Classification of Binary 24 V Interfaces - Functional Safety aspects covered by dynamic testing Edition Timing Characteristics
|
|
|
- Norma Pierce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Position Paper CB24I Classification of Binary 24 V Interfaces - Functional Safety aspects covered by dynamic testing Edition Timing Characteristics nterfaces Test Pulses Functional Safety Interoperability Availabilit Compatibility Heterogeneous Systems April 2017 ZVEI - German Electrical and Electronic Manufacturers Association
2 Classification of Binary 24 V Interfaces Content List of figures 3 List of tables 3 1 Scope and purpose of this document 4 2 Normative references 4 3 Terms and definitions Information source (source) Information sink (sink) Test pulse generation (TG) Test pulse evaluation (TE) Supply voltage Test pulse Test pulse duration ti Test pulse interval T Test pulse delay ti Test pulse phase shift tc ON state OFF state Interface type Class Output current In Leakage current ILeakage Load capacitance CL Inductive load LL 5 4 Minimum information on compatibility to be provided in the manufacturer's documentation Purpose Basic electrical parameters Structure of the identifying key 6 5 Characteristics of interface types Interface type A Static characteristics of interface type A Dynamic characteristics of interface type A Product information to be supplied by the manufacturer Application notes Interface type B Static characteristics of interface type B Dynamic characteristics of interface type B Product information to be supplied by the manufacturer Application notes 12 2
3 5.3 Interface type C Static characteristics of interface type C Dynamic characteristics of interface type C Classification of interface type C (and D) Product information to be supplied by the manufacturer Application note Interface type D Static characteristics of a source of interface type D Dynamic characteristics of a source of interface type D Product information to be supplied by the manufacturer Static characteristics of a sink of interface type D Dynamic characteristics of a sink of interface type D Product information to be supplied by the manufacturer 20 List of figures Figure 5.1-1: Interface type A 8 Figure 5.2-1: Interface type B 10 Figure 5.2-2: Test pulse delay ti much smaller than test pulse duration ti 11 Figure 5.2-3: Test pulse delay t i greater than test pulse delay ti 11 Figure 5.3-1: Interface type C 13 Figure 5.3-2: Dynamic behaviour interface type C 15 Figure 5.4-1: Interface type D 17 Figure 5.4-2: Dynamic behaviour interface type D 18 List of tables Table 4.2-1: Basic electrical parameters 6 Table 5.1-1: Manufacturer information interface type A Source 9 Table 5.1-2: Manufacturer information interface type A Sink 9 Table 5.2-1: Manufacturer information interface type B Source 12 Table 5.2-2: Manufacturer information interface type B Sink 12 Table 5.3-1: Classification for interface type C (and D) 15 Table 5.3-2: Manufacturer information interface type C Source 16 Table 5.3-3: Manufacturer information interface type C Sink 16 Table 5.4-1: Manufacturer information interface type D Source 19 Table 5.4-2: Manufacturer information interface type D Sink 20 3
4 1. Scope and purpose of this document This document describes characteristic features of binary 24V interfaces that use dynamic test pulses. The purpose of this document is to: describe terms and definitions; define characteristics of interface types; specify product information (technical data) per interface type to be supplied by the manufacturer. This document provides a technical description for all interface types. No safety-related assessment is made. 2. Normative references This document refers to additional technical documentation and standards. Please note that references to documents with release dates are limited to this version only. For all other documents, the reference is linked to the latest version (including any amendments). The general requirements set out in IEC :2007 shall apply with respect to the present document where reference is made to them. 3. Terms and definitions Section 3 of IEC :2007 applies in conjunction with the following additions: 3.1 Information source (source) The information source (hereafter referred to as source) is transmitting information to the information sink. The source output is connected to the input of the sink. A source can meet requirements of several interface types at the same time. Note: For example, the source could be a sensor and the sink a control system. The term refers to the generation of the information and not to the generation of the test pulses. Generation of test pulses can be located in different parts of the system, depending on the interface type. 3.2 Information sink (sink) The information sink (hereafter referred to as sink) is receiving information from the information source. The sink input is connected to the output of the source. A sink can meet requirements of several interface types at the same time. Note: For example, the sink could be a control system. The term refers to the analysis of the information and not to the analysis of the test pulses. Analysis of test pulses can be located in different parts of the system, depending on the interface type. 3.3 Test pulse generation (TG) Part of the system that generates test pulses used for system diagnosis. 3.4 Test pulse evaluation (TE) Part of the system that evaluates test pulses for system diagnosis. 3.5 Supply voltage Supply voltage is the voltage continuously supplied to a device. 4
5 3.6 Test pulse A test pulse is a temporary change of a signal voltage level used to verify the proper operation of the output or device or the transmission path. 3.7 Test pulse duration t i The test pulse duration ti is the time from the start of the test pulse (e.g. falling edge) until the end of the test pulse (e.g. rising edge). 3.8 Test pulse interval T The test pulse interval is the time between the start of a test pulse and the start of the next test pulse on the same output. 3.9 Test pulse delay t i The test pulse delay ti is a pulse delay introduced by the source, between the input and the output of the information source Test pulse phase shift t c Time shift of test pulses between different test generation channels (interface type C and interface type D) ON state The ON state of a source is the state in which the source output supplies energy OFF state The OFF state of a source is the de-energised state Interface type The interface type is a standardised interface for transmitters of signals (sources) and receivers of signals (sinks). Generation and analysis of test pulses is specified per interface type Class The class is a group of sources and sinks with compatible technical data within an interface type based on the test pulses in use Output current I n The output current In is the nominal ON state current of an output Leakage current I Leakage The leakage current ILeakage is the remaining current of an output for a source or sink in the OFF state Load capacitance C L The load capacitance CL is the capacitance connected to an electrical output Inductive load L L The inductive load LL is the inductance connected to an electrical output. 5
6 4 Minimum information on compatibility to be provided in the manufacturer's documentation 4.1 Purpose To simplify the compatibility check of device interfaces additional information shall be provided in the manufacturers device documentation. 4.2 Basic electrical parameters These parameters are the basis for the information provided in the manufacturer's documentation. Interface type Maximum electrical resistance of connection cable Maximum capacitive load of test pulse generation TG (cable *1 + input capacitance) A 100 Ω 20 nf * 2 B 100 Ω 20 nf * 2 C 100 Ω 20 nf D 100 Ω 20 nf *1 e.g. cable 0.34 mm 2 5 wires: 60 Ω/km per single wire, 120 nf/km *2 Serial connection to be taken in account. Table 4.2-1: Basic electrical parameters 4.3 Structure of the identifying key The identifying key has the following structure: Source / Sink Interface type (and class) Additional measures "M" Sink / Source Suitable interface type (and class) Suitable interface type (and class) Suitable interface type (and class) First position is the classification of the product. Next, the interface types suitable for this product are specified. Up to three interface types can be indicated. If additional measures are required, this is indicated by the letter "M" in the field "Additional measures". Definition of additional measures shall be provided in the manufacturer's documentation. A row can only contain interface types of the same kind. For products with multiple possible interface types, all possible combinations shall be indicated using several identifying keys. The number of cells and the structure of the identifying key are fixed. 6
7 Examples: a) Manufacturer information for a source of interface type C class 2 (e.g. sensor...): Source: C2 Sink: C1 C2 Explanation: In this case, a source of type C2 is compatible with a sink of type C1 and also with a sink of type C2. b) Manufacturer information for a sink of interface type C class 2 (e.g. safety PLC ): Sink: C2 Source: C2 C3 Explanation: In this case, a sink of type C2 is compatible with a source of type C2 and also with a sink of type C3. c) Manufacturer information for a sink of interface type A (e.g. safety evaluation unit ): Sink: A M Source: A Explanation: In this case, a sink of type A is compatible with a source of type A subject to the additional measures M. Note: For the free classes C0 and D0, the identifying key is not used. These interface types require an individual compatibility test. 7
8 5 Characteristics of interface types 5.1 Interface type A Figure 5.1-1: Interface type A Description: A sink sends test pulses to a source. The test pulses are returned to the sink without any change. If the sink does not receive test pulses the sink will enter a safe state. Cascading (series connection) of several sources is supported by this interface type. Internal resistances Ri of sources connected in series are additive. This needs to be taken into account when determining the expected value for the input voltage at the sink. Examples: Magnetically operated position sensors and limit switches (Reed switches) on hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders.examples of sinks specific to this interface type are electronic control systems Static characteristics of interface type A An interface of a type A sink has an output for test pulse generation (TG). In addition, the sink has an input for test pulse evaluation (TE) An interface of a type A source has a signal input for a test pulse and a signal output for instantaneous output of the test pulse. The electrical data shall be based on IEC :2007 and will not be further addressed here. Sources of type A can be connected in series and allow potentialfree operation Dynamic characteristics of interface type A If information is passed on by a source of type A, no test pulse delay to the output signal occurs. An interface of a type A source does not impose any requirement to timing characteristics of the test pulse. The source does not initiate a test pulse at the output on its own. In the OFF state of the source, test pulses are not passed on. 8
9 5.1.3 Product information to be supplied by the manufacturer The user manual of a type A source interface shall provide additional data as follows: Parameter/Source min. typ. max. Switching current Ii Minimum current Ii min - Maximum current Ii max Switching voltage Ui Minimum voltage Ui min - - Internal resistance Ri (in the switched state) Minimum internal resistance Ri min - Load capacitance CL - - Load inductance LL - - Maximum internal resistance Ri max Maximum capacitance at the output CL max Maximum inductance at the output LL max Potential-free yes/no Table 5.1-1: Manufacturer information interface type A Source The user manual of a type A sink shall provide additional data as follows: Parameter/Sink min. typ. max. Input current Ii (in the ON state) Minimum current Ii min - Maximum current Ii max Output voltage Ui Minimum voltage Ui min - Maximum voltage Ui max Input capacitance Ci - - Maximum capacitance at the input Ci max Table 5.1-2: Manufacturer information interface type A Sink Application notes If multiple sources of type A are connected in series, the total voltage drop has to be considered. 9
10 5.2 Interface type B Figure 5.2-1: Interface type B Description: A sink generates periodic test pulses with a test pulse interval T. The periodic test pulses are delayed by the source by the time ti and returned to the sink without other modification. If the test signals are not passed on to the sink by the source, or if the expected time value of the sink is outside the permissible tolerance limits, the sink will enter a safe state. This interface type allows cascading (series connection) of sources. Test pulse delays ti of sources connected in series are additive. This needs to be taken into account when determining the expected time value for the sink. Examples: Interface type B is often used for position monitoring with sensors (source) of different technologies (inductive / RFID / magnetic / photoelectric / etc.) thanks to its ability for series connection. Examples of sinks specific to this interface type are electronic evaluation units and electronic control systems Static characteristics of interface type B An interface of a type B sink has an output for test pulse generation (TG). In addition, the sink has an input for test pulse evaluation (TE). An interface of a type B source has an input for the signal of the test pulse generation (TG) and an output for the delayed test signal. The electrical data shall be based on IEC :2007 and will not be further addressed here. All signals of this interface type are referenced to the signal ground (GND) Dynamic characteristics of interface type B Two versions of interface type B exist: 1) The test pulse delay ti is much smaller than the test pulse duration ti (see figure 5.2-2). 2) The test pulse delay ti is greater than the pulse duration ti (see figure 5.2-3). 10
11 Figure 5.2-2: Test pulse delay ti much smaller than test pulse duration ti Figure 5.2-3: Test pulse delay ti greater than test pulse delay ti The length of the test pulse duration ti is determined by the sink. If the signal shape (pulse/pause ratio, delay) at the input of the sink is in the expected range, the sink can adopt a release state with regard to the source. If the signal shape does not correspond to the expected time value or if no signal is present, no release occurs in the sink. A "no release" on the part of the source means that no signal is transmitted to the sink. The falling edge and the rising edge of the test input signal of the sink both occur with a test pulse delay of ti at the output of the source. The test pulse delay ti is a deliberately introduced delay time, which clearly differs from parasitic delay times. Typically, the switch-on and switch-off times of the test pulses including their tolerances are much smaller than the test pulse duration ti. 11
12 The timing characteristics of the test pulse generation (TG) are influenced by the capacitive load of the source (Ci) and have an effect on the total time. Furthermore, the input capacitance (Ci) of the sink influences the timing aspects of the test pulse analysis. Knowing the size of this capacitance (Ci) is essential for users of interface type B. It is recommended that the capacitive, inductive and resistive parts of the lines (see 5.2-1) between the sink and the source are taken into account. They have an influence on the signal quality but this will not be further taken into account Product information to be supplied by the manufacturer The user manual of a type B source interface shall provide additional data as follows: Parameter min. typ. max. Test pulse delay ti Minimum test pulse delay ti_min - Maximum test pulse delay ti_max Test pulse duration ti Minimum test pulse duration ti_min - Maximum test pulse duration ti_max Test pulse interval T Minimum test pulse interval Tmin - Maximum test pulse interval Tmax Input capacitance Ci - - Maximum input capacitance Ci_max Table 5.2-1: Manufacturer information interface type B source. The user manual of a type B sink shall provide additional data as follows: Parameter min. typ. max. Test pulse delay ti Minimum test pulse delay ti_min - Maximum test pulse delay ti_max Test pulse duration ti Minimum test pulse duration ti - Maximum test pulse duration ti Test pulse interval T Minimum test pulse interval Tmin - Maximum test pulse interval Tmax Input capacitance Ci - - Maximum input capacitance Ci_max Table 5.2-2: Manufacturer information interface type B Sink Application notes To verify the correct combination of signal sources (e.g. sensors in a plant) and signal sinks (e.g. secondary control system), proceed as follows: Verification of interface types: o Source and sink shall be of interface type B. Verification of time parameters: o o Comparison of the test pulse interval T (min. / max.) of the sink with that of the source. The permissible test pulse interval T of the source shall be in the specified range of the sink. Comparison of the permissible (min. / max.) test pulse duration ti of the source with that of the sink. Ideally, the test pulse duration ti of the sink should be slightly smaller than the max. permissible test pulse duration of the source. The minimum required test pulse duration ti of the source shall be considered. 12
13 o The test pulse delay ti of the source shall correspond to the permissible test pulse delay ti of the sink. Test pulse delays ti of sources connected in series are additive. The test pulse delay ti monitoring allows e.g. detection of wrong wiring as one of the benefits. 5.3 Interface type C Figure 5.3-1: Interface type C Description: A source switches the supply voltage to the output in the ON state. In the OFF state, the output is disconnected from the supply voltage. In the ON state, the source transmits test pulses to the output. The correct function of the output is monitored in the source itself. The sink shall suppress the test pulses of the source to prevent unintentional switching operations. The test pulse generation in the source, the test pulse transmission on the line and the input circuit of the sink shall be matched to avoid an unintended shutdown. The interface type C source itself detects failures of the output switching unit (e.g. in case of a stuck-at-fault). Examples: Interface type C is used as an "OSSD" output (Output Signal Switching Device) e.g. safety outputs for light grids and proximity switches with defined behaviour under fault conditions as per EN etc. The devices, as a source, check the function of their outputs with test pulses. The sink, e.g. control systems, relays or valves, shall not react to these test pulses. If devices have a sink and a source, series connections of devices are possible. Interface type C is, therefore, often used for position monitoring. 13
14 Classes: Sources of interface type C are subdivided in classes according to the timing characteristics of the test pulses. When combining a source and a sink, it shall be ensured that the source always has the same or a higher class (i.e. shorter test pulses) than the sink (see section 5.3.3). Note 1: Verification of electric parameters: The limit values of the sink/source shall not be exceeded. Note 2: The maximum load capacitances and inductances in the input of the sink shall not exceed the maximum values defined in the source. The capacitance and inductance per unit length of the line should be taken into account Static characteristics of interface type C The positive-switching output (P switch) of the source determines the switching status of the system. All signals of this interface type are referenced to the signal ground (GND). The electrical data for interface type C shall be based on IEC :2007 and will not be further addressed here Dynamic characteristics of interface type C Test pulse duration ti The duration of the test pulses ti emitted by a source of a certain class shall not exceed the test pulse duration ti specified in Table Sinks of a certain class of interface type C shall not react functionally to the test pulses defined for this class as per Table An interruption of the test pulses by the source due to further signal edges (e.g. for data transmission) is permissible. The time from the first switch-off until the last switch-on of the output is considered the test pulse length. A sink shall ignore any such interruptions within a defined test pulse duration. Note 1: The test pulses shall be filtered out or suppressed in the sink to ensure that no functional influences occur. Flashing or dimming of an illuminated display indicating the input status is tolerated. Note 2: The timing characteristics of the source's test pulses are influenced by the inductive and capacitive load of the line and the sink. Knowing the size of these values in the sink and the maximum permissible values for a source is essential for users of type C. It is recommended that the capacitive and inductive parts of the lines between the sink and the source are taken into account as they influence the signal quality. This is not topic of this paper. Test pulse interval T The test pulse duration ti should not exceed 1% of the test pulse interval T. If the test pulse duration is greater than 1% of the test pulse interval, the ti/t ratio shall be explicitly mentioned in the technical documentation. Note: Sinks of a certain class of interface type C shall be designed so that the repeated test pulses in the intervals defined in Table will not cause an impermissible drop of the energy level in the input (e.g. coils such as relays and valves). 14
15 5.3.3 Classification of interface type C (and D) Parameter Designation Unit Value minimum nominal maximum Class 0 (generic) Test pulse duration ti,0 µs - free* Class 1 Test pulse duration ti,1 µs Class 2 Test pulse duration ti,2 µs Class 3 Test pulse duration ti,3 µs *) to be specified individually for the individual device. Table 5.3-1: Classification for interface type C (and D) Figure 5.3-2: Dynamic behaviour interface type C 15
16 5.3.4 Product information to be supplied by the manufacturer The user manual of a type C source interface shall provide additional data as follows (see also under 5.3.3): Parameter min. typ. max. Class Classification according to Table Test pulse duration ti Minimum test pulse duration ti_min (*) - Maximum test pulse duration ti_max Test pulse interval T Minimum test pulse interval Tmin (**) - Nominal current IN - - Output current IN Capacitive load CL - - Maximum capacitive load CL_max Inductive load LL (*) - - Maximum inductive load LL_max (*) = optional supplementary information provided by the manufacturer. (**) = to be indicated by the manufacturer if t i/t ratio is greater than 1%. Table 5.3-2: Manufacturer information interface type C Source The user manual of a type C sink shall provide additional data as follows: Parameter min. typ. max. Class Classification according to Table Test pulse duration ti - Maximum test pulse duration ti_max Test pulse interval T Minimum test pulse interval Tmin (**) - Input resistance R Minimum input resistance RL_min - - Capacitive load CL - - Maximum input capacitive load CL_max Inductive load LL (*) - - Maximum input inductive load LL_max (*) = optional supplementary information provided by the manufacturer. Table 5.3-3: Manufacturer information interface type C Sink 16
17 5.3.5 Application notes To verify the correct combination of signal sources (e.g. sensors in a plant) and signal sinks (e.g. downstream control systems), proceed as follows: Verification of interface types: Source and sink shall both be of interface type C. Verification of the class: The class of the sink shall correspond to the class of the source. Note 1: The source shall have the same or a higher class than the sink. For example, a source of class 2 is compatible with a sink of class 1 or 2, but not with a sink of class 3. Note 2: In the case of a generic source or sink, the manufacturer's specifications shall be compared. The maximum test pulse duration of the source shall not exceed the maximum test pulse duration of the sink. Note 3: The guaranteed minimum test pulse interval of the source shall be greater than the requested minimum test pulse interval of the sink. Verification of electric parameters: The load caused by the sink shall not exceed the limits of the source. Note 4: The output current of the source shall meet the requirements of the input resistance of the sink. Note 5: The maximum load capacitances and inductances for the input of the sink are those specified in the source. The capacitance and inductance per unit length of the line should be taken into account. 5.4 Interface type D Figure 5.4-1: Interface type D Interface type D is primarily used for the safe switching of actuators such as contactors, motors and valves, or for complete shut-down of the operating voltage of electric/electronic assemblies and devices. The major difference to the positive-switching output (P switch, see interface type C) is that the return line is also controlled and tested, so that errors in the return line, such as short circuits to 0 V, can be detected. Vagabond voltages due to a shared but floating 0 V connection point will be prevented with this type of connection. In addition, dual-channel switch-off is possible with 2 lines, preventing impermissible switching of the actuator due to a short circuit on one of the conductors. For this purpose, the source transmits test pulses to the sink. The test pulses are analysed by the source. The test pulses are neither distorted nor delayed by the sink. The sink can have capacitive, inductive and resistive parts, e.g. actuators such as valves, contactors or drives, but also full devices. The source is typically a safety controller or a safety switching unit with a bipolar output. 17
18 5.4.1 Static characteristics of a source of interface type D The source has a defined impedance, which shall be included in the technical data. The source can switch a load ON and OFF (bipolar, P/N) within a defined output current range. ON state is defined as the signal level where the sink reaches its ON state (limit is Imax of the source). OFF state is defined as the signal level where the sink reaches its OFF state (limit is Imin of the source) Dynamic characteristics of a source of interface type D Defined test pulses are generated to detect cross faults and short circuits. The test pulse interval and the test pulse duration are to be specified. Figure 5.4-2: Dynamic behaviour interface type D Cyclic testing is causing additional power loss in the source and in the sink. This is based on the dynamic charging and discharging of capacitances and inductances and those values need to be defined for this interface type. 18
19 5.4.3 Product information to be supplied by the manufacturer The user manual of a type D source interface shall provide additional data as follows: Parameter min. typ. max. Class Classification according to table Test pulse duration ti Minimum test pulse duration ti - Maximum test pulse duration ti Test pulse interval T Minimum test pulse interval Tmin - - Leakage current ILeakage of the output in the OFF state Nominal current IN of the output in the ON state - - Maximum output current ILeakage - - Nominal current IN Capacitive load CL - - Maximum capacitive load CL Inductive load LL - - Maximum inductive load LL Table 5.4-1: Manufacturer information interface type D Source Classes Devices of interface type D are subdivided in classes according to the timing characteristics of the test pulses. When combining a source and a sink, it shall be ensured that the source always has the same or a higher class (i.e. shorter test pulses) than the sink (see Classification of interface type C) Static characteristics of a sink of interface type D The sink has a defined impedance which shall be included in the technical data. In particular, it shall be ensured that the required minimum current for the ON state and the maximum permissible leakage current for the OFF state can be met by the source. The sink shall provide the operating mode "bipolar disconnectable" Dynamic characteristics of a sink of interface type D In the event of a bipolar disconnection, the relevant function of the sink shall be deactivated. Limits for the test pulse interval and the test pulse duration shall be defined in case the sink is designed to accept test pulses of the source. Cyclic testing is causing additional power loss in the source and in the sink. This is based on the dynamic charging and discharging of capacitances and inductances and those values need to be defined for this interface type. 19
20 5.4.6 Product information to be supplied by the manufacturer The user manual of a type D sink shall provide additional data as follows: Parameter min. typ. max. Class Classification according to table Test pulse duration ti - - Maximum test pulse duration ti at the input Test pulse interval T Minimum test pulse interval Tmin at the input - - Input resistance R Minimum input resistance RL - - Input current ION in the ON state Input current IOFF in the OFF state - - Maximum input current IONmax - - Maximum input current IOFFmax Input capacitance CL - - Maximum input capacitance CL Input inductance LL - - Maximum input inductance LL Table 5.4-2: Manufacturer information interface type D Sink Classes Devices of interface type D are subdivided in classes according to the timing characteristics of the test pulses. When combining a source and a sink, it shall be ensured that the source always has the same or a higher class (i.e. shorter test pulses) than the sink (see Classification of interface type C) Application note In order to ensure the OFF state of the sink, the maximum input current of the sink for the OFF state shall be greater than the maximum leakage current of the source. 20
21 Imprint Position Paper CB 24 I Classification of binary 24 V Interfaces Functional Safety aspects covered by dynamic testing Publisher: ZVEI German Electrical and Electronic Manufacturers Association e. V. Automation Division Lyoner Straße Frankfurt am Main, Germany Contact: Dr Markus Winzenick Tel winzenick@zvei.org April 2017 Despite the utmost care, the ZVEI accepts no liability for the content. All rights, in particular those relating to saving, copying, distribution and translation are reserved. 21
Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GG507S
 Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GG507S 80236827 / 00 09 / 2016 Contents 1 Preliminary note...3 1.1 Symbols used...3 1.2 Warning signs used...3 2 Safety instructions...4 2.1 Safety-related
Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GG507S 80236827 / 00 09 / 2016 Contents 1 Preliminary note...3 1.1 Symbols used...3 1.2 Warning signs used...3 2 Safety instructions...4 2.1 Safety-related
Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GM705S
 Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GM705S 80236832 / 00 09 / 2016 Contents 1 Preliminary note...3 1.1 Symbols used...3 1.2 Warning signs used...3 2 Safety instructions...4 2.1 Safety-related
Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GM705S 80236832 / 00 09 / 2016 Contents 1 Preliminary note...3 1.1 Symbols used...3 1.2 Warning signs used...3 2 Safety instructions...4 2.1 Safety-related
Current Transducer CTSR 1-P = 1A
 Current Transducer CTSR 1-P I PRN = 1A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic isolation between the primary (high power) and the secondary circuit (electronic circuit).
Current Transducer CTSR 1-P I PRN = 1A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic isolation between the primary (high power) and the secondary circuit (electronic circuit).
Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GG507S / / 2013
 Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GG507S 80005283 / 00 05 / 2013 Contents 1 Preliminary note...3 1.1 Explanation of symbols...3 2 Safety instructions...4 2.1 Safety-related requirements
Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GG507S 80005283 / 00 05 / 2013 Contents 1 Preliminary note...3 1.1 Explanation of symbols...3 2 Safety instructions...4 2.1 Safety-related requirements
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary circuit and the secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer CTSR 0.6-TP/SP2 I PRN = 600 ma For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary circuit and the secondary circuit. Features
Current Transducer CTSR 0.6-TP/SP2 I PRN = 600 ma For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary circuit and the secondary circuit. Features
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current transducer LF 510-S I PN = 500 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated
Current transducer LF 510-S I PN = 500 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated
Test Specification for Type Approval
 A2 (1991) (Rev.1 1993) (Rev.2 1997) (Rev. 2.1 July 1999) (Rev.3 May 2001) (Corr.1 July 2003) (Rev.4 May 2004) (Rev.5 Dec 2006) (Rev.6 Oct 2014) Test Specification for Type Approval.1 General This Test
A2 (1991) (Rev.1 1993) (Rev.2 1997) (Rev. 2.1 July 1999) (Rev.3 May 2001) (Corr.1 July 2003) (Rev.4 May 2004) (Rev.5 Dec 2006) (Rev.6 Oct 2014) Test Specification for Type Approval.1 General This Test
TD62786AP,TD62786AF,TD62787AP,TD62787AF
 TOSHIBA BIPOLAR DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON MONOLITHIC TD62786AP,TD62786AF,TD62787AP,TD62787AF 8CH HIGH VOLTAGE SOURCE DRIVER The TD62786AP / AF series are eight channel huyx non inverting source
TOSHIBA BIPOLAR DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON MONOLITHIC TD62786AP,TD62786AF,TD62787AP,TD62787AF 8CH HIGH VOLTAGE SOURCE DRIVER The TD62786AP / AF series are eight channel huyx non inverting source
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current transducer LF 210-S/SP3 I PN = 100 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated
Current transducer LF 210-S/SP3 I PN = 100 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated
Recommendations for Harmonic and Power Measurements in Electrical Networks
 Recommendations for Harmonic and Power Measurements in Electrical Networks Analysis implementation and reporting requirements regarding grid power quality and equipment loads Power Capacitor Division Recommendations
Recommendations for Harmonic and Power Measurements in Electrical Networks Analysis implementation and reporting requirements regarding grid power quality and equipment loads Power Capacitor Division Recommendations
PROXIMITY SENSOR TERMINOLOGY
 Never use this desk reference for installation or operation of equipment. Refer to manual for installation and operation instructions. The following descriptions refer to the European standard EN 60947-5-2.
Never use this desk reference for installation or operation of equipment. Refer to manual for installation and operation instructions. The following descriptions refer to the European standard EN 60947-5-2.
Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GM504S / / 2010
 Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GM504S 704070 / 01 06 / 2010 Contents 1 Preliminary note 3 1.1 Explanation of symbols 3 2 Safety instructions 4 2.1 Safety-related requirements
Original operating instructions Fail-safe inductive sensor GM504S 704070 / 01 06 / 2010 Contents 1 Preliminary note 3 1.1 Explanation of symbols 3 2 Safety instructions 4 2.1 Safety-related requirements
KNX Powerline PL 110. KNX Association
 KNX Powerline PL 110 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...3 2 Standardisation...3 3 Transmission Process...4 3.1 Phase Coupling...5 3.2 Telegram Transmission...6 3.2.1 Training Sequence...6 3.2.2 Preamble
KNX Powerline PL 110 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...3 2 Standardisation...3 3 Transmission Process...4 3.1 Phase Coupling...5 3.2 Telegram Transmission...6 3.2.1 Training Sequence...6 3.2.2 Preamble
Reactive Power Control Relay RM 2106 / 2112 Operating Instructions. FRAKO Kondensatoren- und Anlagenbau
 Reactive Power Control Relay RM 2106 / 2112 Operating Instructions FRAKO Kondensatoren- und Anlagenbau www.frako.com Figure 1 Front view a b c d e Display for active capacitor stages Display for inductive
Reactive Power Control Relay RM 2106 / 2112 Operating Instructions FRAKO Kondensatoren- und Anlagenbau www.frako.com Figure 1 Front view a b c d e Display for active capacitor stages Display for inductive
TD62081AP,TD62081AF,TD62082AP,TD62082AF TD62083AP,TD62083AF,TD62084AP,TD62084AF
 Toshiba Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD6281AP,TD6281AF,TD6282AP,TD6282AF TD6283AP,TD6283AF,TD6284AP,TD6284AF TD6281~84AP/AF 8ch Darlington Sink Driver The TD6281AP/AF Series are
Toshiba Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD6281AP,TD6281AF,TD6282AP,TD6282AF TD6283AP,TD6283AF,TD6284AP,TD6284AF TD6281~84AP/AF 8ch Darlington Sink Driver The TD6281AP/AF Series are
TD62783AP,TD62783AF,TD62784AP,TD62784AF
 TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD62783,784AP/AF TD62783AP,TD62783AF,TD62784AP,TD62784AF 8 ch High-oltage Source Driver The TD62783AP/AF Series are comprised of eight source
TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD62783,784AP/AF TD62783AP,TD62783AF,TD62784AP,TD62784AF 8 ch High-oltage Source Driver The TD62783AP/AF Series are comprised of eight source
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current transducer LF 2010-S I PN = 2000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated
Current transducer LF 2010-S I PN = 2000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated
EY-EM 522, 523: Remote I/O module, ecolink522, 523
 Product data sheet 94.077 EY-EM 522, 523: Remote I/O module, ecolink522, 523 How energy efficiency is improved Regulation, control, monitoring and optimisation of operational systems, e.g. room automation
Product data sheet 94.077 EY-EM 522, 523: Remote I/O module, ecolink522, 523 How energy efficiency is improved Regulation, control, monitoring and optimisation of operational systems, e.g. room automation
TD62383PG TD62383PG. 8 ch Low Input Active Sink Driver. Features. Pin Assignment (top view) Schematics (each driver)
 8 ch Low Input Active Sink Driver TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD62383PG The TD62383PG is non inverting transistor array which is comprised of eight Low saturation output
8 ch Low Input Active Sink Driver TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD62383PG The TD62383PG is non inverting transistor array which is comprised of eight Low saturation output
TD62308AP,TD62308AF TD62308AP/AF. 4ch Low Input Active High-Current Darlington Sink Driver. Features. Pin Assignment (top view)
 TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD6238AP,TD6238AF 4ch Low Input Active High-Current Darlington Sink Driver TD6238AP/AF The TD6238AP/AF is a non inverting transistor array
TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD6238AP,TD6238AF 4ch Low Input Active High-Current Darlington Sink Driver TD6238AP/AF The TD6238AP/AF is a non inverting transistor array
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current transducer CKSR series N = 6, 5, 25, 5 A Ref: CKSR 6-NP, CKSR 5-NP, CKSR 25-NP, CKSR 5-NP For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary
Current transducer CKSR series N = 6, 5, 25, 5 A Ref: CKSR 6-NP, CKSR 5-NP, CKSR 25-NP, CKSR 5-NP For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary
EY-EM 527: Remote I/O module, ecolink527
 Product data sheet 94.078 EY-EM 527: Remote I/O module, ecolink527 How energy efficiency is improved Regulation, control, monitoring and optimisation of operational systems, e.g. room automation or HVAC
Product data sheet 94.078 EY-EM 527: Remote I/O module, ecolink527 How energy efficiency is improved Regulation, control, monitoring and optimisation of operational systems, e.g. room automation or HVAC
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION. SERIES V: DATA COMMUNICATION OVER THE TELEPHONE NETWORK Interfaces and voice-band modems
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION CCITT V.28 THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE (11/1988) SERIES V: DATA COMMUNICATION OVER THE TELEPHONE NETWORK Interfaces and voice-band
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION CCITT V.28 THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE (11/1988) SERIES V: DATA COMMUNICATION OVER THE TELEPHONE NETWORK Interfaces and voice-band
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current transducer LF 510-S/SP13 I PN = 500 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and
Current transducer LF 510-S/SP13 I PN = 500 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer LF 510-S I P N = 500 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated
Current Transducer LF 510-S I P N = 500 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer HO-NP series I PN = 4, 6, 12, 15 Ref: HO 4-NP, HO 6-NP, HO 12-NP, HO 15-NP For the electronic measurement of current: DC, C, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and
Current Transducer HO-NP series I PN = 4, 6, 12, 15 Ref: HO 4-NP, HO 6-NP, HO 12-NP, HO 15-NP For the electronic measurement of current: DC, C, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and
SPECIFICATION Item no.: T60404-N4646-X764
 Customer: Standard type Customers Part no: Page 1 of 4 Description Closed loop (compensation) Current Sensor with magnetic field probe Printed circuit board mounting Casing and materials UL-listed Electrical
Customer: Standard type Customers Part no: Page 1 of 4 Description Closed loop (compensation) Current Sensor with magnetic field probe Printed circuit board mounting Casing and materials UL-listed Electrical
ULN2803APG,ULN2803AFWG,ULN2804APG,ULN2804AFWG (Manufactured by Toshiba Malaysia)
 TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic ULN2803,04APG/AFWG ULN2803APG,ULN2803AFWG,ULN2804APG,ULN2804AFWG (Manufactured by Toshiba Malaysia) 8ch Darlington Sink Driver The ULN2803APG
TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic ULN2803,04APG/AFWG ULN2803APG,ULN2803AFWG,ULN2804APG,ULN2804AFWG (Manufactured by Toshiba Malaysia) 8ch Darlington Sink Driver The ULN2803APG
TD62318APG,TD62318AFG
 TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD62318APG,TD62318AFG 4ch Low Input Active High-Current Darlington Sink Driver TD62318APG/AFG The TD62318APG and TD62318AFG are non-inverting
TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD62318APG,TD62318AFG 4ch Low Input Active High-Current Darlington Sink Driver TD62318APG/AFG The TD62318APG and TD62318AFG are non-inverting
TECHNICAL TBR 2 BASIS for January 1997 REGULATION
 TECHNICAL TBR 2 BASIS for January 1997 REGULATION Source: ETSI TC-TE Reference: DTBR/TE-005002 ICS: 33.020, 33.040.40 Key words: PDN, testing, type approval, X.25 Attachment requirements for Data Terminal
TECHNICAL TBR 2 BASIS for January 1997 REGULATION Source: ETSI TC-TE Reference: DTBR/TE-005002 ICS: 33.020, 33.040.40 Key words: PDN, testing, type approval, X.25 Attachment requirements for Data Terminal
Type Ordering Code Package TDA Q67000-A5066 P-DIP-8-1
 Control IC for Switched-Mode Power Supplies using MOS-Transistor TDA 4605-3 Bipolar IC Features Fold-back characteristics provides overload protection for external components Burst operation under secondary
Control IC for Switched-Mode Power Supplies using MOS-Transistor TDA 4605-3 Bipolar IC Features Fold-back characteristics provides overload protection for external components Burst operation under secondary
Ref: HO 50-S/SP33, HO 100-S/SP33, HO 150-S/SP33, HO 200-S/SP33, HO 250-S/SP33
 Current Transducer HO-S/SP33 series I PN = 50, 100, 150, 200, 250 A Ref: HO 50-S/SP33, HO 100-S/SP33, HO 150-S/SP33, HO 200-S/SP33, HO 250-S/SP33 For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed...,
Current Transducer HO-S/SP33 series I PN = 50, 100, 150, 200, 250 A Ref: HO 50-S/SP33, HO 100-S/SP33, HO 150-S/SP33, HO 200-S/SP33, HO 250-S/SP33 For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed...,
Proximity Sensor Terminology
 The following descriptions refer to the European standard EN 60947-5-2. of 2007. The specifications given here are intended to be minimum performance values described by the standard. Alignment must not
The following descriptions refer to the European standard EN 60947-5-2. of 2007. The specifications given here are intended to be minimum performance values described by the standard. Alignment must not
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer LF 2010-S/SPA0 I P N = 2000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and
Current Transducer LF 2010-S/SPA0 I P N = 2000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and
Preliminary. MM7100 High-Voltage SPST Digital-Micro-Switch. Product Overview PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET, SEE PAGE 11 FOR DETAILS
 MM7100 High-Voltage SPST Digital-Micro-Switch Product Overview Features: Frequency Range: DC to 750 MHz Low On-State Resistance < 0.30Ω (typ.) Rated Voltage (AC or DC): 400V Rated Current (AC or DC): 2A
MM7100 High-Voltage SPST Digital-Micro-Switch Product Overview Features: Frequency Range: DC to 750 MHz Low On-State Resistance < 0.30Ω (typ.) Rated Voltage (AC or DC): 400V Rated Current (AC or DC): 2A
KSR-Level sensor KSR-Schwimmer-Magnetschalter KSR Contact Protection Relays
 KSR-Level sensor KSR-Schwimmer-Magnetschalter 1001-5 KSR Contact Protection s 1 KSR Contact Protection Type KR230-Ex and KR24-Ex General Description The contact protection relays KR230-Ex and KR24-Ex transmit
KSR-Level sensor KSR-Schwimmer-Magnetschalter 1001-5 KSR Contact Protection s 1 KSR Contact Protection Type KR230-Ex and KR24-Ex General Description The contact protection relays KR230-Ex and KR24-Ex transmit
NUP2105LT3G. Dual Line CAN Bus Protector SOT 23 DUAL BIDIRECTIONAL VOLTAGE SUPPRESSOR 350 W PEAK POWER
 Dual Line CAN Bus Protector The NUP2105L has been designed to protect the CAN transceiver in high speed and fault tolerant networks from ESD and other harmful transient voltage events. This device provides
Dual Line CAN Bus Protector The NUP2105L has been designed to protect the CAN transceiver in high speed and fault tolerant networks from ESD and other harmful transient voltage events. This device provides
High Speed PWM Controller
 High Speed PWM Controller FEATURES Compatible with Voltage or Current Mode Topologies Practical Operation Switching Frequencies to 1MHz 50ns Propagation Delay to Output High Current Dual Totem Pole Outputs
High Speed PWM Controller FEATURES Compatible with Voltage or Current Mode Topologies Practical Operation Switching Frequencies to 1MHz 50ns Propagation Delay to Output High Current Dual Totem Pole Outputs
Regulating Pulse Width Modulators
 Regulating Pulse Width Modulators UC1525A/27A FEATURES 8 to 35V Operation 5.1V Reference Trimmed to ±1% 100Hz to 500kHz Oscillator Range Separate Oscillator Sync Terminal Adjustable Deadtime Control Internal
Regulating Pulse Width Modulators UC1525A/27A FEATURES 8 to 35V Operation 5.1V Reference Trimmed to ±1% 100Hz to 500kHz Oscillator Range Separate Oscillator Sync Terminal Adjustable Deadtime Control Internal
UNIVERSAL SINK DRIVER. Supply. Voltage reference. Thermal protection. Short-circuit to V cc protection. Short-circuit to GND detection
 NJM UNIERSAL SINK DRIER GENERAL DESCRIPTION NJM is a bipolar universal high-current highly protected low side driver with transparent input and ma continuous -current sink capability. A high-level input
NJM UNIERSAL SINK DRIER GENERAL DESCRIPTION NJM is a bipolar universal high-current highly protected low side driver with transparent input and ma continuous -current sink capability. A high-level input
HAL , 508, 509, HAL Hall Effect Sensor Family
 MICRONAS INTERMETALL HAL1...6, 8, 9, HAL16...18 Hall Effect Sensor Family Edition April Feb. 4, 16, 1996 1999 61-36-1DS 61-48-1DS MICRONAS HALxx Contents Page Section Title 3 1. Introduction 3 1.1. Features
MICRONAS INTERMETALL HAL1...6, 8, 9, HAL16...18 Hall Effect Sensor Family Edition April Feb. 4, 16, 1996 1999 61-36-1DS 61-48-1DS MICRONAS HALxx Contents Page Section Title 3 1. Introduction 3 1.1. Features
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer LF 2010-S/SPA7 I P N = 2000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and
Current Transducer LF 2010-S/SPA7 I P N = 2000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and
LED converter Linear / area dimming. Uconverter LCAI 80 W 350 ma one4all V ECO
 Uconverter LCAI 80 W 50 ma oneall 220-20 V ECO Product description Dimmable built-in controlgear for LED Constant current controlgear with 50 ma output current Output power 80 W Nominal lifetime of 50,000
Uconverter LCAI 80 W 50 ma oneall 220-20 V ECO Product description Dimmable built-in controlgear for LED Constant current controlgear with 50 ma output current Output power 80 W Nominal lifetime of 50,000
Components for safety applications Preventa safety modules
 Selection guide Applications Modules For Emergency Stop and limit switch monitoring (modules integrated in Micro PLCs) Conforming to standards Machine IEC 204-, EN 292, EN 48 assemblies EN 60204- Principles
Selection guide Applications Modules For Emergency Stop and limit switch monitoring (modules integrated in Micro PLCs) Conforming to standards Machine IEC 204-, EN 292, EN 48 assemblies EN 60204- Principles
For ultra-high precision measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between primary and secondary. Applications.
 Current Transducer IT 700-S ULTRASTAB I PM = 700 A For ultra-high precision measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between primary and secondary. Features Closed loop (compensated)
Current Transducer IT 700-S ULTRASTAB I PM = 700 A For ultra-high precision measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between primary and secondary. Features Closed loop (compensated)
EIB/KNX Switch Actuators. User manual
 EIB/KNX Switch Actuators User manual IT KNT 004 IT KNT 012 Tel.: +34943627988 E-mail: knx@dinuy.com Web: www.dinuy.com Contents 1. Introduction --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EIB/KNX Switch Actuators User manual IT KNT 004 IT KNT 012 Tel.: +34943627988 E-mail: knx@dinuy.com Web: www.dinuy.com Contents 1. Introduction --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Customer: Standard type Page 1 of 7 Description Fluxgate current sensor with toroidal core PCB mounting
 Customer: Standard type Page 1 of 7 Description Fluxgate current sensor with toroidal core PCB mounting Electrical data Ratings min. typ. max. Unit I P Primary nominal RMS current (1phase / 3phase) 80
Customer: Standard type Page 1 of 7 Description Fluxgate current sensor with toroidal core PCB mounting Electrical data Ratings min. typ. max. Unit I P Primary nominal RMS current (1phase / 3phase) 80
EP-5111, EP-5112, EP-5212, EP-5261, EP-5311, EP-5422, EP-5442
 October 2017 RSTI-EP Slice I/O Specialty Modules EP-5111, EP-5112, EP-5212, EP-5261, EP-5311, EP-5422, EP-5442 Module Status LED Channel Status LED GE provides several RSTi-EP specialty modules, which
October 2017 RSTI-EP Slice I/O Specialty Modules EP-5111, EP-5112, EP-5212, EP-5261, EP-5311, EP-5422, EP-5442 Module Status LED Channel Status LED GE provides several RSTi-EP specialty modules, which
Modulating control valve
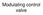 Modulating control valve Automatic modulating valve Automatic modulating valve Diaphragm Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Air filter regulator gauge = AIRSET BALL VALVE GLOBE
Modulating control valve Automatic modulating valve Automatic modulating valve Diaphragm Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Air filter regulator gauge = AIRSET BALL VALVE GLOBE
TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic
 TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD6251PG,TD6251FG,TD6252PG,TD6252FG,TD6253PG,TD6253FG,TD6254PG TD6254FG,TD6255PG,TD6255FG,TD6256PG,TD6256FG,TD6257PG,TD6257FG 7ch Single Driver,
TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TD6251PG,TD6251FG,TD6252PG,TD6252FG,TD6253PG,TD6253FG,TD6254PG TD6254FG,TD6255PG,TD6255FG,TD6256PG,TD6256FG,TD6257PG,TD6257FG 7ch Single Driver,
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer CAS 25-NP/SP2 N = 25 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Closed loop (compensated)
Current Transducer CAS 25-NP/SP2 N = 25 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Closed loop (compensated)
EMD-FL-C-10. Current Monitoring Relay. Data Sheet. Functions. Structure 08/2004
 Current Monitoring Relay Data Sheet 08/2004 Functions Structure Current monitoring of direct and alternating current in 1-phase networks with settable threshold values, starting override and response delay
Current Monitoring Relay Data Sheet 08/2004 Functions Structure Current monitoring of direct and alternating current in 1-phase networks with settable threshold values, starting override and response delay
V P N. Voltage transducer DVM 4200 = 4200 V
 Voltage transducer DVM 42 N = 42 V For the electronic measurement of voltage: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated measurement
Voltage transducer DVM 42 N = 42 V For the electronic measurement of voltage: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated measurement
Please enter the identity code of your device here!
 Operating Instructions DULCOMETER D2C Part 2: Adjustment and Operation, Measured Variables chlorine/chlorine ProMinent D2C2-001-chlorine/chlorine-GB CI 2 /Cl 2 0.50 ppm CLE 0.20 ppm CI DULCOMETER STOP
Operating Instructions DULCOMETER D2C Part 2: Adjustment and Operation, Measured Variables chlorine/chlorine ProMinent D2C2-001-chlorine/chlorine-GB CI 2 /Cl 2 0.50 ppm CLE 0.20 ppm CI DULCOMETER STOP
Residual Current Operated Circuit-Breakers (RCCBs)
 Product Overview Residual Current Operated Circuit-Breakers (RCCBs) Residual current operated circuit-breakers Number of poles Rated current A Rated residual current ma MW Auxiliary contacts can be mounted
Product Overview Residual Current Operated Circuit-Breakers (RCCBs) Residual current operated circuit-breakers Number of poles Rated current A Rated residual current ma MW Auxiliary contacts can be mounted
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current transducer LF 1010-S/SPA2 I PN = 1000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and
Current transducer LF 1010-S/SPA2 I PN = 1000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and
MBC Bipolar Microstep Driver. User s Guide E. Landon Drive Anaheim, CA
 MBC10641 Bipolar Microstep Driver User s Guide A N A H E I M A U T O M A T I O N 4985 E. Landon Drive Anaheim, CA 92807 e-mail: info@anaheimautomation.com (714) 992-6990 fax: (714) 992-0471 website: www.anaheimautomation.com
MBC10641 Bipolar Microstep Driver User s Guide A N A H E I M A U T O M A T I O N 4985 E. Landon Drive Anaheim, CA 92807 e-mail: info@anaheimautomation.com (714) 992-6990 fax: (714) 992-0471 website: www.anaheimautomation.com
MLA High Performance Microstepping Driver. User s Guide E. Landon Drive Anaheim, CA
 MLA10641 High Performance Microstepping Driver User s Guide A N A H E I M A U T O M A T I O N 4985 E. Landon Drive Anaheim, CA 92807 e-mail: info@anaheimautomation.com (714) 992-6990 fax: (714) 992-0471
MLA10641 High Performance Microstepping Driver User s Guide A N A H E I M A U T O M A T I O N 4985 E. Landon Drive Anaheim, CA 92807 e-mail: info@anaheimautomation.com (714) 992-6990 fax: (714) 992-0471
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer IN 1000-S N = 1000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Closed loop (compensated)
Current Transducer IN 1000-S N = 1000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Closed loop (compensated)
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer LESR series N = 6, 15, 25, 5 A Ref: LESR 6-NP, LESR 15-NP, LESR 25-NP, LESR 5-NP For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary
Current Transducer LESR series N = 6, 15, 25, 5 A Ref: LESR 6-NP, LESR 15-NP, LESR 25-NP, LESR 5-NP For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary
PHASED OUT. LED Driver Linear / area fixed output. Driver LCI 35W 350mA 900mA TOP lp TOP series
 Product description Fixed output built-in LED Driver Constant current LED Driver Output current settable 350 900 ma Max. output power 35 W Nominal life-time up to 100,000 h For luminaires of protection
Product description Fixed output built-in LED Driver Constant current LED Driver Output current settable 350 900 ma Max. output power 35 W Nominal life-time up to 100,000 h For luminaires of protection
Unipolar voltage - Current output 4-20 ma Ref: DVL 50-UI, DVL 150-UI, DVL 250-UI, DVL 500-UI, DVL 750-UI, DVL 1000-UI, DVL 1500-UI
 Current Transducer DVL-UI series V PN = 50... 1500 V Unipolar voltage - Current output 4-0 ma Ref: DVL 50-UI, DVL 150-UI, DVL 50-UI, DVL 500-UI, DVL 750-UI, DVL 1000-UI, DVL 1500-UI For the electronic
Current Transducer DVL-UI series V PN = 50... 1500 V Unipolar voltage - Current output 4-0 ma Ref: DVL 50-UI, DVL 150-UI, DVL 50-UI, DVL 500-UI, DVL 750-UI, DVL 1000-UI, DVL 1500-UI For the electronic
PHASED OUT. LED Driver Linear / area fixed output. Driver LCI 20W 150mA 400mA TOP lp TOP series. Product description
 Product description EL Fixed output built-in LED Driver Constant current LED Driver Output current settable 150 400 ma Max. output power 20 W Nominal life-time up to 100,000 h For luminaires of protection
Product description EL Fixed output built-in LED Driver Constant current LED Driver Output current settable 150 400 ma Max. output power 20 W Nominal life-time up to 100,000 h For luminaires of protection
Customer: Standard type Page 1 of 7 Description Fluxgate current sensor with toroidal core PCB mounting
 Customer: Standard type Page 1 of 7 Description Fluxgate current sensor with toroidal core PCB mounting Characteristics Excellent accuracy AEC-Q qualified components Switching open-collector outputs Compact
Customer: Standard type Page 1 of 7 Description Fluxgate current sensor with toroidal core PCB mounting Characteristics Excellent accuracy AEC-Q qualified components Switching open-collector outputs Compact
ULN2003AP,ULN2003AFW,ULN2004AP,ULN2004AFW (Manufactured by Toshiba Malaysia)
 TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic ULN2003,04AP/AFW ULN2003AP,ULN2003AFW,ULN2004AP,ULN2004AFW (Manufactured by Toshiba Malaysia) 7ch Darlington Sink Driver The ULN2003AP/AFW
TOSHIBA Bipolar Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic ULN2003,04AP/AFW ULN2003AP,ULN2003AFW,ULN2004AP,ULN2004AFW (Manufactured by Toshiba Malaysia) 7ch Darlington Sink Driver The ULN2003AP/AFW
High Speed PWM Controller
 High Speed PWM Controller FEATURES Compatible with Voltage or Current Mode Topologies Practical Operation Switching Frequencies to 1MHz 50ns Propagation Delay to Output High Current Dual Totem Pole Outputs
High Speed PWM Controller FEATURES Compatible with Voltage or Current Mode Topologies Practical Operation Switching Frequencies to 1MHz 50ns Propagation Delay to Output High Current Dual Totem Pole Outputs
ic-mj LOW-POWER HALL SENSOR
 Rev C1, Page 1/10 FEATURES Hall sensor for absolute evaluation of magnetic field strength Pulsed cyclic measurements (interrupted), permanently, or triggered Sensitivity adjustable in two stages Digital
Rev C1, Page 1/10 FEATURES Hall sensor for absolute evaluation of magnetic field strength Pulsed cyclic measurements (interrupted), permanently, or triggered Sensitivity adjustable in two stages Digital
PHASED OUT. LED Driver Compact fixed output. Driver LCI 20W 350mA 900mA TOP C TOP series
 EL Product description Fixed output built-in LED Driver Constant current LED Driver Output current settable 30 900 ma Max. output power 20 W Nominal life-time up to 100,000 h For luminaires of protection
EL Product description Fixed output built-in LED Driver Constant current LED Driver Output current settable 30 900 ma Max. output power 20 W Nominal life-time up to 100,000 h For luminaires of protection
TD62083AFNG,TD62084AFNG
 TOSHIBA BIPOLAR DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON MONOLITHIC TD62083AFNG,TD62084AFNG 8ch Darlington Sink Driver The TD62083AFNG and TD62084AFNG are high voltage, high current darlington drivers comprised
TOSHIBA BIPOLAR DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON MONOLITHIC TD62083AFNG,TD62084AFNG 8ch Darlington Sink Driver The TD62083AFNG and TD62084AFNG are high voltage, high current darlington drivers comprised
8V General information. 2 Order data 8V
 8V80.00-8V80.00- General information Modular mechanical design using plug-in modules Integrated line filter Integrated or optional external braking resistor All connections are made using plug-in connectors
8V80.00-8V80.00- General information Modular mechanical design using plug-in modules Integrated line filter Integrated or optional external braking resistor All connections are made using plug-in connectors
Ref: HLSR 10-SM/SP33, HLSR 20-SM/SP33, HLSR 32-SM/SP33, HLSR 40-P/SP33, HLSR 50-SM/SP33
 Current Transducer HLSR-SM/SP33 series I PN = 10... 50 A Ref: HLSR 10-SM/SP33, HLSR 20-SM/SP33, HLSR 32-SM/SP33, HLSR 40-P/SP33, HLSR 50-SM/SP33 For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed...,
Current Transducer HLSR-SM/SP33 series I PN = 10... 50 A Ref: HLSR 10-SM/SP33, HLSR 20-SM/SP33, HLSR 32-SM/SP33, HLSR 40-P/SP33, HLSR 50-SM/SP33 For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed...,
16-Channel CMOS Analog Multiplexer. Memory
 306 16-Channel CMOS Analog Multiplexer FEATURES: RAD-PAK technology radiation-hardened against natural space radiation Total dose hardness: - > 50 Krad (Si), depending upon space mission Excellent Single
306 16-Channel CMOS Analog Multiplexer FEATURES: RAD-PAK technology radiation-hardened against natural space radiation Total dose hardness: - > 50 Krad (Si), depending upon space mission Excellent Single
PHASED OUT. LED Driver Compact fixed output. Driver LCI 10W 150mA 400mA TOP C TOP series. Product description
 Product description EL Fixed output built-in LED Driver Constant current LED Driver Output current settable 15 4 ma Max. output power W Nominal life-time up to, h For luminaires of protection class I and
Product description EL Fixed output built-in LED Driver Constant current LED Driver Output current settable 15 4 ma Max. output power W Nominal life-time up to, h For luminaires of protection class I and
ic-dn ic-dn LOWSIDE SWITCH 3-pin configuration Rev C1, Page 1/10
 Rev C1, Page 1/10 FEATURES 36 V lowside switch/level shifter Decoupling of input and output reference voltages permits control by 5 V logic 200 ma of output current Short-circuit protected Output with
Rev C1, Page 1/10 FEATURES 36 V lowside switch/level shifter Decoupling of input and output reference voltages permits control by 5 V logic 200 ma of output current Short-circuit protected Output with
Part 1: General. Part 3: Mechanical loads Part 4: Climatic loads Part 5: Chemical loads
 ISO 16750-2 (2012) at a glance Road vehicles. Environmental conditions and testing for electrical and electronic equipment Part 2: Electrical loads The relating standards: ISO 16750-2 (2003) ISO 16750-2
ISO 16750-2 (2012) at a glance Road vehicles. Environmental conditions and testing for electrical and electronic equipment Part 2: Electrical loads The relating standards: ISO 16750-2 (2003) ISO 16750-2
Installation Instructions RF identification system Read/write head ANT430 ANT431
 Installation Instructions RF identification system Read/write head ANT430 ANT431 UK 80262949 / 00 04 / 2017 Contents 1 Preliminary note...4 1.1 Symbols used...4 2 Safety instructions...4 2.1 General...4
Installation Instructions RF identification system Read/write head ANT430 ANT431 UK 80262949 / 00 04 / 2017 Contents 1 Preliminary note...4 1.1 Symbols used...4 2 Safety instructions...4 2.1 General...4
S1 Minor (usually reversible) injury S2 Serious (normally irreversible) injury including death
 General data Application Classification of a machine in categories acc. to EN 954- The 98/3/EG machinery directive stipulates that every machine must comply with the applicable guidelines and standards.
General data Application Classification of a machine in categories acc. to EN 954- The 98/3/EG machinery directive stipulates that every machine must comply with the applicable guidelines and standards.
Octal buffer/driver with parity; non-inverting; 3-state
 Rev. 6 14 December 2011 Product data sheet 1. General description 2. Features and benefits 3. Ordering information The is an octal buffer and line driver with parity generation/checking. The can be used
Rev. 6 14 December 2011 Product data sheet 1. General description 2. Features and benefits 3. Ordering information The is an octal buffer and line driver with parity generation/checking. The can be used
Solid State DC Contactor
 Iin(A) Solid State DC Contactor Applications: Main DC Bus Switch DC Motor Bus Switch Battery Disconnect Bus Discharge Description: Sensitron has developed a small footprint High Voltage/High Current DC
Iin(A) Solid State DC Contactor Applications: Main DC Bus Switch DC Motor Bus Switch Battery Disconnect Bus Discharge Description: Sensitron has developed a small footprint High Voltage/High Current DC
TA7291P, TA7291S/SG, TA7291F/FG
 TOSHIBA BIPOLAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON MONOLITHIC TA7291P, TA7291S/SG, TA7291F/FG BRIDGE DRIVER The TA7291P / S/SG / F/FG are Bridge Driver with output voltage control. FEATURES 4 modes available
TOSHIBA BIPOLAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON MONOLITHIC TA7291P, TA7291S/SG, TA7291F/FG BRIDGE DRIVER The TA7291P / S/SG / F/FG are Bridge Driver with output voltage control. FEATURES 4 modes available
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these ratings or any other above those indicated in t
 SP2526 +3.0V to +5.5V USB Power Control Switch Compliant to USB Specifications +3.0V to +5.5V Input Voltage Range Two Independent Power Switches Two Error Flag Outputs, Open Drain 2.7V Undervoltage Lockout
SP2526 +3.0V to +5.5V USB Power Control Switch Compliant to USB Specifications +3.0V to +5.5V Input Voltage Range Two Independent Power Switches Two Error Flag Outputs, Open Drain 2.7V Undervoltage Lockout
Box chopper amplifier BOE
 Box chopper amplifier BOE Description The box chopper amplifier is an always energised Pulse-Wide-Modulated (PWM) H-Bridge for to drive inductive loads with bipolar current in according to an analogue
Box chopper amplifier BOE Description The box chopper amplifier is an always energised Pulse-Wide-Modulated (PWM) H-Bridge for to drive inductive loads with bipolar current in according to an analogue
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer LF 21-S/SPA2 I P N = 2 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated
Current Transducer LF 21-S/SPA2 I P N = 2 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Bipolar and insulated
CROSS Chassis from 160 A to 450 A
 CROSS Chassis from 160 A to 450 A STS CATALOGUE Important note! The technical data enclosed is for general information. Please note that the operating instructions and references indicated on the products
CROSS Chassis from 160 A to 450 A STS CATALOGUE Important note! The technical data enclosed is for general information. Please note that the operating instructions and references indicated on the products
STBC ma standalone linear Li-Ion battery charger with thermal regulation. Datasheet. Features. Applications. Description
 Datasheet 800 ma standalone linear Li-Ion battery charger with thermal regulation Features DFN6 (3 x 3 mm) Programmable charge current up to 800 ma No external MOSFET, sense resistors or blocking diode
Datasheet 800 ma standalone linear Li-Ion battery charger with thermal regulation Features DFN6 (3 x 3 mm) Programmable charge current up to 800 ma No external MOSFET, sense resistors or blocking diode
VIN1 VIN1 EN1 VBIAS EN2 VIN2 VIN2. Applications
 5V DUAL CHANNEL PROGRAMMABLE LOAD SWITCH Description Pin Assignments is an integrated dual N-channel load switch which features an adjustable slew rate that can be set using an external capacitor independently
5V DUAL CHANNEL PROGRAMMABLE LOAD SWITCH Description Pin Assignments is an integrated dual N-channel load switch which features an adjustable slew rate that can be set using an external capacitor independently
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer N = 6, 15, 25, 5 A Ref: LESR 6-NP, LESR 15-NP, LESR 25-NP, LESR 5-NP For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the
Current Transducer N = 6, 15, 25, 5 A Ref: LESR 6-NP, LESR 15-NP, LESR 25-NP, LESR 5-NP For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the
DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER
 DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a switch-mode (chopper), constant-current driver with two channels: one for each winding of a two-phase stepper motor. is equipped with a Disable input
DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a switch-mode (chopper), constant-current driver with two channels: one for each winding of a two-phase stepper motor. is equipped with a Disable input
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic isolation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer CASR series I PN = 6, 5, 25, 5 A Ref: CASR 6-NP, CASR 5-NP, CASR 25-NP, CASR 5-NP For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic isolation between the primary
Current Transducer CASR series I PN = 6, 5, 25, 5 A Ref: CASR 6-NP, CASR 5-NP, CASR 25-NP, CASR 5-NP For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic isolation between the primary
Electrical Description
 History of this Document Rev. no.: Date: Description of change 0 First edition 2 2003-10-08 Section 3: The rated power of the transformer can be increased by 40% if they are equipped with 6 fans for forced
History of this Document Rev. no.: Date: Description of change 0 First edition 2 2003-10-08 Section 3: The rated power of the transformer can be increased by 40% if they are equipped with 6 fans for forced
For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit.
 Current Transducer IN 1000-S I P N = 1000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Closed loop (compensated)
Current Transducer IN 1000-S I P N = 1000 A For the electronic measurement of current: DC, AC, pulsed..., with galvanic separation between the primary and the secondary circuit. Features Closed loop (compensated)
ABB i-bus EIB / KNX Analogue Input AE/S 4.2
 Product Manual ABB i-bus EIB / KNX Analogue Input AE/S 4.2 Intelligent Installation Systems This manual describes the functionality of Analogue Input AE/S 4.2. Subject to changes and errors excepted. Exclusion
Product Manual ABB i-bus EIB / KNX Analogue Input AE/S 4.2 Intelligent Installation Systems This manual describes the functionality of Analogue Input AE/S 4.2. Subject to changes and errors excepted. Exclusion
PHASED OUT. LED Driver Linear / area dimming. Driver LCAI 20W 150mA 400mA ECO lp ECO series
 EL Product description Dimmable built-in LED Driver for LED Constant current LED Driver Output current adjustable between 150 400 ma Max. output power 20 W Nominal life-time up to 100,000 h 5-year guarantee
EL Product description Dimmable built-in LED Driver for LED Constant current LED Driver Output current adjustable between 150 400 ma Max. output power 20 W Nominal life-time up to 100,000 h 5-year guarantee
ULN2803AP,ULN2803AFW,ULN2804AP,ULN2804AFW (Manufactured by Toshiba Malaysia)
 TOSHIBA BIPOLAR DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON MONOLITHIC ULN2803AP,ULN2803AFW,ULN2804AP,ULN2804AFW (Manufactured by Toshiba Malaysia) 8CH DARLINGTON SINK DRIVER The ULN2803AP / AFW Series are high
TOSHIBA BIPOLAR DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON MONOLITHIC ULN2803AP,ULN2803AFW,ULN2804AP,ULN2804AFW (Manufactured by Toshiba Malaysia) 8CH DARLINGTON SINK DRIVER The ULN2803AP / AFW Series are high
PHASED OUT. LED Driver Compact fixed output. Driver LCI 10W 350mA 900mA TOP C TOP series
 EL Product description Fixed output built-in LED Driver Constant current LED Driver Output current settable 35 9 ma Max. output power W Nominal life-time up to, h For luminaires of protection class I and
EL Product description Fixed output built-in LED Driver Constant current LED Driver Output current settable 35 9 ma Max. output power W Nominal life-time up to, h For luminaires of protection class I and
Device circuit breakers Selective power distribution: branch out, individual adaptation, modular extension
 Power & Signal Quality TRABTECH Device circuit breakers Selective power distribution: branch out, individual adaptation, modular extension Interference-free mains supply and signal transmission A constant
Power & Signal Quality TRABTECH Device circuit breakers Selective power distribution: branch out, individual adaptation, modular extension Interference-free mains supply and signal transmission A constant
While DIs may conform to a variety of input characteristics, the most commonly applied ones are IEC Type 1, 2 and 3 (see Figure 1).
 New Digital Input Serializers Catapult Channel Count of Digital Input Modules By Thomas Kugelstadt, Texas Instruments The trend towards increased monitoring in industrial automation and process control
New Digital Input Serializers Catapult Channel Count of Digital Input Modules By Thomas Kugelstadt, Texas Instruments The trend towards increased monitoring in industrial automation and process control
AC/DC sensitive residual current monitoring module RCMB121-
 AC/DC sensitive residual current monitoring module RCMB121- for safe charging of electrical vehicles according to IEC 62752 for IC-CPD and IEC 60364-7-722 for Wall Boxes Vorläufiges Datenblatt RCMB121_D00267_01_D_XXEN/05.2018
AC/DC sensitive residual current monitoring module RCMB121- for safe charging of electrical vehicles according to IEC 62752 for IC-CPD and IEC 60364-7-722 for Wall Boxes Vorläufiges Datenblatt RCMB121_D00267_01_D_XXEN/05.2018
ENS26 Automatic Isolation Unit Product Description
 ENS26 Automatic Isolation Unit Product Description Issue 09/2005 UfE Umweltfreundliche Energieanlagen GmbH Joachim-Jungius-Straße 9 D 18059 Rostock Tel.: +49 3 81 / 405 97 05 Fax: +49 3 81 / 405 97 03
ENS26 Automatic Isolation Unit Product Description Issue 09/2005 UfE Umweltfreundliche Energieanlagen GmbH Joachim-Jungius-Straße 9 D 18059 Rostock Tel.: +49 3 81 / 405 97 05 Fax: +49 3 81 / 405 97 03
TC7SBL66CFU, TC7SBL384CFU
 TOSHIBA CMOS Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TC7SBL66C,384CFU TC7SBL66CFU, TC7SBL384CFU Low Voltage / Low Capacitance Single Bus Switch The TC7SBL66C and TC7SBL384C are a Low Voltage / Low
TOSHIBA CMOS Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TC7SBL66C,384CFU TC7SBL66CFU, TC7SBL384CFU Low Voltage / Low Capacitance Single Bus Switch The TC7SBL66C and TC7SBL384C are a Low Voltage / Low
