Fiber Bragg grating sequential UV-writing method with real-time interferometric sidediffraction
|
|
|
- Helen Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fiber Bragg grating sequential UV-writing method with real-time interferometric sidediffraction position monitoring Kuei-Chu Hsu Department of Photonics & Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Chiao-Tung University, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan, R.O.C. Lih-Gen Sheu Department of Electronic Engineering, Vanung University, Chung-Li, Tao-Yuan 320, Taiwan, R.O.C. Kai-Ping Chuang Center for Measurement Standards, Industrial Technology Research Institute, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan, R.O.C. Shu-Hui Chang and Yinchieh Lai Department of Photonics & Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Chiao-Tung University, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan, R.O.C. Abstract: This work presents a new sequential UV-writing procedure for fabricating long fiber Bragg grating (FBG) devices. To real-time accurately align the position of every exposed FBG section prior to UV exposure, a single-period reference fiber grating with strong refractive index modulation is probed by applying an interferometric side-diffraction method to measure the grating phase as the position reference. In this way the overlapped FBG sections can be connected section-by-section without obvious phase errors, even when the written index-modulation is weak Optical Society of America OCIS codes: ( ) Interferometry; ( ) Bragg reflectors References and links 1. T. Komukai, K. Tamura, and M. Nakazawa, An efficient 0.04-nm apodized fiber Bragg grating and its application to narrow-band spectral filtering, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 9, (1997). 2. J. T. Kringlebotn, J. L. Archambaut, L. Reekie, and D. N. Payne, Er3+:Yb3+-codoped fiber distributedfeedback laser, Opt. Lett. 19, (1994). 3. Naum K. Berger, Boris Levit, Shimie Atkins, and Baruch Fischer, Repetition-rate multiplication of optical pulses using uniform fiber Bragg gratings, Opt. Commun. 221, (2003). 4. M. J. Cole, W. H. Loh, R. I. Laming, M. N. Zervas and S. Barcelos, Moving fiber/phase mask-scanning beam technique for enhanced flexibility in producing fibre gratings with uniform phase mask, Elect. Lett. 31, (1995). 5. I. Petermann, B. Sahlgren, S. Helmfrid, A. T. Friberg, and P.-Y. Fonjallaz, Fabrication of advanced fiber Bragg gratings by use of sequential writing with a continuous-wave ultraviolet laser source, Appl. Opt. 41, (2002). 6. F. El-Diasty, A. Heaney, and T. Erdogan, Analysis of fiber Bragg gratings by a side-diffraction interference technique, Appl. Opt. 40, (2001). 7. K.-P. Chuang, I. L. Wu and Yinchieh Lai, Interferometric side-diffraction position monitoring technique for writing long fiber Bragg gratings, CLEO/IQEC, CThM6 (2004). 8. Mattias Åslund, John Canning, Leon Poladian, and C. Martijn de Sterke, Novel characterization technique with 0.5 ppm spatial accuracy of fringe period in Bragg gratings, Opt. Express 11, (2003). 9. K.-P. Chuang, Y. Lai, and L.-G. Sheu, Pure apodized phase-shifted fiber Bragg gratings fabricated by a two-beam interferometer with polarization control, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 16, (2004). 10. B.-O. Guan, H.-Y. Tam, X.-M. Tao, and X.-Y. Dong, Highly stable fiber Bragg gratings written in hydrogen-loaded fiber, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 12, (2000). (C) 2005 OSA 16 May 2005 / Vol. 13, No. 10 / OPTICS EXPRESS 3795
2 1. Introduction Advanced fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs) with complex grating structures of arbitrary phase shifts and refractive index profiles have been continuously attractive for many optical communication applications, including narrow-band FBG DWDM OADMs, dispersion compensators, phase-shifted DFB fiber lasers and pulse repetition-rate multiplication [1-3]. Several procedures that can realize long and complex FBG structures have recently been developed, such as the moving-fiber-scanning-beam technique [4] and the sequential writing techniques [5]. In these methods, a conventional laser interferometer is typically utilized to monitor the fiber/uv-beam position during the writing process. However, accumulative position reading errors due to interferometer drift and inaccurate grating period estimation have caused significant difficulties on the fabrication of long-length fiber Bragg gratings. To overcome some of these difficulties, in the present paper we utilize the side-diffraction interference method [6] for real-time monitoring the fiber position accurately during the sequential writing process [7]. The side-diffraction interference technique was originally developed for measuring the variation of the grating period and the refractive-index modulation profile of the exposed FBGs [6, 8]. In the literature it has also been suggested that the method can be used as a position control scheme [8]. However, we believe the present paper is the first experimental report on actually using the method for real-time position monitoring during the FBG fabrication process. By directly measuring the grating phase, we can connect adjacent grating sections with accurate phase alignment. In this work, two real-time side-diffraction position monitoring schemes for fabricating long fiber Bragg gratings are investigated. In the first scheme, the side diffraction position monitoring method that probes the just-exposed grating section has been developed to fabricate single-period fiber Bragg gratings. Because the grating phase of the just-exposed grating section is still affected by the later exposures due to the strongly overlap exposure scheme we use, and because it is difficult to form a clear interference pattern for the sidediffraction measurement when the refractive index modulation is lower than , this simple method is only suitable for fabricating single-period fiber FBGs with reasonable strength index modulation. The second scheme employs a reference fiber Bragg grating with a uniform strong refractive index profile fabricated by using the first scheme. The reference grating is placed in parallel to the exposure fiber on the moving stage. Prior to the UV exposure of every FBG section, the reference fiber grating is probed with the side-diffraction method to determine the grating phase as the reference. The measured value can then provide an accurate fiber position reference during the fabrication process. The second scheme shares the same advantage with the first scheme that the accumulative position measurement errors during the long fiber scan can be avoided. Moreover, it also has the following additional advantages. First of all, long FBGs with weak index modulation can be fabricated. The first scheme fails to do this because the resolution of our side-diffraction monitoring scheme is limited to refractive index modulation. Secondly, phase shifts along the fiber grating can be easily inserted. The first scheme fails to do this because with the insertion of phase shifts, the grating phase of the just-exposed section will still not reach the final value due to the strongly-overlapped exposure method we use [9]. Thirdly, the required reference FBG can be fabricated by a similar setup (the first scheme) or by different methods (i.e., the phase mask method). In principle, the second scheme will be capable of fabricating arbitrary FBG refractive index modulation profiles with arbitrary grating phase shifts. Details of the experimental setups and the achieved results for the proposed schemes will be presented during the following sections. 2. Real-time side-diffraction position monitoring by probing the just-exposed section Our first real-time side-diffraction position monitoring method is by probing the just-exposed fiber grating section. Figure 1(a) shows the schematic diagram. A 5-mW single-polarization He-Ne laser beam is expanded with two spherical lenses to achieve a final beam diameter of roughly 3 mm. It is then divided into two probe beams A and B with a polarization beam (C) 2005 OSA 16 May 2005 / Vol. 13, No. 10 / OPTICS EXPRESS 3796
3 splitter. The function of the first half-wave plate is to control the intensity ratio of these two divided beams. The second half-wave plate rotates the polarization of the probe beam B relative to the probe beam A. Probe beam A is then focused onto the exposed fiber with a spherical lens of 20-cm focal length. The first-order Bragg diffraction of probe beam A is generated under the phase-matching Bragg condition sinθ 1 =n B λ / λ B, where θ 1 is the input angle of the probe beam in air, n B is the effective index of the exposed fiber at the Bragg wavelength λ B, and λ is the wavelength of the probe beam. Probe beam B and diffracted probe beam A are combined at the beam combiner with an interference angle of θ 2. A monochrome CCD camera with a pixel width of 7.15-μm is utilized to record the interference pattern produced by probe beams A and B. The visibility of the interference pattern can be optimized by adjusting the two half-wave plates. A frequency-doubled argon-ion laser launches a CW 244-nm single-polarization ultra-violet (UV) beam into a two-beam interferometer. Exposure of the interference UV beams with the FWHM of 6.5 mm forms a periodic UV intensity pattern onto the exposed fiber to induce a single FBG section. The long fiber Bragg grating is achieved by connecting many strongly-overlapped, equally-spaced, Gaussian-shaped FBG sections with accurate grating phase alignment. A half-wave plate is placed in one path of the two interfering beams to obtain pure apodization (flat DC-index modulation) for the final FBG [9]. The translation stage comprises of a linear motor stage and a piezoelectric translator (PZT) stage with sub-nm position resolution. The accurate alignment of the fiber position is achieved by shifting the translation stage by a given distance and then iteratively fine-tuning the PZT stage according to the grating phase measurement of the justexposed grating section. In our preliminary experimental setup, the position monitoring accuracy of the whole system is better than 4 nm, but the accuracy of the position-seeking feedback control loop is only set to be around 5 nm (1% of the grating period) in order to reduce the required position-seeking time. The measurement accuracy we have readily achieved is two-fold better than the estimated accuracy in Ref.[8]. Fig. 1. (a) Real-time side-diffraction position monitoring setup by probing the just-exposed section. SL: spherical lens; BC: beam combiner; PBS: polarization beam splitter; HWP: half wave plate. (b) Typical interference pattern captured by CCD, the pattern after procedure (filtering+taking-real-part) and the calculated phase distribution. (C) 2005 OSA 16 May 2005 / Vol. 13, No. 10 / OPTICS EXPRESS 3797
4 The intensity of the first-order diffracted probe beam A is denoted as I A, and the intensity of the probe beam B is assumed to be I B. The intensity distribution of the interference fringe on the CCD along the x-axis, which is perpendicular to the bisector of the two interfering beams, is given by θ 2 Iint = I A + I B + 2 I AI B cos[ kx 2sin( ) + δ ] (1) 2 where k=2π/λ is the wave vector, θ 2 is the interfering angle and δ is the phase difference between the two interfering beams. The phase difference δ contains two contributions: δ = δ + δ (2) grating path difference where δ grating is the phase change of the diffracted probe beam A caused by the fiber grating, and δ path difference is the phase change caused by the optical path difference between two probe beams. Since δ path difference is constant during the scan, the grating phase change can be inferred from monitoring the phase difference δ. The interference pattern I int is processed by the Fourier transform to obtain the corresponding spatial frequency spectrum. The spectrum is then filtered to keep only the positive frequency part and is inverse-fourier-transformed back to the original domain. The phase δ can then be identified by taking the arg of the processed data. Figure 1(b) shows the typically resulted periodic pattern captured by the CCD camera (grey solid line), the pattern after the filtering+taking-real-part procedure (grey dotted line) and the obtained phase distribution by taking the arg of the filtered data (bold solid line). For producing single period FBGs, the PZT stage is fine tuned until the just-exposed fiber grating phase distribution obtained in this step is the same as that of last step. The UV-beam shutter is then turned on for writing the present FBG section with a given time duration. In practice, the whole algorithm is implemented with the LabVIEW software for automatically controlling the whole exposure process. As an example, this side diffraction position monitoring method that probes the justexposed section has been employed for preparing a single-period fiber grating with strong index-modulation. The fiber used is the photosensitive fiber (Fibercore PS1500) after 1,900- par hydrogen loading at room temperature for several days. The FWHM of the UV beam is about 6.5 mm and the fiber scan step is about 1mm. The final FBG is produced after a 80- section sequential writing to reach a total grating length about 80 mm. The same sidediffraction method [6] is applied to measure the whole refractive index modulation profile of the fabricated fiber grating. Figure 2 shows the measured result. One can see that the fabricated fiber grating profile is substantially uniform. The optical reflection spectrum in the inset of Fig. 2 shows that the Bragg wavelength is μm and there should be no obvious phase errors. Such a FBG will be used as the reference grating for the scheme in next section. (C) 2005 OSA 16 May 2005 / Vol. 13, No. 10 / OPTICS EXPRESS 3798
5 Fig. 2. Refractive index profile and Bragg wavelength of a uniform fiber grating. 3. Real-time side-diffraction position monitoring by probing the reference grating In the second scheme, the experimental setup includes a reference fiber grating and an exposure fiber which are clamped in parallel on the same moving stage. Figure 3(a) depicts the schematic diagram of the system. The reference grating with a strong and uniform refractive index modulation is prepared in advance with the first scheme. The reference fiber grating under probe is adequately uniform and has a sinusoidal index modulation profile n(x) along its fiber axial direction as 2π x n( x) = n0 + Δn cos( + φ( x)) (3) Λ where n 0 is the average refractive index, Δn is the amplitude of refractive index modulation, Λ is the grating period, and φ(x) describes spatial grating phase. The UV-generated interference period is fine tuned to match the reference fiber grating period, even though this restriction can be relaxed since it will only cause a center-wavelength shift. The accurate alignment of the fiber position is achieved by shifting the translation stage by a given distance and then iteratively fine-tuning the PZT stage according to the reference grating phase measurement. The UV-beam shutter is then turned on for writing the present FBG section with a given time duration. Figure 3(b) reveals the flow chart of the whole operation algorithm. In principle, this method should be able to fabricate long fiber Bragg gratings even when the index-modulation is small and with the option for easy insertion of arbitrary phase shifts. (C) 2005 OSA 16 May 2005 / Vol. 13, No. 10 / OPTICS EXPRESS 3799
6 Fig. 3. (a) Real-time side-diffraction position monitoring setup by probing the reference grating. (b) Flow chart of the algorithm. We have verified the feasibility of the proposed method by two examples. The first example is to fabricate a narrowband, Gaussion apodized FBG with a constant DC refractive index modulation along the whole grating. The reference grating with uniform and strong refractive index modulation is probed to identify the related grating phase information. The FWHM of the UV beam is about 6.5 mm and the fiber scan step is about 1.2 mm. The final FBG is produced after a 58-section sequential writing to reach a total grating length about 70 mm. Before the UV writing process, a DC pre-uv treating process is applied to avoid the nonlinear regime when the exposure UV flux is small [10]. Figure 4(a) shows the reflection and transmission spectra of the exposed FBG. The reflection spectrum has a relatively flat top with the sidelobe level below -20 db. The 3-dB bandwidth of the reflection spectrum is only 0.07 nm. The peak refractive index modulation is estimated to be for this 70-mmlong Gaussian apodized FBG, determined by simulation-fitting. This example demonstrates the feasibility for fabricating long fiber Bragg gratings without noticeable phase errors, even when the written index modulation is below the threshold for reliable side-diffraction measurement. The second example is to fabricate a 40-mm-long, single π-phase-shifted Gaussion apodized FBG with a constant DC refractive-index modulation. The scan step during the exposure is about 0.6 mm and the final FBG is achieved by connecting 70 FBG sections. A π phase shift is inserted into the center of the exposure fiber grating during the fabrication process. Figure 4(b) shows the reflection and transmission spectrum of the exposure fiber. As expected, there is a narrow transmission peak within the stop-band due to the resonance caused by the π-phase-shift. This simple example demonstrates the feasibility of fabricating phase-shifted FBGs with the new scheme. (C) 2005 OSA 16 May 2005 / Vol. 13, No. 10 / OPTICS EXPRESS 3800
7 Fig. 4. (a) Reflection and transmission spectra of a 0.07-nm Gaussian apodized 70-mm long FBG. (b) Reflection and transmission spectra of a 40-mm long, π-phase-shift Gaussian apodized FBG. 4. Conclusion In conclusion, we have proposed and demonstrated a real-time fiber position monitoring method for sequential UV-writing processes by using the interferometric side-diffraction technique. This new method (the second scheme) is capable of fabricating long FBGs with weak index modulation and easily to insert phase shifts along the fiber grating. Furthermore, the required reference FBG can be fabricated by a similar setup (the first scheme) or by different methods (i.e., the phase mask method). Several preliminary examples have been experimentally demonstrated for proving the feasibility of the new method. Hopefully this new method is promising for increasing the accuracy and the ease of fabricating complicated long FBG devices. Acknowledgments This research is partially supported by the National Science Council of the Republic of China under the contract NSC E PAE and NSC E Y. Lai s e- mail address is yclai@mail.nctu.edu.tw. (C) 2005 OSA 16 May 2005 / Vol. 13, No. 10 / OPTICS EXPRESS 3801
Novel fiber Bragg grating fabrication system for long gratings with independent apodization and with local phase and wavelength control
 Novel fiber Bragg grating fabrication system for long gratings with independent apodization and with local phase and wavelength control K. M. Chung, 1,* L. Dong, 2 C. Lu, 3 and H.Y. Tam 1 1 Photonics Research
Novel fiber Bragg grating fabrication system for long gratings with independent apodization and with local phase and wavelength control K. M. Chung, 1,* L. Dong, 2 C. Lu, 3 and H.Y. Tam 1 1 Photonics Research
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique
 S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window
 Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2,3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer and Communications Research Laboratories,
Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2,3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer and Communications Research Laboratories,
Bragg and fiber gratings. Mikko Saarinen
 Bragg and fiber gratings Mikko Saarinen 27.10.2009 Bragg grating - Bragg gratings are periodic perturbations in the propagating medium, usually periodic variation of the refractive index - like diffraction
Bragg and fiber gratings Mikko Saarinen 27.10.2009 Bragg grating - Bragg gratings are periodic perturbations in the propagating medium, usually periodic variation of the refractive index - like diffraction
Thermal treatment method for tuning the lasing wavelength of a DFB fiber laser using coil heaters
 Thermal treatment method for tuning the lasing wavelength of a DFB fiber laser using coil heaters Ha Huy Thanh and Bui Trung Dzung National Center for Technology Progress (NACENTECH) C6-Thanh Xuan Bac-Hanoi-Vietnam
Thermal treatment method for tuning the lasing wavelength of a DFB fiber laser using coil heaters Ha Huy Thanh and Bui Trung Dzung National Center for Technology Progress (NACENTECH) C6-Thanh Xuan Bac-Hanoi-Vietnam
Ultra-short distributed Bragg reflector fiber laser for sensing applications
 Ultra-short distributed Bragg reflector fiber laser for sensing applications Yang Zhang 2, Bai-Ou Guan 1,2,*, and Hwa-Yaw Tam 3 1 Institute of Photonics Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632,
Ultra-short distributed Bragg reflector fiber laser for sensing applications Yang Zhang 2, Bai-Ou Guan 1,2,*, and Hwa-Yaw Tam 3 1 Institute of Photonics Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632,
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Pulse shaping with a phase-shifted fiber Bragg grating for antisymmetric pulse generation
 Pulse shaping with a phase-shifted fiber Bragg grating for antisymmetric pulse generation G. Curatu, S. LaRochelle *, C. Paré **, and P.-A. Bélanger Centre d Optique, Photonique et Lasers, Université Laval,
Pulse shaping with a phase-shifted fiber Bragg grating for antisymmetric pulse generation G. Curatu, S. LaRochelle *, C. Paré **, and P.-A. Bélanger Centre d Optique, Photonique et Lasers, Université Laval,
Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature
 Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature Donghui Zhao.a, Xuewen Shu b, Wei Zhang b, Yicheng Lai a, Lin Zhang a, Ian Bennion a a Photonics Research Group,
Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature Donghui Zhao.a, Xuewen Shu b, Wei Zhang b, Yicheng Lai a, Lin Zhang a, Ian Bennion a a Photonics Research Group,
Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro
 Fiber Bragg Gratings for DWDM Optical Networks Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro Overview Introduction. Fabrication. Physical properties.
Fiber Bragg Gratings for DWDM Optical Networks Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro Overview Introduction. Fabrication. Physical properties.
Design of multichannel DWDM fiber Bragg grating filters by Lagrange multiplier constrained optimization
 Design of multichannel DWDM fiber Bragg grating filters by Lagrange multiplier constrained optimization Cheng-Ling Lee Department of Electro-Optical Engineering, National United University, Miaoli, 36,
Design of multichannel DWDM fiber Bragg grating filters by Lagrange multiplier constrained optimization Cheng-Ling Lee Department of Electro-Optical Engineering, National United University, Miaoli, 36,
High stability multiplexed fibre interferometer and its application on absolute displacement measurement and on-line surface metrology
 High stability multiplexed fibre interferometer and its application on absolute displacement measurement and on-line surface metrology Dejiao Lin, Xiangqian Jiang and Fang Xie Centre for Precision Technologies,
High stability multiplexed fibre interferometer and its application on absolute displacement measurement and on-line surface metrology Dejiao Lin, Xiangqian Jiang and Fang Xie Centre for Precision Technologies,
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING
 CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
Spectral Characteristics of Mechanically Induced of Ultralong Period Fiber Gratings (UPFG) as a Pressure Sensor.
 Spectral Characteristics of Mechanically Induced of Ultralong Period Fiber Gratings (UPFG) as a Pressure Sensor. V. Mishra, V V Dwivedi C.U shah University, Surendranagar, Gujrat Abstract. We report here
Spectral Characteristics of Mechanically Induced of Ultralong Period Fiber Gratings (UPFG) as a Pressure Sensor. V. Mishra, V V Dwivedi C.U shah University, Surendranagar, Gujrat Abstract. We report here
Photonics and Optical Communication
 Photonics and Optical Communication (Course Number 300352) Spring 2007 Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/dknipp/ 1 Photonics and Optical Communication
Photonics and Optical Communication (Course Number 300352) Spring 2007 Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/dknipp/ 1 Photonics and Optical Communication
Add Drop Multiplexing By Dispersion Inverted Interference Coupling
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 8, AUGUST 2002 1585 Add Drop Multiplexing By Dispersion Inverted Interference Coupling Mattias Åslund, Leon Poladian, John Canning, and C. Martijn de Sterke
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 8, AUGUST 2002 1585 Add Drop Multiplexing By Dispersion Inverted Interference Coupling Mattias Åslund, Leon Poladian, John Canning, and C. Martijn de Sterke
Temporal differentiation of optical signals using a phase-shifted fiber Bragg grating
 Temporal differentiation of optical signals using a phase-shifted fiber Bragg grating Naum K. Berger, Boris Levit and Baruch Fischer Department of Electrical Engineering, Technion - Israel Institute of
Temporal differentiation of optical signals using a phase-shifted fiber Bragg grating Naum K. Berger, Boris Levit and Baruch Fischer Department of Electrical Engineering, Technion - Israel Institute of
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 High spectral contrast filtering produced by multiple pass reflections from paired Bragg gratings in PTR glass Daniel Ott*, Marc SeGall, Ivan Divliansky, George Venus, Leonid Glebov CREOL, College of Optics
High spectral contrast filtering produced by multiple pass reflections from paired Bragg gratings in PTR glass Daniel Ott*, Marc SeGall, Ivan Divliansky, George Venus, Leonid Glebov CREOL, College of Optics
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings
 A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter
 Research Online ECU Publications 29 Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter Feng Xiao Mingya Shen Budi Juswardy Kamal Alameh This article was originally published as: Xiao, F., Shen, M., Juswardy,
Research Online ECU Publications 29 Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter Feng Xiao Mingya Shen Budi Juswardy Kamal Alameh This article was originally published as: Xiao, F., Shen, M., Juswardy,
Fabrication of large grating by monitoring the latent fringe pattern
 Fabrication of large grating by monitoring the latent fringe pattern Lijiang Zeng a, Lei Shi b, and Lifeng Li c State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments Department of Precision
Fabrication of large grating by monitoring the latent fringe pattern Lijiang Zeng a, Lei Shi b, and Lifeng Li c State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments Department of Precision
Fang-Wen Sheu *, Yi-Syuan Lu Department of Electrophysics, National Chiayi University, Chiayi 60004, Taiwan ABSTRACT
 Determining the relationship between the refractive-index difference of a coiled single-mode optical fiber and its bending radius by a mode-image analysis method Fang-Wen Sheu *, Yi-Syuan Lu Department
Determining the relationship between the refractive-index difference of a coiled single-mode optical fiber and its bending radius by a mode-image analysis method Fang-Wen Sheu *, Yi-Syuan Lu Department
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber
 Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT
 CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation
 A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer & Communications Research Laboratories,
A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer & Communications Research Laboratories,
Simple interferometric fringe stabilization by CCD-based feedback control
 Simple interferometric fringe stabilization by CCD-based feedback control Preston P. Young and Purnomo S. Priambodo, Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Texas at Arlington, P.O. Box 19016,
Simple interferometric fringe stabilization by CCD-based feedback control Preston P. Young and Purnomo S. Priambodo, Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Texas at Arlington, P.O. Box 19016,
Fiber Lasers for EUV Lithography
 Fiber Lasers for EUV Lithography A. Galvanauskas, Kai Chung Hou*, Cheng Zhu CUOS, EECS Department, University of Michigan P. Amaya Arbor Photonics, Inc. * Currently with Cymer, Inc 2009 International Workshop
Fiber Lasers for EUV Lithography A. Galvanauskas, Kai Chung Hou*, Cheng Zhu CUOS, EECS Department, University of Michigan P. Amaya Arbor Photonics, Inc. * Currently with Cymer, Inc 2009 International Workshop
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Princeton University Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University ABSTRACT
 Phase and Amplitude Control Ability using Spatial Light Modulators and Zero Path Length Difference Michelson Interferometer Michael G. Littman, Michael Carr, Jim Leighton, Ezekiel Burke, David Spergel
Phase and Amplitude Control Ability using Spatial Light Modulators and Zero Path Length Difference Michelson Interferometer Michael G. Littman, Michael Carr, Jim Leighton, Ezekiel Burke, David Spergel
RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 9 18, 29 CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER H. Ahmad, M. Z. Zulkifli, S. F. Norizan,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 9 18, 29 CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER H. Ahmad, M. Z. Zulkifli, S. F. Norizan,
Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating. Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel
 Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel Zhijun Yan *, Pouneh Saffari, Kaiming Zhou, Adedotun Adebay, Lin Zhang Photonic Research Group, Aston
Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel Zhijun Yan *, Pouneh Saffari, Kaiming Zhou, Adedotun Adebay, Lin Zhang Photonic Research Group, Aston
Intensity-modulated and temperature-insensitive fiber Bragg grating vibration sensor
 Intensity-modulated and temperature-insensitive fiber Bragg grating vibration sensor Lan Li, Xinyong Dong, Yangqing Qiu, Chunliu Zhao and Yiling Sun Institute of Optoelectronic Technology, China Jiliang
Intensity-modulated and temperature-insensitive fiber Bragg grating vibration sensor Lan Li, Xinyong Dong, Yangqing Qiu, Chunliu Zhao and Yiling Sun Institute of Optoelectronic Technology, China Jiliang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: /NPHOTON
 Supplementary Methods and Data 1. Apparatus Design The time-of-flight measurement apparatus built in this study is shown in Supplementary Figure 1. An erbium-doped femtosecond fibre oscillator (C-Fiber,
Supplementary Methods and Data 1. Apparatus Design The time-of-flight measurement apparatus built in this study is shown in Supplementary Figure 1. An erbium-doped femtosecond fibre oscillator (C-Fiber,
7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP
 7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP Abstract: In this chapter we describe the use of a common path phase sensitive FDOCT set up. The phase measurements
7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP Abstract: In this chapter we describe the use of a common path phase sensitive FDOCT set up. The phase measurements
Recent Developments in Fiber Optic Spectral White-Light Interferometry
 Photonic Sensors (2011) Vol. 1, No. 1: 62-71 DOI: 10.1007/s13320-010-0014-z Review Photonic Sensors Recent Developments in Fiber Optic Spectral White-Light Interferometry Yi JIANG and Wenhui DING School
Photonic Sensors (2011) Vol. 1, No. 1: 62-71 DOI: 10.1007/s13320-010-0014-z Review Photonic Sensors Recent Developments in Fiber Optic Spectral White-Light Interferometry Yi JIANG and Wenhui DING School
Performance Analysis of Chromatic Dispersion Compensation of a Chirped Fiber Grating on a Differential Phase-shift-keyed Transmission
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 13, No. 1, March 2009, pp. 107-111 DOI: 10.3807/JOSK.2009.13.1.107 Performance Analysis of Chromatic Dispersion Compensation of a Chirped Fiber Grating on a
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 13, No. 1, March 2009, pp. 107-111 DOI: 10.3807/JOSK.2009.13.1.107 Performance Analysis of Chromatic Dispersion Compensation of a Chirped Fiber Grating on a
Mode analysis of Oxide-Confined VCSELs using near-far field approaches
 Annual report 998, Dept. of Optoelectronics, University of Ulm Mode analysis of Oxide-Confined VCSELs using near-far field approaches Safwat William Zaki Mahmoud We analyze the transverse mode structure
Annual report 998, Dept. of Optoelectronics, University of Ulm Mode analysis of Oxide-Confined VCSELs using near-far field approaches Safwat William Zaki Mahmoud We analyze the transverse mode structure
Figure1. To construct a light pulse, the electric component of the plane wave should be multiplied with a bell shaped function.
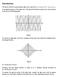 Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin
 Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA
 Optics Communications 252 (2005) 127 131 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA Peng-Chun Peng a, *, Kai-Ming Feng b, Wei-Ren
Optics Communications 252 (2005) 127 131 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA Peng-Chun Peng a, *, Kai-Ming Feng b, Wei-Ren
Outline. Motivation Experimental Set-Up Theory behind the set-up Results Acknowledgements
 Outline Motivation Experimental Set-Up Theory behind the set-up Results Acknowledgements Motivation Attosecond pulses could be used to study time-dependence of atomic dynamics. Greater control of pulse
Outline Motivation Experimental Set-Up Theory behind the set-up Results Acknowledgements Motivation Attosecond pulses could be used to study time-dependence of atomic dynamics. Greater control of pulse
Optimization of Uniform Fiber Bragg Grating Reflection Spectra for Maximum Reflectivity and Narrow Bandwidth
 ISSN (e): 225 35 Vol, 5 Issue,2 February 25 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Optimization of Uniform Fiber Bragg Grating Reflection Spectra for Maximum Reflectivity and
ISSN (e): 225 35 Vol, 5 Issue,2 February 25 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Optimization of Uniform Fiber Bragg Grating Reflection Spectra for Maximum Reflectivity and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
Fibre Bragg Grating. Minoli Arumugam Photonics and Optical Communications Instructor: Prof. Dietmar Knipp Jacobs University Bremen Spring 2007
 Fibre Bragg Grating Minoli Arumugam Photonics and Optical Communications Instructor: Prof. Dietmar Knipp Jacobs University Bremen Spring 2007 What is a Fibre Bragg Grating? It is a type of distributed
Fibre Bragg Grating Minoli Arumugam Photonics and Optical Communications Instructor: Prof. Dietmar Knipp Jacobs University Bremen Spring 2007 What is a Fibre Bragg Grating? It is a type of distributed
Large-Area Interference Lithography Exposure Tool Development
 Large-Area Interference Lithography Exposure Tool Development John Burnett 1, Eric Benck 1 and James Jacob 2 1 Physical Measurements Laboratory, NIST, Gaithersburg, MD, USA 2 Actinix, Scotts Valley, CA
Large-Area Interference Lithography Exposure Tool Development John Burnett 1, Eric Benck 1 and James Jacob 2 1 Physical Measurements Laboratory, NIST, Gaithersburg, MD, USA 2 Actinix, Scotts Valley, CA
Longitudinal mode selection in laser cavity by moiré volume Bragg grating
 Longitudinal mode selection in laser cavity by moiré volume Bragg grating Daniel Ott* a, Vasile Rotar a, Julien Lumeau a, Sergiy Mokhov a, Ivan Divliansky a, Aleksandr Ryasnyanskiy b, Nikolai Vorobiev
Longitudinal mode selection in laser cavity by moiré volume Bragg grating Daniel Ott* a, Vasile Rotar a, Julien Lumeau a, Sergiy Mokhov a, Ivan Divliansky a, Aleksandr Ryasnyanskiy b, Nikolai Vorobiev
External-Cavity Tapered Semiconductor Ring Lasers
 External-Cavity Tapered Semiconductor Ring Lasers Frank Demaria Laser operation of a tapered semiconductor amplifier in a ring-oscillator configuration is presented. In first experiments, 1.75 W time-average
External-Cavity Tapered Semiconductor Ring Lasers Frank Demaria Laser operation of a tapered semiconductor amplifier in a ring-oscillator configuration is presented. In first experiments, 1.75 W time-average
Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification
 Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification Input pulse (single frequency) AWG RF amp Output pulse (chirped) Phase modulator Normalized spectral intensity (db) 64 65 66 67 68 69 1052.4
Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification Input pulse (single frequency) AWG RF amp Output pulse (chirped) Phase modulator Normalized spectral intensity (db) 64 65 66 67 68 69 1052.4
A continuously tunable and filterless optical millimeter-wave generation via frequency octupling
 A continuously tunable and filterless optical millimeter-wave generation via frequency octupling Chun-Ting Lin, 1 * Po-Tsung Shih, 2 Wen-Jr Jiang, 2 Jason (Jyehong) Chen, 2 Peng-Chun Peng, 3 and Sien Chi
A continuously tunable and filterless optical millimeter-wave generation via frequency octupling Chun-Ting Lin, 1 * Po-Tsung Shih, 2 Wen-Jr Jiang, 2 Jason (Jyehong) Chen, 2 Peng-Chun Peng, 3 and Sien Chi
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG)
 Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Temporal coherence characteristics of a superluminescent diode system with an optical feedback mechanism
 VI Temporal coherence characteristics of a superluminescent diode system with an optical feedback mechanism Fang-Wen Sheu and Pei-Ling Luo Department of Applied Physics, National Chiayi University, Chiayi
VI Temporal coherence characteristics of a superluminescent diode system with an optical feedback mechanism Fang-Wen Sheu and Pei-Ling Luo Department of Applied Physics, National Chiayi University, Chiayi
Multi-frequency and multiple phase-shift sinusoidal fringe projection for 3D profilometry
 Multi-frequency and multiple phase-shift sinusoidal fringe projection for 3D profilometry E. B. Li College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Tianjin Universit Tianjin 30007, P. R.
Multi-frequency and multiple phase-shift sinusoidal fringe projection for 3D profilometry E. B. Li College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Tianjin Universit Tianjin 30007, P. R.
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017
 R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
Integrated Photonics based on Planar Holographic Bragg Reflectors
 Integrated Photonics based on Planar Holographic Bragg Reflectors C. Greiner *, D. Iazikov and T. W. Mossberg LightSmyth Technologies, Inc., 86 W. Park St., Ste 25, Eugene, OR 9741 ABSTRACT Integrated
Integrated Photonics based on Planar Holographic Bragg Reflectors C. Greiner *, D. Iazikov and T. W. Mossberg LightSmyth Technologies, Inc., 86 W. Park St., Ste 25, Eugene, OR 9741 ABSTRACT Integrated
FPPO 1000 Fiber Laser Pumped Optical Parametric Oscillator: FPPO 1000 Product Manual
 Fiber Laser Pumped Optical Parametric Oscillator: FPPO 1000 Product Manual 2012 858 West Park Street, Eugene, OR 97401 www.mtinstruments.com Table of Contents Specifications and Overview... 1 General Layout...
Fiber Laser Pumped Optical Parametric Oscillator: FPPO 1000 Product Manual 2012 858 West Park Street, Eugene, OR 97401 www.mtinstruments.com Table of Contents Specifications and Overview... 1 General Layout...
Optical Communications and Networking 朱祖勍. Sept. 25, 2017
 Optical Communications and Networking Sept. 25, 2017 Lecture 4: Signal Propagation in Fiber 1 Nonlinear Effects The assumption of linearity may not always be valid. Nonlinear effects are all related to
Optical Communications and Networking Sept. 25, 2017 Lecture 4: Signal Propagation in Fiber 1 Nonlinear Effects The assumption of linearity may not always be valid. Nonlinear effects are all related to
Photonic Microwave Filter Employing an Opto- VLSI-Based Adaptive Optical Combiner
 Research Online ECU Publications 211 211 Photonic Microwave Filter Employing an Opto- VLSI-Based Adaptive Optical Combiner Haithem Mustafa Feng Xiao Kamal Alameh 1.119/HONET.211.6149818 This article was
Research Online ECU Publications 211 211 Photonic Microwave Filter Employing an Opto- VLSI-Based Adaptive Optical Combiner Haithem Mustafa Feng Xiao Kamal Alameh 1.119/HONET.211.6149818 This article was
Achievement of Arbitrary Bandwidth of a Narrow Bandpass Filter
 Achievement of Arbitrary Bandwidth of a Narrow Bandpass Filter Cheng-Chung ee, Sheng-ui Chen, Chien-Cheng Kuo and Ching-Yi Wei 2 Department of Optics and Photonics/ Thin Film Technology Center, National
Achievement of Arbitrary Bandwidth of a Narrow Bandpass Filter Cheng-Chung ee, Sheng-ui Chen, Chien-Cheng Kuo and Ching-Yi Wei 2 Department of Optics and Photonics/ Thin Film Technology Center, National
Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser
 28 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/Vol. 17, No. 1/January 2000 Man et al. Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser W. S. Man, H. Y. Tam, and
28 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/Vol. 17, No. 1/January 2000 Man et al. Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser W. S. Man, H. Y. Tam, and
Development of innovative fringe locking strategies for vibration-resistant white light vertical scanning interferometry (VSI)
 Development of innovative fringe locking strategies for vibration-resistant white light vertical scanning interferometry (VSI) Liang-Chia Chen 1), Abraham Mario Tapilouw 1), Sheng-Lih Yeh 2), Shih-Tsong
Development of innovative fringe locking strategies for vibration-resistant white light vertical scanning interferometry (VSI) Liang-Chia Chen 1), Abraham Mario Tapilouw 1), Sheng-Lih Yeh 2), Shih-Tsong
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3000 cm 1
 Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression
 Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
DC Index Shifted Dual Grating Based Superstructure Fiber Bragg Grating as Multichannel FBG and Multiparameter Sensor
 IJCTA Vol.8, No.1, Jan-June 2015, Pp.208-212 International Sciences Press, India DC Index Shifted Dual Grating Based Superstructure Fiber Bragg Grating as Multichannel FBG and Multiparameter Sensor Somnath
IJCTA Vol.8, No.1, Jan-June 2015, Pp.208-212 International Sciences Press, India DC Index Shifted Dual Grating Based Superstructure Fiber Bragg Grating as Multichannel FBG and Multiparameter Sensor Somnath
High-Speed Optical Modulators and Photonic Sideband Management
 114 High-Speed Optical Modulators and Photonic Sideband Management Tetsuya Kawanishi National Institute of Information and Communications Technology 4-2-1 Nukui-Kita, Koganei, Tokyo, Japan Tel: 81-42-327-7490;
114 High-Speed Optical Modulators and Photonic Sideband Management Tetsuya Kawanishi National Institute of Information and Communications Technology 4-2-1 Nukui-Kita, Koganei, Tokyo, Japan Tel: 81-42-327-7490;
Single-Frequency, 2-cm, Yb-Doped Silica-Fiber Laser
 Single-Frequency, 2-cm, Yb-Doped Silica-Fiber Laser W. Guan and J. R. Marciante University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics The Institute of Optics Frontiers in Optics 2006 90th OSA Annual
Single-Frequency, 2-cm, Yb-Doped Silica-Fiber Laser W. Guan and J. R. Marciante University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics The Institute of Optics Frontiers in Optics 2006 90th OSA Annual
Simultaneous strain and temperature fiber grating laser sensor based on radio-frequency measurement
 Simultaneous strain and temperature fiber grating laser sensor based on radio-frequency measurement Yan-Nan Tan, 1,2 Yang Zhang, 1 Long Jin, 2 and Bai-Ou Guan 2,* 1 PolyU-DUT Joint Research Center for
Simultaneous strain and temperature fiber grating laser sensor based on radio-frequency measurement Yan-Nan Tan, 1,2 Yang Zhang, 1 Long Jin, 2 and Bai-Ou Guan 2,* 1 PolyU-DUT Joint Research Center for
Spectral Characteristics of Uniform Fiber Bragg Grating With Different Grating Length and Refractive Index Variation
 Spectral Characteristics of Uniform Fiber Bragg Grating With Different Grating Length and efractive Index Variation Chiranjit Ghosh 1, Quazi Md. Alfred 2, Biswajit Ghosh 3 ME (EIE) Student, University
Spectral Characteristics of Uniform Fiber Bragg Grating With Different Grating Length and efractive Index Variation Chiranjit Ghosh 1, Quazi Md. Alfred 2, Biswajit Ghosh 3 ME (EIE) Student, University
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide
 Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
Observational Astronomy
 Observational Astronomy Instruments The telescope- instruments combination forms a tightly coupled system: Telescope = collecting photons and forming an image Instruments = registering and analyzing the
Observational Astronomy Instruments The telescope- instruments combination forms a tightly coupled system: Telescope = collecting photons and forming an image Instruments = registering and analyzing the
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance
 Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film
 Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film Hisashi Akiyama 1, Osami Sasaki 2, and Takamasa Suzuki
Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film Hisashi Akiyama 1, Osami Sasaki 2, and Takamasa Suzuki
E LECTROOPTICAL(EO)modulatorsarekeydevicesinoptical
 286 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 26, NO. 2, JANUARY 15, 2008 Design and Fabrication of Sidewalls-Extended Electrode Configuration for Ridged Lithium Niobate Electrooptical Modulator Yi-Kuei Wu,
286 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 26, NO. 2, JANUARY 15, 2008 Design and Fabrication of Sidewalls-Extended Electrode Configuration for Ridged Lithium Niobate Electrooptical Modulator Yi-Kuei Wu,
Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength Holography
 Reprinted from APPLIED OPTICS. Vol. 10, page 2113, September 1971 Copyright 1971 by the Optical Society of America and reprinted by permission of the copyright owner Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength
Reprinted from APPLIED OPTICS. Vol. 10, page 2113, September 1971 Copyright 1971 by the Optical Society of America and reprinted by permission of the copyright owner Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength
High Energy Non - Collinear OPA
 High Energy Non - Collinear OPA Basics of Operation FEATURES Pulse Duration less than 10 fs possible High Energy (> 80 microjoule) Visible Output Wavelength Tuning Computer Controlled Tuning Range 250-375,
High Energy Non - Collinear OPA Basics of Operation FEATURES Pulse Duration less than 10 fs possible High Energy (> 80 microjoule) Visible Output Wavelength Tuning Computer Controlled Tuning Range 250-375,
A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs
 A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs Yue Tian, Qingjiang Chang, and Yikai Su * State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department
A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs Yue Tian, Qingjiang Chang, and Yikai Su * State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department
Fabrication of microstructures on photosensitive glass using a femtosecond laser process and chemical etching
 Fabrication of microstructures on photosensitive glass using a femtosecond laser process and chemical etching C. W. Cheng* 1, J. S. Chen* 2, P. X. Lee* 2 and C. W. Chien* 1 *1 ITRI South, Industrial Technology
Fabrication of microstructures on photosensitive glass using a femtosecond laser process and chemical etching C. W. Cheng* 1, J. S. Chen* 2, P. X. Lee* 2 and C. W. Chien* 1 *1 ITRI South, Industrial Technology
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus
 Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) phase stabilization. (a) DC output of the MZI with and without phase stabilization. (b) Performance of MZI stabilization
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) phase stabilization. (a) DC output of the MZI with and without phase stabilization. (b) Performance of MZI stabilization
An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm
 An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm Ma Yangwu *, Liang Di ** Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Lab of Modern Optical
An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm Ma Yangwu *, Liang Di ** Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Lab of Modern Optical
Diffractive optical elements for high gain lasers with arbitrary output beam profiles
 Diffractive optical elements for high gain lasers with arbitrary output beam profiles Adam J. Caley, Martin J. Thomson 2, Jinsong Liu, Andrew J. Waddie and Mohammad R. Taghizadeh. Heriot-Watt University,
Diffractive optical elements for high gain lasers with arbitrary output beam profiles Adam J. Caley, Martin J. Thomson 2, Jinsong Liu, Andrew J. Waddie and Mohammad R. Taghizadeh. Heriot-Watt University,
NORIA: flexible automation in Fiber Bragg manufacturing
 NORIA: flexible automation in Fiber Bragg manufacturing REMCO NIEUWLAND, 1 ROBERT RYLANDER, 2 AND PER KARLSSON 2,* 1 Hittech Multin B.V., Laan van Ypenburg 6,2497 GB, The Hague, The Netherlands 2 NorthLab
NORIA: flexible automation in Fiber Bragg manufacturing REMCO NIEUWLAND, 1 ROBERT RYLANDER, 2 AND PER KARLSSON 2,* 1 Hittech Multin B.V., Laan van Ypenburg 6,2497 GB, The Hague, The Netherlands 2 NorthLab
Design of a digital holographic interferometer for the. ZaP Flow Z-Pinch
 Design of a digital holographic interferometer for the M. P. Ross, U. Shumlak, R. P. Golingo, B. A. Nelson, S. D. Knecht, M. C. Hughes, R. J. Oberto University of Washington, Seattle, USA Abstract The
Design of a digital holographic interferometer for the M. P. Ross, U. Shumlak, R. P. Golingo, B. A. Nelson, S. D. Knecht, M. C. Hughes, R. J. Oberto University of Washington, Seattle, USA Abstract The
Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA
 Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA Abstract: Speckle interferometry (SI) has become a complete technique over the past couple of years and is widely used in many branches of
Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA Abstract: Speckle interferometry (SI) has become a complete technique over the past couple of years and is widely used in many branches of
Single-longitudinal mode laser structure based on a very narrow filtering technique
 Single-longitudinal mode laser structure based on a very narrow filtering technique L. Rodríguez-Cobo, 1,* M. A. Quintela, 1 S. Rota-Rodrigo, 2 M. López-Amo 2 and J. M. López-Higuera 1 1 Photonics Engineering
Single-longitudinal mode laser structure based on a very narrow filtering technique L. Rodríguez-Cobo, 1,* M. A. Quintela, 1 S. Rota-Rodrigo, 2 M. López-Amo 2 and J. M. López-Higuera 1 1 Photonics Engineering
Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks
 363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices
 644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
Title. Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori. CitationOptics Express, 18(5): Issue Date Doc URL.
 Title A design method of a fiber-based mode multi/demultip Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 18(5): 4709-4716 Issue Date 2010-03-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/46825
Title A design method of a fiber-based mode multi/demultip Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 18(5): 4709-4716 Issue Date 2010-03-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/46825
Fabrication of Extremely Short Length Fiber Bragg Gratings for Sensor Applications
 Fabrication of Extremely Short Length Fiber Bragg Gratings for Sensor Applications Meng-Chou Wu, Robert S. Rogowski, and Ken K. Tedjojuwono NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, Virginia, USA m.c.wu@larc.nasa.gov
Fabrication of Extremely Short Length Fiber Bragg Gratings for Sensor Applications Meng-Chou Wu, Robert S. Rogowski, and Ken K. Tedjojuwono NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, Virginia, USA m.c.wu@larc.nasa.gov
Optical monitoring technique based on scanning the gain profiles of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers for WDM networks
 Optics Communications () 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Optical monitoring technique based on scanning the gain profiles of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers for WDM networks Chien-Hung Yeh *, Chien-Chung
Optics Communications () 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Optical monitoring technique based on scanning the gain profiles of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers for WDM networks Chien-Hung Yeh *, Chien-Chung
Width of the apodization area in the case of diffractive optical elements with variable efficiency
 Width of the apodization area in the case of diffractive optical elements with variable efficiency Tomasz Osuch 1, Zbigniew Jaroszewicz 1,, Andrzej Kołodziejczyk 3 1 National Institute of Telecommunications,
Width of the apodization area in the case of diffractive optical elements with variable efficiency Tomasz Osuch 1, Zbigniew Jaroszewicz 1,, Andrzej Kołodziejczyk 3 1 National Institute of Telecommunications,
Generation of High-order Group-velocity-locked Vector Solitons
 Generation of High-order Group-velocity-locked Vector Solitons X. X. Jin, Z. C. Wu, Q. Zhang, L. Li, D. Y. Tang, D. Y. Shen, S. N. Fu, D. M. Liu, and L. M. Zhao, * Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Laser
Generation of High-order Group-velocity-locked Vector Solitons X. X. Jin, Z. C. Wu, Q. Zhang, L. Li, D. Y. Tang, D. Y. Shen, S. N. Fu, D. M. Liu, and L. M. Zhao, * Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Laser
Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method.
 PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter
 Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L.
 Sensors & Transducers 04 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Dense Wavelength Division (De) Multiplexers Based on Fiber Bragg Gratings S. BENAMEUR, M. KANDOUCI, C. AUPETIT-THELEMOT,
Sensors & Transducers 04 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Dense Wavelength Division (De) Multiplexers Based on Fiber Bragg Gratings S. BENAMEUR, M. KANDOUCI, C. AUPETIT-THELEMOT,
Investigation of some critical aspects of on-line surface. measurement by a wavelength-division-multiplexing. technique
 Investigation of some critical aspects of on-line surface measurement by a wavelength-division-multiplexing technique Xiangqian Jiang 1, Dejiao Lin 1, Liam Blunt 1, Wei Zhang 2, Lin Zhang 2 1 Center for
Investigation of some critical aspects of on-line surface measurement by a wavelength-division-multiplexing technique Xiangqian Jiang 1, Dejiao Lin 1, Liam Blunt 1, Wei Zhang 2, Lin Zhang 2 1 Center for
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers
 Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
To generate a broadband light source by using mutually injection-locked Fabry-Perot laser diodes
 To generate a broadband light source by using mutually injection-locked Fabry-Perot laser diodes Cheng-Ling Ying 1, Yu-Chieh Chi 2, Chia-Chin Tsai 3, Chien-Pen Chuang 3, and Hai-Han Lu 2a) 1 Department
To generate a broadband light source by using mutually injection-locked Fabry-Perot laser diodes Cheng-Ling Ying 1, Yu-Chieh Chi 2, Chia-Chin Tsai 3, Chien-Pen Chuang 3, and Hai-Han Lu 2a) 1 Department
A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier
 Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2004 Vol.47 No.6 767 772 767 A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier ZHU Heyuan, XU Guang, WANG Tao, QIAN Liejia & FAN Dianyuan State
Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2004 Vol.47 No.6 767 772 767 A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier ZHU Heyuan, XU Guang, WANG Tao, QIAN Liejia & FAN Dianyuan State
