Optimum configuration and design of 1480-nm pumped L-band gain-flattened EDFA using conventional erbium-doped fiber
|
|
|
- Preston Elliott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 September 2000 Ž. Optics Communications Optimum configuration and design of 1480-nm pumped L-band gain-flattened EDFA using conventional erbium-doped fiber Tsair-Chun Liang a,), Yung-Kuang Chen b,1, Jing-Hong Su b, Weng-Hung Tzeng b, Chiek Hu c, Ying-Tso Lin c, Yin-Chieh Lai c,d a Department of Telecommunication Engineering, National Kaohsiung Institute of Marine Technology, Kaohsiung 811, Taiwan b Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Sun Yat-Sen UniÕersity, Kaohsiung 804, Taiwan c Opto-Electronics and Systems Lab., Industrial Technology Research Institute, Chutung, Hsinchu 310, Taiwan d Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Chiao Tung UniÕersity, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan Received 18 May 2000; accepted 4 June 2000 Abstract We theoretically investigate optimum configurations of 1480-pumped L-band Ž nm. gain-flattened erbiumdoped fiber amplifier Ž EDFA., using conventional erbium-doped fiber, for multi-wavelength wavelength division multiplexing Ž WDM. systems. The design criterion of L-band EDFA is to achieve the highest channel output power while keeping the differential channel output power to be F0.7 db among 32 digital baseband channels with low channel noise figure of F5.5 db. A total of nine L-band EDFA configurations are examined and compared. These configurations considered include the dual-forward, dual-backward, and different bi-directional pumping schemes, each with and without the midway optical isolator. Among all configurations, we find that the pump-passed case in forward-and-backward pumping scheme is the best amplifier configuration to offer the highest channel output power with good channel gain uniformity and moderate low noise figure. In addition, the tolerance of the ratio of first-staged EDF length to the total EDF length, and the effects of optical isolation of midway isolator, and pump power degradation on the characteristics of the best configuration are also examined. This investigation provides the EDFA configuration selection for multi-wavelength WDM L-band lightwave systems. q 2000 Published by Elsevier Science B.V. Keywords: Optical amplifier; Erbium-doped fiber amplifier; L-band EDFA; L-band amplifier; Wavelength-division multiplexing; Optical fiber communication 1. Introduction It is vitally important to increase the number of optical channels in wavelength division multiplexing ) Corresponding author. Fax: q ; tcliang@mail.nkimt.edu.tw 1 ykchen@mail.nsysu.edu.tw. Ž WDM. transmission systems. One way to increase channel numbers is to narrow the channel spacing. However, it will worsen the nonlinear effects such as cross-phase modulation Ž XPM. or four-wave mixing Ž FWM. w1,2 x, and makes accurate wavelength control of optical senders necessary. Another way to increase the channel number is to widen the usable wavelength bandwidth in low loss region of the used single-mode fiber r00r$ - see front matter q 2000 Published by Elsevier Science B.V. Ž. PII: S
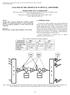
2 52 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers Ž EDFAs. have emerged as vital components for optical fiber networks, serving a wide range of applications from WDM network repeaters to cable-television Ž CATV. power amplifiers and in-line amplifiers. The WDM optical fiber amplifier with a flattened amplification region from to 1560-nm Žconventional band, C-band. has been well investigated w3,4 x. Recently, the other new band, the long wavelength region from 1570 to 1610-nm Ž L-band., has also been widely investigated w5 15x through the use of a long conventional EDF and is very attractive for doubling of the transmission capacity. L-band EDFAs are attractive for application to WDM transmission systems not only as they can increase the amplification wavelength range but they also enable us to construct a WDM transmission system using dispersion-shifted fiber Ž DSF. without any degradation caused by FWM w16 x. The amplification characteristics of L-band ED- FAs by single-staged with a single forward pumped in the 980 and 1480-nm bands have been investiwx 9. Owing to the 1550-nm gated by H. Ono et al. ASE generated by 1480-nm band pumping is the pump source of 1580-nm band amplification and the quantum conversion efficiency to 1550-nm ASE with 1480-nm band pumping is higher than that with 980-nm band pumping, the flattened gain coefficient Ž flatted signal gain to pump power ratio. with nm band pumping were more than twice as high as those with 980-nm band pumping. On the other hand, the noise figure with 1480-nm band pumping was only degraded of 0.5 db by compared with those for 980-nm band pumping. Therefore, the 1480-nm pumping schemes are considered in this work. Several 1480-nm pumped L-band EDFAs have been reported such as the bi-directional forward-and-backward pumping scheme without a midway optical isolator w17 x, dual-backward pumping scheme w8 x, single-forward pumping scheme wx 9, and bi-directional forward-and-backward pumping scheme with a midway isolator w18 x. However, the optimum configuration of such 1480-nm pumped L-band EDFA to offer the imum channel output power with good channel output power uniformity and low noise figure characteristics has not yet been reported. In this paper, we theoretically investigate and compare various 1480-nm pumping EDFA configurations without using external gain equalization technique to amplify 32 digital WDM channel signals operated in the long-wavelength band of nm. The design criterion is to keep the differential channel output power to be F0.7 db among digital channels with low channel noise figure of F5.5 db. These configurations considered include single-stage and two-stage designs in dual-forward, dual-backward, and various bi-directional pumping schemes, each with and without the midway optical isolator. For bi-directional pumping case, the pump-power passed and blocked arrangements are further considered. For the two-stage design, the effects of percentage of first-stage EDF length, and the optical isolation of a midway isolator for the scheme with midway isolator case on the influence of EDFA performance are studied. The effects of pump power and input power of these configurations on EDFA performance are also investigated. A total of nine configurations are examined and compared. The investigation result provides the best L-band EDFA configuration to design both power and in-line amplifiers for multi-wavelength L-band WDM lightwave systems. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, the amplifier configurations with various pumping schemes are firstly introduced, and then the EDFA modeling and simulation considerations are presented. Section 3 presents the optical channel gain, channel output power, and channel noise figure characteristics for various amplifier configurations in dual-forward, dual-backward, and various bi-directional pumping schemes. The effects of pump power, input signal power, the optical isolation of midway isolator, and the percentage of first-stage EDF length of two-stage amplifier structures on the influence of EDFA performance are also investigated in detail. In Section 4, we present the optical channel gain, chan- Fig. 1. Various configurations of 1480-nm-pumped L-band EDFA in Ž. a dual-forward, Ž. b dual-backward, Ž. c bi-directional forward and backward, and Ž. d bi-directional backward and forward pumping schemes.
3 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications
4 54 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications nel noise figure, and the channel ASE power at different position of EDF, especially for the optimum configuration. Finally, we summarize the paper and present our conclusions in Section L-band EDFA configurations and modeling Fig. 1 depicts the high-power low-noise L-band EDFA configurations in Ž. a dual-forward, Ž. b dualbackward, Ž. c bi-directional forward-and-backward, and Ž. d bi-directional backward-and-forward pumping schemes. For each pumping scheme, two pieces of conventional erbium-doped fibers ŽEDF1 and EDF. 2 and two 1480r1580-nm WDM couples are employed to act as the gain media and the pumpr signal combiner, respectively. The dual-forward pumping scheme as shown in Fig. 1Ž. a is named due to the fact that there are two 1480-nm pump semiconductor LDs used and the propagation direction of the pump lights is the same as the signal light. Similarly, the dual-backward pumping as shown in Fig. 1Ž. b is named because two pump LDs are used and the propagation direction of the pump lights is opposite to the signal light. The bi-directional forward-and-backward pumping scheme as shown in Fig. 1Ž. c is named due to two pump laser diodes are used to pump the EDF s from both sides. The bi-directional backward-and-forward pumping scheme as shown in Fig. 1Ž. d is named due to adopting backward-pumping for the first-stage fiber, EDF 1, and forward-pumping for the second-stage fiber, EDF 2. Both dual-forward Ž FF and FFI. and dual-backward Ž BB and BBI. pumping EDFA s are the twostage configurations, in which the midway optical isolator acts as an amplified spontaneous emission Ž ASE. suppression component. The narrowband optical bandpass filter as an ASE suppression component is not considered here due to its inhibition of multiwavelength WDM operation. The forward-and-backward bidirectional pumped EDFA as shown in Fig. 1Ž. c is a two-stage configuration when the inter-stage component is used. There are two operation cases for this amplifier structure; one is the pump-passed case Ž hereafter, FBIp. and another one is the pumpblocked case Ž hereafter, FBIb.. The pump-blocked type as shown in the lower dotted block is the case that when an inter-staged optical isolator is used as the ASE suppressor, in which the forward 1480-nm pump power will be further attenuated by the insertion loss of the midway isolator. On the other hand, the backward 1480-nm pump power will be drastically blocked by the reverse optical isolation of the midway isolator. For the pump-passed case, when a pair of WDM is inserted, the residual pump power is able to pass to the opposite EDF side through the lower 1480-nm path as shown in the upper dotted block. In the mean time, the optical isolator, which is located in the upper optical path, is used to suppress the backward ASE. On the contrary, this two-stage configuration becomes to a single-stage configuration Ž hereafter, FB. when all inter-staged components are removed. The backward-and-forward bi-directional pumped EDFA as shown in Fig. 1Ž. d is also a two-stage configuration whether the inter-stage component is used Ž hereafter, BFI. or not Žhereafter, BF.. Table 1 lists nine kinds of L-band EDFA configurations and their configuration symbols. The simulation tool used in this work is the Lucent Technologies OASIX optical amplifier simulation system Ž Version 2.5., in which the EDFA model used in this work is based on the model by Giles and Desurvire w19 x. The conventional EDF characteristics and EDFA parameters used in the simulations are summarized in Tables 2 and 3, respectively. The insertion loss of each WDM coupler is assumed to be the same with 0.5 db at both 1480 and 1580 nm bands. The isolation of optical isolator is assumed to be 50 db. The 1480-nm pump output power of each pump laser diode is assumed to be 140 mw. A 32-channel signal in the ; nm wavelength range with a channel spacing of 0.8 nm is considered. The input signal power level of each digital channel for each EDFA configuration is set to be y15 dbm at 1580 nm region. There are only two optical connectors used and the others are splicing points for all components within the proposed EDFAs. The insertion loss of each splicing point is assumed to be 0.1 db. Assume that the optical connectors used at the input and output ports of the L-band EDFA are all angled physical contact Ž APC. type with low back-reflection of Fy60 db. The return loss of each splicing point and all other optical components used within the
5 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications Table 1 Nine kinds of L-band EDFA configurations and their configuration symbols Midway optical isolator Pumping schemes Configuration symbols Yes 1. dual forward FFI Yes 2. dual backward BBI Yes 3. bi-directional, forward-backward, pump-blocked FBIb Yes 4. bi-directional, forward-backward, pump-passed FBIp Yes 5. bi-directional, backward-forward BBI No 6. dual forward FF No 7. dual backward BB No 8. bi-directional, forward-backward FB No 9. bi-directional, backward-forward BF EDFA is Fy60 db. Therefore, the optical reflection induced performance degradations of bit-errorrate Ž BER. can be neglected. 3. Characteristic comparison For investigating the optical gain, and noise figure characteristics of each EDFA configuration, the first step is to find the optimum EDF total length of each amplifier configuration for simultaneously achieving the highest channel output power with differential channel output power DP Ž DPsP yp. min of F 0.7 db among 32 digital channels and the noise figure of F5.5 db. Note that the optimum total fiber length here is obtained for imizing the total output power for the EDFA configuration operated at the input power level of y15 dbm for each digital channel. Fig. 2 shows the required optimal EDF total Table 2 Characteristics of conventional erbium-doped fiber used in this work Cutoff wavelength 935 nm Core radius 1.93 mm Index step Ž Dn Numerical aperture Mode field diameter 6.7 mm Background 1.55 mm 0.72 dbrkm 1580 nm 0.4 dbrm Peak absorption 1.53 mm 4.35 dbrm Peak absorption 1.48 mm 1.6 dbrm Erbium concentration 24 y3 6.5=10 m length and the first-stage gain fiber EDF1 length for various amplifier configurations, where EDFtotals EDF1qEDF 2. In order to obtain the optimum EDF total length, we used two iteration loops to achieve total imum output power and the noise figure F5.5 db for each channel for each amplifier configuration. The range of EDF1 and EDF2 lengths set in the simulation are 1;300 m; the increment length of each EDF used in two iteration loops is 1 m. We found that the EDF1 length shorter than the EDF2 length is required for FBIp, BFI, BF, BBI, and BB amplifier configurations. On the other hand, the EDF 1 length of FFI, FF, and FBIb amplifier configurations is about 76;79% of the optimum EDF total length. Among these nine configurations, FBIp scheme re- Table 3 EDFA simulation parameters used in this work Signal wavelengths nm, 32 channels with channel spacing 0.8 nm, separately. Input signal power y15 dbm per channel Pump wavelength 1480 nm Pump power per 140 mw pump laser WDM coupler pump 0.5 db 1480 nm WDM coupler signal 0.5 db 1580 nm Insertion loss of 0.5 db optical isolator Isolation of optical 50 db isolator
6 56 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications Fig. 2. Optimum EDF total length and the EDF1 length for various dual-pumped L-band amplifier configurations, operated with the 1480-nm pump output power of 140 mw for each pump laser diode, and 32-channel signals with a channel spacing of 0.8 nm Ž ; nm. and a channel input power level of y15 dbm. quires the longest optimal EDF total length of 237 m, and BF scheme required the shortest optimal EDF total length of 204 m. Fig. 3 shows Ž. a the channel output power and Ž. b the spectral noise figure characteristics of four amplifier configurations in the optimum EDF lengths without using midway optical isolator. For these four amplifier schemes without using the midway isolator, the FB scheme has the highest channel output power of about 5.3 mw per channel. The FF scheme has the lowest NF of about F 4.4 db. On the contrary, the BF configuration exhibits the lowest output power with rather worse noise figure as compared with other configurations. The noise figure characteristics of F5 db can be maintained only for FB and FF schemes. Fig. 4 shows Ž. a the channel output power and Ž. b the spectral noise figure characteristics of five amplifier configurations with using midway optical isolator operated at the optimum EDF total length condition for the channel input signal of y15 dbm. The low noise figure characteristics of F5 db can only be maintained for FBIp, FBIb and FFI pumping schemes. Note that these schemes are all forward pump for the first-stage fiber EDF 1. The noise figure characteristic for the forward pumping scheme is inherently low due to the nearly full population inversion operation of the first-stage EDF in these two-staged L-band amplifiers. Table 4 summarizes the imum and minimum gains, the imum and minimum noise figures, the ratios of first-stage EDF to the total EDF length, EDF 1 r EDF Total, for these nine EDFA configurations. From the imum output power with satisfied NF point view, among these nine amplifier configurations, FBIp pumping scheme can get the best channel output power of about 6.1 mw per channel with a moderate noise figure of F4.7 db. 4. Characteristics of FBIp configuration Based on the simulation results listed in Table 4, the FBIp pumping scheme is the best L-band EDFA choice for offering the highest channel output power with good channel gain uniformity and low noise figure characteristics for multi-wavelength L-band WDM lightwave systems. Fig. 5 shows the gain and noise figure characteristics at the end of stage-1 and the output port of FBIp-type EDFA, respectively.
7 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications Ž. Ž. Fig. 3. The characteristics of a channel output power and b channel noise figure of four amplifier configurations without using the midway optical isolator. The corresponding noise figure characteristic is 3.6 ;2.9 db for the stage-1 EDFA and 4.3;4.7 db for the cascaded EDFA, respectively. The corresponding channel ASE power evolution at ls nm in the EDF total length within the FBIp configuration is showed in Fig. 6. The EDF total length is 237 m and the midway isolator is put at the 20 m Žthe length of stage-1 EDF.. Note that the ASE power at the 20-m position has a 3.3-dB drop Žfrom y36.7 dbm to y40 dbm. for the solid line and a 53.3-dB drop
8 58 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications Ž. Ž. Fig. 4. The characteristics of a channel output power and b channel noise figure of five amplifier configurations with a midway optical isolator. Ž. from y21.6 dbm to y74.9 dbm for the dash line. The results confirm that the insertion loss of interstaged components including the midway optical isolator is 3.3 db and the optical isolation of midway optical isolator is about 50 db. Fig. 7 shows the imum gain, the differential channel gain DG, and the imum noise figure characteristics of the FBIp scheme as a function of the ratio of EDF1 to the total EDF length. When the ratio of EDF redf Ž %. is G 4.6%, the noise 1 total
9 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications Table 4 The inter-stage isolation and the output characteristics of all configurations by optimum EDF total length used in this work a Characteristics L-band EDFA configurations With midway optical isolator Without midway optical isolator FFI FBIb FBIp BFI BBI FF FB BF BB Insertion loss of inter-stage Ž db EDF length Ž m Single-staged Optimal EDF total length Ž m EDF redf Ž %. 1 total Single-staged G Ž db G min Ž db DG Ž db NF Ž db NF min Ž db DNF Ž db a Lauched with 32 channel signals, each with an input power level of y15 dbm. figure achieves F5.5 db. On the other hand, the ratio region is within 1.2%FEDF redf Ž %. 1 total F 16.9%, the differential channel gain DG off 0.7 db is obtained. So, the ratio of 4.6%; 16.9% of EDF1rEDF total, is the allowable fiber ratio region to meet design criteria of DGF0.7 db and NFF5 db. Fig. 8 shows the effect of input signal power of each channel on the characteristics of imum gain, the differential channel gain DG, and the imum noise figure of the FBIp configuration. For this FBIp scheme, to maintain the output differential channel gain of DGF1 db and the imum noise figure of F5.5 db for 32 input channels, the allowable input power range is from y15 to y14 dbm. When the channel input power range is from y18 to y11 dbm, the differential channel gain DG of F 3 db Fig. 5. The evolution of spectral channel gain and noise figure characteristics of the first-staged and the cascaded-staged amplifier for FBIp-type configurations.
10 60 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications Fig. 6. The forward and backward ASE channel power evolution at ls nm for the FBIp configuration versus the position of EDF length. and the imum noise figure of F5.5 db can be obtained for 32 input channels. The optical isolation effect of the midway optical isolator on the channel gain and noise figure characteristics of the FBIp configuration is shown in Fig. 9. We find that the channel output power characteristics are independent on the midway isolator when the isolation is greater than and equal to 18 db. Fig. 10 Fig. 7. The effect of EDF redf Ž %. on the differential channel gain DG, imum gain G and imum noise figure NF characteristics of the FBIp-type EDFA. 1 total
11 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications Fig. 8. The effect of input signal power of each channel on the differential channel gain DG, imum gain G figure NF characteristics of the FBIp-type EDFA., and imum noise shows the imum gain, the differential channel gain DG, and the imum noise figure versus the pump power of each laser diode. The imum channel gain is gradually increasing and the imum noise figure is gradually decreasing when the pump power of each laser diode is increasing, each Fig. 9. The effect of optical isolation of midway optical isolator on the differential channel gain DG, imum gain G noise figure NF characteristics of the FBIp-type EDFA., and imum
12 62 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications Fig. 10. The effect of pump power degradation of each pump laser diode on the differential channel gain DG, imum gain G imum noise figure NF characteristics of the FBIp-type EDFA., and with an input power of y15 dbm per channel. The allowable pump power range of each laser diode is from 119 to 142 mw. That is, it allows a power degradation range of 23 mw of each pump LDs. Fig. 11 illustrates the output spectrum of the FBIp-type EDFA with 32 input signal channels with a channel spacing of 0.8 nm. In this work we also used a 980-nm pump laser diode to replace with the first pump laser in this FBlp L-band amplifier to investigate the character- Fig. 11. Calculated optical output spectrum of the FBIp-type EDFA with launched 32 channels, each with y15 dbm input power level.
13 ( ) T.-C. Liang et al.roptics Communications istics of such 980-nm forward pumped and 1480-nm backward pumped Ž 980-nm q 1480-nm. FBlp scheme. We found that the gain spectrum profile of the 980-nmq 1480-nm pumped FBlp scheme with a 32-channel WDM signals are almost the same as that of the 1480-nmq 1480-nm pumped FBlp scheme, but with a lower channel output power with reduction of about 1 db, and therefore a reduction of total amplifier output power of about 25 mw, and improved noise figure characteristics of about 0.3 to 0.1 db. In consequence, from the high channel output with low gain variation of -0.7 db and low noise figure of - 5 db point of view, the 1480-nmq 1480-nm pumped FBlp scheme is better than the 980-nmq 1480-nm pumped FBlp scheme. 5. Conclusions We have theoretically investigated various configurations of 1480-nm pumped L-band EDFA to simultaneously achieve high gain Ž G 20 db. with low differential channel gain of DGF0.7 db and low noise figure of F5.5 db. A total of nine L-band EDFA configurations using conventional EDF, operated at 32 digital channels with y15 dbm input power per channel, have been examined and compared. Among these configurations, it is found that the pump-passed case in forward-and- backward pumping scheme, FBIp, is the best amplifier configuration to offer the highest output power and gain Ž G s db, G s db. min with moderate low noise figure Ž NF s4.7 db.. The isolation of midway isolator of G 18 db is satisfied for the FBIp-type configuration. Another advantage is that this scheme allows a large fiber length ratio range of 4.6%;16.9% of EDF1rEDF total, which relaxes the construction of L-band EDFA. In addition, the pump power degradation of up to 23 mw is allowed for this configuration to maintain the characteristics of DGF0.7 db and NFF4.8 db, but at the expense of about 0.6 db degradation of channel gain. Among these configurations, the single-staged forward-andbackward pumping scheme, FB, without using any inter-staged component can offer the second high output power and gain ŽG s db, G s min db. with moderate low noise figure ŽNFs 4.7 db.. The investigation result provides the L-band EDFA configuration selection for multi-wavelength WDM lightwave systems. Acknowledgements This work was supported by the Opto-Electronics and Systems Lab., Industrial Technology Research Institute, Chutung, Hsinchu 310, of Taiwan. References wx 1 D. Marcuse, A.R. Chraplyvy, R.W. Tkach, IEEErOSA J. Lightware Technol. 12 Ž wx 2 N. Shibata, R.P. Braun, R.G. Waarts, IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-23 Ž wx 3 E. Desurvire, Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers: Principles and Applications, John Wiley and Sons, New York, wx 4 A. Bjarklev, Optical Fiber Amplifiers: Design and System Applications, Artech House, Boston and London, wx 5 J.F. Massicott, J.R. Armitage, R. Wyatt, B.J. Ainslie, S.P. Craigryan, Electron. Lett. 26 Ž wx 6 J.F. Massicott, R. Wyatt, B.J. Ainslie, Electron. Lett. 28 Ž wx 7 H. Ono, M. Yamada, Y. Ohishi, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 9 Ž wx 8 H. Ono, M. Yamada, T. Kanamori, S. Sudo, Y. Ohishi, Electron. Lett. 33 Ž wx 9 H. Ono, M. Yamada, S. Sudo, Y. Ohishi, Electron. Lett. 33 Ž w10x H. Ono, M. Yamada, T. Kanamori, Y. Ohishi, Electron. Lett. 33 Ž w11x H. Ono, M. Yamada, M. Shimizu, Y. Ohishi, Electron. Lett. 34 Ž w12x H. Ono, M. Yamada, T. Kanamori, S. Sudo, Y. Ohishi, J. Lightwave Technol. 17 Ž w13x K.I. Suzuki, H. Masuda, S. Kawai, K. Aida, K. Nakagawa, Electron. Lett. 33 Ž w14x T. Sakamoto, J. Kani, M. Jinno, S. Aisawa, M. Fukui, M. Yamada, K. Oguchi, Electron. Lett. 34 Ž w15x H.S. Chung, M.S. Lee, D. Lee, N. Park, D.J. DiGiovanni, Electron. Lett. 35 Ž w16x M. Jinno, T. Sakamoto, J. Kani, S. Aisawa, K. Oda, M. Fukui, H. Ono, K. Oguchi, Electron. Lett. 33 Ž w17x H. Ono, M. Yamada, M. Shimizu, Y. Ohishi, Electron. Lett. 34 Ž w18x T. Sakamoto, K. Hattori, J. Kani, M. Fukutoku, M. Fukui, M. Jinno, K. Oguchi, Electron. Lett. 34 Ž w19x C.R. Giles, E. Desurvire, J. Lightwave Technol. 9 Ž
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique
 S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
Gain-clamping techniques in two-stage double-pass L-band EDFA
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 66, No. 3 journal of March 2006 physics pp. 539 545 Gain-clamping techniques in two-stage double-pass L-band EDFA S W HARUN 1, N Md SAMSURI 2 and H AHMAD 2 1 Faculty
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 66, No. 3 journal of March 2006 physics pp. 539 545 Gain-clamping techniques in two-stage double-pass L-band EDFA S W HARUN 1, N Md SAMSURI 2 and H AHMAD 2 1 Faculty
A novel 3-stage structure for a low-noise, high-gain and gain-flattened L-band erbium doped fiber amplifier *
 Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE ISSN 9-9 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn A novel -stage structure for a low-noise, high-gain and gain-flattened L-band erbium doped fiber amplifier
Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE ISSN 9-9 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn A novel -stage structure for a low-noise, high-gain and gain-flattened L-band erbium doped fiber amplifier
Wideband Rare-earth-doped Fiber Amplification Technologies Gain Bandwidth Expansion in the C and L bands
 Wideband Rare-earth-doped Fiber Amplification Technologies Gain Bandwidth Expansion in the C and L bands Tadashi Sakamoto, Atsushi Mori, Hiroji Masuda, and Hirotaka Ono Abstract We are expanding the gain
Wideband Rare-earth-doped Fiber Amplification Technologies Gain Bandwidth Expansion in the C and L bands Tadashi Sakamoto, Atsushi Mori, Hiroji Masuda, and Hirotaka Ono Abstract We are expanding the gain
Linear cavity erbium-doped fiber laser with over 100 nm tuning range
 Linear cavity erbium-doped fiber laser with over 100 nm tuning range Xinyong Dong, Nam Quoc Ngo *, and Ping Shum Network Technology Research Center, School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Nanyang
Linear cavity erbium-doped fiber laser with over 100 nm tuning range Xinyong Dong, Nam Quoc Ngo *, and Ping Shum Network Technology Research Center, School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Nanyang
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber
 Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE C AND L BAND ERBIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS (C,L-EDFAs)
 DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE C AND L BAND ERBIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS (C,L-EDFAs) Ahmet Altuncu Arif Başgümüş Burçin Uzunca Ekim Haznedaroğlu e-mail: altuncu@dumlupinar.edu.tr e-mail:
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE C AND L BAND ERBIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS (C,L-EDFAs) Ahmet Altuncu Arif Başgümüş Burçin Uzunca Ekim Haznedaroğlu e-mail: altuncu@dumlupinar.edu.tr e-mail:
Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window
 Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2,3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer and Communications Research Laboratories,
Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2,3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer and Communications Research Laboratories,
Variable Gain-Flattened L-band Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier 1
 ISSN 1054-660X, Laser Physics, 2011, Vol. 21, No. 9, pp. 1638 1644. Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 2011. Original Text Astro, Ltd., 2011. FIBER OPTICS Variable Gain-Flattened L-band Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier
ISSN 1054-660X, Laser Physics, 2011, Vol. 21, No. 9, pp. 1638 1644. Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 2011. Original Text Astro, Ltd., 2011. FIBER OPTICS Variable Gain-Flattened L-band Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier
Optical monitoring technique based on scanning the gain profiles of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers for WDM networks
 Optics Communications () 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Optical monitoring technique based on scanning the gain profiles of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers for WDM networks Chien-Hung Yeh *, Chien-Chung
Optics Communications () 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Optical monitoring technique based on scanning the gain profiles of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers for WDM networks Chien-Hung Yeh *, Chien-Chung
New pumping scheme for high gain and low noise figure in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier
 New pumping scheme for high gain and low noise figure in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier V. Sinivasagam, 1,3a) Mustafa A. G. Abushagur, 1,2 K. Dimyati, 3 and F. Tumiran 1 1 Photronix (M) Sdn. Bhd., G05,
New pumping scheme for high gain and low noise figure in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier V. Sinivasagam, 1,3a) Mustafa A. G. Abushagur, 1,2 K. Dimyati, 3 and F. Tumiran 1 1 Photronix (M) Sdn. Bhd., G05,
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis
 EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis Narruvala Lokesh, kranthi Kumar Katam,Prof. Jabeena A Vellore Institute of Technology VIT University, Vellore, India Abstract : Optical network that apply wavelength division
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis Narruvala Lokesh, kranthi Kumar Katam,Prof. Jabeena A Vellore Institute of Technology VIT University, Vellore, India Abstract : Optical network that apply wavelength division
EDFA WDM Optical Network using GFF
 EDFA WDM Optical Network using GFF Shweta Bharti M. Tech, Digital Communication, (Govt. Women Engg. College, Ajmer), Rajasthan, India ABSTRACT This paper describes the model and simulation of EDFA WDM
EDFA WDM Optical Network using GFF Shweta Bharti M. Tech, Digital Communication, (Govt. Women Engg. College, Ajmer), Rajasthan, India ABSTRACT This paper describes the model and simulation of EDFA WDM
Emerging Subsea Networks
 Highly efficient submarine C+L EDFA with serial architecture Douglas O. M. de Aguiar, Reginaldo Silva (Padtec S/A) Giorgio Grasso, Aldo Righetti, Fausto Meli (Fondazione Cife) Email: douglas.aguiar@padtec.com.br
Highly efficient submarine C+L EDFA with serial architecture Douglas O. M. de Aguiar, Reginaldo Silva (Padtec S/A) Giorgio Grasso, Aldo Righetti, Fausto Meli (Fondazione Cife) Email: douglas.aguiar@padtec.com.br
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements HW #5 is assigned (due April 9) April 9 th class will be in
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements HW #5 is assigned (due April 9) April 9 th class will be in
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode
 Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode Chien Hung Yeh, 1* Fu Yuan Shih, 2 Chia Hsuan Wang, 3 Chi Wai Chow, 3 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Information and Communications
Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode Chien Hung Yeh, 1* Fu Yuan Shih, 2 Chia Hsuan Wang, 3 Chi Wai Chow, 3 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Information and Communications
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4, 116, 12M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4, 116, 12M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
AN EFFICIENT L-BAND ERBIUM-DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIER WITH ZIRCONIA-YTTRIA-ALUMINUM CO-DOPED SILICA FIBER
 Journal of Non - Oxide Glasses Vol. 10, No. 3, July - September 2018, p. 65-70 AN EFFICIENT L-BAND ERBIUM-DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIER WITH ZIRCONIA-YTTRIA-ALUMINUM CO-DOPED SILICA FIBER A. A. ALMUKHTAR a, A.
Journal of Non - Oxide Glasses Vol. 10, No. 3, July - September 2018, p. 65-70 AN EFFICIENT L-BAND ERBIUM-DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIER WITH ZIRCONIA-YTTRIA-ALUMINUM CO-DOPED SILICA FIBER A. A. ALMUKHTAR a, A.
The Report of Gain Performance Characteristics of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA)
 The Report of Gain Performance Characteristics of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) Masruri Masruri (186520) 22/05/2008 1 Laboratory Setup The laboratory setup using in this laboratory experiment
The Report of Gain Performance Characteristics of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) Masruri Masruri (186520) 22/05/2008 1 Laboratory Setup The laboratory setup using in this laboratory experiment
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Design System
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 53 ( 2013 ) 294 302 Malaysian Technical Universities Conference on Engineering & Technology 2012, MUCET 2012 Part -1 Electronic and Electrical
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 53 ( 2013 ) 294 302 Malaysian Technical Universities Conference on Engineering & Technology 2012, MUCET 2012 Part -1 Electronic and Electrical
Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators. by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings
 Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings Paper no: 1471 S. Y. Set, H. Geiger, R. I. Laming, M. J. Cole and L. Reekie Optoelectronics Research
Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings Paper no: 1471 S. Y. Set, H. Geiger, R. I. Laming, M. J. Cole and L. Reekie Optoelectronics Research
Optical Fibre Amplifiers Continued
 1 Optical Fibre Amplifiers Continued Stavros Iezekiel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Cyprus ECE 445 Lecture 09 Fall Semester 2016 2 ERBIUM-DOPED FIBRE AMPLIFIERS BASIC
1 Optical Fibre Amplifiers Continued Stavros Iezekiel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Cyprus ECE 445 Lecture 09 Fall Semester 2016 2 ERBIUM-DOPED FIBRE AMPLIFIERS BASIC
Gain characteristics of a 210 km hybrid Raman/erbium-doped fiber amplified loop
 Optics Communications 261 (2006) 152 157 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Gain characteristics of a 210 km hybrid Raman/erbium-doped fiber amplified loop Gaston E. Tudury a,b, Jonathan Hu b, *, Brian S.
Optics Communications 261 (2006) 152 157 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Gain characteristics of a 210 km hybrid Raman/erbium-doped fiber amplified loop Gaston E. Tudury a,b, Jonathan Hu b, *, Brian S.
A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation
 A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer & Communications Research Laboratories,
A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer & Communications Research Laboratories,
ESTIMATION OF NOISE FIGURE USING GFF WITH HYBRID QUAD PUMPING
 IJCRR Vol 05 issue 13 Section: Technology Category: Research Received on: 19/12/12 Revised on: 16/01/13 Accepted on: 09/02/13 ESTIMATION OF NOISE FIGURE USING GFF WITH HYBRID QUAD PUMPING V.R. Prakash,
IJCRR Vol 05 issue 13 Section: Technology Category: Research Received on: 19/12/12 Revised on: 16/01/13 Accepted on: 09/02/13 ESTIMATION OF NOISE FIGURE USING GFF WITH HYBRID QUAD PUMPING V.R. Prakash,
RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University
 Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Last Lecture Topics Course introduction Ray optics & optical
Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Last Lecture Topics Course introduction Ray optics & optical
Performance Analysis of EDFA for Different Pumping Configurations at High Data Rate
 Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Electrical and Electronics Engineering Volume 13 Issue 9 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global
Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Electrical and Electronics Engineering Volume 13 Issue 9 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global
BROAD-BAND rare-earth-doped fiber sources have been
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 8, AUGUST 1997 1587 Feedback Effects in Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier/Source for Open-Loop Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Hee Gap Park, Kyoung Ah Lim, Young-Jun Chin,
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 8, AUGUST 1997 1587 Feedback Effects in Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier/Source for Open-Loop Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Hee Gap Park, Kyoung Ah Lim, Young-Jun Chin,
Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber
 Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber I. H. M. Nadzar 1 and N. A.Awang 1* 1 Faculty of Science, Technology and Human Development, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor,
Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber I. H. M. Nadzar 1 and N. A.Awang 1* 1 Faculty of Science, Technology and Human Development, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor,
Performance analysis of Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier at different pumping configurations
 Performance analysis of Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier at different pumping configurations Mayur Date M.E. Scholar Department of Electronics and Communication Ujjain Engineering College, Ujjain (M.P.) datemayur3@gmail.com
Performance analysis of Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier at different pumping configurations Mayur Date M.E. Scholar Department of Electronics and Communication Ujjain Engineering College, Ujjain (M.P.) datemayur3@gmail.com
EDFA SIMULINK MODEL FOR ANALYZING GAIN SPECTRUM AND ASE. Stephen Z. Pinter
 EDFA SIMULINK MODEL FOR ANALYZING GAIN SPECTRUM AND ASE Stephen Z. Pinter Ryerson University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering spinter@ee.ryerson.ca December, 2003 ABSTRACT A Simulink model
EDFA SIMULINK MODEL FOR ANALYZING GAIN SPECTRUM AND ASE Stephen Z. Pinter Ryerson University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering spinter@ee.ryerson.ca December, 2003 ABSTRACT A Simulink model
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 15, 37 48, 2010 TEMPERATURE INSENSITIVE BROAD AND FLAT GAIN C-BAND EDFA BASED ON MACRO-BENDING
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 15, 37 48, 2010 TEMPERATURE INSENSITIVE BROAD AND FLAT GAIN C-BAND EDFA BASED ON MACRO-BENDING P. Hajireza Optical Fiber Devices Group Multimedia University
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 15, 37 48, 2010 TEMPERATURE INSENSITIVE BROAD AND FLAT GAIN C-BAND EDFA BASED ON MACRO-BENDING P. Hajireza Optical Fiber Devices Group Multimedia University
Performance of optical automatic gain control EDFA with dual-oscillating control lasers
 Optics Communications 224 (2003) 281 287 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Performance of optical automatic gain control EDFA with dual-oscillating control lasers Chun-Liu Zhao a,b,c, *, Bai-Ou Guan a,b,
Optics Communications 224 (2003) 281 287 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Performance of optical automatic gain control EDFA with dual-oscillating control lasers Chun-Liu Zhao a,b,c, *, Bai-Ou Guan a,b,
Optical Amplifiers (Chapter 6)
 Optical Amplifiers (Chapter 6) General optical amplifier theory Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (SOA) Raman Amplifiers Erbium-doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFA) Read Chapter 6, pp. 226-266 Loss & dispersion
Optical Amplifiers (Chapter 6) General optical amplifier theory Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (SOA) Raman Amplifiers Erbium-doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFA) Read Chapter 6, pp. 226-266 Loss & dispersion
All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration
 1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
Burst-mode EDFA based on a mid-position gain flattening filter with an overpumping configuration for variable traffic conditions in a WDM environment
 Opt Quant Electron (8) :61 66 DOI 1.17/s118-8-913-x Burst-mode EDFA based on a mid-position gain flattening filter with an overpumping configuration for variable traffic conditions in a WDM environment
Opt Quant Electron (8) :61 66 DOI 1.17/s118-8-913-x Burst-mode EDFA based on a mid-position gain flattening filter with an overpumping configuration for variable traffic conditions in a WDM environment
Active mode-locking of miniature fiber Fabry-Perot laser (FFPL) in a ring cavity
 Active mode-locking of miniature fiber Fabry-Perot laser (FFPL) in a ring cavity Shinji Yamashita (1)(2) and Kevin Hsu (3) (1) Dept. of Frontier Informatics, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences The University
Active mode-locking of miniature fiber Fabry-Perot laser (FFPL) in a ring cavity Shinji Yamashita (1)(2) and Kevin Hsu (3) (1) Dept. of Frontier Informatics, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences The University
Investigation of Performance Analysis of EDFA Amplifier. Using Different Pump Wavelengths and Powers
 Investigation of Performance Analysis of EDFA Amplifier Using Different Pump Wavelengths and Powers Ramandeep Kaur, Parkirti, Rajandeep Singh ABSTRACT In this paper, an investigation of the performance
Investigation of Performance Analysis of EDFA Amplifier Using Different Pump Wavelengths and Powers Ramandeep Kaur, Parkirti, Rajandeep Singh ABSTRACT In this paper, an investigation of the performance
Analysis and Review of EDFA
 918 Analysis and Review of EDFA 1 Dipika Pradhan, 2 Vivekanand Mishra 1, 2 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, S. V. National Institute of Technology Surat, India Abstract - Optical
918 Analysis and Review of EDFA 1 Dipika Pradhan, 2 Vivekanand Mishra 1, 2 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, S. V. National Institute of Technology Surat, India Abstract - Optical
Optical Fiber Amplifiers. Scott Freese. Physics May 2008
 Optical Fiber Amplifiers Scott Freese Physics 262 2 May 2008 Partner: Jared Maxson Abstract The primary goal of this experiment was to gain an understanding of the basic components of an Erbium doped fiber
Optical Fiber Amplifiers Scott Freese Physics 262 2 May 2008 Partner: Jared Maxson Abstract The primary goal of this experiment was to gain an understanding of the basic components of an Erbium doped fiber
An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources and a Novel Bidirectional Reach Extender
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 15, No. 3, September 2011, pp. 222-226 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2011.15.3.222 An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 15, No. 3, September 2011, pp. 222-226 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2011.15.3.222 An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources
CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 9 18, 29 CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER H. Ahmad, M. Z. Zulkifli, S. F. Norizan,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 9 18, 29 CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER H. Ahmad, M. Z. Zulkifli, S. F. Norizan,
Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks.
 Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks. Hercules Simos * National and Kapodistrian University
Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks. Hercules Simos * National and Kapodistrian University
Transient Control in Dynamically Reconfigured Networks with Cascaded Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers
 Transient Control in Dynamically Reconfigured Networks with Cascaded Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers Lei Zong, Ting Wang lanezong@nec-labs.com NEC Laboratories America, Princeton, New Jersey, USA WOCC 2007
Transient Control in Dynamically Reconfigured Networks with Cascaded Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers Lei Zong, Ting Wang lanezong@nec-labs.com NEC Laboratories America, Princeton, New Jersey, USA WOCC 2007
Performance Analysis of WDM Network Based On EDFA Amplifier with Different Pumping Techniques
 Performance Analysis of WDM Network Based On EDFA Amplifier with Different Pumping Techniques Varsha Honde* varshahonde@gmail.com* Anuja Mhatre anujamhatre93@yahoo.com Sourabh Tonde sourabhtonde2511@gmail.com
Performance Analysis of WDM Network Based On EDFA Amplifier with Different Pumping Techniques Varsha Honde* varshahonde@gmail.com* Anuja Mhatre anujamhatre93@yahoo.com Sourabh Tonde sourabhtonde2511@gmail.com
Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source
 JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. X, NO. XX, XXXX XXX 1 Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source Jérôme Vasseur, Jianjun Yu Senior Member,
JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. X, NO. XX, XXXX XXX 1 Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source Jérôme Vasseur, Jianjun Yu Senior Member,
Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA
 Optics Communications 252 (2005) 127 131 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA Peng-Chun Peng a, *, Kai-Ming Feng b, Wei-Ren
Optics Communications 252 (2005) 127 131 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA Peng-Chun Peng a, *, Kai-Ming Feng b, Wei-Ren
Optical Communications and Networking 朱祖勍. Oct. 9, 2017
 Optical Communications and Networking Oct. 9, 2017 1 Optical Amplifiers In optical communication systems, the optical signal from the transmitter are attenuated by the fiber and other passive components
Optical Communications and Networking Oct. 9, 2017 1 Optical Amplifiers In optical communication systems, the optical signal from the transmitter are attenuated by the fiber and other passive components
Improvisation of Gain and Bit-Error Rate for an EDFA-WDM System using Different Filters
 Improvisation of Gain and Bit-Error Rate for an EDFA-WDM System using Different Filters Sharmila M M.Tech LEOE Department of physics College of engineering guindy Chennai 600025 India. Abstract: The Gain
Improvisation of Gain and Bit-Error Rate for an EDFA-WDM System using Different Filters Sharmila M M.Tech LEOE Department of physics College of engineering guindy Chennai 600025 India. Abstract: The Gain
Gain Flattened L-Band EDFA -Raman Hybrid Amplifier by Bidirectional Pumping technique
 Gain Flattened L-Band EDFA -Raman Hybrid Amplifier by Bidirectional Pumping technique Avneet Kour 1, Neena Gupta 2 1,2 Electronics and Communication Department, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh
Gain Flattened L-Band EDFA -Raman Hybrid Amplifier by Bidirectional Pumping technique Avneet Kour 1, Neena Gupta 2 1,2 Electronics and Communication Department, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh
Performance Evaluation of Hybrid (Raman+EDFA) Optical Amplifiers in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed Optical Transmission System
 Performance Evaluation of Hybrid (Raman+EDFA) Optical Amplifiers in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed Optical Transmission System Gagandeep Singh Walia 1, Kulwinder Singh 2, Manjit Singh Bhamrah 3
Performance Evaluation of Hybrid (Raman+EDFA) Optical Amplifiers in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed Optical Transmission System Gagandeep Singh Walia 1, Kulwinder Singh 2, Manjit Singh Bhamrah 3
Practical Aspects of Raman Amplifier
 Practical Aspects of Raman Amplifier Contents Introduction Background Information Common Types of Raman Amplifiers Principle Theory of Raman Gain Noise Sources Related Information Introduction This document
Practical Aspects of Raman Amplifier Contents Introduction Background Information Common Types of Raman Amplifiers Principle Theory of Raman Gain Noise Sources Related Information Introduction This document
To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks
 289 To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks Areet Aulakh 1, Kulwinder Singh Malhi 2 1 Student, M.Tech, ECE department, Punjabi University,
289 To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks Areet Aulakh 1, Kulwinder Singh Malhi 2 1 Student, M.Tech, ECE department, Punjabi University,
Elements of Optical Networking
 Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Performance Analysis of Designing a Hybrid Optical Amplifier (HOA) for 32 DWDM Channels in L-band by using EDFA and Raman Amplifier
 Performance Analysis of Designing a Hybrid Optical Amplifier (HOA) for 32 DWDM Channels in L-band by using EDFA and Raman Amplifier Aied K. Mohammed, PhD Department of Electrical Engineering, University
Performance Analysis of Designing a Hybrid Optical Amplifier (HOA) for 32 DWDM Channels in L-band by using EDFA and Raman Amplifier Aied K. Mohammed, PhD Department of Electrical Engineering, University
Recon gurable WDM add/drop multiplexer based on optical switches and bre Bragg gratings
 Optical and Quantum Electronics 31 (1999) 77±83 Recon gurable WDM add/drop multiplexer based on optical switches and bre Bragg gratings SHIEN-KUEI LIAW Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National
Optical and Quantum Electronics 31 (1999) 77±83 Recon gurable WDM add/drop multiplexer based on optical switches and bre Bragg gratings SHIEN-KUEI LIAW Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers
 Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
Bit error rate and cross talk performance in optical cross connect with wavelength converter
 Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 295 Bit error rate and cross talk performance in optical cross connect with wavelength converter M. S. Islam and S. P. Majumder Department of
Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 295 Bit error rate and cross talk performance in optical cross connect with wavelength converter M. S. Islam and S. P. Majumder Department of
Research Article Output Signal Power Analysis in Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier with Pump Power and Length Variation Using Various Pumping Techniques
 ISRN Electronics Volume 213, Article ID 31277, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/31277 Research Article Output Signal Power Analysis in Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier with Power and Length Variation Using
ISRN Electronics Volume 213, Article ID 31277, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/31277 Research Article Output Signal Power Analysis in Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier with Power and Length Variation Using
Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm
 15 February 2000 Ž. Optics Communications 175 2000 209 213 www.elsevier.comrlocateroptcom Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm F. Koch ), S.V. Chernikov,
15 February 2000 Ž. Optics Communications 175 2000 209 213 www.elsevier.comrlocateroptcom Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm F. Koch ), S.V. Chernikov,
To generate a broadband light source by using mutually injection-locked Fabry-Perot laser diodes
 To generate a broadband light source by using mutually injection-locked Fabry-Perot laser diodes Cheng-Ling Ying 1, Yu-Chieh Chi 2, Chia-Chin Tsai 3, Chien-Pen Chuang 3, and Hai-Han Lu 2a) 1 Department
To generate a broadband light source by using mutually injection-locked Fabry-Perot laser diodes Cheng-Ling Ying 1, Yu-Chieh Chi 2, Chia-Chin Tsai 3, Chien-Pen Chuang 3, and Hai-Han Lu 2a) 1 Department
DIRECT MODULATION WITH SIDE-MODE INJECTION IN OPTICAL CATV TRANSPORT SYSTEMS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 73 82, 2009 DIRECT MODULATION WITH SIDE-MODE INJECTION IN OPTICAL CATV TRANSPORT SYSTEMS W.-J. Ho, H.-H. Lu, C.-H. Chang, W.-Y. Lin, and H.-S. Su
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 73 82, 2009 DIRECT MODULATION WITH SIDE-MODE INJECTION IN OPTICAL CATV TRANSPORT SYSTEMS W.-J. Ho, H.-H. Lu, C.-H. Chang, W.-Y. Lin, and H.-S. Su
Power Transients in Hybrid Optical Amplifier (EDFA + DFRA) Cascades
 Power Transients in Hybrid Optical Amplifier (EDFA + DFRA) Cascades Bárbara Dumas and Ricardo Olivares Electronic Engineering Department Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María Valparaíso, Chile bpilar.dumas@gmail.com,
Power Transients in Hybrid Optical Amplifier (EDFA + DFRA) Cascades Bárbara Dumas and Ricardo Olivares Electronic Engineering Department Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María Valparaíso, Chile bpilar.dumas@gmail.com,
Demonstration of multi-cavity optoelectronic oscillators based on multicore fibers
 Demonstration of multi-cavity optoelectronic oscillators based on multicore fibers Sergi García, Javier Hervás and Ivana Gasulla ITEAM Research Institute Universitat Politècnica de València, Valencia,
Demonstration of multi-cavity optoelectronic oscillators based on multicore fibers Sergi García, Javier Hervás and Ivana Gasulla ITEAM Research Institute Universitat Politècnica de València, Valencia,
International Journal of Computational Intelligence and Informatics, Vol. 2: No. 4, January - March Bandwidth of 13GHz
 Simulation and Analysis of GFF at WDM Mux Bandwidth of 13GHz Warsha Balani Department of ECE, BIST Bhopal, India balani.warsha@gmail.com Manish Saxena Department of ECE,BIST Bhopal, India manish.saxena2008@gmail.com
Simulation and Analysis of GFF at WDM Mux Bandwidth of 13GHz Warsha Balani Department of ECE, BIST Bhopal, India balani.warsha@gmail.com Manish Saxena Department of ECE,BIST Bhopal, India manish.saxena2008@gmail.com
MULTIFREQUENCY CONTINUOUS WAVE ERBIUM DOPED FIBER NON-RESONANT OPTICAL SOURCE
 2007 Poznańskie Warsztaty Telekomunikacyjne Poznań 6-7 grudnia 2007 POZNAN POZNAN UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITYOF OF TECHNOLOGY ACADEMIC ACADEMIC JOURNALS JOURNALS No 54 Electrical Engineering 2007 Andrzej DOBROGOWSKI*
2007 Poznańskie Warsztaty Telekomunikacyjne Poznań 6-7 grudnia 2007 POZNAN POZNAN UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITYOF OF TECHNOLOGY ACADEMIC ACADEMIC JOURNALS JOURNALS No 54 Electrical Engineering 2007 Andrzej DOBROGOWSKI*
Gain Flattening Improvements With Two Cascade Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier In WDM Systems
 International Academic Institute for Science and Technology International Academic Journal of Science and Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, 2016, pp. 36-42. ISSN 2454-3896 International Academic Journal of Science
International Academic Institute for Science and Technology International Academic Journal of Science and Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, 2016, pp. 36-42. ISSN 2454-3896 International Academic Journal of Science
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WDM AND EDFA IN C-BAND FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol13issue1/ijrras_13_1_26.pdf PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WDM AND EDFA IN C-BAND FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM M.M. Ismail, M.A. Othman, H.A. Sulaiman, M.H. Misran & M.A. Meor
www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol13issue1/ijrras_13_1_26.pdf PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WDM AND EDFA IN C-BAND FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM M.M. Ismail, M.A. Othman, H.A. Sulaiman, M.H. Misran & M.A. Meor
The Reduction of FWM effects using Duobinary Modulation in a Two-Channel D-WDM System
 The Reduction of FWM effects using Duobinary Modulation in a Two-Channel D-WDM System Laxman Tawade 1, Balasaheb Deokate 2 Department of Electronic and Telecommunication Vidya Pratishthan s College of
The Reduction of FWM effects using Duobinary Modulation in a Two-Channel D-WDM System Laxman Tawade 1, Balasaheb Deokate 2 Department of Electronic and Telecommunication Vidya Pratishthan s College of
Inherent Enhancement of Gain Flatness and Achievement of Broad Gain Bandwidth in Erbium-Doped Silica Fiber Amplifiers
 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 38, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2002 149 Inherent Enhancement of Gain Flatness and Achievement of Broad Gain Bandwidth in Erbium-Doped Silica Fiber Amplifiers Uh-Chan Ryu,
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 38, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2002 149 Inherent Enhancement of Gain Flatness and Achievement of Broad Gain Bandwidth in Erbium-Doped Silica Fiber Amplifiers Uh-Chan Ryu,
Comparison of Various Configurations of Hybrid Raman Amplifiers
 IJCST Vo l. 3, Is s u e 4, Oc t - De c 2012 ISSN : 0976-8491 (Online) ISSN : 2229-4333 (Print) Comparison of Various Configurations of Hybrid Raman Amplifiers Sunil Gautam Dept. of ECE, Shaheed Bhagat
IJCST Vo l. 3, Is s u e 4, Oc t - De c 2012 ISSN : 0976-8491 (Online) ISSN : 2229-4333 (Print) Comparison of Various Configurations of Hybrid Raman Amplifiers Sunil Gautam Dept. of ECE, Shaheed Bhagat
Fiberoptic Communication Systems By Dr. M H Zaidi. Optical Amplifiers
 Optical Amplifiers Optical Amplifiers Optical signal propagating in fiber suffers attenuation Optical power level of a signal must be periodically conditioned Optical amplifiers are a key component in
Optical Amplifiers Optical Amplifiers Optical signal propagating in fiber suffers attenuation Optical power level of a signal must be periodically conditioned Optical amplifiers are a key component in
Effect of ASE on Performance of EDFA for 1479nm-1555nm Wavelength Range
 Effect of ASE on Performance of EDFA for 1479nm-1555nm Wavelength Range Inderpreet Kaur, Neena Gupta Deptt. of Electrical & Electronics Engg. Chandigarh University Gharuan, India Dept. of Electronics &
Effect of ASE on Performance of EDFA for 1479nm-1555nm Wavelength Range Inderpreet Kaur, Neena Gupta Deptt. of Electrical & Electronics Engg. Chandigarh University Gharuan, India Dept. of Electronics &
O. Mahran 1,2 and A.A.Samir 1
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 1, January-2015 1306 The Effect of the Amplifier Length on the Gain and Noise Figure of the Er/Yb Co-Doped Waveguide Amplifiers
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 1, January-2015 1306 The Effect of the Amplifier Length on the Gain and Noise Figure of the Er/Yb Co-Doped Waveguide Amplifiers
Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion
 36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
Optics Communications
 Optics Communications 284 (11) 2327 2336 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Multiwavelength lasers with homogeneous gain and
Optics Communications 284 (11) 2327 2336 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Multiwavelength lasers with homogeneous gain and
Chapter 12: Optical Amplifiers: Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs)
 Chapter 12: Optical Amplifiers: Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs) Prof. Dr. Yaocheng SHI ( 时尧成 ) yaocheng@zju.edu.cn http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/yaocheng 1 Traditional Optical Communication System Loss
Chapter 12: Optical Amplifiers: Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs) Prof. Dr. Yaocheng SHI ( 时尧成 ) yaocheng@zju.edu.cn http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/yaocheng 1 Traditional Optical Communication System Loss
Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers
 ECE 6323 Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers Semiconductor optical amplifier Others: stimulated Raman, optical parametric Advanced application:
ECE 6323 Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers Semiconductor optical amplifier Others: stimulated Raman, optical parametric Advanced application:
Emerging Subsea Networks
 EVALUATION OF NONLINEAR IMPAIRMENT FROM NARROW- BAND UNPOLARIZED IDLERS IN COHERENT TRANSMISSION ON DISPERSION-MANAGED SUBMARINE CABLE SYSTEMS Masashi Binkai, Keisuke Matsuda, Tsuyoshi Yoshida, Naoki Suzuki,
EVALUATION OF NONLINEAR IMPAIRMENT FROM NARROW- BAND UNPOLARIZED IDLERS IN COHERENT TRANSMISSION ON DISPERSION-MANAGED SUBMARINE CABLE SYSTEMS Masashi Binkai, Keisuke Matsuda, Tsuyoshi Yoshida, Naoki Suzuki,
Photonic devices based on optical fibers for telecommunication applications
 Photonic devices based on optical fibers for telecommunication applications Pantelis Velanas * National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Department of Informatics and Telecommunications, University
Photonic devices based on optical fibers for telecommunication applications Pantelis Velanas * National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Department of Informatics and Telecommunications, University
An All-Optical Gain-Controlled Amplifier for Bidirectional Transmission
 An All-Optical Gain-Controlled Amplifier for Bidirectional Transmission Bo-Hun Choi, Kyung-Jin Hong, Chang-Bong Kim, and Yong Hyub Won A novel all-optical gain-controlled (AOGC) bidirectional amplifier
An All-Optical Gain-Controlled Amplifier for Bidirectional Transmission Bo-Hun Choi, Kyung-Jin Hong, Chang-Bong Kim, and Yong Hyub Won A novel all-optical gain-controlled (AOGC) bidirectional amplifier
Rayleigh-Based Raman Fiber Laser With Passive Erbium-Doped Fiber for Secondary Pumping Effect in Remote L-Band Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier
 University of Malaya From the SelectedWorks of Faisal Rafiq Mahamd Adikan June, 2012 With Passive Erbium-Doped Fiber for Secondary Pumping Effect in Remote L-Band Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier Faisal Rafiq
University of Malaya From the SelectedWorks of Faisal Rafiq Mahamd Adikan June, 2012 With Passive Erbium-Doped Fiber for Secondary Pumping Effect in Remote L-Band Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier Faisal Rafiq
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion
 Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Eye-Diagram-Based Evaluation of RZ and NRZ Modulation Methods in a 10-Gb/s Single-Channel and a 160-Gb/s WDM Optical Networks
 International Journal of Optics and Applications 2017, 7(2): 31-36 DOI: 10.5923/j.optics.20170702.01 Eye-Diagram-Based Evaluation of RZ and NRZ Modulation Methods in a 10-Gb/s Single-Channel and a 160-Gb/s
International Journal of Optics and Applications 2017, 7(2): 31-36 DOI: 10.5923/j.optics.20170702.01 Eye-Diagram-Based Evaluation of RZ and NRZ Modulation Methods in a 10-Gb/s Single-Channel and a 160-Gb/s
Optical Fiber Amplifiers
 Optical Fiber Amplifiers Yousif Ahmed Omer 1 and Dr. Hala Eldaw Idris 2 1,2 Department of communication Faculty of Engineering, AL-Neelain University, Khartoum, Sudan Publishing Date: June 15, 2016 Abstract
Optical Fiber Amplifiers Yousif Ahmed Omer 1 and Dr. Hala Eldaw Idris 2 1,2 Department of communication Faculty of Engineering, AL-Neelain University, Khartoum, Sudan Publishing Date: June 15, 2016 Abstract
Utilizing Self-Seeding RSOA with Faraday Rotator Mirror for Colorless Access Network
 Utilizing Self-Seeding RSOA with Faraday Rotator Mirror for Colorless Access Network Yu-Fu Wu a, Jinu-Yu Sung a, and Chi-Wai Chow a, and Chien-Hung Yeh* b,c a Department of Photonics and Institute of Electro-Optical
Utilizing Self-Seeding RSOA with Faraday Rotator Mirror for Colorless Access Network Yu-Fu Wu a, Jinu-Yu Sung a, and Chi-Wai Chow a, and Chien-Hung Yeh* b,c a Department of Photonics and Institute of Electro-Optical
Current Trends in Unrepeatered Systems
 Current Trends in Unrepeatered Systems Wayne Pelouch (Xtera, Inc.) Email: wayne.pelouch@xtera.com Xtera, Inc. 500 W. Bethany Drive, suite 100, Allen, TX 75013, USA. Abstract: The current trends in unrepeatered
Current Trends in Unrepeatered Systems Wayne Pelouch (Xtera, Inc.) Email: wayne.pelouch@xtera.com Xtera, Inc. 500 W. Bethany Drive, suite 100, Allen, TX 75013, USA. Abstract: The current trends in unrepeatered
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor
 Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS
 MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
Analysis of Gain and NF using Raman and hybrid RFA-EDFA
 Analysis of Gain and NF using Raman and hybrid RFA-EDFA Abdallah M. Hassan 1, Ashraf Aboshosha 2, Mohamed B. El_Mashade 3 Electrical Engineering Dept., Faculty of Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Nasr
Analysis of Gain and NF using Raman and hybrid RFA-EDFA Abdallah M. Hassan 1, Ashraf Aboshosha 2, Mohamed B. El_Mashade 3 Electrical Engineering Dept., Faculty of Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Nasr
A PIECE WISE LINEAR SOLUTION FOR NONLINEAR SRS EFFECT IN DWDM FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 9 A PIECE WISE LINEAR SOLUION FOR NONLINEAR SRS EFFEC IN DWDM FIBER OPIC COMMUNICAION SYSEMS M. L. SINGH and I. S. HUDIARA Department of Electronics echnology Guru Nanak Dev University Amritsar-005, India
9 A PIECE WISE LINEAR SOLUION FOR NONLINEAR SRS EFFEC IN DWDM FIBER OPIC COMMUNICAION SYSEMS M. L. SINGH and I. S. HUDIARA Department of Electronics echnology Guru Nanak Dev University Amritsar-005, India
Erbium-Doper Fiber Amplifiers
 Seminar presentation Erbium-Doper Fiber Amplifiers 27.11.2009 Ville Pale Presentation Outline History of EDFA EDFA operating principle Stimulated Emission Stark Splitting Gain Gain flatness Gain Saturation
Seminar presentation Erbium-Doper Fiber Amplifiers 27.11.2009 Ville Pale Presentation Outline History of EDFA EDFA operating principle Stimulated Emission Stark Splitting Gain Gain flatness Gain Saturation
Fiber Parametric Amplifiers for Wavelength Band Conversion
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 8, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2002 527 Fiber Parametric Amplifiers for Wavelength Band Conversion Mohammed N. Islam and Özdal Boyraz, Student Member, IEEE
IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 8, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2002 527 Fiber Parametric Amplifiers for Wavelength Band Conversion Mohammed N. Islam and Özdal Boyraz, Student Member, IEEE
Effects of MPI noise on various modulation formats in distributed Raman amplified system
 Optics Communications 255 (25) 41 45 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Effects of MPI noise on various modulation formats in distributed Raman amplified system S.B. Jun *, E.S. Son, H.Y. Choi, K.H. Han, Y.C.
Optics Communications 255 (25) 41 45 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Effects of MPI noise on various modulation formats in distributed Raman amplified system S.B. Jun *, E.S. Son, H.Y. Choi, K.H. Han, Y.C.
Performance Analysis of Direct Detection-Based Modulation Formats for WDM Long-Haul Transmission Systems Abstract 1.0 Introduction
 Performance Analysis of Direct Detection-Based Modulation Formats for WDM Long-Haul Transmission Systems PRLightCOM Broadband Solutions Pvt. Ltd. Bangalore, Karnataka, INDIA Abstract During the last decade,
Performance Analysis of Direct Detection-Based Modulation Formats for WDM Long-Haul Transmission Systems PRLightCOM Broadband Solutions Pvt. Ltd. Bangalore, Karnataka, INDIA Abstract During the last decade,
EDFA Applications in Test & Measurement
 EDFA Applications in Test & Measurement White Paper PN 200-0600-00 Revision 1.1 September 2003 Calmar Optcom, Inc www.calamropt.com Overview Erbium doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs) amplify optical pulses
EDFA Applications in Test & Measurement White Paper PN 200-0600-00 Revision 1.1 September 2003 Calmar Optcom, Inc www.calamropt.com Overview Erbium doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs) amplify optical pulses
Compact Optical Fiber Amplifiers with Fast AGC or for Analog Signal Transmission
 Compact Optical Fiber Amplifiers with Fast AGC or for Analog Signal Transmission by Mikiya Suzuki *, Toshiharu Izumikawa *, Katsuhiko Iwashita * 2, Kazutaka Shimoosako * 2, Shinichi Takashima * 3, Toru
Compact Optical Fiber Amplifiers with Fast AGC or for Analog Signal Transmission by Mikiya Suzuki *, Toshiharu Izumikawa *, Katsuhiko Iwashita * 2, Kazutaka Shimoosako * 2, Shinichi Takashima * 3, Toru
Simultaneous pulse amplification and compression in all-fiber-integrated pre-chirped large-mode-area Er-doped fiber amplifier
 Simultaneous pulse amplification and compression in all-fiber-integrated pre-chirped large-mode-area Er-doped fiber amplifier Gong-Ru Lin 1 *, Ying-Tsung Lin, and Chao-Kuei Lee 2 1 Graduate Institute of
Simultaneous pulse amplification and compression in all-fiber-integrated pre-chirped large-mode-area Er-doped fiber amplifier Gong-Ru Lin 1 *, Ying-Tsung Lin, and Chao-Kuei Lee 2 1 Graduate Institute of
