ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
|
|
|
- Jemimah Morris
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reflectance Fabry-Perot modulator utilizing electro-optic ZnO thin film Vikash Gulia* and Sanjeev Kumar Department of Physics and Astrophysics, University of Delhi, Delhi-117, India. * ABSTRACT Electro-optic effect in ZnO thin film prepared by rf magnetron sputtering technique is demonstrated. The effect is measured using the reflection of light polarized with the electric vector parallel to the plane of incidence of light. The reflected light intensity changes with the applied electric field and shows a modulation of about 1.5% at an applied voltage of 32V at an angle of incidence of 42.8 for Ag(Å)/ZnO(1.3µm)/Au(1Å)/Glass reflection Fabry-Perot modulator structure. The results suggest the potential of ZnO thin film for application as a thin film based reflection Fabry-Perot light intensity modulator. Keywords: electro-optic modulation, reflectance Fabry-Perot modulator, integrated optics. 1. INTRODUCTION Fabry-Perot modulator is a device incorporating an electro-optic material in the spacer layer of a Fabry-Perot device which creates a structure whose optical reflection and transmission characteristics depend on the applied voltage. Electro-optic modulators are widely used in broadband fiber-optic communication system due to their well defined transfer functions, large output optical power, wide bandwidth, high extinction ratio and low wavelength dependence. The primary role of electro-optic thin film materials in photonic devices is to modulate light waves with respect to their optical phase or amplitude. Such modulations can be achieved by means of electric field controlled indices of refraction in electro-optic thin film materials through their electro-optic effects. The characterization of the electro-optic properties of these thin film materials is of great importance. For many device applications the thickness of the electro-optic films is usually smaller or comparable to the light wavelength. Accurate and reliable detection of electro-optic effects in these thin film materials has remained a difficult and sometimes a challenging task, particularly so when films are grown on opaque substrates. Integrated optical modulators using organic as well as inorganic electro-optic media may adopt three different designs namely transmission devices, wave-guide devices and reflection devices. Transmission modulators are not compatible with the opaque substrates and their usage is thus limited. Successes were reported in the study of electro-optic effects of thin films grown on opaque substrates by using reflection mode measurement with an intensity detection approach 1-4. Incident Light Reflected Light Ag ( Ǻ) ZnO (1.3 µm) Au/Cr (1 Ǻ) Ordinary Glass Figure1: Reflection Fabry-Perot modulator structure.
2 A number of thin film electro-optic materials including lithium niobate(linbo 3 ), lead lanthanum zirconate titanate(plzt), lead zirconate titanate(pzt), potassium dihydrogen phosphate(kdp), ammonium dihydrogen phosphate(adp), barium titanate, zinc oxide(zno) and various organic polymers have exhibited attractive birefrengent electro-optic effect when deposited on suitable substrates 5-8. These thin film materials have been the focus of many studies for optical modulation. Though all these materials posses very good electro-optic properties but thin film growth of most of these materials using rf magnetron sputtering technique demands high temperature processing and hence they are difficult to grow. Even though Zinc oxide (ZnO) thin films with c-axis orientation exhibit strong piezoelectric and promising electro-optic properties 9 and can be easily grown in thin film form, a very little attention has been paid to the electro-optic characterization of these thin films. In the present work, the fabrication and performance of a ZnO thin film based Fabry-Perot electro-optic modulator operating in reflection mode at wavelength 6328 Å is described. The reflection Fabry-Perot modulator (RFPM) consists of a partially reflecting metallic layer, an electro-optic layer and a fully reflecting bottom layer. The partially reflecting layer provides impedance matching at discrete optical-path lengths which depend on the electro-optic film thickness, index of refraction and angle of incidence. The thickness of this layer depends most critically on the linear optical properties of the electro-optic film and metal and to a lesser extent on the electro-optic film thickness. 2. EXPERIMENTAL In order to fabricate the reflection Fabry-Perot modulator structure and model its performance, it is necessary to precisely control and determine the index of refraction and thickness of all the layers. A fully reflecting thin film of Cr/Au (1 Å) was thermally evaporated onto an ordinary glass substrate which has a refractive index n of 1.5 at nm. A thin film of ZnO (1.3µm) was deposited onto the Au/Cr/Glass structure by using rf magnetron sputtering technique. Finally a partially reflecting thin film of Ag ( Å) was thermally evaporated onto the ZnO/Au/Cr/Glass structure. The values of the dielectric constants of the Au and Ag layers were taken to be i and i respectively from the literature 1. Fig. 1 shows the reflection Fabry-Perot modulator structure utilizing electro-optic ZnO thin film. All the films ZnO, Cr/Au, and Ag were characterized for their thickness information using Dektak II-A surface profiler. Structural characterization of the ZnO thin films was done by X-ray diffraction method. Electro-optic ZnO thin film was grown using a rf magnetron sputtering technique. The rf power of W was applied to the 6 metallic Zn target in a reactive gas ambient of Ar and O 2. The mixed gases ratio of Ar to O 2 is :. The sputtering pressure in the chamber was maintained at 1 m Torr during deposition. p-polarized He-Ne Laser Analyzer DC Power supply Sample Photodetector Laser power meter Figure 2: Experimental setup for the measurement of reflected light intensity. Electro-optic characteristics of ZnO thin film based reflection Fabry-Perot modulator was studied using a measuring setup as shown in Fig. 2. A linearly polarized light beam with with p-polarization (electric vector parallel to plane of incidence) was incident on the RFPM surface at an angle θ. After passing through the analyzer, the component of the reflected light with the polarization parallel to the incidence plane was detected by a photo-detector. Variation in the reflected intensity was studied with angle of incidence. A sharp dip in the reflected intensity was experimentally observed at 43.6 degree which is in close agreement with the results obtained by theoretical simulations. When an electric field was applied along the direction of optic axis of ZnO film using top and bottom reflecting metallic layers as electrodes, an intensity change of the reflected light due to the change of the index of refraction of ZnO thin film was observed.
3 The light source used in the experiment was a nm He-Ne laser with the electric vector parallel to the plane of incidence. A XYθ rotation stage with rotational as well as two linear perpendicular motions and digital read out of angle procured from micro-controle (France) was used in the experiment. The least count of angle recorder was.1 degree i.e. seconds. The intensity of laser light was measured using an optical power meter (Newport 18C). 3. THEORY With the application of an external electric field across an optical medium, the distribution of electrons as well as orientation of molecules within it get disturbed. The bound electrons in the molecules of the optical medium move in a direction opposite to the applied electric field and nuclei are displaced in the direction of applied electric field. The optical medium is said to be polarized and electric dipole moment of the medium is written as p= N.e.d. Dipole moment is also written as p= N.α.E, where α= polarizability, and also p= ε. χ.e, where χ= susceptibility. N stands for the no. of molecules in the optical medium, e stands for the total charge of positive or negative particles in a molecule and d denotes separation between charges in each molecule. From the above equations it is clear that dipole moment is directly proportional to the polarizability. A change in the dipole moment changes the polarizability of the optical medium which in turn brings out a change in the susceptibility of the medium in accordance with the relation χ= N. α/ ε. A change in the susceptibility changes the dielectric constant of the medium as both are related to each other through the relation K= 1+ χ. Therefore we can say that a change in polarizabilty causes a change in the dielectric constant of the optical medium which in turn brings out a change in the refractive index of the optical medium. The reflectance of the RFPM structure is evaluated theoretically by using Fresnel s relation given as R= 1r ijklm 1 2 Where Fresnel reflection coefficient is given as r ijklm = (r ij +r jklm *exp*(2ik z1 d 1 ))/(1+r ij *r jklm *exp(2ik z1 d 1 )) In the absence of an external electric field, a light wave polarized normal to the z-direction (i.e. in x-y plane) travels as a principal wave with ordinary refractive index n o. Depending on the refractive indices and thickness of two metallic films and the electro-optic film, a phase difference is introduced among the reflected rays and the transmitted rays. When the condition for destructive interference is satisfied, dips are observed in the reflected at different values of angle of incidence. In the presence of an external electric field E z, the refractive index for a wave propagating along the optic axis of the electro-optic film and polarized along x-axis is given as, n x = n -(1/2).n 3. r 13.E z similarly, the refractive index for a wave propagating along the optic axis of the electro-optic film and polarized along y- axis is given as, n y = n -(1/2).n 3. r 13.E z where r 13 is electro-optic coefficient of the ZnO thin film used as an electro-optic media in the experiment. Changes in the refractive indices n o and n e of the electro-optic film with the applied voltage cause a shift in the angle of dip. Initially the structure is adjusted at an incident angle close to the angle of dip. A change in the reflected intensity is observed upon the application of electric field across the electro-optic film and the modulation of reflected intensity is thereby achieved. All the layers and especially the electro-optic film should be smooth and should have a parallel interface for efficient excitation of the Fabry-Perot modes. This demands highly polished and flat substrates and deposition of uniform and thin films. 4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION For a Fabry-Perot structure having the configuration Ag/ZnO(1.3µm)/Au(1Å)/Glass, the angle of dip is found to depend on the thickness of topmost partially reflecting layer. The angle of dip showed a decrease with an increase in the thickness of topmost partially reflecting layer upto a thickness of Å and after that it remained unchanged as shown in Fig. 3. The value of reflectance (%) at dip is also found to depend on the thickness of topmost partially reflecting layer. A reflectance (%) at dip is found to first decrease with an increase in the thickness of topmost layer and after Å it starts increasing as shown in Fig. 4. Fig. 3 and Fig. 4 show theoretical and experimental variations of angle of dip and reflectance (%) at dip with the thickness of topmost layer. It may be noted that both theoretical and experimental curves are in well agreement with each other. The small deviation in the theoretical and experimental results may be attributed to the use of theoretical values of dielectric constants of all the layers in the RFPM structure. Since the dielectric constant depend upon the growth conditions of all the layers so a small deviation in the theoretical and experimental values is
4 obvious. Therefore on the basis of above studies it was concluded that the dip is sharpest at a particular thickness of Å for the topmost layer in Ag/ZnO(1.3µm)/Au(1Å)/Glass Fabry-Perot structure. Experimentally the Fabry-Perot structure having the composition Ag(Å)/ZnO(1.3µm)/Au(1Å)/Glass was fabricated Angle of dip (Degree) 45 Dip Reflectance (%) Thickness of topmost layer (Angstrom) Thickness of topmost layer (Angstrom) Figure 3: Plot of angle of dip vs. thickness of topmost layer for Ag/ZnO(1.3µm)/Au(1Å)/Glass RFPM structure. Figure 4: Plot of dip reflectance (%) vs. thickness of topmost layer for Ag/ZnO(1.3µm)/Au(1Å)/Glass RFPM structure. Variation in the reflected intensity was studied with the angle of incidence in reflection Fabry-Perot modulator structure and it was concluded that a dip is observed in the reflected intensity at a particular value of angle of incidence in the absence of external electric field. The value of angle of dip is found to depend most critically on the thickness of topmost partially reflecting layer and electro-optic layer Ez= V/micron Ez= 25V/micron Reflectance (%) Angle of incidence (Degree) Reflectance (%) Angle of incidence (Degrees) Figure 5: Plot of reflectance (%) vs. angle of incidence for Ag(Å)/ZnO(1.3µm)/Au(1Å)/Glass RFPM structure. Figure 6: Plot of experimentally observed reflectance (%) vs. angle of incidence for Ag(Å)/ZnO(1.3µm)/Au(1Å)/Glass RFPM structure.
5 The highly reflecting bottom electrode is required to be smooth and highly reflecting and its thickness is not so critical as far as the angle of dip is concerned. Angle of dip and reflectance (%) at dip remains unaffected with an increase in the thickness of bottom layer in the reflection Fabry-Perot modulator structure provided the bottom layer is highly reflecting. The performance of the fabricated device (Ag(Å)/ZnO(1.3µm)/Au(1Å)/Glass) as a light intensity modulator was examined experimentally using the measuring set-up as shown in the Fig. 2. In the absence of external electric field a sharp dip in the reflected intensity was observed at an angle of incidence of 43.6 as shown in the Fig. 5. The electrooptic modulation of a p-polarized 3 mw (632.8 nm) laser beam was studied by applying a dc voltage across the silver and gold electrodes. The applied voltage varies the refractive index of the ZnO thin film, which results in a horizontal shift in the reflectance versus θ curve. Since the angle of incidence remains fixed, the reflectance is therefore modulated. Once modulation was observed it was maximized by adjusting θ. A modulation of 1.5% was observed in the reflected intensity at an applied electric field of 25V/µm at an angle of incidence of 42.8 degree as shown in the Fig CONCLUSIONS Device fabrication and the performance of a reflectance modulator in which the intensity of a nm laser beam reflected from the topmost reflecting layer of the modulator is electrically varied, has been demonstrated. A thin film reflection Fabry-Perot modulator has been fabricated incorporating ZnO thin film as an electro-optic media. Using this device as a light intensity modulator a modulation of 1.5 % was achieved at an applied electric field of 25V/µm. The present results show the potential of ZnO electro-optic thin films for thin film electro-optic modulator applications. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors benefited greatly from the enlightening discussions and suggestions from Dr. K. Sreenivas. The authors would like to thank Dr. K. Sreenivas for providing experimental facilities to carry out the experimental work. One of the authors (VG) would like to thank University Grants Commission, India for providing a research fellowship. REFERENCES 1. Reflectance modulator utilizing an electro-optic polymer film: C. B. Rider, J. S. Schildkraut, and M. Scozzafava,, J. Appl. Phys, 7, 29(1991). 2. Electro-optic measurements of thin film materials by means of reflection differential ellipsometry: F. Wang, E. Furman, and G. H. Haertling, J. Appl. Phys., 78,9(1995). 3. Electro-optic effects of PLZT thin films M. Ishida, H. Matsunami, and T. Tanaka,, Appl. Phys. Lett., vol (1977). 4. Characterization of electro-optic polymer films by use of decal deposited reflection Fabry-Perot microcavities: P. Pretre, L. M. Wu, R. A. Hill, and A. Knoesen, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, 15, 379(1997). 5. Comparison of electro-optic lead-lanthanum zirconate titanate films on crystalline and glass substrates: K. D. Preston and G. H. Heartling,, Appl. Phys. Lett.,, 2831(1992). 6. Integrated PLZT thin film waveguide modulators: A. Wegner et al, Ferroelectrics, 116,195(1991). 7. H. Adachi et al, Electro-optic effects of (Pb,La)(Zr,Ti)O 3 thin films prepared by rf planar magnetron sputtering, Appl. Phys. Lett., 42, 867(1983). 8. Birefrengent bistability in (Pb,La)(Zr,Ti)O 3 thin films with a ferroelectric-semiconductor interface: F. Wang and G. H. Heartling, Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 63, 17(1993). 9. Electro-optic property of ZnO:X (X= Li, Mg) thin films: T. Nagata et al,, J. Crys. Growth, 237, 533,(2). 1. Y. C. Shen et al, A new optical method for detecting laser generated acoustic pulse in solution, Analytical Sciences, 17, 458 (1).
The 34th International Physics Olympiad
 The 34th International Physics Olympiad Taipei, Taiwan Experimental Competition Wednesday, August 6, 2003 Time Available : 5 hours Please Read This First: 1. Use only the pen provided. 2. Use only the
The 34th International Physics Olympiad Taipei, Taiwan Experimental Competition Wednesday, August 6, 2003 Time Available : 5 hours Please Read This First: 1. Use only the pen provided. 2. Use only the
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin
 Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus
 Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors
 846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
Electro-optic Electric Field Sensor Utilizing Ti:LiNbO 3 Symmetric Mach-Zehnder Interferometers
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 16, No. 1, March 2012, pp. 47-52 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2012.16.1.047 Electro-optic Electric Field Sensor Utilizing Ti:LiNbO 3 Symmetric Mach-Zehnder
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 16, No. 1, March 2012, pp. 47-52 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2012.16.1.047 Electro-optic Electric Field Sensor Utilizing Ti:LiNbO 3 Symmetric Mach-Zehnder
STUDY OF VIBRATION MODAL ESTIMATION FOR COMPOSITE BEAM WITH PZT THIN FILM SENSOR SYSTEM
 STUDY OF VIBRATION MODAL ESTIMATION FOR COMPOSITE BEAM WITH PZT THIN FILM SENSOR SYSTEM Nobuo Oshima, Takehito Fukuda and Shinya Motogi Faculty of Engineering, Osaka City University 3-3-38, Sugimoto, Sumiyoshi-ku,
STUDY OF VIBRATION MODAL ESTIMATION FOR COMPOSITE BEAM WITH PZT THIN FILM SENSOR SYSTEM Nobuo Oshima, Takehito Fukuda and Shinya Motogi Faculty of Engineering, Osaka City University 3-3-38, Sugimoto, Sumiyoshi-ku,
In their earliest form, bandpass filters
 Bandpass Filters Past and Present Bandpass filters are passive optical devices that control the flow of light. They can be used either to isolate certain wavelengths or colors, or to control the wavelengths
Bandpass Filters Past and Present Bandpass filters are passive optical devices that control the flow of light. They can be used either to isolate certain wavelengths or colors, or to control the wavelengths
Lecture 04: Solar Imaging Instruments
 Hale COLLAGE (NJIT Phys-780) Topics in Solar Observation Techniques Lecture 04: Solar Imaging Instruments Wenda Cao New Jersey Institute of Technology Valentin M. Pillet National Solar Observatory SDO
Hale COLLAGE (NJIT Phys-780) Topics in Solar Observation Techniques Lecture 04: Solar Imaging Instruments Wenda Cao New Jersey Institute of Technology Valentin M. Pillet National Solar Observatory SDO
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Principles of Optics for Engineers
 Principles of Optics for Engineers Uniting historically different approaches by presenting optical analyses as solutions of Maxwell s equations, this unique book enables students and practicing engineers
Principles of Optics for Engineers Uniting historically different approaches by presenting optical analyses as solutions of Maxwell s equations, this unique book enables students and practicing engineers
Chap. 8. Electro-Optic Devices
 Chap. 8. Electro-Optic Devices - The effect of an applied electric field on the propagation of em radiation. - light modulators, spectral tunable filters, electro-optical filters, beam deflectors 8.1.
Chap. 8. Electro-Optic Devices - The effect of an applied electric field on the propagation of em radiation. - light modulators, spectral tunable filters, electro-optical filters, beam deflectors 8.1.
Photonics and Optical Communication
 Photonics and Optical Communication (Course Number 300352) Spring 2007 Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/dknipp/ 1 Photonics and Optical Communication
Photonics and Optical Communication (Course Number 300352) Spring 2007 Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/dknipp/ 1 Photonics and Optical Communication
Supplementary Information for. Surface Waves. Angelo Angelini, Elsie Barakat, Peter Munzert, Luca Boarino, Natascia De Leo,
 Supplementary Information for Focusing and Extraction of Light mediated by Bloch Surface Waves Angelo Angelini, Elsie Barakat, Peter Munzert, Luca Boarino, Natascia De Leo, Emanuele Enrico, Fabrizio Giorgis,
Supplementary Information for Focusing and Extraction of Light mediated by Bloch Surface Waves Angelo Angelini, Elsie Barakat, Peter Munzert, Luca Boarino, Natascia De Leo, Emanuele Enrico, Fabrizio Giorgis,
Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications by Stuart M. Wentworth Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
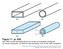 Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
Fiber-Optic Polarizer Using Resonant Tunneling through a Multilayer Overlay
 Fiber-Optic Polarizer Using Resonant Tunneling through a Multilayer Overlay Arun Kumar, Rajeev Jindal, and R. K. Varshney Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi 110 016 India
Fiber-Optic Polarizer Using Resonant Tunneling through a Multilayer Overlay Arun Kumar, Rajeev Jindal, and R. K. Varshney Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi 110 016 India
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING
 CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
PhE102-VASE. PHE102 Variable Angle Spectroscopic Ellipsometer. Angstrom Advanced Inc. Angstrom Advanced. Angstrom Advanced
 Angstrom Advanced PhE102-VASE PHE102 Variable Angle Spectroscopic Ellipsometer Angstrom Advanced Instruments for Thin Film and Semiconductor Applications sales@angstromadvanced.com www.angstromadvanced.com
Angstrom Advanced PhE102-VASE PHE102 Variable Angle Spectroscopic Ellipsometer Angstrom Advanced Instruments for Thin Film and Semiconductor Applications sales@angstromadvanced.com www.angstromadvanced.com
Experimental Competition
 37 th International Physics Olympiad Singapore 8 17 July 2006 Experimental Competition Wed 12 July 2006 Experimental Competition Page 2 List of apparatus and materials Label Component Quantity Label Component
37 th International Physics Olympiad Singapore 8 17 July 2006 Experimental Competition Wed 12 July 2006 Experimental Competition Page 2 List of apparatus and materials Label Component Quantity Label Component
Laser Speckle Reducer LSR-3000 Series
 Datasheet: LSR-3000 Series Update: 06.08.2012 Copyright 2012 Optotune Laser Speckle Reducer LSR-3000 Series Speckle noise from a laser-based system is reduced by dynamically diffusing the laser beam. A
Datasheet: LSR-3000 Series Update: 06.08.2012 Copyright 2012 Optotune Laser Speckle Reducer LSR-3000 Series Speckle noise from a laser-based system is reduced by dynamically diffusing the laser beam. A
IV Assembly and Automation of the SPR Spectrometer
 IV Assembly and Automation of the SPR Spectrometer This chapter is dedicated to the description of the experimental set-up and the procedure used to perform SPR measurements. We start with a schematic
IV Assembly and Automation of the SPR Spectrometer This chapter is dedicated to the description of the experimental set-up and the procedure used to perform SPR measurements. We start with a schematic
Supporting Information: Achromatic Metalens over 60 nm Bandwidth in the Visible and Metalens with Reverse Chromatic Dispersion
 Supporting Information: Achromatic Metalens over 60 nm Bandwidth in the Visible and Metalens with Reverse Chromatic Dispersion M. Khorasaninejad 1*, Z. Shi 2*, A. Y. Zhu 1, W. T. Chen 1, V. Sanjeev 1,3,
Supporting Information: Achromatic Metalens over 60 nm Bandwidth in the Visible and Metalens with Reverse Chromatic Dispersion M. Khorasaninejad 1*, Z. Shi 2*, A. Y. Zhu 1, W. T. Chen 1, V. Sanjeev 1,3,
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 4
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 4 Modal Propagation of Light in an Optical Fiber Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 4 Modal Propagation of Light in an Optical Fiber Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
OPTICAL NETWORKS. Building Blocks. A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005
 OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT
 CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
MAGNETO-DIELECTRIC COMPOSITES WITH FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACE LAYERS
 MAGNETO-DIELECTRIC COMPOSITES WITH FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACE LAYERS M. Hawley 1, S. Farhat 1, B. Shanker 2, L. Kempel 2 1 Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Michigan State University;
MAGNETO-DIELECTRIC COMPOSITES WITH FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACE LAYERS M. Hawley 1, S. Farhat 1, B. Shanker 2, L. Kempel 2 1 Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Michigan State University;
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT
 ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (E-O) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (E-O) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
Investigation of the Near-field Distribution at Novel Nanometric Aperture Laser
 Investigation of the Near-field Distribution at Novel Nanometric Aperture Laser Tiejun Xu, Jia Wang, Liqun Sun, Jiying Xu, Qian Tian Presented at the th International Conference on Electronic Materials
Investigation of the Near-field Distribution at Novel Nanometric Aperture Laser Tiejun Xu, Jia Wang, Liqun Sun, Jiying Xu, Qian Tian Presented at the th International Conference on Electronic Materials
Research Report. IBM Research. Ultrafast All-Optical Switching: Photonic Engineering of Resonator Structures with Organic Nonlinear Kerr Materials
 RZ 3605 (# 99615) 04/25/05 Physics 6 pages Research Report Ultrafast All-Optical Switching: Photonic Engineering of Resonator Structures with Organic Nonlinear Kerr Materials R.F. Mahrt 1,, N. Moll 1,
RZ 3605 (# 99615) 04/25/05 Physics 6 pages Research Report Ultrafast All-Optical Switching: Photonic Engineering of Resonator Structures with Organic Nonlinear Kerr Materials R.F. Mahrt 1,, N. Moll 1,
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber. Xavier Fernando Ryerson University
 Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson University The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson University The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Symmetrically coated pellicle beam splitters for dual quarter-wave retardation in reflection and transmission
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 1-1-2002 Symmetrically coated pellicle beam splitters for dual quarter-wave retardation
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 1-1-2002 Symmetrically coated pellicle beam splitters for dual quarter-wave retardation
Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 12, Number 3, 2009, 308 316 Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals Daniela DRAGOMAN 1, Adrian DINESCU 2, Raluca MÜLLER2, Cristian KUSKO 2, Alex.
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 12, Number 3, 2009, 308 316 Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals Daniela DRAGOMAN 1, Adrian DINESCU 2, Raluca MÜLLER2, Cristian KUSKO 2, Alex.
Mode analysis of Oxide-Confined VCSELs using near-far field approaches
 Annual report 998, Dept. of Optoelectronics, University of Ulm Mode analysis of Oxide-Confined VCSELs using near-far field approaches Safwat William Zaki Mahmoud We analyze the transverse mode structure
Annual report 998, Dept. of Optoelectronics, University of Ulm Mode analysis of Oxide-Confined VCSELs using near-far field approaches Safwat William Zaki Mahmoud We analyze the transverse mode structure
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Mode imaging and selection in strongly coupled nanoantennas Jer-Shing Huang 1,*, Johannes Kern 1, Peter Geisler 1, Pia Weimann 2, Martin Kamp 2, Alfred Forchel 2, Paolo Biagioni
Supporting Information Mode imaging and selection in strongly coupled nanoantennas Jer-Shing Huang 1,*, Johannes Kern 1, Peter Geisler 1, Pia Weimann 2, Martin Kamp 2, Alfred Forchel 2, Paolo Biagioni
EXPRIMENT 3 COUPLING FIBERS TO SEMICONDUCTOR SOURCES
 EXPRIMENT 3 COUPLING FIBERS TO SEMICONDUCTOR SOURCES OBJECTIVES In this lab, firstly you will learn to couple semiconductor sources, i.e., lightemitting diodes (LED's), to optical fibers. The coupling
EXPRIMENT 3 COUPLING FIBERS TO SEMICONDUCTOR SOURCES OBJECTIVES In this lab, firstly you will learn to couple semiconductor sources, i.e., lightemitting diodes (LED's), to optical fibers. The coupling
University of New Orleans. Jian Liu. Rasheed M.A. Azzam University of New Orleans,
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 10-1-1996 Infrared quarter-wave reflection retarders designed with high-spatial-frequency
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 10-1-1996 Infrared quarter-wave reflection retarders designed with high-spatial-frequency
plasmonic nanoblock pair
 Nanostructured potential of optical trapping using a plasmonic nanoblock pair Yoshito Tanaka, Shogo Kaneda and Keiji Sasaki* Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 1-2,
Nanostructured potential of optical trapping using a plasmonic nanoblock pair Yoshito Tanaka, Shogo Kaneda and Keiji Sasaki* Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 1-2,
Supplementary information for Stretchable photonic crystal cavity with
 Supplementary information for Stretchable photonic crystal cavity with wide frequency tunability Chun L. Yu, 1,, Hyunwoo Kim, 1, Nathalie de Leon, 1,2 Ian W. Frank, 3 Jacob T. Robinson, 1,! Murray McCutcheon,
Supplementary information for Stretchable photonic crystal cavity with wide frequency tunability Chun L. Yu, 1,, Hyunwoo Kim, 1, Nathalie de Leon, 1,2 Ian W. Frank, 3 Jacob T. Robinson, 1,! Murray McCutcheon,
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER
 CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
Electronically tunable fabry-perot interferometers with double liquid crystal layers
 Electronically tunable fabry-perot interferometers with double liquid crystal layers Kuen-Cherng Lin *a, Kun-Yi Lee b, Cheng-Chih Lai c, Chin-Yu Chang c, and Sheng-Hsien Wong c a Dept. of Computer and
Electronically tunable fabry-perot interferometers with double liquid crystal layers Kuen-Cherng Lin *a, Kun-Yi Lee b, Cheng-Chih Lai c, Chin-Yu Chang c, and Sheng-Hsien Wong c a Dept. of Computer and
Large aperture tunable ultra narrow band Fabry-Perot-Bragg filter
 Large aperture tunable ultra narrow band Fabry-Perot-Bragg filter Julien Lumeau *, Vadim Smirnov, Fabien Lemarchand 3, Michel Lequime 3 and Leonid B. Glebov School of Optics/CREOL, University of Central
Large aperture tunable ultra narrow band Fabry-Perot-Bragg filter Julien Lumeau *, Vadim Smirnov, Fabien Lemarchand 3, Michel Lequime 3 and Leonid B. Glebov School of Optics/CREOL, University of Central
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information S1. Theory of TPQI in a lossy directional coupler Following Barnett, et al. [24], we start with the probability of detecting one photon in each output of a lossy, symmetric beam
Supplementary Information S1. Theory of TPQI in a lossy directional coupler Following Barnett, et al. [24], we start with the probability of detecting one photon in each output of a lossy, symmetric beam
Analysis of the Tunable Asymmetric Fiber F-P Cavity for Fiber Strain Sensor Edge-Filter Demodulation
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 4, No. 4, 014: 338 343 Analysis of the Tunable Asymmetric Fiber F-P Cavity for Fiber Strain Sensor Edge-Filter Demodulation Haotao CHEN and Youcheng LIANG * Guangzhou Ivia Aviation
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 4, No. 4, 014: 338 343 Analysis of the Tunable Asymmetric Fiber F-P Cavity for Fiber Strain Sensor Edge-Filter Demodulation Haotao CHEN and Youcheng LIANG * Guangzhou Ivia Aviation
Influence of dielectric substrate on the responsivity of microstrip dipole-antenna-coupled infrared microbolometers
 Influence of dielectric substrate on the responsivity of microstrip dipole-antenna-coupled infrared microbolometers Iulian Codreanu and Glenn D. Boreman We report on the influence of the dielectric substrate
Influence of dielectric substrate on the responsivity of microstrip dipole-antenna-coupled infrared microbolometers Iulian Codreanu and Glenn D. Boreman We report on the influence of the dielectric substrate
NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR WAVELENGTH SELEC- TIVE SWITCHING BASED OPTICAL NETWORKS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 93 100, 2009 NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR WAVELENGTH SELEC- TIVE SWITCHING BASED OPTICAL NETWORKS A. Banerjee
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 93 100, 2009 NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR WAVELENGTH SELEC- TIVE SWITCHING BASED OPTICAL NETWORKS A. Banerjee
The electric field for the wave sketched in Fig. 3-1 can be written as
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Light consists of an electric field and a magnetic field that oscillate at very high rates, of the order of 10 14 Hz. These fields travel in wavelike fashion at very high speeds.
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Light consists of an electric field and a magnetic field that oscillate at very high rates, of the order of 10 14 Hz. These fields travel in wavelike fashion at very high speeds.
A Laser-Based Thin-Film Growth Monitor
 TECHNOLOGY by Charles Taylor, Darryl Barlett, Eric Chason, and Jerry Floro A Laser-Based Thin-Film Growth Monitor The Multi-beam Optical Sensor (MOS) was developed jointly by k-space Associates (Ann Arbor,
TECHNOLOGY by Charles Taylor, Darryl Barlett, Eric Chason, and Jerry Floro A Laser-Based Thin-Film Growth Monitor The Multi-beam Optical Sensor (MOS) was developed jointly by k-space Associates (Ann Arbor,
Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat.
 Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat. Scattering: The changes in direction of light confined within an OF, occurring due to imperfection in
Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat. Scattering: The changes in direction of light confined within an OF, occurring due to imperfection in
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77. Table of Contents 1
 Efficient single photon detection from 500 nm to 5 μm wavelength: Supporting Information F. Marsili 1, F. Bellei 1, F. Najafi 1, A. E. Dane 1, E. A. Dauler 2, R. J. Molnar 2, K. K. Berggren 1* 1 Department
Efficient single photon detection from 500 nm to 5 μm wavelength: Supporting Information F. Marsili 1, F. Bellei 1, F. Najafi 1, A. E. Dane 1, E. A. Dauler 2, R. J. Molnar 2, K. K. Berggren 1* 1 Department
Optical Communications and Networking 朱祖勍. Sept. 25, 2017
 Optical Communications and Networking Sept. 25, 2017 Lecture 4: Signal Propagation in Fiber 1 Nonlinear Effects The assumption of linearity may not always be valid. Nonlinear effects are all related to
Optical Communications and Networking Sept. 25, 2017 Lecture 4: Signal Propagation in Fiber 1 Nonlinear Effects The assumption of linearity may not always be valid. Nonlinear effects are all related to
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Compact Distributed Phase Shifters at X-Band Using BST
 Integrated Ferroelectrics, 56: 1087 1095, 2003 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1058-4587 print/ 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580390259623 Compact Distributed Phase Shifters at X-Band Using
Integrated Ferroelectrics, 56: 1087 1095, 2003 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1058-4587 print/ 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580390259623 Compact Distributed Phase Shifters at X-Band Using
attosnom I: Topography and Force Images NANOSCOPY APPLICATION NOTE M06 RELATED PRODUCTS G
 APPLICATION NOTE M06 attosnom I: Topography and Force Images Scanning near-field optical microscopy is the outstanding technique to simultaneously measure the topography and the optical contrast of a sample.
APPLICATION NOTE M06 attosnom I: Topography and Force Images Scanning near-field optical microscopy is the outstanding technique to simultaneously measure the topography and the optical contrast of a sample.
Optical Interconnection in Silicon LSI
 The Fifth Workshop on Nanoelectronics for Tera-bit Information Processing, 1 st Century COE, Hiroshima University Optical Interconnection in Silicon LSI Shin Yokoyama, Yuichiro Tanushi, and Masato Suzuki
The Fifth Workshop on Nanoelectronics for Tera-bit Information Processing, 1 st Century COE, Hiroshima University Optical Interconnection in Silicon LSI Shin Yokoyama, Yuichiro Tanushi, and Masato Suzuki
Infrared broadband 50%-50% beam splitters for s- polarized light
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 7-1-2006 Infrared broadband 50%-50% beam splitters for s- polarized light R.
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 7-1-2006 Infrared broadband 50%-50% beam splitters for s- polarized light R.
Fiber Optic Sensing Applications Based on Optical Propagation Mode Time Delay Measurement
 R ESEARCH ARTICLE ScienceAsia 7 (1) : 35-4 Fiber Optic Sensing Applications Based on Optical Propagation Mode Time Delay Measurement PP Yupapin a * and S Piengbangyang b a Lightwave Technology Research
R ESEARCH ARTICLE ScienceAsia 7 (1) : 35-4 Fiber Optic Sensing Applications Based on Optical Propagation Mode Time Delay Measurement PP Yupapin a * and S Piengbangyang b a Lightwave Technology Research
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1234855/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Taxel-Addressable Matrix of Vertical-Nanowire Piezotronic Transistors for Active/Adaptive Tactile Imaging Wenzhuo Wu,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1234855/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Taxel-Addressable Matrix of Vertical-Nanowire Piezotronic Transistors for Active/Adaptive Tactile Imaging Wenzhuo Wu,
Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter
 Research Online ECU Publications 29 Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter Feng Xiao Mingya Shen Budi Juswardy Kamal Alameh This article was originally published as: Xiao, F., Shen, M., Juswardy,
Research Online ECU Publications 29 Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter Feng Xiao Mingya Shen Budi Juswardy Kamal Alameh This article was originally published as: Xiao, F., Shen, M., Juswardy,
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: Signature:
 Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
 Chapter 5 5.1 What are the factors that determine the thickness of a polystyrene waveguide formed by spinning a solution of dissolved polystyrene onto a substrate? density of polymer concentration of polymer
Chapter 5 5.1 What are the factors that determine the thickness of a polystyrene waveguide formed by spinning a solution of dissolved polystyrene onto a substrate? density of polymer concentration of polymer
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Wireless thin film transistor based on micro magnetic induction coupling antenna Byoung Ok Jun 1, Gwang Jun Lee 1, Jong Gu Kang 1,2, Seung Uk Kim 1, Ji Woong Choi 1, Seung Nam
Supplementary Information Wireless thin film transistor based on micro magnetic induction coupling antenna Byoung Ok Jun 1, Gwang Jun Lee 1, Jong Gu Kang 1,2, Seung Uk Kim 1, Ji Woong Choi 1, Seung Nam
Model Series 400X User s Manual. DC-100 MHz Electro-Optic Phase Modulators
 Model Series 400X User s Manual DC-100 MHz Electro-Optic Phase Modulators 400412 Rev. D 2 Is a registered trademark of New Focus, Inc. Warranty New Focus, Inc. guarantees its products to be free of defects
Model Series 400X User s Manual DC-100 MHz Electro-Optic Phase Modulators 400412 Rev. D 2 Is a registered trademark of New Focus, Inc. Warranty New Focus, Inc. guarantees its products to be free of defects
BANDWIDTH WIDENING TECHNIQUES FOR DIRECTIVE ANTENNAS BASED ON PARTIALLY REFLECTING SURFACES
 BANDWIDTH WIDENING TECHNIQUES FOR DIRECTIVE ANTENNAS BASED ON PARTIALLY REFLECTING SURFACES Halim Boutayeb, Tayeb Denidni, Mourad Nedil To cite this version: Halim Boutayeb, Tayeb Denidni, Mourad Nedil.
BANDWIDTH WIDENING TECHNIQUES FOR DIRECTIVE ANTENNAS BASED ON PARTIALLY REFLECTING SURFACES Halim Boutayeb, Tayeb Denidni, Mourad Nedil To cite this version: Halim Boutayeb, Tayeb Denidni, Mourad Nedil.
E LECTROOPTICAL(EO)modulatorsarekeydevicesinoptical
 286 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 26, NO. 2, JANUARY 15, 2008 Design and Fabrication of Sidewalls-Extended Electrode Configuration for Ridged Lithium Niobate Electrooptical Modulator Yi-Kuei Wu,
286 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 26, NO. 2, JANUARY 15, 2008 Design and Fabrication of Sidewalls-Extended Electrode Configuration for Ridged Lithium Niobate Electrooptical Modulator Yi-Kuei Wu,
Copyright 2004 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers.
 Copyright 2004 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in SPIE Proceedings, Volume 5160 and is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of SPIE. One print or
Copyright 2004 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in SPIE Proceedings, Volume 5160 and is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of SPIE. One print or
A miniature all-optical photoacoustic imaging probe
 A miniature all-optical photoacoustic imaging probe Edward Z. Zhang * and Paul C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK http://www.medphys.ucl.ac.uk/research/mle/index.htm
A miniature all-optical photoacoustic imaging probe Edward Z. Zhang * and Paul C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK http://www.medphys.ucl.ac.uk/research/mle/index.htm
Laser Telemetric System (Metrology)
 Laser Telemetric System (Metrology) Laser telemetric system is a non-contact gauge that measures with a collimated laser beam (Refer Fig. 10.26). It measure at the rate of 150 scans per second. It basically
Laser Telemetric System (Metrology) Laser telemetric system is a non-contact gauge that measures with a collimated laser beam (Refer Fig. 10.26). It measure at the rate of 150 scans per second. It basically
Acoustic Velocity Independent Ultrasonic Flow-Meter
 flotek.g 2017- Innovative Solutions in Flow Measurement and Control - Oil, Water and Gas August 28-30, 2017, FCRI, Palakkad, Kerala, India Acoustic Velocity Independent Ultrasonic Flow-Meter ABSTRACT Shalini
flotek.g 2017- Innovative Solutions in Flow Measurement and Control - Oil, Water and Gas August 28-30, 2017, FCRI, Palakkad, Kerala, India Acoustic Velocity Independent Ultrasonic Flow-Meter ABSTRACT Shalini
Si Nano-Photonics Innovate Next Generation Network Systems and LSI Technologies
 Si Nano-Photonics Innovate Next Generation Network Systems and LSI Technologies NISHI Kenichi, URINO Yutaka, OHASHI Keishi Abstract Si nanophotonics controls light by employing a nano-scale structural
Si Nano-Photonics Innovate Next Generation Network Systems and LSI Technologies NISHI Kenichi, URINO Yutaka, OHASHI Keishi Abstract Si nanophotonics controls light by employing a nano-scale structural
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber
 Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic wave Ray Theory Light
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic wave Ray Theory Light
Characterization of Silicon-based Ultrasonic Nozzles
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 7, No. 2, pp. 123 127 (24) 123 Characterization of licon-based Ultrasonic Nozzles Y. L. Song 1,2 *, S. C. Tsai 1,3, Y. F. Chou 4, W. J. Chen 1, T. K. Tseng
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 7, No. 2, pp. 123 127 (24) 123 Characterization of licon-based Ultrasonic Nozzles Y. L. Song 1,2 *, S. C. Tsai 1,3, Y. F. Chou 4, W. J. Chen 1, T. K. Tseng
Will contain image distance after raytrace Will contain image height after raytrace
 Name: LASR 51 Final Exam May 29, 2002 Answer all questions. Module numbers are for guidance, some material is from class handouts. Exam ends at 8:20 pm. Ynu Raytracing The first questions refer to the
Name: LASR 51 Final Exam May 29, 2002 Answer all questions. Module numbers are for guidance, some material is from class handouts. Exam ends at 8:20 pm. Ynu Raytracing The first questions refer to the
Infrared Perfect Absorbers Fabricated by Colloidal Mask Etching of Al-Al 2 O 3 -Al Trilayers
 Supporting Information Infrared Perfect Absorbers Fabricated by Colloidal Mask Etching of Al-Al 2 O 3 -Al Trilayers Thang Duy Dao 1,2,3,*, Kai Chen 1,2, Satoshi Ishii 1,2, Akihiko Ohi 1,2, Toshihide Nabatame
Supporting Information Infrared Perfect Absorbers Fabricated by Colloidal Mask Etching of Al-Al 2 O 3 -Al Trilayers Thang Duy Dao 1,2,3,*, Kai Chen 1,2, Satoshi Ishii 1,2, Akihiko Ohi 1,2, Toshihide Nabatame
NEW LASER ULTRASONIC INTERFEROMETER FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS B.Pouet and S.Breugnot Bossa Nova Technologies; Venice, CA, USA
 NEW LASER ULTRASONIC INTERFEROMETER FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS B.Pouet and S.Breugnot Bossa Nova Technologies; Venice, CA, USA Abstract: A novel interferometric scheme for detection of ultrasound is presented.
NEW LASER ULTRASONIC INTERFEROMETER FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS B.Pouet and S.Breugnot Bossa Nova Technologies; Venice, CA, USA Abstract: A novel interferometric scheme for detection of ultrasound is presented.
An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm
 An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm Ma Yangwu *, Liang Di ** Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Lab of Modern Optical
An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm Ma Yangwu *, Liang Di ** Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Lab of Modern Optical
Physics of Waveguide Photodetectors with Integrated Amplification
 Physics of Waveguide Photodetectors with Integrated Amplification J. Piprek, D. Lasaosa, D. Pasquariello, and J. E. Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa
Physics of Waveguide Photodetectors with Integrated Amplification J. Piprek, D. Lasaosa, D. Pasquariello, and J. E. Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa
Tunable Color Filters Based on Metal-Insulator-Metal Resonators
 Chapter 6 Tunable Color Filters Based on Metal-Insulator-Metal Resonators 6.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss the culmination of Chapters 3, 4, and 5. We report a method for filtering white light
Chapter 6 Tunable Color Filters Based on Metal-Insulator-Metal Resonators 6.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss the culmination of Chapters 3, 4, and 5. We report a method for filtering white light
Optical MEMS pressure sensor based on a mesa-diaphragm structure
 Optical MEMS pressure sensor based on a mesa-diaphragm structure Yixian Ge, Ming WanJ *, and Haitao Yan Jiangsu Key Lab on Opto-Electronic Technology, School of Physical Science and Technology, Nanjing
Optical MEMS pressure sensor based on a mesa-diaphragm structure Yixian Ge, Ming WanJ *, and Haitao Yan Jiangsu Key Lab on Opto-Electronic Technology, School of Physical Science and Technology, Nanjing
Supplementary Figure S1. Characterization using X-ray diffraction (XRD). (a) Starting titanium (Ti) foil used for the synthesis (JCPDS No ).
 Supplementary Figure S1. Characterization using X-ray diffraction (XRD). (a) Starting titanium (Ti) foil used for the synthesis (JCPDS No. 65-3362). (b) Oxidized Rutile titanium dioxide (TiO 2 ) obtained
Supplementary Figure S1. Characterization using X-ray diffraction (XRD). (a) Starting titanium (Ti) foil used for the synthesis (JCPDS No. 65-3362). (b) Oxidized Rutile titanium dioxide (TiO 2 ) obtained
Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.15, No.2, 1 6 Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna Hiroshi Hashiguchi a), Toshihiko Baba, and Hiroyuki Arai Graduate School of
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.15, No.2, 1 6 Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna Hiroshi Hashiguchi a), Toshihiko Baba, and Hiroyuki Arai Graduate School of
Narrowing spectral width of green LED by GMR structure to expand color mixing field
 Narrowing spectral width of green LED by GMR structure to expand color mixing field S. H. Tu 1, Y. C. Lee 2, C. L. Hsu 1, W. P. Lin 1, M. L. Wu 1, T. S. Yang 1, J. Y. Chang 1 1. Department of Optical and
Narrowing spectral width of green LED by GMR structure to expand color mixing field S. H. Tu 1, Y. C. Lee 2, C. L. Hsu 1, W. P. Lin 1, M. L. Wu 1, T. S. Yang 1, J. Y. Chang 1 1. Department of Optical and
Radial Polarization Converter With LC Driver USER MANUAL
 ARCoptix Radial Polarization Converter With LC Driver USER MANUAL Arcoptix S.A Ch. Trois-portes 18 2000 Neuchâtel Switzerland Mail: info@arcoptix.com Tel: ++41 32 731 04 66 Principle of the radial polarization
ARCoptix Radial Polarization Converter With LC Driver USER MANUAL Arcoptix S.A Ch. Trois-portes 18 2000 Neuchâtel Switzerland Mail: info@arcoptix.com Tel: ++41 32 731 04 66 Principle of the radial polarization
Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 74, 47 52, 2018 Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application Gobinda Sen * and Santanu Das Abstract A frequency tunable multi-layer
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 74, 47 52, 2018 Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application Gobinda Sen * and Santanu Das Abstract A frequency tunable multi-layer
Achievement of Arbitrary Bandwidth of a Narrow Bandpass Filter
 Achievement of Arbitrary Bandwidth of a Narrow Bandpass Filter Cheng-Chung ee, Sheng-ui Chen, Chien-Cheng Kuo and Ching-Yi Wei 2 Department of Optics and Photonics/ Thin Film Technology Center, National
Achievement of Arbitrary Bandwidth of a Narrow Bandpass Filter Cheng-Chung ee, Sheng-ui Chen, Chien-Cheng Kuo and Ching-Yi Wei 2 Department of Optics and Photonics/ Thin Film Technology Center, National
New application of liquid crystal lens of active polarized filter for micro camera
 New application of liquid crystal lens of active polarized filter for micro camera Giichi Shibuya, * Nobuyuki Okuzawa, and Mitsuo Hayashi Department Devices Development Center, Technology Group, TDK Corporation,
New application of liquid crystal lens of active polarized filter for micro camera Giichi Shibuya, * Nobuyuki Okuzawa, and Mitsuo Hayashi Department Devices Development Center, Technology Group, TDK Corporation,
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 20 at the start of class
 PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
A NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR DWDM OPTICAL NETWORKS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 11, 213 223, 2010 A NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR DWDM OPTICAL NETWORKS A. Banerjee Department of Electronics and Communication
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 11, 213 223, 2010 A NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR DWDM OPTICAL NETWORKS A. Banerjee Department of Electronics and Communication
Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings
 Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu Optical Engineering 52(9), 091708 (September 2013) Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu
Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu Optical Engineering 52(9), 091708 (September 2013) Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu
High-Speed Scalable Silicon-MoS 2 P-N Heterojunction Photodetectors
 High-Speed Scalable Silicon-MoS 2 P-N Heterojunction Photodetectors Veerendra Dhyani 1, and Samaresh Das 1* 1 Centre for Applied Research in Electronics, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi-110016,
High-Speed Scalable Silicon-MoS 2 P-N Heterojunction Photodetectors Veerendra Dhyani 1, and Samaresh Das 1* 1 Centre for Applied Research in Electronics, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi-110016,
Optical behavior. Reading assignment. Topic 10
 Reading assignment Optical behavior Topic 10 Askeland and Phule, The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4 th Ed.,Ch. 0. Shackelford, Materials Science for Engineers, 6 th Ed., Ch. 16. Chung, Composite
Reading assignment Optical behavior Topic 10 Askeland and Phule, The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4 th Ed.,Ch. 0. Shackelford, Materials Science for Engineers, 6 th Ed., Ch. 16. Chung, Composite
First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation
 SLAC 95 6913 June 1995 First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation Hung-chi Lihn, Pamela Kung, Chitrlada Settakorn, and Helmut Wiedemann Applied Physics Department and Stanford Linear
SLAC 95 6913 June 1995 First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation Hung-chi Lihn, Pamela Kung, Chitrlada Settakorn, and Helmut Wiedemann Applied Physics Department and Stanford Linear
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 8, August ISSN Design and analysis Narrowband filters
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 8, August-2013 1854 Design and analysis Narrowband filters Gaillan H.Abdullah *,Bushra.R.Mahdi **, Farah G. *g_altayar@yahoo.com,boshera65m@yahoo.com
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 8, August-2013 1854 Design and analysis Narrowband filters Gaillan H.Abdullah *,Bushra.R.Mahdi **, Farah G. *g_altayar@yahoo.com,boshera65m@yahoo.com
ARCoptix. Radial Polarization Converter. Arcoptix S.A Ch. Trois-portes Neuchâtel Switzerland Mail: Tel:
 ARCoptix Radial Polarization Converter Arcoptix S.A Ch. Trois-portes 18 2000 Neuchâtel Switzerland Mail: info@arcoptix.com Tel: ++41 32 731 04 66 Radially and azimuthally polarized beams generated by Liquid
ARCoptix Radial Polarization Converter Arcoptix S.A Ch. Trois-portes 18 2000 Neuchâtel Switzerland Mail: info@arcoptix.com Tel: ++41 32 731 04 66 Radially and azimuthally polarized beams generated by Liquid
Physics 476LW. Advanced Physics Laboratory - Microwave Optics
 Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Microwave Radiation Introduction Setup The purpose of this lab is to better understand the various ways that interference of EM radiation manifests itself. However,
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Microwave Radiation Introduction Setup The purpose of this lab is to better understand the various ways that interference of EM radiation manifests itself. However,
Waves Mechanical vs. Electromagnetic Mechanical Electromagnetic Transverse vs. Longitudinal Behavior of Light
 PSC1341 Chapter 4 Waves Chapter 4: Wave Motion A.. The Behavior of Light B. The E-M spectrum C. Equations D. Reflection, Refraction, Lenses and Diffraction E. Constructive Interference, Destructive Interference
PSC1341 Chapter 4 Waves Chapter 4: Wave Motion A.. The Behavior of Light B. The E-M spectrum C. Equations D. Reflection, Refraction, Lenses and Diffraction E. Constructive Interference, Destructive Interference
Nanophotonic trapping for precise manipulation of biomolecular arrays
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.79 Nanophotonic trapping for precise manipulation of biomolecular arrays Mohammad Soltani, Jun Lin, Robert A. Forties, James T. Inman, Summer N. Saraf,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.79 Nanophotonic trapping for precise manipulation of biomolecular arrays Mohammad Soltani, Jun Lin, Robert A. Forties, James T. Inman, Summer N. Saraf,
Femtosecond laser microfabrication in. Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca
 Femtosecond laser microfabrication in polymers Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca laser microfabrication focus laser beam on material s surface laser microfabrication laser microfabrication laser microfabrication
Femtosecond laser microfabrication in polymers Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca laser microfabrication focus laser beam on material s surface laser microfabrication laser microfabrication laser microfabrication
Angela Piegari ENEA, Optical Coatings Laboratory, Roma, Italy
 Optical Filters for Space Instrumentation Angela Piegari ENEA, Optical Coatings Laboratory, Roma, Italy Trieste, 18 February 2015 Optical Filters Optical Filters are commonly used in Space instruments
Optical Filters for Space Instrumentation Angela Piegari ENEA, Optical Coatings Laboratory, Roma, Italy Trieste, 18 February 2015 Optical Filters Optical Filters are commonly used in Space instruments
