P1 Chapter 10 :: Trigonometric Identities & Equations
|
|
|
- Karin Lee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 P1 Chapter 10 :: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Last modified: 20 th August 2017
2 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: Practise questions by chapter, including past paper Edexcel questions and extension questions (e.g. MAT). Teachers: you can create student accounts (or students can register themselves).
3 Chapter Overview Those who did IGCSE Further Maths or Additional Maths will be familiar with this content. Exact trigonometric values for 30, 45, 90 were in the GCSE syllabus. 1:: Know exact trig values for 30, 45, 60 and understand unit circle. 3:: Solve equations of the form sin nθ = k and sin θ ± α = k Solve sin 2x cos 2x + 1 = 0, for 0 x < :: Use identities sin x cos x sin 2 x + cos 2 x 1 tan x and Show that 3 sin 2 x + 7 sin x = cos 2 x 4 can be written in the form 4 sin 2 x + 7 sin x + 3 = 0 4:: Solve equations which are quadratic in sin/cos/tan. Solve, for 0 x < 360, the equation 4 sin 2 x + 9 cos x 6 = 0
4 sin/cos/tan of 30, 45, 60 You will frequently encounter angles of 30, 60, 45 in geometric problems. Why? We see these angles in equilateral triangles and half squares. Although you will always have a calculator, you need to know how to derive these. All you need to remember:! Draw half a unit square and half an equilateral triangle of side sin 45 = 1 2 cos 45 = 1 2 tan 45 = sin 30 = 1 2 cos 30 = 3 2 tan 30 = 1 3 sin 60 = 3 2 cos 60 = 1 2 tan 60 = 3
5 The Unit Circle and Trigonometry For values of θ in the range 0 < θ < 90, you know that sin θ and cos θ are lengths on a right-angled triangle: θ 1 cos θ sin θ But how do we get the rest of the graph for sin, cos and tan when 90 θ 360?! The point P on a unit circle, such that OP makes an angle θ with the positive x-axis, has coordinates cos θ, sin θ. OP has gradient tan θ. O y 1 θ P cos θ, sin θ x And what would be the gradient of the bold line? m = Δy sin θ = Δx But also: tan θ = opp adj m = tan θ cos θ = sin θ cos θ Angles are always measured anticlockwise. (Further Mathematicians will encounter the same when they get to Complex Numbers) We can consider the coordinate cos θ, sin θ as θ increases from 0 to 360
6 Mini-Exercise Use the unit circle to determine each value in the table, using either 0, +ve, -ve, 1, -1 or undefined. Recall that the point on the unit circle has coordinate (cos θ, sin θ) and OP has gradient tan θ. x-value y-value Gradient of OP. cos θ sin θ tan θ cos θ sin θ tan θ θ = 0 y P x θ = 180 P y θ x < θ < < θ < 270 y 1 θ P x +ve +ve +ve θ y x -ve -ve +ve P θ = 90 P y θ x 0 1 Undefined (vertical lines don t have a well-defined gradient) θ = 270 θ P y x 0 1 Undefined 90 < θ < 180 P y θ x -ve +ve -ve 270 < θ < 360 P θ y x +ve -ve -ve
7 The Unit Circle and Trigonometry The unit circles explains the behaviour of these trigonometric graphs beyond 90. However, the easiest way to remember whether sin x, cos x, tan x are positive or negative is to just do a very quick sketch (preferably mentally!) of the corresponding graph. y positive for 0 < x < 180 y = sin x x negative for 180 < x < 360 Note: The textbook uses something called CAST diagrams. I will not be using them in these slides, but you may wish to look at these technique as an alternative approach to various problems in the chapter.
8 A Few Trigonometric Angle Laws The following are all easily derivable using a quick sketch of a trigonometric graph, and are merely a convenience so you don t always have to draw out a graph every time. You are highly encouraged to memorise these so that you can do exam questions faster. y = sin x 1 sin x = sin 180 x e.g. sin 150 = sin We saw this in the previous chapter when covering the ambiguous case when using the sine rule cos x = cos 360 x e.g. cos 330 = cos 30 sin and cos repeat every 360 but tan every 180 e.g. sin 390 = sin 30 sin x = cos 90 x e.g. sin 50 = cos 40 y = cos x y = sin x Remember from the previous chapter that cosine by definition is the sine of the complementary angle. This was/is never covered in the textbook but caught everyone by surprise when it came up in a C3 exam.
9 Examples Without a calculator, work out the value of each below. tan 225 = tan 45 = 1 tan 210 = tan 30 = 1 3 sin 150 = sin 30 = 1 2 cos 300 = cos 60 = 1 2 tan repeats every 180 so can subtract 180 For sin we can subtract from 180. For cos we can subtract from 360. Use the laws where you can, but otherwise just draw out a quick sketch of the graph. sin x = sin 180 x cos x = cos 360 x sin, cos repeat every 360 but tan every 180 sin 45 = sin 45 = 1 2 cos 750 = cos 30 = 3 2 cos repeats every 360. We have to resort to a sketch for this one y = sin x x Froflections: It s not hard to see from the graph that in general, sin x = sin x. Even more generally, a function f is known as an odd function if f x = f(x). tan is similarly odd as tan x = tan x. cos 120 = cos 60 = Again, let s just use a graph y = cos x x A function is even if f x = f(x). Examples are f x = cos(x) and f x = x 2 as cos x = cos(x) and x 2 = x 2. You do not need to know this for the exam. The graph is rotationally symmetric about 90. Since 120 is 30 above 90, we get the same y value for = 60, except negative.
10 Test Your Understanding Without a calculator, work out the value of each below. cos 315 = cos 45 = 1 2 sin 420 = sin 60 = 3 2 tan 120 = tan 60 = 3 sin x = sin 180 x cos x = cos 360 x sin, cos repeat every 360 but tan every 180 tan 45 = tan 45 = 1 sin 135 = sin 45 = 1 2
11 Exercise 10A/B Pearson Pure Mathematics Year 1/AS Page 207, 209
12 Trigonometric Identities Returning to our point on the unit circle O θ 1 cos θ P sin θ 1 Then tan θ = sin θ cos θ 2 Pythagoras gives you... You are really uncool if you get this reference. sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ = 1 sin 2 θ is a shorthand for sin θ 2. It does NOT mean the sin is being squared this does not make sense as sin is a function, and not a quantity that we can square!
13 Application of identities #1: Proofs Prove that 1 tan θ sin θ cos θ cos 2 θ LHS = 1 sin θ sin θ cos θ cos θ Fro Tip #1: Turn any tan s into sin s and cos s. sin x tan x = cos x sin 2 x + cos 2 x = 1 = 1 sin2 θ cosθ cos θ = 1 sin 2 θ = cos 2 θ = RHS Recall that means equivalent to, and just means the LHS is always equal to the RHS for all values of θ. From Chapter 7 ( Proofs ) we saw that usually the best method is to manipulate one side (e.g. LHS) until we get to the other (RHS).
14 More Examples Edexcel C2 June 2012 Paper 1 Q16 Prove that tan θ + 1 tan θ 1 sin θ cos θ LHS sin θ cos θ + cos θ sin θ Simplify 5 5 sin 2 θ 5 1 sin 2 θ 5 cos 2 θ sin2 θ sin θ cos θ + sin2 θ + cos 2 θ sin θ cos θ cos2 θ sin θ cos θ Fro Tip #3: Look out for 1 sin 2 θ and 1 cos 2 θ. Students often don t spot that these can be simplified. 1 sin θ cos θ RHS Fro Tip #2: In any addition/subtraction involving at least one fraction (with trig functions), always combine algebraically into one.
15 Test Your Understanding Prove that tan x cos x 1 cos 2 x 1 Prove that cos4 θ sin 4 θ cos 2 θ 1 tan 2 θ LHS sin x cos x cos x sin 2 x sin x sin x 1 LHS cos2 θ + sin 2 θ cos 2 θ sin 2 θ cos 2 θ cos2 θ sin 2 θ cos 2 cos2 θ θ cos 2 θ sin2 θ cos 2 θ 1 tan 2 θ RHS AQA IGCSE Further Maths Worksheet Prove that tan 2 θ 1 cos 2 θ 1 LHS sin2 θ cos 2 θ 1 cos2 θ cos 2 θ 1 cos 2 θ cos2 θ cos 2 θ 1 cos 2 θ 1 RHS
16 Exercise 10C Pearson Pure Mathematics Year 1/AS Page Extension: [MAT C] The simultaneous equations in x, y, cos θ x sin θ y = 2 sin θ x + sin θ y = 1 are solvable: A) for all values of θ in range 0 θ < 2π B) except for one value of θ in range 0 θ < 2π C) except for two values of θ in range 0 θ < 2π D) except for three values of θ in range 0 θ < 2π For convenience let s = sin θ and c = cos θ. As we d usually do for simultaneous equations, we could make coefficients of x terms the same: scx s 2 y = 2s scx + c 2 y = c Then subtracting: s 2 + c 2 y = c 2s y = c 2s Similarly making y terms the same, we yield x = 2c + s x, y are defined for every value of θ, so the answer is (A). Why might it have not been (A)? Suppose x = 2 cos θ+sinθ sin θ be defined whenever sin θ = 0.. This would not
17 Solving Trigonometric Equations Remember those trigonometric angle laws (on the right) earlier this chapter? They re about to become super freakin useful! Reminder of trig laws : sin x = sin 180 x cos x = cos 360 x sin, cos repeat every 360 but tan every 180 Solve sin θ = 1 2 in the interval 0 θ 360. θ = sin = 30 or θ = = 150 Froculator Note: When you do sin 1, cos 1 and tan 1 on a calculator, it gives you only one value, known as the principal value. Solve 5 tan θ = 10 in the interval 180 θ < 180 tan θ = 10 5 = 2 θ = tan 1 (2) = 63.4 (1dp) or θ = = dp Fro Tip: Look out for the solution range required. 180 θ < 180 is a particularly common one. tan repeats every 180, so can add/subtract 180 as we please.
18 Slightly Harder Ones Solve sin θ = 1 in the interval 0 θ θ = sin = 30 or θ = = 210 or θ = = 330 This is not in range. In general you should have 2 solutions per 360 (except when at a peak or trough of the trig graph) Note that we ve had to use a second law, i.e. that sin repeats every 360. Solve sin θ = 3 cos θ in the interval 0 θ 360. sin θ cos θ = 3 tan θ = 3 θ = tan 1 3 = 60 or θ = = 240 Hint: The problem here is that we have two different trig functions. Is there anything we can divide both sides by so we only have one trig function?
19 Test Your Understanding Solve 2 cos θ = 3 in the interval 0 θ 360. cos θ = 3 2 θ = cos 1 3 = 30 2 or θ = = 330 Solve 3 sin θ = cos θ in the interval 180 θ 180. tan θ = 1 3 θ = tan 1 13 = 30 or θ = = 150
20 Exercise 10D Pearson Pure Mathematics Year 1/AS Page
21 Harder Equations Harder questions replace the angle θ with a linear expression. Solve cos 3x = 1 2 in the interval 0 x x < x = cos = 120 3x = 120, 240, 480, 600, 840, 960 x = 40, 80, 160, 200, 280, 320 Froflections: As mentioned before, in general you tend to get a pair of values per 360 (for any of sin/cos/tan), except for cosθ = ±1 or sin θ = ±1: y y = cos x STEP 1: Adjust the range of values for θ to match the expression inside the cos. STEP 2: Immediately after applying an inverse trig function (and BEFORE dividing by 3!), find all solutions up to the end of the interval. STEP 3: Then do final manipulation to each value x Thus once getting your first pair of values (e.g. using sin 180 θ or cos(360 θ) to get the second value), keep adding 360 to generate new pairs.
22 Further Example Solve sin(2x + 30 ) = 1 2 in the interval 0 x x x + 30 = 45, 135, 405, 495 2x = 15, 105, 375, 465 x = 7.5, 52.5, 187.5, To get from x to 2x + 30 we double and add 30. So do the same to the upper and lower bound!
23 Test Your Understanding Edexcel C2 Jan 2013 Q4
24 Exercise 10E Pearson Pure Mathematics Year 1/AS Page
25 Quadratics in sin/cos/tan We saw that an equation can be quadratic in something, e.g. x 2 x + 1 = 0 is quadratic in x, meaning that x could be replaced with another variable, say y, to produce a quadratic equation y 2 2y + 1 = 0. Solve 5 sin 2 x + 3 sin x 2 = 0 in the interval 0 x 360. Method 1: Use a substitution. Let y = sin x Then 5y 2 + 3y 2 = 0 5y 2 y + 1 = 0 y = 2 5 or y = 1 sin x = 2 or sin x = 1 5 x = 23. 6, , or x = 270 Method 2: Factorise without substitution. This is the same, but we imagine sin x as a single variable and hence factorise immediately. 5 sin x 2 sin x + 1 = 0 sin x = 2 or sin x = 1 5 x = 23. 6, , or x = 270 Fropinion: I d definitely advocate Method 2 provided you feel confident with it. Method 1 feels clunky.
26 More Examples Solve tan 2 θ = 4 in the interval 0 x 360. tan θ = 2 or tan θ = 2 θ = 63.4, or θ = 63.4, 116.6, Missing the negative case would result in the loss of multiple marks. Beware! 63.4 was outside the range so we had to add 180 twice. Solve 2 cos 2 x + 9 sin x = 3 sin 2 x in the interval 180 x sin 2 x + sin x = 3 sin 2 x 2 2 sin 2 x + sin x = 3 sin 2 x 5 sin 2 x sin x 2 = 0 5 sin x + 1 sin x 2 = 0 sin x = 1 or sin x = 2 5 x = 168.5, 11.5 Tip: We have an identity involving sin 2 and cos 2, so it makes sense to change the squared one that would match all the others.
27 Test Your Understanding Edexcel C2 Jan 2010 Q2
28 Exercise 10F Pearson Pure Mathematics Year 1/AS Page Extension 1 [MAT C] In the range 0 x < 360, the equation sin 2 x + 3 sin x cos x + 2 cos 2 x = 0 Has how many solutions? 2 There are multiple ways to do this, including factorising LHS to (sin x + cos x)(sin x + 2 cos x), but dividing by cos 2 x gives: tan 2 x + 3 tan x + 2 = 0 tan x + 1 tan x + 2 = 0 tan x = 1 or tan x = 2 tan always gives a pair of solutions per 360, so there are 4 solutions. [MAT E] As x varies over the real numbers, the largest value taken by the function 4 sin 2 x + 4 cos x equals what? 4 4 cos 2 x + 4 cos x = 4 cos 2 x + 4 cos x = cos x 2 2 We can make cos x = 1, thus giving 2 a maximum value of 6 2 = 36.
4.3. Trigonometric Identities. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Trigonometric Identities 4.3 Introduction trigonometric identity is a relation between trigonometric expressions which is true for all values of the variables (usually angles. There are a very large number
Trigonometric Identities 4.3 Introduction trigonometric identity is a relation between trigonometric expressions which is true for all values of the variables (usually angles. There are a very large number
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas
 Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions. By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh
 Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks. Mathematics. Accelerated GSE Pre-Calculus Unit 4: Trigonometric Identities
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Pre-Calculus Unit 4: Trigonometric Identities These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Pre-Calculus Unit 4: Trigonometric Identities These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
Trigonometry Review Page 1 of 14
 Trigonometry Review Page of 4 Appendix D has a trigonometric review. This material is meant to outline some of the proofs of identities, help you remember the values of the trig functions at special values,
Trigonometry Review Page of 4 Appendix D has a trigonometric review. This material is meant to outline some of the proofs of identities, help you remember the values of the trig functions at special values,
Figure 1. The unit circle.
 TRIGONOMETRY PRIMER This document will introduce (or reintroduce) the concept of trigonometric functions. These functions (and their derivatives) are related to properties of the circle and have many interesting
TRIGONOMETRY PRIMER This document will introduce (or reintroduce) the concept of trigonometric functions. These functions (and their derivatives) are related to properties of the circle and have many interesting
Name: A Trigonometric Review June 2012
 Name: A Trigonometric Review June 202 This homework will prepare you for in-class work tomorrow on describing oscillations. If you need help, there are several resources: tutoring on the third floor of
Name: A Trigonometric Review June 202 This homework will prepare you for in-class work tomorrow on describing oscillations. If you need help, there are several resources: tutoring on the third floor of
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y
Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I
 MAC 1114 Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize the fundamental identities: reciprocal identities, quotient identities,
MAC 1114 Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize the fundamental identities: reciprocal identities, quotient identities,
Trigonometry. An Overview of Important Topics
 Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Chapter 3, Part 1: Intro to the Trigonometric Functions
 Haberman MTH 11 Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter 3, Part 1: Intro to the Trigonometric Functions In Example 4 in Section I: Chapter, we observed that a circle rotating about its center (i.e.,
Haberman MTH 11 Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter 3, Part 1: Intro to the Trigonometric Functions In Example 4 in Section I: Chapter, we observed that a circle rotating about its center (i.e.,
cos 2 x + sin 2 x = 1 cos(u v) = cos u cos v + sin u sin v sin(u + v) = sin u cos v + cos u sin v
 Concepts: Double Angle Identities, Power Reducing Identities, Half Angle Identities. Memorized: cos x + sin x 1 cos(u v) cos u cos v + sin v sin(u + v) cos v + cos u sin v Derive other identities you need
Concepts: Double Angle Identities, Power Reducing Identities, Half Angle Identities. Memorized: cos x + sin x 1 cos(u v) cos u cos v + sin v sin(u + v) cos v + cos u sin v Derive other identities you need
Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations
 Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations Lesson Package MHF4U Chapter 4/5 Part 2 Outline Unit Goal: By the end of this unit, you will be able to solve trig equations and prove trig identities.
Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations Lesson Package MHF4U Chapter 4/5 Part 2 Outline Unit Goal: By the end of this unit, you will be able to solve trig equations and prove trig identities.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
WARM UP. 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) Factor the expression x 2 2x Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing.
 WARM UP Monday, December 8, 2014 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) 2 2. Factor the expression x 2 2x 8 3. Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Distinguish between
WARM UP Monday, December 8, 2014 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) 2 2. Factor the expression x 2 2x 8 3. Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Distinguish between
MATH Week 10. Ferenc Balogh Winter. Concordia University
 MATH 20 - Week 0 Ferenc Balogh Concordia University 2008 Winter Based on the textbook J. Stuart, L. Redlin, S. Watson, Precalculus - Mathematics for Calculus, 5th Edition, Thomson All figures and videos
MATH 20 - Week 0 Ferenc Balogh Concordia University 2008 Winter Based on the textbook J. Stuart, L. Redlin, S. Watson, Precalculus - Mathematics for Calculus, 5th Edition, Thomson All figures and videos
PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW
 PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW Introduction This review sheet is a summary of most of the main topics that you should already be familiar with from your pre-calculus and trigonometry course(s), and which
PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW Introduction This review sheet is a summary of most of the main topics that you should already be familiar with from your pre-calculus and trigonometry course(s), and which
Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7
 A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Spring 2013 Eliminating Powers From Trig Functions
A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Spring 2013 Eliminating Powers From Trig Functions
1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle
 Pre- Calculus Mathematics 12 5.1 Trigonometric Functions Goal: 1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle Measuring Angles: Angles in Standard
Pre- Calculus Mathematics 12 5.1 Trigonometric Functions Goal: 1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle Measuring Angles: Angles in Standard
Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws
 Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws GRAPHING SINE AND COSINE Graph of sine function: Plotting every angle and its corresponding sine value, which is the y-coordinate, for different angles on the unit
Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws GRAPHING SINE AND COSINE Graph of sine function: Plotting every angle and its corresponding sine value, which is the y-coordinate, for different angles on the unit
Algebra 2/Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & 2: Trigonometry Mega-Session. The Unit Circle
 Algebra /Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & : Trigonometry Mega-Session Trigonometry (Definition) - The branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles
Algebra /Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & : Trigonometry Mega-Session Trigonometry (Definition) - The branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles
1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Exercise 1 Sketch a graph of y = cos(t). Label the multiples of π 2 and π 4 on your plot, as well as the amplitude and the period of the function. (Feel free to sketch the unit
1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Exercise 1 Sketch a graph of y = cos(t). Label the multiples of π 2 and π 4 on your plot, as well as the amplitude and the period of the function. (Feel free to sketch the unit
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Trigonometric identities
 Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
Year 10 Term 1 Homework
 Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 1 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 6 Year 10 Term 1 Week 6 Homework 1 6.1 Triangle trigonometry................................... 1 6.1.1 The
Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 1 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 6 Year 10 Term 1 Week 6 Homework 1 6.1 Triangle trigonometry................................... 1 6.1.1 The
Math 1205 Trigonometry Review
 Math 105 Trigonometry Review We begin with the unit circle. The definition of a unit circle is: x + y =1 where the center is (0, 0) and the radius is 1. An angle of 1 radian is an angle at the center of
Math 105 Trigonometry Review We begin with the unit circle. The definition of a unit circle is: x + y =1 where the center is (0, 0) and the radius is 1. An angle of 1 radian is an angle at the center of
Chapter 2: Pythagoras Theorem and Trigonometry (Revision)
 Chapter 2: Pythagoras Theorem and Trigonometry (Revision) Paper 1 & 2B 2A 3.1.3 Triangles Understand a proof of Pythagoras Theorem. Understand the converse of Pythagoras Theorem. Use Pythagoras 3.1.3 Triangles
Chapter 2: Pythagoras Theorem and Trigonometry (Revision) Paper 1 & 2B 2A 3.1.3 Triangles Understand a proof of Pythagoras Theorem. Understand the converse of Pythagoras Theorem. Use Pythagoras 3.1.3 Triangles
2. Be able to evaluate a trig function at a particular degree measure. Example: cos. again, just use the unit circle!
 Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 5
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY MATH 1205 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY INTRODUCTION 3 1. IDENTITIES AND ADDITION FORMULAS 5 FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES 5 PROVING IDENTITIES
MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY MATH 1205 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY INTRODUCTION 3 1. IDENTITIES AND ADDITION FORMULAS 5 FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES 5 PROVING IDENTITIES
MAT01A1. Appendix D: Trigonometry
 MAT01A1 Appendix D: Trigonometry Dr Craig 12 February 2019 Introduction Who: Dr Craig What: Lecturer & course coordinator for MAT01A1 Where: C-Ring 508 acraig@uj.ac.za Web: http://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com
MAT01A1 Appendix D: Trigonometry Dr Craig 12 February 2019 Introduction Who: Dr Craig What: Lecturer & course coordinator for MAT01A1 Where: C-Ring 508 acraig@uj.ac.za Web: http://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com
13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions. Section 13.4
 13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 1 13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 2 Key Concept Section 13.4 3 Key Concept Section 13.4 4 Key Concept Section
13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 1 13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 2 Key Concept Section 13.4 3 Key Concept Section 13.4 4 Key Concept Section
the input values of a function. These are the angle values for trig functions
 SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
Unit 8 Trigonometry. Math III Mrs. Valentine
 Unit 8 Trigonometry Math III Mrs. Valentine 8A.1 Angles and Periodic Data * Identifying Cycles and Periods * A periodic function is a function that repeats a pattern of y- values (outputs) at regular intervals.
Unit 8 Trigonometry Math III Mrs. Valentine 8A.1 Angles and Periodic Data * Identifying Cycles and Periods * A periodic function is a function that repeats a pattern of y- values (outputs) at regular intervals.
JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 3.5. TRIGONOMETRY 5 (Trigonometric identities & wave-forms) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 3.5 TRIGONOMETRY 5 (Trigonometric identities & wave-forms by A.J.Hobson 3.5.1 Trigonometric identities 3.5. Amplitude, wave-length, frequency and phase-angle UNIT 3.5 - TRIGONOMETRY
JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 3.5 TRIGONOMETRY 5 (Trigonometric identities & wave-forms by A.J.Hobson 3.5.1 Trigonometric identities 3.5. Amplitude, wave-length, frequency and phase-angle UNIT 3.5 - TRIGONOMETRY
Siyavula textbooks: Grade 12 Maths. Collection Editor: Free High School Science Texts Project
 Siyavula textbooks: Grade 12 Maths Collection Editor: Free High School Science Texts Project Siyavula textbooks: Grade 12 Maths Collection Editor: Free High School Science Texts Project Authors: Free
Siyavula textbooks: Grade 12 Maths Collection Editor: Free High School Science Texts Project Siyavula textbooks: Grade 12 Maths Collection Editor: Free High School Science Texts Project Authors: Free
Exercise 1. Consider the following figure. The shaded portion of the circle is called the sector of the circle corresponding to the angle θ.
 1 Radian Measures Exercise 1 Consider the following figure. The shaded portion of the circle is called the sector of the circle corresponding to the angle θ. 1. Suppose I know the radian measure of the
1 Radian Measures Exercise 1 Consider the following figure. The shaded portion of the circle is called the sector of the circle corresponding to the angle θ. 1. Suppose I know the radian measure of the
Lesson 1 6. Algebra: Variables and Expression. Students will be able to evaluate algebraic expressions.
 Lesson 1 6 Algebra: Variables and Expression Students will be able to evaluate algebraic expressions. P1 Represent and analyze patterns, rules and functions with words, tables, graphs and simple variable
Lesson 1 6 Algebra: Variables and Expression Students will be able to evaluate algebraic expressions. P1 Represent and analyze patterns, rules and functions with words, tables, graphs and simple variable
Exam: Friday 4 th May How to Revise. What to use to revise:
 National 5 Mathematics Exam Revision Questions Exam: Friday 4 th May 2018 How to Revise Use this booklet for homework Come to after school revision classes Come to the Easter holiday revision class There
National 5 Mathematics Exam Revision Questions Exam: Friday 4 th May 2018 How to Revise Use this booklet for homework Come to after school revision classes Come to the Easter holiday revision class There
Lesson 27: Sine and Cosine of Complementary and Special Angles
 Lesson 7 M Classwork Example 1 If α and β are the measurements of complementary angles, then we are going to show that sin α = cos β. In right triangle ABC, the measurement of acute angle A is denoted
Lesson 7 M Classwork Example 1 If α and β are the measurements of complementary angles, then we are going to show that sin α = cos β. In right triangle ABC, the measurement of acute angle A is denoted
Solutions to Exercises, Section 5.6
 Instructor s Solutions Manual, Section 5.6 Exercise 1 Solutions to Exercises, Section 5.6 1. For θ = 7, evaluate each of the following: (a) cos 2 θ (b) cos(θ 2 ) [Exercises 1 and 2 emphasize that cos 2
Instructor s Solutions Manual, Section 5.6 Exercise 1 Solutions to Exercises, Section 5.6 1. For θ = 7, evaluate each of the following: (a) cos 2 θ (b) cos(θ 2 ) [Exercises 1 and 2 emphasize that cos 2
Trigonometry. David R. Wilkins
 Trigonometry David R. Wilkins 1. Trigonometry 1. Trigonometry 1.1. Trigonometric Functions There are six standard trigonometric functions. They are the sine function (sin), the cosine function (cos), the
Trigonometry David R. Wilkins 1. Trigonometry 1. Trigonometry 1.1. Trigonometric Functions There are six standard trigonometric functions. They are the sine function (sin), the cosine function (cos), the
Unit 5 Investigating Trigonometry Graphs
 Mathematics IV Frameworks Student Edition Unit 5 Investigating Trigonometry Graphs 1 st Edition Table of Contents INTRODUCTION:... 3 What s Your Temperature? Learning Task... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Mathematics IV Frameworks Student Edition Unit 5 Investigating Trigonometry Graphs 1 st Edition Table of Contents INTRODUCTION:... 3 What s Your Temperature? Learning Task... Error! Bookmark not defined.
MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review. Fall 2017
 MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review Fall 2017 Topics Covered Section 4.1: Angles and Their Measure Section 4.2: Trigonometric Functions Defined on the Unit Circle Section 4.3: Right Triangle Geometry Section 4.4:
MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review Fall 2017 Topics Covered Section 4.1: Angles and Their Measure Section 4.2: Trigonometric Functions Defined on the Unit Circle Section 4.3: Right Triangle Geometry Section 4.4:
Trigonometric Functions
 Trigonometric Functions Q1 : Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures: (i) 25 (ii) - 47 30' (iii) 240 (iv) 520 (i) 25 We know that 180 = π radian (ii) â 47 30' â 47 30' =
Trigonometric Functions Q1 : Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures: (i) 25 (ii) - 47 30' (iii) 240 (iv) 520 (i) 25 We know that 180 = π radian (ii) â 47 30' â 47 30' =
Graphing Sine and Cosine
 The problem with average monthly temperatures on the preview worksheet is an example of a periodic function. Periodic functions are defined on p.254 Periodic functions repeat themselves each period. The
The problem with average monthly temperatures on the preview worksheet is an example of a periodic function. Periodic functions are defined on p.254 Periodic functions repeat themselves each period. The
MAT01A1. Appendix D: Trigonometry
 MAT01A1 Appendix D: Trigonometry Dr Craig 14 February 2017 Introduction Who: Dr Craig What: Lecturer & course coordinator for MAT01A1 Where: C-Ring 508 acraig@uj.ac.za Web: http://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com
MAT01A1 Appendix D: Trigonometry Dr Craig 14 February 2017 Introduction Who: Dr Craig What: Lecturer & course coordinator for MAT01A1 Where: C-Ring 508 acraig@uj.ac.za Web: http://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com
Pythagorean Identity. Sum and Difference Identities. Double Angle Identities. Law of Sines. Law of Cosines
 Review for Math 111 Final Exam The final exam is worth 30% (150/500 points). It consists of 26 multiple choice questions, 4 graph matching questions, and 4 short answer questions. Partial credit will be
Review for Math 111 Final Exam The final exam is worth 30% (150/500 points). It consists of 26 multiple choice questions, 4 graph matching questions, and 4 short answer questions. Partial credit will be
Prerequisite Knowledge: Definitions of the trigonometric ratios for acute angles
 easures, hape & pace EXEMPLAR 28 Trigonometric Identities Objective: To explore some relations of trigonometric ratios Key Stage: 3 Learning Unit: Trigonometric Ratios and Using Trigonometry Materials
easures, hape & pace EXEMPLAR 28 Trigonometric Identities Objective: To explore some relations of trigonometric ratios Key Stage: 3 Learning Unit: Trigonometric Ratios and Using Trigonometry Materials
Graphs of sin x and cos x
 Graphs of sin x and cos x One cycle of the graph of sin x, for values of x between 0 and 60, is given below. 1 0 90 180 270 60 1 It is this same shape that one gets between 60 and below). 720 and between
Graphs of sin x and cos x One cycle of the graph of sin x, for values of x between 0 and 60, is given below. 1 0 90 180 270 60 1 It is this same shape that one gets between 60 and below). 720 and between
Precalculus Second Semester Final Review
 Precalculus Second Semester Final Review This packet will prepare you for your second semester final exam. You will find a formula sheet on the back page; these are the same formulas you will receive for
Precalculus Second Semester Final Review This packet will prepare you for your second semester final exam. You will find a formula sheet on the back page; these are the same formulas you will receive for
Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.
 MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
Mathematics UNIT FIVE Trigonometry II. Unit. Student Workbook. Lesson 1: Trigonometric Equations Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days
 Mathematics 0- Student Workbook Unit 5 Lesson : Trigonometric Equations Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric Identities I Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric
Mathematics 0- Student Workbook Unit 5 Lesson : Trigonometric Equations Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric Identities I Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Lesson : Trigonometric
Unit 5. Algebra 2. Name:
 Unit 5 Algebra 2 Name: 12.1 Day 1: Trigonometric Functions in Right Triangles Vocabulary, Main Topics, and Questions Definitions, Diagrams and Examples Theta Opposite Side of an Angle Adjacent Side of
Unit 5 Algebra 2 Name: 12.1 Day 1: Trigonometric Functions in Right Triangles Vocabulary, Main Topics, and Questions Definitions, Diagrams and Examples Theta Opposite Side of an Angle Adjacent Side of
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 0 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometr An angle is in standard position if its verte is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive ais. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 0 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometr An angle is in standard position if its verte is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive ais. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Calculus for the Life Sciences
 Calculus for the Life Sciences Lecture Notes Joseph M. Mahaffy, jmahaffy@mail.sdsu.edu Department of Mathematics and Statistics Dynamical Systems Group Computational Sciences Research Center San Diego
Calculus for the Life Sciences Lecture Notes Joseph M. Mahaffy, jmahaffy@mail.sdsu.edu Department of Mathematics and Statistics Dynamical Systems Group Computational Sciences Research Center San Diego
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS
 7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS Ferris Wheel Height As a Function of Time The London Eye Ferris Wheel measures 450 feet in diameter and turns continuously, completing a single rotation once every
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS Ferris Wheel Height As a Function of Time The London Eye Ferris Wheel measures 450 feet in diameter and turns continuously, completing a single rotation once every
Unit 7 Trigonometric Identities and Equations 7.1 Exploring Equivalent Trig Functions
 Unit 7 Trigonometric Identities and Equations 7.1 Exploring Equivalent Trig Functions When we look at the graphs of sine, cosine, tangent and their reciprocals, it is clear that there will be points where
Unit 7 Trigonometric Identities and Equations 7.1 Exploring Equivalent Trig Functions When we look at the graphs of sine, cosine, tangent and their reciprocals, it is clear that there will be points where
Arkansas Tech University MATH 1203: Trigonometry Dr. Marcel B. Finan. Review Problems for Test #3
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 1203: Trigonometry Dr. Marcel B. Finan Review Problems for Test #3 Exercise 1 The following is one cycle of a trigonometric function. Find an equation of this graph. Exercise
Arkansas Tech University MATH 1203: Trigonometry Dr. Marcel B. Finan Review Problems for Test #3 Exercise 1 The following is one cycle of a trigonometric function. Find an equation of this graph. Exercise
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
( x "1) 2 = 25, x 3 " 2x 2 + 5x "12 " 0, 2sin" =1.
 Unit Analytical Trigonometry Classwork A) Verifying Trig Identities: Definitions to know: Equality: a statement that is always true. example:, + 7, 6 6, ( + ) 6 +0. Equation: a statement that is conditionally
Unit Analytical Trigonometry Classwork A) Verifying Trig Identities: Definitions to know: Equality: a statement that is always true. example:, + 7, 6 6, ( + ) 6 +0. Equation: a statement that is conditionally
Section 2.4 General Sinusoidal Graphs
 Section. General Graphs Objective: any one of the following sets of information about a sinusoid, find the other two: ) the equation ) the graph 3) the amplitude, period or frequency, phase displacement,
Section. General Graphs Objective: any one of the following sets of information about a sinusoid, find the other two: ) the equation ) the graph 3) the amplitude, period or frequency, phase displacement,
Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet
 Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet In this unit, students will be able to: Convert angle measures from degrees to radians and radians to degrees. Find the measure of an angle given the lengths of the intercepted
Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet In this unit, students will be able to: Convert angle measures from degrees to radians and radians to degrees. Find the measure of an angle given the lengths of the intercepted
Directions: Show all of your work. Use units and labels and remember to give complete answers.
 AMS II QTR 4 FINAL EXAM REVIEW TRIANGLES/PROBABILITY/UNIT CIRCLE/POLYNOMIALS NAME HOUR This packet will be collected on the day of your final exam. Seniors will turn it in on Friday June 1 st and Juniors
AMS II QTR 4 FINAL EXAM REVIEW TRIANGLES/PROBABILITY/UNIT CIRCLE/POLYNOMIALS NAME HOUR This packet will be collected on the day of your final exam. Seniors will turn it in on Friday June 1 st and Juniors
Name Date Class. Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period
 Name Date Class 14-1 Practice A Graphs of Sine and Cosine Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period. 1.. Use f(x) = sinx or g(x) = cosx as a guide. Identify
Name Date Class 14-1 Practice A Graphs of Sine and Cosine Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period. 1.. Use f(x) = sinx or g(x) = cosx as a guide. Identify
Algebra and Trig. I. The graph of
 Algebra and Trig. I 4.5 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions The graph of The graph of. The trigonometric functions can be graphed in a rectangular coordinate system by plotting points whose coordinates
Algebra and Trig. I 4.5 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions The graph of The graph of. The trigonometric functions can be graphed in a rectangular coordinate system by plotting points whose coordinates
Double Integrals over More General Regions
 Jim Lambers MAT 8 Spring Semester 9-1 Lecture 11 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1. in Stewart and Sections 5.3 and 5.4 in Marsden and Tromba. ouble Integrals over More General Regions We have
Jim Lambers MAT 8 Spring Semester 9-1 Lecture 11 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1. in Stewart and Sections 5.3 and 5.4 in Marsden and Tromba. ouble Integrals over More General Regions We have
Unit 6 Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors
 Unit Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors Multiple Choice Portion SHOW ALL WORK! 1. How many radians are in 1800? 10 10π Name: Per: 180 180π 2. On the unit circle shown, which radian measure is located at ( 2,
Unit Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors Multiple Choice Portion SHOW ALL WORK! 1. How many radians are in 1800? 10 10π Name: Per: 180 180π 2. On the unit circle shown, which radian measure is located at ( 2,
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS
 7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS *SECTION: 6.1 DCP List: periodic functions period midline amplitude Pg 247- LECTURE EXAMPLES: Ferris wheel, 14,16,20, eplain 23, 28, 32 *SECTION: 6.2 DCP List: unit
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS *SECTION: 6.1 DCP List: periodic functions period midline amplitude Pg 247- LECTURE EXAMPLES: Ferris wheel, 14,16,20, eplain 23, 28, 32 *SECTION: 6.2 DCP List: unit
6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions. The smallest number p with the above property is called the period of the function.
 Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
Math 122: Final Exam Review Sheet
 Exam Information Math 1: Final Exam Review Sheet The final exam will be given on Wednesday, December 1th from 8-1 am. The exam is cumulative and will cover sections 5., 5., 5.4, 5.5, 5., 5.9,.1,.,.4,.,
Exam Information Math 1: Final Exam Review Sheet The final exam will be given on Wednesday, December 1th from 8-1 am. The exam is cumulative and will cover sections 5., 5., 5.4, 5.5, 5., 5.9,.1,.,.4,.,
The Sine Function. Precalculus: Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 Concepts: Graphs of Sine, Cosine, Sinusoids, Terminology (amplitude, period, phase shift, frequency). The Sine Function Domain: x R Range: y [ 1, 1] Continuity: continuous for all x Increasing-decreasing
Concepts: Graphs of Sine, Cosine, Sinusoids, Terminology (amplitude, period, phase shift, frequency). The Sine Function Domain: x R Range: y [ 1, 1] Continuity: continuous for all x Increasing-decreasing
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions
 Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Section 8 Radian and Degree Measure Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Right Triangle Trigonometry
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Section 8 Radian and Degree Measure Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Right Triangle Trigonometry
Trigonometric Equations
 Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY
 INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY 7 INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY 8 8. Introduction There is perhaps nothing which so occupies the middle position of mathematics as trigonometry. J.F. Herbart (890) You have
INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY 7 INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY 8 8. Introduction There is perhaps nothing which so occupies the middle position of mathematics as trigonometry. J.F. Herbart (890) You have
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
Precalculus Lesson 9.2 Graphs of Polar Equations Mrs. Snow, Instructor
 Precalculus Lesson 9.2 Graphs of Polar Equations Mrs. Snow, Instructor As we studied last section points may be described in polar form or rectangular form. Likewise an equation may be written using either
Precalculus Lesson 9.2 Graphs of Polar Equations Mrs. Snow, Instructor As we studied last section points may be described in polar form or rectangular form. Likewise an equation may be written using either
Math 102 Key Ideas. 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry. 1. Consider the following right triangle: c b
 Math 10 Key Ideas 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry 1. Consider the following right triangle: A c b B θ C a sin θ = b length of side opposite angle θ = c length of hypotenuse cosθ = a length of side adjacent
Math 10 Key Ideas 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry 1. Consider the following right triangle: A c b B θ C a sin θ = b length of side opposite angle θ = c length of hypotenuse cosθ = a length of side adjacent
Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas
 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas MATH 160, Precalculus J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 011 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to: use multiple-angle formulas to rewrite
Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas MATH 160, Precalculus J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 011 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to: use multiple-angle formulas to rewrite
Section 7.6 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 4 Section 7. Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the sine and cosine function. The input values will be the angle in radians so we will be using x is
4 Section 7. Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the sine and cosine function. The input values will be the angle in radians so we will be using x is
MATH 1112 FINAL EXAM REVIEW e. None of these. d. 1 e. None of these. d. 1 e. None of these. e. None of these. e. None of these.
 I. State the equation of the unit circle. MATH 111 FINAL EXAM REVIEW x y y = 1 x+ y = 1 x = 1 x + y = 1 II. III. If 1 tan x =, find sin x for x in Quadrant IV. 1 1 1 Give the exact value of each expression.
I. State the equation of the unit circle. MATH 111 FINAL EXAM REVIEW x y y = 1 x+ y = 1 x = 1 x + y = 1 II. III. If 1 tan x =, find sin x for x in Quadrant IV. 1 1 1 Give the exact value of each expression.
Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes. Professor Miguel Ornelas
 Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes Professor Miguel Ornelas 1 M. Ornelas Math 180 Lecture Notes Section 6.1 Section 6.1 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Verify the identity. a. sin x + cos x cot x = csc
Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes Professor Miguel Ornelas 1 M. Ornelas Math 180 Lecture Notes Section 6.1 Section 6.1 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Verify the identity. a. sin x + cos x cot x = csc
2.5 Amplitude, Period and Frequency
 2.5 Amplitude, Period and Frequency Learning Objectives Calculate the amplitude and period of a sine or cosine curve. Calculate the frequency of a sine or cosine wave. Graph transformations of sine and
2.5 Amplitude, Period and Frequency Learning Objectives Calculate the amplitude and period of a sine or cosine curve. Calculate the frequency of a sine or cosine wave. Graph transformations of sine and
MHF4U. Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School. Unit 4 Radian Measure 5 Video Lessons
 MHF4U Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School Unit 4 Radian Measure 5 Video Lessons Allow no more than 1 class days for this unit! This includes time for review and to write
MHF4U Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School Unit 4 Radian Measure 5 Video Lessons Allow no more than 1 class days for this unit! This includes time for review and to write
Exactly Evaluating Even More Trig Functions
 Exactly Evaluating Even More Trig Functions Pre/Calculus 11, Veritas Prep. We know how to find trig functions of certain, special angles. Using our unit circle definition of the trig functions, as well
Exactly Evaluating Even More Trig Functions Pre/Calculus 11, Veritas Prep. We know how to find trig functions of certain, special angles. Using our unit circle definition of the trig functions, as well
While you wait: For a-d: use a calculator to evaluate: Fill in the blank.
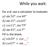 While you wait: For a-d: use a calculator to evaluate: a) sin 50 o, cos 40 o b) sin 25 o, cos65 o c) cos o, sin 79 o d) sin 83 o, cos 7 o Fill in the blank. a) sin30 = cos b) cos57 = sin Trigonometric
While you wait: For a-d: use a calculator to evaluate: a) sin 50 o, cos 40 o b) sin 25 o, cos65 o c) cos o, sin 79 o d) sin 83 o, cos 7 o Fill in the blank. a) sin30 = cos b) cos57 = sin Trigonometric
In this section, you will learn the basic trigonometric identities and how to use them to prove other identities.
 4.6 Trigonometric Identities Solutions to equations that arise from real-world problems sometimes include trigonometric terms. One example is a trajectory problem. If a volleyball player serves a ball
4.6 Trigonometric Identities Solutions to equations that arise from real-world problems sometimes include trigonometric terms. One example is a trajectory problem. If a volleyball player serves a ball
Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure. Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles?
 Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles? You re riding on a Ferris wheel and wonder how fast you are traveling. Before you got on the ride, the operator told you
Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles? You re riding on a Ferris wheel and wonder how fast you are traveling. Before you got on the ride, the operator told you
You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3)
 You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3) LEQ: How do we identify and use basic trigonometric identities to find trigonometric values & use basic trigonometric identities to simplify
You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3) LEQ: How do we identify and use basic trigonometric identities to find trigonometric values & use basic trigonometric identities to simplify
Honors Algebra 2 w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals
 Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
MAC 1114 REVIEW FOR EXAM #2 Chapters 3 & 4
 MAC 111 REVIEW FOR EXAM # Chapters & This review is intended to aid you in studying for the exam. This should not be the only thing that you do to prepare. Be sure to also look over your notes, textbook,
MAC 111 REVIEW FOR EXAM # Chapters & This review is intended to aid you in studying for the exam. This should not be the only thing that you do to prepare. Be sure to also look over your notes, textbook,
How to Graph Trigonometric Functions
 How to Graph Trigonometric Functions This handout includes instructions for graphing processes of basic, amplitude shifts, horizontal shifts, and vertical shifts of trigonometric functions. The Unit Circle
How to Graph Trigonometric Functions This handout includes instructions for graphing processes of basic, amplitude shifts, horizontal shifts, and vertical shifts of trigonometric functions. The Unit Circle
of the whole circumference.
 TRIGONOMETRY WEEK 13 ARC LENGTH AND AREAS OF SECTORS If the complete circumference of a circle can be calculated using C = 2πr then the length of an arc, (a portion of the circumference) can be found by
TRIGONOMETRY WEEK 13 ARC LENGTH AND AREAS OF SECTORS If the complete circumference of a circle can be calculated using C = 2πr then the length of an arc, (a portion of the circumference) can be found by
Section 2.7 Proving Trigonometric Identities
 Sec. 2.7 Proving Trigonometric Identities 87 Section 2.7 Proving Trigonometric Identities In this section, we use the identities presented in Section 2.6 to do two different tasks: ) to simplify a trigonometric
Sec. 2.7 Proving Trigonometric Identities 87 Section 2.7 Proving Trigonometric Identities In this section, we use the identities presented in Section 2.6 to do two different tasks: ) to simplify a trigonometric
Trig functions are examples of periodic functions because they repeat. All periodic functions have certain common characteristics.
 Trig functions are examples of periodic functions because they repeat. All periodic functions have certain common characteristics. The sine wave is a common term for a periodic function. But not all periodic
Trig functions are examples of periodic functions because they repeat. All periodic functions have certain common characteristics. The sine wave is a common term for a periodic function. But not all periodic
Amplitude, Reflection, and Period
 SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
3. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the cosine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians).
 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Desmos Activity 1. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the sine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians). sin 0 sin π 2 sin π
Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Desmos Activity 1. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the sine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians). sin 0 sin π 2 sin π
Math 104 Final Exam Review
 Math 04 Final Exam Review. Find all six trigonometric functions of θ if (, 7) is on the terminal side of θ.. Find cosθ and sinθ if the terminal side of θ lies along the line y = x in quadrant IV.. Find
Math 04 Final Exam Review. Find all six trigonometric functions of θ if (, 7) is on the terminal side of θ.. Find cosθ and sinθ if the terminal side of θ lies along the line y = x in quadrant IV.. Find
Algebra 2/Trig AIIT.13 AIIT.15 AIIT.16 Reference Angles/Unit Circle Notes. Name: Date: Block:
 Algebra 2/Trig AIIT.13 AIIT.15 AIIT.16 Reference Angles/Unit Circle Notes Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Trig Functions in a Circle Circle with radius r, centered around origin (x 2 + y 2 = r 2 ) Drop
Algebra 2/Trig AIIT.13 AIIT.15 AIIT.16 Reference Angles/Unit Circle Notes Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Trig Functions in a Circle Circle with radius r, centered around origin (x 2 + y 2 = r 2 ) Drop
Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides
 MPM2D: Principles of Mathematics Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides J. Garvin Slide 1/15 Recap State the three primary trigonometric ratios for A in ABC. Slide 2/15 Recap State
MPM2D: Principles of Mathematics Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides J. Garvin Slide 1/15 Recap State the three primary trigonometric ratios for A in ABC. Slide 2/15 Recap State
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions We know from previously studying the periodicity of the trigonometric functions that the sine and cosine functions repeat themselves after 2 radians.
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions We know from previously studying the periodicity of the trigonometric functions that the sine and cosine functions repeat themselves after 2 radians.
