Omar E ROOD 1, Han-Sheng CHEN 2, Rodney L LARSON 3 And Richard F NOWAK 4 SUMMARY
|
|
|
- Lynn Garrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH FLOW, HIGH PERFORMANCE HYDRAULIC SERVO VALVES AND CONTROL METHODOLOGIES IN SUPPORT OF FUTURE SUPER LARGE SCALE SHAKING TABLE FACILITIES Omar E ROOD 1, Han-Sheng CHEN 2, Rodney L LARSON 3 And Richard F NOWAK 4 SUMMARY The earthquake engineering research community has had to wrestle with the uncertainties created by shaking table (dynamic) experiments conducted on less than full scale models due to limitations in shaking table size and payload capacity. The potential value of being able to study the failure mechanisms of full size structures under realistic earthquake motions in a controlled laboratory setting has long been recognized. A shake table having this capability would have a surface area of approximately 15x20 meter. Accelerating a table of such size with a specimen greater than 1000 ton would require a large number of high force hydraulic actuators with precise servovalve control. MTS Systems Corporation has completed development of a new class of high flow, high performance hydraulic servovalves to support super large scale shaking table facilities. This paper will describe the design of a new 4 stage hydraulic servovalve and present performance data from bench top flow testing conducted on a small production quantity of these valves. The digital control methods utilized for real time control of a 6x6 meter prototype table driven with (8) 500 ton force hydraulic actuators will also be presented with table performance data demonstrating the effectiveness of these methods. The data contained in this paper support the conclusion that high fidelity seismic simulations using full scale structures is now possible. The previous limitation of precise control of large hydraulic actuators in a dynamic mode has been eliminated through advanced servovalve design and application of digital control methodologies. INTRODUCTION The Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake Disaster in 1995 produced a level of urban destruction that was previously beyond imagination. A visionary project to create a super large scale testing facility was quickly conceived and put into motion by Japan s National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention (NEID). This new vision called for a 3 dimensional shaking table facility large enough to study the dynamic failure mechanisms of full scale structures weighing as much as 1200 ton [NEID Document 1999]. MTS Systems Corporation was contracted for the design and manufacture of a new class of high performance servovalves to support this project. The shaking table performance requirements indicated that a unique servovalve design concept was necessary. It was determined that a servovalve with a peak flow of 15,000 liter per minute with a pressure drop of 160 kg/cm 2 would best optimize the many performance goals. The high flow and high frequency performance requirements were meet by a four stage electro hydraulic valve design MTS Systems Corporation, Technology Drive, Eden Prairie, MN , U.S.A., omar.rood@mts.commts Systems Corpo MTS Systems Corporation, Technology Drive, Eden Prairie, MN , U.S.A., omar.rood@mts.commts Systems Corpo MTS Systems Corporation, Technology Drive, Eden Prairie, MN , U.S.A., omar.rood@mts.commts Systems Corpo MTS Systems Corporation, Technology Drive, Eden Prairie, MN , U.S.A., omar.rood@mts.com
2 The first and second stages consist of a torque motor and 20 lpm spool valve. An armature and flapper assembly (1 st stage) control the volume of oil ported through the spool valve (2 nd stage) based on a current applied across the coil. The 2 nd stage spool ports oil to the larger intermediate stage spool valve. The position of the intermediate spool is kept under closed loop control through the use of a Linear Variable Differential Transformer. The intermediate stage spool can supply 630 lpm of oil to the main stage spool. The main stage spool provides supply pressure to the hydraulic actuator through 100 millimeter diameter control ports. A LVDT on the main stage spool provides closed loop control of up to 15,000 lpm of oil through the main stage. A photograph of the valve is shown in Figure 1. Pilot (1 st & 2 nd ) Stage - 20 lpm Intermediate (3 rd ) Stage -630 lpm Main (4 th ) Stage 15,000 lpm 915 mm 475 mm Figure 1 15,000 LPM Four Stage Servovalve (10,000 lpm with 70 kg/cm 2 pressure drop) A production run of 16 valve assemblies was completed in late Each valve was subjected to performance evaluations prior to delivery. The initial design requirements and measured performance of the servovalves are shown in Table 1. Table 1 Design Target & Measured Performance Metric Target Measured Performance Rated flow at pressure drop of 15,000 liters/minute 15,000 liters/minute maximum flow 100% Full Flow Frequency > 20 Hertz > 25 Hertz Small signal 90 point > 30 Hertz 30 Hz with PID controller Null leakage < 100 liters/minute Approximately liters/minute Lapping % < 0.1% (about.05% maximum) Drain Flow < 2 liters/minute Drain flow is about liters/minute Maximum Phase Angle between < 2º for all valves Most valves tuned within 1ºof each Additional bench top flow tests were conducted to determine the valves dynamic response characteristics to very low level command inputs. This input sensitivity was of concern due to the large main stage spool. The large 4 stage servovalve was shown to have excellent small signal sensitivity. Figure 2 demonstrates that the 4th stage spool moves easily with less than 0.1% command change. The main stage spool position feedback is offset from the command signal to allow viewing of command and feedback dynamic change. The full scale command voltage for the main stage spool is 10 volts. 2
3 Figure 2 - Input Sensitivity The shaking table test facility will not be able to supply a continuous flow of hydraulic oil at constant pressure due to the prohibitive facilities costs. As is common practice, a large bank of hydraulic accumulators will be utilized to store pressurized hydraulic oil for discharge when conducting a shaking table test. This creates a pressure drop in the oil supply as the test is being conducted. This change in pressure can have adverse affects on the fidelity of the simulation if the servovalve response has a high sensitivity to supply pressure. Figure 3 shows the valve response to a pressure change from 210 kg/cm 2 to 170 kg/cm 2 and then back to 210 kg/cm 2. The valves main stage spool shifts approximately 0.3 % of full scale opening despite the dramatic step change in supply pressure. Figure 3 - Pressure Sensitivity SERVOVALVE CONTROLLER The design of the valve controller determines the dynamic performance that can be achieved with any servovalve. It was understood from practice that a standard PID Controller would not be able to close the 4th stage control loop and achieve satisfactory results. The use of single and double derivative lead terms were proposed for increasing the frequency response of the servovalve. The sum of the two lead terms, as shown in Equation 1, were added to the proportional control error signal as shown in Figure 4. It was necessary to add a low pass filter to the lead terms to eliminate high frequency noise. The valve controller and lead terms were implemented with a modified version of a standard MTS Digital Seismic Controller. Sum of Lead Terms = (K L ) x (s) x (s+ α) {1} Where s = j x ω = j x 2 x π x frequency 3
4 j = (-1) ½ K L = Lead term gain α = constant x 2 π x frequency o α S S+ α Feed Forw ard Lead T erm s K L In put from Table Σ K p Proportional Gain Σ D/A 3rd Stage 4th Stage Rate Gain Balance Feedback Figure 4 Valve Controller Block Diagram Figures 5 and 6 show the result of using the two lead terms to extend the bandwidth of the servovalve. A flat transfer function magnitude was demonstrated to 100 Hz. The linerization of the phase angle allows the performance of several valves to be matched within a very tight band. This was a critical requirement of the valve design as each horizontal actuator on the prototype table required the combined flow from three valves, and the table motion is the result from many individual actuators. The actual phase match for the production run of 16 servovalves was within 1 degree for frequencies as high as 35 Hz. Figure 5 - Magnitude Response Figure 6 - Phase Response The lead terms help open the 3 rd stage of the valve which extends the maximum frequency at which full flow can be developed through the 4 th stage of the valve. Figure 7 displays the maximum performance of the 4 stage valve main spool opening. The plot indicates that the valve is capable of switching a flow of 15,000 lpm of pressurized oil 25 times per second. 4
5 Figure 7 - Maximum Flow Performance TABLE PERFORMANCE A prototype of the planned 15x20 meter shaking table system was constructed at the Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Shipyard in Shimonoseki, Japan to evaluate the new servovalves, high force actuators, control methods, and other new system components. The prototype table measured 6x6 meter and utilized (8) full size 500 ton force dynamic actuators for 6 DOF motion. Each horizontal actuator was supplied by three servovalves, providing 2.0 meters/second velocity capability. One servovalve supplied each vertical actuator providing 0.7 meters/second velocity capability[ogawa, Ohtani, Katayama, & Shibata 1999]. The total moving mass of the table, test specimen, actuator pistons and flexible linkages was 350 ton. A photograph of the prototype shaking table is shown in Figure 8. The servovalves, and corresponding table motion, were controlled by a modified MTS Digital Seismic Control system. A variety of compensation routines were provided to reduce the effects of mechanical resonant behavior within the system. The 4 stage servovalves provided sufficient dynamic response to Figure 8 6x6 Meter Prototype Table with (16) 15,000 lpm Servovalves execute the corrections needed to compensate for multiple disturbances. Figure 9 compares transfer function measurements of the desired and achieved lateral motions with and without compensation. The plot demonstrates that the servovalves and controller were successful in compensating the response of the table for 5
6 the affects of two significant resonant behaviors [Larson 1998]. The compensation technique was based on the application of nonlinear notch filtering in the control loop. Figure 9 - Prototype Table Response (Lateral Magnitude) The acceleration response of the vertical axis is shown in Figure 10. The plot shows the magnitude response of the table using three different tuning techniques. A standard PID Displacement control loop shows that the system response would start to roll off almost immediately. The 25 Hz resonance prevents the addition of higher gain settings to boost system response. A Three Variable Control Scheme allows the system to be tuned to a frequency just past the first resonance. The addition of a non-linear notch filter in the control loop about the 25 Hz resonance allows for aggressive system tuning out to a frequency of 50 Hz. The notch filter allows for higher gain settings without the damaging excitations created by system and specimen dynamics. Figure 10 - Prototype Table Vertical Response CONCLUSION A new high performance, high flow four stage servovalve has been developed to support super large scale shaking table facilities. The servovalve is capable of supplying 15,000 lpm of pressurized hydraulic oil at frequencies up to 25 Hz with advanced digital servo control. This is the largest servovalve ever manufactured. Bench top flow testing indicates that the new servovalve design meets or exceeds all performance criteria. A prototype of a super large shaking table was created to test the feasibility of such a project. A 6x6 meter table with 6 degree of freedom capability was constructed using (8) 500 ton force dynamic actuators. A total of (16) 6
7 of the new 4 stage servovalves were used to control the table motion. The total moving mass of the table, actuator piston rods, specimen and attached linkages was 350 ton. The table demonstrated that acceptable simulation fidelity is now possible for super large scale shaking tables. A proposed project for a table measuring 15x20 meters is in the construction phase. It will soon be possible to study the dynamic failure mechanisms of full size civil engineering structures in a controlled laboratory environment. REFERENCES Larson, R.L., Internal MTS documentation on development tests for NEID 6x6 meter 6 DOF Prototype Table, Unpublished documentation of MTS Systems Corporation (1998) National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention, World s Largest Shaking Table Takes Shape in Japan, Brochure of NEID Science and Technology Agency, Japan, WWW: Ogawa, N., Ohtani, K., Katayama, T., and Shibata, H., World s Largest Shaking Table Takes Shape in Japan A Summary of Construction Plan & Technical Development, No.K3-A1-JP, SmiRT-15, Seoul, Korea, August, 1999 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors would like to acknowledge the many persons within the National Institute of Earth Science and Disaster Prevention that have worked to make this visionary project possible 7
UTILIZING MODERN DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING FOR IMPROVEMENT OF LARGE SCALE SHAKING TABLE PERFORMANCE
 UTILIZING MODERN DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING FOR IMPROVEMENT OF LARGE SCALE SHAKING TABLE PERFORMANCE Richard F. NOWAK 1, David A. KUSNER 2, Rodney L. LARSON 3 And Bradford K. THOEN 4 SUMMARY The modern
UTILIZING MODERN DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING FOR IMPROVEMENT OF LARGE SCALE SHAKING TABLE PERFORMANCE Richard F. NOWAK 1, David A. KUSNER 2, Rodney L. LARSON 3 And Bradford K. THOEN 4 SUMMARY The modern
Module 4 TEST SYSTEM Part 2. SHAKING TABLE CONTROLLER ASSOCIATED SOFTWARES Dr. J.C. QUEVAL, CEA/Saclay
 Module 4 TEST SYSTEM Part 2 SHAKING TABLE CONTROLLER ASSOCIATED SOFTWARES Dr. J.C. QUEVAL, CEA/Saclay DEN/DM2S/SEMT/EMSI 11/03/2010 1 2 Electronic command Basic closed loop control The basic closed loop
Module 4 TEST SYSTEM Part 2 SHAKING TABLE CONTROLLER ASSOCIATED SOFTWARES Dr. J.C. QUEVAL, CEA/Saclay DEN/DM2S/SEMT/EMSI 11/03/2010 1 2 Electronic command Basic closed loop control The basic closed loop
Electro-hydraulic Servo Valve Systems
 Fluidsys Training Centre, Bangalore offers an extensive range of skill-based and industry-relevant courses in the field of Pneumatics and Hydraulics. For more details, please visit the website: https://fluidsys.org
Fluidsys Training Centre, Bangalore offers an extensive range of skill-based and industry-relevant courses in the field of Pneumatics and Hydraulics. For more details, please visit the website: https://fluidsys.org
Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Tool Spindle
 Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Tool Spindle David. J. Hopkins, Paul Geraghty Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 7000 East Ave, MS/L-792, Livermore, CA. 94550 Abstract Proper configurations
Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Tool Spindle David. J. Hopkins, Paul Geraghty Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 7000 East Ave, MS/L-792, Livermore, CA. 94550 Abstract Proper configurations
A Machine Tool Controller using Cascaded Servo Loops and Multiple Feedback Sensors per Axis
 A Machine Tool Controller using Cascaded Servo Loops and Multiple Sensors per Axis David J. Hopkins, Timm A. Wulff, George F. Weinert Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 7000 East Ave, L-792, Livermore,
A Machine Tool Controller using Cascaded Servo Loops and Multiple Sensors per Axis David J. Hopkins, Timm A. Wulff, George F. Weinert Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 7000 East Ave, L-792, Livermore,
Fatigue testing. Fatigue design
 Fatigue testing Lecture at SP Technical Research Institute of Sweden April 14, 2008 Gunnar Kjell SP Building Technology and Mechanics E-mail: gunnar.kjell@sp.se Fatigue design Need for material data (Distribution
Fatigue testing Lecture at SP Technical Research Institute of Sweden April 14, 2008 Gunnar Kjell SP Building Technology and Mechanics E-mail: gunnar.kjell@sp.se Fatigue design Need for material data (Distribution
Position Control of a Hydraulic Servo System using PID Control
 Position Control of a Hydraulic Servo System using PID Control ABSTRACT Dechrit Maneetham Mechatronics Engineering Program Rajamangala University of Technology Thanyaburi Pathumthani, THAIAND. (E-mail:Dechrit_m@hotmail.com)
Position Control of a Hydraulic Servo System using PID Control ABSTRACT Dechrit Maneetham Mechatronics Engineering Program Rajamangala University of Technology Thanyaburi Pathumthani, THAIAND. (E-mail:Dechrit_m@hotmail.com)
Control Servo Design for Inverted Pendulum
 JGW-T1402132-v2 Jan. 14, 2014 Control Servo Design for Inverted Pendulum Takanori Sekiguchi 1. Introduction In order to acquire and keep the lock of the interferometer, RMS displacement or velocity of
JGW-T1402132-v2 Jan. 14, 2014 Control Servo Design for Inverted Pendulum Takanori Sekiguchi 1. Introduction In order to acquire and keep the lock of the interferometer, RMS displacement or velocity of
The Air Bearing Throughput Edge By Kevin McCarthy, Chief Technology Officer
 159 Swanson Rd. Boxborough, MA 01719 Phone +1.508.475.3400 dovermotion.com The Air Bearing Throughput Edge By Kevin McCarthy, Chief Technology Officer In addition to the numerous advantages described in
159 Swanson Rd. Boxborough, MA 01719 Phone +1.508.475.3400 dovermotion.com The Air Bearing Throughput Edge By Kevin McCarthy, Chief Technology Officer In addition to the numerous advantages described in
Hybrid Shaker Technology for Wide-band Vibration Test Systems
 Hybrid Shaker Technology for Wide-band Vibration Test Systems Mr. Katsuhiko Nakamura 1, Mr. Kazuyoshi Ueno 1 Dr. John Goodfellow 2 1 IMV Corporation, R&D Centre, 2-6-10 Take-jima, Nishi-yodogawa-ku, Osaka,
Hybrid Shaker Technology for Wide-band Vibration Test Systems Mr. Katsuhiko Nakamura 1, Mr. Kazuyoshi Ueno 1 Dr. John Goodfellow 2 1 IMV Corporation, R&D Centre, 2-6-10 Take-jima, Nishi-yodogawa-ku, Osaka,
(i) Sine sweep (ii) Sine beat (iii) Time history (iv) Continuous sine
 A description is given of one way to implement an earthquake test where the test severities are specified by the sine-beat method. The test is done by using a biaxial computer aided servohydraulic test
A description is given of one way to implement an earthquake test where the test severities are specified by the sine-beat method. The test is done by using a biaxial computer aided servohydraulic test
Exploration of Uni-axial Shaketable Dynamics
 CU-NEES-08-05 NEES at CU Boulder 01000110 01001000 01010100 The George E Brown, Jr. Network for Earthquake Engineering Simulation Exploration of Uni-axial Shaketable Dynamics By Ryan Doheny University
CU-NEES-08-05 NEES at CU Boulder 01000110 01001000 01010100 The George E Brown, Jr. Network for Earthquake Engineering Simulation Exploration of Uni-axial Shaketable Dynamics By Ryan Doheny University
Developments in vibrator control
 Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 58, 33 40 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.2009.00848.x Developments in vibrator control D. Boucard and G. Ollivrin Sercel France, PO Box 439, 44474 Carquefou Cedex, France Received
Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 58, 33 40 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.2009.00848.x Developments in vibrator control D. Boucard and G. Ollivrin Sercel France, PO Box 439, 44474 Carquefou Cedex, France Received
Hydraulic Actuator Control Using an Multi-Purpose Electronic Interface Card
 Hydraulic Actuator Control Using an Multi-Purpose Electronic Interface Card N. KORONEOS, G. DIKEAKOS, D. PAPACHRISTOS Department of Automation Technological Educational Institution of Halkida Psaxna 34400,
Hydraulic Actuator Control Using an Multi-Purpose Electronic Interface Card N. KORONEOS, G. DIKEAKOS, D. PAPACHRISTOS Department of Automation Technological Educational Institution of Halkida Psaxna 34400,
Response spectrum Time history Power Spectral Density, PSD
 A description is given of one way to implement an earthquake test where the test severities are specified by time histories. The test is done by using a biaxial computer aided servohydraulic test rig.
A description is given of one way to implement an earthquake test where the test severities are specified by time histories. The test is done by using a biaxial computer aided servohydraulic test rig.
MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots I Winter Feedback Control USARSim
 MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots I Winter 2011 Feedback Control USARSim Transforming Accelerations into Position Estimates In a perfect world It s not a perfect world. We have noise and bias in our acceleration
MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots I Winter 2011 Feedback Control USARSim Transforming Accelerations into Position Estimates In a perfect world It s not a perfect world. We have noise and bias in our acceleration
DYNAMIC LOAD SIMULATOR (DLS): STRATEGIES AND APPLICATIONS
 15th ASCE Engineering Mechanics Conference June 2-5, 2002, Columbia University, New York, NY EM 2002 DYNAMIC LOAD SIMULATOR (DLS): STRATEGIES AND APPLICATIONS Swaroop Yalla 1, Associate Member ASCE and
15th ASCE Engineering Mechanics Conference June 2-5, 2002, Columbia University, New York, NY EM 2002 DYNAMIC LOAD SIMULATOR (DLS): STRATEGIES AND APPLICATIONS Swaroop Yalla 1, Associate Member ASCE and
Electro-Hydraulic 4-Way Directional Servo Valve Model 4 WS 2 E.10 and 4 WSE 2 E. 10 (Series 4X) PSI (315 bar) K K
 Electro-Hydraulic -Way Directional Servo Valve Model WS 2 E. and WSE 2 E. (Series X) Size (D 5)... 6 PSI (5 bar)... 2 GPM (75 L/min) R 29 586/6.98 R 29 586/6.98 Replaces: 5.9 Features: Servo valve for
Electro-Hydraulic -Way Directional Servo Valve Model WS 2 E. and WSE 2 E. (Series X) Size (D 5)... 6 PSI (5 bar)... 2 GPM (75 L/min) R 29 586/6.98 R 29 586/6.98 Replaces: 5.9 Features: Servo valve for
Real Time Hybrid Seismic Test System User s Manual. State University of New York at Buffalo (SUNY) US EQT
 Real Time Hybrid Seismic Test System User s Manual l State University of New York at Buffalo (SUNY) US1.17858.EQT Copyright information Contact information Publication information 2003 MTS Systems Corporation.
Real Time Hybrid Seismic Test System User s Manual l State University of New York at Buffalo (SUNY) US1.17858.EQT Copyright information Contact information Publication information 2003 MTS Systems Corporation.
Performance of the CGS six DOF Shaking Table on the Harmonic Signal Reproduction
 P P Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engineering OnlineFirst (2017) paper 9033 https://doi.org/10.3311/ppci.9033 Creative Commons Attribution b Performance of the CGS six DOF Shaking Table on the Harmonic
P P Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engineering OnlineFirst (2017) paper 9033 https://doi.org/10.3311/ppci.9033 Creative Commons Attribution b Performance of the CGS six DOF Shaking Table on the Harmonic
Non-linear Control of a Piezoelectric Two Stage Servovalve
 The 15th Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power, SICFP 17, June 7-9, 217, Linköping, Sweden Non-linear Control of a Piezoelectric Two Stage Servovalve Johan Persson, Andrew Plummer, Chris
The 15th Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power, SICFP 17, June 7-9, 217, Linköping, Sweden Non-linear Control of a Piezoelectric Two Stage Servovalve Johan Persson, Andrew Plummer, Chris
Application of AD698 Measuring Circuit in Valvistor Hydraulic Cartridge Valve
 Sensors & Transducers 214 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Application of AD698 Measuring Circuit in Valvistor Hydraulic Cartridge Valve * Suming Li Long Quan Yilong Liang Institute
Sensors & Transducers 214 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Application of AD698 Measuring Circuit in Valvistor Hydraulic Cartridge Valve * Suming Li Long Quan Yilong Liang Institute
Application Note #2442
 Application Note #2442 Tuning with PL and PID Most closed-loop servo systems are able to achieve satisfactory tuning with the basic Proportional, Integral, and Derivative (PID) tuning parameters. However,
Application Note #2442 Tuning with PL and PID Most closed-loop servo systems are able to achieve satisfactory tuning with the basic Proportional, Integral, and Derivative (PID) tuning parameters. However,
Modeling and Control of Mold Oscillation
 ANNUAL REPORT UIUC, August 8, Modeling and Control of Mold Oscillation Vivek Natarajan (Ph.D. Student), Joseph Bentsman Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering University of Illinois at UrbanaChampaign
ANNUAL REPORT UIUC, August 8, Modeling and Control of Mold Oscillation Vivek Natarajan (Ph.D. Student), Joseph Bentsman Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering University of Illinois at UrbanaChampaign
Tuning of Controller for Electro-Hydraulic System Using Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
 Tuning of Controller for Electro-Hydraulic System Using Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) Sachin Kumar Mishra 1, Prof. Kuldeep Kumar Swarnkar 2 Electrical Engineering Department 1, 2, MITS, Gwaliore 1,
Tuning of Controller for Electro-Hydraulic System Using Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) Sachin Kumar Mishra 1, Prof. Kuldeep Kumar Swarnkar 2 Electrical Engineering Department 1, 2, MITS, Gwaliore 1,
MAGNETIC LEVITATION SUSPENSION CONTROL SYSTEM FOR REACTION WHEEL
 IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Engineering & Technology (IMPACT: IJRET) ISSN 2321-8843 Vol. 1, Issue 4, Sep 2013, 1-6 Impact Journals MAGNETIC LEVITATION SUSPENSION CONTROL SYSTEM FOR REACTION
IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Engineering & Technology (IMPACT: IJRET) ISSN 2321-8843 Vol. 1, Issue 4, Sep 2013, 1-6 Impact Journals MAGNETIC LEVITATION SUSPENSION CONTROL SYSTEM FOR REACTION
ACTUATORS AND SENSORS. Joint actuating system. Servomotors. Sensors
 ACTUATORS AND SENSORS Joint actuating system Servomotors Sensors JOINT ACTUATING SYSTEM Transmissions Joint motion low speeds high torques Spur gears change axis of rotation and/or translate application
ACTUATORS AND SENSORS Joint actuating system Servomotors Sensors JOINT ACTUATING SYSTEM Transmissions Joint motion low speeds high torques Spur gears change axis of rotation and/or translate application
4-Way Servo Valve Model 4 WS. 2 E , (Series 2X) with Mounting Pattern to DIN or CETOP RP 115 H PSI (315 bar) H/A 3012 H/A 3013
 4-Way Servo Valve Model 4 WS. 2 E. 16..., (Series 2X) with Mounting attern to DIN 24 3 or CETO R 11 H Size 16... 40 SI (31 bar)... 3 GM (0 L/min) R 29 91/06.98 R 29 91/06.98 Replaces: 0.94 2 stage servo
4-Way Servo Valve Model 4 WS. 2 E. 16..., (Series 2X) with Mounting attern to DIN 24 3 or CETO R 11 H Size 16... 40 SI (31 bar)... 3 GM (0 L/min) R 29 91/06.98 R 29 91/06.98 Replaces: 0.94 2 stage servo
New Long Stroke Vibration Shaker Design using Linear Motor Technology
 New Long Stroke Vibration Shaker Design using Linear Motor Technology The Modal Shop, Inc. A PCB Group Company Patrick Timmons Calibration Systems Engineer Mark Schiefer Senior Scientist Long Stroke Shaker
New Long Stroke Vibration Shaker Design using Linear Motor Technology The Modal Shop, Inc. A PCB Group Company Patrick Timmons Calibration Systems Engineer Mark Schiefer Senior Scientist Long Stroke Shaker
Computer Numeric Control
 Computer Numeric Control TA202A 2017-18(2 nd ) Semester Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kanpur Computer Numeric Control A system in which actions are controlled by the direct
Computer Numeric Control TA202A 2017-18(2 nd ) Semester Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kanpur Computer Numeric Control A system in which actions are controlled by the direct
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING BANGLADESH UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY EEE 402 : CONTROL SYSTEMS SESSIONAL
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING BANGLADESH UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY EEE 402 : CONTROL SYSTEMS SESSIONAL Experiment No. 1(a) : Modeling of physical systems and study of
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING BANGLADESH UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY EEE 402 : CONTROL SYSTEMS SESSIONAL Experiment No. 1(a) : Modeling of physical systems and study of
Advanced Motion Control Optimizes Mechanical Micro-Drilling
 Advanced Motion Control Optimizes Mechanical Micro-Drilling The following discussion will focus on how to implement advanced motion control technology to improve the performance of mechanical micro-drilling
Advanced Motion Control Optimizes Mechanical Micro-Drilling The following discussion will focus on how to implement advanced motion control technology to improve the performance of mechanical micro-drilling
AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR AND AUTOMATIC LOAD FREQUENCY CONTROL IN TWO-AREA POWER SYSTEM
 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR AND AUTOMATIC LOAD FREQUENCY CONTROL IN TWO-AREA POWER SYSTEM ABSTRACT [1] Nitesh Thapa, [2] Nilu Murmu, [3] Aditya Narayan, [4] Birju Besra Dept. of Electrical and Electronics
AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR AND AUTOMATIC LOAD FREQUENCY CONTROL IN TWO-AREA POWER SYSTEM ABSTRACT [1] Nitesh Thapa, [2] Nilu Murmu, [3] Aditya Narayan, [4] Birju Besra Dept. of Electrical and Electronics
Acceleration Tracking Performance of the UCSD-NEES Shake Table
 Acceleration Tracking Performance of the UCSD-NEES Shake Table J. E. Luco 1 ; O. Ozcelik 2 ; and J. P. Conte 3 Abstract: The main objective of this paper is to investigate the tracking signal reproduction
Acceleration Tracking Performance of the UCSD-NEES Shake Table J. E. Luco 1 ; O. Ozcelik 2 ; and J. P. Conte 3 Abstract: The main objective of this paper is to investigate the tracking signal reproduction
Dynamic Vibration Absorber
 Part 1B Experimental Engineering Integrated Coursework Location: DPO Experiment A1 (Short) Dynamic Vibration Absorber Please bring your mechanics data book and your results from first year experiment 7
Part 1B Experimental Engineering Integrated Coursework Location: DPO Experiment A1 (Short) Dynamic Vibration Absorber Please bring your mechanics data book and your results from first year experiment 7
DRAFT Expected performance of type-bp SAS in bkagra
 DRAFT Expected performance of type-bp SAS in bkagra December 27, 216 Yoshinori Fujii Table of Contents 1 Expected performance of type-bp SAS in bkagra 2 1.1 Overview.................................................
DRAFT Expected performance of type-bp SAS in bkagra December 27, 216 Yoshinori Fujii Table of Contents 1 Expected performance of type-bp SAS in bkagra 2 1.1 Overview.................................................
2-Way Proportional Logic Cartridge Valve Model FE.. (Series 1X and 2X) PSI (315 bar) F with electrical connection 12 X Y
 RA 9 /6.98 -Way Proportional Logic Cartridge Valve Model FE.. (Series X and X) Size 6... 6... 6 PSI (5 bar)... 75 GPM (8 L/min) RA 9 /6.98 Replaces: 5.9 Characteristics: Single land throttle valve (main
RA 9 /6.98 -Way Proportional Logic Cartridge Valve Model FE.. (Series X and X) Size 6... 6... 6 PSI (5 bar)... 75 GPM (8 L/min) RA 9 /6.98 Replaces: 5.9 Characteristics: Single land throttle valve (main
Elements of Haptic Interfaces
 Elements of Haptic Interfaces Katherine J. Kuchenbecker Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics University of Pennsylvania kuchenbe@seas.upenn.edu Course Notes for MEAM 625, University
Elements of Haptic Interfaces Katherine J. Kuchenbecker Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics University of Pennsylvania kuchenbe@seas.upenn.edu Course Notes for MEAM 625, University
SHAKING TABLE. SHAKING TABLE Rev. 03/02/10
 SHAKING TABLE SHAKING TABLE Rev. 03/02/10 HACER CLIC PARA INTRODUCIR EL TÍTULO 1. GENERAL 2. PERFORMANCE 3. SYSTEM SIZING 4. CONTROL SYSTEM 5. CONCLUSION 6. CONTACT 2 HACER CLIC PARA INTRODUCIR EL TÍTULO
SHAKING TABLE SHAKING TABLE Rev. 03/02/10 HACER CLIC PARA INTRODUCIR EL TÍTULO 1. GENERAL 2. PERFORMANCE 3. SYSTEM SIZING 4. CONTROL SYSTEM 5. CONCLUSION 6. CONTACT 2 HACER CLIC PARA INTRODUCIR EL TÍTULO
Proportional Directional Control Valves Series D*FH and D*FM General Description Operation Features Series D*FH Series D*FM
 Catalog HY14-255/ echnical Information General Description eries D*FH is a high response, proportional servovalve with an on-board drive amplifier. he D*FM is a high response, direct actuated servovalve
Catalog HY14-255/ echnical Information General Description eries D*FH is a high response, proportional servovalve with an on-board drive amplifier. he D*FM is a high response, direct actuated servovalve
Introduction to Servo Control & PID Tuning
 Introduction to Servo Control & PID Tuning Presented to: Agenda Introduction to Servo Control Theory PID Algorithm Overview Tuning & General System Characterization Oscillation Characterization Feed-forward
Introduction to Servo Control & PID Tuning Presented to: Agenda Introduction to Servo Control Theory PID Algorithm Overview Tuning & General System Characterization Oscillation Characterization Feed-forward
Position Control of a Servopneumatic Actuator using Fuzzy Compensation
 Session 1448 Abstract Position Control of a Servopneumatic Actuator using Fuzzy Compensation Saravanan Rajendran 1, Robert W.Bolton 2 1 Department of Industrial Engineering 2 Department of Engineering
Session 1448 Abstract Position Control of a Servopneumatic Actuator using Fuzzy Compensation Saravanan Rajendran 1, Robert W.Bolton 2 1 Department of Industrial Engineering 2 Department of Engineering
A Subsidiary of Regal-Beloit Corporation. AC Inverter Terminology
 AP200-9/01 Acceleration The rate of change in velocity as a function of time. Acceleration usually refers to increasing velocity and deceleration to decreasing velocity. Acceleration Boost During acceleration,
AP200-9/01 Acceleration The rate of change in velocity as a function of time. Acceleration usually refers to increasing velocity and deceleration to decreasing velocity. Acceleration Boost During acceleration,
Application of Gain Scheduling Technique to a 6-Axis Articulated Robot using LabVIEW R
 Application of Gain Scheduling Technique to a 6-Axis Articulated Robot using LabVIEW R ManSu Kim #,1, WonJee Chung #,2, SeungWon Jeong #,3 # School of Mechatronics, Changwon National University Changwon,
Application of Gain Scheduling Technique to a 6-Axis Articulated Robot using LabVIEW R ManSu Kim #,1, WonJee Chung #,2, SeungWon Jeong #,3 # School of Mechatronics, Changwon National University Changwon,
of harmonic cancellation algorithms The internal model principle enable precision motion control Dynamic control
 Dynamic control Harmonic cancellation algorithms enable precision motion control The internal model principle is a 30-years-young idea that serves as the basis for a myriad of modern motion control approaches.
Dynamic control Harmonic cancellation algorithms enable precision motion control The internal model principle is a 30-years-young idea that serves as the basis for a myriad of modern motion control approaches.
7th Edoardo Amaldi Conference on Gravitational Waves (Amaldi7)
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series (8) 4 doi:.88/74-6596///4 Lock Acquisition Studies for Advanced Interferometers O Miyakawa, H Yamamoto LIGO Laboratory 8-34, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Journal of Physics: Conference Series (8) 4 doi:.88/74-6596///4 Lock Acquisition Studies for Advanced Interferometers O Miyakawa, H Yamamoto LIGO Laboratory 8-34, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
A Control Method of the Force Loading Electro-hydraulic Servo System Based on BRF Jing-Wen FANG1,a,*, Ji-Shun LI1,2,b, Fang YANG1, Yu-Jun XUE2
 nd Annual International Conference on Advanced Material Engineering (AME 016) A Control Method of the Force Loading Electro-hydraulic Servo System Based on BRF Jing-Wen FANG1,a,*, Ji-Shun LI1,,b, Fang
nd Annual International Conference on Advanced Material Engineering (AME 016) A Control Method of the Force Loading Electro-hydraulic Servo System Based on BRF Jing-Wen FANG1,a,*, Ji-Shun LI1,,b, Fang
Experiment 9. PID Controller
 Experiment 9 PID Controller Objective: - To be familiar with PID controller. - Noting how changing PID controller parameter effect on system response. Theory: The basic function of a controller is to execute
Experiment 9 PID Controller Objective: - To be familiar with PID controller. - Noting how changing PID controller parameter effect on system response. Theory: The basic function of a controller is to execute
Conventional geophone topologies and their intrinsic physical limitations, determined
 Magnetic innovation in velocity sensing Low -frequency with passive Conventional geophone topologies and their intrinsic physical limitations, determined by the mechanical construction, limit their velocity
Magnetic innovation in velocity sensing Low -frequency with passive Conventional geophone topologies and their intrinsic physical limitations, determined by the mechanical construction, limit their velocity
-binary sensors and actuators (such as an on/off controller) are generally more reliable and less expensive
 Process controls are necessary for designing safe and productive plants. A variety of process controls are used to manipulate processes, however the most simple and often most effective is the PID controller.
Process controls are necessary for designing safe and productive plants. A variety of process controls are used to manipulate processes, however the most simple and often most effective is the PID controller.
Load Observer and Tuning Basics
 Load Observer and Tuning Basics Feature Use & Benefits Mark Zessin Motion Solution Architect Rockwell Automation PUBLIC INFORMATION Rev 5058-CO900E Questions Addressed Why is Motion System Tuning Necessary?
Load Observer and Tuning Basics Feature Use & Benefits Mark Zessin Motion Solution Architect Rockwell Automation PUBLIC INFORMATION Rev 5058-CO900E Questions Addressed Why is Motion System Tuning Necessary?
Latest Control Technology in Inverters and Servo Systems
 Latest Control Technology in Inverters and Servo Systems Takao Yanase Hidetoshi Umida Takashi Aihara. Introduction Inverters and servo systems have achieved small size and high performance through the
Latest Control Technology in Inverters and Servo Systems Takao Yanase Hidetoshi Umida Takashi Aihara. Introduction Inverters and servo systems have achieved small size and high performance through the
CONTROLLER DESIGN ON ARX MODEL OF ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR
 Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences ISSN 1112-9867 Research Article Special Issue Available online at http://www.jfas.info MODELING AND CONTROLLER DESIGN ON ARX MODEL OF ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR
Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences ISSN 1112-9867 Research Article Special Issue Available online at http://www.jfas.info MODELING AND CONTROLLER DESIGN ON ARX MODEL OF ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR
TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER TITLE PAGE DECLARATION DEDICATION ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ABSTRACT ABSTRAK
 vii TABLES OF CONTENTS CHAPTER TITLE PAGE DECLARATION DEDICATION ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ABSTRACT ABSTRAK TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES LIST OF ABREVIATIONS LIST OF SYMBOLS LIST OF APPENDICES
vii TABLES OF CONTENTS CHAPTER TITLE PAGE DECLARATION DEDICATION ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ABSTRACT ABSTRAK TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES LIST OF ABREVIATIONS LIST OF SYMBOLS LIST OF APPENDICES
Design and Implementation of the Control System for a 2 khz Rotary Fast Tool Servo
 Design and Implementation of the Control System for a 2 khz Rotary Fast Tool Servo Richard C. Montesanti a,b, David L. Trumper b a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA b Massachusetts
Design and Implementation of the Control System for a 2 khz Rotary Fast Tool Servo Richard C. Montesanti a,b, David L. Trumper b a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA b Massachusetts
Modeling of Electro Mechanical Actuator with Inner Loop controller
 Modeling of Electro Mechanical Actuator with Inner Loop controller Patchigalla Vinay 1, P Mallikarjuna Rao 2 1PG scholar, Dept.of EEE, Andhra Universit(A),Visakhapatnam,India 2Professor, Dept.of EEE, Andhra
Modeling of Electro Mechanical Actuator with Inner Loop controller Patchigalla Vinay 1, P Mallikarjuna Rao 2 1PG scholar, Dept.of EEE, Andhra Universit(A),Visakhapatnam,India 2Professor, Dept.of EEE, Andhra
Advanced Servo Tuning
 Advanced Servo Tuning Dr. Rohan Munasinghe Department of Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering University of Moratuwa Servo System Elements position encoder Motion controller (software) Desired
Advanced Servo Tuning Dr. Rohan Munasinghe Department of Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering University of Moratuwa Servo System Elements position encoder Motion controller (software) Desired
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER
 VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
Active Stabilization of a Mechanical Structure
 Active Stabilization of a Mechanical Structure L. Brunetti 1, N. Geffroy 1, B. Bolzon 1, A. Jeremie 1, J. Lottin 2, B. Caron 2, R. Oroz 2 1- Laboratoire d Annecy-le-Vieux de Physique des Particules LAPP-IN2P3-CNRS-Université
Active Stabilization of a Mechanical Structure L. Brunetti 1, N. Geffroy 1, B. Bolzon 1, A. Jeremie 1, J. Lottin 2, B. Caron 2, R. Oroz 2 1- Laboratoire d Annecy-le-Vieux de Physique des Particules LAPP-IN2P3-CNRS-Université
TigreSAT 2010 &2011 June Monthly Report
 2010-2011 TigreSAT Monthly Progress Report EQUIS ADS 2010 PAYLOAD No changes have been done to the payload since it had passed all the tests, requirements and integration that are necessary for LSU HASP
2010-2011 TigreSAT Monthly Progress Report EQUIS ADS 2010 PAYLOAD No changes have been done to the payload since it had passed all the tests, requirements and integration that are necessary for LSU HASP
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10770-2 Second edition 2012-12-01 Hydraulic fluid power Electrically modulated hydraulic control valves Part 2: Test methods for three-port directional flow-control valves Transmissions
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10770-2 Second edition 2012-12-01 Hydraulic fluid power Electrically modulated hydraulic control valves Part 2: Test methods for three-port directional flow-control valves Transmissions
SERVO VALVES. Maximum Flow. Maximum Operating Pressure MPa (PSI) U.S.GPM Page. Graphic Symbols.
 I SERVO VALVES Valve Graphic Symbols Maximum Operating Pressure MPa (PSI) Maximum Flow U.S.GPM.5 1 2 5 50 0 0 500 1 2 3 5 30 50 0 0 300 500 00 00 L/min Page Direct High Speed Linear Servo Valves LSVG-03
I SERVO VALVES Valve Graphic Symbols Maximum Operating Pressure MPa (PSI) Maximum Flow U.S.GPM.5 1 2 5 50 0 0 500 1 2 3 5 30 50 0 0 300 500 00 00 L/min Page Direct High Speed Linear Servo Valves LSVG-03
elevation drive. The best performance of the system is currently characterized by 3 00 steps.
 Submillimeter Array Technical Memorandum Number 4 December 6, 996 Performance of the Elevation Drive System Eric Keto Abstract This memo reports on measurements and modeling of the performance of the elevation
Submillimeter Array Technical Memorandum Number 4 December 6, 996 Performance of the Elevation Drive System Eric Keto Abstract This memo reports on measurements and modeling of the performance of the elevation
An Improved Analytical Model for Efficiency Estimation in Design Optimization Studies of a Refrigerator Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 An Improved Analytical Model for Efficiency Estimation in Design Optimization Studies
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 An Improved Analytical Model for Efficiency Estimation in Design Optimization Studies
Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies
 Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies S Prem Kumar 1 J V Pavan Chand 1 B Pangedaiah 1 1. Assistant professor of Laki Reddy Balireddy College Of Engineering, Mylavaram Abstract - As the
Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies S Prem Kumar 1 J V Pavan Chand 1 B Pangedaiah 1 1. Assistant professor of Laki Reddy Balireddy College Of Engineering, Mylavaram Abstract - As the
MEMS Optical Scanner "ECO SCAN" Application Notes. Ver.0
 MEMS Optical Scanner "ECO SCAN" Application Notes Ver.0 Micro Electro Mechanical Systems Promotion Dept., Visionary Business Center The Nippon Signal Co., Ltd. 1 Preface This document summarizes precautions
MEMS Optical Scanner "ECO SCAN" Application Notes Ver.0 Micro Electro Mechanical Systems Promotion Dept., Visionary Business Center The Nippon Signal Co., Ltd. 1 Preface This document summarizes precautions
Servo Tuning. Dr. Rohan Munasinghe Department. of Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering University of Moratuwa. Thanks to Dr.
 Servo Tuning Dr. Rohan Munasinghe Department. of Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering University of Moratuwa Thanks to Dr. Jacob Tal Overview Closed Loop Motion Control System Brain Brain Muscle
Servo Tuning Dr. Rohan Munasinghe Department. of Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering University of Moratuwa Thanks to Dr. Jacob Tal Overview Closed Loop Motion Control System Brain Brain Muscle
Fundamentals of Servo Motion Control
 Fundamentals of Servo Motion Control The fundamental concepts of servo motion control have not changed significantly in the last 50 years. The basic reasons for using servo systems in contrast to open
Fundamentals of Servo Motion Control The fundamental concepts of servo motion control have not changed significantly in the last 50 years. The basic reasons for using servo systems in contrast to open
LSV(H)G Series High-speed Linear Servo Valves
 LSV(H)G Series High-speed Linear Servo Valves LSVG-03 (3/8) & LSVHG-04/06/10 (1/2,3/4,1) Sub-plate Mounting LSVG/LSVHG Series High-Speed Linear Servo Valves offer extremely high response and excellent
LSV(H)G Series High-speed Linear Servo Valves LSVG-03 (3/8) & LSVHG-04/06/10 (1/2,3/4,1) Sub-plate Mounting LSVG/LSVHG Series High-Speed Linear Servo Valves offer extremely high response and excellent
Experiment VI: The LRC Circuit and Resonance
 Experiment VI: The ircuit and esonance I. eferences Halliday, esnick and Krane, Physics, Vol., 4th Ed., hapters 38,39 Purcell, Electricity and Magnetism, hapter 7,8 II. Equipment Digital Oscilloscope Digital
Experiment VI: The ircuit and esonance I. eferences Halliday, esnick and Krane, Physics, Vol., 4th Ed., hapters 38,39 Purcell, Electricity and Magnetism, hapter 7,8 II. Equipment Digital Oscilloscope Digital
Proportional Directional Control Valves Nominal sizes 16 and 25
 Proportional Directional Control Valves Nominal sizes 16 and 25 Pilot operated, electrically adjustable Interface acc. to DIN 24 340 and ISO 4401 PN [p max. ] = 315 bar 7502968.06.01.06 Description Design
Proportional Directional Control Valves Nominal sizes 16 and 25 Pilot operated, electrically adjustable Interface acc. to DIN 24 340 and ISO 4401 PN [p max. ] = 315 bar 7502968.06.01.06 Description Design
Advanced High-Frequency 6-DOF Vibration Testing Using the Tensor System
 Advanced High-Frequency 6-DOF Vibration Testing Using the Tensor System Joel Hoksbergen, Team Corporation 1 Abstract Commercially available vibration test systems able to reproduce and accurately control
Advanced High-Frequency 6-DOF Vibration Testing Using the Tensor System Joel Hoksbergen, Team Corporation 1 Abstract Commercially available vibration test systems able to reproduce and accurately control
Exercise 6. Open-Loop Speed Control EXERCISE OBJECTIVE
 Exercise 6 Open-Loop Speed Control EXERCISE OBJECTIVE To understand what is open-loop speed control; To learn how to sense the speed of the trainer Bidirectional Motor; To control the speed of the trainer
Exercise 6 Open-Loop Speed Control EXERCISE OBJECTIVE To understand what is open-loop speed control; To learn how to sense the speed of the trainer Bidirectional Motor; To control the speed of the trainer
profile Using intelligent servo drives to filter mechanical resonance and improve machine accuracy in printing and converting machinery
 profile Drive & Control Using intelligent servo drives to filter mechanical resonance and improve machine accuracy in printing and converting machinery Challenge: Controlling machine resonance the white
profile Drive & Control Using intelligent servo drives to filter mechanical resonance and improve machine accuracy in printing and converting machinery Challenge: Controlling machine resonance the white
Nanomotion Tech Note 105 Using AC and DC Modes with Nanomotion AB2 Driver in Closed-Loop for Nanometer Level Positioning
 Nanomotion Tech Note 105 Using AC and DC Modes with Nanomotion AB2 Driver in Closed-Loop for Nanometer Level Positioning Rev A March 28, 2006 1. Introduction - Ultra- High Resolution in DC Mode Nanomotion
Nanomotion Tech Note 105 Using AC and DC Modes with Nanomotion AB2 Driver in Closed-Loop for Nanometer Level Positioning Rev A March 28, 2006 1. Introduction - Ultra- High Resolution in DC Mode Nanomotion
Motomatic Servo Control
 Exercise 2 Motomatic Servo Control This exercise will take two weeks. You will work in teams of two. 2.0 Prelab Read through this exercise in the lab manual. Using Appendix B as a reference, create a block
Exercise 2 Motomatic Servo Control This exercise will take two weeks. You will work in teams of two. 2.0 Prelab Read through this exercise in the lab manual. Using Appendix B as a reference, create a block
DIN (NFPA/ISO/CETOP) NG6 (3) NG10
 Technical nformation General escription proportional directional control valves are direct operated solenoid valves with electronic spool position feedback, and on-board integrated control electronics.
Technical nformation General escription proportional directional control valves are direct operated solenoid valves with electronic spool position feedback, and on-board integrated control electronics.
2B34 DEVELOPMENT OF A HYDRAULIC PARALLEL LINK TYPE OF FORCE DISPLAY
 2B34 DEVELOPMENT OF A HYDRAULIC PARALLEL LINK TYPE OF FORCE DISPLAY -Improvement of Manipulability Using Disturbance Observer and its Application to a Master-slave System- Shigeki KUDOMI*, Hironao YAMADA**
2B34 DEVELOPMENT OF A HYDRAULIC PARALLEL LINK TYPE OF FORCE DISPLAY -Improvement of Manipulability Using Disturbance Observer and its Application to a Master-slave System- Shigeki KUDOMI*, Hironao YAMADA**
+ + G c (s G p (s. a) What is overall transfer closed-loop transfer function θ(s)
 Problem 1 (35 pts) Department of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology 2.14 Analysis and Design of Feedback Control Systems Fall 2004 Quiz 1 Wednesday October 6, 2004 OPEN BOOK A
Problem 1 (35 pts) Department of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology 2.14 Analysis and Design of Feedback Control Systems Fall 2004 Quiz 1 Wednesday October 6, 2004 OPEN BOOK A
A DESIGN TO DIGITALIZE HYDRAULIC CYLINDER CONTROL OF A MACHINE TOOL
 Nigerian Journal of Technology, Vol. 16, No. 1 September 1995 ACHI 47 A DESIGN TO DIGITALIZE HYDRAULIC CYLINDER CONTROL OF A MACHINE TOOL by P. B. U. Achi Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering Department
Nigerian Journal of Technology, Vol. 16, No. 1 September 1995 ACHI 47 A DESIGN TO DIGITALIZE HYDRAULIC CYLINDER CONTROL OF A MACHINE TOOL by P. B. U. Achi Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering Department
Electrical Drives I. Week 4-5-6: Solid state dc drives- closed loop control of phase controlled DC drives
 Electrical Drives I Week 4-5-6: Solid state dc drives- closed loop control of phase controlled DC drives DC Drives control- DC motor without control Speed Control Strategy: below base speed: V t control
Electrical Drives I Week 4-5-6: Solid state dc drives- closed loop control of phase controlled DC drives DC Drives control- DC motor without control Speed Control Strategy: below base speed: V t control
Resonance Tube. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory. 2.1 Air As A Spring. 2.2 Traveling Sound Waves in Air
 Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Advanced Digital Motion Control Using SERCOS-based Torque Drives
 Advanced Digital Motion Using SERCOS-based Torque Drives Ying-Yu Tzou, Andes Yang, Cheng-Chang Hsieh, and Po-Ching Chen Power Electronics & Motion Lab. Dept. of Electrical and Engineering National Chiao
Advanced Digital Motion Using SERCOS-based Torque Drives Ying-Yu Tzou, Andes Yang, Cheng-Chang Hsieh, and Po-Ching Chen Power Electronics & Motion Lab. Dept. of Electrical and Engineering National Chiao
Basic NC and CNC. Dr. J. Ramkumar Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering Micro machining Lab, I.I.T. Kanpur
 Basic NC and CNC Dr. J. Ramkumar Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering Micro machining Lab, I.I.T. Kanpur Micro machining Lab, I.I.T. Kanpur Outline 1. Introduction to CNC machine 2. Component
Basic NC and CNC Dr. J. Ramkumar Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering Micro machining Lab, I.I.T. Kanpur Micro machining Lab, I.I.T. Kanpur Outline 1. Introduction to CNC machine 2. Component
Proportional directional valves
 01/10 Proportional directional valves 6.12 Type 4WRPEH6...L2X NG 6 Up to 315 bar Up to 40L /min Contents Function and configuration 02 Ordering code 03 Symbols 03 Technical data 04 Electrical connection
01/10 Proportional directional valves 6.12 Type 4WRPEH6...L2X NG 6 Up to 315 bar Up to 40L /min Contents Function and configuration 02 Ordering code 03 Symbols 03 Technical data 04 Electrical connection
Hybrid Input Shaping and Non-collocated PID Control of a Gantry Crane System: Comparative Assessment
 Hybrid Input Shaping and Non-collocated PID Control of a Gantry Crane System: Comparative Assessment M.A. Ahmad, R.M.T. Raja Ismail and M.S. Ramli Faculty of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Universiti
Hybrid Input Shaping and Non-collocated PID Control of a Gantry Crane System: Comparative Assessment M.A. Ahmad, R.M.T. Raja Ismail and M.S. Ramli Faculty of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Universiti
CDS 101/110a: Lecture 8-1 Frequency Domain Design
 CDS 11/11a: Lecture 8-1 Frequency Domain Design Richard M. Murray 17 November 28 Goals: Describe canonical control design problem and standard performance measures Show how to use loop shaping to achieve
CDS 11/11a: Lecture 8-1 Frequency Domain Design Richard M. Murray 17 November 28 Goals: Describe canonical control design problem and standard performance measures Show how to use loop shaping to achieve
Closed-Loop Position Control, Proportional Mode
 Exercise 4 Closed-Loop Position Control, Proportional Mode EXERCISE OBJECTIVE To describe the proportional control mode; To describe the advantages and disadvantages of proportional control; To define
Exercise 4 Closed-Loop Position Control, Proportional Mode EXERCISE OBJECTIVE To describe the proportional control mode; To describe the advantages and disadvantages of proportional control; To define
PID-control and open-loop control
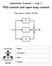 Automatic Control Lab 1 PID-control and open-loop control This version: October 24 2011 P I D REGLERTEKNIK Name: P-number: AUTOMATIC LINKÖPING CONTROL Date: Passed: 1 Introduction The purpose of this
Automatic Control Lab 1 PID-control and open-loop control This version: October 24 2011 P I D REGLERTEKNIK Name: P-number: AUTOMATIC LINKÖPING CONTROL Date: Passed: 1 Introduction The purpose of this
EXAMINATION Hydraulic Servo Systems, TMHP51/TEN1
 EXAMINATION Page 1(7) EXAMINATION Hydraulic Servo Systems, TMHP51/TEN1 Date: 2013-08-30, 08:00 Room: TR4 Number of questions: 5 Responsible teacher: Magnus Sethson, (magnus.sethson@liu.se) Phone number
EXAMINATION Page 1(7) EXAMINATION Hydraulic Servo Systems, TMHP51/TEN1 Date: 2013-08-30, 08:00 Room: TR4 Number of questions: 5 Responsible teacher: Magnus Sethson, (magnus.sethson@liu.se) Phone number
System Inputs, Physical Modeling, and Time & Frequency Domains
 System Inputs, Physical Modeling, and Time & Frequency Domains There are three topics that require more discussion at this point of our study. They are: Classification of System Inputs, Physical Modeling,
System Inputs, Physical Modeling, and Time & Frequency Domains There are three topics that require more discussion at this point of our study. They are: Classification of System Inputs, Physical Modeling,
CHAPTER 2 D-Q AXES FLUX MEASUREMENT IN SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES
 22 CHAPTER 2 D-Q AXES FLUX MEASUREMENT IN SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES 2.1 INTRODUCTION For the accurate analysis of synchronous machines using the two axis frame models, the d-axis and q-axis magnetic characteristics
22 CHAPTER 2 D-Q AXES FLUX MEASUREMENT IN SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES 2.1 INTRODUCTION For the accurate analysis of synchronous machines using the two axis frame models, the d-axis and q-axis magnetic characteristics
Electronics and Instrumentation Name ENGR-4220 Fall 1999 Section Modeling the Cantilever Beam Supplemental Info for Project 1.
 Name ENGR-40 Fall 1999 Section Modeling the Cantilever Beam Supplemental Info for Project 1 The cantilever beam has a simple equation of motion. If we assume that the mass is located at the end of the
Name ENGR-40 Fall 1999 Section Modeling the Cantilever Beam Supplemental Info for Project 1 The cantilever beam has a simple equation of motion. If we assume that the mass is located at the end of the
DIGITAL CASCADE PRESSURE AND POSITION REGULATOR FOR ELECTROHYDRAULIC STEERING SYSTEM 140
 SAT-9.3-1-HP-13 DIGITAL CASCADE PRESSURE AND POSITION REGULATOR FOR ELECTROHYDRAULIC STEERING SYSTEM 140 Alexander Mitov, Jordan Kralev, Ilcho Angelov, Assist.Prof. Alexander Stojanov Mitov, Ph.D., Technical
SAT-9.3-1-HP-13 DIGITAL CASCADE PRESSURE AND POSITION REGULATOR FOR ELECTROHYDRAULIC STEERING SYSTEM 140 Alexander Mitov, Jordan Kralev, Ilcho Angelov, Assist.Prof. Alexander Stojanov Mitov, Ph.D., Technical
Summary. Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic ( ) (1) Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and
 Timothy Dean*, John Quigley, Scott MacDonald, and Colin Readman, WesternGeco. Summary Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic surveys. Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and hydraulic
Timothy Dean*, John Quigley, Scott MacDonald, and Colin Readman, WesternGeco. Summary Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic surveys. Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and hydraulic
Understanding PID Control
 1 of 5 2/20/01 1:15 PM Understanding PID Control Familiar examples show how and why proportional-integral-derivative controllers behave the way they do. Keywords: Process control Control theory Controllers
1 of 5 2/20/01 1:15 PM Understanding PID Control Familiar examples show how and why proportional-integral-derivative controllers behave the way they do. Keywords: Process control Control theory Controllers
Sloshing of Liquid in Partially Filled Container An Experimental Study
 Sloshing of Liquid in Partially Filled Container An Experimental Study P. Pal Department of Civil Engineering, MNNIT Allahabad, India. E-mail: prpal2k@gmail.com Abstract This paper deals with the experimental
Sloshing of Liquid in Partially Filled Container An Experimental Study P. Pal Department of Civil Engineering, MNNIT Allahabad, India. E-mail: prpal2k@gmail.com Abstract This paper deals with the experimental
Box chopper amplifier BOE
 Box chopper amplifier BOE Description The box chopper amplifier is an always energised Pulse-Wide-Modulated (PWM) H-Bridge for to drive inductive loads with bipolar current in according to an analogue
Box chopper amplifier BOE Description The box chopper amplifier is an always energised Pulse-Wide-Modulated (PWM) H-Bridge for to drive inductive loads with bipolar current in according to an analogue
S42 Pump Electrical Displacement Control (EDC)
 MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE Electrical Installation S42 Pump Electrical Displacement Control (EDC) powersolutions.danfoss.com Revision history Table of revisions Date Changed Rev September 2015 Converted
MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE Electrical Installation S42 Pump Electrical Displacement Control (EDC) powersolutions.danfoss.com Revision history Table of revisions Date Changed Rev September 2015 Converted
Uses an off-the shelf motor drive and menu-driven software. Magnet array on moving armature/ piston. Coil array on fixed stator/ cylinder.
 The performance of electromagnetic actuators in motion systems A ServoRam electromagnetic actuator provides:- Extreme positioning accuracy, independent of load or velocity Speeds to 80 metres/second Thrusts
The performance of electromagnetic actuators in motion systems A ServoRam electromagnetic actuator provides:- Extreme positioning accuracy, independent of load or velocity Speeds to 80 metres/second Thrusts
