Exercise 5: PWM and Control Theory
|
|
|
- Augustine Summers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exercise 5: PWM and Control Theory Overview In the previous sessions, we have seen how to use the input capture functionality of a microcontroller to capture external events. This functionality can also be used to measure the frequency of external signals (the measurement of the button press time was a very simple example for this scenario). In this exercise, we will learn how to generate control signals for driving external devices and how to combine both features. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is an efficient way to control analog circuits using digital signals. It is used in a wide variety of applications. As its name suggests, the control information is modulated in the width of a pulse. Figure 1 depicts three example PWM signals. Signal a) is a PWM signal with 25 % duty cycle, that is, the signal is high for one quarter of the time in one period and is low for the rest of the time. Signals b) and c) have a duty cycle of 50 % and 75 %, respectively. a) high low b) mean c) period Figure 1: PWM Signals with 25 %, 50 % and 75 % Duty Cycle and respective Mean Values. The mean value of a PWM signal (shown as dashed horizontal lines in figure 1) is an analog voltage value between 0 V and the high voltage of the digital signal, typically 5 V. This means that if the period of the PWM signal is reasonable short and the device attached to it behaves inertially, it will actually respond as if controlled by an analog signal with that analog voltage! Exercise 5.1 We will now develop an application to control the brightness of LEDs. Atmega168 provides several mechanisms to generate PWM signals. For simplicity, we will stick to Fast PWM Mode. a) What are the mean voltages corresponding to the PWM signals shown in figure 1, given a high voltage of 5 V? b) Read the manual to understand how the Fast PWM Mode works. Find out the following information from the relevant sections in chapter 15 of the manual: 1/5
2 Which pins can be used for PWM output when using Timer1? Which configuration do we need on those pins (e.g., do we need to configure them as output pins)? If we use the WGM 14, how does the PWM generator work for Compare Channel A? How can the period and the duty cycle be controlled? What is the difference between inverted and non-inverted PWM? How can we configure the microcontroller to generate such signals? c) Develop a pwm_init() function that takes the period in milliseconds as input parameter and initializes the timer to generate a PWM signal with 50 % duty cycle on OC1A using WGM 14. It is acceptable if the range for the input parameter is between 0 ms and 1,000 ms. Use the LEDs to visualize the PWM output. d) Develop a pwm_set() function that can be used to change the duty cycle of the PWM signal. It should receive the new duty cycle value (between 0 and 100) as input parameter. The PWM period should not be changed by the function. e) As you have seen in the previous steps, the blinking of the LEDs is visible for large period values. Reduce the period of the PWM signal at a duty cycle of 50 % to find the value where the blinking is no longer visible. Which frequency does the period value correspond to? f) Develop an application that receives commands on the serial port and adjusts the duty cycle of PWM signal accordingly. For example, the duty cycle of PWM signal is increased upon receiving a + character and decreased upon receiving a - character. Use a period of about 10 ms. Make sure that you can control the brightness of LEDs by configuring the duty cycle. Driving a DC Motor We will now combine the functionality of input capture and PWM signal generation in an illustrating example. Imagine you have a model car that is driven by a battery-powered DC motor. We want the car to drive at a constant speed, even if there is load on the motor because the car is currently driving uphill or the battery power is low. Of course we can not always guarantee that the motor will reach the designated speed, but in this exercise we will at least try to do so. We will use a PWM signal to drive the motor. The goal is to measure how fast the motor drives and compare this with the desired speed. If the motor is too slow, we will increase the PWM duty cycle, otherwise we will decrease it. This nebavior actually describes a simple controller that tries to minimize the difference ( error ) between the desired speed and the actual speed. Unfortunately this exercise does not feature a real model car, but you are of course free to apply your results to a setup of your own ;) For completing the tasks, you receive an extra printed circuit board with a DC motor and a light barrier. A disc is attached to the motor axis. Some parts of the disc are transparent, some are not. We will use the disc in combination with the light barrier to measure the current motor speed. Note that you should never directly attach a component with a high power consumption (like a motor) to a microcontroller, because the high current that occurs while running it would destroy the controller. To circumvent this issue, we use special electronic components on the printed circuit board that allow us to directly attach it to a PWM signal generated by the microcontroller. Exercise 5.2 a) Attach the DC motor board to STK500 so that you can feed a PWM signal to the motor. Do not forget to also connect the power supply pins on the motor board (+5V, GND), they are needed for the electronic components on the board to work properly. Which pin connections do you need? 2/5
3 b) Use the program from exercise 5.1 f) to test the motor at different speeds. Find out the approximate minimum duty cycle at which the motor runs and the maximum duty cycle from where increasing the value does not have any visible effect (listen to the sound of the motor). When finding the minimum duty cycle, is there a difference between the motor already turning at a higher speed or turning it on from stand? c) What happens if you hold the motor so that the axis is arranged vertically? Determining the Speed of a Motor There are multiple methods that can be used to measure the speed of a motor. One method is to attach a magnet to the motor axis and use a sensor that detects the magnetic field to measure the number of rounds per minute. The approach we are using is an optical way of measuring the motor speed. There is a small light barrier mounted on the motor board. In addition to that, a disk is mounted on the motor axis. Half of the disk is opaque and the other half is transparent. When the opaque area of the disk is in between the light barrier, the light is blocked. Otherwise, the light can be detected by the receiving part of the light barrier. This optical information is transformed to a voltage by the electrical circuit on the motor board, which can be finally evaluated by the microcontroller. We will use input capture interrupts for this purpose. Note that you can not see the light that the light barrier produces, as it is in the infrared spectrum. Exercise 5.3 a) Which resolution (in degrees) can we achieve from the light barrier when using the following encoder disks and if... i)... only the rising or falling edges are considered? ii)... rising and falling edges are considered? b) Although not of interest in the current setup, can you imagine a way to measure the direction in which the motor is turning? c) Attach the signal called Schmitt-Trigger OUT to the input capture pin of the microcontroller. Make sure that jumper JP2 is set to the position 1-2 (not 2-3). Extend your program from exercise 5.1 f) so that measures the time between two successive input capture events (it is up to you whether you want to recognize the falling and/or rising edge(s)). From that on, calculate the time per round (depending on the number of edged per round) and the rounds per minute. Make sure that the rounds per minute is calculated correctly, you will need it for the subsequent exercises. Do all the calculations in the ISR and store the most recent result in a global variable. In the main program, periodically dump the current values to the debug console. Note that you should disable interrupts in the main program before accessing the global variables to ensure that the ISR does not write to the values in parallel. Since we are using input capture, this does not reduce the precision as long as interrupts are only disabled for a short amount of time. 3/5
4 Hints To use PWM signal to drive the DC motor, use the rather small period value (e.g. 100 µs), otherwise the light barrier signal may become noisy and distort your input capture events. You might need to use small prescaler as well to achieve better resolution. If you happen to encounter problems with floating point computations for small numbers, you might want to try using fixed-point numbers instead of floating-point numbers: for intermediate calculations, you can scale the values up by a proper scaling factor, use integer arithmetic and then scale them down again afterwards. Listing 1 shows how the simplified original code to compute the time interval between two capture events may look like using floating-point numbers, where t 1 and t 2 are the timestamps of two successive captured events, T is the MAX value of the timer and p is the associated real-time interval for T. To avoid using floating-point numbers, we could use fixed-point arithmetic as shown in listing 2. Listing 1: Floating-point based calculation of motor speed 1 f l o a t calcroundsperminute ( f l o a t t1, t2, p ) 2 { 3 / Compute the f r a c t i o n in one timer p e r i o d. Note that the i n t e r v a l / 4 / v a r i a b l e must be o f type f l o a t, o t h e r w i s e the r e s u l t i s always 0! / 5 f l o a t i n t e r v a l = ( t2 t1 )/T; 6 7 / Compute the r e a l time i n us / 8 i n t e r v a l = p ; 9 10 / Return rounds per minute / 11 return i n t e r v a l / ; 12 } Listing 2: Fix-point based calculation of motor speed 1 f l o a t calcroundsperminute ( f l o a t t1, t2, p ) 2 { 3 / S c a l e numbers up. The value 1000 i s j u s t f o r demonstration, you / 4 / should pick up a value that i s l a r g e enough f o r your a p p l i c a t i o n. / 5 uint32 t s1 = t1 1000; 6 uint32 t s2 = t2 1000; 7 8 / Compute the f r a c t i o n in one timer p e r i o d. Now the a b s o l u t e / 9 / value o f the r e s u l t can be s a f e l y s t o r e d in an i n t e g e r. / 10 uint32 t i n t e r v a l = ( s2 s1 )/T; / Compute the r e a l time i n us / 13 i n t e r v a l = i n t e r v a l p ; / S c a l e down an r e t u r n rounds per minute / 16 return i n t e r v a l / ; 17 } 4/5
5 Control Theory One of the requirements for our (so far virtual) model car was that the speed of the motor should be constant. Until now, we have seen that the motor speed may change even if we do not change the duty cycle of the PWM signal. Hence, we need to dynamically adapt the PWM frequency given the current speed of the motor. This is a typical problem from the control systems area. We will now implement a simple yet effective controller to achieve the desired task. One of the essential features of a controller is a feedback loop, which means that the current state of the system is fed back to controller after the controller has set a new control value. The controller we will use is a PI controller. PI means proportional and integral controller. It basically works as follows: the controller has thee input values. The first one is the so called system deviation d, that is the difference of the measured value (so-called actual value) v m to the desired value (so-called setpoint value) v s. The second and third inputs are the proportial coefficient c p and the integral coefficient c i. The output s is the new setpoint for the system. A pseudo-code algorithm for a PI controller is shown in listing 3. Listing 3: PI controller pseudocode 1 input(c p); input(c i) // R e t r i e v e c o n t r o l parameters 2 t old time() 3 v forever { 6 input(v m); input(v s) // R e t r i e v e a c t u a l value and s e t p o i n t value 7 8 t cur time() // C a l c u l a t e how much time has passed 9 t t cur t old 10 t old t cur d v m v s // PI c o n t r o l l e r 13 v v + c i d 14 s c p d + v t output(s) // Output c o n t r o l value 17 } Motor Speed Control Exercise 5.4 a) Extend your previous program(s) so that it controls the speed of the DC motor using a PI controller. Output the current rounds per minute to the debug cosole (about every second). It should still be possible to input the new desired value (in rounds per minute) over the serial interface. Start with control parameters c p = 0.1 and c i = 0. Describe the behavior of the motor. b) Now set c p = c i = 0.1. What happens? c) Optimize the control parameters so that the motor reacts as fast as possible when you change the desired value. d) In contrast to your previous experience from exercise 5.2 c), what happens if you hold the motor so that the axis is arranged vertically? 5/5
ME 333 Assignment 7 and 8 PI Control of LED/Phototransistor Pair. Overview
 ME 333 Assignment 7 and 8 PI Control of LED/Phototransistor Pair Overview For this assignment, you will be controlling the light emitted from and received by an LED/phototransistor pair. There are many
ME 333 Assignment 7 and 8 PI Control of LED/Phototransistor Pair Overview For this assignment, you will be controlling the light emitted from and received by an LED/phototransistor pair. There are many
Timer 0 Modes of Operation. Normal Mode Clear Timer on Compare Match (CTC) Fast PWM Mode Phase Corrected PWM Mode
 Timer 0 Modes of Operation Normal Mode Clear Timer on Compare Match (CTC) Fast PWM Mode Phase Corrected PWM Mode PWM - Introduction Recall: PWM = Pulse Width Modulation We will mostly use it for controlling
Timer 0 Modes of Operation Normal Mode Clear Timer on Compare Match (CTC) Fast PWM Mode Phase Corrected PWM Mode PWM - Introduction Recall: PWM = Pulse Width Modulation We will mostly use it for controlling
GE423 Laboratory Assignment 6 Robot Sensors and Wall-Following
 GE423 Laboratory Assignment 6 Robot Sensors and Wall-Following Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Learn about the sensors available on the robot for environment sensing. 2. Learn about classical wall-following
GE423 Laboratory Assignment 6 Robot Sensors and Wall-Following Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Learn about the sensors available on the robot for environment sensing. 2. Learn about classical wall-following
Chapter 7: The motors of the robot
 Chapter 7: The motors of the robot Learn about different types of motors Learn to control different kinds of motors using open-loop and closedloop control Learn to use motors in robot building 7.1 Introduction
Chapter 7: The motors of the robot Learn about different types of motors Learn to control different kinds of motors using open-loop and closedloop control Learn to use motors in robot building 7.1 Introduction
EE 308 Spring S12 SUBSYSTEMS: PULSE WIDTH MODULATION, A/D CONVERTER, AND SYNCHRONOUS SERIAN INTERFACE
 9S12 SUBSYSTEMS: PULSE WIDTH MODULATION, A/D CONVERTER, AND SYNCHRONOUS SERIAN INTERFACE In this sequence of three labs you will learn to use the 9S12 S hardware sybsystem. WEEK 1 PULSE WIDTH MODULATION
9S12 SUBSYSTEMS: PULSE WIDTH MODULATION, A/D CONVERTER, AND SYNCHRONOUS SERIAN INTERFACE In this sequence of three labs you will learn to use the 9S12 S hardware sybsystem. WEEK 1 PULSE WIDTH MODULATION
Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control
 Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 13.11.2014
Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 13.11.2014
EE 308 Lab Spring 2009
 9S12 Subsystems: Pulse Width Modulation, A/D Converter, and Synchronous Serial Interface In this sequence of three labs you will learn to use three of the MC9S12's hardware subsystems. WEEK 1 Pulse Width
9S12 Subsystems: Pulse Width Modulation, A/D Converter, and Synchronous Serial Interface In this sequence of three labs you will learn to use three of the MC9S12's hardware subsystems. WEEK 1 Pulse Width
νµθωερτψυιοπασδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθωερτ ψυιοπασδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθωερτψυιοπα σδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθωερτψυιοπασδφγηϕκ χϖβνµθωερτψυιοπασδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθ
 θωερτψυιοπασδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθωερτψ υιοπασδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθωερτψυιοπασδ φγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθωερτψυιοπασδφγηϕκλζ ξχϖβνµθωερτψυιοπασδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµ EE 331 Design Project Final Report θωερτψυιοπασδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθωερτψ
θωερτψυιοπασδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθωερτψ υιοπασδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθωερτψυιοπασδ φγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθωερτψυιοπασδφγηϕκλζ ξχϖβνµθωερτψυιοπασδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµ EE 331 Design Project Final Report θωερτψυιοπασδφγηϕκλζξχϖβνµθωερτψ
CSE 3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory Lab 5 Digital Control System
 Introduction CSE 3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory Lab 5 Digital Control System The purpose of this lab is to introduce you to digital control systems. The most basic function of a control system is to
Introduction CSE 3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory Lab 5 Digital Control System The purpose of this lab is to introduce you to digital control systems. The most basic function of a control system is to
Project Final Report: Directional Remote Control
 Project Final Report: by Luca Zappaterra xxxx@gwu.edu CS 297 Embedded Systems The George Washington University April 25, 2010 Project Abstract In the project, a prototype of TV remote control which reacts
Project Final Report: by Luca Zappaterra xxxx@gwu.edu CS 297 Embedded Systems The George Washington University April 25, 2010 Project Abstract In the project, a prototype of TV remote control which reacts
FABO ACADEMY X ELECTRONIC DESIGN
 ELECTRONIC DESIGN MAKE A DEVICE WITH INPUT & OUTPUT The Shanghaino can be programmed to use many input and output devices (a motor, a light sensor, etc) uploading an instruction code (a program) to it
ELECTRONIC DESIGN MAKE A DEVICE WITH INPUT & OUTPUT The Shanghaino can be programmed to use many input and output devices (a motor, a light sensor, etc) uploading an instruction code (a program) to it
Using Magnetic Sensors for Absolute Position Detection and Feedback. Kevin Claycomb University of Evansville
 Using Magnetic Sensors for Absolute Position Detection and Feedback. Kevin Claycomb University of Evansville Using Magnetic Sensors for Absolute Position Detection and Feedback. Abstract Several types
Using Magnetic Sensors for Absolute Position Detection and Feedback. Kevin Claycomb University of Evansville Using Magnetic Sensors for Absolute Position Detection and Feedback. Abstract Several types
EE 314 Spring 2003 Microprocessor Systems
 EE 314 Spring 2003 Microprocessor Systems Laboratory Project #9 Closed Loop Control Overview and Introduction This project will bring together several pieces of software and draw on knowledge gained in
EE 314 Spring 2003 Microprocessor Systems Laboratory Project #9 Closed Loop Control Overview and Introduction This project will bring together several pieces of software and draw on knowledge gained in
For this exercise, you will need a partner, an Arduino kit (in the plastic tub), and a laptop with the Arduino programming environment.
 Physics 222 Name: Exercise 6: Mr. Blinky This exercise is designed to help you wire a simple circuit based on the Arduino microprocessor, which is a particular brand of microprocessor that also includes
Physics 222 Name: Exercise 6: Mr. Blinky This exercise is designed to help you wire a simple circuit based on the Arduino microprocessor, which is a particular brand of microprocessor that also includes
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 comparators. It covers the main features of the ultra-lowpower comparators and some
 Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 comparators. It covers the main features of the ultra-lowpower comparators and some application examples. 1 The two comparators inside STM32 microcontroller
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 comparators. It covers the main features of the ultra-lowpower comparators and some application examples. 1 The two comparators inside STM32 microcontroller
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the FlexTimer or FTM module for Kinetis K series MCUs. In this session, you ll learn about the FTM, its
 Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the FlexTimer or FTM module for Kinetis K series MCUs. In this session, you ll learn about the FTM, its main features and the application benefits of leveraging
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the FlexTimer or FTM module for Kinetis K series MCUs. In this session, you ll learn about the FTM, its main features and the application benefits of leveraging
Micromouse Meeting #3 Lecture #2. Power Motors Encoders
 Micromouse Meeting #3 Lecture #2 Power Motors Encoders Previous Stuff Microcontroller pick one yet? Meet your team Some teams were changed High Level Diagram Power Everything needs power Batteries Supply
Micromouse Meeting #3 Lecture #2 Power Motors Encoders Previous Stuff Microcontroller pick one yet? Meet your team Some teams were changed High Level Diagram Power Everything needs power Batteries Supply
Workshops Elisava Introduction to programming and electronics (Scratch & Arduino)
 Workshops Elisava 2011 Introduction to programming and electronics (Scratch & Arduino) What is programming? Make an algorithm to do something in a specific language programming. Algorithm: a procedure
Workshops Elisava 2011 Introduction to programming and electronics (Scratch & Arduino) What is programming? Make an algorithm to do something in a specific language programming. Algorithm: a procedure
The light sensor, rotation sensor, and motors may all be monitored using the view function on the RCX.
 Review the following material on sensors. Discuss how you might use each of these sensors. When you have completed reading through this material, build a robot of your choosing that has 2 motors (connected
Review the following material on sensors. Discuss how you might use each of these sensors. When you have completed reading through this material, build a robot of your choosing that has 2 motors (connected
An External Command Reading White line Follower Robot
 EE-712 Embedded System Design: Course Project Report An External Command Reading White line Follower Robot 09405009 Mayank Mishra (mayank@cse.iitb.ac.in) 09307903 Badri Narayan Patro (badripatro@ee.iitb.ac.in)
EE-712 Embedded System Design: Course Project Report An External Command Reading White line Follower Robot 09405009 Mayank Mishra (mayank@cse.iitb.ac.in) 09307903 Badri Narayan Patro (badripatro@ee.iitb.ac.in)
Understanding the Arduino to LabVIEW Interface
 E-122 Design II Understanding the Arduino to LabVIEW Interface Overview The Arduino microcontroller introduced in Design I will be used as a LabVIEW data acquisition (DAQ) device/controller for Experiments
E-122 Design II Understanding the Arduino to LabVIEW Interface Overview The Arduino microcontroller introduced in Design I will be used as a LabVIEW data acquisition (DAQ) device/controller for Experiments
CHAPTER 4 CONTROL ALGORITHM FOR PROPOSED H-BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER
 65 CHAPTER 4 CONTROL ALGORITHM FOR PROPOSED H-BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER 4.1 INTRODUCTION Many control strategies are available for the control of IMs. The Direct Torque Control (DTC) is one of the most
65 CHAPTER 4 CONTROL ALGORITHM FOR PROPOSED H-BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER 4.1 INTRODUCTION Many control strategies are available for the control of IMs. The Direct Torque Control (DTC) is one of the most
EE-110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Labs Introduction to Arduino
 EE-110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Labs 10-11 Introduction to Arduino In this lab we will introduce the idea of using a microcontroller as a tool for controlling
EE-110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Labs 10-11 Introduction to Arduino In this lab we will introduce the idea of using a microcontroller as a tool for controlling
Microcontrollers and Interfacing
 Microcontrollers and Interfacing Week 07 digital input, debouncing, interrupts and concurrency College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University 1 this week digital input push-button
Microcontrollers and Interfacing Week 07 digital input, debouncing, interrupts and concurrency College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University 1 this week digital input push-button
Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control
 Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 05.11.2015
Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 05.11.2015
Mechatronics Engineering and Automation Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University MCT-151, Spring 2015 Lab-4: Electric Actuators
 Mechatronics Engineering and Automation Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University MCT-151, Spring 2015 Lab-4: Electric Actuators Ahmed Okasha, Assistant Lecturer okasha1st@gmail.com Objective Have a
Mechatronics Engineering and Automation Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University MCT-151, Spring 2015 Lab-4: Electric Actuators Ahmed Okasha, Assistant Lecturer okasha1st@gmail.com Objective Have a
PSoC Academy: How to Create a PSoC BLE Android App Lesson 9: BLE Robot Schematic 1
 1 All right, now we re ready to walk through the schematic. I ll show you the quadrature encoders that drive the H-Bridge, the PWMs, et cetera all the parts on the schematic. Then I ll show you the configuration
1 All right, now we re ready to walk through the schematic. I ll show you the quadrature encoders that drive the H-Bridge, the PWMs, et cetera all the parts on the schematic. Then I ll show you the configuration
AVR PWM 11 Aug In the table below you have symbols used in the text. The meaning of symbols is the same in the entire guide.
 Aquaticus PWM guide AVR PWM 11 Aug 29 Introduction This guide describes principles of PWM for Atmel AVR micro controllers. It is not complete documentation for PWM nor AVR timers but tries to lighten some
Aquaticus PWM guide AVR PWM 11 Aug 29 Introduction This guide describes principles of PWM for Atmel AVR micro controllers. It is not complete documentation for PWM nor AVR timers but tries to lighten some
Single-Phase Grid-Tied Inverter (PWM Rectifier/Inverter)
 Exercise 2 Single-Phase Grid-Tied Inverter (PWM Rectifier/Inverter) EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the singlephase grid-tied inverter. DISCUSSION OUTLINE
Exercise 2 Single-Phase Grid-Tied Inverter (PWM Rectifier/Inverter) EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the singlephase grid-tied inverter. DISCUSSION OUTLINE
Power Factor Correction in Digital World. Abstract. 1 Introduction. 3 Advantages of Digital PFC over traditional Analog PFC.
 Power Factor Correction in Digital World By Nitin Agarwal, STMicroelectronics Pvt. Ltd., India Abstract There are various reasons why power factor correction circuit is used in various power supplies in
Power Factor Correction in Digital World By Nitin Agarwal, STMicroelectronics Pvt. Ltd., India Abstract There are various reasons why power factor correction circuit is used in various power supplies in
Pulse-Width-Modulation Motor Speed Control with a PIC (modified from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 14 Pulse-Width-Modulation Motor Speed Control with a PIC (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x PIC 16F88 18P-DIP microcontroller 3x 0.1 F capacitors 1x 12-button numeric
Laboratory 14 Pulse-Width-Modulation Motor Speed Control with a PIC (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x PIC 16F88 18P-DIP microcontroller 3x 0.1 F capacitors 1x 12-button numeric
Experiment#6: Speaker Control
 Experiment#6: Speaker Control I. Objectives 1. Describe the operation of the driving circuit for SP1 speaker. II. Circuit Description The circuit of speaker and driver is shown in figure# 1 below. The
Experiment#6: Speaker Control I. Objectives 1. Describe the operation of the driving circuit for SP1 speaker. II. Circuit Description The circuit of speaker and driver is shown in figure# 1 below. The
ECE 511: FINAL PROJECT REPORT GROUP 7 MSP430 TANK
 ECE 511: FINAL PROJECT REPORT GROUP 7 MSP430 TANK Team Members: Andrew Blanford Matthew Drummond Krishnaveni Das Dheeraj Reddy 1 Abstract: The goal of the project was to build an interactive and mobile
ECE 511: FINAL PROJECT REPORT GROUP 7 MSP430 TANK Team Members: Andrew Blanford Matthew Drummond Krishnaveni Das Dheeraj Reddy 1 Abstract: The goal of the project was to build an interactive and mobile
Lab 1.2 Joystick Interface
 Lab 1.2 Joystick Interface Lab 1.0 + 1.1 PWM Software/Hardware Design (recap) The previous labs in the 1.x series put you through the following progression: Lab 1.0 You learnt some theory behind how one
Lab 1.2 Joystick Interface Lab 1.0 + 1.1 PWM Software/Hardware Design (recap) The previous labs in the 1.x series put you through the following progression: Lab 1.0 You learnt some theory behind how one
Measuring Distance Using Sound
 Measuring Distance Using Sound Distance can be measured in various ways: directly, using a ruler or measuring tape, or indirectly, using radio or sound waves. The indirect method measures another variable
Measuring Distance Using Sound Distance can be measured in various ways: directly, using a ruler or measuring tape, or indirectly, using radio or sound waves. The indirect method measures another variable
PIC Functionality. General I/O Dedicated Interrupt Change State Interrupt Input Capture Output Compare PWM ADC RS232
 PIC Functionality General I/O Dedicated Interrupt Change State Interrupt Input Capture Output Compare PWM ADC RS232 General I/O Logic Output light LEDs Trigger solenoids Transfer data Logic Input Monitor
PIC Functionality General I/O Dedicated Interrupt Change State Interrupt Input Capture Output Compare PWM ADC RS232 General I/O Logic Output light LEDs Trigger solenoids Transfer data Logic Input Monitor
Lab 2: Blinkie Lab. Objectives. Materials. Theory
 Lab 2: Blinkie Lab Objectives This lab introduces the Arduino Uno as students will need to use the Arduino to control their final robot. Students will build a basic circuit on their prototyping board and
Lab 2: Blinkie Lab Objectives This lab introduces the Arduino Uno as students will need to use the Arduino to control their final robot. Students will build a basic circuit on their prototyping board and
Design of Joint Controller Circuit for PA10 Robot Arm
 Design of Joint Controller Circuit for PA10 Robot Arm Sereiratha Phal and Manop Wongsaisuwan Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, 10330, Thailand.
Design of Joint Controller Circuit for PA10 Robot Arm Sereiratha Phal and Manop Wongsaisuwan Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, 10330, Thailand.
Mate Serial Communications Guide This guide is only relevant to Mate Code Revs. of 4.00 and greater
 Mate Serial Communications Guide This guide is only relevant to Mate Code Revs. of 4.00 and greater For additional information contact matedev@outbackpower.com Page 1 of 20 Revision History Revision 2.0:
Mate Serial Communications Guide This guide is only relevant to Mate Code Revs. of 4.00 and greater For additional information contact matedev@outbackpower.com Page 1 of 20 Revision History Revision 2.0:
RX23T inverter ref. kit
 RX23T inverter ref. kit Deep Dive October 2015 YROTATE-IT-RX23T kit content Page 2 YROTATE-IT-RX23T kit: 3-ph. Brushless Motor Specs Page 3 Motors & driving methods supported Brushless DC Permanent Magnet
RX23T inverter ref. kit Deep Dive October 2015 YROTATE-IT-RX23T kit content Page 2 YROTATE-IT-RX23T kit: 3-ph. Brushless Motor Specs Page 3 Motors & driving methods supported Brushless DC Permanent Magnet
ME 461 Laboratory #2 Timers and Pulse-Width Modulation
 ME 461 Laboratory #2 Timers and Pulse-Width Modulation Goals: 1. Understand how to use timers to control the frequency at which events occur. 2. Generate PWM signals using Timer A. 3. Explore the frequency
ME 461 Laboratory #2 Timers and Pulse-Width Modulation Goals: 1. Understand how to use timers to control the frequency at which events occur. 2. Generate PWM signals using Timer A. 3. Explore the frequency
LAB 3 TIMER FUNCTIONS: BOLT DROP AND SQUARE WAVE
 LAB 3 TIMER FUNCTIONS: BOLT DROP AND SQUARE WAVE OBJECTIVE This lab will use MC6811 to perform time measurements. Part I will perform time measurements on a dropping bolt using input capture (IC) timer
LAB 3 TIMER FUNCTIONS: BOLT DROP AND SQUARE WAVE OBJECTIVE This lab will use MC6811 to perform time measurements. Part I will perform time measurements on a dropping bolt using input capture (IC) timer
Grundlagen Microcontroller Counter/Timer. Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss
 Grundlagen Microcontroller Counter/Timer Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Counter/Timer Lecture Overview Counter Timer Prescaler Input Capture Output Compare PWM 2 important feature of microcontroller
Grundlagen Microcontroller Counter/Timer Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Counter/Timer Lecture Overview Counter Timer Prescaler Input Capture Output Compare PWM 2 important feature of microcontroller
LINE MAZE SOLVING ROBOT
 LINE MAZE SOLVING ROBOT EEE 456 REPORT OF INTRODUCTION TO ROBOTICS PORJECT PROJECT OWNER: HAKAN UÇAROĞLU 2000502055 INSTRUCTOR: AHMET ÖZKURT 1 CONTENTS I- Abstract II- Sensor Circuit III- Compare Circuit
LINE MAZE SOLVING ROBOT EEE 456 REPORT OF INTRODUCTION TO ROBOTICS PORJECT PROJECT OWNER: HAKAN UÇAROĞLU 2000502055 INSTRUCTOR: AHMET ÖZKURT 1 CONTENTS I- Abstract II- Sensor Circuit III- Compare Circuit
ECEN 449: Microprocessor System Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University
 ECEN 449: Microprocessor System Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Prof. Sunil P Khatri (Lab exercise created and tested by Ramu Endluri, He Zhou, Andrew Douglass
ECEN 449: Microprocessor System Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Prof. Sunil P Khatri (Lab exercise created and tested by Ramu Endluri, He Zhou, Andrew Douglass
Microcontroller Based Closed Loop Speed and Position Control of DC Motor
 International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 2249 8958, Volume-3, Issue-5, June 2014 Microcontroller Based Closed Loop Speed and Position Control of DC Motor Panduranga Talavaru,
International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 2249 8958, Volume-3, Issue-5, June 2014 Microcontroller Based Closed Loop Speed and Position Control of DC Motor Panduranga Talavaru,
Lecture 2 Exercise 1a. Lecture 2 Exercise 1b
 Lecture 2 Exercise 1a 1 Design a converter that converts a speed of 60 miles per hour to kilometers per hour. Make the following format changes to your blocks: All text should be displayed in bold. Constant
Lecture 2 Exercise 1a 1 Design a converter that converts a speed of 60 miles per hour to kilometers per hour. Make the following format changes to your blocks: All text should be displayed in bold. Constant
High Current DC Motor Driver Manual
 High Current DC Motor Driver Manual 1.0 INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW This driver is one of the latest smart series motor drivers designed to drive medium to high power brushed DC motor with current capacity
High Current DC Motor Driver Manual 1.0 INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW This driver is one of the latest smart series motor drivers designed to drive medium to high power brushed DC motor with current capacity
Motor Control Demonstration Lab
 Motor Control Demonstration Lab JIM SIBIGTROTH and EDUARDO MONTAÑEZ Freescale Semiconductor launched by Motorola, 8/16 Bit MCU Division, Austin, TX 78735, USA. Email: j.sibigtroth@freescale.com eduardo.montanez@freescale.com
Motor Control Demonstration Lab JIM SIBIGTROTH and EDUARDO MONTAÑEZ Freescale Semiconductor launched by Motorola, 8/16 Bit MCU Division, Austin, TX 78735, USA. Email: j.sibigtroth@freescale.com eduardo.montanez@freescale.com
Module 5. DC to AC Converters. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 DC to AC Converters Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 37 Sine PWM and its Realization Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 After completion of this lesson, the reader shall be able to: 1. Explain
Module 5 DC to AC Converters Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 37 Sine PWM and its Realization Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 After completion of this lesson, the reader shall be able to: 1. Explain
Lab 5: Inverted Pendulum PID Control
 Lab 5: Inverted Pendulum PID Control In this lab we will be learning about PID (Proportional Integral Derivative) control and using it to keep an inverted pendulum system upright. We chose an inverted
Lab 5: Inverted Pendulum PID Control In this lab we will be learning about PID (Proportional Integral Derivative) control and using it to keep an inverted pendulum system upright. We chose an inverted
Standard single-purpose processors: Peripherals
 3-1 Chapter 3 Standard single-purpose processors: Peripherals 3.1 Introduction A single-purpose processor is a digital system intended to solve a specific computation task. The processor may be a standard
3-1 Chapter 3 Standard single-purpose processors: Peripherals 3.1 Introduction A single-purpose processor is a digital system intended to solve a specific computation task. The processor may be a standard
Serial communication inverter. Lab bench scenario. Inverter Board, A/D, D/A, PWM, Filters, Encoders. Inverter board. and Dimmer introduction
 Inverter Board, A/D, D/A, PWM, Filters, Encoders and Dimmer introduction 20181004 Gunnar Lindstedt Serial communication inverter Lund University, Sweden Lab bench scenario Inverter board PC 9pole Dsub
Inverter Board, A/D, D/A, PWM, Filters, Encoders and Dimmer introduction 20181004 Gunnar Lindstedt Serial communication inverter Lund University, Sweden Lab bench scenario Inverter board PC 9pole Dsub
Objectives: Learn what an Arduino is and what it can do Learn what an LED is and how to use it Be able to wire and program an LED to blink
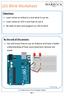 Objectives: Learn what an Arduino is and what it can do Learn what an LED is and how to use it Be able to wire and program an LED to blink By the end of this session: You will know how to use an Arduino
Objectives: Learn what an Arduino is and what it can do Learn what an LED is and how to use it Be able to wire and program an LED to blink By the end of this session: You will know how to use an Arduino
ENGR 1110: Introduction to Engineering Lab 7 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
 ENGR 1110: Introduction to Engineering Lab 7 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Supplies Needed Motor control board, Transmitter (with good batteries), Receiver Equipment Used Oscilloscope, Function Generator,
ENGR 1110: Introduction to Engineering Lab 7 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Supplies Needed Motor control board, Transmitter (with good batteries), Receiver Equipment Used Oscilloscope, Function Generator,
Microcontrollers: Lecture 3 Interrupts, Timers. Michele Magno
 Microcontrollers: Lecture 3 Interrupts, Timers Michele Magno 1 Calendar 07.04.2017: Power consumption; Low power States; Buses, Memory, GPIOs 20.04.2017 Serial Communications 21.04.2017 Programming STM32
Microcontrollers: Lecture 3 Interrupts, Timers Michele Magno 1 Calendar 07.04.2017: Power consumption; Low power States; Buses, Memory, GPIOs 20.04.2017 Serial Communications 21.04.2017 Programming STM32
2.017 DESIGN OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ROBOTIC SYSTEMS Fall 2009 Lab 4: Motor Control. October 5, 2009 Dr. Harrison H. Chin
 2.017 DESIGN OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ROBOTIC SYSTEMS Fall 2009 Lab 4: Motor Control October 5, 2009 Dr. Harrison H. Chin Formal Labs 1. Microcontrollers Introduction to microcontrollers Arduino microcontroller
2.017 DESIGN OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ROBOTIC SYSTEMS Fall 2009 Lab 4: Motor Control October 5, 2009 Dr. Harrison H. Chin Formal Labs 1. Microcontrollers Introduction to microcontrollers Arduino microcontroller
LM4: The timer unit of the MC9S12DP256B/C
 Objectives - To explore the Enhanced Capture Timer unit (ECT) of the MC9S12DP256B/C - To program a real-time clock signal with a fixed period and display it using the onboard LEDs (flashing light) - To
Objectives - To explore the Enhanced Capture Timer unit (ECT) of the MC9S12DP256B/C - To program a real-time clock signal with a fixed period and display it using the onboard LEDs (flashing light) - To
Lab 2.2 Custom slave programmable interface
 Lab 2.2 Custom slave programmable interface Introduction In the previous labs, you used a system integration tool (Qsys) to create a full FPGA-based system comprised of a processor, on-chip memory, a JTAG
Lab 2.2 Custom slave programmable interface Introduction In the previous labs, you used a system integration tool (Qsys) to create a full FPGA-based system comprised of a processor, on-chip memory, a JTAG
MICROCONTROLLER TUTORIAL II TIMERS
 MICROCONTROLLER TUTORIAL II TIMERS WHAT IS A TIMER? We use timers every day - the simplest one can be found on your wrist A simple clock will time the seconds, minutes and hours elapsed in a given day
MICROCONTROLLER TUTORIAL II TIMERS WHAT IS A TIMER? We use timers every day - the simplest one can be found on your wrist A simple clock will time the seconds, minutes and hours elapsed in a given day
UNIVERSAL PNEUMATIC TRANSDUCER FEATURES
 UNIVERSAL PNEUMATIC TRANSDUCER FEATURES Non-bleed device (no air consumption in steady state) 3-15 PSI adjustable. Internal accurate closed loop control Optional pressure feedback signal Jumper selectable
UNIVERSAL PNEUMATIC TRANSDUCER FEATURES Non-bleed device (no air consumption in steady state) 3-15 PSI adjustable. Internal accurate closed loop control Optional pressure feedback signal Jumper selectable
Published by: PIONEER RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT GROUP ( 1
 Biomimetic Based Interactive Master Slave Robots T.Anushalalitha 1, Anupa.N 2, Jahnavi.B 3, Keerthana.K 4, Shridevi.S.C 5 Dept. of Telecommunication, BMSCE Bangalore, India. Abstract The system involves
Biomimetic Based Interactive Master Slave Robots T.Anushalalitha 1, Anupa.N 2, Jahnavi.B 3, Keerthana.K 4, Shridevi.S.C 5 Dept. of Telecommunication, BMSCE Bangalore, India. Abstract The system involves
Temperature Monitoring and Fan Control with Platform Manager 2
 August 2013 Introduction Technical Note TN1278 The Platform Manager 2 is a fast-reacting, programmable logic based hardware management controller. Platform Manager 2 is an integrated solution combining
August 2013 Introduction Technical Note TN1278 The Platform Manager 2 is a fast-reacting, programmable logic based hardware management controller. Platform Manager 2 is an integrated solution combining
UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA FACULTY OF ENGINEERING. SENG 466 Software for Embedded and Mechatronic Systems. Project 1 Report. May 25, 2006.
 UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SENG 466 Software for Embedded and Mechatronic Systems Project 1 Report May 25, 2006 Group 3 Carl Spani Abe Friesen Lianne Cheng 03-24523 01-27747 01-28963
UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SENG 466 Software for Embedded and Mechatronic Systems Project 1 Report May 25, 2006 Group 3 Carl Spani Abe Friesen Lianne Cheng 03-24523 01-27747 01-28963
ECE 445 Senior Design Laboratory. Fall Individual Progress Report. Automatic Pill Dispenser
 ECE 445 Senior Design Laboratory Fall 2017 Individual Progress Report Automatic Pill Dispenser Iskandar Aripov (aripov2) Team Members: Iskandar Aripov Mattew Colletti Instructor: Prof. Arne Fliflet TA:
ECE 445 Senior Design Laboratory Fall 2017 Individual Progress Report Automatic Pill Dispenser Iskandar Aripov (aripov2) Team Members: Iskandar Aripov Mattew Colletti Instructor: Prof. Arne Fliflet TA:
Generator Speed Controller Model GSC 1
 enerator Speed Controller odel SC 1 RA 29 977/09.95 Replaces: 4.92 Self contained controller for driving electrical power generators with a hydrostatic transmission 16 Bit microprocessor based controller
enerator Speed Controller odel SC 1 RA 29 977/09.95 Replaces: 4.92 Self contained controller for driving electrical power generators with a hydrostatic transmission 16 Bit microprocessor based controller
SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY AND PUBLIC MANAGEMENT ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT
 SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY AND PUBLIC MANAGEMENT ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT Course ENGT 3260 Microcontrollers Summer III 2015 Instructor: Dr. Maged Mikhail Project Report Submitted By: Nicole Kirch 7/10/2015
SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY AND PUBLIC MANAGEMENT ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT Course ENGT 3260 Microcontrollers Summer III 2015 Instructor: Dr. Maged Mikhail Project Report Submitted By: Nicole Kirch 7/10/2015
Generating DTMF Tones Using Z8 Encore! MCU
 Application Note Generating DTMF Tones Using Z8 Encore! MCU AN024802-0608 Abstract This Application Note describes how Zilog s Z8 Encore! MCU is used as a Dual-Tone Multi- (DTMF) signal encoder to generate
Application Note Generating DTMF Tones Using Z8 Encore! MCU AN024802-0608 Abstract This Application Note describes how Zilog s Z8 Encore! MCU is used as a Dual-Tone Multi- (DTMF) signal encoder to generate
Arduino Control of Tetrix Prizm Robotics. Motors and Servos Introduction to Robotics and Engineering Marist School
 Arduino Control of Tetrix Prizm Robotics Motors and Servos Introduction to Robotics and Engineering Marist School Motor or Servo? Motor Faster revolution but less Power Tetrix 12 Volt DC motors have a
Arduino Control of Tetrix Prizm Robotics Motors and Servos Introduction to Robotics and Engineering Marist School Motor or Servo? Motor Faster revolution but less Power Tetrix 12 Volt DC motors have a
ATmega16A Microcontroller
 ATmega16A Microcontroller Timers 1 Timers Timer 0,1,2 8 bits or 16 bits Clock sources: Internal clock, Internal clock with prescaler, External clock (timer 2), Special input pin 2 Features The choice of
ATmega16A Microcontroller Timers 1 Timers Timer 0,1,2 8 bits or 16 bits Clock sources: Internal clock, Internal clock with prescaler, External clock (timer 2), Special input pin 2 Features The choice of
Ultimate Actuator Drivebox 30A Quick start guide
 2016 Ultimate Actuator Drivebox 30A Quick start guide info@e-tronix.cz e-tronix s.r.o. 1.1.2016 OBSAH Identification... 3 Serial Number... 3 Manufacturer and reseller contact... 4 Before Start... 4 UAD30A
2016 Ultimate Actuator Drivebox 30A Quick start guide info@e-tronix.cz e-tronix s.r.o. 1.1.2016 OBSAH Identification... 3 Serial Number... 3 Manufacturer and reseller contact... 4 Before Start... 4 UAD30A
UNIVERSAL INPUT TO PULSE CONVERTER MODULE
 UNIVERSAL INPUT TO PULSE CONVERTER MODULE FEATURES Optional feedback input for closed loop control Jumper selectable analog input DIP switch selectable input/output pulse types Open collector or 24VAC
UNIVERSAL INPUT TO PULSE CONVERTER MODULE FEATURES Optional feedback input for closed loop control Jumper selectable analog input DIP switch selectable input/output pulse types Open collector or 24VAC
Select the single most appropriate response for each question.
 ECE 362 Final Lab Practical - 1 - Practice Exam / Solution PART 1: Multiple Choice Select the single most appropriate response for each question. Note that none of the above MAY be a VALID ANSWER. (Solution
ECE 362 Final Lab Practical - 1 - Practice Exam / Solution PART 1: Multiple Choice Select the single most appropriate response for each question. Note that none of the above MAY be a VALID ANSWER. (Solution
COSC 3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory
 Introduction COSC 3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory Lab 5 Temperature Controller Your task will be to design a temperature controller using the Dragon12 board that will maintain the temperature of an object
Introduction COSC 3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory Lab 5 Temperature Controller Your task will be to design a temperature controller using the Dragon12 board that will maintain the temperature of an object
Using Optical Isolation Amplifiers in Power Inverters for Voltage, Current and Temperature Sensing
 Using Optical Isolation Amplifiers in Power Inverters for Voltage, Current and Temperature Sensing by Hong Lei Chen, Product Manager, Avago Technologies Abstract Many industrial equipments and home appliances
Using Optical Isolation Amplifiers in Power Inverters for Voltage, Current and Temperature Sensing by Hong Lei Chen, Product Manager, Avago Technologies Abstract Many industrial equipments and home appliances
Rochester Institute of Technology Real Time and Embedded Systems: Project 2a
 Rochester Institute of Technology Real Time and Embedded Systems: Project 2a Overview: Design and implement a STM32 Discovery board program exhibiting multitasking characteristics in simultaneously controlling
Rochester Institute of Technology Real Time and Embedded Systems: Project 2a Overview: Design and implement a STM32 Discovery board program exhibiting multitasking characteristics in simultaneously controlling
J. La Favre Using Arduino with Raspberry Pi February 7, 2018
 As you have already discovered, the Raspberry Pi is a very capable digital device. Nevertheless, it does have some weaknesses. For example, it does not produce a clean pulse width modulation output (unless
As you have already discovered, the Raspberry Pi is a very capable digital device. Nevertheless, it does have some weaknesses. For example, it does not produce a clean pulse width modulation output (unless
Computer Controlled Curve Tracer
 Computer Controlled Curve Tracer Christopher Curro The Cooper Union New York, NY Email: chris@curro.cc David Katz The Cooper Union New York, NY Email: katz3@cooper.edu Abstract A computer controlled curve
Computer Controlled Curve Tracer Christopher Curro The Cooper Union New York, NY Email: chris@curro.cc David Katz The Cooper Union New York, NY Email: katz3@cooper.edu Abstract A computer controlled curve
Module: Arduino as Signal Generator
 Name/NetID: Teammate/NetID: Module: Laboratory Outline In our continuing quest to access the development and debugging capabilities of the equipment on your bench at home Arduino/RedBoard as signal generator.
Name/NetID: Teammate/NetID: Module: Laboratory Outline In our continuing quest to access the development and debugging capabilities of the equipment on your bench at home Arduino/RedBoard as signal generator.
ECE251: Tuesday October 3 0
 ECE251: Tuesday October 3 0 Timer Module Continued Review Pulse Input Characterization Output Pulses Pulse Count Capture Homework #6 due Thursday Lab 7 (Maskable Interrupts/ SysTick Timer) this week. Significant
ECE251: Tuesday October 3 0 Timer Module Continued Review Pulse Input Characterization Output Pulses Pulse Count Capture Homework #6 due Thursday Lab 7 (Maskable Interrupts/ SysTick Timer) this week. Significant
A MORON'S GUIDE TO TIMER/COUNTERS v2.2. by
 A MORON'S GUIDE TO TIMER/COUNTERS v2.2 by RetroDan@GMail.com TABLE OF CONTENTS: 1. THE PAUSE ROUTINE 2. WAIT-FOR-TIMER "NORMAL" MODE 3. WAIT-FOR-TIMER "NORMAL" MODE (Modified) 4. THE TIMER-COMPARE METHOD
A MORON'S GUIDE TO TIMER/COUNTERS v2.2 by RetroDan@GMail.com TABLE OF CONTENTS: 1. THE PAUSE ROUTINE 2. WAIT-FOR-TIMER "NORMAL" MODE 3. WAIT-FOR-TIMER "NORMAL" MODE (Modified) 4. THE TIMER-COMPARE METHOD
Digital Debug With Oscilloscopes Lab Experiment
 Digital Debug With Oscilloscopes A collection of lab exercises to introduce you to digital debugging techniques with a digital oscilloscope. Revision 1.0 Page 1 of 23 Revision 1.0 Page 2 of 23 Copyright
Digital Debug With Oscilloscopes A collection of lab exercises to introduce you to digital debugging techniques with a digital oscilloscope. Revision 1.0 Page 1 of 23 Revision 1.0 Page 2 of 23 Copyright
Feedback Devices. By John Mazurkiewicz. Baldor Electric
 Feedback Devices By John Mazurkiewicz Baldor Electric Closed loop systems use feedback signals for stabilization, speed and position information. There are a variety of devices to provide this data, such
Feedback Devices By John Mazurkiewicz Baldor Electric Closed loop systems use feedback signals for stabilization, speed and position information. There are a variety of devices to provide this data, such
ME 461 Laboratory #5 Characterization and Control of PMDC Motors
 ME 461 Laboratory #5 Characterization and Control of PMDC Motors Goals: 1. Build an op-amp circuit and use it to scale and shift an analog voltage. 2. Calibrate a tachometer and use it to determine motor
ME 461 Laboratory #5 Characterization and Control of PMDC Motors Goals: 1. Build an op-amp circuit and use it to scale and shift an analog voltage. 2. Calibrate a tachometer and use it to determine motor
Jaguar Motor Controller (Stellaris Brushed DC Motor Control Module with CAN)
 Jaguar Motor Controller (Stellaris Brushed DC Motor Control Module with CAN) 217-3367 Ordering Information Product Number Description 217-3367 Stellaris Brushed DC Motor Control Module with CAN (217-3367)
Jaguar Motor Controller (Stellaris Brushed DC Motor Control Module with CAN) 217-3367 Ordering Information Product Number Description 217-3367 Stellaris Brushed DC Motor Control Module with CAN (217-3367)
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems (Output Compare and PWM) Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones
 CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems (Output Compare and PWM) Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones 1 Announcements HW8: Due Sunday 10/29 (midnight) Exam 2: In class Thursday 11/9 This object detection lab
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems (Output Compare and PWM) Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones 1 Announcements HW8: Due Sunday 10/29 (midnight) Exam 2: In class Thursday 11/9 This object detection lab
HAW-Arduino. Sensors and Arduino F. Schubert HAW - Arduino 1
 HAW-Arduino Sensors and Arduino 14.10.2010 F. Schubert HAW - Arduino 1 Content of the USB-Stick PDF-File of this script Arduino-software Source-codes Helpful links 14.10.2010 HAW - Arduino 2 Report for
HAW-Arduino Sensors and Arduino 14.10.2010 F. Schubert HAW - Arduino 1 Content of the USB-Stick PDF-File of this script Arduino-software Source-codes Helpful links 14.10.2010 HAW - Arduino 2 Report for
Iowa State University Electrical and Computer Engineering. E E 452. Electric Machines and Power Electronic Drives
 Electrical and Computer Engineering E E 452. Electric Machines and Power Electronic Drives Laboratory #5 Buck Converter Embedded Code Generation Summary In this lab, you will design the control application
Electrical and Computer Engineering E E 452. Electric Machines and Power Electronic Drives Laboratory #5 Buck Converter Embedded Code Generation Summary In this lab, you will design the control application
Laboratory Exercise 1 Microcontroller Board with Driver Board
 Laboratory Exercise 1 Microcontroller Board with Driver Board The purpose of this lab exercises is to demonstrate how the Microcontroller Board can be used to control motors connected to the Driver Board
Laboratory Exercise 1 Microcontroller Board with Driver Board The purpose of this lab exercises is to demonstrate how the Microcontroller Board can be used to control motors connected to the Driver Board
Total Hours Registration through Website or for further details please visit (Refer Upcoming Events Section)
 Total Hours 110-150 Registration Q R Code Registration through Website or for further details please visit http://www.rknec.edu/ (Refer Upcoming Events Section) Module 1: Basics of Microprocessor & Microcontroller
Total Hours 110-150 Registration Q R Code Registration through Website or for further details please visit http://www.rknec.edu/ (Refer Upcoming Events Section) Module 1: Basics of Microprocessor & Microcontroller
ISSN Vol.05,Issue.01, January-2017, Pages:
 WWW.IJITECH.ORG ISSN 2321-8665 Vol.05,Issue.01, January-2017, Pages:0028-0032 Digital Control Strategy for Four Quadrant Operation of Three Phase BLDC Motor with Load Variations MD. HAFEEZUDDIN 1, KUMARASWAMY
WWW.IJITECH.ORG ISSN 2321-8665 Vol.05,Issue.01, January-2017, Pages:0028-0032 Digital Control Strategy for Four Quadrant Operation of Three Phase BLDC Motor with Load Variations MD. HAFEEZUDDIN 1, KUMARASWAMY
Lab Exercise 9: Stepper and Servo Motors
 ME 3200 Mechatronics Laboratory Lab Exercise 9: Stepper and Servo Motors Introduction In this laboratory exercise, you will explore some of the properties of stepper and servomotors. These actuators are
ME 3200 Mechatronics Laboratory Lab Exercise 9: Stepper and Servo Motors Introduction In this laboratory exercise, you will explore some of the properties of stepper and servomotors. These actuators are
Design of double loop-locked system for brush-less DC motor based on DSP
 International Conference on Advanced Electronic Science and Technology (AEST 2016) Design of double loop-locked system for brush-less DC motor based on DSP Yunhong Zheng 1, a 2, Ziqiang Hua and Li Ma 3
International Conference on Advanced Electronic Science and Technology (AEST 2016) Design of double loop-locked system for brush-less DC motor based on DSP Yunhong Zheng 1, a 2, Ziqiang Hua and Li Ma 3
EE 308 Spring 2006 FINAL PROJECT: INTERFACING AND MOTOR CONTROL WEEK 1 PORT EXPANSION FOR THE MC9S12
 FINAL PROJECT: INTERFACING AND MOTOR CONTROL In this sequence of labs you will learn how to interface with additional hardware and implement a motor speed control system. WEEK 1 PORT EXPANSION FOR THE
FINAL PROJECT: INTERFACING AND MOTOR CONTROL In this sequence of labs you will learn how to interface with additional hardware and implement a motor speed control system. WEEK 1 PORT EXPANSION FOR THE
OVEN INDUSTRIES, INC. Model 5C7-362
 OVEN INDUSTRIES, INC. OPERATING MANUAL Model 5C7-362 THERMOELECTRIC MODULE TEMPERATURE CONTROLLER TABLE OF CONTENTS Features... 1 Description... 2 Block Diagram... 3 RS232 Communications Connections...
OVEN INDUSTRIES, INC. OPERATING MANUAL Model 5C7-362 THERMOELECTRIC MODULE TEMPERATURE CONTROLLER TABLE OF CONTENTS Features... 1 Description... 2 Block Diagram... 3 RS232 Communications Connections...
Electric Bike BLDC Hub Motor Control Using the Z8FMC1600 MCU
 Application Note Electric Bike BLDC Hub Motor Control Using the Z8FMC1600 MCU AN026002-0608 Abstract This application note describes a controller for a 200 W, 24 V Brushless DC (BLDC) motor used to power
Application Note Electric Bike BLDC Hub Motor Control Using the Z8FMC1600 MCU AN026002-0608 Abstract This application note describes a controller for a 200 W, 24 V Brushless DC (BLDC) motor used to power
Enhancing Analog Signal Generation by Digital Channel Using Pulse-Width Modulation
 Enhancing Analog Signal Generation by Digital Channel Using Pulse-Width Modulation Angelo Zucchetti Advantest angelo.zucchetti@advantest.com Introduction Presented in this article is a technique for generating
Enhancing Analog Signal Generation by Digital Channel Using Pulse-Width Modulation Angelo Zucchetti Advantest angelo.zucchetti@advantest.com Introduction Presented in this article is a technique for generating
Course Introduction. Content 20 pages 3 questions. Learning Time 30 minutes
 Purpose The intent of this course is to provide you with information about the main features of the S08 Timer/PWM (TPM) interface module and how to configure and use it in common applications. Objectives
Purpose The intent of this course is to provide you with information about the main features of the S08 Timer/PWM (TPM) interface module and how to configure and use it in common applications. Objectives
University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 Electrical Engineering Design II Fall 2013
 Exercise 1: PWM Modulator University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 Electrical Engineering Design II Fall 2013 Lab 3: Power-System Components and
Exercise 1: PWM Modulator University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 Electrical Engineering Design II Fall 2013 Lab 3: Power-System Components and
DC SERVO MOTOR CONTROL SYSTEM
 DC SERVO MOTOR CONTROL SYSTEM MODEL NO:(PEC - 00CE) User Manual Version 2.0 Technical Clarification /Suggestion : / Technical Support Division, Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd., Plot No :75,Electronics Estate,
DC SERVO MOTOR CONTROL SYSTEM MODEL NO:(PEC - 00CE) User Manual Version 2.0 Technical Clarification /Suggestion : / Technical Support Division, Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd., Plot No :75,Electronics Estate,
