Lab 1: Testing and Measurement on the r-one
|
|
|
- Florence Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab 1: Testing and Measurement on the r-one Note: This lab is not graded. However, we will discuss the results in class, and think just how embarrassing it will be for me to call on you and you don t have the work complete... 1 Testing your Robot In this section, you will test most of the sensors and actuators on your robot. You will need a partner for some of these activities, and you will both need working robots and GUIs. Setup your robot and download the the r-one GUI: Turn your robot off and plug it into your computer. Turn it on and note the serial port that it connects to using the device manager. Connect to this port with the r-one GUI. 1.1 Encoders Write down the position value (the ticks ) of the left and right encoders. Push the robot forward 10 cm, being sure to keep the wheels from slipping (i.e. make sure the wheels turn). Record the new position values of the left and right encoders. What do the encoder ticks seem to be measuring? What is their resolution (mm/tick)? Encoder values (initial) =, Encoder values (final) =, Quantity measured and resolution =,
2 1.2 Motors Click on the Sync Motors button, the grey circle under the picture of the robot. Select the PWM mode for the motor control. Click on the up buttons to give positive pulse-width modulation (PWM 1 ) to both motors. What is the minimum PWM you need to get the robot to move forward on level ground? Use your tape measure and a stop watch to measure the speed of the robot. Repeat this speed measurement for the maximum PWM. Min PWM and min speed =, Max PWM and max speed =, 1.3 Light Sensors Cover the robot s front-right light sensor with your finger. Record the values from this sensor. Point robot to the ceiling lights and record the maximum value from a light sensor. Light sensor min and max =, 1.4 Bump Sensors Note the values of the bump sensors (middle circle on the GUI) while you move the bump skirt. Can you get a single sensor to activate? Two? Three? How would you compute the direction of the obstacle? Bump Sensor Notes =,, 1.5 IR Obstacle Sensors Observe the display of IR obstacles on the GUI (right circle). Slowly move your hands around the robot. What do all these lines mean? Can you get a single sensor pair to activate? Two? Three? How would you compute the direction of the obstacle? What is the maximum range to detect a wall? IR obstacle notes =,, IR obstacle max range = 1.6 Accelerometer Record the x, y, and z values of the accelerometer while the robot is resting on your desk. Based on these measurements, what are the units of this sensor? In what direction is the z-axis pointed? Accelerometer x, y, z =,, Accelerometer units and z-axis direction =, 1 We will define this term next class. It is the amount of power you are giving to each motor
3 1.7 Gyroscope Watch the values of the gyroscope while you are moving the robot. What does this seem to be measuring? How is it different from gyroscopes we talked about in class. If this question doesn t make any sense, isn t it still a really cool sensor? Thoughtful answer = Cool? = 1.8 IR communications Find a partner. Place your robot around 50cm from each other on a flat surface. Look for their robot to appear on the neighbor map (the left side of the GUI). Use your tape measure to measure the range at which communication becomes unreliable. Note: IR communications uses light, so the transmitter robot needs to be on the same plane as the receiver robot. IR communications max range = 1.9 Radio communications Type a radio message in the textbox by radio. Hit enter at the end of your message and verify your message on another person/team s GUI. Note the range at which radio communication becomes unreliable. This range will be large, you can use floor tiles to measure the range. Radio communications max range = 2 Measuring voltages on the robot 2.1 Multimeter A multimeter is a primary tool of electrical engineers. It is used to take a variety of electrical measurements; such as voltage, current, and resistance. In this lab, we will measure the direct current (DC) voltage of various points on the robot. The smallest voltage on the robot is 0 volts, and the largest is 5 volts. The multimeter can read DC voltage on several different range settings. Since the largest voltage on the robot is 5 volts, we want to set the multimeter s dial to the smallest voltage range that is greater than 5v, which is DCV 20 on your meters. If the multimeter is set to some large voltage, like 600V, the readings from the robot would be so small that it would barely read. In contrast, if the range were set to millivolts, the robot s voltage would exceed the range of this setting. The multimeter has two probes, one black and one red. The black probe is for ground. In electrical engineering, ground is a reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured. To prevent damaging your robot, keep the black probe on the robot s ground and do not touch (short-circuit) the red probe to anything but the indicated test points. Use the accompanying sheet to identify the places on the robot to measure voltage. To connect your multimeter to the robot s ground, put the black probe on TP1, or the small square hole directly to the right of it, inside the white rectangle. The red probe will touch other components of the
4 robot in order to measure the voltage across two points. If you get a negative voltage reading, it means that your test leads are reversed. 2.2 Battery and System Voltage Use the multimeter to see the change in voltage on the main power supply when the robot is powered on. Turn the robot off, place the red probe on the via, and record the multimeter reading: Battery voltage TP3 (off) = System voltage TP2 (off) = Turn on the robot and take another multimeter reading. What voltage does it read now? Battery voltage TP3 (on) = System voltage TP2 (on) = Does this reading make sense? 2.3 Switches Setup the GUI and connect your robot. Verify that you can control motors and read light sensors. Put the red probe on TP5, which is the signal for the red button. Record the voltage when you push the button and when you are not pushing the button: Button voltage TP5 (released) = Button voltage TP5 (pressed) = Why do you think you get these particular voltages? Does it seem reversed? 2.4 Light Sensor The robot has three light sensors. We will measure the front right (FR) sensor. Near the FR light sensor, put your probe on TP12. Record the voltage reading from this sensor and the number from the GUI with the robot just sitting on the desk. Record these same two measurements with the sensor covered, and then with a flashlight pointed at it. Light sensor voltage TP12, GUI value (initial) =, Light sensor voltage TP12, GUI value (covered) =, Light sensor voltage TP12, GUI value (flashlight) =, How does this data differ from the readings of the button? Can you get any voltage you want by moving the flashlight and covering the sensor? 2.5 Motors Record the voltage reading from the two pulse width modulation (PWM) channels for the left motor. Use the GUI to set the PWM for the left motor to the specified values:
5 PWM voltage A, B TP14, TP15 (PWM setting = 0) =, PWM voltage A, B TP14, TP15 (PWM = 50%) =, PWM voltage A, B TP14, TP15 (PWM = 75%) =, PWM voltage A, B TP14, TP15 (PWM = 100%) =, PWM voltage A, B TP14, TP15 (PWM = -50%) =, How are the A and B PWM voltages different? What is the range of the measured voltage? How does the measured voltage compare to the PWM value from the GUI and the system voltage from Section 2.2? 2.6 Encoders Record the voltage reading from the left encoder channels. Use the GUI to set the PWM for the left motor to the specified values: Encoder voltage A, B TP16, TP17 (PWM = 0) =, Encoder voltage A, B TP16, TP17 (PWM = 50%) =, Encoder voltage A, B TP16, TP17 (PWM = 75%) =, Encoder voltage A, B TP16, TP17 (PWM = 100%) =, Encoder voltage A, B TP16, TP17 (PWM = -75%) =, How are the A and B encoder channels different? What is the range of the measured voltage? How does the measured voltage compare to the PWM value and the system voltage? How do these measurements compare to the PWM voltages from above? What were you expecting?
Experiment P55: Light Intensity vs. Position (Light Sensor, Motion Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P55-1 Experiment P55: (Light Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file illuminance 30 m 500/700 P55 Light vs. Position P55_LTVM.SWS
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P55-1 Experiment P55: (Light Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file illuminance 30 m 500/700 P55 Light vs. Position P55_LTVM.SWS
Parts to be supplied by the student: Breadboard and wires IRLZ34N N-channel enhancement-mode power MOSFET transistor
 University of Utah Electrical & Computer Engineering Department ECE 1250 Lab 3 Electronic Speed Control and Pulse Width Modulation A. Stolp, 12/31/12 Rev. Objectives 1 Introduce the Oscilloscope and learn
University of Utah Electrical & Computer Engineering Department ECE 1250 Lab 3 Electronic Speed Control and Pulse Width Modulation A. Stolp, 12/31/12 Rev. Objectives 1 Introduce the Oscilloscope and learn
PHY 112L Activity 2 Electronics Primer
 PHY 112L Activity 2 Electronics Primer Name: Section: ID #: Date: Lab Partners: TA initials: Objectives 1. Introduce the power supply and multimeter commonly used to analyze electric circuits 2. Understand
PHY 112L Activity 2 Electronics Primer Name: Section: ID #: Date: Lab Partners: TA initials: Objectives 1. Introduce the power supply and multimeter commonly used to analyze electric circuits 2. Understand
Robotics using Lego Mindstorms EV3 (Intermediate)
 Robotics using Lego Mindstorms EV3 (Intermediate) Facebook.com/roboticsgateway @roboticsgateway Robotics using EV3 Are we ready to go Roboticists? Does each group have at least one laptop? Do you have
Robotics using Lego Mindstorms EV3 (Intermediate) Facebook.com/roboticsgateway @roboticsgateway Robotics using EV3 Are we ready to go Roboticists? Does each group have at least one laptop? Do you have
Chapter 14. using data wires
 Chapter 14. using data wires In this fifth part of the book, you ll learn how to use data wires (this chapter), Data Operations blocks (Chapter 15), and variables (Chapter 16) to create more advanced programs
Chapter 14. using data wires In this fifth part of the book, you ll learn how to use data wires (this chapter), Data Operations blocks (Chapter 15), and variables (Chapter 16) to create more advanced programs
An Introduction to Programming using the NXT Robot:
 An Introduction to Programming using the NXT Robot: exploring the LEGO MINDSTORMS Common palette. Student Workbook for independent learners and small groups The following tasks have been completed by:
An Introduction to Programming using the NXT Robot: exploring the LEGO MINDSTORMS Common palette. Student Workbook for independent learners and small groups The following tasks have been completed by:
Parts of a Lego RCX Robot
 Parts of a Lego RCX Robot RCX / Brain A B C The red button turns the RCX on and off. The green button starts and stops programs. The grey button switches between 5 programs, indicated as 1-5 on right side
Parts of a Lego RCX Robot RCX / Brain A B C The red button turns the RCX on and off. The green button starts and stops programs. The grey button switches between 5 programs, indicated as 1-5 on right side
Thanks to Autocheck function, it is possible to perform a complete check-up of the robot thanks to a stepby-step
 2.3.23 Autocheck Thanks to Autocheck function, it is possible to perform a complete check-up of the robot thanks to a stepby-step procedure. In order to carry out the procedure, it is important to establish
2.3.23 Autocheck Thanks to Autocheck function, it is possible to perform a complete check-up of the robot thanks to a stepby-step procedure. In order to carry out the procedure, it is important to establish
Some prior experience with building programs in Scratch is assumed. You can find some introductory materials here:
 Robotics 1b Building an mbot Program Some prior experience with building programs in Scratch is assumed. You can find some introductory materials here: http://www.mblock.cc/edu/ The mbot Blocks The mbot
Robotics 1b Building an mbot Program Some prior experience with building programs in Scratch is assumed. You can find some introductory materials here: http://www.mblock.cc/edu/ The mbot Blocks The mbot
Experiment 4.B. Position Control. ECEN 2270 Electronics Design Laboratory 1
 Experiment 4.B Position Control Electronics Design Laboratory 1 Procedures 4.B.1 4.B.2 4.B.3 4.B.4 Read Encoder with Arduino Position Control by Counting Encoder Pulses Demo Setup Extra Credit Electronics
Experiment 4.B Position Control Electronics Design Laboratory 1 Procedures 4.B.1 4.B.2 4.B.3 4.B.4 Read Encoder with Arduino Position Control by Counting Encoder Pulses Demo Setup Extra Credit Electronics
Overview of Teaching Motion using MEMS Accelerometers
 Overview of Teaching Motion using MEMS Accelerometers Introduction to the RET MEMS Research Project I participated in a Research Experience for Teachers (RET) program sponsored by UC Santa Barbara and
Overview of Teaching Motion using MEMS Accelerometers Introduction to the RET MEMS Research Project I participated in a Research Experience for Teachers (RET) program sponsored by UC Santa Barbara and
The light sensor, rotation sensor, and motors may all be monitored using the view function on the RCX.
 Review the following material on sensors. Discuss how you might use each of these sensors. When you have completed reading through this material, build a robot of your choosing that has 2 motors (connected
Review the following material on sensors. Discuss how you might use each of these sensors. When you have completed reading through this material, build a robot of your choosing that has 2 motors (connected
Electrical Measurements
 Electrical Measurements INTRODUCTION In this section, electrical measurements will be discussed. This will be done by using simple experiments that introduce a DC power supply, a multimeter, and a simplified
Electrical Measurements INTRODUCTION In this section, electrical measurements will be discussed. This will be done by using simple experiments that introduce a DC power supply, a multimeter, and a simplified
Your EdVenture into Robotics 10 Lesson plans
 Your EdVenture into Robotics 10 Lesson plans Activity sheets and Worksheets Find Edison Robot @ Search: Edison Robot Call 800.962.4463 or email custserv@ Lesson 1 Worksheet 1.1 Meet Edison Edison is a
Your EdVenture into Robotics 10 Lesson plans Activity sheets and Worksheets Find Edison Robot @ Search: Edison Robot Call 800.962.4463 or email custserv@ Lesson 1 Worksheet 1.1 Meet Edison Edison is a
Module 1, Lesson 2 Introduction to electricity. Student. 45 minutes
 Module 1, Lesson 2 Introduction to electricity 45 minutes Student Purpose of this lesson Explanations of fundamental quantities of electrical circuits, including voltage, current and resistance. Use a
Module 1, Lesson 2 Introduction to electricity 45 minutes Student Purpose of this lesson Explanations of fundamental quantities of electrical circuits, including voltage, current and resistance. Use a
Medidores de vibración salida RS232 Datalogger VT-8204 LUTRON manual ingles
 English usermanual VT-8204 Vibration Tachometer Your purchase of this VIBRATION TACHOMETER marks a step forward for you into the field of precision measurement. Although this VIBRATION TACHOMETER is a
English usermanual VT-8204 Vibration Tachometer Your purchase of this VIBRATION TACHOMETER marks a step forward for you into the field of precision measurement. Although this VIBRATION TACHOMETER is a
PHYSICS 220 LAB #1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION
 /53 pts Name: Partners: PHYSICS 22 LAB #1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES 1. To learn about three complementary ways to describe motion in one dimension words, graphs, and vector diagrams. 2. To acquire
/53 pts Name: Partners: PHYSICS 22 LAB #1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES 1. To learn about three complementary ways to describe motion in one dimension words, graphs, and vector diagrams. 2. To acquire
PocketLab Weather Getting Started Guide
 Display and Record Sensor Data 1. To record data, press the Record button on the graph screen. The current data will clear and the app will record new sensor data. 2. To stop the data recording, press
Display and Record Sensor Data 1. To record data, press the Record button on the graph screen. The current data will clear and the app will record new sensor data. 2. To stop the data recording, press
Experiment P01: Understanding Motion I Distance and Time (Motion Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P01-1 Experiment P01: Understanding Motion I Distance and Time (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file linear motion 30 m 500 or 700 P01
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P01-1 Experiment P01: Understanding Motion I Distance and Time (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file linear motion 30 m 500 or 700 P01
Programming Design. ROBOTC Software
 Programming Design ROBOTC Software Behavior-Based Programming A behavior is anything your robot does Turning on a single motor or servo Three main types of behaviors 1. Complex behaviors Robot performs
Programming Design ROBOTC Software Behavior-Based Programming A behavior is anything your robot does Turning on a single motor or servo Three main types of behaviors 1. Complex behaviors Robot performs
Lab Exercise 9: Stepper and Servo Motors
 ME 3200 Mechatronics Laboratory Lab Exercise 9: Stepper and Servo Motors Introduction In this laboratory exercise, you will explore some of the properties of stepper and servomotors. These actuators are
ME 3200 Mechatronics Laboratory Lab Exercise 9: Stepper and Servo Motors Introduction In this laboratory exercise, you will explore some of the properties of stepper and servomotors. These actuators are
Lab 3 DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW
 43 Name Date Partners Lab 3 DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS + - VOLTS OBJECTIVES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in a circuit. To understand
43 Name Date Partners Lab 3 DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS + - VOLTS OBJECTIVES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in a circuit. To understand
I.1 Smart Machines. Unit Overview:
 I Smart Machines I.1 Smart Machines Unit Overview: This unit introduces students to Sensors and Programming with VEX IQ. VEX IQ Sensors allow for autonomous and hybrid control of VEX IQ robots and other
I Smart Machines I.1 Smart Machines Unit Overview: This unit introduces students to Sensors and Programming with VEX IQ. VEX IQ Sensors allow for autonomous and hybrid control of VEX IQ robots and other
Lab book. Exploring Robotics (CORC3303)
 Lab book Exploring Robotics (CORC3303) Dept of Computer and Information Science Brooklyn College of the City University of New York updated: Fall 2011 / Professor Elizabeth Sklar UNIT A Lab, part 1 : Robot
Lab book Exploring Robotics (CORC3303) Dept of Computer and Information Science Brooklyn College of the City University of New York updated: Fall 2011 / Professor Elizabeth Sklar UNIT A Lab, part 1 : Robot
C - Underground Exploration
 C - Underground Exploration You've discovered an underground system of tunnels under the planet surface, but they are too dangerous to explore! Let's get our robot to explore instead. 2017 courses.techcamp.org.uk/
C - Underground Exploration You've discovered an underground system of tunnels under the planet surface, but they are too dangerous to explore! Let's get our robot to explore instead. 2017 courses.techcamp.org.uk/
Studuino Icon Programming Environment Guide
 Studuino Icon Programming Environment Guide Ver 0.9.6 4/17/2014 This manual introduces the Studuino Software environment. As the Studuino programming environment develops, these instructions may be edited
Studuino Icon Programming Environment Guide Ver 0.9.6 4/17/2014 This manual introduces the Studuino Software environment. As the Studuino programming environment develops, these instructions may be edited
Lab 4 Ohm s Law and Resistors
 ` Lab 4 Ohm s Law and Resistors What You Need To Know: The Physics One of the things that students have a difficult time with when they first learn about circuits is the electronics lingo. The lingo and
` Lab 4 Ohm s Law and Resistors What You Need To Know: The Physics One of the things that students have a difficult time with when they first learn about circuits is the electronics lingo. The lingo and
1. Mechanical Arms Hardware
 TC.0.1 Analysis 1. Mechanical Arms Hardware TP 8.1: ATLAS apparatus must be able to simulate touch actions on a touchscreen MFD. TP 8.2: ATLAS apparatus must be able to simulate drag and drop actions on
TC.0.1 Analysis 1. Mechanical Arms Hardware TP 8.1: ATLAS apparatus must be able to simulate touch actions on a touchscreen MFD. TP 8.2: ATLAS apparatus must be able to simulate drag and drop actions on
LAB 2 Circuit Tools and Voltage Waveforms
 LAB 2 Circuit Tools and Voltage Waveforms OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with a DC power supply and setting the output voltage. 2. Learn how to measure voltages & currents using a Digital Multimeter. 3.
LAB 2 Circuit Tools and Voltage Waveforms OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with a DC power supply and setting the output voltage. 2. Learn how to measure voltages & currents using a Digital Multimeter. 3.
EE 308 Lab Spring 2009
 9S12 Subsystems: Pulse Width Modulation, A/D Converter, and Synchronous Serial Interface In this sequence of three labs you will learn to use three of the MC9S12's hardware subsystems. WEEK 1 Pulse Width
9S12 Subsystems: Pulse Width Modulation, A/D Converter, and Synchronous Serial Interface In this sequence of three labs you will learn to use three of the MC9S12's hardware subsystems. WEEK 1 Pulse Width
Lab 8: Introduction to the e-puck Robot
 Lab 8: Introduction to the e-puck Robot This laboratory requires the following equipment: C development tools (gcc, make, etc.) C30 programming tools for the e-puck robot The development tree which is
Lab 8: Introduction to the e-puck Robot This laboratory requires the following equipment: C development tools (gcc, make, etc.) C30 programming tools for the e-puck robot The development tree which is
Experiment P02: Understanding Motion II Velocity and Time (Motion Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P02-1 Experiment P02: Understanding Motion II Velocity and Time (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file linear motion 30 m 500 or 700
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P02-1 Experiment P02: Understanding Motion II Velocity and Time (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file linear motion 30 m 500 or 700
RC Altimeter #2 BASIC Altitude data recording and monitoring system 3/8/2009 Page 2 of 11
 Introduction... 3 How it works... 3 Key features... 3 System requirements... 3 Hardware... 4 Specifications... 4 Using the RC Altimeter #2 BASIC module... 5 Powering the module... 5 Mounting the module...
Introduction... 3 How it works... 3 Key features... 3 System requirements... 3 Hardware... 4 Specifications... 4 Using the RC Altimeter #2 BASIC module... 5 Powering the module... 5 Mounting the module...
e d u c a t i o n Detect Dark Line Objectives Connect Teacher s Notes
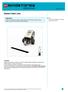 e d u c a t i o n Objectives Learn how to make the robot interact with the environment: Detect a line drawn on the floor by means of its luminosity. Hint You will need a flashlight or other light source
e d u c a t i o n Objectives Learn how to make the robot interact with the environment: Detect a line drawn on the floor by means of its luminosity. Hint You will need a flashlight or other light source
Teacher s Guide - Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor)
 Teacher s Guide - Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Circuits P51 LR Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity)
Teacher s Guide - Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Circuits P51 LR Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity)
INTRODUCTION TO DATA STUDIO
 1 INTRODUCTION TO DATA STUDIO PART I: FAMILIARIZATION OBJECTIVE To become familiar with the operation of the Passport/Xplorer digital instruments and the DataStudio software. INTRODUCTION We will use the
1 INTRODUCTION TO DATA STUDIO PART I: FAMILIARIZATION OBJECTIVE To become familiar with the operation of the Passport/Xplorer digital instruments and the DataStudio software. INTRODUCTION We will use the
EE 308 Spring S12 SUBSYSTEMS: PULSE WIDTH MODULATION, A/D CONVERTER, AND SYNCHRONOUS SERIAN INTERFACE
 9S12 SUBSYSTEMS: PULSE WIDTH MODULATION, A/D CONVERTER, AND SYNCHRONOUS SERIAN INTERFACE In this sequence of three labs you will learn to use the 9S12 S hardware sybsystem. WEEK 1 PULSE WIDTH MODULATION
9S12 SUBSYSTEMS: PULSE WIDTH MODULATION, A/D CONVERTER, AND SYNCHRONOUS SERIAN INTERFACE In this sequence of three labs you will learn to use the 9S12 S hardware sybsystem. WEEK 1 PULSE WIDTH MODULATION
Height Limited Switch
 Height Limited Switch Manual version: 1.0 Content Introduction...3 How it works...3 Key features...3 Hardware...4 Motor cut-off settings...4 Specification...4 Using the RC HLS #1 module...5 Powering the
Height Limited Switch Manual version: 1.0 Content Introduction...3 How it works...3 Key features...3 Hardware...4 Motor cut-off settings...4 Specification...4 Using the RC HLS #1 module...5 Powering the
MULTIMETER TRAINING UNIT QUICKSTART GUIDE
 MULTIMETER TRAINING UNIT QUICKSTART GUIDE MULTIMETER TRAINING UNIT 1 MULTIMETER TRAINING UNIT CONTENTS General Information... 2 Battery... 3 Voltage Drop... 4 Alternator... 5 Frequency... 6 Millivolts...
MULTIMETER TRAINING UNIT QUICKSTART GUIDE MULTIMETER TRAINING UNIT 1 MULTIMETER TRAINING UNIT CONTENTS General Information... 2 Battery... 3 Voltage Drop... 4 Alternator... 5 Frequency... 6 Millivolts...
A servo is an electric motor that takes in a pulse width modulated signal that controls direction and speed. A servo has three leads:
 Project 4: Arduino Servos Part 1 Description: A servo is an electric motor that takes in a pulse width modulated signal that controls direction and speed. A servo has three leads: a. Red: Current b. Black:
Project 4: Arduino Servos Part 1 Description: A servo is an electric motor that takes in a pulse width modulated signal that controls direction and speed. A servo has three leads: a. Red: Current b. Black:
HANDS-ON ACTIVITY 4 BUILDING SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS BACKGROUND WIRING DIRECTIONS
 ACTIVITY 4 BUILDING SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS BACKGROUND Make sure you read the background in Activity 3 before doing this activity. WIRING DIRECTIONS Materials per group of two: one or two D-cells
ACTIVITY 4 BUILDING SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS BACKGROUND Make sure you read the background in Activity 3 before doing this activity. WIRING DIRECTIONS Materials per group of two: one or two D-cells
Grade Level: High School 9 th 12 th grades Lesson: Electromagnets: Winding Things Up! Type of Lesson: Inquiry Lab Activity. Length of Lesson: 45 min.
 Subject: College Prep/Conceptual Physics Grade Level: High School 9 th 12 th grades Lesson: Electromagnets: Winding Things Up! Type of Lesson: Inquiry Lab Activity Teacher: Michelle Boggs Length of Lesson:
Subject: College Prep/Conceptual Physics Grade Level: High School 9 th 12 th grades Lesson: Electromagnets: Winding Things Up! Type of Lesson: Inquiry Lab Activity Teacher: Michelle Boggs Length of Lesson:
CURIE Academy, Summer 2014 Lab 2: Computer Engineering Software Perspective Sign-Off Sheet
 Lab : Computer Engineering Software Perspective Sign-Off Sheet NAME: NAME: DATE: Sign-Off Milestone TA Initials Part 1.A Part 1.B Part.A Part.B Part.C Part 3.A Part 3.B Part 3.C Test Simple Addition Program
Lab : Computer Engineering Software Perspective Sign-Off Sheet NAME: NAME: DATE: Sign-Off Milestone TA Initials Part 1.A Part 1.B Part.A Part.B Part.C Part 3.A Part 3.B Part 3.C Test Simple Addition Program
understanding sensors
 The LEGO MINDSTORMS EV3 set includes three types of sensors: Touch, Color, and Infrared. You can use these sensors to make your robot respond to its environment. For example, you can program your robot
The LEGO MINDSTORMS EV3 set includes three types of sensors: Touch, Color, and Infrared. You can use these sensors to make your robot respond to its environment. For example, you can program your robot
DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW
 July 15, 2008 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law 1 Name Date Partners DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action
July 15, 2008 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law 1 Name Date Partners DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action
Fall Lab2_ET150.docx
 Required Parts, Software and Equipment Parts EET 150 Dc and c Voltage Measurements Component /Value Quantity 4 cell battery holder 1 2 cell battery holder 2 batteries 8 Computer/Monitor c line Cord 1 Step-down
Required Parts, Software and Equipment Parts EET 150 Dc and c Voltage Measurements Component /Value Quantity 4 cell battery holder 1 2 cell battery holder 2 batteries 8 Computer/Monitor c line Cord 1 Step-down
Physics 4B, Lab # 2 Circuit Tools and Voltage Waveforms
 Physics 4B, Lab # 2 Circuit Tools and Voltage Waveforms OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with a DC power supply and setting the output voltage. 2. Learn how to measure voltages & currents using a Digital
Physics 4B, Lab # 2 Circuit Tools and Voltage Waveforms OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with a DC power supply and setting the output voltage. 2. Learn how to measure voltages & currents using a Digital
Master Op-Doc/Test Plan
 Power Supply Master Op-Doc/Test Plan Define Engineering Specs Establish battery life Establish battery technology Establish battery size Establish number of batteries Establish weight of batteries Establish
Power Supply Master Op-Doc/Test Plan Define Engineering Specs Establish battery life Establish battery technology Establish battery size Establish number of batteries Establish weight of batteries Establish
STRUCTURE SENSOR QUICK START GUIDE
 STRUCTURE SENSOR 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS WELCOME TO YOUR NEW STRUCTURE SENSOR 2 WHAT S INCLUDED IN THE BOX 2 CHARGING YOUR STRUCTURE SENSOR 3 CONNECTING YOUR STRUCTURE SENSOR TO YOUR IPAD 4 Attaching Structure
STRUCTURE SENSOR 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS WELCOME TO YOUR NEW STRUCTURE SENSOR 2 WHAT S INCLUDED IN THE BOX 2 CHARGING YOUR STRUCTURE SENSOR 3 CONNECTING YOUR STRUCTURE SENSOR TO YOUR IPAD 4 Attaching Structure
Chabot College Physics Lab Ohm s Law & Simple Circuits Scott Hildreth
 Chabot College Physics Lab Ohm s Law & Simple Circuits Scott Hildreth Goals: Learn how to make simple circuits, measuring resistances, currents, and voltages across components. Become more comfortable
Chabot College Physics Lab Ohm s Law & Simple Circuits Scott Hildreth Goals: Learn how to make simple circuits, measuring resistances, currents, and voltages across components. Become more comfortable
+ A Supply B. C Load D
 17 E7 E7.1 OHM'S LAW AND RESISTANCE NETWORKS OBJECT The objects of this experiment are to determine the voltage-current relationship for a resistor and to verify the series and parallel resistance formulae.
17 E7 E7.1 OHM'S LAW AND RESISTANCE NETWORKS OBJECT The objects of this experiment are to determine the voltage-current relationship for a resistor and to verify the series and parallel resistance formulae.
Wireless Occupancy Sensor User Guide
 Wireless Occupancy Sensor Wireless Occupancy Sensor User Guide This Manual covers both the Wide angle and the Narrow long range occupancy sensor. Dialight Part Numbers described here-in are: WOSU22BG2
Wireless Occupancy Sensor Wireless Occupancy Sensor User Guide This Manual covers both the Wide angle and the Narrow long range occupancy sensor. Dialight Part Numbers described here-in are: WOSU22BG2
Lab 5: Real DC Circuits
 Physics 2020, Fall 2010 Lab 5 page 1 of 7 Circle your lab day and time. Your name: Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri TA name: 8-10 10-12 12-2 2-4 4-6 INTRODUCTION Lab 5: Real DC Circuits The field of electronics has
Physics 2020, Fall 2010 Lab 5 page 1 of 7 Circle your lab day and time. Your name: Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri TA name: 8-10 10-12 12-2 2-4 4-6 INTRODUCTION Lab 5: Real DC Circuits The field of electronics has
Experiment 3. Ohm s Law. Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current.
 Experiment 3 Ohm s Law 3.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 3 Ohm s Law 3.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 2. Ohm s Law. Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current.
 Experiment 2 Ohm s Law 2.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 2 Ohm s Law 2.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Deriving Consistency from LEGOs
 Deriving Consistency from LEGOs What we have learned in 6 years of FLL and 7 years of Lego Robotics by Austin and Travis Schuh 1 2006 Austin and Travis Schuh, all rights reserved Objectives Basic Building
Deriving Consistency from LEGOs What we have learned in 6 years of FLL and 7 years of Lego Robotics by Austin and Travis Schuh 1 2006 Austin and Travis Schuh, all rights reserved Objectives Basic Building
Scorpion Antennas Controller. Instruction Manual. Firmware V11.8 November Please Read This Manual Completely Before Operating The Controller
 Firmware V11.8 November 2012 Please Read This Manual Completely Before Operating The Controller Contents Introduction:... 3 Installation:... 3 Using the Scorpion Antennas Controller... 5 Tuning Your Dipole...
Firmware V11.8 November 2012 Please Read This Manual Completely Before Operating The Controller Contents Introduction:... 3 Installation:... 3 Using the Scorpion Antennas Controller... 5 Tuning Your Dipole...
SOP for Micro Mechanical Analyzer
 Page 1 of 7 SOP for Micro Mechanical Analyzer Note: This document is frequently updated; if you feel that information should be added, please indicate that to the facility manager (Currently Philip Carubia;
Page 1 of 7 SOP for Micro Mechanical Analyzer Note: This document is frequently updated; if you feel that information should be added, please indicate that to the facility manager (Currently Philip Carubia;
Lab 06: Ohm s Law and Servo Motor Control
 CS281: Computer Systems Lab 06: Ohm s Law and Servo Motor Control The main purpose of this lab is to build a servo motor control circuit. As with prior labs, there will be some exploratory sections designed
CS281: Computer Systems Lab 06: Ohm s Law and Servo Motor Control The main purpose of this lab is to build a servo motor control circuit. As with prior labs, there will be some exploratory sections designed
PRESENTED BY HUMANOID IIT KANPUR
 SENSORS & ACTUATORS Robotics Club (Science and Technology Council, IITK) PRESENTED BY HUMANOID IIT KANPUR October 11th, 2017 WHAT ARE WE GOING TO LEARN!! COMPARISON between Transducers Sensors And Actuators.
SENSORS & ACTUATORS Robotics Club (Science and Technology Council, IITK) PRESENTED BY HUMANOID IIT KANPUR October 11th, 2017 WHAT ARE WE GOING TO LEARN!! COMPARISON between Transducers Sensors And Actuators.
Experiment P36: Resonance Modes and the Speed of Sound (Voltage Sensor, Power Amplifier)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P36-1 Experiment P36: Resonance Modes and the Speed of Sound (Voltage Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File waves 45
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P36-1 Experiment P36: Resonance Modes and the Speed of Sound (Voltage Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File waves 45
1. Controlling the DC Motors
 E11: Autonomous Vehicles Lab 5: Motors and Sensors By this point, you should have an assembled robot and Mudduino to power it. Let s get things moving! In this lab, you will write code to test your motors
E11: Autonomous Vehicles Lab 5: Motors and Sensors By this point, you should have an assembled robot and Mudduino to power it. Let s get things moving! In this lab, you will write code to test your motors
Lab #1: Electrical Measurements I Resistance
 Lab #: Electrical Measurements I esistance Goal: Learn to measure basic electrical quantities; study the effect of measurement apparatus on the quantities being measured by investigating the internal resistances
Lab #: Electrical Measurements I esistance Goal: Learn to measure basic electrical quantities; study the effect of measurement apparatus on the quantities being measured by investigating the internal resistances
How to draw the CB South Kerf Bent Clock:
 How to draw the CB South Kerf Bent Clock: Open sketch up, use the Product Design and Woodworking template with Inches as the units. If there is a person in the drawing space, you can delete him/her. When
How to draw the CB South Kerf Bent Clock: Open sketch up, use the Product Design and Woodworking template with Inches as the units. If there is a person in the drawing space, you can delete him/her. When
Quantizer step: volts Input Voltage [V]
![Quantizer step: volts Input Voltage [V] Quantizer step: volts Input Voltage [V]](/thumbs/96/126541381.jpg) EE 101 Fall 2008 Date: Lab Section # Lab #8 Name: A/D Converter and ECEbot Power Abstract Partner: Autonomous robots need to have a means to sense the world around them. For example, the bumper switches
EE 101 Fall 2008 Date: Lab Section # Lab #8 Name: A/D Converter and ECEbot Power Abstract Partner: Autonomous robots need to have a means to sense the world around them. For example, the bumper switches
Test Procedure for Nanometric Discriminator Cards for Wire Chambers. James Clarke
 Test Procedure for Nanometric Discriminator Cards for Wire Chambers James Clarke November 26, 2013 To test a discriminator card, first ensure you have the proper equipment. For our setup, we had three
Test Procedure for Nanometric Discriminator Cards for Wire Chambers James Clarke November 26, 2013 To test a discriminator card, first ensure you have the proper equipment. For our setup, we had three
instead we hook it up to a potential difference of 60 V? instead we hook it up to a potential difference of 240 V?
 Introduction In this lab we will examine the concepts of electric current and potential in a circuit. We first look at devices (like batteries) that are used to generate electrical energy that we can use
Introduction In this lab we will examine the concepts of electric current and potential in a circuit. We first look at devices (like batteries) that are used to generate electrical energy that we can use
A Day in the Life CTE Enrichment Grades 3-5 mblock Robotics - Simple Programs
 Activity 1 - Play Music A Day in the Life CTE Enrichment Grades 3-5 mblock Robotics - Simple Programs Computer Science Unit One of the simplest things that we can do, to make something cool with our robot,
Activity 1 - Play Music A Day in the Life CTE Enrichment Grades 3-5 mblock Robotics - Simple Programs Computer Science Unit One of the simplest things that we can do, to make something cool with our robot,
Current, resistance, and Ohm s law
 Current, resistance, and Ohm s law Apparatus DC voltage source set of alligator clips 2 pairs of red and black banana clips 3 round bulb 2 bulb sockets 2 battery holders or 1 two-battery holder 2 1.5V
Current, resistance, and Ohm s law Apparatus DC voltage source set of alligator clips 2 pairs of red and black banana clips 3 round bulb 2 bulb sockets 2 battery holders or 1 two-battery holder 2 1.5V
Mechatronics Laboratory Assignment 3 Introduction to I/O with the F28335 Motor Control Processor
 Mechatronics Laboratory Assignment 3 Introduction to I/O with the F28335 Motor Control Processor Recommended Due Date: By your lab time the week of February 12 th Possible Points: If checked off before
Mechatronics Laboratory Assignment 3 Introduction to I/O with the F28335 Motor Control Processor Recommended Due Date: By your lab time the week of February 12 th Possible Points: If checked off before
Two Hour Robot. Lets build a Robot.
 Lets build a Robot. Our robot will use an ultrasonic sensor and servos to navigate it s way around a maze. We will be making 2 voltage circuits : A 5 Volt for our ultrasonic sensor, sound and lights powered
Lets build a Robot. Our robot will use an ultrasonic sensor and servos to navigate it s way around a maze. We will be making 2 voltage circuits : A 5 Volt for our ultrasonic sensor, sound and lights powered
Laboratory Project 1a: Power-Indicator LED's
 2240 Laboratory Project 1a: Power-Indicator LED's Abstract-You will construct and test two LED power-indicator circuits for your breadboard in preparation for building the Electromyogram circuit in Lab
2240 Laboratory Project 1a: Power-Indicator LED's Abstract-You will construct and test two LED power-indicator circuits for your breadboard in preparation for building the Electromyogram circuit in Lab
Mechatronics Engineering and Automation Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University MCT-151, Spring 2015 Lab-4: Electric Actuators
 Mechatronics Engineering and Automation Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University MCT-151, Spring 2015 Lab-4: Electric Actuators Ahmed Okasha, Assistant Lecturer okasha1st@gmail.com Objective Have a
Mechatronics Engineering and Automation Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University MCT-151, Spring 2015 Lab-4: Electric Actuators Ahmed Okasha, Assistant Lecturer okasha1st@gmail.com Objective Have a
Never power this piano with anything other than a standard 9V battery!
 Welcome to the exciting world of Digital Electronics! Who is this kit intended for? This kit is intended for anyone from ages 13 and above and assumes no previous knowledge in the field of hobby electronics.
Welcome to the exciting world of Digital Electronics! Who is this kit intended for? This kit is intended for anyone from ages 13 and above and assumes no previous knowledge in the field of hobby electronics.
Resistance Apparatus EM-8812
 Instruction Manual with Experiment Guide and Teachers Notes 012-09573A Resistance Apparatus EM-8812 Resistance Apparatus Table of Contents Contents Introduction...........................................................
Instruction Manual with Experiment Guide and Teachers Notes 012-09573A Resistance Apparatus EM-8812 Resistance Apparatus Table of Contents Contents Introduction...........................................................
Lab 1: Electric Potential and Electric Field
 2 Lab 1: Electric Potential and Electric Field I. Before you come to lab... A. Read the following chapters from the text (Giancoli): 1. Chapter 21, sections 3, 6, 8, 9 2. Chapter 23, sections 1, 2, 5,
2 Lab 1: Electric Potential and Electric Field I. Before you come to lab... A. Read the following chapters from the text (Giancoli): 1. Chapter 21, sections 3, 6, 8, 9 2. Chapter 23, sections 1, 2, 5,
Introduction to the EXPANSION HUB
 Introduction to the EXPANSION HUB REV ROBOTICS - EXPANSION HUB revrobotics.com ANOTHER CONTROLLER CHOICE MODERN ROBOTICS REV ROBOTICS The Expansion hub does not replace the Modern Robotics System. It is
Introduction to the EXPANSION HUB REV ROBOTICS - EXPANSION HUB revrobotics.com ANOTHER CONTROLLER CHOICE MODERN ROBOTICS REV ROBOTICS The Expansion hub does not replace the Modern Robotics System. It is
A - Debris on the Track
 A - Debris on the Track Rocks have fallen onto the line for the robot to follow, blocking its path. We need to make the program clever enough to not get stuck! 2017 https://www.hamiltonbuhl.com/teacher-resources
A - Debris on the Track Rocks have fallen onto the line for the robot to follow, blocking its path. We need to make the program clever enough to not get stuck! 2017 https://www.hamiltonbuhl.com/teacher-resources
A - Debris on the Track
 A - Debris on the Track Rocks have fallen onto the line for the robot to follow, blocking its path. We need to make the program clever enough to not get stuck! 2018 courses.techcamp.org.uk/ Page 1 of 7
A - Debris on the Track Rocks have fallen onto the line for the robot to follow, blocking its path. We need to make the program clever enough to not get stuck! 2018 courses.techcamp.org.uk/ Page 1 of 7
Two Dimensional Motion Activity (Projectile Motion)
 Two Dimensional Motion Activity (Projectile Motion) Purpose A projectile launched into the air either horizontally or at an angle represents Two Dimensional Motion. Using a launcher and two photogates,
Two Dimensional Motion Activity (Projectile Motion) Purpose A projectile launched into the air either horizontally or at an angle represents Two Dimensional Motion. Using a launcher and two photogates,
Revision for Grade 7 in Unit #1&3
 Your Name:.... Grade 7 / SEION 1 Matching :Match the terms with its explanations. Write the matching letter in the correct box. he first one has been done for you. (1 mark each) erm Explanation 1. electrical
Your Name:.... Grade 7 / SEION 1 Matching :Match the terms with its explanations. Write the matching letter in the correct box. he first one has been done for you. (1 mark each) erm Explanation 1. electrical
Experiment 9: Electrical Measurements
 xperiment 9: lectrical Measurements 1. Obtain 3 batteries with holders, 2 identical flashlight bulbs with holders, leads (wires) with alligator clips, and a multimeter. 2. Using the Multimeter a. There
xperiment 9: lectrical Measurements 1. Obtain 3 batteries with holders, 2 identical flashlight bulbs with holders, leads (wires) with alligator clips, and a multimeter. 2. Using the Multimeter a. There
LAB 1 AN EXAMPLE MECHATRONIC SYSTEM: THE FURBY
 LAB 1 AN EXAMPLE MECHATRONIC SYSTEM: THE FURBY Objectives Preparation Tools To see the inner workings of a commercial mechatronic system and to construct a simple manual motor speed controller and current
LAB 1 AN EXAMPLE MECHATRONIC SYSTEM: THE FURBY Objectives Preparation Tools To see the inner workings of a commercial mechatronic system and to construct a simple manual motor speed controller and current
A - Debris on the Track
 A - Debris on the Track Rocks have fallen onto the line for the robot to follow, blocking its path. We need to make the program clever enough to not get stuck! Step 1 2017 courses.techcamp.org.uk/ Page
A - Debris on the Track Rocks have fallen onto the line for the robot to follow, blocking its path. We need to make the program clever enough to not get stuck! Step 1 2017 courses.techcamp.org.uk/ Page
Western Kansas Lego Robotics Competition April 16, 2018 Fort Hays State University
 Western Kansas Lego Robotics Competition April 16, 2018 Fort Hays State University WELCOME FHSU is hosting our 12 th annual Lego robotics competition. The competition is open to all area middle school
Western Kansas Lego Robotics Competition April 16, 2018 Fort Hays State University WELCOME FHSU is hosting our 12 th annual Lego robotics competition. The competition is open to all area middle school
FLL Coaches Clinic Chassis and Attachments. Patrick R. Michaud
 FLL Coaches Clinic Chassis and Attachments Patrick R. Michaud pmichaud@pobox.com Erik Jonsson School of Engineering and Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas September 23, 2017 Presentation Outline
FLL Coaches Clinic Chassis and Attachments Patrick R. Michaud pmichaud@pobox.com Erik Jonsson School of Engineering and Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas September 23, 2017 Presentation Outline
Agent-based/Robotics Programming Lab II
 cis3.5, spring 2009, lab IV.3 / prof sklar. Agent-based/Robotics Programming Lab II For this lab, you will need a LEGO robot kit, a USB communications tower and a LEGO light sensor. 1 start up RoboLab
cis3.5, spring 2009, lab IV.3 / prof sklar. Agent-based/Robotics Programming Lab II For this lab, you will need a LEGO robot kit, a USB communications tower and a LEGO light sensor. 1 start up RoboLab
Micro Wizard Instructions
 How to install your Fast Track flashing light display timer model K1 with optional remote start switch (If you have ordered the Quick Mount or have a Best Track, disregard this section and refer to the
How to install your Fast Track flashing light display timer model K1 with optional remote start switch (If you have ordered the Quick Mount or have a Best Track, disregard this section and refer to the
due Thursday 10/14 at 11pm (Part 1 appears in a separate document. Both parts have the same submission deadline.)
 CS2 Fall 200 Project 3 Part 2 due Thursday 0/4 at pm (Part appears in a separate document. Both parts have the same submission deadline.) You must work either on your own or with one partner. You may discuss
CS2 Fall 200 Project 3 Part 2 due Thursday 0/4 at pm (Part appears in a separate document. Both parts have the same submission deadline.) You must work either on your own or with one partner. You may discuss
OZOBOT BASIC TRAINING LESSON 1 WHAT IS OZOBOT?
 OZOBOT BASIC TRAINING LESSON 1 WHAT IS OZOBOT? What students will learn What kind of a robot is Ozobot? How does Ozobot sense its environment and move in it? How can you give commands to Ozobot? Topics
OZOBOT BASIC TRAINING LESSON 1 WHAT IS OZOBOT? What students will learn What kind of a robot is Ozobot? How does Ozobot sense its environment and move in it? How can you give commands to Ozobot? Topics
Course materials and schedule are at. positron.hep.upenn.edu/p364
 Physics 364, Fall 2014, Lab #1 Name: (using breadboards; measuring voltage, current, and resistance) Wednesday, August 27 (section 401); Thursday, August 28 (section 402) Course materials and schedule
Physics 364, Fall 2014, Lab #1 Name: (using breadboards; measuring voltage, current, and resistance) Wednesday, August 27 (section 401); Thursday, August 28 (section 402) Course materials and schedule
Activity 2: Opto Receiver
 Activity 2: Opto Receiver Time Required: 45 minutes Materials List Group Size: 2 Each pair needs: One each of: One Activity 2 bag containing: o Two 10 μf Electrolytic Capacitors o 47 μf Electrolytic Capacitor
Activity 2: Opto Receiver Time Required: 45 minutes Materials List Group Size: 2 Each pair needs: One each of: One Activity 2 bag containing: o Two 10 μf Electrolytic Capacitors o 47 μf Electrolytic Capacitor
Sten-Bot Robot Kit Stensat Group LLC, Copyright 2013
 Sten-Bot Robot Kit Stensat Group LLC, Copyright 2013 Legal Stuff Stensat Group LLC assumes no responsibility and/or liability for the use of the kit and documentation. There is a 90 day warranty for the
Sten-Bot Robot Kit Stensat Group LLC, Copyright 2013 Legal Stuff Stensat Group LLC assumes no responsibility and/or liability for the use of the kit and documentation. There is a 90 day warranty for the
Built-in soft-start feature. Up-Slope and Down-Slope. Power-Up safe start feature. Motor will only start if pulse of 1.5ms is detected.
 Thank You for purchasing our TRI-Mode programmable DC Motor Controller. Our DC Motor Controller is the most flexible controller you will find. It is user-programmable and covers most applications. This
Thank You for purchasing our TRI-Mode programmable DC Motor Controller. Our DC Motor Controller is the most flexible controller you will find. It is user-programmable and covers most applications. This
ENGR 1110: Introduction to Engineering Lab 7 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
 ENGR 1110: Introduction to Engineering Lab 7 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Supplies Needed Motor control board, Transmitter (with good batteries), Receiver Equipment Used Oscilloscope, Function Generator,
ENGR 1110: Introduction to Engineering Lab 7 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Supplies Needed Motor control board, Transmitter (with good batteries), Receiver Equipment Used Oscilloscope, Function Generator,
Robots are similar to humans if you consider that both use inputs and outputs to sense and react to the world.
 Activity 3.1.1 Inputs and Outputs for CT Introduction Robots are similar to humans if you consider that both use inputs and outputs to sense and react to the world. Most humans use five senses to perceive
Activity 3.1.1 Inputs and Outputs for CT Introduction Robots are similar to humans if you consider that both use inputs and outputs to sense and react to the world. Most humans use five senses to perceive
A3 Pro INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Oct 25, 2017 Revision IMPORTANT NOTES
 A3 Pro INSTRUCTION MANUAL Oct 25, 2017 Revision IMPORTANT NOTES 1. Radio controlled (R/C) models are not toys! The propellers rotate at high speed and pose potential risk. They may cause severe injury
A3 Pro INSTRUCTION MANUAL Oct 25, 2017 Revision IMPORTANT NOTES 1. Radio controlled (R/C) models are not toys! The propellers rotate at high speed and pose potential risk. They may cause severe injury
EEL5666C IMDL Spring 2006 Student: Andrew Joseph. *Alarm-o-bot*
 EEL5666C IMDL Spring 2006 Student: Andrew Joseph *Alarm-o-bot* TAs: Adam Barnett, Sara Keen Instructor: A.A. Arroyo Final Report April 25, 2006 Table of Contents Abstract 3 Executive Summary 3 Introduction
EEL5666C IMDL Spring 2006 Student: Andrew Joseph *Alarm-o-bot* TAs: Adam Barnett, Sara Keen Instructor: A.A. Arroyo Final Report April 25, 2006 Table of Contents Abstract 3 Executive Summary 3 Introduction
Sample Pages. Classroom Activities for the Busy Teacher: NXT. 2 nd Edition. Classroom Activities for the Busy Teacher: NXT -
 Classroom Activities for the Busy Teacher: NXT 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Chapter 1: Introduction... 1 Chapter 2: What is a robot?... 5 Chapter 3: Flowcharting... 11 Chapter 4: DomaBot Basics... 15
Classroom Activities for the Busy Teacher: NXT 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Chapter 1: Introduction... 1 Chapter 2: What is a robot?... 5 Chapter 3: Flowcharting... 11 Chapter 4: DomaBot Basics... 15
UNIT1. Keywords page 13-14
 UNIT1 Keywords page 13-14 What is a Robot? A robot is a machine that can do the work of a human. Robots can be automatic, or they can be computer-controlled. Robots are a part of everyday life. Most robots
UNIT1 Keywords page 13-14 What is a Robot? A robot is a machine that can do the work of a human. Robots can be automatic, or they can be computer-controlled. Robots are a part of everyday life. Most robots
