Generating of short pulses with high amplitudes by using of standard Current-Feedback-Amplifier.
|
|
|
- Suzanna Baldwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Generating of short pulses with high amplitudes by using of standard Current-Feedback-Amplifier. Franz Peter Zantis, Dipl.-Ing.(TU) RWTH Aachen University, Physical Institut IIIa, Electronic Workshop The traditional method to generate pulses in the range of some nanoseconds with high amplitudes, is the using of the avalanche-effect of transistors. However the problem with this method is the poor possibility for parameterizing. That was the trigger to look for a different way: under using of modern electronic components, a pulse generator, which is parameterizable, was developed. The parameters can be set by using a Windows- or Linux-PC. The pulse width can be adjusted in the range of ns; the pulse amplitude in the range of V and the pulse repetition rate in the range of 1 Hz to 50 khz. 1 Introduction In physical experiments of particle physics, often short pulses with relatively high energy are necessary. In the current application, a pulser, which is to be developed, must feed an antenna to generate electromagnetic pulses. In other applications it is used to generate ultrashort light pulses with LEDs. To generate this pulses, the avalanche effect of a transistor can be used. As described e.g. in [1]. But, with this solution, parameterization is not, or only possible with great effort. A different way is the use of the ECL-technique (details see [9]). With this, parameterization is possible. However, the pulses which comes from an ECL-circuit have very small amplitudes. This means, that an amplifier is mandatory. This is an additional expenditure and an amplifier has maybe not a good influence to the signal shape. But that is not all: the ECLtechniques is also outmoded and the components are not easy to get. The new upcoming CF-Amplifiers (CFA = Current Feedback Amplifier) with slew rates higher than 6V/ns was the trigger for the idea to generate the pulse inside of the output circuit. This makes the use of an amplification of a generated raw-pulse needless. 1
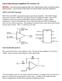
2 2 The Idea The basic idea of this application is to use a Current Feedback Amplifier as comparator. This is unusual, because of the fact, that at minimum one of both inputs of an CFA is a current input. So it must be compared a voltage with a current - which is impossible on the first view. The concept of the pulse-shaper can be seen in figure 1. A standard microcontroller generates a trigger pulse with individual repetition rate. As described, the CFA works as comparator. The incoming pulse is connected to the positive (voltage-) input (+IN). At this time, the output of the VFA is at low level. So the positive potential at the input +IN of the CFA is higher than the equivalent positive potential at the current input -IN. As result the output of the CFA goes to high-level with its maximum slew-rate and T1 opens. The pulse appears at R7. It is feeded by C2. The trigger pulse from the microcontroller with the amplitude circuit R1 and C1. u t 1 C1( P ˆ R1 C t) = U (1 e ) {Eq. 2.1} Uˆ P goes also to the delay For small t ( t < RC), the voltage at C is approximated a linear function (see [2]) ˆ t uc ( t) = U P (1 ( 1)) {Eq. 2.2} R1 C1 The "slew rate" of the RC-circuit is in this case: sr R1C1 Uˆ P = {Eq. 2.3} R1 C1 The VFA works also as a comparator. It compares the constant voltage of U ref with the voltage at the condenser C1, which increases with a short delay from the pulse (according to Eq. 2.2). If the amplitude at C1 is higher than U ref, the output of the VFA goes to high and changes the voltage level at IN of the CFA. Here, the slew-rate of the VFA must be considered. Of course, also the slope of the pulse, which comes from the microcontroller, has influence of the delay. So, there are three variables, which have influence to the delay, with which the CFA can be switched. - the slope of the incoming trigger pulse from the microcontroller s U P - the "slew rate" of the RC-circuit sr RC - the slew rate of the VFA sr VFA This makes the calculation complicate. Additional, the layout of the circuit board is not free of parasitic capacitive and inductive components. This has e.g. influence on the value of C1. A very fast VFA needs a bigger capacity of C1. In the best case, if 2
3 sr VFA >> sr RC and sr VFA >> s U P the slew rate of the VFA can be unconsidered. On the other hand: with a sufficient slow VFA, the other two variables can be ignored and C1 can be dispensed. However, the question is, if in this case the delay, to toggle the CFA is may be too long to meet the needed pulse width. If the output of the VFA changes to high, the output of the CFA changes to low level and T1 closes. Apart from the discussed influence of the slew rates, the pulse width depends on the value of the voltage U ref. The higher the value of U ref, the wider is the pulse at the output. The values of U ref can be varied in a linear way, between 0 V < U ref << Uˆ p Not easy to dimension are the resistors R2, R3 and R5. The resistors form an electrical charge balance for "-IN" as a counterbalance to the potential at "+IN". Fig.1: Concept of the circuit. 3
4 May be in some applications (where amplitudes of about 12V are sufficient) T1 is not necessary and the pulse can be taken immediately from the CFA. Depending on the kind of CFA it can be used in single supply-mode. If T1 is necessary, than it is helpful that the CFA can deliver negative voltage at the output. This will accelerate to switch off T1 by sucking of the charge carriers which are located on the gate of the transistor (see also [8]). 3 Selecting the components With respect on the availability and to limit or lower warehousing, the aim was in this case, to use standard electronic components. The choice fell on the CFA-amplifier THS3202 from Texas Instruments, because of its high slew rate about 9 V/ns. Additional, this component can deliver output currents up to 115 ma and voltages up to 13 V. This is helpful to toggle the FET at the output. Details about the THS3202 can be found in [5]. In fact, the THS3202 is designed to work in HF amplifier. The basic idea here was now, to use this component as a comparator. This mode of operation is not recommended from the manufacturer of this component. They do not support this. However, it works - how this application shows. For the VFA the type LM6172 is used. The slew rate of this device is 3V/ns. This is fast for a VFA. Details about the LM6172 can be found in [6]. For selecting the FET, the Gate-Source-capacity is a very important point. It must be as small as possible. On the other hand, only a transistor which supports a high drain-source voltage, can supply high output amplitude. Both requirements are contradictory, so that a careful selection of the type is necessary. The type MRFE6VS25NR1 (details see [7]) satisfies both contradictory features for the task very well. With the type, output pulses with amplitudes up to 120V (including a safety distance) are realisable. If instead of an FET a bipolar transistor should be used, [8] can be helpful to get a short switching time. 4 Circuit diagram and design details The complete circuit diagram of the pulser is shown in fig. 3. In fig. 2 the core circuit of the pulser is shown. The trigger-pulse comes in from a microcontroller. It is amplified with factor 2 by the operational amplifier U4A. The output of U4A goes immediately to the output circuit IC2 (CFA, THS3202). This works as comparator and the output jumps to high. T1 opens and the pulse appears at K1 (Antenna). 4
5 It must be considered, that the energy for the pulse cannot come from the power supply, because the pulses are too short. The layout of the PCB, with its parasitic components, makes this impossible. Rather the energy comes from the capacitor C2. It must be placed very close to the output and the transistor T1. The condenser C2 must be designed for the maximum output voltages (more than 84 V in this case). On the other hand: any parasitic inductance in C2 degrades the output pulse. To avoid inductive components, the capacity should be as small as possible. Used is a capacity about 100nF. It reaches for impulse durations up to 100 ns if the load has 50 Ω and 2% amplitude-decrease at the end of the pulse is allowed. U U t 100ns 2 C RC 50Ω 100 nf = e = e 0,98 {Eq. 4.1} There are two CFAs in the same case of the THS3202. The second one is used to get an additional amplification of the output-signal if needed. This can be the case, if a different FET is used or the output of the CFA may be used without further parts. The amplification-factor is 2. Depending on which of the CFA should control T1, R26 or R11 is mounted. The VFA U4B compares the voltage at C4 with a DC-voltage which comes from R27 or from an Digital-to-analogue-converter (DAU). As soon the voltage at C4 is higher as these DCvoltage, the output of U4B changes the current potential at "-IN.A" of the CFA. As result, the output of the CFA IC2 changes from high to low and T1 closes. The time between opening T1 and closing T1 depends on the time constant of R9/C4 and the slew rate of the VFA U4B. It is possible to work only with the slew-rate of the VFA, if the rest of the circuit can follow. An important point is, that the CFA IC2 works as comparator however the negative input " IN.A" is a current input. It is hard to determine the dimension of the resistors, which are necessary, to get the right working point as comparator. In this case, the resistors R33 and R2 forms together with the internal resistant of IC2 a voltage divider. Whereby the based voltage-potential is determined by the VFA U4B. R25 works as feedback-resistor. With CFAs this resistor is a must to avoid unstable operation. However - it limits the possible smallest pulse width. All in all, the resistors R33, R2 and R25 form together with the current-input "-IN.A" of the CFA a careful tuned "potential-scale". The values for this resistors have been determined empirically. 5
6 HV-Generation Fig.2: Core circuit of the pulser. Very important is to generate the layout of this circuit very careful. A lot of experience is necessary. The condenser C2 must be placed very close to T1 respectively the output. For designing HF circuits or circuits to handle fast data/pulses, big mass-areas are recommended. However this is not good for CFA. The area around the negative (current-) input mustn't have mass-areas. The lines between the components should be as short as possible. Especially between the output of the CFA and the gate of T1. Also between the output of U4A and U4B and the input of the CFA. And also between the CFA and the passive components around it (C9, C10, C12, C13, R25, R33, R2). On the other hand, capacitive feedback between output and input of the THS3202 can result in oscillation. So the components have to be placed close together, but in a way which avoids capacitive feedback. The output of the CFA changes between negative and positive supply voltage. It is never on 0V. This means, that the CFA must deliver always relative high currents. It is recommended to glue a heatsink on the CFA. In this application the transistor T1 do not need a heatsink. The transferred power in the moment when the pulse appears at a load of 50 Ω is up to (84V ) 50Ω 2 = 141,12 W {Eq. 4.2} 6
7 But the duration is not more than 100 ns. The pause until the next pulse, depends on the repetition rate. In this case, the maximum repetition rate is 50 khz respectively 20 µs. This is 200 times longer than the maximum pulse width. The on-resistance of the transistor is small, but however, if the complete power would be implemented into the transistor, the resulting averaged power is round about 141,12 W 700mW 200 This is the reason, why the transistor does not need a heatsink. 5 Controlling the parameters Controlling the parameters works in this case via a Standard PC and USB-interface. With the help of a Cyrix-processor, which is in the module IO-Warrior56, the USB-protocol is changed into SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface). Details to the SPI-Bus can be found in [10]. Relevant for the pulse width is the voltage at the negative input of U4B. With K5 one can decide if the pulse width should be determined manual via R27 or via a digital-to-analogue converter (which is connected to the SPI-Bus) from the PC. The repetition rate is controlled by a separate module U1 which gets the desired value from the SPI-bus. This module works with an MPS430F2013-microcontroller which works as generator. It produces pulses with a amplitude of 3,3 V and a constant width of 40 µs. With K6 one can decide if the trigger pulses come from U1 or from an external generator. The pulse amplitude is determined by the module "HV-Generation". It is an independent working boost converter. The basic concept is similar to an application from [3] and [4]. The value of the output voltage is controlled via the SPI-Bus. In the first application the pulser works to produce electromagnetic pulses via an antenna. For this application the voltage can be changed between 18 and 84 V. the help of an antenna, the value can be changed between 18 and 84 V. Fig. 4 shows an example pulse of the described pulser. Fig. 5 shows the top side of the prototype and fig. 6 the screen of the control program. 7
8 Fig.3: The complete circuit diagram. This pulser is supplied from an accumulator of a model-helicopter. 8
9 Fig.4: Example pulse with a width of approximately 5 ns and an amplitude of about 54V. The load was 50Ω. VFA CFA Transistor T1 Fig.5: Prototype, top view (heatsink on the CFA is not mounted). 9
10 Fig.6: Screen of the control program. 10
11 Literature [1] W.M. Henebry "Avalanche Transistor Circuits" The review of scientific instruments, Vol.32, November 1961, beginning on page 1198 [2] F.P. Zantis "Eulersche Funktionen euler functions" elrad, Hannover, March 1990, beginning on page 92 [3] F. P. Zantis "Stromversorgung ohne Stress Power supplies without stress" Elektor publishing, Aachen 2011, ISBN [4] F.P. Zantis "Schaltnetzteile Switching power supplies" Elektor publishing, Aachen 1994, ISBN X [5] Texas Instruments "THS GHz, Low distortion, Dual current-feedback amplifiers" January 2010 [6] National Semiconductors "LM6172 Dual high speed, Low power, Low distortion, Voltage Feedback amplifiers" September 2004 [7] Freescale Seminconductors "RF Power LDMOS Transistor MRFE6VS25NR1" June 2012 [8] F.P. Zantis "Optimierung des Schaltverhaltens von Bipolartransistoren - Optimization of the switching behavior of bipolar transistors" Elektronik, Munich, February 1994, beginning on page 84 [9] Machon, et.al. "Friedrich Tabellenbuch Elektrotechnik/Elektronik Table book electrotechnique/electronic" Bildungsverlag E1NS publishing, Siegburg 2012, ISBN [10] F.P. Zantis "Data transfer via SPI" Presentation at the Electronics Conference, FZJ Jülich, 11th to 13nd March
Parameter Optimization for Rise Time of Sub nanosecond Pulser Based on Avalanche Transistors
 Parameter Optimization for Rise Time of Sub nanosecond Pulser Based on Avalanche Transistors Ming-xiang Gao, Yan-zhao Xie, Ya-han Hu Xi an Jiaotong University 2017/05/08 Contents 1 Introduction 2 Principles
Parameter Optimization for Rise Time of Sub nanosecond Pulser Based on Avalanche Transistors Ming-xiang Gao, Yan-zhao Xie, Ya-han Hu Xi an Jiaotong University 2017/05/08 Contents 1 Introduction 2 Principles
Analogue circuit design for RF immunity
 Analogue circuit design for RF immunity By EurIng Keith Armstrong, C.Eng, FIET, SMIEEE, www.cherryclough.com First published in The EMC Journal, Issue 84, September 2009, pp 28-32, www.theemcjournal.com
Analogue circuit design for RF immunity By EurIng Keith Armstrong, C.Eng, FIET, SMIEEE, www.cherryclough.com First published in The EMC Journal, Issue 84, September 2009, pp 28-32, www.theemcjournal.com
Chapter.8: Oscillators
 Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
Chapter 13: Comparators
 Chapter 13: Comparators So far, we have used op amps in their normal, linear mode, where they follow the op amp Golden Rules (no input current to either input, no voltage difference between the inputs).
Chapter 13: Comparators So far, we have used op amps in their normal, linear mode, where they follow the op amp Golden Rules (no input current to either input, no voltage difference between the inputs).
Type Ordering Code Package TDA Q67000-A5066 P-DIP-8-1
 Control IC for Switched-Mode Power Supplies using MOS-Transistor TDA 4605-3 Bipolar IC Features Fold-back characteristics provides overload protection for external components Burst operation under secondary
Control IC for Switched-Mode Power Supplies using MOS-Transistor TDA 4605-3 Bipolar IC Features Fold-back characteristics provides overload protection for external components Burst operation under secondary
HIGH LOW Astable multivibrators HIGH LOW 1:1
 1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
LM148/LM248/LM348 Quad 741 Op Amps
 Quad 741 Op Amps General Description The LM148 series is a true quad 741. It consists of four independent, high gain, internally compensated, low power operational amplifiers which have been designed to
Quad 741 Op Amps General Description The LM148 series is a true quad 741. It consists of four independent, high gain, internally compensated, low power operational amplifiers which have been designed to
GATE & DRAIN Probe heads specifications
 GATE & DRAIN Probe heads specifications Page 1 /18 October 11, Ref 01102011 Table of contents 1 Main Characteristic of the Pulse IV System 3 1.1 General Description 3 1.2 Main features 4 1.3 Pulse Timing
GATE & DRAIN Probe heads specifications Page 1 /18 October 11, Ref 01102011 Table of contents 1 Main Characteristic of the Pulse IV System 3 1.1 General Description 3 1.2 Main features 4 1.3 Pulse Timing
EUP V/12V Synchronous Buck PWM Controller DESCRIPTION FEATURES APPLICATIONS. Typical Application Circuit. 1
 5V/12V Synchronous Buck PWM Controller DESCRIPTION The is a high efficiency, fixed 300kHz frequency, voltage mode, synchronous PWM controller. The device drives two low cost N-channel MOSFETs and is designed
5V/12V Synchronous Buck PWM Controller DESCRIPTION The is a high efficiency, fixed 300kHz frequency, voltage mode, synchronous PWM controller. The device drives two low cost N-channel MOSFETs and is designed
Preamplifier shaper: The preamplifier. The shaper. The Output.
 Preamplifier shaper: In previous simulations I just tried to reach the speed limits. The only way to realise this was by using a lot of current, about 1 ma through the input transistor. This gives in the
Preamplifier shaper: In previous simulations I just tried to reach the speed limits. The only way to realise this was by using a lot of current, about 1 ma through the input transistor. This gives in the
SGM8631/2/3 6MHz, Rail-to-Rail I/O CMOS Operational Amplifiers
 /2/3 6MHz, Rail-to-Rail I/O PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The (single), SGM8632 (dual) and SGM8633 (single with shutdown) are low noise, low voltage, and low power operational amplifiers that can be designed into
/2/3 6MHz, Rail-to-Rail I/O PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The (single), SGM8632 (dual) and SGM8633 (single with shutdown) are low noise, low voltage, and low power operational amplifiers that can be designed into
LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier
 LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part
LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part
Electronic Counters. Sistemi Virtuali di Acquisizione Dati Prof. Alessandro Pesatori
 Electronic Counters 1 Electronic counters Frequency measurement Period measurement Frequency ratio measurement Time interval measurement Total measurements between two signals 2 Electronic counters Frequency
Electronic Counters 1 Electronic counters Frequency measurement Period measurement Frequency ratio measurement Time interval measurement Total measurements between two signals 2 Electronic counters Frequency
Frequently Asked Questions DAT & ZX76 Series Digital Step Attenuators
 Frequently Asked Questions DAT & ZX76 Series Digital Step Attenuators 1. What is the definition of "Switching Control Frequency"? The switching control frequency is the frequency of the control signals.
Frequently Asked Questions DAT & ZX76 Series Digital Step Attenuators 1. What is the definition of "Switching Control Frequency"? The switching control frequency is the frequency of the control signals.
AERO2705 Space Engineering 1 Week 7 The University of Sydney
 AERO2705 Space Engineering 1 Week 7 The University of Sydney Presenter Mr. Warwick Holmes Executive Director Space Engineering School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering The University
AERO2705 Space Engineering 1 Week 7 The University of Sydney Presenter Mr. Warwick Holmes Executive Director Space Engineering School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering The University
Driver Amplifier for 7 Tesla MRI Smart Power Amplifier
 Driver Amplifier for 7 Tesla MRI Smart Power Amplifier presented by Kevin Kolpatzeck supervised by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus Solbach Institute of Microwave and RF Technology University of Duisburg Essen Contents
Driver Amplifier for 7 Tesla MRI Smart Power Amplifier presented by Kevin Kolpatzeck supervised by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus Solbach Institute of Microwave and RF Technology University of Duisburg Essen Contents
AltiumLive 2017: Component selection for EMC
 AltiumLive 2017: Component selection for EMC Martin O Hara Victory Lighting Ltd Munich, 24-25 October 2017 Component Selection Passives resistors, capacitors and inductors Discrete diodes, bipolar transistors,
AltiumLive 2017: Component selection for EMC Martin O Hara Victory Lighting Ltd Munich, 24-25 October 2017 Component Selection Passives resistors, capacitors and inductors Discrete diodes, bipolar transistors,
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences, University of California
 Chapter 8 NOISE, GAIN AND BANDWIDTH IN ANALOG DESIGN Robert G. Meyer Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences, University of California Trade-offs between noise, gain and bandwidth are
Chapter 8 NOISE, GAIN AND BANDWIDTH IN ANALOG DESIGN Robert G. Meyer Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences, University of California Trade-offs between noise, gain and bandwidth are
Pb-free lead plating; RoHS compliant
 Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Pb-free lead plating; RoHS compliant SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone,
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Pb-free lead plating; RoHS compliant SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone,
Research and implementation of 100 A pulsed current source pulse edge compression
 April 016, 3(: 73 78 www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/10058885 The Journal of China Universities of Posts and Telecommunications http://jcupt.bupt.edu.cn Research and implementation of 100 A pulsed
April 016, 3(: 73 78 www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/10058885 The Journal of China Universities of Posts and Telecommunications http://jcupt.bupt.edu.cn Research and implementation of 100 A pulsed
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
UC284x, UC384x, UC384xY CURRENT-MODE PWM CONTROLLERS
 Optimized for Off-Line and dc-to-dc Converters Low Start-Up Current (
Optimized for Off-Line and dc-to-dc Converters Low Start-Up Current (
LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF442 dual low power operational amplifiers provide many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM1458 while
LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF442 dual low power operational amplifiers provide many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM1458 while
LF411 Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, JFET input operational amplifiers with very low input offset voltage and guaranteed input
Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, JFET input operational amplifiers with very low input offset voltage and guaranteed input
GaN Power ICs: Integration Drives Performance
 GaN Power ICs: Integration Drives Performance Stephen Oliver, VP Sales & Marketing stephen.oliver@navitassemi.com Bodo s Power Conference, Munich December 5 th, 2017 Navitas Semiconductor Inc. World s
GaN Power ICs: Integration Drives Performance Stephen Oliver, VP Sales & Marketing stephen.oliver@navitassemi.com Bodo s Power Conference, Munich December 5 th, 2017 Navitas Semiconductor Inc. World s
Figure 1 RC Based Soft Start Circuit. Path of charge during startup shown in red.
 P a g e 1 1 Effects of Gate RC Soft Start The LM25066A has a power-limiting feature to help protect the external MOSFET (keep it operating under its SOA curve). However, for designs with large load currents
P a g e 1 1 Effects of Gate RC Soft Start The LM25066A has a power-limiting feature to help protect the external MOSFET (keep it operating under its SOA curve). However, for designs with large load currents
SGM8621/2/3/4 3MHz, Rail-to-Rail I/O CMOS Operational Amplifiers
 SGM8621/2/3/4 3MHz, Rail-to-Rail I/O PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The SGM8621 (single), SGM8622 (dual), SGM8623 (single with shutdown) and SGM8624 (quad) are low noise, low voltage, and low power operational amplifiers,
SGM8621/2/3/4 3MHz, Rail-to-Rail I/O PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The SGM8621 (single), SGM8622 (dual), SGM8623 (single with shutdown) and SGM8624 (quad) are low noise, low voltage, and low power operational amplifiers,
HA-2600, HA Features. 12MHz, High Input Impedance Operational Amplifiers. Applications. Pinouts. Ordering Information
 HA26, HA26 September 998 File Number 292.3 2MHz, High Input Impedance Operational Amplifiers HA26/26 are internally compensated bipolar operational amplifiers that feature very high input impedance (MΩ,
HA26, HA26 September 998 File Number 292.3 2MHz, High Input Impedance Operational Amplifiers HA26/26 are internally compensated bipolar operational amplifiers that feature very high input impedance (MΩ,
Application Note Receivers MLX71120/21 With LNA1-SAW-LNA2 configuration
 Designing with MLX71120 and MLX71121 receivers using a SAW filter between LNA1 and LNA2 Scope Many receiver applications, especially those for automotive keyless entry systems require good sensitivity
Designing with MLX71120 and MLX71121 receivers using a SAW filter between LNA1 and LNA2 Scope Many receiver applications, especially those for automotive keyless entry systems require good sensitivity
High Voltage Pulser Circuits By Ching Chu, Sr. Applications Engineer
 High Voltage Circuits By Ching Chu, Sr. Applications Engineer AN-H53 Application Note Introduction The high voltage pulser circuit shown in Figure 1 utilizes s complementary P- and N-channel transistors
High Voltage Circuits By Ching Chu, Sr. Applications Engineer AN-H53 Application Note Introduction The high voltage pulser circuit shown in Figure 1 utilizes s complementary P- and N-channel transistors
MIC4421/4422. Bipolar/CMOS/DMOS Process. General Description. Features. Applications. Functional Diagram. 9A-Peak Low-Side MOSFET Driver
 9A-Peak Low-Side MOSFET Driver Micrel Bipolar/CMOS/DMOS Process General Description MIC4421 and MIC4422 MOSFET drivers are rugged, efficient, and easy to use. The MIC4421 is an inverting driver, while
9A-Peak Low-Side MOSFET Driver Micrel Bipolar/CMOS/DMOS Process General Description MIC4421 and MIC4422 MOSFET drivers are rugged, efficient, and easy to use. The MIC4421 is an inverting driver, while
LDO Regulator Stability Using Ceramic Output Capacitors
 LDO Regulator Stability Using Ceramic Output Capacitors Introduction Ultra-low ESR capacitors such as ceramics are highly desirable because they can support fast-changing load transients and also bypass
LDO Regulator Stability Using Ceramic Output Capacitors Introduction Ultra-low ESR capacitors such as ceramics are highly desirable because they can support fast-changing load transients and also bypass
LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier
 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count low, but
Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count low, but
TDA7000 for narrowband FM reception
 TDA7 for narrowband FM reception Author: Author: W.V. Dooremolen INTRODUCTION Today s cordless telephone sets make use of duplex communication with carrier frequencies of about.7mhz and 49MHz. In the base
TDA7 for narrowband FM reception Author: Author: W.V. Dooremolen INTRODUCTION Today s cordless telephone sets make use of duplex communication with carrier frequencies of about.7mhz and 49MHz. In the base
Cascode Oscillation in Audio Amplifiers
 Cascode Oscillation in Audio Amplifiers About 80mV pk-pk oscillation at ~182MHz was noted on the oscilloscope during routine debugging of a cascoded front end circuit for a high power balanced symmetrical
Cascode Oscillation in Audio Amplifiers About 80mV pk-pk oscillation at ~182MHz was noted on the oscilloscope during routine debugging of a cascoded front end circuit for a high power balanced symmetrical
14 MHz Single Side Band Receiver
 EPFL - LEG Laboratoires à options 8 ème semestre MHz Single Side Band Receiver. Objectives. The objective of this work is to calculate and adjust the key elements of an Upper Side Band Receiver in the
EPFL - LEG Laboratoires à options 8 ème semestre MHz Single Side Band Receiver. Objectives. The objective of this work is to calculate and adjust the key elements of an Upper Side Band Receiver in the
Downloaded from edlib.asdf.res.in
 ASDF India Proceedings of the Intl. Conf. on Innovative trends in Electronics Communication and Applications 2014 242 Design and Implementation of Ultrasonic Transducers Using HV Class-F Power Amplifier
ASDF India Proceedings of the Intl. Conf. on Innovative trends in Electronics Communication and Applications 2014 242 Design and Implementation of Ultrasonic Transducers Using HV Class-F Power Amplifier
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5)
 Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur Name of the Lab: Applied Electronics Lab
 Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur Name of the Lab: Applied Electronics Lab Subject Code: 1620408 Experiment-1 Aim: To obtain the characteristics of field effect transistor (FET). Theory: The Field Effect
Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur Name of the Lab: Applied Electronics Lab Subject Code: 1620408 Experiment-1 Aim: To obtain the characteristics of field effect transistor (FET). Theory: The Field Effect
AMPTEK INC. 14 DeAngelo Drive, Bedford MA U.S.A FAX:
 DeAngelo Drive, Bedford MA 01730 U.S.A. +1 781 27-2242 FAX: +1 781 27-3470 sales@amptek.com www.amptek.com (AN20-2, Revision 3) TESTING The can be tested with a pulser by using a small capacitor (usually
DeAngelo Drive, Bedford MA 01730 U.S.A. +1 781 27-2242 FAX: +1 781 27-3470 sales@amptek.com www.amptek.com (AN20-2, Revision 3) TESTING The can be tested with a pulser by using a small capacitor (usually
CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION
 168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN
 LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
LM3647 Universal Battery Charger for Li-Ion, Ni-MH and Ni-Cd Batteries
 LM3647 Universal Battery Charger for Li-Ion, Ni-MH and Ni-Cd Batteries 1.0 General Description The LM3647 is a charge controller for Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion), Nickel-Metal Hydride (Ni-MH) and Nickel-Cadmium
LM3647 Universal Battery Charger for Li-Ion, Ni-MH and Ni-Cd Batteries 1.0 General Description The LM3647 is a charge controller for Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion), Nickel-Metal Hydride (Ni-MH) and Nickel-Cadmium
James Lunsford HW2 2/7/2017 ECEN 607
 James Lunsford HW2 2/7/2017 ECEN 607 Problem 1 Part A Figure 1: Negative Impedance Converter To find the input impedance of the above NIC, we use the following equations: V + Z N V O Z N = I in, V O kr
James Lunsford HW2 2/7/2017 ECEN 607 Problem 1 Part A Figure 1: Negative Impedance Converter To find the input impedance of the above NIC, we use the following equations: V + Z N V O Z N = I in, V O kr
Multiple Instrument Station Module
 Multiple Instrument Station Module Digital Storage Oscilloscope Vertical Channels Sampling rate Bandwidth Coupling Input impedance Vertical sensitivity Vertical resolution Max. input voltage Horizontal
Multiple Instrument Station Module Digital Storage Oscilloscope Vertical Channels Sampling rate Bandwidth Coupling Input impedance Vertical sensitivity Vertical resolution Max. input voltage Horizontal
LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers
 LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13600 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers each with
LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13600 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers each with
THS MHz HIGH-SPEED AMPLIFIER
 THS41 27-MHz HIGH-SPEED AMPLIFIER Very High Speed 27 MHz Bandwidth (Gain = 1, 3 db) 4 V/µsec Slew Rate 4-ns Settling Time (.1%) High Output Drive, I O = 1 ma Excellent Video Performance 6 MHz Bandwidth
THS41 27-MHz HIGH-SPEED AMPLIFIER Very High Speed 27 MHz Bandwidth (Gain = 1, 3 db) 4 V/µsec Slew Rate 4-ns Settling Time (.1%) High Output Drive, I O = 1 ma Excellent Video Performance 6 MHz Bandwidth
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
Once the DS1821 comes up as a thermostat it will not return to 1-wire mode until it receives a special signal sequence, as follows:
 DS1821 Reset Circuit Introduction The Dallas DS1821 "Programmable Digital Thermostat and Thermometer" is a member of the "1 Wire" family of interface chips but has a number of peculiarities not shared
DS1821 Reset Circuit Introduction The Dallas DS1821 "Programmable Digital Thermostat and Thermometer" is a member of the "1 Wire" family of interface chips but has a number of peculiarities not shared
Handy dandy little circuit #17 #17
 Handy dandy little circuit #17 #17 Download # 17 in PDF There are a lot of alarm systems on the market but you might be inclined to build your own. This little project can be put together using inexpensive
Handy dandy little circuit #17 #17 Download # 17 in PDF There are a lot of alarm systems on the market but you might be inclined to build your own. This little project can be put together using inexpensive
BM6312 FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION APPLICATIONS. High-performance current mode PWM Controller. Product Specification
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION BM6312 is a high-performance current mode PWM control IC designed for AC/DC convertor, which built-in high-voltage power switch tube and supplies continuous output power of 12W within
GENERAL DESCRIPTION BM6312 is a high-performance current mode PWM control IC designed for AC/DC convertor, which built-in high-voltage power switch tube and supplies continuous output power of 12W within
ericssonz LBI-38640E MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR VHF TRANSMITTER SYNTHESIZER MODULE 19D902780G1 DESCRIPTION
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR VHF TRANSMITTER SYNTHESIZER MODULE 19D902780G1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION........................................... Front Cover GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS...................................
MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR VHF TRANSMITTER SYNTHESIZER MODULE 19D902780G1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION........................................... Front Cover GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS...................................
Long Range Passive RF-ID Tag With UWB Transmitter
 Long Range Passive RF-ID Tag With UWB Transmitter Seunghyun Lee Seunghyun Oh Yonghyun Shim seansl@umich.edu austeban@umich.edu yhshim@umich.edu About RF-ID Tag What is a RF-ID Tag? An object for the identification
Long Range Passive RF-ID Tag With UWB Transmitter Seunghyun Lee Seunghyun Oh Yonghyun Shim seansl@umich.edu austeban@umich.edu yhshim@umich.edu About RF-ID Tag What is a RF-ID Tag? An object for the identification
Using LME49810 to Build a High-Performance Power Amplifier Part I
 Using LME49810 to Build a High-Performance Power Amplifier Part I Panson Poon Introduction Although switching or Class-D amplifiers are gaining acceptance to audiophile community, linear amplification
Using LME49810 to Build a High-Performance Power Amplifier Part I Panson Poon Introduction Although switching or Class-D amplifiers are gaining acceptance to audiophile community, linear amplification
LF353 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF353 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
LF353 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
print close Basic Comparison of NE555 and LM386
 print close Electronic Design Petre Petrov Fri, 2015-03-06 10:27 The bipolar NE555 timer IC is widely used in inductorless dc-dc converters, most frequently in doubling and inverting converters. However,
print close Electronic Design Petre Petrov Fri, 2015-03-06 10:27 The bipolar NE555 timer IC is widely used in inductorless dc-dc converters, most frequently in doubling and inverting converters. However,
LF155/LF156/LF355/LF356/LF357 JFET Input Operational Amplifiers
 JFET Input Operational Amplifiers General Description These are the first monolithic JFET input operational amplifiers to incorporate well matched, high voltage JFETs on the same chip with standard bipolar
JFET Input Operational Amplifiers General Description These are the first monolithic JFET input operational amplifiers to incorporate well matched, high voltage JFETs on the same chip with standard bipolar
HA MHz, High Slew Rate, High Output Current Buffer. Description. Features. Applications. Ordering Information. Pinouts.
 SEMICONDUCTOR HA-2 November 99 Features Voltage Gain...............................99 High Input Impedance.................... kω Low Output Impedance....................... Ω Very High Slew Rate....................
SEMICONDUCTOR HA-2 November 99 Features Voltage Gain...............................99 High Input Impedance.................... kω Low Output Impedance....................... Ω Very High Slew Rate....................
INFN Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro, Marzo 2007 FRONT-END ELECTRONICS PART 2
 INFN Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro, 6-30 Marzo 007 FRONT-END ELECTRONICS PART Francis ANGHINOLFI Wednesday 8 March 007 Francis.Anghinolfi@cern.ch v1 1 FRONT-END Electronics Part A little bit about signal
INFN Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro, 6-30 Marzo 007 FRONT-END ELECTRONICS PART Francis ANGHINOLFI Wednesday 8 March 007 Francis.Anghinolfi@cern.ch v1 1 FRONT-END Electronics Part A little bit about signal
Input Filter Design for Switching Power Supplies Michele Sclocchi Application Engineer National Semiconductor
 Input Filter Design for Switching Power Supplies Michele Sclocchi Application Engineer National Semiconductor The design of a switching power supply has always been considered a kind of magic and art,
Input Filter Design for Switching Power Supplies Michele Sclocchi Application Engineer National Semiconductor The design of a switching power supply has always been considered a kind of magic and art,
Model 310H Fast 800V Pulse Generator
 KEY FEATURES Temperature Stability +/-5ppm 100 V to 800 V into 50 Ω
KEY FEATURES Temperature Stability +/-5ppm 100 V to 800 V into 50 Ω
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LM148/LM248/LM348 Quad 741 Op Amps General Description The LM148 series
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LM148/LM248/LM348 Quad 741 Op Amps General Description The LM148 series
High-Voltage High-Current Stepper Motor Driver IK6019A TECHNICAL DATA
 TECHNICAL DATA High-Voltage High-Current Stepper Motor Driver IK6019A FEATURES Eight Power Output LDMOS Transistors Driving Dual Stepping Motor Output Current 250mA per Driver Output Voltage 24V Reset
TECHNICAL DATA High-Voltage High-Current Stepper Motor Driver IK6019A FEATURES Eight Power Output LDMOS Transistors Driving Dual Stepping Motor Output Current 250mA per Driver Output Voltage 24V Reset
FSFR-XS Series Fairchild Power Switch (FPS ) for Half-Bridge Resonant Converters
 February 203 FSFR-XS Series Fairchild Power Switch (FPS ) for Half-Bridge Resonant Converters Features Variable Frequency Control with 50% Duty Cycle for Half-Bridge Resonant Converter Topology High Efficiency
February 203 FSFR-XS Series Fairchild Power Switch (FPS ) for Half-Bridge Resonant Converters Features Variable Frequency Control with 50% Duty Cycle for Half-Bridge Resonant Converter Topology High Efficiency
Electronic Buzzer for Blind
 EE318 Electronic Design Lab Project Report, EE Dept, IIT Bombay, April 2009 Electronic Buzzer for Blind Group no. B08 Vaibhav Chaudhary (06007018) Anuj Jain (06007019)
EE318 Electronic Design Lab Project Report, EE Dept, IIT Bombay, April 2009 Electronic Buzzer for Blind Group no. B08 Vaibhav Chaudhary (06007018) Anuj Jain (06007019)
Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques
 Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques The electronics signals that we ve looked at so far have been analog that means the information is continuous. A voltage of 5.3V represents different information that
Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques The electronics signals that we ve looked at so far have been analog that means the information is continuous. A voltage of 5.3V represents different information that
SGM8631/2/3/4 470μA, 6MHz, Rail-to-Rail I/O CMOS Operational Amplifiers
 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The SGM863 (single), SGM863 (dual), SGM8633 (single with shutdown) and SGM8634 (quad) are low noise, low voltage, and low power operational amplifiers, that can be designed into a wide
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The SGM863 (single), SGM863 (dual), SGM8633 (single with shutdown) and SGM8634 (quad) are low noise, low voltage, and low power operational amplifiers, that can be designed into a wide
7. EMV Fachtagung. EMV-gerechtes Filterdesign. 23. April 2009, TU-Graz. Dr. Gunter Winkler (TU Graz) Dr. Bernd Deutschmann (Infineon Technologies AG)
 7. EMV Fachtagung 23. April 2009, TU-Graz EMV-gerechtes Filterdesign Dr. Gunter Winkler (TU Graz) Dr. Bernd Deutschmann (Infineon Technologies AG) Page 1 Agenda Filter design basics Filter Attenuation
7. EMV Fachtagung 23. April 2009, TU-Graz EMV-gerechtes Filterdesign Dr. Gunter Winkler (TU Graz) Dr. Bernd Deutschmann (Infineon Technologies AG) Page 1 Agenda Filter design basics Filter Attenuation
Application Note AN-1052
 Application Note AN-05 Using the IR7x Linear Current Sensing ICs By Jonathan Adams. Basic Functionality.... Bootstrap Circuit... 3. Retrieving Analog Current Signal at the Output... 3. Passive Filters...
Application Note AN-05 Using the IR7x Linear Current Sensing ICs By Jonathan Adams. Basic Functionality.... Bootstrap Circuit... 3. Retrieving Analog Current Signal at the Output... 3. Passive Filters...
LF412 Low Offset, Low Drift Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF412 Low Offset, Low Drift Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, JFET input operational amplifiers with very low input offset voltage and guaranteed
LF412 Low Offset, Low Drift Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, JFET input operational amplifiers with very low input offset voltage and guaranteed
LM6118/LM6218 Fast Settling Dual Operational Amplifiers
 Fast Settling Dual Operational Amplifiers General Description The LM6118/LM6218 are monolithic fast-settling unity-gain-compensated dual operational amplifiers with ±20 ma output drive capability. The
Fast Settling Dual Operational Amplifiers General Description The LM6118/LM6218 are monolithic fast-settling unity-gain-compensated dual operational amplifiers with ±20 ma output drive capability. The
Wireless Communication
 Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Dr.-Ing. Ulrich L. Rohde
 Dr.-Ing. Ulrich L. Rohde Noise in Oscillators with Active Inductors Presented to the Faculty 3 : Mechanical engineering, Electrical engineering and industrial engineering, Brandenburg University of Technology
Dr.-Ing. Ulrich L. Rohde Noise in Oscillators with Active Inductors Presented to the Faculty 3 : Mechanical engineering, Electrical engineering and industrial engineering, Brandenburg University of Technology
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
HIGH RIPPLE-REJECTION LOW DROPOUT MIDDLE OUTPUT CURRENT CMOS VOLTAGE REGULATOR
 Rev.2.3_ HIGH RIPPLE-REJECTION LOW DROPOUT MIDDLE OUTPUT CURRENT CMOS VOLTAGE REGULATOR S-1131 Series The S-1131 Series is a positive voltage regulator with a low dropout voltage, high output voltage accuracy,
Rev.2.3_ HIGH RIPPLE-REJECTION LOW DROPOUT MIDDLE OUTPUT CURRENT CMOS VOLTAGE REGULATOR S-1131 Series The S-1131 Series is a positive voltage regulator with a low dropout voltage, high output voltage accuracy,
Designing reliable and high density power solutions with GaN. Created by: Masoud Beheshti Presented by: Paul L Brohlin
 Designing reliable and high density power solutions with GaN Created by: Masoud Beheshti Presented by: Paul L Brohlin What will I get out of this presentation? Why GaN? Integration for System Performance
Designing reliable and high density power solutions with GaN Created by: Masoud Beheshti Presented by: Paul L Brohlin What will I get out of this presentation? Why GaN? Integration for System Performance
PC Pandey: Lecture notes PCB Design, EE Dept, IIT Bombay, rev. April 03. Topics
 PC Pandey: Lecture notes PCB Design, EE Dept,, rev. April 03 1 PC Pandey: Lecture notes PCB Design, EE Dept,, rev. April 03 2 PCB DESIGN Dr. P. C. Pandey EE Dept, Revised Aug 07 Topics 1.General Considerations
PC Pandey: Lecture notes PCB Design, EE Dept,, rev. April 03 1 PC Pandey: Lecture notes PCB Design, EE Dept,, rev. April 03 2 PCB DESIGN Dr. P. C. Pandey EE Dept, Revised Aug 07 Topics 1.General Considerations
TDA 4700 TDA Control IC for Single-Ended and Push-Pull Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS)
 Control IC for Single-Ended and Push-Pull Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) TDA 4700 Features Feed-forward control (line hum suppression) Symmetry inputs for push-pull converter (TDA 4700) Push-pull
Control IC for Single-Ended and Push-Pull Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) TDA 4700 Features Feed-forward control (line hum suppression) Symmetry inputs for push-pull converter (TDA 4700) Push-pull
TOSHIBA BiCD Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TB62757FPG
 TOSHIBA BiCD Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic Step Up Type DC/DC Converter for White LED The is a high efficient Step-Up Type DC/DC Converter specially designed for constant current driving
TOSHIBA BiCD Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic Step Up Type DC/DC Converter for White LED The is a high efficient Step-Up Type DC/DC Converter specially designed for constant current driving
Course Introduction. Content: 19 pages 3 questions. Learning Time: 30 minutes
 Course Introduction Purpose: This course discusses techniques that can be applied to reduce problems in embedded control systems caused by electromagnetic noise Objectives: Gain a basic knowledge about
Course Introduction Purpose: This course discusses techniques that can be applied to reduce problems in embedded control systems caused by electromagnetic noise Objectives: Gain a basic knowledge about
Chapter 2 Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion
 09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
Dr. P. C. Pandey. EE Dept, IIT Bombay. Rev. Jan 16
 1 PCB DESIGN Dr. P. C. Pandey EE Dept, IIT Bombay Rev. Jan 16 2 Topics 1.General Considerations in Layout Design 2.Layout Design for Analog Circuits 3.Layout Design for Digital Circuits 4. Artwork Considerations
1 PCB DESIGN Dr. P. C. Pandey EE Dept, IIT Bombay Rev. Jan 16 2 Topics 1.General Considerations in Layout Design 2.Layout Design for Analog Circuits 3.Layout Design for Digital Circuits 4. Artwork Considerations
EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter
 EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter ECE Department, Tufts University Spring 2008 1 Objective This laboratory exercise is the second part of the EE12 project of building an AM transmitter in
EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter ECE Department, Tufts University Spring 2008 1 Objective This laboratory exercise is the second part of the EE12 project of building an AM transmitter in
ETIN25 Analogue IC Design. Laboratory Manual Lab 2
 Department of Electrical and Information Technology LTH ETIN25 Analogue IC Design Laboratory Manual Lab 2 Jonas Lindstrand Martin Liliebladh Markus Törmänen September 2011 Laboratory 2: Design and Simulation
Department of Electrical and Information Technology LTH ETIN25 Analogue IC Design Laboratory Manual Lab 2 Jonas Lindstrand Martin Liliebladh Markus Törmänen September 2011 Laboratory 2: Design and Simulation
Figure 1: Closed Loop System
 SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
Hardware Platforms and Sensors
 Hardware Platforms and Sensors Tom Spink Including material adapted from Bjoern Franke and Michael O Boyle Hardware Platform A hardware platform describes the physical components that go to make up a particular
Hardware Platforms and Sensors Tom Spink Including material adapted from Bjoern Franke and Michael O Boyle Hardware Platform A hardware platform describes the physical components that go to make up a particular
Universal Generator of Ultra-Wideband Pulses
 74 P. PROTIVA, J. MRKVICA, J. MACHÁČ, UNIVERSAL GENERATOR OF ULTRA-WIDEBAND PULSES Universal Generator of Ultra-Wideband Pulses Pavel PROTIVA 1, Jan MRKVICA 2, Jan MACHÁČ 1 1 Dept. of Electromagnetic Field,
74 P. PROTIVA, J. MRKVICA, J. MACHÁČ, UNIVERSAL GENERATOR OF ULTRA-WIDEBAND PULSES Universal Generator of Ultra-Wideband Pulses Pavel PROTIVA 1, Jan MRKVICA 2, Jan MACHÁČ 1 1 Dept. of Electromagnetic Field,
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
Concepts to be Reviewed
 Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 3 Operational Amplifiers, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Reviewed Operational
Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 3 Operational Amplifiers, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Reviewed Operational
LM193/LM293/LM393/LM2903 Low Power Low Offset Voltage Dual Comparators
 LM193/LM293/LM393/LM2903 Low Power Low Offset Voltage Dual Comparators General Description The LM193 series consists of two independent precision voltage comparators with an offset voltage specification
LM193/LM293/LM393/LM2903 Low Power Low Offset Voltage Dual Comparators General Description The LM193 series consists of two independent precision voltage comparators with an offset voltage specification
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
DATA SHEET. TDA8415 TV and VTR stereo/dual sound processor with integrated filters and I 2 C-bus control INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET TV and VTR stereo/dual sound processor with integrated filters and I 2 C-bus control File under Integrated Circuits, IC02 May 1989 with integrated filters and I 2 C-bus control
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET TV and VTR stereo/dual sound processor with integrated filters and I 2 C-bus control File under Integrated Circuits, IC02 May 1989 with integrated filters and I 2 C-bus control
LM6172 Dual High Speed, Low Power, Low Distortion, Voltage Feedback Amplifiers
 LM6172 Dual High Speed, Low Power, Low Distortion, Voltage Feedback Amplifiers General Description The LM6172 is a dual high speed voltage feedback amplifier. It is unity-gain stable and provides excellent
LM6172 Dual High Speed, Low Power, Low Distortion, Voltage Feedback Amplifiers General Description The LM6172 is a dual high speed voltage feedback amplifier. It is unity-gain stable and provides excellent
Lecture 6: Electronics Beyond the Logic Switches Xufeng Kou School of Information Science and Technology ShanghaiTech University
 Lecture 6: Electronics Beyond the Logic Switches Xufeng Kou School of Information Science and Technology ShanghaiTech University EE 224 Solid State Electronics II Lecture 3: Lattice and symmetry 1 Outline
Lecture 6: Electronics Beyond the Logic Switches Xufeng Kou School of Information Science and Technology ShanghaiTech University EE 224 Solid State Electronics II Lecture 3: Lattice and symmetry 1 Outline
CHAPTER 4 ULTRA WIDE BAND LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER DESIGN
 93 CHAPTER 4 ULTRA WIDE BAND LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER DESIGN 4.1 INTRODUCTION Ultra Wide Band (UWB) system is capable of transmitting data over a wide spectrum of frequency bands with low power and high data
93 CHAPTER 4 ULTRA WIDE BAND LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER DESIGN 4.1 INTRODUCTION Ultra Wide Band (UWB) system is capable of transmitting data over a wide spectrum of frequency bands with low power and high data
A DESIGN EXPERIMENT FOR MEASUREMENT OF THE SPECTRAL CONTENT OF SUBSTRATE NOISE IN MIXED-SIGNAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
 A DESIGN EXPERIMENT FOR MEASUREMENT OF THE SPECTRAL CONTENT OF SUBSTRATE NOISE IN MIXED-SIGNAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Marc van Heijningen, John Compiet, Piet Wambacq, Stéphane Donnay and Ivo Bolsens IMEC
A DESIGN EXPERIMENT FOR MEASUREMENT OF THE SPECTRAL CONTENT OF SUBSTRATE NOISE IN MIXED-SIGNAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Marc van Heijningen, John Compiet, Piet Wambacq, Stéphane Donnay and Ivo Bolsens IMEC
Constant Current Switching Regulator for White LED
 Constant Current Switching Regulator for White LED FP7201 General Description The FP7201 is a Boost DC-DC converter specifically designed to drive white LEDs with constant current. The device can support
Constant Current Switching Regulator for White LED FP7201 General Description The FP7201 is a Boost DC-DC converter specifically designed to drive white LEDs with constant current. The device can support
Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter
 Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter 3.1 Introduction DC/DC Converter efficiently converts unregulated DC voltage to a regulated DC voltage with better efficiency and high power density.
Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter 3.1 Introduction DC/DC Converter efficiently converts unregulated DC voltage to a regulated DC voltage with better efficiency and high power density.
Op Amp Booster Designs
 Op Amp Booster Designs Although modern integrated circuit operational amplifiers ease linear circuit design, IC processing limits amplifier output power. Many applications, however, require substantially
Op Amp Booster Designs Although modern integrated circuit operational amplifiers ease linear circuit design, IC processing limits amplifier output power. Many applications, however, require substantially
