MATRIX TECHNICAL NOTES MTN-109
|
|
|
- Nickolas Washington
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 200 WOOD AVENUE, MIDDLESEX, NJ PHONE (732) MATRIX TECHNICAL NOTES MTN-109 THE RELATIONSHIP OF INTERCEPT POINTS COMPOSITE DISTORTIONS AND NOISE POWER RATIOS Amplifiers, mixers, diode attenuators, and some passive devices can generate intermodulation distortion. These distortion products are a result of a nonlinear transfer characteristic. A common specification, related to distortion, for amplifiers and mixers is the Intercept Point. If the input Vs output of a device is displayed graphically on a db Vs db scale, the slope of the linear portion will be 1. If second order distortion products are displayed on the same scale they will have a slope of 2, third order distortion products will have a slope of 3, etc. In most cases distortion products above third order are not important but these rules are still valid. The Intercept Point is the point where the linear extension of the particular distortion intersects the linear extension of the input Vs output line. Usually intercept points are given in terms of output power but in some cases, for example mixers, intercept points are given in terms of input power. When making distortion calculations, it is necessary to specify, or at least be consistent, as to where (input or output) the results apply. To be more correct the intercept point should be named the Two Tone Intercept point because two tones are used as the signal source. Two tones will generate third order distortion products 3A, 3B, 2A + B, 2A - B, 2B + A and 2B - A. This method of measuring distortion was developed so that narrow band amplifiers could be measured. The only third order products that fall in band, in narrow band amplifier, are 2A - B and 2B - A. MATRIX TEST EQUIPMENT, INC. MTN-109 October 10, 2005 Page 1/9
2 OUTPUT IN dbm INPUT IN dbm Figure 1, TWO TONE SECOND AND THIRD ORDER DISTORTION PRODUCTS. INPUT LEVEL FOR ONE TONE, VS OUTPUT SIGNALS AND DISTORTIONS RELATIVE TO ONE TONE The method of making the measurement is to insert two closely spaced equal level carriers into the device under test. The distortion products are then measured and compared with the level of one of the signals. The graphic representation of the distortions is valuable because it allows insight into the behavior of the distortion products. If the signal levels are 20 db below the third order intercept point, then the third order distortion will be 40 db below the signal. MATRIX TEST EQUIPMENT, INC. MTN-109 October 10, 2005 Page 2/9
3 In a similar way it is obvious that if the signal levels are 20 db below the second order intercept point, then the second order distortion will be 20 db below the signal. It is also possible to measure the third order intercept point by using 3 frequencies instead of 2. Actually there are advantages to using 3 frequencies because the products will be stronger by 6 db. If third order measurements are made using 3 frequencies, the magnitude of the products must be reduced by 6 db in order to agree with the common definition of Third Order Intercept. MULTIPLE CARRIERS If we now consider the case of many carriers in a broadband system, the problem becomes more complicated. Consider a CATV system with many equally spaced carriers. Now we note that the distortion products 2A - B and 2B - A are no longer important. This is because there are fewer of them and they are one half the amplitude (- 6 db) of the now dominant distortion products, A + / - B + / - C, where A < B < C. (See MATRIX TECHNICAL NOTE MTN-108) These beats are referred to as COMPOSITE TRIPLE BEAT or COMPOSITE THIRD ORDER distortions. They are named composite distortions because they are made up of a composite of discrete distortions. They fall in a narrow range of frequencies near the carrier frequency and are measured as a group. The carriers are assumed spaced by some frequency (usually 6 MHz) and are not coherent. If they were coherent (or phase locked) the beats would also be coherent. The frequency variation of the carriers, which is on the order of a few KHz, causes the beats to have a band-spread of about 20 KHz. The spectrum of the beats resembles noise because it is made up of many carriers. In general the power in the composite of the beats is the sum of all the power in the individual beats. It is only necessary to find the power on one distortion beat and the total number of beats to determine the composite beat. MATRIX TEST EQUIPMENT, INC. MTN-109 October 10, 2005 Page 3/9
4 COMPOSITE THIRD ORDER DISTORTION For equally spaced carriers, the total number of composite distortion products of the A +/- B + /- C variety can be closely approximated by; Number of beats (mid band) = 3N 2 /8 Number of beats (band edge) = N 2 /4 The beats that dominate multiple channel systems are the A +/- B +/- C beats because these beats are 6 db stronger than the 2A - B and 2B - A beats. Consider the following example, an amplifier is operating with 20 channels with the level of each carrier 40 db below the intercept point. We know from our definition of intercept point that the 2A - B distortions must be 80 db below carriers and the A +/- B +/- C distortions must be 80+6 = 74 db or 74 db below the carrier. We also know that in the middle of the band, there are 3N 2 /8 distortion beats. For example if: N=20 Number of beats (mid band) = 3N 2 /8 = 150 = db (in terms of power ratio) We can assume that all the distortion beats have the same amplitude and will add as powers. In the example above the A +/- B +/ - C products were 74 db below the carrier but we have 150 of them and if they add as powers then the CTB will be = db, this is db below the carrier. In general: (1) CTB(dB) = -2(P i - P s )db + 6dB + 10 LOG (3N 2 /8)dB Mid band This can also be written as: (2) CTB(dB) = -2(P i - P s )db dB +20 LOG(N)dB Mid band (3) CTB(dB) = 2(P i - P s )db + 20 LOG (N)dB Band edge MATRIX TEST EQUIPMENT, INC. MTN-109 October 10, 2005 Page 4/9
5 CTB = Composite third order distortion (db) P i = Power level at the third order intercept point (dbm) P s = Power level of each carrier (dbm) N = Total number of carries COMPOSITE THIRD ORDER DISTORTION AND TOTAL SIGNAL POWER At times it will be useful to calculate CTB products considering the total signal power input as opposed to the single carrier power. We may write: (4) P T = Total Power = P s dbm + 10 LOG (N) db (5) P s = P T - 10 LOG (N) db From (2) we may write: (6) CTB(dB) = -2(P i +P T 10 LOG(N )db dB + 20 LOG (N)dB For a flat input spectrum (7) CTB(dB) = -2(P i - P T )db db Band Center and (8) CTB(dB) = -2(P i - P T )db Band Edge We note that the CTB is independent of the number of carriers but related only to the total power of the carriers. For CW signals: EXAMPLES MATRIX TEST EQUIPMENT, INC. MTN-109 October 10, 2005 Page 5/9
6 Number of CW carriers 100 Power of each carrier -25 dbm Third order Intercept Point +20 dbm With 100 carriers each with 25 dbm, the total power is: (9) P T = -25dBm + 10 LOG (100) (10) P T = -5 dbm From (7) the CTB at Mid Band would be: (11) CTB(dB) = - 2(P i - P T )db dB (12) CTB(dB) = -2(20 - ( -5 ))db +1.74dB= Mid Band NOISE POWER RATIO Noise Power Ratio is a method of measuring the intermodulation distortion by using shaped high level noise as a substitute for multiple carriers. This is used in conjunction with a narrow band notch filter. Intermodulation products result in excess noise at the notch frequency. The measurement of the ratio of the flat noise to the noise in the notch is a useful measure. If we extend the above analysis by increasing the number of carriers, the input spectrum eventually approaches the spectrum of band limited Gaussian noise. Now instead of dealing with carrier power we will use Noise Power Density (dbm/hz). (13) P T (dbm) = Input noise power density(dbm/hz) +10 LOG( Bandwidth in Hz) (14) CTB(dB) = -2(P i (dbm) - P T (dbm)) +1.74dB Mid Band COMPOSITE SECOND ORDER DISTORTION MATRIX TEST EQUIPMENT, INC. MTN-109 October 10, 2005 Page 6/9
7 It is now obvious that a similar approach can be used to calculate the composite second order (CSO) distortion from the second order intercept point. Using the relations found in MATRIX TECHNICAL NOTE MTN -108 Number of beats (Below carrier) = N(1 - (f/(f H - f L + d))) Number of beats (Above carrier) = (N - 1)(f - 2f L - d)/(f H - f L - d) In general: (15) CSO(dB) = - (P i - P s )db + 10 LOG(Number of Distortion products)db P i P s N f f H f L d = Power level at the second order intercept point (dbm) = Power level of each carrier (dbm) = Number of carriers = Frequency of distortion product in MHz = Frequency of highest channel in MHz = Frequency of lowest channel in MHz = Frequency separation between channels in MHz There are far fewer second order beats than third order beats but the magnitude of each beat may be stronger that the third order beat. In most high quality amplifiers push-pull circuits are used to reduce the second order distortion. This has the result of increasing the level of the second order intercept point but does not alter its slope. CROSSMODULATION MATRIX TEST EQUIPMENT, INC. MTN-109 October 10, 2005 Page 7/9
8 X-MOD or crossmodulation is a third order distortion that is also related to the third order intercept point. It can also be considered a composite distortion similar to CSO and CTB. Here the reference calibration level is not the carrier but the level of the fully modulated sideband. Further consideration must be given to the fact that the crossmodulation distortion products are coherent and add as voltages and that each carrier generates two products. Crossmodulation, which can also result from other effects, here are assumed to be the result of only the third order nonlinearity determined by the intercept point. (16) X-MOD= -2(P i - P s )db +6dB + 20 LOG(N)dB For comparison from (1) X-MOD = Crossmodulation below 100% modulation (db) P i = Power level at the third order intercept point (dbm) P s = Power level of each carrier (dbm) N = Total number of carriers (17) CTB(dB) = -2(P i - P s )db + 6dB + 10 LOG (3N 2 /8)dB Mid band (18) CTB(dB) = -2(P i - P s )db dB + 20 LOG (N)dB Mid band Note that the X-MOD distortion is independent of the carrier frequency and at band center, the crossmodulation is 4.26 higher (poorer) than the CTB. However the measured CTB will be 2.5 db lower because of the measurement error of the spectrum analyzer. See the following paragraph. The net result is that the measured X-MOD will measure greater that the CTB by: 2.5 db dB or 6.76dB. MATRIX TEST EQUIPMENT, INC. MTN-109 October 10, 2005 Page 8/9
9 POSSIBLE SOURCES OF ERROR It is now important to emphasize some of the problems related to the measurement of CSO, CTB, and crossmodulation. The common method of making composite distortion measurements uses a spectrum analyzer operating in the LOG display mode. In this mode, spectrum analyzers measure noise and noise-like signals in error. They measure noise as approximately 2.5 db weaker than the actual power. The spectrum analyzer method has become the "definition" of the distortion. This may result in discrepancies among the measuring methods. Great caution is required when correlating or interpreting measurements by other methods. Crossmodulation measurements can also be a problem. Using a spectrum analyzer to measure the distortion sidebands directly can result in large errors. The desired measurement is actually amplitude crossmodulation. Many active devices generate phase crossmodulation with magnitudes that are 30 db above the amplitude crossmodulation. The spectrum analyzer can not differentiate between the amplitude and phase sidebands and as a result great measurement errors can occur. There are several valid methods for measuring crossmodulation, one is covered in MTN-110. The equations used for calculating the distortion products were derived by Dr. Thomas B. Warren. Interpretations, opinions, explanations and other errors are the responsibility of Jack Kouzoujian, Matrix Test Equipment Inc. MATRIX TEST EQUIPMENT, INC. MTN-109 October 10, 2005 Page 9/9
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters
 High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
COMPUTER ASSISTED RF PERFORMANCE TESTING. Warner Amex Cable Communications Inc Plainfield, NJ
 COMPUTER ASSISTED RF PERFORMANCE TESTING Jeck Koscinski Director of Product Engineering Dan Earley Staff Engineer Warner Amex Cable Communications Inc Plainfield, NJ ABSTRACT Evaluating the RF performance
COMPUTER ASSISTED RF PERFORMANCE TESTING Jeck Koscinski Director of Product Engineering Dan Earley Staff Engineer Warner Amex Cable Communications Inc Plainfield, NJ ABSTRACT Evaluating the RF performance
Measuring 3rd order Intercept Point (IP3 / TOI) of an amplifier
 Measuring 3rd order Intercept Point (IP3 / TOI) of an amplifier Why measuring IP3 / TOI? IP3 is an important parameter for nonlinear systems like mixers or amplifiers which helps to verify the quality
Measuring 3rd order Intercept Point (IP3 / TOI) of an amplifier Why measuring IP3 / TOI? IP3 is an important parameter for nonlinear systems like mixers or amplifiers which helps to verify the quality
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 115 2011 Test Method for Reverse Path (Upstream) Intermodulation Using Two Carriers NOTICE The Society of Cable
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 115 2011 Test Method for Reverse Path (Upstream) Intermodulation Using Two Carriers NOTICE The Society of Cable
Broadband System - J
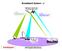 Broadband System - J Satellites are spaced every 2nd degrees above earth "C" Band Toward satellite 6.0 GHz Toward earth 4.0 GHz "L" Band Toward satellite 14.0 GHz Toward earth 12.0 GHz TV TRANSMITTER Headend
Broadband System - J Satellites are spaced every 2nd degrees above earth "C" Band Toward satellite 6.0 GHz Toward earth 4.0 GHz "L" Band Toward satellite 14.0 GHz Toward earth 12.0 GHz TV TRANSMITTER Headend
QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A 40MHZ TO 900MHZ DIRECT CONVERSION QUADRATURE DEMODULATOR
 DESCRIPTION QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A LT5517 Demonstration circuit 678A is a 40MHz to 900MHz Direct Conversion Quadrature Demodulator featuring the LT5517. The LT 5517 is a direct
DESCRIPTION QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A LT5517 Demonstration circuit 678A is a 40MHz to 900MHz Direct Conversion Quadrature Demodulator featuring the LT5517. The LT 5517 is a direct
Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance
 Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance Mixer Terms Defined Statistical Processing Applied to Mixers Today's stringent demands for precise electronic systems place a heavy burden
Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance Mixer Terms Defined Statistical Processing Applied to Mixers Today's stringent demands for precise electronic systems place a heavy burden
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
C. Mixers. frequencies? limit? specifications? Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device.
 9/13/2007 Mixers notes 1/1 C. Mixers Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device. HO: Mixers Q: How efficient is a typical mixer at creating signals
9/13/2007 Mixers notes 1/1 C. Mixers Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device. HO: Mixers Q: How efficient is a typical mixer at creating signals
Measuring Non-linear Amplifiers
 Measuring Non-linear Amplifiers Transceiver Components & Measuring Techniques MM3 Jan Hvolgaard Mikkelsen Radio Frequency Integrated Systems and Circuits Division Aalborg University 27 Agenda Non-linear
Measuring Non-linear Amplifiers Transceiver Components & Measuring Techniques MM3 Jan Hvolgaard Mikkelsen Radio Frequency Integrated Systems and Circuits Division Aalborg University 27 Agenda Non-linear
PARAMETER CONDITIONS TYPICAL PERFORMANCE Operating Supply Voltage 3.1V to 3.5V Supply Current V CC = 3.3V, LO applied 152mA
 DESCRIPTION LT5578 Demonstration circuit 1545A-x is a high linearity upconverting mixer featuring the LT5578. The LT 5578 is a high performance upconverting mixer IC optimized for output frequencies in
DESCRIPTION LT5578 Demonstration circuit 1545A-x is a high linearity upconverting mixer featuring the LT5578. The LT 5578 is a high performance upconverting mixer IC optimized for output frequencies in
Keysight Technologies Pulsed Antenna Measurements Using PNA Network Analyzers
 Keysight Technologies Pulsed Antenna Measurements Using PNA Network Analyzers White Paper Abstract This paper presents advances in the instrumentation techniques that can be used for the measurement and
Keysight Technologies Pulsed Antenna Measurements Using PNA Network Analyzers White Paper Abstract This paper presents advances in the instrumentation techniques that can be used for the measurement and
Keysight Technologies Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range. Application Note
 Keysight Technologies Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range Application Note 02 Keysight Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range Application Note 1. Introduction
Keysight Technologies Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range Application Note 02 Keysight Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range Application Note 1. Introduction
Application Note 106 IP2 Measurements of Wideband Amplifiers v1.0
 Application Note 06 v.0 Description Application Note 06 describes the theory and method used by to characterize the second order intercept point (IP 2 ) of its wideband amplifiers. offers a large selection
Application Note 06 v.0 Description Application Note 06 describes the theory and method used by to characterize the second order intercept point (IP 2 ) of its wideband amplifiers. offers a large selection
ULTRALINEAR SUPER TRUNK AMPLIFIERS
 ULTRALINEAR SUPER TRUNK AMPLIFIERS Oleg Borisov Panagiev Department of Radiocommunications, Technical University of Sofia, Bulgaria 8 Kl. Ohridski Blvd, 1000 Sofia, tel. 02 965 2284, e-mail: olcomol@yahoo.com
ULTRALINEAR SUPER TRUNK AMPLIFIERS Oleg Borisov Panagiev Department of Radiocommunications, Technical University of Sofia, Bulgaria 8 Kl. Ohridski Blvd, 1000 Sofia, tel. 02 965 2284, e-mail: olcomol@yahoo.com
Keysight Technologies Making Accurate Intermodulation Distortion Measurements with the PNA-X Network Analyzer, 10 MHz to 26.5 GHz
 Keysight Technologies Making Accurate Intermodulation Distortion Measurements with the PNA-X Network Analyzer, 10 MHz to 26.5 GHz Application Note Overview This application note describes accuracy considerations
Keysight Technologies Making Accurate Intermodulation Distortion Measurements with the PNA-X Network Analyzer, 10 MHz to 26.5 GHz Application Note Overview This application note describes accuracy considerations
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE Measurement Procedure for Noise Power Ratio
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 119 2006 Measurement Procedure for Noise Power Ratio NOTICE The Society of Cable Telecommunications Engineers
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 119 2006 Measurement Procedure for Noise Power Ratio NOTICE The Society of Cable Telecommunications Engineers
HF Receivers, Part 2
 HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
LINEAR MICROWAVE FIBER OPTIC LINK SYSTEM DESIGN
 LINEAR MICROWAVE FIBER OPTIC LINK SYSTEM DESIGN John A. MacDonald and Allen Katz Linear Photonics, LLC Nami Lane, Suite 7C, Hamilton, NJ 869 69-584-5747 macdonald@linphotonics.com LINEAR PHOTONICS, LLC
LINEAR MICROWAVE FIBER OPTIC LINK SYSTEM DESIGN John A. MacDonald and Allen Katz Linear Photonics, LLC Nami Lane, Suite 7C, Hamilton, NJ 869 69-584-5747 macdonald@linphotonics.com LINEAR PHOTONICS, LLC
Agilent AN How to Characterize CATV Amplifiers Effectively
 Agilent AN 1288-4 How to Characterize CATV Amplifiers Effectively Application Note Using the Agilent 4396B RF Network/Spectrum/ Impedance Analyzer Page Contents 3 Introduction 3 1. CATV System Configuration
Agilent AN 1288-4 How to Characterize CATV Amplifiers Effectively Application Note Using the Agilent 4396B RF Network/Spectrum/ Impedance Analyzer Page Contents 3 Introduction 3 1. CATV System Configuration
Satellite Communications: Part 4 Signal Distortions & Errors and their Relation to Communication Channel Specifications. Howard Hausman April 1, 2010
 Satellite Communications: Part 4 Signal Distortions & Errors and their Relation to Communication Channel Specifications Howard Hausman April 1, 2010 Satellite Communications: Part 4 Signal Distortions
Satellite Communications: Part 4 Signal Distortions & Errors and their Relation to Communication Channel Specifications Howard Hausman April 1, 2010 Satellite Communications: Part 4 Signal Distortions
QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 1455A 5MHZ TO 1600MHZ HIGH LINEARITY DIRECT QUADRATURE MODULATOR LTC5598 DESCRIPTION
 LTC5598 DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuit 1455A is a high linearity direct quadrature modulator featuring the LTC5598. The LTC 5598 is a direct I/Q modulator designed for high performance wireless applications,
LTC5598 DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuit 1455A is a high linearity direct quadrature modulator featuring the LTC5598. The LTC 5598 is a direct I/Q modulator designed for high performance wireless applications,
Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper
 Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
The Schottky Diode Mixer. Application Note 995
 The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
3.2 Measuring Frequency Response Of Low-Pass Filter :
 2.5 Filter Band-Width : In ideal Band-Pass Filters, the band-width is the frequency range in Hz where the magnitude response is at is maximum (or the attenuation is at its minimum) and constant and equal
2.5 Filter Band-Width : In ideal Band-Pass Filters, the band-width is the frequency range in Hz where the magnitude response is at is maximum (or the attenuation is at its minimum) and constant and equal
MEASURING HUM MODULATION USING MATRIX MODEL HD-500 HUM DEMODULATOR
 MEASURING HUM MODULATION USING MATRIX MODEL HD-500 HUM DEMODULATOR The SCTE defines hum modulation as, The amplitude distortion of a signal caused by the modulation of the signal by components of the power
MEASURING HUM MODULATION USING MATRIX MODEL HD-500 HUM DEMODULATOR The SCTE defines hum modulation as, The amplitude distortion of a signal caused by the modulation of the signal by components of the power
ECE 440L. Experiment 1: Signals and Noise (1 week)
 ECE 440L Experiment 1: Signals and Noise (1 week) I. OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this experiment, you should be able to: 1. Use the signal generators and filters in the lab to generate and filter noise
ECE 440L Experiment 1: Signals and Noise (1 week) I. OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this experiment, you should be able to: 1. Use the signal generators and filters in the lab to generate and filter noise
INSTALLATION MANUAL. CTA-30RK-550 Rack Mount Distribution Amplifier
 INSTALLATION MANUAL CTA-30RK-550 Rack Mount Distribution Amplifier 1 PACKAGE CONTENTS This package contains: One CTA-30RK-550 Rack Mount Distribution Amplifier One CTA-30RK-550 instruction manual PRODUCT
INSTALLATION MANUAL CTA-30RK-550 Rack Mount Distribution Amplifier 1 PACKAGE CONTENTS This package contains: One CTA-30RK-550 Rack Mount Distribution Amplifier One CTA-30RK-550 instruction manual PRODUCT
RFPD2650 GaAs/GaN Power Doubler Hybrid 45MHz to 1003MHz
 GaAs/GaN Power Doubler Hybrid 45MHz to 1003MHz The RFPD2650 is a Hybrid Power Doubler amplifier module. The part employs GaAs phemt die and GaN HEMT die, has extremely high output capability, and is operated
GaAs/GaN Power Doubler Hybrid 45MHz to 1003MHz The RFPD2650 is a Hybrid Power Doubler amplifier module. The part employs GaAs phemt die and GaN HEMT die, has extremely high output capability, and is operated
Academic and Research Staff. Prof. P. L. Penfield, Jr. Prof. D. H. Steinbrecher. Graduate Students
 II. SOLID-STATE MICROWAVE ELECTRONICS Academic and Research Staff Prof. P. L. Penfield, Jr. Prof. D. H. Steinbrecher Graduate Students E. L. Caples R. H. S. Kwong D. F. Peterson A. Chu H. Po A. INTERMODULATION
II. SOLID-STATE MICROWAVE ELECTRONICS Academic and Research Staff Prof. P. L. Penfield, Jr. Prof. D. H. Steinbrecher Graduate Students E. L. Caples R. H. S. Kwong D. F. Peterson A. Chu H. Po A. INTERMODULATION
PXIe Contents SPECIFICATIONS. 14 GHz and 26.5 GHz Vector Signal Analyzer
 SPECIFICATIONS PXIe-5668 14 GHz and 26.5 GHz Vector Signal Analyzer These specifications apply to the PXIe-5668 (14 GHz) Vector Signal Analyzer and the PXIe-5668 (26.5 GHz) Vector Signal Analyzer with
SPECIFICATIONS PXIe-5668 14 GHz and 26.5 GHz Vector Signal Analyzer These specifications apply to the PXIe-5668 (14 GHz) Vector Signal Analyzer and the PXIe-5668 (26.5 GHz) Vector Signal Analyzer with
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture
 RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD
 Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Measurement Procedure for Noise Power Ratio NOTICE The Society of Cable Telecommunications Engineers (SCTE) / International Society of Broadband
Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Measurement Procedure for Noise Power Ratio NOTICE The Society of Cable Telecommunications Engineers (SCTE) / International Society of Broadband
DIRECT MODULATION WITH SIDE-MODE INJECTION IN OPTICAL CATV TRANSPORT SYSTEMS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 73 82, 2009 DIRECT MODULATION WITH SIDE-MODE INJECTION IN OPTICAL CATV TRANSPORT SYSTEMS W.-J. Ho, H.-H. Lu, C.-H. Chang, W.-Y. Lin, and H.-S. Su
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 73 82, 2009 DIRECT MODULATION WITH SIDE-MODE INJECTION IN OPTICAL CATV TRANSPORT SYSTEMS W.-J. Ho, H.-H. Lu, C.-H. Chang, W.-Y. Lin, and H.-S. Su
Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection
 Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection Aim: overview of existing methods and techniques Terms used: -Data entities conveying meaning (of information) -Signals data
Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection Aim: overview of existing methods and techniques Terms used: -Data entities conveying meaning (of information) -Signals data
Measuring ACPR of W-CDMA signals with a spectrum analyzer
 Measuring ACPR of W-CDMA signals with a spectrum analyzer When measuring power in the adjacent channels of a W-CDMA signal, requirements for the dynamic range of a spectrum analyzer are very challenging.
Measuring ACPR of W-CDMA signals with a spectrum analyzer When measuring power in the adjacent channels of a W-CDMA signal, requirements for the dynamic range of a spectrum analyzer are very challenging.
Noise and Distortion in Microwave System
 Noise and Distortion in Microwave System Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 1 Introduction Noise is a random process from many sources: thermal,
Noise and Distortion in Microwave System Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 1 Introduction Noise is a random process from many sources: thermal,
RF, Microwave & Wireless. All rights reserved
 RF, Microwave & Wireless All rights reserved 1 Non-Linearity Phenomenon All rights reserved 2 Physical causes of nonlinearity Operation under finite power-supply voltages Essential non-linear characteristics
RF, Microwave & Wireless All rights reserved 1 Non-Linearity Phenomenon All rights reserved 2 Physical causes of nonlinearity Operation under finite power-supply voltages Essential non-linear characteristics
INLAND CHAPTER OF THE SCTE
 INLAND CHAPTER OF THE SCTE DISTORTION IN THE DIGITAL WORLD Prepared By: Ted Chesley NW Tech Ops Mgr Time Warner Cable Portland, OR SCTE Vendor Show June 28, 2011 OVERVIEW As the CATV industry moves deeper
INLAND CHAPTER OF THE SCTE DISTORTION IN THE DIGITAL WORLD Prepared By: Ted Chesley NW Tech Ops Mgr Time Warner Cable Portland, OR SCTE Vendor Show June 28, 2011 OVERVIEW As the CATV industry moves deeper
APPLICATION NOTE 3942 Optimize the Buffer Amplifier/ADC Connection
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Communications Circuits > APP 3942 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > High-Speed Interconnect > APP 3942
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Communications Circuits > APP 3942 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > High-Speed Interconnect > APP 3942
Keysight Technologies 8 Hints for Making Better Measurements Using RF Signal Generators. Application Note
 Keysight Technologies 8 Hints for Making Better Measurements Using RF Signal Generators Application Note 02 Keysight 8 Hints for Making Better Measurements Using RF Signal Generators - Application Note
Keysight Technologies 8 Hints for Making Better Measurements Using RF Signal Generators Application Note 02 Keysight 8 Hints for Making Better Measurements Using RF Signal Generators - Application Note
Frequency-Dependent Distortion Mechanism in a Broadband Amplifier
 Frequency-Dependent Distortion Mechanism in a Broadband Amplifier Jodi Steel, Anthony Parker Electronics Department, Macquarie University, Australia jodis, tonyp@ieee.org March 25, 1999 Abstract Investigation
Frequency-Dependent Distortion Mechanism in a Broadband Amplifier Jodi Steel, Anthony Parker Electronics Department, Macquarie University, Australia jodis, tonyp@ieee.org March 25, 1999 Abstract Investigation
DATA SHEET. BGY785A 750 MHz, 18.5 db gain push-pull amplifier DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS. Product specification Supersedes data of 1999 Mar 30
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D252 BGY785A 750 MHz, 18.5 db gain push-pull amplifier Supersedes data of 1999 Mar 30 2001 Nov 15 FEATURES Excellent linearity Extremely low noise Silicon
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D252 BGY785A 750 MHz, 18.5 db gain push-pull amplifier Supersedes data of 1999 Mar 30 2001 Nov 15 FEATURES Excellent linearity Extremely low noise Silicon
 HF Receiver Testing: Issues & Advances (also presented at APDXC 2014, Osaka, Japan, November 2014) Adam Farson VA7OJ Copyright 2014 North Shore Amateur Radio Club NSARC HF Operators HF RX Testing 1 HF
HF Receiver Testing: Issues & Advances (also presented at APDXC 2014, Osaka, Japan, November 2014) Adam Farson VA7OJ Copyright 2014 North Shore Amateur Radio Club NSARC HF Operators HF RX Testing 1 HF
CPD POINTER PNM ENABLED CPD DETECTION FOR THE HFC NETWORK WHITE PAPER ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY
 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY CPD POINTER PNM ENABLED CPD DETECTION FOR THE HFC NETWORK WHITE PAPER 185 AINSLEY DRIVE SYRACUSE, NY 13210 800.448.1655 I WWW.ARCOMDIGITAL.COM The continued evolution of Proactive Network
ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY CPD POINTER PNM ENABLED CPD DETECTION FOR THE HFC NETWORK WHITE PAPER 185 AINSLEY DRIVE SYRACUSE, NY 13210 800.448.1655 I WWW.ARCOMDIGITAL.COM The continued evolution of Proactive Network
INTRODUCTION. LPL App Note RF IN G 1 F 1. Laser Diode OPTICAL OUT. P out. Link Length. P in OPTICAL IN. Photodiode G 2 F 2 RF OUT
 INTRODUCTION RF IN Today s system designer may be faced with several technology choices for communications links for satellite microwave remoting, cellular/broadband services, or distribution of microwave
INTRODUCTION RF IN Today s system designer may be faced with several technology choices for communications links for satellite microwave remoting, cellular/broadband services, or distribution of microwave
C/N Ratio at Low Carrier Frequencies in SFQ
 Application Note C/N Ratio at Low Carrier Frequencies in SFQ Products: TV Test Transmitter SFQ 7BM09_0E C/N ratio at low carrier frequencies in SFQ Contents 1 Preliminaries... 3 2 Description of Ranges...
Application Note C/N Ratio at Low Carrier Frequencies in SFQ Products: TV Test Transmitter SFQ 7BM09_0E C/N ratio at low carrier frequencies in SFQ Contents 1 Preliminaries... 3 2 Description of Ranges...
Some Aspects Regarding the Measurement of the Adjacent Channel Interference for Frequency Hopping Radio Systems
 Some Aspects Regarding the Measurement of the Adjacent Channel Interference for Frequency Hopping Radio Systems PAUL BECHET, RADU MITRAN, IULIAN BOULEANU, MIRCEA BORA Communications and Information Systems
Some Aspects Regarding the Measurement of the Adjacent Channel Interference for Frequency Hopping Radio Systems PAUL BECHET, RADU MITRAN, IULIAN BOULEANU, MIRCEA BORA Communications and Information Systems
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY
 Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
HP Archive. This vintage Hewlett Packard document was preserved and distributed by www. hparchive.com Please visit us on the web!
 HP Archive This vintage Hewlett Packard document was preserved and distributed by www. hparchive.com Please visit us on the web! On-line curator: Glenn Robb This document is for FREE distribution only!
HP Archive This vintage Hewlett Packard document was preserved and distributed by www. hparchive.com Please visit us on the web! On-line curator: Glenn Robb This document is for FREE distribution only!
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
Complex Sounds. Reading: Yost Ch. 4
 Complex Sounds Reading: Yost Ch. 4 Natural Sounds Most sounds in our everyday lives are not simple sinusoidal sounds, but are complex sounds, consisting of a sum of many sinusoids. The amplitude and frequency
Complex Sounds Reading: Yost Ch. 4 Natural Sounds Most sounds in our everyday lives are not simple sinusoidal sounds, but are complex sounds, consisting of a sum of many sinusoids. The amplitude and frequency
Contents. CALIBRATION PROCEDURE NI PXIe GHz and 14 GHz RF Vector Signal Analyzer
 CALIBRATION PROCEDURE NI PXIe-5665 3.6 GHz and 14 GHz RF Vector Signal Analyzer This document contains the verification procedures for the National Instruments PXIe-5665 (NI 5665) RF vector signal analyzer
CALIBRATION PROCEDURE NI PXIe-5665 3.6 GHz and 14 GHz RF Vector Signal Analyzer This document contains the verification procedures for the National Instruments PXIe-5665 (NI 5665) RF vector signal analyzer
Optical Single Sideband Modulation and Optical Carrier Power Reduction and CATV Networks
 Optical Single Sideband Modulation and Optical Carrier Power Reduction and CATV Networks by: Hatice Kosek Outline Optical Single Sideband Modulation Techniques Optical Carrier Power Reduction Techniques
Optical Single Sideband Modulation and Optical Carrier Power Reduction and CATV Networks by: Hatice Kosek Outline Optical Single Sideband Modulation Techniques Optical Carrier Power Reduction Techniques
Michael F. Toner, et. al.. "Distortion Measurement." Copyright 2000 CRC Press LLC. <
 Michael F. Toner, et. al.. "Distortion Measurement." Copyright CRC Press LLC. . Distortion Measurement Michael F. Toner Nortel Networks Gordon W. Roberts McGill University 53.1
Michael F. Toner, et. al.. "Distortion Measurement." Copyright CRC Press LLC. . Distortion Measurement Michael F. Toner Nortel Networks Gordon W. Roberts McGill University 53.1
PXIe Contents CALIBRATION PROCEDURE. Reconfigurable 6 GHz RF Vector Signal Transceiver with 200 MHz Bandwidth
 IBRATION PROCEDURE PXIe-5646 Reconfigurable 6 GHz Vector Signal Transceiver with 200 MHz Bandwidth This document contains the verification and adjustment procedures for the PXIe-5646 vector signal transceiver.
IBRATION PROCEDURE PXIe-5646 Reconfigurable 6 GHz Vector Signal Transceiver with 200 MHz Bandwidth This document contains the verification and adjustment procedures for the PXIe-5646 vector signal transceiver.
UNIT 2. Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator. Ans. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
NEW HFC OPTIMIZATION PARADIGM FOR THE DIGITAL ERA. Jan de Nijs (TNO), Jeroen Boschma (TNO), Maciej Muzalewski (VECTOR) and Pawel Meissner (VECTOR)
 NEW HFC OPTIMIZATION PARADIGM FOR THE DIGITAL ERA Jan de Nijs (TNO), Jeroen Boschma (TNO), Maciej Muzalewski (VECTOR) and Pawel Meissner (VECTOR) Abstract A cost-effective way to expand the capacity of
NEW HFC OPTIMIZATION PARADIGM FOR THE DIGITAL ERA Jan de Nijs (TNO), Jeroen Boschma (TNO), Maciej Muzalewski (VECTOR) and Pawel Meissner (VECTOR) Abstract A cost-effective way to expand the capacity of
amplifiers Phoenix Communication Technologies AMPLIFIERS PAGE DROP AMPLIFIERS DISTRIBUTION AMPLIFIER
 Phoenix Communication Technologies AMPLIFIERS DROP AMPLIFIERS DISTRIBUTION AMPLIFIER PAGE C2 C7 07-2001 ANDES Industries, Inc. C2 drop f e a t u r e s 6 kv surge withstand on each port 1, 2, or 4-port
Phoenix Communication Technologies AMPLIFIERS DROP AMPLIFIERS DISTRIBUTION AMPLIFIER PAGE C2 C7 07-2001 ANDES Industries, Inc. C2 drop f e a t u r e s 6 kv surge withstand on each port 1, 2, or 4-port
Making Noise in RF Receivers Simulate Real-World Signals with Signal Generators
 Making Noise in RF Receivers Simulate Real-World Signals with Signal Generators Noise is an unwanted signal. In communication systems, noise affects both transmitter and receiver performance. It degrades
Making Noise in RF Receivers Simulate Real-World Signals with Signal Generators Noise is an unwanted signal. In communication systems, noise affects both transmitter and receiver performance. It degrades
Noise by the Numbers
 Noise by the Numbers 1 What can I do with noise? The two primary applications for white noise are signal jamming/impairment and reference level comparison. Signal jamming/impairment is further divided
Noise by the Numbers 1 What can I do with noise? The two primary applications for white noise are signal jamming/impairment and reference level comparison. Signal jamming/impairment is further divided
Appendix. Harmonic Balance Simulator. Page 1
 Appendix Harmonic Balance Simulator Page 1 Harmonic Balance for Large Signal AC and S-parameter Simulation Harmonic Balance is a frequency domain analysis technique for simulating distortion in nonlinear
Appendix Harmonic Balance Simulator Page 1 Harmonic Balance for Large Signal AC and S-parameter Simulation Harmonic Balance is a frequency domain analysis technique for simulating distortion in nonlinear
Contents. CALIBRATION PROCEDURE NI PXIe-5668R 14 GHz and 26.5 GHz Signal Analyzer
 CALIBRATION PROCEDURE NI PXIe-5668R 14 GHz and 26.5 GHz Signal Analyzer This document contains the verification procedures for the National Instruments PXIe-5668R (NI 5668R) vector signal analyzer (VSA)
CALIBRATION PROCEDURE NI PXIe-5668R 14 GHz and 26.5 GHz Signal Analyzer This document contains the verification procedures for the National Instruments PXIe-5668R (NI 5668R) vector signal analyzer (VSA)
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM)
 Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
FCC ID: A3LSLS-BD106Q. Report No.: HCT-RF-1801-FC003. Plot Data for Output Port 2_QPSK 9 khz ~ 150 khz Middle channel 150 khz ~ 30 MHz Low channel
 Plot Data for Output Port 2_QPSK 9 khz ~ 150 khz Middle channel 150 khz ~ 30 MHz Low channel 30 MHz ~ 1 GHz Middle channel 1 GHz ~ 2.491 GHz Low channel 2.695 GHz ~ 12.75 GHz High channel 12.75 GHz ~ 26.5
Plot Data for Output Port 2_QPSK 9 khz ~ 150 khz Middle channel 150 khz ~ 30 MHz Low channel 30 MHz ~ 1 GHz Middle channel 1 GHz ~ 2.491 GHz Low channel 2.695 GHz ~ 12.75 GHz High channel 12.75 GHz ~ 26.5
Measurement of Distortion in Multi-tone Modulation Fiber-based analog CATV Transmission System
 5 th SASTech 011, Khavaran Higher-education Institute, Mashhad, Iran. May 1-14. 1 Measurement of Distortion in Multi-tone Modulation Fiber-based analog CATV Transmission System Morteza Abdollahi Sharif
5 th SASTech 011, Khavaran Higher-education Institute, Mashhad, Iran. May 1-14. 1 Measurement of Distortion in Multi-tone Modulation Fiber-based analog CATV Transmission System Morteza Abdollahi Sharif
SECTION 7: FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS. MAE 3401 Modeling and Simulation
 SECTION 7: FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS MAE 3401 Modeling and Simulation 2 Response to Sinusoidal Inputs Frequency Domain Analysis Introduction 3 We ve looked at system impulse and step responses Also interested
SECTION 7: FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS MAE 3401 Modeling and Simulation 2 Response to Sinusoidal Inputs Frequency Domain Analysis Introduction 3 We ve looked at system impulse and step responses Also interested
Technical Article A DIRECT QUADRATURE MODULATOR IC FOR 0.9 TO 2.5 GHZ WIRELESS SYSTEMS
 Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
DATA SHEET. BGY MHz, 22 db gain push-pull amplifier DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS. Product specification Supersedes data of 1994 Feb 07.
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET ndbook, halfpage M3D252 BGY587 550 MHz, 22 db gain push-pull amplifier Supersedes data of 1994 Feb 07 2001 Nov 27 FEATURES Excellent linearity Extremely low noise Silicon
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET ndbook, halfpage M3D252 BGY587 550 MHz, 22 db gain push-pull amplifier Supersedes data of 1994 Feb 07 2001 Nov 27 FEATURES Excellent linearity Extremely low noise Silicon
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits. Module 7
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
SC5307A/SC5308A 100 khz to 6 GHz RF Downconverter. Datasheet SignalCore, Inc.
 SC5307A/SC5308A 100 khz to 6 GHz RF Downconverter Datasheet 2017 SignalCore, Inc. support@signalcore.com P RODUCT S PECIFICATIONS Definition of Terms The following terms are used throughout this datasheet
SC5307A/SC5308A 100 khz to 6 GHz RF Downconverter Datasheet 2017 SignalCore, Inc. support@signalcore.com P RODUCT S PECIFICATIONS Definition of Terms The following terms are used throughout this datasheet
Demo Circuit DC550A Quick Start Guide.
 May 12, 2004 Demo Circuit DC550A. Introduction Demo circuit DC550A demonstrates operation of the LT5514 IC, a DC-850MHz bandwidth open loop transconductance amplifier with high impedance open collector
May 12, 2004 Demo Circuit DC550A. Introduction Demo circuit DC550A demonstrates operation of the LT5514 IC, a DC-850MHz bandwidth open loop transconductance amplifier with high impedance open collector
Residual Phase Noise Measurement Extracts DUT Noise from External Noise Sources By David Brandon and John Cavey
 Residual Phase Noise easurement xtracts DUT Noise from xternal Noise Sources By David Brandon [david.brandon@analog.com and John Cavey [john.cavey@analog.com Residual phase noise measurement cancels the
Residual Phase Noise easurement xtracts DUT Noise from xternal Noise Sources By David Brandon [david.brandon@analog.com and John Cavey [john.cavey@analog.com Residual phase noise measurement cancels the
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 145 2013 Test Method for Second Harmonic Distortion of ives Using a Single Carrier NOTICE The Society of Cable
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 145 2013 Test Method for Second Harmonic Distortion of ives Using a Single Carrier NOTICE The Society of Cable
HD Radio FM Transmission. System Specifications
 HD Radio FM Transmission System Specifications Rev. G December 14, 2016 SY_SSS_1026s TRADEMARKS HD Radio and the HD, HD Radio, and Arc logos are proprietary trademarks of ibiquity Digital Corporation.
HD Radio FM Transmission System Specifications Rev. G December 14, 2016 SY_SSS_1026s TRADEMARKS HD Radio and the HD, HD Radio, and Arc logos are proprietary trademarks of ibiquity Digital Corporation.
Reconfigurable 6 GHz Vector Signal Transceiver with I/Q Interface
 SPECIFICATIONS PXIe-5645 Reconfigurable 6 GHz Vector Signal Transceiver with I/Q Interface Contents Definitions...2 Conditions... 3 Frequency...4 Frequency Settling Time... 4 Internal Frequency Reference...
SPECIFICATIONS PXIe-5645 Reconfigurable 6 GHz Vector Signal Transceiver with I/Q Interface Contents Definitions...2 Conditions... 3 Frequency...4 Frequency Settling Time... 4 Internal Frequency Reference...
An Investigation into the Effects of Sampling on the Loop Response and Phase Noise in Phase Locked Loops
 An Investigation into the Effects of Sampling on the Loop Response and Phase oise in Phase Locked Loops Peter Beeson LA Techniques, Unit 5 Chancerygate Business Centre, Surbiton, Surrey Abstract. The majority
An Investigation into the Effects of Sampling on the Loop Response and Phase oise in Phase Locked Loops Peter Beeson LA Techniques, Unit 5 Chancerygate Business Centre, Surbiton, Surrey Abstract. The majority
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering. Lecture 8 November 8, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University
 ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 8 November 8, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University System Noise Figure Signal S1 Noise N1 GAIN = G Signal G x S1 Noise G x (N1+No) Self Noise
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 8 November 8, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University System Noise Figure Signal S1 Noise N1 GAIN = G Signal G x S1 Noise G x (N1+No) Self Noise
Compact Model Fiber Deep Node 862 MHz with 42/54 MHz Split
 Optoelectronics Compact Model 90090 Fiber Deep Node 862 MHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The Scientific-Atlanta Compact Model 90090 Fiber Deep Node is a small, low-cost, 110V AC powered node that addresses
Optoelectronics Compact Model 90090 Fiber Deep Node 862 MHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The Scientific-Atlanta Compact Model 90090 Fiber Deep Node is a small, low-cost, 110V AC powered node that addresses
Noise Power Ratio the Analytical Way. Robert L. Howald Motorola Broadband Communications Sector
 Noise Power Ratio the Analytical Way Robert L. Howald Motorola Broadband Communications Sector Michael Aviles Motorola Broadband Communications Sector Introduction Noise power ratio (NPR) testing is a
Noise Power Ratio the Analytical Way Robert L. Howald Motorola Broadband Communications Sector Michael Aviles Motorola Broadband Communications Sector Introduction Noise power ratio (NPR) testing is a
Technician License Course Chapter 2. Lesson Plan Module 3 Modulation and Bandwidth
 Technician License Course Chapter 2 Lesson Plan Module 3 Modulation and Bandwidth The Basic Radio Station What Happens During Radio Communication? Transmitting (sending a signal): Information (voice, data,
Technician License Course Chapter 2 Lesson Plan Module 3 Modulation and Bandwidth The Basic Radio Station What Happens During Radio Communication? Transmitting (sending a signal): Information (voice, data,
VHF LAND MOBILE SERVICE
 RFS21 December 1991 (Issue 1) SPECIFICATION FOR RADIO APPARATUS: VHF LAND MOBILE SERVICE USING AMPLITUDE MODULATION WITH 12.5 khz CARRIER FREQUENCY SEPARATION Communications Division Ministry of Commerce
RFS21 December 1991 (Issue 1) SPECIFICATION FOR RADIO APPARATUS: VHF LAND MOBILE SERVICE USING AMPLITUDE MODULATION WITH 12.5 khz CARRIER FREQUENCY SEPARATION Communications Division Ministry of Commerce
Technical Note. HVM Receiver Noise Figure Measurements
 Technical Note HVM Receiver Noise Figure Measurements Joe Kelly, Ph.D. Verigy 1/13 Abstract In the last few years, low-noise amplifiers (LNA) have become integrated into receiver devices that bring signals
Technical Note HVM Receiver Noise Figure Measurements Joe Kelly, Ph.D. Verigy 1/13 Abstract In the last few years, low-noise amplifiers (LNA) have become integrated into receiver devices that bring signals
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Introduction to Receivers
 Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Cisco Prisma II 1.2 GHz High Density Long Reach Multiwave Transmitter
 Data Sheet Cisco Prisma II 1.2 GHz High Density Long Reach Multiwave Transmitter The Cisco Prisma II 1.2 GHz High Density Long Reach Multiwave (HD-LRMW) Transmitter (Figure 1) is the CATV industry s first
Data Sheet Cisco Prisma II 1.2 GHz High Density Long Reach Multiwave Transmitter The Cisco Prisma II 1.2 GHz High Density Long Reach Multiwave (HD-LRMW) Transmitter (Figure 1) is the CATV industry s first
A Guide to Calibrating Your Spectrum Analyzer
 A Guide to Calibrating Your Application Note Introduction As a technician or engineer who works with electronics, you rely on your spectrum analyzer to verify that the devices you design, manufacture,
A Guide to Calibrating Your Application Note Introduction As a technician or engineer who works with electronics, you rely on your spectrum analyzer to verify that the devices you design, manufacture,
Processor Setting Fundamentals -or- What Is the Crossover Point?
 The Law of Physics / The Art of Listening Processor Setting Fundamentals -or- What Is the Crossover Point? Nathan Butler Design Engineer, EAW There are many misconceptions about what a crossover is, and
The Law of Physics / The Art of Listening Processor Setting Fundamentals -or- What Is the Crossover Point? Nathan Butler Design Engineer, EAW There are many misconceptions about what a crossover is, and
HFDN-40.0 Rev. 2; 08/10
 Design Note: HFDN-40.0 Rev. 2; 08/10 Obtaining Larger Output Signals in GPON ONT Video Overlay Applications Using the MAX3654 AVAILABLE Obtaining Large Output Signals in GPON ONT Video Overlay Applications
Design Note: HFDN-40.0 Rev. 2; 08/10 Obtaining Larger Output Signals in GPON ONT Video Overlay Applications Using the MAX3654 AVAILABLE Obtaining Large Output Signals in GPON ONT Video Overlay Applications
Fourier Analysis. Chapter Introduction Distortion Harmonic Distortion
 Chapter 5 Fourier Analysis 5.1 Introduction The theory, practice, and application of Fourier analysis are presented in the three major sections of this chapter. The theory includes a discussion of Fourier
Chapter 5 Fourier Analysis 5.1 Introduction The theory, practice, and application of Fourier analysis are presented in the three major sections of this chapter. The theory includes a discussion of Fourier
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 126 2013 Test Method for Distortion of 2-way Amplifiers Caused by Insufficient Isolation of Built in Diplex Filter
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 126 2013 Test Method for Distortion of 2-way Amplifiers Caused by Insufficient Isolation of Built in Diplex Filter
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM Method for measurements of radio noise
 Rec. ITU-R SM.1753 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM.1753 Method for measurements of radio noise (Question ITU-R 1/45) (2006) Scope For radio noise measurements there is a need to have a uniform, frequency-independent
Rec. ITU-R SM.1753 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM.1753 Method for measurements of radio noise (Question ITU-R 1/45) (2006) Scope For radio noise measurements there is a need to have a uniform, frequency-independent
California Eastern Laboratories
 California Eastern Laboratories 750MHz Power Doubler and Push-Pull CATV Hybrid Modules Using Gallium Arsenide D. McNamara*, Y. Fukasawa**, Y. Wakabayashi**, Y. Shirakawa**, Y. Kakuta** *California Eastern
California Eastern Laboratories 750MHz Power Doubler and Push-Pull CATV Hybrid Modules Using Gallium Arsenide D. McNamara*, Y. Fukasawa**, Y. Wakabayashi**, Y. Shirakawa**, Y. Kakuta** *California Eastern
Accurate Phase Noise Measurements Made Cost Effective
 MTTS 2008 MicroApps Accurate Phase Noise Measurements Made Cost Effective author : Jason Breitbarth, PhD. Boulder, Colorado, USA Presentation Outline Phase Noise Intro Additive and Absolute Oscillator
MTTS 2008 MicroApps Accurate Phase Noise Measurements Made Cost Effective author : Jason Breitbarth, PhD. Boulder, Colorado, USA Presentation Outline Phase Noise Intro Additive and Absolute Oscillator
Title: New High Efficiency Intermodulation Cancellation Technique for Single Stage Amplifiers.
 Title: New High Efficiency Intermodulation Cancellation Technique for Single Stage Amplifiers. By: Ray Gutierrez Micronda LLC email: ray@micronda.com February 12, 2008. Introduction: This article provides
Title: New High Efficiency Intermodulation Cancellation Technique for Single Stage Amplifiers. By: Ray Gutierrez Micronda LLC email: ray@micronda.com February 12, 2008. Introduction: This article provides
Analog Circuits and Systems
 Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 21: Filters 1 Review Integrators as building blocks of filters Frequency compensation in negative feedback systems Opamp and LDO frequency compensation
Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 21: Filters 1 Review Integrators as building blocks of filters Frequency compensation in negative feedback systems Opamp and LDO frequency compensation
DATA SHEET. BGD MHz, 20 db gain power doubler amplifier DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS. Product specification Supersedes data of 1999 Mar 26
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D252 BGD804 860 MHz, 20 db gain power doubler amplifier Supersedes data of 1999 Mar 26 2001 Nov 01 FEATURES Excellent linearity Extremely low noise Silicon
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D252 BGD804 860 MHz, 20 db gain power doubler amplifier Supersedes data of 1999 Mar 26 2001 Nov 01 FEATURES Excellent linearity Extremely low noise Silicon
FREQUENCY AGILE FM MODULATOR INSTRUCTION BOOK IB
 FMT615C FREQUENCY AGILE FM MODULATOR INSTRUCTION BOOK IB1215-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION SUBJECT 1.0 Introduction 2.0 Installation & Operating Instructions 3.0 Specification 4.0 Functional Description
FMT615C FREQUENCY AGILE FM MODULATOR INSTRUCTION BOOK IB1215-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION SUBJECT 1.0 Introduction 2.0 Installation & Operating Instructions 3.0 Specification 4.0 Functional Description
