Advanced Digital Signal Processing Part 2: Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals
|
|
|
- Alberta Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advanced Digital Signal Processing Part 2: Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Gerhard Schmidt Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel Faculty of Engineering Institute of Electrical Engineering and Information Engineering Digital Signal Processing and System Theory
2 Contents Introduction Digital processing of continuous-time signals Sampling and sampling theorem (repetition) Quantization Analog-to-digital (AD) and digital-to-analog (DA) conversion DFT and FFT Digital filters Multi-rate digital signal processing Slide II-2
3 Basic System Refined digital signal processing system: Analog input signal Anti-aliasing lowpass filter Sample and hold circuit AD converter Digital input signal Digital signal processing Analog output signal Lowpass reconstruction filter Sample and hold circuit DA converter Digital output signal Slide II-3
4 Sampling Part 1 Basic idea: Generation of discrete-time signals from continuous-time signals. Ideal sampling: An ideally sampled signal with a periodic impulse train is obtained by multiplication of the continuous-time signal where is the Dirac delta function and the sampling period. We obtain using the gating property of Dirac delta functions Slide II-4
5 Sampling Part 2 Ideal sampling: The lengths of Dirac deltas correspond to their weightings! Slide II-5
6 Sampling Part 3 How does the Fourier transform look like? Fourier transform of an impulse train with A multiplication in the time domain represents a convolution in the Fourier domain, thus we obtain for the spectrum of the signal : Inserting the spectrum of an impulse train leads to Periodically repeated copies of multiples of the sampling frequency!, shifted by integer Slide II-6
7 Sampling Part 4 How does the Fourier transform look like? Fourier transform of a bandlimited analog input signal, highest frequency is. Fourier transform of the Dirac impulse train. Result of the convolution is evident that when or, the replicas of do not overlap. In this case can be recovered by ideal lowpass filtering (later called sampling theorem ). If the condition above does not hold, i.e. if, the copies of overlap and the signal cannot be recovered by lowpass filtering. The distortion in the gray shaded areas are called aliasing.. It Slide II-7
8 Sampling Part 5 Non-ideal sampling Modeling the sampling operation with the Dirac impulse train is not a feasible model in real life, since we always need a finite amount of time for acquiring a signal sample. Non-ideally sampled signals are obtained by multiplication of a continuous-time signal with a periodic rectangular window function : with denotes the rectangular prototype window with Slide II-8
9 Sampling Part 6 Fourier transform of : The Fourier transform of the rectangular time window can be computed as a function (see examples of the Fourier transform): Using this result for computing the Fourier transform of leads to inserting the result from above and using the gating property of Dirac delta functions inserting the definition of Slide II-9
10 Sampling Part 7 Fourier transform of : Transforming the signal into the frequency domain leads to Using this result for computing the Fourier transform of leads to We can deduce the following: Compared to the result in the ideal sampling case here each repeated spectrum at the center frequency is weighted with the term. The energy is proportional to. This is problematic since in order to approximate the ideal case we would like to choose the parameter as small as possible. Slide II-10
11 Sampling Part 8 Sampling performed by a sample-and-hold (S/H) circuit: Sample-andhold command Analog pre-amplifier Input S H Sample and hold S Convert command AD converter Status Tracking in sample (T) H Holding (H) S H To computer or communication channel Sample-and-hold output H S S H S The goal is to continuously sample the input signal and to hold that value constant as long as it takes for the AD converter to obtain its digital representation. Ideal S/H circuit introduces no distortion and can be modeled as an ideal sampler. As a result: drawbacks for the non-ideal sampling case can be avoided (all results for the ideal case hold here as well). Figure following [Proakis, Manolakis, 1996] Slide II-11
12 Sampling Theorem Part 1 Reconstruction of an ideally sampled signal by ideal lowpass filtering: Slide II-12
13 Sampling Theorem Part 2 Reconstruction of an ideally sampled signal by ideal lowpass filtering: In order to get the input signal back after reconstruction, i.e., the conditions and have both to be satisfied. In this case, we get We now choose the cutoff frequency of the lowpass filter as. This satisfies both conditions from above. An ideal lowpass filter (see before) can be described by its time and frequency response: Slide II-13
14 Sampling Theorem Part 3 Reconstruction of an ideally sampled signal by ideal lowpass filtering: Combining everything leads to: changing the order of the summation and the integration inserting the properties of the Dirac distribution Result: Every band-limited continuous-time signal with can be uniquely recovered from its samples according to This is called the ideal interpolation formula, and the si-function is named ideal interpolation function! Slide II-14
15 Sampling Theorem Part 4 Reconstruction of a continuous-time signal using ideal interpolation: Basic principle: From [Proakis, Manolakis, 1996] Anti-aliasing lowpass filtering: In order to avoid aliasing, the continuous-time input signal has to be bandlimited by means of an anti-aliasing lowpass-filter with cut-off frequency prior to sampling, such that the sampling theorem is satisfied. Slide II-15
16 Reconstruction with Sample-and-Hold Circuits Part 1 Signal reconstruction: In practice, a reconstruction is carried out by combining a DA converter with a sample-and-hold circuit, followed by a lowpass reconstruction filter. Digital input signal DA converter Sample-andhold circuit Lowpass (reconstruction) filter A DA converter accepts electrical signals that correspond to binary words as input, and delivers an output voltage or current being proportional to the value of the binary word for every clock interval. Often, the application on an input code word yields a high-amplitude transient at the output of the DA converter ( glitch ). Thus, the sample-and-hold circuit serves as a deglitcher. Slide II-16
17 Reconstruction with Sample-and-Hold Circuits Part 2 Analysis: The sample and hold circuit has the impulse response which can be transformed into the frequency response Consequences: No sharp cutoff frequency response characteristics. Thus, we have undesirable frequency components (above ), which can be removed by passing through a lowpass reconstruction filter. This operation is equivalent to smoothing the staircase-like signal after the sample-and-hold operation. When we now suppose that the reconstruction filter is an ideal lowpass with cutoff frequency and an amplification of one, the only distortion in the reconstructed signal is due to the sample-and-hold operation: However, in case of non-ideal reconstruction filters we have additional distortions. Slide II-17
18 Reconstruction with Sample-and-Hold Circuits Part 3 Spectral interpretation of the reconstruction process: Magnitude frequency response of the ideally sampled continuous-time signal. Frequency response of the sample-and-hold circuit (phase factor omitted). Magnitude frequency response after the sample-and-hold circuit. Magnitude frequency response of the lowpass reconstruction filter. Magnitude frequency response of the reconstructed continuous-time signal. Distortion due to the sinc function may be corrected by pre-biasing the reconstruction filter. Slide II-18
19 Quantization Part 1 Basics: Conversion carried out by an AD converter involves quantization of the sampled input signal and the encoding of the resulting binary representation. Quantization is a non-linear and non-invertible process which realizes the mapping where the amplitude is taken from a finite alphabet. The signal amplitude range is divided into intervals using the decision levels : Quantization level Decision level Amplitude Slide II-19
20 Quantization Part 2 Basics (continued): The mapping is denoted as Uniform or linear quantizers with constant quantization step size used in signal processing applications: are very often Two main types of linear quantizers: Midtread quantizer - zero is assigned as a quantization level. Midrise quantizer - zero is assigned as a decision level. Example: Midtread quantizer with levels and range Range Amplitude of quantizer Slide II-20
21 Quantization Part 3 Basics (continued): The quantization error signal (with respect to the unquantized signal) is defined as Without reaching the limits of the quantizer we get for the quantization error If the dynamic range of the input signal is larger than the range of the quantizer, the samples exceeding the quantizer range are clipped, which leads to Slide II-21
22 Quantization Part 4 Quantization characteristic for a midtread quantizer with (3 bits): Mirrored at zero and inverted From [Proakis, Manolakis, 1996] Slide II-22
23 Quantization Part 5 Coding: The coding process in an AD converter assigns a binary number to each quantization level. With a word length of bits we can represent binary numbers, which yields The step size or the resolution of the AD converter is given as with the range of the quantizer. Two s complement representation is used in most fixed-point DSPs: A -bit binary fraction with denoting the most significant bit (MSB) and the least significant bit (LSB), represents the value Slide II-23
24 Quantization Part 6 Commonly used bipolar codes: Number Positive reference Negative reference Sign and magnitude Two s complement Offset binary One s complement +7 +7/8-7/ /4-3/ /8-5/ /2-1/ /8-3/ /4-1/ /8-1/ ( ) ( ) /8 +1/ /4 +1/ /8 +3/ /1 +1/ /8 +5/ /4 +3/ /8 +7/ Slide II-24
25 Quantization Part 7 Commonly used bipolar codes: Conversions to integer numbers: Sign and magnitude: Two s complement: Offset binary: One s complement: Slide II-25
26 Quantization Part 8 Quantization error: The quantization error is modeled as noise, which is added to the unquantized signal: Real system Mathematical model Assumptions: The quantization error range. The error sequence is modeled as a stationary white noise. The error sequence is uncorrelated with the signal sequence. The signal sequence is assumed to have zero mean. The assumptions do not hold in general, but they are fairly well satisfied for large quantizer word lengths. Slide II-26
27 Quantization Part 9 Quantization error (continued): The effect of quantization errors (or quantization noise) on the resulting signal evaluated in terms of the signal- to-noise ratio (SNR) in decibels (db): can be where denotes the signal power and the power of the quantization noise. Quantization noise is assumed to be uniformly distributed in the range : The variance of the quantization noise can be computed as Inserting our definition of the resolution of an AD converter yields Slide II-27
28 Quantization Part 10 Quantization error (continued): Inserting the result from the last slide into our SNR formula yields Remarks: denots here the root-mean-square (RMS) amplitude of the signal. If is too small, the SNR drops as well. If is too large, the range of the AD converter might be exceeded. The signal amplitude has to be matched carefully to the range of the AD converter! Slide II-28
29 Analog-to-Digital Converter Realizations Part 1 Flash AD converters: From [Mitra, 2000], with Analog comparator : resolution in bits Analog input voltage is simultaneously compared with a set of separated reference voltage levels by means of a set of analog comparators. The locations of the comparator circuits indicate the range of the input voltage. All output bits are developed simultaneously. Thus, a very fast conversion is possible. The hardware requirements for this type of converter increase exponentially with an increase in resolution. Flash converters are used for low-resultion and high-speed conversion applications. Slide II-29
30 Analog-to-Digital Converter Realizations Part 2 Serial AD converters: Saw tooth generator Impulse generator And gate Counter Pulse duration modulation: Pulse duration: The counter is detecting the amount of ones that are leaving the and gate. This amount is proportional to it results in. Slide II-30
31 Digital-to-Analog Converter Realizations Part 1 Possible realization: Switches, that are controlled by bits: Sign bit Analysis for : with actually Due to linearity we get: (conductance) This results in (if we neglect the offset): It s important to meet the accuracy requirements for the resistors (especially due to the large range of values). Slide II-31
32 Analog-to-Digital Converter Realizations Part 2 Circuit analysis: Understanding of the circuit if only a single bit is set to one on the one hand and for an arbitrary bit setup on the other hand at the blackboard. However, for reason of simplicity we assume that the sign bit is set such, that we have a positive output voltage. Details at the blackboard! Slide II-32
33 Partner Work Part 1 Questions Part 1: Partner work Please think about the following questions and try to find answers (first group discussions, afterwards broad discussion in the whole group). What are the necessary components if you want to replace an analog system by a digital one? What to you need to know about the involved systems and signals? What kind of converter type would you use for different applications? Which system properties are important to make this decision? Slide II-33
34 Partner Work Part 2 Questions Part 2: What is meant by digital?.... Can you think of applications where analog processing would be beneficial compared to digital processing? Give examples for such applications!.... What happens if you neglect anti-aliasing filtering before sampling? Slide II-34
35 Summary Introduction Digital processing of continuous-time signals Sampling and sampling theorem (repetition) Quantization Analog-to-digital (AD) and digital-to-analog (DA) conversion DFT and FFT Digital filters Multi-rate digital signal processing Slide II-35
Advanced Digital Signal Processing Part 5: Digital Filters
 Advanced Digital Signal Processing Part 5: Digital Filters Gerhard Schmidt Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel Faculty of Engineering Institute of Electrical and Information Engineering Digital Signal
Advanced Digital Signal Processing Part 5: Digital Filters Gerhard Schmidt Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel Faculty of Engineering Institute of Electrical and Information Engineering Digital Signal
Chapter 2: Digitization of Sound
 Chapter 2: Digitization of Sound Acoustics pressure waves are converted to electrical signals by use of a microphone. The output signal from the microphone is an analog signal, i.e., a continuous-valued
Chapter 2: Digitization of Sound Acoustics pressure waves are converted to electrical signals by use of a microphone. The output signal from the microphone is an analog signal, i.e., a continuous-valued
145M Final Exam Solutions page 1 May 11, 2010 S. Derenzo R/2. Vref. Address encoder logic. Exclusive OR. Digital output (8 bits) V 1 2 R/2
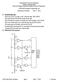 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Department 145M Microcomputer Interfacing Lab Final Exam Solutions May 11, 2010 1.1 Handshaking steps: When
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Department 145M Microcomputer Interfacing Lab Final Exam Solutions May 11, 2010 1.1 Handshaking steps: When
Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals
 Chapter 4 Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals 清大電機系林嘉文 cwlin@ee.nthu.edu.tw 03-5731152 Original PowerPoint slides prepared by S. K. Mitra 4-1-1 Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Digital
Chapter 4 Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals 清大電機系林嘉文 cwlin@ee.nthu.edu.tw 03-5731152 Original PowerPoint slides prepared by S. K. Mitra 4-1-1 Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Digital
Digital Processing of
 Chapter 4 Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals 清大電機系林嘉文 cwlin@ee.nthu.edu.tw 03-5731152 Original PowerPoint slides prepared by S. K. Mitra 4-1-1 Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Digital
Chapter 4 Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals 清大電機系林嘉文 cwlin@ee.nthu.edu.tw 03-5731152 Original PowerPoint slides prepared by S. K. Mitra 4-1-1 Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Digital
Lecture Schedule: Week Date Lecture Title
 http://elec3004.org Sampling & More 2014 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at The University of Queensland Lecture Schedule: Week Date Lecture Title 1 2-Mar Introduction 3-Mar
http://elec3004.org Sampling & More 2014 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at The University of Queensland Lecture Schedule: Week Date Lecture Title 1 2-Mar Introduction 3-Mar
Sampling and Reconstruction of Analog Signals
 Sampling and Reconstruction of Analog Signals Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to convert an analog signal to a discrete-time sequence via sampling (ii) Ability to construct an analog signal
Sampling and Reconstruction of Analog Signals Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to convert an analog signal to a discrete-time sequence via sampling (ii) Ability to construct an analog signal
Sampling and Signal Processing
 Sampling and Signal Processing Sampling Methods Sampling is most commonly done with two devices, the sample-and-hold (S/H) and the analog-to-digital-converter (ADC) The S/H acquires a continuous-time signal
Sampling and Signal Processing Sampling Methods Sampling is most commonly done with two devices, the sample-and-hold (S/H) and the analog-to-digital-converter (ADC) The S/H acquires a continuous-time signal
Sampling and Pulse Trains
 Sampling and Pulse Trains Sampling and interpolation Practical interpolation Pulse trains Analog multiplexing Sampling Theorem Sampling theorem: a signal g(t) with bandwidth B can be reconstructed exactly
Sampling and Pulse Trains Sampling and interpolation Practical interpolation Pulse trains Analog multiplexing Sampling Theorem Sampling theorem: a signal g(t) with bandwidth B can be reconstructed exactly
Module 3 : Sampling and Reconstruction Problem Set 3
 Module 3 : Sampling and Reconstruction Problem Set 3 Problem 1 Shown in figure below is a system in which the sampling signal is an impulse train with alternating sign. The sampling signal p(t), the Fourier
Module 3 : Sampling and Reconstruction Problem Set 3 Problem 1 Shown in figure below is a system in which the sampling signal is an impulse train with alternating sign. The sampling signal p(t), the Fourier
Time division multiplexing The block diagram for TDM is illustrated as shown in the figure
 CHAPTER 2 Syllabus: 1) Pulse amplitude modulation 2) TDM 3) Wave form coding techniques 4) PCM 5) Quantization noise and SNR 6) Robust quantization Pulse amplitude modulation In pulse amplitude modulation,
CHAPTER 2 Syllabus: 1) Pulse amplitude modulation 2) TDM 3) Wave form coding techniques 4) PCM 5) Quantization noise and SNR 6) Robust quantization Pulse amplitude modulation In pulse amplitude modulation,
! Multi-Rate Filter Banks (con t) ! Data Converters. " Anti-aliasing " ADC. " Practical DAC. ! Noise Shaping
 Lecture Outline ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing! (con t)! Data Converters Lec 11: February 16th, 2017 Data Converters, Noise Shaping " Anti-aliasing " ADC " Quantization "! Noise Shaping 2! Use filter
Lecture Outline ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing! (con t)! Data Converters Lec 11: February 16th, 2017 Data Converters, Noise Shaping " Anti-aliasing " ADC " Quantization "! Noise Shaping 2! Use filter
Design IV. E232 Spring 07
 Design IV Spring 07 Class 8 Bruce McNair bmcnair@stevens.edu 8-1/38 Computerized Data Acquisition Measurement system architecture System under test sensor sensor sensor sensor signal conditioning signal
Design IV Spring 07 Class 8 Bruce McNair bmcnair@stevens.edu 8-1/38 Computerized Data Acquisition Measurement system architecture System under test sensor sensor sensor sensor signal conditioning signal
Chapter 2 Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion
 09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
Understanding Digital Signal Processing
 Understanding Digital Signal Processing Richard G. Lyons PRENTICE HALL PTR PRENTICE HALL Professional Technical Reference Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 www.photr,com Contents Preface xi 1 DISCRETE
Understanding Digital Signal Processing Richard G. Lyons PRENTICE HALL PTR PRENTICE HALL Professional Technical Reference Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 www.photr,com Contents Preface xi 1 DISCRETE
Islamic University of Gaza. Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Spring-2011
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Spring-2011 DSP Laboratory (EELE 4110) Lab#4 Sampling and Quantization OBJECTIVES: When you have completed this assignment,
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Spring-2011 DSP Laboratory (EELE 4110) Lab#4 Sampling and Quantization OBJECTIVES: When you have completed this assignment,
Electronics A/D and D/A converters
 Electronics A/D and D/A converters Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács, Dr. György Bognár, Dr. Péter G. Szabó BME DED December 1, 2014 1 / 26 Introduction The world is analog, signal processing nowadays is
Electronics A/D and D/A converters Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács, Dr. György Bognár, Dr. Péter G. Szabó BME DED December 1, 2014 1 / 26 Introduction The world is analog, signal processing nowadays is
CHAPTER 4. PULSE MODULATION Part 2
 CHAPTER 4 PULSE MODULATION Part 2 Pulse Modulation Analog pulse modulation: Sampling, i.e., information is transmitted only at discrete time instants. e.g. PAM, PPM and PDM Digital pulse modulation: Sampling
CHAPTER 4 PULSE MODULATION Part 2 Pulse Modulation Analog pulse modulation: Sampling, i.e., information is transmitted only at discrete time instants. e.g. PAM, PPM and PDM Digital pulse modulation: Sampling
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
 ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS Definition An analog-to-digital converter is a device which converts continuous signals to discrete digital numbers. Basics An analog-to-digital converter (abbreviated ADC,
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS Definition An analog-to-digital converter is a device which converts continuous signals to discrete digital numbers. Basics An analog-to-digital converter (abbreviated ADC,
ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing
 ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 11: February 20, 2018 Data Converters, Noise Shaping Lecture Outline! Review: Multi-Rate Filter Banks " Quadrature Mirror Filters! Data Converters " Anti-aliasing
ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 11: February 20, 2018 Data Converters, Noise Shaping Lecture Outline! Review: Multi-Rate Filter Banks " Quadrature Mirror Filters! Data Converters " Anti-aliasing
PROBLEM SET 6. Note: This version is preliminary in that it does not yet have instructions for uploading the MATLAB problems.
 PROBLEM SET 6 Issued: 2/32/19 Due: 3/1/19 Reading: During the past week we discussed change of discrete-time sampling rate, introducing the techniques of decimation and interpolation, which is covered
PROBLEM SET 6 Issued: 2/32/19 Due: 3/1/19 Reading: During the past week we discussed change of discrete-time sampling rate, introducing the techniques of decimation and interpolation, which is covered
FFT Analyzer. Gianfranco Miele, Ph.D
 FFT Analyzer Gianfranco Miele, Ph.D www.eng.docente.unicas.it/gianfranco_miele g.miele@unicas.it Introduction It is a measurement instrument that evaluates the spectrum of a time domain signal applying
FFT Analyzer Gianfranco Miele, Ph.D www.eng.docente.unicas.it/gianfranco_miele g.miele@unicas.it Introduction It is a measurement instrument that evaluates the spectrum of a time domain signal applying
!"!#"#$% Lecture 2: Media Creation. Some materials taken from Prof. Yao Wang s slides RECAP
 Lecture 2: Media Creation Some materials taken from Prof. Yao Wang s slides RECAP #% A Big Umbrella Content Creation: produce the media, compress it to a format that is portable/ deliverable Distribution:
Lecture 2: Media Creation Some materials taken from Prof. Yao Wang s slides RECAP #% A Big Umbrella Content Creation: produce the media, compress it to a format that is portable/ deliverable Distribution:
EC 2301 Digital communication Question bank
 EC 2301 Digital communication Question bank UNIT I Digital communication system 2 marks 1.Draw block diagram of digital communication system. Information source and input transducer formatter Source encoder
EC 2301 Digital communication Question bank UNIT I Digital communication system 2 marks 1.Draw block diagram of digital communication system. Information source and input transducer formatter Source encoder
UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System. Mr. Manoj Rajale
 UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System Mr. Manoj Rajale Syllabus Interfacing of Sensors / Actuators to DAQ system, Bit width, Sampling theorem, Sampling Frequency, Aliasing, Sample and hold
UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System Mr. Manoj Rajale Syllabus Interfacing of Sensors / Actuators to DAQ system, Bit width, Sampling theorem, Sampling Frequency, Aliasing, Sample and hold
Digital Signal Processing
 Digital Signal Processing Fourth Edition John G. Proakis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University Boston, Massachusetts Dimitris G. Manolakis MIT Lincoln Laboratory Lexington,
Digital Signal Processing Fourth Edition John G. Proakis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University Boston, Massachusetts Dimitris G. Manolakis MIT Lincoln Laboratory Lexington,
The need for Data Converters
 The need for Data Converters ANALOG SIGNAL (Speech, Images, Sensors, Radar, etc.) PRE-PROCESSING (Filtering and analog to digital conversion) DIGITAL PROCESSOR (Microprocessor) POST-PROCESSING (Digital
The need for Data Converters ANALOG SIGNAL (Speech, Images, Sensors, Radar, etc.) PRE-PROCESSING (Filtering and analog to digital conversion) DIGITAL PROCESSOR (Microprocessor) POST-PROCESSING (Digital
Analyzing A/D and D/A converters
 Analyzing A/D and D/A converters 2013. 10. 21. Pálfi Vilmos 1 Contents 1 Signals 3 1.1 Periodic signals 3 1.2 Sampling 4 1.2.1 Discrete Fourier transform... 4 1.2.2 Spectrum of sampled signals... 5 1.2.3
Analyzing A/D and D/A converters 2013. 10. 21. Pálfi Vilmos 1 Contents 1 Signals 3 1.1 Periodic signals 3 1.2 Sampling 4 1.2.1 Discrete Fourier transform... 4 1.2.2 Spectrum of sampled signals... 5 1.2.3
System on a Chip. Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft
 System on a Chip Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft Lecture 5: Data Conversion ADC Background/Theory Examples Background Physical systems are typically analogue To apply digital signal processing, the analogue signal
System on a Chip Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft Lecture 5: Data Conversion ADC Background/Theory Examples Background Physical systems are typically analogue To apply digital signal processing, the analogue signal
DIGITAL COMMUNICATION
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Spring 00 Yrd. Doç. Dr. Burak Kelleci OUTLINE Quantization Pulse-Code Modulation THE QUANTIZATION PROCESS A continuous signal has
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Spring 00 Yrd. Doç. Dr. Burak Kelleci OUTLINE Quantization Pulse-Code Modulation THE QUANTIZATION PROCESS A continuous signal has
Analog to digital and digital to analog converters
 Analog to digital and digital to analog converters A/D converter D/A converter ADC DAC ad da Number bases Decimal, base, numbers - 9 Binary, base, numbers and Oktal, base 8, numbers - 7 Hexadecimal, base
Analog to digital and digital to analog converters A/D converter D/A converter ADC DAC ad da Number bases Decimal, base, numbers - 9 Binary, base, numbers and Oktal, base 8, numbers - 7 Hexadecimal, base
The Fundamentals of Mixed Signal Testing
 The Fundamentals of Mixed Signal Testing Course Information The Fundamentals of Mixed Signal Testing course is designed to provide the foundation of knowledge that is required for testing modern mixed
The Fundamentals of Mixed Signal Testing Course Information The Fundamentals of Mixed Signal Testing course is designed to provide the foundation of knowledge that is required for testing modern mixed
Cyber-Physical Systems ADC / DAC
 Cyber-Physical Systems ADC / DAC ICEN 553/453 Fall 2018 Prof. Dola Saha 1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Ø ADC is important almost to all application fields Ø Converts a continuous-time voltage signal
Cyber-Physical Systems ADC / DAC ICEN 553/453 Fall 2018 Prof. Dola Saha 1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Ø ADC is important almost to all application fields Ø Converts a continuous-time voltage signal
Concordia University. Discrete-Time Signal Processing. Lab Manual (ELEC442) Dr. Wei-Ping Zhu
 Concordia University Discrete-Time Signal Processing Lab Manual (ELEC442) Course Instructor: Dr. Wei-Ping Zhu Fall 2012 Lab 1: Linear Constant Coefficient Difference Equations (LCCDE) Objective In this
Concordia University Discrete-Time Signal Processing Lab Manual (ELEC442) Course Instructor: Dr. Wei-Ping Zhu Fall 2012 Lab 1: Linear Constant Coefficient Difference Equations (LCCDE) Objective In this
 UNIT III -- DATA AND PULSE COMMUNICATION PART-A 1. State the sampling theorem for band-limited signals of finite energy. If a finite energy signal g(t) contains no frequency higher than W Hz, it is completely
UNIT III -- DATA AND PULSE COMMUNICATION PART-A 1. State the sampling theorem for band-limited signals of finite energy. If a finite energy signal g(t) contains no frequency higher than W Hz, it is completely
Lecture Outline. ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing. Anti-Aliasing Filter with ADC ADC. Oversampled ADC. Oversampled ADC
 Lecture Outline ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 12: February 21st, 2017 Data Converters, Noise Shaping (con t)! Data Converters " Anti-aliasing " ADC " Quantization "! Noise Shaping 2 Anti-Aliasing
Lecture Outline ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 12: February 21st, 2017 Data Converters, Noise Shaping (con t)! Data Converters " Anti-aliasing " ADC " Quantization "! Noise Shaping 2 Anti-Aliasing
Laboratory Manual 2, MSPS. High-Level System Design
 No Rev Date Repo Page 0002 A 2011-09-07 MSPS 1 of 16 Title High-Level System Design File MSPS_0002_LM_matlabSystem_A.odt Type EX -- Laboratory Manual 2, Area MSPS ES : docs : courses : msps Created Per
No Rev Date Repo Page 0002 A 2011-09-07 MSPS 1 of 16 Title High-Level System Design File MSPS_0002_LM_matlabSystem_A.odt Type EX -- Laboratory Manual 2, Area MSPS ES : docs : courses : msps Created Per
The Sampling Theorem:
 The Sampling Theorem: Aim: Experimental verification of the sampling theorem; sampling and message reconstruction (interpolation). Experimental Procedure: Taking Samples: In the first part of the experiment
The Sampling Theorem: Aim: Experimental verification of the sampling theorem; sampling and message reconstruction (interpolation). Experimental Procedure: Taking Samples: In the first part of the experiment
QUESTION BANK. SUBJECT CODE / Name: EC2301 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION UNIT 2
 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: ECE SEMESTER: V SUBJECT CODE / Name: EC2301 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION UNIT 2 BASEBAND FORMATTING TECHNIQUES 1. Why prefilterring done before sampling [AUC NOV/DEC 2010] The signal
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: ECE SEMESTER: V SUBJECT CODE / Name: EC2301 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION UNIT 2 BASEBAND FORMATTING TECHNIQUES 1. Why prefilterring done before sampling [AUC NOV/DEC 2010] The signal
ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing
 ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 12: February 21st, 2017 Data Converters, Noise Shaping (con t) Lecture Outline! Data Converters " Anti-aliasing " ADC " Quantization " Practical DAC! Noise Shaping
ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 12: February 21st, 2017 Data Converters, Noise Shaping (con t) Lecture Outline! Data Converters " Anti-aliasing " ADC " Quantization " Practical DAC! Noise Shaping
Sampling and Pulse Code Modulation Chapter 6
 Sampling and Pulse Code Modulation Chapter 6 Dr. Yun Q. Shi Dept of Electrical & Computer Engineering New Jersey Institute of Technology shi@njit.edu Sampling Theorem A Signal is said to be band-limited
Sampling and Pulse Code Modulation Chapter 6 Dr. Yun Q. Shi Dept of Electrical & Computer Engineering New Jersey Institute of Technology shi@njit.edu Sampling Theorem A Signal is said to be band-limited
EEE 309 Communication Theory
 EEE 309 Communication Theory Semester: January 2017 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Associate Professor Department of EEE, BUET Email: mfarhadhossain@eee.buet.ac.bd Office: ECE 331, ECE Building Types of Modulation
EEE 309 Communication Theory Semester: January 2017 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Associate Professor Department of EEE, BUET Email: mfarhadhossain@eee.buet.ac.bd Office: ECE 331, ECE Building Types of Modulation
Chapter-2 SAMPLING PROCESS
 Chapter-2 SAMPLING PROCESS SAMPLING: A message signal may originate from a digital or analog source. If the message signal is analog in nature, then it has to be converted into digital form before it can
Chapter-2 SAMPLING PROCESS SAMPLING: A message signal may originate from a digital or analog source. If the message signal is analog in nature, then it has to be converted into digital form before it can
DIGITAL processing has become ubiquitous, and is the
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 59, NO. 4, APRIL 2011 1491 Multichannel Sampling of Pulse Streams at the Rate of Innovation Kfir Gedalyahu, Ronen Tur, and Yonina C. Eldar, Senior Member, IEEE
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 59, NO. 4, APRIL 2011 1491 Multichannel Sampling of Pulse Streams at the Rate of Innovation Kfir Gedalyahu, Ronen Tur, and Yonina C. Eldar, Senior Member, IEEE
EEE 309 Communication Theory
 EEE 309 Communication Theory Semester: January 2016 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Associate Professor Department of EEE, BUET Email: mfarhadhossain@eee.buet.ac.bd Office: ECE 331, ECE Building Part 05 Pulse Code
EEE 309 Communication Theory Semester: January 2016 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Associate Professor Department of EEE, BUET Email: mfarhadhossain@eee.buet.ac.bd Office: ECE 331, ECE Building Part 05 Pulse Code
(i) Understanding of the characteristics of linear-phase finite impulse response (FIR) filters
 FIR Filter Design Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding of the characteristics of linear-phase finite impulse response (FIR) filters (ii) Ability to design linear-phase FIR filters according
FIR Filter Design Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding of the characteristics of linear-phase finite impulse response (FIR) filters (ii) Ability to design linear-phase FIR filters according
Chapter 7. Introduction. Analog Signal and Discrete Time Series. Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition
 Chapter 7 Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition Material from Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements; Figliola, Third Edition Introduction Integrating analog electrical transducers with
Chapter 7 Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition Material from Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements; Figliola, Third Edition Introduction Integrating analog electrical transducers with
Module 3 : Sampling & Reconstruction Lecture 26 : Ideal low pass filter
 Module 3 : Sampling & Reconstruction Lecture 26 : Ideal low pass filter Objectives: Scope of this Lecture: We saw that the ideal low pass filter can be used to reconstruct the original Continuous time
Module 3 : Sampling & Reconstruction Lecture 26 : Ideal low pass filter Objectives: Scope of this Lecture: We saw that the ideal low pass filter can be used to reconstruct the original Continuous time
A-D and D-A Converters
 Chapter 5 A-D and D-A Converters (No mathematical derivations) 04 Hours 08 Marks When digital devices are to be interfaced with analog devices (or vice a versa), Digital to Analog converter and Analog
Chapter 5 A-D and D-A Converters (No mathematical derivations) 04 Hours 08 Marks When digital devices are to be interfaced with analog devices (or vice a versa), Digital to Analog converter and Analog
ECE 2111 Signals and Systems Spring 2012, UMD Experiment 9: Sampling
 ECE 2111 Signals and Systems Spring 2012, UMD Experiment 9: Sampling Objective: In this experiment the properties and limitations of the sampling theorem are investigated. A specific sampling circuit will
ECE 2111 Signals and Systems Spring 2012, UMD Experiment 9: Sampling Objective: In this experiment the properties and limitations of the sampling theorem are investigated. A specific sampling circuit will
Lecture #6: Analog-to-Digital Converter
 Lecture #6: Analog-to-Digital Converter All electrical signals in the real world are analog, and their waveforms are continuous in time. Since most signal processing is done digitally in discrete time,
Lecture #6: Analog-to-Digital Converter All electrical signals in the real world are analog, and their waveforms are continuous in time. Since most signal processing is done digitally in discrete time,
Experiment 8: Sampling
 Prepared By: 1 Experiment 8: Sampling Objective The objective of this Lab is to understand concepts and observe the effects of periodically sampling a continuous signal at different sampling rates, changing
Prepared By: 1 Experiment 8: Sampling Objective The objective of this Lab is to understand concepts and observe the effects of periodically sampling a continuous signal at different sampling rates, changing
ECE 556 BASICS OF DIGITAL SPEECH PROCESSING. Assıst.Prof.Dr. Selma ÖZAYDIN Spring Term-2017 Lecture 2
 ECE 556 BASICS OF DIGITAL SPEECH PROCESSING Assıst.Prof.Dr. Selma ÖZAYDIN Spring Term-2017 Lecture 2 Analog Sound to Digital Sound Characteristics of Sound Amplitude Wavelength (w) Frequency ( ) Timbre
ECE 556 BASICS OF DIGITAL SPEECH PROCESSING Assıst.Prof.Dr. Selma ÖZAYDIN Spring Term-2017 Lecture 2 Analog Sound to Digital Sound Characteristics of Sound Amplitude Wavelength (w) Frequency ( ) Timbre
INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS LABORATORY IV. Binary Pulse Amplitude Modulation and Pulse Code Modulation
 INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Introduction: LABORATORY IV Binary Pulse Amplitude Modulation and Pulse Code Modulation In this lab we will explore some of the elementary characteristics of binary
INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Introduction: LABORATORY IV Binary Pulse Amplitude Modulation and Pulse Code Modulation In this lab we will explore some of the elementary characteristics of binary
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject Name: Digital Communication Techniques
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject Code: EC1351 Year/Sem: III/IV Subject Name: Digital Communication Techniques UNIT I PULSE MODULATION
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject Code: EC1351 Year/Sem: III/IV Subject Name: Digital Communication Techniques UNIT I PULSE MODULATION
Experiment 2 Effects of Filtering
 Experiment 2 Effects of Filtering INTRODUCTION This experiment demonstrates the relationship between the time and frequency domains. A basic rule of thumb is that the wider the bandwidth allowed for the
Experiment 2 Effects of Filtering INTRODUCTION This experiment demonstrates the relationship between the time and frequency domains. A basic rule of thumb is that the wider the bandwidth allowed for the
QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold
 QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold circuit 2. What is the difference between natural sampling
QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold circuit 2. What is the difference between natural sampling
(i) Understanding of the characteristics of linear-phase finite impulse response (FIR) filters
 FIR Filter Design Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding of the characteristics of linear-phase finite impulse response (FIR) filters (ii) Ability to design linear-phase FIR filters according
FIR Filter Design Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding of the characteristics of linear-phase finite impulse response (FIR) filters (ii) Ability to design linear-phase FIR filters according
CT111 Introduction to Communication Systems Lecture 9: Digital Communications
 CT111 Introduction to Communication Systems Lecture 9: Digital Communications Yash M. Vasavada Associate Professor, DA-IICT, Gandhinagar 31st January 2018 Yash M. Vasavada (DA-IICT) CT111: Intro to Comm.
CT111 Introduction to Communication Systems Lecture 9: Digital Communications Yash M. Vasavada Associate Professor, DA-IICT, Gandhinagar 31st January 2018 Yash M. Vasavada (DA-IICT) CT111: Intro to Comm.
Waveform Encoding - PCM. BY: Dr.AHMED ALKHAYYAT. Chapter Two
 Chapter Two Layout: 1. Introduction. 2. Pulse Code Modulation (PCM). 3. Differential Pulse Code Modulation (DPCM). 4. Delta modulation. 5. Adaptive delta modulation. 6. Sigma Delta Modulation (SDM). 7.
Chapter Two Layout: 1. Introduction. 2. Pulse Code Modulation (PCM). 3. Differential Pulse Code Modulation (DPCM). 4. Delta modulation. 5. Adaptive delta modulation. 6. Sigma Delta Modulation (SDM). 7.
Audio /Video Signal Processing. Lecture 1, Organisation, A/D conversion, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau
 Audio /Video Signal Processing Lecture 1, Organisation, A/D conversion, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau Gerald Schuller gerald.schuller@tu ilmenau.de Organisation: Lecture each week, 2SWS, Seminar
Audio /Video Signal Processing Lecture 1, Organisation, A/D conversion, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau Gerald Schuller gerald.schuller@tu ilmenau.de Organisation: Lecture each week, 2SWS, Seminar
Lecture 9, ANIK. Data converters 1
 Lecture 9, ANIK Data converters 1 What did we do last time? Noise and distortion Understanding the simplest circuit noise Understanding some of the sources of distortion 502 of 530 What will we do today?
Lecture 9, ANIK Data converters 1 What did we do last time? Noise and distortion Understanding the simplest circuit noise Understanding some of the sources of distortion 502 of 530 What will we do today?
Analogue Interfacing. What is a signal? Continuous vs. Discrete Time. Continuous time signals
 Analogue Interfacing What is a signal? Signal: Function of one or more independent variable(s) such as space or time Examples include images and speech Continuous vs. Discrete Time Continuous time signals
Analogue Interfacing What is a signal? Signal: Function of one or more independent variable(s) such as space or time Examples include images and speech Continuous vs. Discrete Time Continuous time signals
The Digital Linear Amplifier
 The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 7, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau
 Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 7, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau (Also see: Lecture ADSP, Slides 06) In discrete, digital signal we use the normalized frequency, T = / f s =: it is without a
Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 7, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau (Also see: Lecture ADSP, Slides 06) In discrete, digital signal we use the normalized frequency, T = / f s =: it is without a
6 Sampling. Sampling. The principles of sampling, especially the benefits of coherent sampling
 Note: Printed Manuals 6 are not in Color Objectives This chapter explains the following: The principles of sampling, especially the benefits of coherent sampling How to apply sampling principles in a test
Note: Printed Manuals 6 are not in Color Objectives This chapter explains the following: The principles of sampling, especially the benefits of coherent sampling How to apply sampling principles in a test
Data Converter Topics. Suggested Reference Texts
 Data Converter Topics Basic Operation of Data Converters Uniform sampling and reconstruction Uniform amplitude quantization Characterization and Testing Common ADC/DAC Architectures Selected Topics in
Data Converter Topics Basic Operation of Data Converters Uniform sampling and reconstruction Uniform amplitude quantization Characterization and Testing Common ADC/DAC Architectures Selected Topics in
Advantages of Analog Representation. Varies continuously, like the property being measured. Represents continuous values. See Figure 12.
 Analog Signals Signals that vary continuously throughout a defined range. Representative of many physical quantities, such as temperature and velocity. Usually a voltage or current level. Digital Signals
Analog Signals Signals that vary continuously throughout a defined range. Representative of many physical quantities, such as temperature and velocity. Usually a voltage or current level. Digital Signals
Lab.3. Tutorial : (draft) Introduction to CODECs
 Lab.3. Tutorial : (draft) Introduction to CODECs Fig. Basic digital signal processing system Definition A codec is a device or computer program capable of encoding or decoding a digital data stream or
Lab.3. Tutorial : (draft) Introduction to CODECs Fig. Basic digital signal processing system Definition A codec is a device or computer program capable of encoding or decoding a digital data stream or
CHAPTER. delta-sigma modulators 1.0
 CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER Conventional delta-sigma modulators 1.0 This Chapter presents the traditional first- and second-order DSM. The main sources for non-ideal operation are described together with some commonly
CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER Conventional delta-sigma modulators 1.0 This Chapter presents the traditional first- and second-order DSM. The main sources for non-ideal operation are described together with some commonly
Lecture 3 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 2. EE4900/EE6720 Digital Communications
 EE4900/EE6720: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 3 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 2 Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
EE4900/EE6720: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 3 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 2 Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
ME scope Application Note 01 The FFT, Leakage, and Windowing
 INTRODUCTION ME scope Application Note 01 The FFT, Leakage, and Windowing NOTE: The steps in this Application Note can be duplicated using any Package that includes the VES-3600 Advanced Signal Processing
INTRODUCTION ME scope Application Note 01 The FFT, Leakage, and Windowing NOTE: The steps in this Application Note can be duplicated using any Package that includes the VES-3600 Advanced Signal Processing
Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection
 Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection Aim: overview of existing methods and techniques Terms used: -Data entities conveying meaning (of information) -Signals data
Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection Aim: overview of existing methods and techniques Terms used: -Data entities conveying meaning (of information) -Signals data
A/D Converter An electronic circuit that transforms an analog signal into a digital form that can be used by a computer or other digital circuits.
 Digital Audio Terms A/D Converter An electronic circuit that transforms an analog signal into a digital form that can be used by a computer or other digital circuits. Aliasing An undesirable effect that
Digital Audio Terms A/D Converter An electronic circuit that transforms an analog signal into a digital form that can be used by a computer or other digital circuits. Aliasing An undesirable effect that
Fundamentals of Digital Communication
 Fundamentals of Digital Communication Network Infrastructures A.A. 2017/18 Digital communication system Analog Digital Input Signal Analog/ Digital Low Pass Filter Sampler Quantizer Source Encoder Channel
Fundamentals of Digital Communication Network Infrastructures A.A. 2017/18 Digital communication system Analog Digital Input Signal Analog/ Digital Low Pass Filter Sampler Quantizer Source Encoder Channel
Signals and Systems. Lecture 13 Wednesday 6 th December 2017 DR TANIA STATHAKI
 Signals and Systems Lecture 13 Wednesday 6 th December 2017 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Continuous time versus discrete time Continuous time
Signals and Systems Lecture 13 Wednesday 6 th December 2017 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Continuous time versus discrete time Continuous time
EECS 452 Midterm Exam (solns) Fall 2012
 EECS 452 Midterm Exam (solns) Fall 2012 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: # Points Section I /40 Section
EECS 452 Midterm Exam (solns) Fall 2012 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: # Points Section I /40 Section
Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals. Reference chapter 4 in Oppenheim and Schafer.
 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Reference chapter 4 in Oppenheim and Schafer. Periodic Sampling of Continuous Signals T = sampling period fs = sampling frequency when expressing frequencies in radians
Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Reference chapter 4 in Oppenheim and Schafer. Periodic Sampling of Continuous Signals T = sampling period fs = sampling frequency when expressing frequencies in radians
Speech Coding in the Frequency Domain
 Speech Coding in the Frequency Domain Speech Processing Advanced Topics Tom Bäckström Aalto University October 215 Introduction The speech production model can be used to efficiently encode speech signals.
Speech Coding in the Frequency Domain Speech Processing Advanced Topics Tom Bäckström Aalto University October 215 Introduction The speech production model can be used to efficiently encode speech signals.
EE 210 Lab Exercise #4 D/A & A/D Converters
 EE 210 Lab Exercise #4 D/A & A/D Converters Introduction This lab deals with simple resistive circuits to perform Digital-to-Analog (D/A) conversion. We also introduce the use of a basic Analog-to-Digital
EE 210 Lab Exercise #4 D/A & A/D Converters Introduction This lab deals with simple resistive circuits to perform Digital-to-Analog (D/A) conversion. We also introduce the use of a basic Analog-to-Digital
Communications I (ELCN 306)
 Communications I (ELCN 306) c Samy S. Soliman Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department Cairo University, Egypt Email: samy.soliman@cu.edu.eg Website: http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/samysoliman
Communications I (ELCN 306) c Samy S. Soliman Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department Cairo University, Egypt Email: samy.soliman@cu.edu.eg Website: http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/samysoliman
Linear Time-Invariant Systems
 Linear Time-Invariant Systems Modules: Wideband True RMS Meter, Audio Oscillator, Utilities, Digital Utilities, Twin Pulse Generator, Tuneable LPF, 100-kHz Channel Filters, Phase Shifter, Quadrature Phase
Linear Time-Invariant Systems Modules: Wideband True RMS Meter, Audio Oscillator, Utilities, Digital Utilities, Twin Pulse Generator, Tuneable LPF, 100-kHz Channel Filters, Phase Shifter, Quadrature Phase
System analysis and signal processing
 System analysis and signal processing with emphasis on the use of MATLAB PHILIP DENBIGH University of Sussex ADDISON-WESLEY Harlow, England Reading, Massachusetts Menlow Park, California New York Don Mills,
System analysis and signal processing with emphasis on the use of MATLAB PHILIP DENBIGH University of Sussex ADDISON-WESLEY Harlow, England Reading, Massachusetts Menlow Park, California New York Don Mills,
Digital to Analog Conversion. Data Acquisition
 Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Digital to Analog Conversion Data Acquisition DACs or D/A converters are used to convert digital signals representing binary numbers into proportional analog voltages.
Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Digital to Analog Conversion Data Acquisition DACs or D/A converters are used to convert digital signals representing binary numbers into proportional analog voltages.
7.1 Introduction 7.2 Why Digitize Analog Sources? 7.3 The Sampling Process 7.4 Pulse-Amplitude Modulation Time-Division i i Modulation 7.
 Chapter 7 Digital Representation of Analog Signals Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Contents 7.1 Introduction 7.2
Chapter 7 Digital Representation of Analog Signals Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Contents 7.1 Introduction 7.2
Multirate Digital Signal Processing
 Multirate Digital Signal Processing Basic Sampling Rate Alteration Devices Up-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer factor Down-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer
Multirate Digital Signal Processing Basic Sampling Rate Alteration Devices Up-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer factor Down-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer
Signals A Preliminary Discussion EE442 Analog & Digital Communication Systems Lecture 2
 Signals A Preliminary Discussion EE442 Analog & Digital Communication Systems Lecture 2 The Fourier transform of single pulse is the sinc function. EE 442 Signal Preliminaries 1 Communication Systems and
Signals A Preliminary Discussion EE442 Analog & Digital Communication Systems Lecture 2 The Fourier transform of single pulse is the sinc function. EE 442 Signal Preliminaries 1 Communication Systems and
SIGMA-DELTA CONVERTER
 SIGMA-DELTA CONVERTER (1995: Pacífico R. Concetti Western A. Geophysical-Argentina) The Sigma-Delta A/D Converter is not new in electronic engineering since it has been previously used as part of many
SIGMA-DELTA CONVERTER (1995: Pacífico R. Concetti Western A. Geophysical-Argentina) The Sigma-Delta A/D Converter is not new in electronic engineering since it has been previously used as part of many
Signals and Systems Using MATLAB
 Signals and Systems Using MATLAB Second Edition Luis F. Chaparro Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh, PA, USA AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK
Signals and Systems Using MATLAB Second Edition Luis F. Chaparro Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh, PA, USA AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK
Appendix B. Design Implementation Description For The Digital Frequency Demodulator
 Appendix B Design Implementation Description For The Digital Frequency Demodulator The DFD design implementation is divided into four sections: 1. Analog front end to signal condition and digitize the
Appendix B Design Implementation Description For The Digital Frequency Demodulator The DFD design implementation is divided into four sections: 1. Analog front end to signal condition and digitize the
Infocommunication. Sampling, Quantization. - Bálint TÓTH, BME TMIT -
 Infocommunication Sampling, Quantization - Bálint TÓTH, BME TMIT - Overview PPT is for demonstration, not for learning! Analog signals problem: noise, distortion Digital signals what are the benefits?
Infocommunication Sampling, Quantization - Bálint TÓTH, BME TMIT - Overview PPT is for demonstration, not for learning! Analog signals problem: noise, distortion Digital signals what are the benefits?
Music 270a: Fundamentals of Digital Audio and Discrete-Time Signals
 Music 270a: Fundamentals of Digital Audio and Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego October 3, 2016 1 Continuous vs. Discrete signals
Music 270a: Fundamentals of Digital Audio and Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego October 3, 2016 1 Continuous vs. Discrete signals
Communications IB Paper 6 Handout 3: Digitisation and Digital Signals
 Communications IB Paper 6 Handout 3: Digitisation and Digital Signals Jossy Sayir Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering University of Cambridge jossy.sayir@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent
Communications IB Paper 6 Handout 3: Digitisation and Digital Signals Jossy Sayir Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering University of Cambridge jossy.sayir@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent
Gábor C. Temes. School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Oregon State University. 1/25
 Gábor C. Temes School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Oregon State University temes@ece.orst.edu 1/25 Noise Intrinsic (inherent) noise: generated by random physical effects in the devices.
Gábor C. Temes School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Oregon State University temes@ece.orst.edu 1/25 Noise Intrinsic (inherent) noise: generated by random physical effects in the devices.
Pulse Code Modulation
 Pulse Code Modulation EE 44 Spring Semester Lecture 9 Analog signal Pulse Amplitude Modulation Pulse Width Modulation Pulse Position Modulation Pulse Code Modulation (3-bit coding) 1 Advantages of Digital
Pulse Code Modulation EE 44 Spring Semester Lecture 9 Analog signal Pulse Amplitude Modulation Pulse Width Modulation Pulse Position Modulation Pulse Code Modulation (3-bit coding) 1 Advantages of Digital
Digital Signal Processing
 Digital Signal Processing System Analysis and Design Paulo S. R. Diniz Eduardo A. B. da Silva and Sergio L. Netto Federal University of Rio de Janeiro CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface page xv Introduction
Digital Signal Processing System Analysis and Design Paulo S. R. Diniz Eduardo A. B. da Silva and Sergio L. Netto Federal University of Rio de Janeiro CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface page xv Introduction
KINGS DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING DIGITAL COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUES YEAR/SEM: III / VI BRANCH : ECE PULSE MODULATION
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUB.NAME : EC1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUES BRANCH : ECE YEAR/SEM: III / VI UNIT I PULSE MODULATION PART A (2
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUB.NAME : EC1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUES BRANCH : ECE YEAR/SEM: III / VI UNIT I PULSE MODULATION PART A (2
Figure 1: Block diagram of Digital signal processing
 Experiment 3. Digital Process of Continuous Time Signal. Introduction Discrete time signal processing algorithms are being used to process naturally occurring analog signals (like speech, music and images).
Experiment 3. Digital Process of Continuous Time Signal. Introduction Discrete time signal processing algorithms are being used to process naturally occurring analog signals (like speech, music and images).
(Refer Slide Time: 3:11)
 Digital Communication. Professor Surendra Prasad. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi. Lecture-2. Digital Representation of Analog Signals: Delta Modulation. Professor:
Digital Communication. Professor Surendra Prasad. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi. Lecture-2. Digital Representation of Analog Signals: Delta Modulation. Professor:
IIR Filter Design Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to design analog Butterworth filters
 IIR Filter Design Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to design analog Butterworth filters (ii) Ability to design lowpass IIR filters according to predefined specifications based on analog
IIR Filter Design Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to design analog Butterworth filters (ii) Ability to design lowpass IIR filters according to predefined specifications based on analog
