signs and Ranges of Function Values Pythagorean
1 Trigonometric Identities
 MTH 120 Spring 2008 Essex County College Division of Mathematics Handout Version 6 1 January 29, 2008 1 Trigonometric Identities 1.1 Review of The Circular Functions At this point in your mathematical
MTH 120 Spring 2008 Essex County College Division of Mathematics Handout Version 6 1 January 29, 2008 1 Trigonometric Identities 1.1 Review of The Circular Functions At this point in your mathematical
WESI 205 Workbook. 1 Review. 2 Graphing in 3D
 1 Review 1. (a) Use a right triangle to compute the distance between (x 1, y 1 ) and (x 2, y 2 ) in R 2. (b) Use this formula to compute the equation of a circle centered at (a, b) with radius r. (c) Extend
1 Review 1. (a) Use a right triangle to compute the distance between (x 1, y 1 ) and (x 2, y 2 ) in R 2. (b) Use this formula to compute the equation of a circle centered at (a, b) with radius r. (c) Extend
MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW version2
 MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW version2 Problems 1 3 refer to triangle ABC, with =. Find the remaining angle(s) and side(s). 1. =50, =25 a) =40,=32.6,=21.0 b) =50,=21.0,=32.6 c) =40,=21.0,=32.6 d) =50,=32.6,=21.0
MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW version2 Problems 1 3 refer to triangle ABC, with =. Find the remaining angle(s) and side(s). 1. =50, =25 a) =40,=32.6,=21.0 b) =50,=21.0,=32.6 c) =40,=21.0,=32.6 d) =50,=32.6,=21.0
Jim Lambers Math 1B Fall Quarter Final Exam Practice Problems
 Jim Lambers Math 1B Fall Quarter 2004-05 Final Exam Practice Problems The following problems are indicative of the types of problems that will appear on the Final Exam, which will be given on Monday, December
Jim Lambers Math 1B Fall Quarter 2004-05 Final Exam Practice Problems The following problems are indicative of the types of problems that will appear on the Final Exam, which will be given on Monday, December
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 5
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY MATH 1205 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY INTRODUCTION 3 1. IDENTITIES AND ADDITION FORMULAS 5 FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES 5 PROVING IDENTITIES
MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY MATH 1205 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY INTRODUCTION 3 1. IDENTITIES AND ADDITION FORMULAS 5 FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES 5 PROVING IDENTITIES
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y
Trigonometric Equations
 Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review. Fall 2017
 MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review Fall 2017 Topics Covered Section 4.1: Angles and Their Measure Section 4.2: Trigonometric Functions Defined on the Unit Circle Section 4.3: Right Triangle Geometry Section 4.4:
MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review Fall 2017 Topics Covered Section 4.1: Angles and Their Measure Section 4.2: Trigonometric Functions Defined on the Unit Circle Section 4.3: Right Triangle Geometry Section 4.4:
2 Event is equally likely to occur or not occur. When all outcomes are equally likely, the theoretical probability that an event A will occur is:
 10.3 TEKS a.1, a.4 Define and Use Probability Before You determined the number of ways an event could occur. Now You will find the likelihood that an event will occur. Why? So you can find real-life geometric
10.3 TEKS a.1, a.4 Define and Use Probability Before You determined the number of ways an event could occur. Now You will find the likelihood that an event will occur. Why? So you can find real-life geometric
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms
 NAME DATE PERIOD Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms Words Formula The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any b and its h. Model Step 1: Write the Step 2: Replace letters with information from picture
NAME DATE PERIOD Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms Words Formula The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any b and its h. Model Step 1: Write the Step 2: Replace letters with information from picture
Name: Which equation is represented in the graph? Which equation is represented by the graph? 1. y = 2 sin 2x 2. y = sin x. 1.
 Name: Print Close Which equation is represented in the graph? Which equation is represented by the graph? y = 2 sin 2x y = sin x y = 2 sin x 4. y = sin 2x Which equation is represented in the graph? 4.
Name: Print Close Which equation is represented in the graph? Which equation is represented by the graph? y = 2 sin 2x y = sin x y = 2 sin x 4. y = sin 2x Which equation is represented in the graph? 4.
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions We know from previously studying the periodicity of the trigonometric functions that the sine and cosine functions repeat themselves after 2 radians.
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions We know from previously studying the periodicity of the trigonometric functions that the sine and cosine functions repeat themselves after 2 radians.
3. (12 %) Find an equation of the tangent plane at the point (2,2,1) to the surface. u = t. Find z t. v = se t.
 EXAM - Math 17 NAME: I.D.: Instrction: Circle yor answers and show all yor work clearly. Messing arond may reslt in losing credits, since the grader may be forced to pick the worst to grade. Soltions with
EXAM - Math 17 NAME: I.D.: Instrction: Circle yor answers and show all yor work clearly. Messing arond may reslt in losing credits, since the grader may be forced to pick the worst to grade. Soltions with
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 0 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometr An angle is in standard position if its verte is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive ais. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 0 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometr An angle is in standard position if its verte is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive ais. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Trigonometry LESSON ONE - Degrees and Radians Lesson Notes
 8 = 6 Trigonometry LESSON ONE - Degrees and Radians Example : Define each term or phrase and draw a sample angle. Angle in standard position. b) Positive and negative angles. Draw. c) Reference angle.
8 = 6 Trigonometry LESSON ONE - Degrees and Radians Example : Define each term or phrase and draw a sample angle. Angle in standard position. b) Positive and negative angles. Draw. c) Reference angle.
Chapter 8. Analytic Trigonometry. 8.1 Trigonometric Identities
 Chapter 8. Analytic Trigonometry 8.1 Trigonometric Identities Fundamental Identities Reciprocal Identities: 1 csc = sin sec = 1 cos cot = 1 tan tan = 1 cot tan = sin cos cot = cos sin Pythagorean Identities:
Chapter 8. Analytic Trigonometry 8.1 Trigonometric Identities Fundamental Identities Reciprocal Identities: 1 csc = sin sec = 1 cos cot = 1 tan tan = 1 cot tan = sin cos cot = cos sin Pythagorean Identities:
