4/17/01. Design Seminar. Agilent EEsof Customer Education and Applications. MESFET Power Amplifier Design: Small Signal Approach
|
|
|
- Aubrey Wheeler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Design Seminar Agilent EEsof Customer Education and Applications MESFET Power Amplifier Design: Small Signal Approach 1
2 About the Author Al Sweet PhD, Cornell University Design Engineering: RF/microwave circuits Consultant to the industry since Author: MMIC and MIC Amplifier and Oscillator Design, Artech House, Page 2 BIOGRAHPICAL SKETCH Al Sweet is a consultant to industry in the area of RF and Microwave circuit design. He began consulting in 1979, after working for MA/COM, Varian Associates, and the Watkins-Johnson Company after completing his PhD degree at Cornell University in Between 1992 and 1997 Al worked full time for Rockwell and Wireless Data Corp (where he was Vice President of Engineering), but returned to Consulting in Today he is very active as a design consultant in all facets of RF and Microwave circuit design, and his clients include many of the leading wireless companies in Silicon Valley and around the World. In 1990 Al published an industry standard text/reference book MMIC and MIC Amplifier and Oscillator Design (Artech House, 1990) in which he describes design as a methodical process from specification definition to circuit fabrication. Al is married and has seven grown children. His hobbies include amateur radio, many forms of music (he plays guitar and enjoys listening to music CD s), reading, and travel. He and his wife Fran and their dog Pacey (a 90 pound Doberman) live in a turn of the century Craftsman house in Alameda California. 2
3 Basic engineering problem: How to design a Power Amplifier without a large signal device model? Many device manufacturers do not supply large signal device models for their devices. Most often the only design data supplied is the device small signal S-parameters and static IV curves. This data is sufficient to perform a first order power amplifier design using the load line method first described by Steve Cripps. Page 3 Power amplifiers are inherently large signal components because their behavior as power saturation is approached is nonlinear by nature. However, in many cases, designers have only a set of measured small signal S parameters as a starting point for representing the active device in circuit simulations. Since these S parameters are only applicable to small signal levels, it is not clear how the design is to be accomplished in terms of maximizing RF power output and linearity at large signal levels. A first order design may be done by following a method first described by Steve Cripps, in which the device s static IV curves are used to determine a large signal load line impedance (RL), which is used as the goal impedance to be presented to the device s drain terminals by the output matching circuit. By following this method, the designer may optimize the output circuit for maximum RF power output and at the same time optimize the input circuit for best input match and maximum gain. In general the output match will be poor, because it is intentionally mismatched inorder to achieve maximum RF power generation (I.e. the output match is optimized on RL rather than the device's S22). 3
4 Limitations of this technique Optimizes for max Psat only Only effective for class A and AB operation No estimated intermod levels: IMR3, IMR5, IP3 No estimated harmonic levels No estimated ACPR (for digital modulations) Page 4 The small signal design technique has its limitations. The output circuit is optimized for maximum saturated RF power, but not necessarily maximum linear power. This means that there is no way to directly calculate the 1 db compressed power output. Also, there is no way to directly calculate the amplifier s two tone intermodulation behavior as described by the parameters IMR3, IMR5, IP3, and IP5. In order to estimate these important parameters, the designer must rely either on measurements or rules of thumb. Two important rules of thumb that apply to MESFET amplifier design are: P-1dB is approximately 1 db less than Psat. IP3 is approximately 10 to 12 db greater than P-1dB. 4
5 Topics Solving for Max Power using Small Signal Techniques Design Flow (step-by-step) Specifications Choosing a device Calculating load line resistance from IV curves Matching Networks Distributed vs Lumped Simulations: Gain, input match, and output match Extracting Package Parasitics Maximize Power: matching to the load line resistance Amplifier stability as measured by the K factor Page 5 This slide presents a table of contents for the rest of the seminar. 5
6 Basic Design Process Flow Device choice: cascaded requirement Matching topology: freq & BW Bias Circuit: Class A & pwr supply requirement s Optimize: S11 and S21 Recalculate S11 and S21 & check K >1 (wideband) Add Stability Elements (if necessary) Optimize: Output Match to R load Extract pkg parasitics from S-parms Construct load line R from I-V curves Result: Max Power Output Page 6 DESIGN PROCESS STEPS: Device choice based on the requirements of the cascaded chain of amplifier stages. Be sure that the entire chain goes smoothly into saturation together. No one stage should start to saturate first. Choose a matching topology based on frequency, bandwidth, cost goals, and experience. Choose a bias circuit based on class of operation and power supply requirements. MESFETS require negative gate voltage, which must be provided with the biasing circuit. For highly linear operation, class A operation is recommended. In class A operation, the DC drain current will be 1/2 of the device s Imax. Optimize the input circuit for gain and input match. Determine RL for the device s static IV curves. Extract the package parasitic elements, they will be part of the overall output matching circuit. Optimize the output circuit for best match to RL (this condition will maximize RF power output). If necessary, add circuit elements to insure wideband unconditional stability. 6
7 Small Signal Design Process Represented Graphically Input match for maximum Gain RF IN Input Match Output Match RF OUT Output match for maximum Power Same output matching circuit R L Package Model Output Match RF OUT Page 7 GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF THE SMALL SIGNAL DESIGN PROCESS: Use the device s small signal S-parameters to simulate and optimize gain and input match. Use the device s IV curves to determine RL which serves as a target for the output matching circuit in order to present RL to the device s internal drain terminals, in order to maximize RF power output. This technique is based on a theorem from basic network theory that states that if a network provides a good match to a complex load, then the network s output impedance is equal to the complex conjugate of the load impedance. In our case, the load impedance is RL, which is pure real, so the impedance presented by the optimized output circuit to the device s drain terminals is the complex conjugate of RL which is also RL, since the imaginary part of the load impedance is zero. 7
8 Calculating MESFET load line (RL) for Max RF power from its IV curves Current Load Line Class A Operation for best linearity Imax Imax/2 Bias Point RL = 2(Vb-Vs) / Imax Pout = Imax (Vb-Vs) / 4 Pdc=Vb Imax / 2 Eff = (Vb-Vs) / 2Vb Vs = 2.0 Volts (Approx) Imax = 1.2 Idss (Approx) Knee voltage Vs Vb Voltage Bias (2Vb-Vs) Voltage Potential Breakdown Region Page 8 The proper output impedance for maximum RF power generation can be determined either from measurements, or from a graphical construction using the device s static IV characteristics. A maximum power output load line may be graphically constructed upon the device s static IV characteristics It is this load line resistance, RL, that must be presented by the output matching circuit to the device s output terminals. For maximum linearity it is very important to choose a load line specifically for class A, which is the most linear class of operation. By maximizing its linearity an amplifier is made best suited for operation with digital modulations such as CDMA or TDMA. 8
9 Calculation of Load line Resistance From Bias Voltage and Power Output RL vs Pout for class A Operation RL in ohms R L = (Vb - Vs) 2 2 * Pout RL= 64 / (2*Pout) Vb-Vs = 8 Vb-Vs = Pout in watts RL= 9/ (2*Pout) Page 9 A plot of RL=SQR(Vb-Vs)/2Pout, which in class A operation calculates RL as a function of power output, with bias conditions (i.e. Vb-Vs) as a parameter. Based on the IV graphical construction, a simple calculation of RL in terms of power output is shown Notice that the bias voltage is a parameter of this calculation. Based on only the output power requirement and the anticipated drain-to-source voltage, RL can be calculated directly Load pull experiments have shown that in addition to a pure real load line resistance, it is also necessary when matching to take into account a small reactive component, represented by a capacitor, Cds, in parallel with RL. The value of Cds has been found from experiments to be approximately.10 pf per mm of total gate width. 9
10 Calculation of Minimum Breakdown Voltage vs RL Vb = +10 V (fixed) Vbr G-D MINIMUM (Vbr) gd FOR VARIABLE RL Vbr(gd) > (2PoRL) + Vb +Vpinch-off RL in OHMS Vbr = ( 8RL ) Vbr = ( 4RL ) Po = 1 WATT Po = 2 WATTS Po = 4 WATTS Vbr = ( 2RL ) Page 10 BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE HAS A KEY ROLE IN DETERMINING A GaAs MESFET DEVICE S BIAS VOLTAGE AND OUTPUT POWER LIMITATIONS BASED ON RELIABILITY CONSIDERATIONS. Device reliability is a very important part of every power amplifier design effort. Avalanche breakdown between device contacts is the primary source of non-thermal device failures. How breakdown voltage relates to bias conditions and RF signal levels is the topic of this discussion. We now consider the conditions and considerations that must apply to gain an understanding of this important topic. Class A GaAs MESFET power amplifiers are designed to present an optimum load line resistance to the device s drain-to-source terminals in order to achieve maximum power output for a given set of bias conditions. This load line resistance can easily be determined graphically from the static IV curve construction. What if a non-optimum load resistance is presented to the device s output terminals? If the load resistance is less than the optimum value, the peak RF output voltage will be reduced, decreasing the risk of breakdown failure. However, if the load resistance is greater than the optimum value, the peak RF voltage is increased, which increases the risk of failure. The above plot relates RL, power output, and breakdown. 10
11 Specification Summary with Simulation Applicability SPEC VALUE Small Signal Simulation Large Signal Simulation Freq Gain Match K Psat Plin IP3 Harmonics ACPR 0.9 to 2 GHz db :1 > to +45 dbm +25 to +40 dbm +45 to +60 dbm 30 to 50 dbc 45 to 60 dbc yes yes yes yes yes no no no no yes yes yes yes yes yes yes yes yes Page 11 SPECIFICATION TYPICAL VALUES S.S. SIMULATIONS L.S. SIMULATIONS DIGITAL MOD SIMULATIONS FREQUENCY.90 TO 2.0 GHz YES YES GAIN db YES YES IN/OUT MATCH :1 YES YES STABILITY, K >1.0 YES YES LOAD LINE MATCH 1-10 OHMS YES YES DC VOLTAGE 5 TO 15 VOLTS YES YES DC CURRENT 1 TO 5 AMPS YES YES Pout, SATUARTED 30 TO 45 dbm YES YES Pout, LINEAR 25 TO 40 dbm YES IMR3 30 TO 50 dbc YES IMR5 40 TO 60 dbc YES IP3 45 TO 60 dbm YES IP5 45 TO 60 dbm YES IP3 - P-1dB 12 TO 18 db YES 2nd, 3rd HARM 30 TO 50 dbc YES ACPR 45 TO 60 dbc YES 11
12 Device Data Sheet: Fujitsu FLL351ME Calculate RL from IV curves Page 12 DEVICE CHOICE: We choose the Fujitsu FLL351ME device because it is capable of providing +35 dbm power output with up to 11 db gain. This device is a candidate for the output stage of many types of cellular and PCS infrastructure amplifiers. Notice that the device s static IV curves are provided on this page of the data sheet. 12
13 Device Data Sheet: S-parameters Values at 1.8 GHz Page 13 This page of the FLL351ME s data sheet provides the device s small signal S- parameters which must be read into the simulator in order to calculate gain, match, and stability factor K. 13
14 Device Data Sheet: S-parameters Enter S-parameters into simulator (S2P file) to calculate gain and match: Page 14 This page of the FLL351ME s data sheet provides the device s small signal S- parameters which must be read into the simulator in order to calculate gain, match, and stability factor K. 14
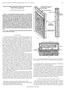
15 Data Sheet - Matching Topology Recommended evaluation circuit for achieving Gain and RF power Page 15 Fujitsu recommends an evaluation circuit for the FLL351ME, which is pictured above. This circuit is a distributed topology, and is printed on a printed circuit board with a dielectric constant of 9.7 and a thickness of.65 mm. This circuit serves the purpose of providing device users with a matching circuit that is capable of demonstrating the gain and power output capabilities of the device at one frequency (2.3 GHz). We will use this circuit as the starting point in applying the small signal design process. 15
16 FLL351ME Load Line Calculation: RL in Class A Operation Derived from the IV Curves: FLL351ME Vbias = 10 volts Vs = 1.8 volts Idss = 1.2 A RL = 2 (10-1.8) (1.2 * 1.2) = 11.4 Ohms Page 16 The above calculation is based on applying the equation for RL to the measured IV parameters of the Fujitsu FLL351ME device which are shown on the data sheet. 16
17 Device Output Circuit: Model Includes Package Elements Internal drain terminals L S R S R L CDS L S R S To Output Matching Network Package Model Page 17 MODEL FOR THE MESFET S OUTPUT CIRCUIT: In optimizing the output circuit to provide exactly RL at the MESFET s internal drain terminals, it is very important to include all other device output circuit elements as a part of the output matching network. The device s Cds and all drain and source package parasitic elements must be included as a part of the total output matching circuit. The package parasitic elements are obtained by extracting them from the device s small signal S parameters. If the device is not packaged, but is in bare chip form (either hybrid or MMIC construction), the package elements can be ignored, simplifying the output matching circuits. Of course any bond wires must still be included as circuit elements. 17
18 Lumped Element Matching Topology Most useful at Low Frequencies V GS V DS RF In FET RF Out Input Matching Output Matching Page 18 LUMPED MATCHING CIRCUIT TOPOLOGY: Matching circuits perform two functions: Matching circuits transform the 50 Ohm source and load impedances to the proper impedance to match the gate and drain of the MESFET for high gain and maximum RF power output. Matching circuits contain reactive elements, and therefore are frequency selective. Matching circuits also determine an amplifier s center frequency and bandwidth. The lumped element matching circuit shown above is most useful at low frequencies where the small size of lumped capacitors and wound inductors have an important over the larger wavelength dependent distributed circuits. This particular lumped matching circuit has a low pass topology. High pass topologies can also be used, as can hybrids between the two. If necessary to achieve a good match over the required bandwidth, additional sections may be added. In general it is advisable to minimize the number of sections, to reduce both circuit complexity and parts cost. Bias is provided by a choke inductor and a bypass capacitor place in both the gate and drain circuits. Input and output are DC blocked with series capacitors. 18
19 Distributed Element Matching Topology Most useful at High Frequencies V gs V ds RF In λ/4 λ/4 FET RF Out Page 19 DISTRIBUTED ELEMENT MATCHING: The above matching circuit is topologically identical to the previously discussed lumped matching circuit. In the distributed circuit, inductors have been replaced with long, narrow microstrip lines. Shunt capacitors have been replaced by short, wide microstrip lines. Bias chokes are replaced with 1/4 wavelength microstrip lines. Distributed matching circuits are most useful at higher frequencies because their element lengths are scaled with frequency, which means that similar circuits become progressively smaller at higher frequencies. Low frequency distributed circuits may be too large to be practical. 19
20 Evaluation Circuit: Fujitsu FLL351ME Fujitsu s Distributed Topology (ADS layout): DC block cap DC block cap mesfet RF in RF out choke choke Page 20 This circuit is shown on page 358 of Fujitsu s 1997 Microwave Semiconductor Databook. The PCB is 26 mils thick, with a relative dielectric constant of 9.7. Blocking capacitors at the input and the output have been added. Choke inductors for gate and drain biasing have also been added. We will next simulated the performance of this circuit. 20
21 Simulation Setup: FLL351ME First pass using Fujitsu s data sheet evaluation circuit: NOTE: S2P file from data sheet IN OUT G bias TRLs D bias Page 21 The complete single ended FLL351ME amplifier can be simulated by ADS. The results will be a calculation of small signal gain, input and output match, isolation, and the stability factor K. The ADS optimizer can be used to optimize circuit elements to improve performance if this is necessary. 21
22 Measurement Equations Inserted on the schematic for use with optimization (if desired). Required for optimizer GOAL. Stability factor equation is built into the ADS system K=(1-sqS11-sqS22+sqD)/2S12S21 where: D=(S11S22-S12S21) Page 22 The complete single ended amplifier can be simulated by ADS. The results will be the calculation of small signal gain, input and output match, isolation, and the stability factor K. The ADS optimizer can be used to optimize circuit elements to improve performance if this is necessary. 22
23 Initial Simulation Results Gain (m1), Input match (m2), Output match (m2) db NOTE: Reverse Isolation (S12) also shown in blue. Freq in GHz Next consider match for power Page 23 Small signal gain, input match, and output match performance looks quite good. Gain is over 10.0 db, and the input and output match, while not too bad at 1.8 GHz are actually peaked in performance at a slightly higher in frequency where the Fujitsu design example is centered. It is expected that output match will be poor when it is adjusted to match RL, for maximum power generation. It is clearly seen from the plot that at frequencies higher than 1.8 GHz, where the design is centered, the output match is degrading while the input match is improving. This is a result of optimizing the output match for maximum power. 23
24 Device Output Matching Options for obtaining Package Parasitics: Obtain from the device s manufacturer Measure the package parasitics EM package modeling Extract from device S-parameters Page 24 As preparation for optimizing the output circuit for maximum RF power generation, it is necessary to determine the device s package parasitic elements. These elements must be determined because they are a part of the total output matching network. If the package cannot be obtained from the device supplier, they must be either measured ( a very difficult procedure), or calculated (requiring a full EM simulation), or extracted from the device s small signal S parameters. By far the most straight forward technique is extraction, whose procedure will be described in the next few slides. 24
25 Equivalent Circuit: Packaged MESFET Extracting the Package Parasitics Package parasitic elements Intrinsic device model elements Page 25 The equivalent circuit of a packaged MESFET device is composed of a set of intrinsic device elements plus a set of package parasitic elements. The equivalent circuit shown in this slide shown the boundary between the two types of circuit elements. 25
26 Setup: Extracting Package Parasitics (1 of 2) Measured S-params port1 port2 Optimization Results: port3 port4 Intrinsic device model Page 26 EXTRACTING PACKAGE PARASITIC ELEMENTS FROM THE MEASURED SMALL SIGNAL S-PARAMETERS. An important consideration in designing power amplifiers using packaged GaAs MESFET devices is to accurately determine the package parasitic elements, which affect all simulations, because these elements are a part of both the complete input and output matching circuits. This is a critical consideration in the output matching circuit because this circuit matches to the device s load resistance, RL and not the measured S-parameters, which contain the package parasitic elements. The load line resistance, RL, which is the impedance which the output matching network must present to the device, is transformed by these parasitic elements. Therefore, the package elements become an important part of the overall output matching circuit. All successful design efforts must include the effects of these package elements. The ADS circuit schematic is based on the ADS example amodeib_pri under mw_ckts. 26
27 Setup: Extracting Package Parasitics (2 of 2) Meas Eqn deltas used in Goal Expressions Page 27 EXTRACTING PACKAGE PARASITIC ELEMENTS FROM THE MEASURED SMALL SIGNAL S-PARAMETERS. An important consideration in designing power amplifiers using packaged GaAs MESFET devices is to accurately determine the package parasitic elements, which affect all simulations, because these elements are a part of both the complete input and output matching circuits. This is a critical consideration in the output matching circuit because this circuit matches to the device s load resistance, RL and not the measured S-parameters, which contain the package parasitic elements. The load line resistance, RL, which is the impedance which the output matching network must present to the device, is transformed by these parasitic elements. Therefore, the package elements become an important part of the overall output matching circuit. All successful design efforts must include the effects of these package elements. The ADS circuit schematic is based on the ADS example amodeib_pri under mw_ckts. 27
28 Measured vs Modeled Results Measured S parameters (red) Optimized equivalent circuit (blue) Optimized Equivalent Circuit Measured Spar Page 28 The package parasitic elements are modeled simply as a series RL circuit in series with the gate, the drain, and the source ports. This equivalent circuit can be analyzed by using Agilent/EESOF ADS to simulate the model s schematic diagram. By using the ADS optimizer, simulated S-parameters of the model can be adjusted to come arbitrarily close to the measured small signal S-parameters of a given device. All circuit elements designated as variables of the optimization process will be iteratively varied in order to home in on close agreement between the equivalent circuit and the measured S- parameters. To facilitate a fast and accurate optimization, it is very important to begin the process with as many of the device s equivalent circuit elements set close to their realistic values. The non-package elements of the device s equivalent circuit may be calculated by applying the device s total gate width, W, in mm, to the a set of approximate, scaleable, small signal GaAs MESFET model elements based on class A operation at IDSS/2, and Vds of 8.0 Volts. This set of device parameters is: Cgs = 1.0 pf/mm Rin = 4.1 Ohms - mm Cds =.20 pf/mm Cgd =.04 pf/mm Rds = 184 Ohms - mm Gm =.082 S/mm 28
29 Simulation Setup: Output Match to RL for Max RF Power Simulation to determine the Output circuit s Match to RL using Fujitsu s evaluation circuit: Drain Parasitics MLIN MLIN S11 Source Parasitics FET Output: R L = 11.4 ohms Cds = 1 pf S-param port Z = 50 ohms (num=1) Page 29 SIMULATING THE AMPLIFIER S POWER PERFORMANCE BASED ON A MEASURED SMALL SIGNAL S-PARAMETER DEVICE MODEL AND THE DEVICE S IV CURVE. If a designer has only measured small signal S-parameters as a device model (along with a measure static IV characteristic) available as a starting point for a power amplifier design project, it is imperative that he/she initially optimize and fix the element values of the output matching circuit at the values necessary to achieve the best possible match to RL (the load line resistance for maximum power generation). The element values in the input matching circuit can then be optimized to improve gain or input match without affecting power output. Prior to optimization, the output circuit must be modeled as completely as possible, and then optimized for the best match to R L at the operating frequency. Extracted drain and source package parasitic elements must be included in this model these elements determine much or all of the series matching inductance. Also, it is very important to include all component parasitic elements in the ADS schematic. Parasitic elements associated with vias, smt capacitors, smt resistors, and inductors are examples. Be sure to contact the component s manufacturer to determine the exact value of each parasitic. Remember that a simulation is only as accurate as the completeness of its model 29
30 Output Match to RL S11 of: -8 db is not good enough... Page 30 The output match is resonant at the correct frequency, however the value of the match is marginal. This indicates a match which is not properly adjusted to RL which is calculated to be 11 Ohms for the FLL351ME device. 30
31 Schematic for Simulating Z Presented to the Device s Internal Drain Terminals S11 Drain Parasitics MLINs from data sheet Bias Network not included in simulation. No effect on RF Page 31 To determine how far away the matching circuit is from providing the target RL of 11.4 Ohms to the device s drain terminal, the circuit simulation schematic diagram is modified to measure the impedance presented by the total output matching network (terminated in a 50 Ohm load) to the device s drain terminals. Bias circuit effects are ignored as minor in this simulation. 31
32 Load Z Presented to the Drain For Max Power: Drain must see RL=11.4 Ohms (calc from IV curves) At 1.8 GHz, RL is about 19 Ohms vs Ohms calculated from the IV curves on the data sheet. Need to Optimize! Page 32 By simulating the matching impedance presented to the device s drain terminals, we confirm that the real part of the impedance is nearly 20 Ohms, rather than the required 11 Ohms. This means the device is not properly matched for maximum power output. 32
33 Optimize to Improve Match to R L Optimize for Max Power Drain Parasitics MLIN MLIN S11 Source Parasitics FET Output: R L = 11.4 ohms Cds = 1 pf Page 33 OPTIMIZING THE AMPLIFIER S PERFORMANCE BASED ON A MEASURED SMALL SIGNAL S-PARAMETER DEVICE MODEL AND THE DEVICE S IV CURVE. If a designer has only measured small signal S-parameters as a device model (along with a measure static IV characteristic) available as a starting point for a power amplifier design project, it is imperative that he/she initially optimize and fix the element values of the output matching circuit at the values necessary to achieve the best possible match to RL (the load line resistance for maximum power generation). The element values in the input matching circuit can then be optimized to improve gain or input match without affecting power output. Prior to optimization, the output circuit must be modeled as completely as possible, and then optimized for the best match to R L at the operating frequency. Extracted drain and source package parasitic elements must be included in this model these elements determine much or all of the series matching inductance. Also, it is very important to include all component parasitic elements in the ADS schematic. Parasitic elements associated with vias, smt capacitors, smt resistors, and inductors are examples. Be sure to contact the component s manufacturer to determine the exact value of each parasitic. Remember that a simulation is only as accurate as the completeness of its model 33
34 Results: Improved Match to R L After S11 Optimization: -15 db return loss Page 34 By using the ADS optimizer to adjust the output circuit element values for best match to RL=11.4 Ohms, the output match is significantly improved. The return is now approaching -15 db, indicating a good match to RL. 34
35 Load Z after Optimizing R L Match R L close to calculated value: At 1.8 GHz R L = Ohms (real part) Next step: stability... Page 35 By again simulating the impedance presented by the optimized output circuit to the device s drain terminals, we confirm that the real part of the impedance is now very close to 11 Ohms. This means that the device s output is now properly matched for maximum RF power generation. 35
36 Amplifier Stability Factor (K) Simulated Results for the Single Ended FLL351ME Amp Area of low Frequency conditional stability (0<K<1.0) indicates need for adding a stabilization network. Use measurement equation from ADS S-parameter palette Page 36 Next, the ADS simulation is used to evaluate the stability of the amplifier over a wide band of frequencies. We find that the stability of the amplifier is unconditional at the operating frequency, but is reduced to conditionally stable at low frequencies. This is a common result because large power MESFET s have very high transconductance, leading to potentially high gain at low frequencies. This high low frequency gain can cause stability problems, which must be corrected by adding a stabilizing network. 36
37 Add a Shorted Stub/50 Ohm Resistor Stabilization Network to Amplifier Input 1/4 wavelength shorted stub = open circuit at 1.8 GHz and short circuit at low frequencies. Reduced low frequency gain improves stability. Page 37 For unconditional stability, the amplifier s stability factor, K, must be greater than 1.0 for all frequencies. To aid stability a simple network consisting of a 50 Ohm resistor in series with a 1/4 wavelength shorted stub is placed in shunt with the single ended amplifier's input. This network greatly enhances a power amplifier s stability at low frequencies, where stability problems often occur due to the high value of a power MESFET s transconductance. 37
38 K results with the Stabilization Network Plotted Stability Factor K NOTE: When necessary, optimize the stabilization network for K > 1.0 (unconditional stability) over a wide bandwidth by adjusting the shorted stub and the termination resistor. Page 38 By including the 50 Ohm resistor/shorted 1/4 wavelength stub stability network, the low frequency stability of the amplifier is significantly improved. Next we will check the gain and match of the amplifier with the both the optimized output circuit and the stability network in place. 38
39 Final Simulation with the Output Circuit Optimized for Max Power Gain (m1), Input match (m2), Output match (m2) Page 39 This slide shows the final simulation of gain, input match, and output match with the optimized output circuit and the stability network in place. Notice that gain has decreased slightly (about.7 db), and output match is not as good as in the first simulation. Both results are to be expected because optimizing the output circuit for best power match, will mismatch the output relative to the devices small signal S parameters (S22), causing both the gain and the output match to degrade slightly. However, overall, the gain and match performance remains very good, with the new assurance that RF power generation is maximized and overall stability is excellent. 39
40 End of Design Seminar... Page 40 40
41 References Bahl, Inder, Microwave Solid State Circuit Design (Wiley 1988) Vendelin, George, A. Pavio and E. Rohde, Microwave Circuit Design (Wiley 1990) Razavi, R.F. Microelectronics (Prentice Hall 1998) Pozar, Microwave Engineering, 2nd. Ed. (Wiley 1998) Cripps, Stephen, RF Power Amplifiers for Wireless Communication (Artech House 1999) Abrie, Pietr, RF and Microwave Amplifier Design (Artech House 1999) Sweet, Allen A., MIC and MMIC Amplifier and Oscillator Circuit Design (Artech House 1990) Page 41 References Bahl, Inder, Microwave Solid State Circuit Design (Wiley 1988) Vendelin, George, A. Pavio and E. Rohde, Microwave Circuit Design (Wiley 1990) Razavi, R.F. Microelectronics (Prentice Hall 1998) Pozar, Microwave Engineering, 2nd. Ed. (Wiley 1998) Cripps, Stephen, RF Power Amplifiers for Wireless Communication (Artech House 1999) Abrie, Pietr, RF and Microwave Amplifier Design (Artech House 1999) Sweet, Allen A., MIC and MMIC Amplifier and Oscillator Circuit Design (Artech House 1990) 41
42 易迪拓培训 专注于微波 射频 天线设计人才的培养网址 : A D S 视频培训课程推荐 ADS Advanced Design System 是由原美国安捷伦科技 ( 现更名为是德科技 ) 推出的微波射频电路 通信系统和 MMIC/RFIC 仿真设计软件, 其功能强大 应用广泛, 被国内高校 科研院所和大型科技公司使用广为使用 掌握 ADS 无疑能提升相关设计领域工程师的技术实力 提高工作效率 为了帮助工程技术人员更好 更快的学习掌握 ADS 的使用, 易迪拓培训 ( 特聘多年 ADS 使用经验的资深专家精心制作推出了多套 ADS 视频培训课程, 由浅入深 全面系统地讲授了 ADS 在微波射频电路设计 通信系统设计和电磁仿真设计方面的仿真设计和应用操作 其中, 视频课程多以设计实例边操作边讲解, 工程实践强, 且直观易学, 能够帮助您在最短的时间内学会使用 ADS, 并把 ADS 真正应用到设计研发工作中去... ADS 学习培训课程套装该套装是易迪拓培训和微波 EDA 网联合推出的迄今为止国内最全面 最权威的 ADS 培训教程, 共包含 10 门 ADS 学习培训课程 课程是由具有多年 ADS 使用经验的微波射频与通信系统设计领域资深专家讲解, 并多结合设计实例, 由浅入深 详细而又全面地讲解了 ADS 在微波射频电路设计 通信系统设计和电磁仿真设计方面的内容 能让您在最短的时间内学会使用 ADS, 迅速提升个人技术能力, 把 ADS 真正应用到实际研发工作中去, 成为 ADS 设计专家... 课程网址 : 更多 ADS 视频培训课程 : 两周学会 ADS 中文视频培训教程最新版 ADS 的入门和进阶培训课程, 适合 ADS2011 ~ ADS2014 以及更新版本 ADS 的学习 是 ADS 初学者的最佳课程, 网址 : ADS 射频模拟电路设计详解 中文视频教程本课程基于新版的 ADS 软件, 由李明洋老师讲授, 讲解了 ADS 在微波射频模拟电路设计中的具体应用, 视频课程, 直观易学, 网址 : ADS 高低阻抗线微带滤波器设计 (ADS2014 版 ) 中文视频教程该门课程旨在帮助学员快速 全面 透彻地理解高低阻抗线微带滤波器的设计原理和设计步骤, 帮助学员学会并掌握使用 ADS 软件仿真分析和优化设计微带线滤波器的实际操作 ; 课程网址 : 更多 ADS 培训课程, 敬请浏览 :
43 ` 专注于微波 射频 天线设计人才的培养易迪拓培训网址 : 关于易迪拓培训 : 易迪拓培训 ( 由数名来自于研发第一线的资深工程师发起成立, 一直致力和专注于微波 射频 天线设计研发人才的培养 ; 后于 2006 年整合合并微波 EDA 网 ( 现已发展成为国内最大的微波射频和天线设计人才培养基地, 成功推出多套微波射频以及天线设计相关培训课程和 ADS HFSS 等专业软件使用培训课程, 广受客户好评 ; 并先后与人民邮电出版社 电子工业出版社合作出版了多本专业图书, 帮助数万名工程师提升了专业技术能力 客户遍布中兴通讯 研通高频 埃威航电 国人通信等多家国内知名公司, 以及台湾工业技术研究院 永业科技 全一电子等多家台湾地区企业 我们的课程优势 : 成立于 2004 年,10 多年丰富的行业经验 一直专注于微波射频和天线设计工程师的培养, 更了解该行业对人才的要求 视频课程 既能达到现场培训的效果, 又能免除您舟车劳顿的辛苦, 学习工作两不误 经验丰富的一线资深工程师讲授, 结合实际工程案例, 直观 实用 易学 联系我们 : 易迪拓培训官网 : 微波 EDA 网 : 官方淘宝店 : 专注于微波 射频 天线设计人才的培养易迪拓培训官方网址 : 淘宝网店 :
Advanced Design System. Release 2005A New Features
 Advanced Design System Release 2005A New Features 2005A: Focus on Simulation Technology Improvements 2005A Delivers Faster, Smarter, Stronger Simulators: DC simulator Harmonic Balance simulator Momentum
Advanced Design System Release 2005A New Features 2005A: Focus on Simulation Technology Improvements 2005A Delivers Faster, Smarter, Stronger Simulators: DC simulator Harmonic Balance simulator Momentum
ADS for your RF Board Design Flow
 Bart Van Hecke Agilent EEsof EDA Page 1 Agilent EEsof EDA Global solution provider and #1 supplier of RF EDA tools Unique position as the only company delivering Test&Measurement solutions as well as EDA
Bart Van Hecke Agilent EEsof EDA Page 1 Agilent EEsof EDA Global solution provider and #1 supplier of RF EDA tools Unique position as the only company delivering Test&Measurement solutions as well as EDA
GSM/GPRS. By Mendy Ouzillou Silicon Laboratories Inc. Austin, TX GSM 3GPP (GSM) burst current) GSM900 DCS V
 GSM/GPRS By Mendy Ouzillou Silicon Laboratories Inc. Austin, TX GSM Q ( ) 3GPP (GSM) burst current) GSM900 DCS1800 50 Ω 3.5 V 25 3.7 V www.silabs.com/pa-calculations 32.75 (GSM) dbm (DCS) 29.75 dbm 1-3)
GSM/GPRS By Mendy Ouzillou Silicon Laboratories Inc. Austin, TX GSM Q ( ) 3GPP (GSM) burst current) GSM900 DCS1800 50 Ω 3.5 V 25 3.7 V www.silabs.com/pa-calculations 32.75 (GSM) dbm (DCS) 29.75 dbm 1-3)
A SMALL PASSIVE UHF RFID TAG FOR METALLIC ITEM IDENTIFICATION. Mun Leng Ng, Kin Seong Leong, and Peter H. Cole
 A SMALL PASSIVE UHF RFID TAG FOR METALLIC ITEM IDENTIFICATION Mun Leng Ng, Kin Seong Leong, and Peter H. Cole Auto-ID Laboratory, School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Adelaide
A SMALL PASSIVE UHF RFID TAG FOR METALLIC ITEM IDENTIFICATION Mun Leng Ng, Kin Seong Leong, and Peter H. Cole Auto-ID Laboratory, School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Adelaide
High frequency ratio antenna for RFID tags
 High frequency ratio antenna for RFID tags Jieh-Sen Kuo *(1), Jyun-Jie Wang (2), and Chih-Yu Huang (3) (1) Department of Electronic Engineering, Kao-Yuan University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan 821, Republic of
High frequency ratio antenna for RFID tags Jieh-Sen Kuo *(1), Jyun-Jie Wang (2), and Chih-Yu Huang (3) (1) Department of Electronic Engineering, Kao-Yuan University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan 821, Republic of
Appendix 6-3: HFSS 3D Excitations
 Appendix 6-3: HFSS 3D Excitations 2015.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS HFSS 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. HFSS Design Setup GUI Mesh Design Setup Solve HPC Geometry Materials Boundaries Solve Setup Excitations 2
Appendix 6-3: HFSS 3D Excitations 2015.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS HFSS 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. HFSS Design Setup GUI Mesh Design Setup Solve HPC Geometry Materials Boundaries Solve Setup Excitations 2
HETERO JUNCTION FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR NE4210M01
 查询 供应商 PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET HETERO JUNCTION FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR C to Ku BAND SUPER LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER N-CHANNEL HJ-FET DESCRIPTION The is a Hetero Junction FET that utilizes the hetero junction
查询 供应商 PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET HETERO JUNCTION FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR C to Ku BAND SUPER LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER N-CHANNEL HJ-FET DESCRIPTION The is a Hetero Junction FET that utilizes the hetero junction
V GG -V TO. rout = Saturation Region I OUT. Vout V SAT V GS V OUT. Sheet 1 of 10. Cascode Current Mirror
 1 of 10 Cascode Current Mirror he main property/feature of a current source/sink is that the current though the device is independent of the voltage across it. Figure 1 shows the most basic of current
1 of 10 Cascode Current Mirror he main property/feature of a current source/sink is that the current though the device is independent of the voltage across it. Figure 1 shows the most basic of current
Ansoft HFSS Antenna Design Kit Design Parameters
 Ansoft HFSS Antenna Design Kit Arien Sligar 2007 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Wire Monopole Low Linear Narrow Monopole Radius Feed Gap Monopole Length Ref: Balanis, Constantine.
Ansoft HFSS Antenna Design Kit Arien Sligar 2007 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Wire Monopole Low Linear Narrow Monopole Radius Feed Gap Monopole Length Ref: Balanis, Constantine.
FDTD Modeling of Noise in Computer Packages
 FDTD Modeling of Noise in Computer Packages Wiren Dale Becker IBM East Fishkill Raj Mittra University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Abstract In this paper, we discuss the electromagnetic modeling of
FDTD Modeling of Noise in Computer Packages Wiren Dale Becker IBM East Fishkill Raj Mittra University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Abstract In this paper, we discuss the electromagnetic modeling of
Internal Compact Dual-Band Printed Loop Antenna for Mobile Phone Application
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 55, NO. 5, MAY 2007 1457 Internal Compact Dual-Band Printed Loop Antenna for Mobile Phone Application Yun-Wen Chi and Kin-Lu Wong Abstract A novel dual-band
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 55, NO. 5, MAY 2007 1457 Internal Compact Dual-Band Printed Loop Antenna for Mobile Phone Application Yun-Wen Chi and Kin-Lu Wong Abstract A novel dual-band
Technology. F. Tabatabai, Member, IEEE, H.S. Al-Raweshidy, Senior Member, IEEE. filter, normally do not possess high quality factor at the
 Proceedings of Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference 2007 C and Ka-Band Wide Bandpass Filter Using LTCC Technology F. Tabatabai, Member, IEEE, H.S. Al-Raweshidy, Senior Member, IEEE Brunel University, Department
Proceedings of Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference 2007 C and Ka-Band Wide Bandpass Filter Using LTCC Technology F. Tabatabai, Member, IEEE, H.S. Al-Raweshidy, Senior Member, IEEE Brunel University, Department
ULTRAWIDEBAND (UWB) communications have attracted
 294 IEEE ANTENNAS AND WIRELESS PROPAGATION LETTERS, VOL. 5, 2006 Circular and Elliptical CPW-Fed Slot and Microstrip-Fed Antennas for Ultrawideband Applications Evangelos S. Angelopoulos, Argiris Z. Anastopoulos,
294 IEEE ANTENNAS AND WIRELESS PROPAGATION LETTERS, VOL. 5, 2006 Circular and Elliptical CPW-Fed Slot and Microstrip-Fed Antennas for Ultrawideband Applications Evangelos S. Angelopoulos, Argiris Z. Anastopoulos,
Topic 7: Harmonic Balance. ADS 2001 Fundamentals - Sept, 2001 Slide 7-1
 Topic 7: Harmonic Balance ADS 2001 Fundamentals - Sept, 2001 Slide 7-1 Harmonic Balance Simulation Analyze circuits with Linear and Non-linear components: You define the tones, harmonics, and power levels
Topic 7: Harmonic Balance ADS 2001 Fundamentals - Sept, 2001 Slide 7-1 Harmonic Balance Simulation Analyze circuits with Linear and Non-linear components: You define the tones, harmonics, and power levels
DESIGN, SIMULATION, FABRICATION AND TESTING OF IMPROVED HYBRID WIDEBAND MICROSTRIP BALUN CIRCUITS AT 2.4 GHz
 DESIGN, SIMULATION, FABRICATION AND TESTING OF IMPROVED HYBRID WIDEBAND MICROSTRIP BALUN CIRCUITS AT 2.4 GHz Preeti Leela Nelapati B.Tech, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, 26 Vijay Desai B.Tech,
DESIGN, SIMULATION, FABRICATION AND TESTING OF IMPROVED HYBRID WIDEBAND MICROSTRIP BALUN CIRCUITS AT 2.4 GHz Preeti Leela Nelapati B.Tech, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, 26 Vijay Desai B.Tech,
Design of a 1.6-mW LC-tuned VCO for 2.4GHz in 0.18-um RF CMOS technology
 Stein Erik Weberg RFIC Design Engineer and Bertel-Eivind Flaten R&D Director March, 2002 Turning RF IC technology into successful design Design of a 1.6-mW LC-tuned VCO for 2.4GHz in 0.18-um RF CMOS technology
Stein Erik Weberg RFIC Design Engineer and Bertel-Eivind Flaten R&D Director March, 2002 Turning RF IC technology into successful design Design of a 1.6-mW LC-tuned VCO for 2.4GHz in 0.18-um RF CMOS technology
R. Dehdasht-Heydari, H. R. Hassani, and A. R. Mallahzadeh
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 81, 183 195, 2008 A NEW 2 18 GHZ QUAD-RIDGED HORN ANTENNA R. Dehdasht-Heydari, H. R. Hassani, and A. R. Mallahzadeh Electrical Engineering Department Shahed
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 81, 183 195, 2008 A NEW 2 18 GHZ QUAD-RIDGED HORN ANTENNA R. Dehdasht-Heydari, H. R. Hassani, and A. R. Mallahzadeh Electrical Engineering Department Shahed
AUTOMATIC Gain Control (AGC) circuits are employed
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: ANALOG AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 45, NO. 3, MARCH 1998 283 On the Design of Constant Settling Time AGC Circuits John M. Khoury, Senior Member, IEEE
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: ANALOG AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 45, NO. 3, MARCH 1998 283 On the Design of Constant Settling Time AGC Circuits John M. Khoury, Senior Member, IEEE
BROADBAND INTEGRATED DTV ANTENNA FOR USB DONGLE APPLICATION
 REFERENCES 1. G.V. Eleftheriades, A.K. Iyer, and P.C. Kremer, Planar negative refractive index media using periodically L-C loaded transmission lines, IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 50 (2002), 2702 2712.
REFERENCES 1. G.V. Eleftheriades, A.K. Iyer, and P.C. Kremer, Planar negative refractive index media using periodically L-C loaded transmission lines, IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 50 (2002), 2702 2712.
Sheet 1 of 10. Vout. Cgd1. Vin. gm g. gm1. Cascode CMOS Circuit
 of 0 Cascode CMOS Circuit The cascode is a combination of a common-source device with a common-gate load. This has the effect of increasing the output impedance but minimises the Miller effect making it
of 0 Cascode CMOS Circuit The cascode is a combination of a common-source device with a common-gate load. This has the effect of increasing the output impedance but minimises the Miller effect making it
SPUR REDUCTION TECHNIQUES IN DIRECT DIGITAL SYNTHESIZERS
 Published in the Proceedings of the 1993 International Frequency Control Symposium. SPUR REDUCTION TECHNIQUES IN DIRECT DIGITAL SYNTHESIZERS Victor S. Reinhardt Hughes Space and Communications Company
Published in the Proceedings of the 1993 International Frequency Control Symposium. SPUR REDUCTION TECHNIQUES IN DIRECT DIGITAL SYNTHESIZERS Victor S. Reinhardt Hughes Space and Communications Company
ACTIVE and passive imaging at millimeter wavelengths
 714 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 58, NO. 3, MARCH 2010 High Permittivity Dielectric Rod Waveguide as an Antenna Array Element for Millimeter Waves J. Patrik Pousi, Dmitri V. Lioubtchenko,
714 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 58, NO. 3, MARCH 2010 High Permittivity Dielectric Rod Waveguide as an Antenna Array Element for Millimeter Waves J. Patrik Pousi, Dmitri V. Lioubtchenko,
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IEC 61169-2 QC 220200 Second edition 2007-02 Radio-frequency connectors Part 2: Sectional specification Radio frequency coaxial connectors of type 9,52 Reference number IEC 61169-2:2007(E)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IEC 61169-2 QC 220200 Second edition 2007-02 Radio-frequency connectors Part 2: Sectional specification Radio frequency coaxial connectors of type 9,52 Reference number IEC 61169-2:2007(E)
A Horizontally Polarized Omnidirectional Printed Antenna for WLAN Applications
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 54, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2006 3551 where the center pin is in contact with the hot electrode of the CPW line and the four grounding pins are soldered to
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 54, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2006 3551 where the center pin is in contact with the hot electrode of the CPW line and the four grounding pins are soldered to
A BROADBAND MICROSTRIP ANTENNA ARRAY FOR LMDS APPLICATIONS
 TABLE 1 Normalized Differential Phase Shift Between Forward and Backward Wave at 3.5 GHz Normalized Differential Phase Shift Ž k 0. Ž deg. 0 90 10 6.6568e-004 4.6596e-004 20 1.3390e-003 1.3979e-003 30
TABLE 1 Normalized Differential Phase Shift Between Forward and Backward Wave at 3.5 GHz Normalized Differential Phase Shift Ž k 0. Ž deg. 0 90 10 6.6568e-004 4.6596e-004 20 1.3390e-003 1.3979e-003 30
THE majority of current global positioning satellite (GPS)
 1618 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 45, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1997 A Dual-Band Circularly Polarized Aperture-Coupled Stacked Microstrip Antenna for Global Positioning Satellite David M.
1618 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 45, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1997 A Dual-Band Circularly Polarized Aperture-Coupled Stacked Microstrip Antenna for Global Positioning Satellite David M.
Signal Integrity and PCB layout considerations for DDR2-800 Mb/s and DDR3 Memories
 Signal Integrity and PCB layout considerations for DDR2-800 Mb/s and DDR3 Memories Fidus Systems Inc. 900, Morrison Drive, Ottawa, Ontario, K2H 8K7, Canada Chris Brennan, Cristian Tudor, Eric Schroeter,
Signal Integrity and PCB layout considerations for DDR2-800 Mb/s and DDR3 Memories Fidus Systems Inc. 900, Morrison Drive, Ottawa, Ontario, K2H 8K7, Canada Chris Brennan, Cristian Tudor, Eric Schroeter,
A Technique for an Array to Generate Circular Polarization with Linearly Polarized Elements
 EEE TRANSACTONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATON, VOL. AP-34, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 1986 1113 A Technique for an Array to Generate Circular Polarization with Linearly Polarized Elements Abstrut-A method is presented
EEE TRANSACTONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATON, VOL. AP-34, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 1986 1113 A Technique for an Array to Generate Circular Polarization with Linearly Polarized Elements Abstrut-A method is presented
Balanced antipodal Vivaldi antenna for wide bandwidth phased arrays
 Balanced antipodal Vivaldi antenna for wide bandwidth phased arrays J.D.S. Langley P.S. Hall P. Newham ndexing terms: Vivald antenna, Phased arrays, Wide bandlimited arrays, Stripline antenna Abstract:
Balanced antipodal Vivaldi antenna for wide bandwidth phased arrays J.D.S. Langley P.S. Hall P. Newham ndexing terms: Vivald antenna, Phased arrays, Wide bandlimited arrays, Stripline antenna Abstract:
Planar Printed Strip Monopole With a Closely-Coupled Parasitic Shorted Strip for Eight-Band LTE/GSM/UMTS Mobile Phone
 3426 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 58, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2010 [15] M. Cheffena and T. Ekman, Dynamic model of signal fading due to swaying vegetation, EURASIP J. Wireless Commun. Networking.
3426 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 58, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2010 [15] M. Cheffena and T. Ekman, Dynamic model of signal fading due to swaying vegetation, EURASIP J. Wireless Commun. Networking.
Colpitts Oscillator Tutorial
 1 of 10 olpitts Oscillator Tutorial J P Silr E-mail: john@rfic.co.uk 1 ABSTAT This paper will describe the design and test of a low noise VHF olpitts voltage controlled oscillator (VO), designed to operate
1 of 10 olpitts Oscillator Tutorial J P Silr E-mail: john@rfic.co.uk 1 ABSTAT This paper will describe the design and test of a low noise VHF olpitts voltage controlled oscillator (VO), designed to operate
CBT/CBT32 Bluetooth Testers
 Version 03.00 CBT/CBT32 Bluetooth Testers July 2007 Fast and comprehensive RF and audio measurements for development, production, and verification Highly flexible troubleshooting in R & D Very short measurement
Version 03.00 CBT/CBT32 Bluetooth Testers July 2007 Fast and comprehensive RF and audio measurements for development, production, and verification Highly flexible troubleshooting in R & D Very short measurement
Traveling-Wave Slot Antennas *
 1624 1PROCEEDINGS OF THE I.R.E. November Traveling-Wave Slot Antennas * J. N. HINESt, ASSOCIATE, IRE, V. H. RUMSEYt, SENIOR MEMBER, IRE, AND C. H. WALTERt, ASSOCIATE, IRE Summary-The traveling-wave slot
1624 1PROCEEDINGS OF THE I.R.E. November Traveling-Wave Slot Antennas * J. N. HINESt, ASSOCIATE, IRE, V. H. RUMSEYt, SENIOR MEMBER, IRE, AND C. H. WALTERt, ASSOCIATE, IRE Summary-The traveling-wave slot
IN THE PAST, various designs have been proposed in the
 48 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 1, JANUARY 1999 A Novel Waveguide-to-Microstrip Transition for Millimeter-Wave Module Applications Frank J. Villegas, Member, IEEE,
48 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 1, JANUARY 1999 A Novel Waveguide-to-Microstrip Transition for Millimeter-Wave Module Applications Frank J. Villegas, Member, IEEE,
Design and Optimization of CMOS RF Power Amplifiers
 166 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 36, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2001 Design and Optimization of CMOS RF Power Amplifiers Ravi Gupta, Associate Member, IEEE, Brian M. Ballweber, Member, IEEE, and David
166 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 36, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2001 Design and Optimization of CMOS RF Power Amplifiers Ravi Gupta, Associate Member, IEEE, Brian M. Ballweber, Member, IEEE, and David
BALUNS ARE A key component of double-balanced
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 1999 1841 Design and Characterization of Multilayer Spiral Transmission-Line Baluns Yeong J. Yoon, Yicheng Lu, Member, IEEE,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 1999 1841 Design and Characterization of Multilayer Spiral Transmission-Line Baluns Yeong J. Yoon, Yicheng Lu, Member, IEEE,
New circuit configurations for designing digital phase shifters
 New circuit configurations for designing 0-80 digital phase shifters B.S. Yarman, BSc, PhD Indexing terms: Microwave circuits networks, Digital circuits, Circuit theory design Abstract: Four novel digital
New circuit configurations for designing 0-80 digital phase shifters B.S. Yarman, BSc, PhD Indexing terms: Microwave circuits networks, Digital circuits, Circuit theory design Abstract: Four novel digital
Estimating Directivity and Gain of Antennas
 Estimating Directivity and Gain of Antennas Warren L. Stutzman Antenna Group Center for Wireless Telecommunications Bradley Department of Electrical Engineering Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
Estimating Directivity and Gain of Antennas Warren L. Stutzman Antenna Group Center for Wireless Telecommunications Bradley Department of Electrical Engineering Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
DEFECTED ground structures (DGSs) yield low-pass performance
 2160 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 54, NO. 5, MAY 2006 Quasi-Static Modeling of Defected Ground Structure Nemai Chandra Karmakar, Senior Member, IEEE, Sushim Mukul Roy, and
2160 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 54, NO. 5, MAY 2006 Quasi-Static Modeling of Defected Ground Structure Nemai Chandra Karmakar, Senior Member, IEEE, Sushim Mukul Roy, and
THERE IS a demand for millimeter-wave and
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 4, APRIL 1999 419 A High-Power Fixed-Tuned Millimeter-Wave Balanced Frequency Doubler David W. Porterfield, Member, IEEE, Thomas W. Crowe,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 4, APRIL 1999 419 A High-Power Fixed-Tuned Millimeter-Wave Balanced Frequency Doubler David W. Porterfield, Member, IEEE, Thomas W. Crowe,
D ular in Japan. Several types of subscriber antennas for
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 44, NO. 4, NOVEMBER 1995 149 A Single-Layer Slotted Leaky Waveguide Array Antenna for Mobile Reception of Direct Broadcast from Satellite Jiro Hirokawa,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 44, NO. 4, NOVEMBER 1995 149 A Single-Layer Slotted Leaky Waveguide Array Antenna for Mobile Reception of Direct Broadcast from Satellite Jiro Hirokawa,
IP2 and IP3 Nonlinearity Specifications for 3G/WCDMA Receivers Chris W. Liu, Morten Damgaard, Broadcom Corporation
 IP and IP Nonlinearity Specifications for G/WCDMA Receivers Chris W. Liu, Morten Damgaard, Broadcom Corporation The complete analysis of the nonlinearity requirements of a WCDMA direct conversion (Zero-IF)
IP and IP Nonlinearity Specifications for G/WCDMA Receivers Chris W. Liu, Morten Damgaard, Broadcom Corporation The complete analysis of the nonlinearity requirements of a WCDMA direct conversion (Zero-IF)
Design and Technology of Microwave and Millimeterwave LTCC Circuits and Systems
 Design and Technology of Microwave and Millimeterwave LTCC Circuits and Systems Ingo Wolff, Life-Fellow, IEEE IMST GmbH Carl-Friedrich-Gauss-Str. 2 D-47475 Kamp-Lintfort, Germany Abstract LTCC technology
Design and Technology of Microwave and Millimeterwave LTCC Circuits and Systems Ingo Wolff, Life-Fellow, IEEE IMST GmbH Carl-Friedrich-Gauss-Str. 2 D-47475 Kamp-Lintfort, Germany Abstract LTCC technology
Chipless RFID Tag Using Hybrid Coding Technique Arnaud Vena, Etienne Perret, Member, IEEE, and Smail Tedjini, Senior Member, IEEE
 3356 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 59, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2011 Chipless RFID Tag Using Hybrid Coding Technique Arnaud Vena, Etienne Perret, Member, IEEE, and Smail Tedjini, Senior
3356 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 59, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2011 Chipless RFID Tag Using Hybrid Coding Technique Arnaud Vena, Etienne Perret, Member, IEEE, and Smail Tedjini, Senior
IN THE last several years, various types of periodic structures
 2968 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 53, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2005 Compact Super-Wide Bandpass Substrate Integrated Waveguide (SIW) Filters Zhang-Cheng Hao, Wei Hong, Member, IEEE,
2968 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 53, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2005 Compact Super-Wide Bandpass Substrate Integrated Waveguide (SIW) Filters Zhang-Cheng Hao, Wei Hong, Member, IEEE,
9 Static Induction Devices
 9 Static Induction Devices Bogdan M. Wilamowski, Ph.D. Alabama Microelectronics Science and Technology Center, Auburn University, Alabama, USA Summary... 133 9.1 Introduction... 133 9.2 Theory of Static
9 Static Induction Devices Bogdan M. Wilamowski, Ph.D. Alabama Microelectronics Science and Technology Center, Auburn University, Alabama, USA Summary... 133 9.1 Introduction... 133 9.2 Theory of Static
ON Power Switching Switcher Solution For consumer electronics. Andy Buk Asia Product Marketing Manager April 2004
 ON Power Switching Switcher Solution For consumer electronics Andy Buk Asia Product Marketing Manager April 2004 Asian Business Unit Analogue Products Marketing Team US Business Unit Analogue Products
ON Power Switching Switcher Solution For consumer electronics Andy Buk Asia Product Marketing Manager April 2004 Asian Business Unit Analogue Products Marketing Team US Business Unit Analogue Products
Big Data and High Performance Computing
 Big Data and High Performance Computing Big data and high performance computing focus on academic research and technology development in areas of high performance computing platform architecture, parallel
Big Data and High Performance Computing Big data and high performance computing focus on academic research and technology development in areas of high performance computing platform architecture, parallel
AK5383 Enhanced Dual Bit Σ 96kHz 24-Bit ADC
 AK5383 Enhanced Dual Bit Σ 96kHz 24Bit ADC GENERAL DESCRIPTION The AK5383 is a 24bit, 128x oversampling 2ch A/D Converter for professional digital audio systems. The modulator in the AK5383 uses the new
AK5383 Enhanced Dual Bit Σ 96kHz 24Bit ADC GENERAL DESCRIPTION The AK5383 is a 24bit, 128x oversampling 2ch A/D Converter for professional digital audio systems. The modulator in the AK5383 uses the new
The art of UHF RFID antenna design: impedance matching and size-reduction techniques
 The art of UHF RFID antenna design: impedance matching and size-reduction techniques Published in IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, Vo.50, N.1, Jan. 2008 Gaetano Marrocco Dipartimento di Informatica
The art of UHF RFID antenna design: impedance matching and size-reduction techniques Published in IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, Vo.50, N.1, Jan. 2008 Gaetano Marrocco Dipartimento di Informatica
Electrical Engineering
 Electrical Engineering Educational Objectives This major aims to cultivate well-grounded, practical, creative and all-round research talents who are well developed in morality, intelligence and physical
Electrical Engineering Educational Objectives This major aims to cultivate well-grounded, practical, creative and all-round research talents who are well developed in morality, intelligence and physical
Passive intermodulation interference in communication systems
 ~ ~~ Passive intermodulation interference in communication systems n multifrequency communications environments, such as land mobile radio sites, satellite earth stations, ships and surveillance aircraft,
~ ~~ Passive intermodulation interference in communication systems n multifrequency communications environments, such as land mobile radio sites, satellite earth stations, ships and surveillance aircraft,
MESFET Distributed Amplifier Design Guidelines
 268 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHIWQUES, VOL. MTT-32, NO. 3, MARCH 1984 MESFET Disribued Amplifier Design Guidelines JAMES B. BEYER, SENIOR MEMBER, IEEE, S. N. PRASAD, MEMBER, IEEE, ROBERT
268 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHIWQUES, VOL. MTT-32, NO. 3, MARCH 1984 MESFET Disribued Amplifier Design Guidelines JAMES B. BEYER, SENIOR MEMBER, IEEE, S. N. PRASAD, MEMBER, IEEE, ROBERT
Slicing of Aspect-Oriented Programs Based on Reduced Dynamic Dependence Graph *
 ISSN 1673-9418 CODEN JKYTA8 E-mail: fcst@vip.163.com Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology http://www.ceaj.org 1673-9418/2011/05(03)-0229-09 Tel: +86-10-51616056 DOI: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2011.03.004
ISSN 1673-9418 CODEN JKYTA8 E-mail: fcst@vip.163.com Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology http://www.ceaj.org 1673-9418/2011/05(03)-0229-09 Tel: +86-10-51616056 DOI: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2011.03.004
A Self-Adaptive Low-Voltage Current Mode ASK Demodulator for RFID Tags
 A Self-Adaptive Low-Voltage Current Mode ASK Demodulator for RFID Tags Wei Liu, Yongming Li, Chun Zhang, Zhihua Wang Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology Institute of Microelectronics,
A Self-Adaptive Low-Voltage Current Mode ASK Demodulator for RFID Tags Wei Liu, Yongming Li, Chun Zhang, Zhihua Wang Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology Institute of Microelectronics,
LM117/LM217/LM V to 37V Adjustable voltage regulators. Feature summary. Description. Order code
 1.2V to 37V Adjustable voltage regulators Feature summary Output voltage range: 1.2 to 37V Output current in excess of 1.5A 0.1% Line and load regulation Floating operation for high voltages Complete series
1.2V to 37V Adjustable voltage regulators Feature summary Output voltage range: 1.2 to 37V Output current in excess of 1.5A 0.1% Line and load regulation Floating operation for high voltages Complete series
GAMI Newsletter. Foreword. News. News Industry Projects Training Events Contact. News Industry Projects Training Events Contact
 Foreword Dear Partners and Friends, The Global Advanced Manufacturing Institute is aiming at implementing Operational Excellence to manufacturing companies in China. During the first quarter of 2016, we
Foreword Dear Partners and Friends, The Global Advanced Manufacturing Institute is aiming at implementing Operational Excellence to manufacturing companies in China. During the first quarter of 2016, we
WiFi 雷达 无所不在的感知 清华大学软件学院
 WiFi 雷达 无所不在的感知 杨铮 清华大学软件学院 Outline Introduction Background Methods & Applications Conclusion 2 WiFi Signals Everywhere Visualization of WiFi signals by Luis Hernan 3 WiFi as Radar? WiFi Radar Omnipresent
WiFi 雷达 无所不在的感知 杨铮 清华大学软件学院 Outline Introduction Background Methods & Applications Conclusion 2 WiFi Signals Everywhere Visualization of WiFi signals by Luis Hernan 3 WiFi as Radar? WiFi Radar Omnipresent
SVPWM 三相电压源型逆变器的死区时间效应可能会导致电压损失, 电流波形畸变和转矩脉动. 为了改善电流波形, 减少转矩脉动, 详细分析了死区时间对输出电压的影响, 并提出了 SVPWM A
 18 1 2013 2 Vol 18 No 1 JOURNAL OF HARBIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Feb 2013 SVPWM 150050 三相电压源型逆变器的死区时间效应可能会导致电压损失, 电流波形畸变和转矩脉动 为了改善电流波形, 减少转矩脉动, 详细分析了死区时间对输出电压的影响, 并提出了 SVPWM 死区时间的补偿方法 该方法通过改变传统的
18 1 2013 2 Vol 18 No 1 JOURNAL OF HARBIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Feb 2013 SVPWM 150050 三相电压源型逆变器的死区时间效应可能会导致电压损失, 电流波形畸变和转矩脉动 为了改善电流波形, 减少转矩脉动, 详细分析了死区时间对输出电压的影响, 并提出了 SVPWM 死区时间的补偿方法 该方法通过改变传统的
8 English P.20 한국의 P.21 中 文 P.22
 8 English P. 20 한국의 P. 21 中文 P. 22 인터넷 시스템 이용가이드 络 统 0120-615-919 support@broad-e.co.jp http://b-cubic.com/user/ 英 :If you have any inquiries about settings or connection please contact the Internet
8 English P. 20 한국의 P. 21 中文 P. 22 인터넷 시스템 이용가이드 络 统 0120-615-919 support@broad-e.co.jp http://b-cubic.com/user/ 英 :If you have any inquiries about settings or connection please contact the Internet
第 21 届中国国际工业博览会. China International Industry Fair 2019
 第 21 届中国国际工业博览会 China International Industry Fair 2019 国家会展中心 ( 上海 ) 2019 年 9 月 17 日 -21 日 National Exhibition and Convention Center (Shanghai) 17-21 September 2019 组织机构 ORGANIZING STRUCTURE 主办单位 工业和信息化部
第 21 届中国国际工业博览会 China International Industry Fair 2019 国家会展中心 ( 上海 ) 2019 年 9 月 17 日 -21 日 National Exhibition and Convention Center (Shanghai) 17-21 September 2019 组织机构 ORGANIZING STRUCTURE 主办单位 工业和信息化部
Table of Contents. DS177-ZH LUXEON V2 Product Datasheet Lumileds Holding B.V. All rights reserved.
 Illumination LUXEON V2 卓越性能 更多可用光 久经验证的封装 设计 LUXEON V2 是一种基于芯片级封装 (CSP 的高功率圆顶 LED 针对定向应用 进行了优化 传承了 Lumileds 在同类产品中的领先地位 LUXEON V2 具备 优越的效能和稳健性 采用 3 条式 3535 封装 可通过与 LUXEON TX 辐射模 式相匹配加快产品的上市时间 同时通过在更高驱动电流下提供无与伦比的
Illumination LUXEON V2 卓越性能 更多可用光 久经验证的封装 设计 LUXEON V2 是一种基于芯片级封装 (CSP 的高功率圆顶 LED 针对定向应用 进行了优化 传承了 Lumileds 在同类产品中的领先地位 LUXEON V2 具备 优越的效能和稳健性 采用 3 条式 3535 封装 可通过与 LUXEON TX 辐射模 式相匹配加快产品的上市时间 同时通过在更高驱动电流下提供无与伦比的
The Design of Small Slot Arrays
 214 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. AP-26, NO. 2, MARCH 1978 3) The 75 percent BW element design over qurter-hemisphere mximum VSWR vlue of 16, nd consequently, to be prcticl, will
214 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. AP-26, NO. 2, MARCH 1978 3) The 75 percent BW element design over qurter-hemisphere mximum VSWR vlue of 16, nd consequently, to be prcticl, will
本科专业人才培养计划 机械学科大类分册 华中科技大学教务处 二 O 一五年七月
 本科专业人才培养计划 机械学科大类分册 华中科技大学教务处 二 O 一五年七月 目 录 1 3 * 20 * 34 *46 62 75 80 81 * 91 * 99 * 108 116 126 128 * 146 * 155 166 178 179 193 207 注 : 带 * 者不属于机械学科大类专业 1 机械科学与工程学院 华中科技大学机械科学与工程学院前身系华中工学院机械工程系,1988
本科专业人才培养计划 机械学科大类分册 华中科技大学教务处 二 O 一五年七月 目 录 1 3 * 20 * 34 *46 62 75 80 81 * 91 * 99 * 108 116 126 128 * 146 * 155 166 178 179 193 207 注 : 带 * 者不属于机械学科大类专业 1 机械科学与工程学院 华中科技大学机械科学与工程学院前身系华中工学院机械工程系,1988
WiMAX 技术培训系列 ( 一 ) OFDM 物理层技术初探 MCG 赵昕 2006 年 2 月. All rights reserved 2006, Alcatel Shanghai Bell
 WiMAX 技术培训系列 ( 一 ) OFDM 物理层技术初探 MCG 赵昕 2006 年 2 月 目录 Page 2 一. 为什么出现 WiMAX? 二. 什么是 WiMAX? 三. 什么是 OFDM/OFDMA? 四.WiMAX 的 PHY 层五.WiMAX 接入过程 Page 3 一. 为什么出现 WiMAX? 一. 为什么出现 WiMAX? 移动通信的发展过程正在从 3Any 向 Olympics
WiMAX 技术培训系列 ( 一 ) OFDM 物理层技术初探 MCG 赵昕 2006 年 2 月 目录 Page 2 一. 为什么出现 WiMAX? 二. 什么是 WiMAX? 三. 什么是 OFDM/OFDMA? 四.WiMAX 的 PHY 层五.WiMAX 接入过程 Page 3 一. 为什么出现 WiMAX? 一. 为什么出现 WiMAX? 移动通信的发展过程正在从 3Any 向 Olympics
Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor: Additional Concepts
 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor: Additional Concepts Describe and analyze subthreshold conduction. Analyze channel length modulation. Consider the effects of a decrease in carrier mobility
Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor: Additional Concepts Describe and analyze subthreshold conduction. Analyze channel length modulation. Consider the effects of a decrease in carrier mobility
EMF Safety and Actions in China Telecom
 4 th ITU Green Standards Week EMF Safety and Actions in China Telecom Tan Rumeng China Telecommunications Corp. 25 September 2014 Outline 31 Background 2 EMF safety in China 3 EMF actions in China Telecom
4 th ITU Green Standards Week EMF Safety and Actions in China Telecom Tan Rumeng China Telecommunications Corp. 25 September 2014 Outline 31 Background 2 EMF safety in China 3 EMF actions in China Telecom
电池柜 B32 Battery Cabinet B32. 安装说明 Installation Instruction
 电池柜 B Cabinet B 安装说明 Installation Instruction 目录 Contents 一 概述 Summarize 二 电池柜的组成 cabinet composing 三 电池柜的安装步骤 Installation method 四 电池柜的接线图 The wiring diagrams for battery cabinet 敬请周知 操作之前, 请详细阅读使用手册,
电池柜 B Cabinet B 安装说明 Installation Instruction 目录 Contents 一 概述 Summarize 二 电池柜的组成 cabinet composing 三 电池柜的安装步骤 Installation method 四 电池柜的接线图 The wiring diagrams for battery cabinet 敬请周知 操作之前, 请详细阅读使用手册,
Brief Introduction to Degree Program in Control. Science and Engineering (0811)
 Brief Introduction to Degree Program in Control Science and Engineering (0811) I. Brief Introduction to the Discipline 1. Orientation and Goal Southwest Jiaotong University (SWJTU) is one of the oldest
Brief Introduction to Degree Program in Control Science and Engineering (0811) I. Brief Introduction to the Discipline 1. Orientation and Goal Southwest Jiaotong University (SWJTU) is one of the oldest
中华人民共和国国家计量技术规范 定量包装商品净含量计量检验规则
 National Metrology Technical Specifications of the People's Republic of China 中华人民共和国国家计量技术规范 JJF 1070-2005 Rules of Metrological Testing for Net Quantity of Products in Prepackages with Fixed Content
National Metrology Technical Specifications of the People's Republic of China 中华人民共和国国家计量技术规范 JJF 1070-2005 Rules of Metrological Testing for Net Quantity of Products in Prepackages with Fixed Content
Stars Snub Twilight Premiere 明星怠慢 暮光之城 首映式
 Stars Snub Twilight Premiere 明星怠慢 暮光之城 首映式 1 Stars Snub Twilight Premiere 明星怠慢 暮光之城 首映式 Dedicated Fans Left Disappointed 忠实的粉丝们大失所望 Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习
Stars Snub Twilight Premiere 明星怠慢 暮光之城 首映式 1 Stars Snub Twilight Premiere 明星怠慢 暮光之城 首映式 Dedicated Fans Left Disappointed 忠实的粉丝们大失所望 Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习
1 st 5G Algorithm Competition SCMA
 1 st 5G Algorithm Competition SCMA Task Description Requirements 要求 : SCMA 下一代无线通信的稀疏码多址接入 多址接入是无线通信物理层最核心的技术之一, 它使得无线基站能区分并同时服务多个终端用户 现有系统采用正交的多址接入方式, 即多个用户通过在不同维度上 ( 频分 时分 码分等 ) 正交划分的资源来接入, 现在 4G 系统中采用的
1 st 5G Algorithm Competition SCMA Task Description Requirements 要求 : SCMA 下一代无线通信的稀疏码多址接入 多址接入是无线通信物理层最核心的技术之一, 它使得无线基站能区分并同时服务多个终端用户 现有系统采用正交的多址接入方式, 即多个用户通过在不同维度上 ( 频分 时分 码分等 ) 正交划分的资源来接入, 现在 4G 系统中采用的
The audience has given us a lot of positive feedback, some typical ones are listed below:
 NEWSLETTER December 2010 Successful Closing of 2 nd Sharing Best Practice Workshop The 2 nd Sharing Best Practice Workshop held on 2 nd and 3 rd of December, 2010 at the Nansha Grand Hotel cohosted by
NEWSLETTER December 2010 Successful Closing of 2 nd Sharing Best Practice Workshop The 2 nd Sharing Best Practice Workshop held on 2 nd and 3 rd of December, 2010 at the Nansha Grand Hotel cohosted by
从 新 开始! IEEE 新内容 新服务 新活动
 从 新 开始! IEEE 新内容 新服务 新活动 中科院第六届电子资源培训周 湖北武汉,2015 年 4 月 27-30 日 igroup 陈伟 内容 IEEE Xplore 内容更新 IEEE Xplore 功能更新 IEEE/iGroup 与图书馆携手新活动 关于 IEEE World s largest technical membership association with nearly
从 新 开始! IEEE 新内容 新服务 新活动 中科院第六届电子资源培训周 湖北武汉,2015 年 4 月 27-30 日 igroup 陈伟 内容 IEEE Xplore 内容更新 IEEE Xplore 功能更新 IEEE/iGroup 与图书馆携手新活动 关于 IEEE World s largest technical membership association with nearly
US SERIES CONNECTOR FOR AUTOMOBILES
 US SERIES CONNECTOR FOR AUTOMOBILES Specifications of Terminals 0.64 Inline/ Device mm 2 Applicable wire size(mm 2 ) AWG Cable overall diameter(mm) Applicable tab thickness(mm) Contact resistance initial
US SERIES CONNECTOR FOR AUTOMOBILES Specifications of Terminals 0.64 Inline/ Device mm 2 Applicable wire size(mm 2 ) AWG Cable overall diameter(mm) Applicable tab thickness(mm) Contact resistance initial
TEL: voltage is sensed by the isolation amplifier inputs over a low value resistor connected in parallel with the input pins. The analog lineari
 TEL:033922 Designing with High Performance Hermetic Analog Isolation Amplifier, HCPL1 By Jamshed Namdar Khan Optocoupler Applications Engineer Avago Technologies Abstract Optocouplers today are a ubiquitous
TEL:033922 Designing with High Performance Hermetic Analog Isolation Amplifier, HCPL1 By Jamshed Namdar Khan Optocoupler Applications Engineer Avago Technologies Abstract Optocouplers today are a ubiquitous
为了满足客户不同的焊接需求需要, 莱丹研发了最新的 HEMTEK ST 焊接导向件, 可应用于厚达 4mm/0.16 英寸材料的焊接
 1. Produkt-Neuheiten / Product News NEW Guide for the HEMTEK ST Plastic Welding > Technical Textiles & Industrial Fabrics 1.1 New Guide - HEMTEK ST 最新可调节焊接导向件 (4mm) 为了满足客户不同的焊接需求需要, 莱丹研发了最新的 HEMTEK ST
1. Produkt-Neuheiten / Product News NEW Guide for the HEMTEK ST Plastic Welding > Technical Textiles & Industrial Fabrics 1.1 New Guide - HEMTEK ST 最新可调节焊接导向件 (4mm) 为了满足客户不同的焊接需求需要, 莱丹研发了最新的 HEMTEK ST
National Standard of the People's Republic of China 中华人民共和国国家标准
 UDC GB National Standard of the People's Republic of China 中华人民共和国国家标准 P GB/T 50062 2008 Code for Design of Relaying Protection and Automatic Device of Electric Power Installations 电力装置的继电保护和自动装置设计规范 Issued
UDC GB National Standard of the People's Republic of China 中华人民共和国国家标准 P GB/T 50062 2008 Code for Design of Relaying Protection and Automatic Device of Electric Power Installations 电力装置的继电保护和自动装置设计规范 Issued
US SEALED SERIES. Structure. Features 特点. Connector M Connector F
 US SEALED SERIES Structure Connector M Connector F Features 特点 Housing Housing TPA TPA Terminal Terminal Wire Seal Wire Seal US sealed series comply with SAE/USCAR-2. This series consits of 0.64mm, 1.5mm,
US SEALED SERIES Structure Connector M Connector F Features 特点 Housing Housing TPA TPA Terminal Terminal Wire Seal Wire Seal US sealed series comply with SAE/USCAR-2. This series consits of 0.64mm, 1.5mm,
How to Write a Quality Technical Paper and Where to Publish within IEEE 如何撰写高质量科技论文以及在 IEEE 进行论文发表
 How to Write a Quality Technical Paper and Where to Publish within IEEE 如何撰写高质量科技论文以及在 IEEE 进行论文发表 Orignal Speaker, Prof. Saifur Rahman Joseph R. Loring Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering
How to Write a Quality Technical Paper and Where to Publish within IEEE 如何撰写高质量科技论文以及在 IEEE 进行论文发表 Orignal Speaker, Prof. Saifur Rahman Joseph R. Loring Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Mechatronics Engineering Course Introduction
 Mechatronics Engineering Course Introduction Prof. Tianmiao Wang Prof. Li Wen School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation Beihang University Professor biography Tianmiao Wang, Full Professor He worked
Mechatronics Engineering Course Introduction Prof. Tianmiao Wang Prof. Li Wen School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation Beihang University Professor biography Tianmiao Wang, Full Professor He worked
3DD13005ED 主要参数 MAIN CHARACTERISTICS
 主要参数 MAIN CHAACTEISTICS I C V CEO P C (IPAK/126/126S/220HF) P C (DPAK/TO-252) P C (TO-220C/262/263) NPN 型高压功率开关晶体管 HIGH VOLTAGE FAST-SWITCHING NPN POWE TANSISTO 4A 400V 40W 50W 75W 用途 节能灯 电子镇流器 高频开关电源
主要参数 MAIN CHAACTEISTICS I C V CEO P C (IPAK/126/126S/220HF) P C (DPAK/TO-252) P C (TO-220C/262/263) NPN 型高压功率开关晶体管 HIGH VOLTAGE FAST-SWITCHING NPN POWE TANSISTO 4A 400V 40W 50W 75W 用途 节能灯 电子镇流器 高频开关电源
2012 照明产品手册 北高智科技有限公司. 欲了解更多产品资讯 或访问 青岛电话 南京电话 深圳电话
 www.honestar. com 2012 照明产品手册 欲了解更多产品资讯 请邮件至sales@honestar.com 或访问 北高智科技有限公司 深圳电话 86-755-86018818 南京电话 86-25-84725121 青岛电话 86-532-807122 上海电话 86-21-54071246 北京电话 86-10-82358601 西安电话 86-29-686180 杭州电话 86-571-374993
www.honestar. com 2012 照明产品手册 欲了解更多产品资讯 请邮件至sales@honestar.com 或访问 北高智科技有限公司 深圳电话 86-755-86018818 南京电话 86-25-84725121 青岛电话 86-532-807122 上海电话 86-21-54071246 北京电话 86-10-82358601 西安电话 86-29-686180 杭州电话 86-571-374993
Measuring the performance of Knowledge Transfer from Universities to Industry in China. ZHONG Wei Renmin Univ
 Measuring the performance of Knowledge Transfer from Universities to Industry in China ZHONG Wei Renmin Univ 1 Outline What is knowledge transfer, and how can it be measured? Surveys of Knowledge Transfer
Measuring the performance of Knowledge Transfer from Universities to Industry in China ZHONG Wei Renmin Univ 1 Outline What is knowledge transfer, and how can it be measured? Surveys of Knowledge Transfer
YOUR VISION OUR MISSION. Cloud Home. connected car 一条龙服务全面的研发和生产能力.
 YOUR VISION OUR MISSION Cloud Home connected car 一条龙服务全面的研发和生产能力 www.carcommunications.de 创新的技术 独特的用户友好性以及一流的服务相结合, 确保我们的产品 25 年多以来能成功占领市场 在我们的成功因素中, 员工起着核心作用, 他们以专业知识和工作热情每天致力于从时尚潮流和创新理念中创造出创新产品 因此我们的企业目标是
YOUR VISION OUR MISSION Cloud Home connected car 一条龙服务全面的研发和生产能力 www.carcommunications.de 创新的技术 独特的用户友好性以及一流的服务相结合, 确保我们的产品 25 年多以来能成功占领市场 在我们的成功因素中, 员工起着核心作用, 他们以专业知识和工作热情每天致力于从时尚潮流和创新理念中创造出创新产品 因此我们的企业目标是
RACL Activity Class AC Drawing Watercolor Teacher: Liu, Katie WeChat ID: l_katie22
 Teacher: Liu, Katie lkatie.0322@gmail.com 919-917-3667 WeChat ID: l_katie22 Hi, my name is Katie Liu and I m a senior at Raleigh Charter High School a s well as a RACL alumna! I ve been pursuing art for
Teacher: Liu, Katie lkatie.0322@gmail.com 919-917-3667 WeChat ID: l_katie22 Hi, my name is Katie Liu and I m a senior at Raleigh Charter High School a s well as a RACL alumna! I ve been pursuing art for
Warp knitting 经编机 MLF 46 / 24. Multibar Raschel machine for the production of high-quality elastic and rigid lace 生产高品质无弹和弹力花边的多梳拉舍尔经编机
 Warp knitting 经编机 MLF 46 / 24 Multibar Raschel machine for the production of high-quality elastic and rigid lace 生产高品质无弹和弹力花边的多梳拉舍尔经编机 Karl Mayer WARP KNITTING An All-rounder to create EXPRESSIVE ALL-OVER
Warp knitting 经编机 MLF 46 / 24 Multibar Raschel machine for the production of high-quality elastic and rigid lace 生产高品质无弹和弹力花边的多梳拉舍尔经编机 Karl Mayer WARP KNITTING An All-rounder to create EXPRESSIVE ALL-OVER
DATA SHEET. BSP126 N-channel enhancement mode vertical D-MOS transistor DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET N-channel enhancement mode vertical File under Discrete Semiconductors, SC13b April 1995 DESCRIPTION N-channel enhancement mode vertical in a miniature SOT223 envelope
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET N-channel enhancement mode vertical File under Discrete Semiconductors, SC13b April 1995 DESCRIPTION N-channel enhancement mode vertical in a miniature SOT223 envelope
Warp knitting 经编机 MLF 46 / 24 MLF 60 / 32. Multibar Raschel machines for the production of high-quality elastic and rigid lace 生产高品质无弹和弹力花边的多梳拉舍尔经编机
 Warp knitting 经编机 MLF 46 / 24 MLF 60 / 32 Multibar Raschel machines for the production of high-quality elastic and rigid lace 生产高品质无弹和弹力花边的多梳拉舍尔经编机 Karl Mayer WARP KNITTING All-rounder to create EXPRESSIVE
Warp knitting 经编机 MLF 46 / 24 MLF 60 / 32 Multibar Raschel machines for the production of high-quality elastic and rigid lace 生产高品质无弹和弹力花边的多梳拉舍尔经编机 Karl Mayer WARP KNITTING All-rounder to create EXPRESSIVE
Mixed Frequency Allocation Strategy for GSM-R
 Mixed Frequency Allocation Strategy for GSM-R Xiao-Li Jiang, Xu Li State Key Laboratory of Rail Traffic Control and Safety (Beijing Jiaotong University), Beijing, 100044, China Abstract: In this paper,
Mixed Frequency Allocation Strategy for GSM-R Xiao-Li Jiang, Xu Li State Key Laboratory of Rail Traffic Control and Safety (Beijing Jiaotong University), Beijing, 100044, China Abstract: In this paper,
Long-Awaited Film 期待已久的影片
 Long-Awaited Film 期待已久的影片 1 Long-Awaited Film 期待已久的影片 Stars Turn Out for the Premiere in London 明星亮相伦敦首映式 Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 : Sex and the City was a
Long-Awaited Film 期待已久的影片 1 Long-Awaited Film 期待已久的影片 Stars Turn Out for the Premiere in London 明星亮相伦敦首映式 Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 : Sex and the City was a
Fabrication of Schottky Diode in Standard CMOS Process
 Fabrication of Schottky Diode in Standard CMOS Process Qiang Li, Junyu Wang,Yifeng Han, Hao Min, Feng Zhou (State Key Lab of ASIC&System, Fudan University, Shang Hai 200433) Abstract- This paper describes
Fabrication of Schottky Diode in Standard CMOS Process Qiang Li, Junyu Wang,Yifeng Han, Hao Min, Feng Zhou (State Key Lab of ASIC&System, Fudan University, Shang Hai 200433) Abstract- This paper describes
2013 第二届中国工业机器人高峰论坛 2012 年国家工信部发布了 智能制造装备产业 十二五 发展规划, 工业机器人作为 智能制造装备的重要组成部分, 已经迎来了其战略性的发展契机 各地机器人产业园如雨后 春笋, 与此同时, 国际 国内机器人企业加速上马上线 在机器人产业红火的同时, 如何规
 2013 第二届中国工业机器人高峰论坛 前言 2012 年国家工信部发布了 智能制造装备产业 十二五 发展规划, 工业机器人作为 智能制造装备的重要组成部分, 已经迎来了其战略性的发展契机 各地机器人产业园如雨后 春笋, 与此同时, 国际 国内机器人企业加速上马上线 在机器人产业红火的同时, 如何规 范发展 和谐发展, 如何顺应应用发展趋势研发 提升技术含量越来越成为机器人发展面临 的新课题 中国国际工业博览会暨
2013 第二届中国工业机器人高峰论坛 前言 2012 年国家工信部发布了 智能制造装备产业 十二五 发展规划, 工业机器人作为 智能制造装备的重要组成部分, 已经迎来了其战略性的发展契机 各地机器人产业园如雨后 春笋, 与此同时, 国际 国内机器人企业加速上马上线 在机器人产业红火的同时, 如何规 范发展 和谐发展, 如何顺应应用发展趋势研发 提升技术含量越来越成为机器人发展面临 的新课题 中国国际工业博览会暨
Cigars in Hong Kong, China
 Cigars in Hong Kong, China Customer Service Hotline:400-666-1917 Page 1 of 11 一 调研说明中商情报网全新发布的 Cigars in Hong Kong, China 主要依据国家统计局 国家发改委 商务部 中国海关 国务院发展研究中心 行业协会 工商 税务 海关 国内外相关刊物的基础信息以及行业研究单位等公布和提供的大量资料,
Cigars in Hong Kong, China Customer Service Hotline:400-666-1917 Page 1 of 11 一 调研说明中商情报网全新发布的 Cigars in Hong Kong, China 主要依据国家统计局 国家发改委 商务部 中国海关 国务院发展研究中心 行业协会 工商 税务 海关 国内外相关刊物的基础信息以及行业研究单位等公布和提供的大量资料,
SITRANS F flowmeters SITRANS F US. SITRANS FUS880 (retrofit kit) 4/218 Siemens FI
 SITRNS F flowmeters Siemens G 2007 Overview pplication Irrigation systems Irrigation distribution systems Pumping stations Canal laterals On-farm outlets Water well production rip and sprinkler irrigation
SITRNS F flowmeters Siemens G 2007 Overview pplication Irrigation systems Irrigation distribution systems Pumping stations Canal laterals On-farm outlets Water well production rip and sprinkler irrigation
SMART Manufacturing Technologies - A Chinese Approach to Sustainable Manufacturing-
 ICSM AMT Center at Tongji University Shanghai SMART Manufacturing Technologies - A Chinese Approach to Sustainable Manufacturing- Dr. Ö.S. Ganiyusufoglu -. 葛兴福 Consultant to Chairman of Shenyang Machine
ICSM AMT Center at Tongji University Shanghai SMART Manufacturing Technologies - A Chinese Approach to Sustainable Manufacturing- Dr. Ö.S. Ganiyusufoglu -. 葛兴福 Consultant to Chairman of Shenyang Machine
Version:2.0 M1+/M2/M3
 Version:2.0 M1+/M2/M3 Safety Information CAUTION: To reduce the risk of electric shock, do not remove any cover(or the rear section). No user serviceable parts inside. Refer servicing to qualified service
Version:2.0 M1+/M2/M3 Safety Information CAUTION: To reduce the risk of electric shock, do not remove any cover(or the rear section). No user serviceable parts inside. Refer servicing to qualified service
TEL: the op-amp output would tend to swing to the negative rail (in this case the ground voltage) causing the current to flow. The I PD is
 TEL:0755-833968 Overview of High Performance Analog Optocouplers Application Note 357 Designing Analog Circuits Using the HCNR0 Internally, the HCNR0 analog optocoupler consists of two photo detectors
TEL:0755-833968 Overview of High Performance Analog Optocouplers Application Note 357 Designing Analog Circuits Using the HCNR0 Internally, the HCNR0 analog optocoupler consists of two photo detectors
Fiber 鄄 coupled Diode Laser Flexible Processing Source for Metal Sheet Welding
 第 33 卷摇 212 年 8 月 第 8 期 发摇光摇学摇报 CHINESE JOURNAL OF LUMINESCENCE Vol 郾 33 No 郾 8 Aug., 212 Article ID: 1 鄄 732(212)8 鄄 895 鄄 6 Fiber 鄄 coupled Diode Laser Flexible Processing Source for Metal Sheet Welding
第 33 卷摇 212 年 8 月 第 8 期 发摇光摇学摇报 CHINESE JOURNAL OF LUMINESCENCE Vol 郾 33 No 郾 8 Aug., 212 Article ID: 1 鄄 732(212)8 鄄 895 鄄 6 Fiber 鄄 coupled Diode Laser Flexible Processing Source for Metal Sheet Welding
Compoundtek Your Dedicated Silicon Photonics Partner Compoundtek 您的专属硅光子合作伙伴
 Silicon Photonics Compoundtek Your Dedicated Silicon Photonics Partner Compoundtek 您的专属硅光子合作伙伴 Dedicated 8 Silicon Photonics enhanced foundry services with world class production capabilities. Read More
Silicon Photonics Compoundtek Your Dedicated Silicon Photonics Partner Compoundtek 您的专属硅光子合作伙伴 Dedicated 8 Silicon Photonics enhanced foundry services with world class production capabilities. Read More
