Fiber Optic Sensing Applications Based on Optical Propagation Mode Time Delay Measurement
|
|
|
- Phillip Shields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 R ESEARCH ARTICLE ScienceAsia 7 (1) : 35-4 Fiber Optic Sensing Applications Based on Optical Propagation Mode Time Delay Measurement PP Yupapin a * and S Piengbangyang b a Lightwave Technology Research Center, Department of Applied Physics, Faculty of Science King Mongkut s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang, Bangkok 15, Thailand. b National Metrology Institute, Ministry of Science Technology and Environment, Bangkok 14, Thailand. * Corresponding author, yupapin.preecha@kmitl.ac.th Received Sep 1999 Accepted 18 Aug ABSTRACT This paper presents the study of the feasibility of using a linearly polarized, highly coherent source, ie HeNe laser with wavelength of 63.8 nm, to produce the optical mode delay time in an optical fiber for the use of sensing applications. Results obtained have shown that the propagation mode delay time measurement in term of optical path difference of 5 µm was achieved respect to the external applied force of 5 N, on the sensing fiber. Other sensing applications such as displacement and bending sensors were also investigated, where the change in optical path difference in term of output detected mode shift of 7 µm was recorded associating with the sensing displacement. The limitation of this measurement due to the sensing fiber bending radius of mm was noted. KEYWORDS: laser application, optical fiber sensor, fiber optic device. INTRODUCTION Optical techniques for measurement were widely used in many areas of applications 1-3, where the different schemes of sensor systems were investigated using laser applications 4-8. Most of them used low coherent laser sources to produce light beams for the sensor systems, where either optical intensity or phase of the optical field formed the required measurement information. The conventional technique for white light interferometry(wli) was presented by Ning et al, 7 using laser diode. While the use of phase information to form the measurement was investigated and described, using WLI in both theory and experiment by Wang et al, 8-1 where the resolution of measurement could be improved by using two alternative sources interferometer. WLI was also demonstrated by Yupapin et al 3,6 for the study of photo-elastic material characterizations with the use for sensor applications, where the problem of WLI was light source stability ie a laser diode, causing the problem of long period of operation. The problem of the system employed was easily damage low coherent source due to the power supply voltage fluctuation and circuitry complexity, then the use of highly coherent source was attractive to investigate for sensor applications. HeNe laser was the one known as a highly coherent source which popularly used for intensity measurement technique. This study was demonstrated that the use of a highly coherent source such as HeNe laser for sensor applications, using phase ie optical path difference (OPD) of the traveling light in the optical fibers to form the required information in term of the change of the output light mode position, which could be implemented the required measurement. OPERATING PRINCIPLES 1. System analysis The theoretical treatment of physical optics by incorporating the nature of light, where the wave equation in an isotropic media with simple harmonic motion is satisfied the scalar wave equation as ψ (,) zt = 1 ψ (,) zt (1) c t where t is time, c is the speed of light, ψ(z, t) is the wave function, and z is distance in the direction of the input traveling wave into the medium refractive index n 1. The phase difference between the input plane (z o ) and output plane (z 1 ) is the product of the optical path difference and k, which is given as [ ] φ ( x) = π ( n1 1) d( x) + z () λ where k=π/λ, d(x) is the traveling distance between planes z 1 and z o.
2 36 ScienceAsia 7 (1) Any monochromatic light at wavelength λ that propagates parallel to the z axis which the light wave at plane z o represented by ψ(,) z t = Cos ( ωt kz o ) (3) This is spatially modulated by the optical element whose transmitted magnitude is a(x) and whose phase is φ. From equation (), where z = z 1 -z o, light at plane z 1 therefore represented by [ ] ψ(,) z t = a( x) Cos ωt kz o φ( x) (4) which shows that light is modulated in the magnitude and phase. To use the phasor notation then the wave equation becomes [ ω φ( )] zt ax e j t kz o x ψ(,) = () (5) where the complex transmittance of the optical element is represented as jφ( x) + j[ ωt kz o φ( x) ] = ψ(,) zt ax () e (6) The complex transmitted amplitude of several elements in series, as we expect such as a x a x a x a x e j [ 1( x ) + ( x ) + 3( ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) x )] = φ φ φ (7) and the associated real valued represented of the light is A photo-detector responds to the time average of I(x, t) to produce the current g(x) that is a function of only the space variable g(x) = < I (x,t) > = a (x) (11) The system in the study is concerned the photocurrent or the optical field intensity which is in the form as in equation(1).. Propagation modes The optical field(e) from a linearly polarized light in xy-plane of a highly coherent source is expressed in term of the Gaussian light output beam as x + y Exy (, ) = Eo exp (1) ω where x and y are the laser beam coordinates, E o is the optical field amplitude, ω o is the initial beam width, i.e. z =, a laser beam width (ω) is given as ω() z = ω z o + 1 r 1 (13) where r is a spherical mirror radius. Consider light modes propagation in a fiber which is described by a normalized wave number (V) as V = π ana (14) λ where λ is a light source wavelength, a is a fiber optic core radius, and NA is a fiber optic numerical aperture. The number of propagation modes(n) is given by a 4 (x) = a1( x) a( x) a3( x) cos[ ωt kzo φ1( x) φ( x) φ3( x)] (8) Any physical detector senses the intensity of light, defined as I( xyz,, ) = a( xyzt,,, ) a*( xyzt,,, ) (9) N V for single mode fiber, and N V 4 for multimode fiber. (15a) (15b) For the real valued version of the equation (8) and find that the intensity at plane z 1 becomes I = a( x) Cos[ ωt kzo φ ( x)] (1) Consider the optical field intensity (I) of the transmitted light through the optical bulky grating which is detected by a photo-detector, the grating transfer function of the optical output is expressed as Ix ( ) = a { + Cos ( x)} 1 ϕ (16)
3 ScienceAsia 7 (1) 37 where ϕ (x) = (φ 1 -φ ) is the phase difference of two propagation modes, a is a signal amplitude. The optical output intensity is associated with equation (16), the phase difference [ϕ (x)] is observed in term of OPD by moving the detector position to obtain the optimum detected intensity position, then the measurement relationship of the change between phase and optical path difference is observed. The mode separation of the transmitted light modes through the bulky grating is given as the equation mλ = a(sinθi + sin θm) (17) where a is a grating period, θ i and θ m is the incident and diffraction angles respectively, m is the light diffraction order, λ is the light source wavelength. Any change of light mode traveling path is effect to the output light mode separation, i.e. OPD which is observed and detected by a photo-detector respect to the change on the sensing fiber which will be discussed in the following sections. 3. Sensing Applications There are other factors of fiber bending to take into account in addition for sensor considerations, which can be divided into two general cases as following. The fiber micro-bending sensitivity, is represented by L/ D, where the mechanical design of the bending sensing device, associated with [ D/ F] 11 is expressed as L = L D F D F (18) where L is the fiber transmission length, F is the applied force, and D is the deformation length of the fiber normal to its axis. Sensitivity to micro-bending, or large L/ D, is increased by small values of numerical aperture, a large number of deformations, optimized perturbation period, and a large core diameter relative to cladding diameter. Mechanical design considerations may against some of those selections, since to maximize D/ F, a small diameter fiber, few bends, and a large perturbation wavelength are desire. One example of the many influences on the total sensitivity of the micro-bending sensor is given by the length dependence of micro-bending sensitivity, it is written as L α D l q (19) where l is the length of the micro-bent fiber, and <q 1. A fiber with a perfectly absorbent jacket would have q = 1 and a sensitivity that depended linearly on the sensing length. The another application is the fiber optic strain sensor, (ie strain = applied force/ fiber length), then equation (18) can be used similarly to micro-bending sensor. In this scheme, the transmission term L is relatively changed to the applied force with respect to the fiber coupling length an shown in Fig 1. Both schemes, the transmission light is detected by a detector after passing through the transmission grating. The detector output light modes are observed relating to the applied physical parameters. Strain and bending measurements are observed by using the applied force on the sensing unit which the effects are transformed into the fiber bending section, ie the optical path difference of the propagation modes. In application, a system may be employed by using the another single mode fiber known as polarization maintaining fiber(hibi fiber), having highly birefringent fiber as a sensing fiber. The broader applications such as temperature sensor and the difference fiber optic characteristics can be investigated. A change in temperature T of a fiber changes the fiber length due to thermal expansion or contraction, and change the refractive index. Thus, if the phase of the transmitted light ϕ = (πln)/λ, the following may be written as 1 φ π n dl l dn = T + λ dt dt HeNe Laser From Light Source L1 Chopper Optical Fiber Sensing Unit SM, MM Displacement Microbend Deformer () Fig 1. The illustration of the experimental system, and a sensing unit. L1, L: Lenses, SM: Single mode fiber, MM: Multimode fiber, G: Grating, and D:Photdetector. L Oscilloscopes G First-Order Zeroth-Order D Light Coupled Out of Fiber to Photo Detector
4 38 ScienceAsia 7 (1) for an ordinary single mode fiber, and φ d π n dl ld n = T λ + dt dt (1) for a HiBi fiber, where l is the fiber length, n is the refractive index of the sensing fiber, and λ is the light source wavelength. The change of the optical phase due to mode propagation time delay will change the output intensity as described by equation(16). The difference between equations () and (1) is that the ordinary mode fiber is supposed to be completely symmetry then the fiber birefringence is vanished, the latter case of equation (1) is the special fiber called polarization maintaining fiber which the fiber birefringence is presented, for temperature sensor applications. The change of temperature affects to the change of fiber length and birefrngence. The relationship between temperature and phase or light intensity is the detected parameter using a photo-detector, where the detected intensity is specified by output wavelength variation as in equation (17). EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS Light from He Ne laser with wavelength of 63.8 nm was linearly polarized then launched into a length of single mode/multimode fiber, with 6 meters long as shown in Fig. 1, before entering into a sensing fiber and bulky optical grating. The bulky grating with 1 lines in 1 milliimeter was aligned with 1 cm apart from a detector. In order to avoid the background noise from the direct current, then a mechanical chopper was employed to chop the light beam being the ac signal i.e increasing the signal to noise ratio of the detected signals. A single Gaussian mode from HeNe laser was chopped then launched and split into several modes by traveling through the length of delivery fiber and sensing unit, before entering into a bulky grating. The output light was detected by a detector and shown on the oscilloscope. The change of light path due to the external applied physical parameters such as the external applied forces were formed and identified position by moving the detector position to obtain the maximum signal amplitude and OPD. This may be related to the change of the required information such as force and displacement. In this work, the applied force was applied on the sensing unit by using the series of calibrated masses. The measurements were made of 5 times for each data point. The increment of scanning resolution and applied of 1 microns and. N were used for displacement and force measurement respectively. Fig shows the change of the detector position (optical path difference) from light traveling trough the sensing unit which was formed and detected using single mode fiber and multimode fibers respectively, where the measured values of mode Intensity (arb.unit) Intensity (arb.unit) Intensity (arb.unit) Detector Position (micron) (c) applied force reference reference applied force Detector Position (micron) D 1max D d d 1max d max D - d reference applied force Detector Position (micron) D max Fig. Shows graphs of the detected output mode position intensities either with or without force (reference), using, single mode fiber, multimode fiber, and (c) the measurement (D-d) of the change of the detector position using multimode fiber. Where D and d is the distance of the center peak of the reference signal. D max and d max is the center peak signal with respect to the applied force.
5 ScienceAsia 7 (1) 39 separation of 5 µm was achieved. Generally, propagation modes separation is obtained from mode propagation time delay along a fiber forming the reference position ie 1st order mode position. The change of physical parameters along the sensing fiber was induced the change of first order mode and detected by the detection device, then was measured. In this study, the change in propagation modes of traveling light in the fiber means the change in spectral width ie wavelength, which is observed. Fig 3 shows the result of the change of mode position / wavelength difference which was induced by the applied force, where the change of the detector position/opd of 5 µm was noted associating with the applied force of 5 N, SM: single mode fiber, MM: multimode fiber. The presented data was used the statistical method then plotted with systematical error bar of 1 micron. The change of first order mode of 7 and 9 µm was observed respecting to the sensing displacement of.5 mm, for multimode and single mode fiber respectively. The increasing of propagation modes was effected the output detection measurement which may be obtained from the intensity noise of the neighboring harmonics ie Sensing Unit Displacement (micron) Sensing Unit Displacement (micron) Force (N) MM SM Sensing Unit Displacement (micron) MM SM Fig 3. Graphs of the relationship between the change of mode detection position with respect to the applied force and sensing unit displacement. SM: Single mode fiber, MM:Multimode fiber Force (N) (c) Force (N) (d) Fig 4. Graphs of the measurement hysteresis for the force sensing experimental system using single mode and multimode fiber, the displacement experimental scheme using single mode (c), and multimode fiber(d).
6 4 ScienceAsia 7 (1) modes. Fig 4 shows the result of the measurement hysteresis of the systems for force and displacement measurements, using either single or multimode mode fibers having small hysteresis for both systems. CONCLUSION The study of the use of a highly coherent source for sensing application was presented. The subject of this study was concentrated on the simple measurement technique which widely used for sensor and optical metrology applications. Results have shown the potential of using a technique of light mode separation measurement in such a fiber for force, fiber bending, and displacement sensors. The detected resolution of the output mode separations was founded in the range of 1 microns. To improve the resolution, the scanning device such as a nano-scanning device using piezoelectric transducer(pzt) system may be employed. However, the signal detection levels may limit the measurement due to the invalid values of SNR. The comparison of the systems use ordinary single mode fiber and multimode fiber was proposed, the single mode fiber has shown more advantage than the one using multimode fiber. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS REFERENCES 1. Weir K et al (1994) Accurate measurement of small displacement using optical techniques. Int J Optoelectronics 9, Yupapin et al (1998) Dynamic measurement of thin liquid film parameters using high-speed ellipsometry. Sensors Actuators A 65, Wang A et al (199) Optical fiber pressure sensor based on photoelasticity and its applications. J Lightwave Technol 1, Yupapin PP and Kusamran S (1993) Photoelastic material characteristics based on the stress-induced effects for sensor applications, Smart Mater Struct Vol, 1993, Yupapin PP et al (1996) Fiber optic force sensor and its applications. Thammasart Int J of Sci and Technol 1, Yupapin PVP et al (1993) An optical pressure sensor using a low - coherence light source with a photoelastic sensing element. Sensors and Actuators A 36, Ning YN et al (1989) Characteristics of laser Diodes for interferometric use. Appl Opt 8, Yupapin PVP et al (1995) A study of polarization maintaining fiber characteristics with applications to force and displacement sensing. J Laser Applications 7, Wang DN et al (1993 The optimized wavelength combinations of two broadband sources for white light interferometry. J Lightwave Technol 11, Wang DN et al (1994) Alternative white light interferometer. J Lightwave Technol 1, Udd E (1995) Fiber optics smart structures, John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York. 1. Udd E (1991) Fiber optics sensors:an Introduction for Engineers and Scientists, Toronto: John Wiley & Sons. The authors are pleased to acknowledge some support from the National Electronic and Computer Technology Center (NECTEC) by way of a research scholarship to Assoc Prof Dr Preecha Yupapin.
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT
 CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
High stability multiplexed fibre interferometer and its application on absolute displacement measurement and on-line surface metrology
 High stability multiplexed fibre interferometer and its application on absolute displacement measurement and on-line surface metrology Dejiao Lin, Xiangqian Jiang and Fang Xie Centre for Precision Technologies,
High stability multiplexed fibre interferometer and its application on absolute displacement measurement and on-line surface metrology Dejiao Lin, Xiangqian Jiang and Fang Xie Centre for Precision Technologies,
Diffractive Axicon application note
 Diffractive Axicon application note. Introduction 2. General definition 3. General specifications of Diffractive Axicons 4. Typical applications 5. Advantages of the Diffractive Axicon 6. Principle of
Diffractive Axicon application note. Introduction 2. General definition 3. General specifications of Diffractive Axicons 4. Typical applications 5. Advantages of the Diffractive Axicon 6. Principle of
Fiber Optic Communications Communication Systems
 INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET
 LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
Intensity Modulation. Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington. W. Wang
 Intensity Modulation Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Why Intensity Modulation Simple optical setup Broadband or mono-chormatic light source Less sensitive but
Intensity Modulation Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Why Intensity Modulation Simple optical setup Broadband or mono-chormatic light source Less sensitive but
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
The 34th International Physics Olympiad
 The 34th International Physics Olympiad Taipei, Taiwan Experimental Competition Wednesday, August 6, 2003 Time Available : 5 hours Please Read This First: 1. Use only the pen provided. 2. Use only the
The 34th International Physics Olympiad Taipei, Taiwan Experimental Competition Wednesday, August 6, 2003 Time Available : 5 hours Please Read This First: 1. Use only the pen provided. 2. Use only the
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin
 Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Real-Time Scanning Goniometric Radiometer for Rapid Characterization of Laser Diodes and VCSELs
 Real-Time Scanning Goniometric Radiometer for Rapid Characterization of Laser Diodes and VCSELs Jeffrey L. Guttman, John M. Fleischer, and Allen M. Cary Photon, Inc. 6860 Santa Teresa Blvd., San Jose,
Real-Time Scanning Goniometric Radiometer for Rapid Characterization of Laser Diodes and VCSELs Jeffrey L. Guttman, John M. Fleischer, and Allen M. Cary Photon, Inc. 6860 Santa Teresa Blvd., San Jose,
Experimental Physics. Experiment C & D: Pulsed Laser & Dye Laser. Course: FY12. Project: The Pulsed Laser. Done by: Wael Al-Assadi & Irvin Mangwiza
 Experiment C & D: Course: FY1 The Pulsed Laser Done by: Wael Al-Assadi Mangwiza 8/1/ Wael Al Assadi Mangwiza Experiment C & D : Introduction: Course: FY1 Rev. 35. Page: of 16 1// In this experiment we
Experiment C & D: Course: FY1 The Pulsed Laser Done by: Wael Al-Assadi Mangwiza 8/1/ Wael Al Assadi Mangwiza Experiment C & D : Introduction: Course: FY1 Rev. 35. Page: of 16 1// In this experiment we
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2002 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2002 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. FOUR 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2002 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. FOUR 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing
 Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing Dr. Jim Burge Associate Professor Optical Sciences and Astronomy University of Arizona jburge@optics.arizona.edu 520-621-8182 Computer Generated Holograms
Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing Dr. Jim Burge Associate Professor Optical Sciences and Astronomy University of Arizona jburge@optics.arizona.edu 520-621-8182 Computer Generated Holograms
Test procedures Page: 1 of 5
 Test procedures Page: 1 of 5 1 Scope This part of document establishes uniform requirements for measuring the numerical aperture of optical fibre, thereby assisting in the inspection of fibres and cables
Test procedures Page: 1 of 5 1 Scope This part of document establishes uniform requirements for measuring the numerical aperture of optical fibre, thereby assisting in the inspection of fibres and cables
Fang-Wen Sheu *, Yi-Syuan Lu Department of Electrophysics, National Chiayi University, Chiayi 60004, Taiwan ABSTRACT
 Determining the relationship between the refractive-index difference of a coiled single-mode optical fiber and its bending radius by a mode-image analysis method Fang-Wen Sheu *, Yi-Syuan Lu Department
Determining the relationship between the refractive-index difference of a coiled single-mode optical fiber and its bending radius by a mode-image analysis method Fang-Wen Sheu *, Yi-Syuan Lu Department
AgilOptics mirrors increase coupling efficiency into a 4 µm diameter fiber by 750%.
 Application Note AN004: Fiber Coupling Improvement Introduction AgilOptics mirrors increase coupling efficiency into a 4 µm diameter fiber by 750%. Industrial lasers used for cutting, welding, drilling,
Application Note AN004: Fiber Coupling Improvement Introduction AgilOptics mirrors increase coupling efficiency into a 4 µm diameter fiber by 750%. Industrial lasers used for cutting, welding, drilling,
Photonic Signals. and Systems. An Introduction. NabeelA.Riza/Ph.D. Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering University College Cork
 Photonic Signals and Systems An Introduction NabeelA.Riza/Ph.D. Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering University College Cork Cork, Ireland New York Chicago San Francisco Lisbon London Madrid
Photonic Signals and Systems An Introduction NabeelA.Riza/Ph.D. Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering University College Cork Cork, Ireland New York Chicago San Francisco Lisbon London Madrid
Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing
 Journal of Computer Science 2 (): 09-3, 2006 ISSN 549-3636 Science Publications, 2006 Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing Yas A. Alsultanny Computer Science Department, Amman Arab University for
Journal of Computer Science 2 (): 09-3, 2006 ISSN 549-3636 Science Publications, 2006 Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing Yas A. Alsultanny Computer Science Department, Amman Arab University for
Optical systems have carrier frequencies of ~100 THz. This corresponds to wavelengths from µm.
 Introduction A communication system transmits information form one place to another. This could be from one building to another or across the ocean(s). Many systems use an EM carrier wave to transmit information.
Introduction A communication system transmits information form one place to another. This could be from one building to another or across the ocean(s). Many systems use an EM carrier wave to transmit information.
INTERFEROMETRIC VIBRATION DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 62, No. 3, P. 671 677, 2010 Dedicated to the 50 th LASER Anniversary (LASERFEST-50) INTERFEROMETRIC VIBRATION DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT F. GAROI 1, P.C. LOGOFATU 1, D.
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 62, No. 3, P. 671 677, 2010 Dedicated to the 50 th LASER Anniversary (LASERFEST-50) INTERFEROMETRIC VIBRATION DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT F. GAROI 1, P.C. LOGOFATU 1, D.
Quasi distributed strain sensing in cantilever beams by use of modal interference
 Quasi distributed strain sensing in cantilever beams by use of modal interference *S.K.Ghorai and Dilip Kumar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra,Ranchi-83515
Quasi distributed strain sensing in cantilever beams by use of modal interference *S.K.Ghorai and Dilip Kumar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra,Ranchi-83515
Analysis of Tilted Grating Etalon for DWDM Demultiplexer
 Analysis of Tilted Grating Etalon for DWDM Demultiplexer 71 Analysis of Tilted Grating Etalon for DWDM Demultiplexer Sommart Sang-Ngern, Non-member and Athikom Roeksabutr, Member ABSTRACT This paper theoretically
Analysis of Tilted Grating Etalon for DWDM Demultiplexer 71 Analysis of Tilted Grating Etalon for DWDM Demultiplexer Sommart Sang-Ngern, Non-member and Athikom Roeksabutr, Member ABSTRACT This paper theoretically
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
Lecture 2: Interference
 Lecture 2: Interference λ S 1 d S 2 Lecture 2, p.1 Today Interference of sound waves Two-slit interference Lecture 2, p.2 Review: Wave Summary ( ) ( ) The formula y x,t = Acoskx ωt describes a harmonic
Lecture 2: Interference λ S 1 d S 2 Lecture 2, p.1 Today Interference of sound waves Two-slit interference Lecture 2, p.2 Review: Wave Summary ( ) ( ) The formula y x,t = Acoskx ωt describes a harmonic
High Sensitivity Interferometric Detection of Partial Discharges for High Power Transformer Applications
 High Sensitivity Interferometric Detection of Partial Discharges for High Power Transformer Applications Carlos Macià-Sanahuja and Horacio Lamela-Rivera Optoelectronics and Laser Technology group, Universidad
High Sensitivity Interferometric Detection of Partial Discharges for High Power Transformer Applications Carlos Macià-Sanahuja and Horacio Lamela-Rivera Optoelectronics and Laser Technology group, Universidad
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus
 Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II
 Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II Generating negative groupdelay dispersion angular dispersion Pulse compression Prisms Gratings Chirped mirrors Chirped vs. transform-limited A transform-limited pulse:
Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II Generating negative groupdelay dispersion angular dispersion Pulse compression Prisms Gratings Chirped mirrors Chirped vs. transform-limited A transform-limited pulse:
Ratiometric Wavelength Monitor Based on Singlemode-Multimode-Singlemode Fiber Structure
 Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Articles School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering 8-1-1 Ratiometric Wavelength Monitor Based on Singlemode-Multimode-Singlemode Fiber Structure Agus Hatta
Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Articles School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering 8-1-1 Ratiometric Wavelength Monitor Based on Singlemode-Multimode-Singlemode Fiber Structure Agus Hatta
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT
 ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (E-O) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (E-O) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
Physical Optics. Diffraction.
 Physical Optics. Diffraction. Interference Young s interference experiment Thin films Coherence and incoherence Michelson interferometer Wave-like characteristics of light Huygens-Fresnel principle Interference.
Physical Optics. Diffraction. Interference Young s interference experiment Thin films Coherence and incoherence Michelson interferometer Wave-like characteristics of light Huygens-Fresnel principle Interference.
Development of a Low Cost 3x3 Coupler. Mach-Zehnder Interferometric Optical Fibre Vibration. Sensor
 Development of a Low Cost 3x3 Coupler Mach-Zehnder Interferometric Optical Fibre Vibration Sensor Kai Tai Wan Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering, Brunel University London, UB8 3PH,
Development of a Low Cost 3x3 Coupler Mach-Zehnder Interferometric Optical Fibre Vibration Sensor Kai Tai Wan Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering, Brunel University London, UB8 3PH,
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: Signature:
 Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
SPRAY DROPLET SIZE MEASUREMENT
 SPRAY DROPLET SIZE MEASUREMENT In this study, the PDA was used to characterize diesel and different blends of palm biofuel spray. The PDA is state of the art apparatus that needs no calibration. It is
SPRAY DROPLET SIZE MEASUREMENT In this study, the PDA was used to characterize diesel and different blends of palm biofuel spray. The PDA is state of the art apparatus that needs no calibration. It is
An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm
 An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm Ma Yangwu *, Liang Di ** Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Lab of Modern Optical
An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm Ma Yangwu *, Liang Di ** Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Lab of Modern Optical
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING
 CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
Fiber Optic Communication Systems. Unit-05: Types of Fibers. https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif
 Unit-05: Types of Fibers https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro 1 Optical Fiber Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro
Unit-05: Types of Fibers https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro 1 Optical Fiber Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro
ANALYSIS OF MICROBEND SENSOR ON BASIS OF DIMENSIONS OF OPTICAL FIBER USED
 ANALYSIS OF MICROBEND SENSOR ON BASIS OF DIMENSIONS OF OPTICAL FIBER USED Daisy Gogoi Electrical Engineering, Jorhat Engineering College, Dibrugarh University, (India) ABSTRACT In this paper an intensity
ANALYSIS OF MICROBEND SENSOR ON BASIS OF DIMENSIONS OF OPTICAL FIBER USED Daisy Gogoi Electrical Engineering, Jorhat Engineering College, Dibrugarh University, (India) ABSTRACT In this paper an intensity
Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film
 Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film Hisashi Akiyama 1, Osami Sasaki 2, and Takamasa Suzuki
Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film Hisashi Akiyama 1, Osami Sasaki 2, and Takamasa Suzuki
Fabry Perot Resonator (CA-1140)
 Fabry Perot Resonator (CA-1140) The open frame Fabry Perot kit CA-1140 was designed for demonstration and investigation of characteristics like resonance, free spectral range and finesse of a resonator.
Fabry Perot Resonator (CA-1140) The open frame Fabry Perot kit CA-1140 was designed for demonstration and investigation of characteristics like resonance, free spectral range and finesse of a resonator.
RECENTLY, using near-field scanning optical
 1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
Part 1: Standing Waves - Measuring Wavelengths
 Experiment 7 The Microwave experiment Aim: This experiment uses microwaves in order to demonstrate the formation of standing waves, verifying the wavelength λ of the microwaves as well as diffraction from
Experiment 7 The Microwave experiment Aim: This experiment uses microwaves in order to demonstrate the formation of standing waves, verifying the wavelength λ of the microwaves as well as diffraction from
Department of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Harbin Institute of Technology Shenzhen Graduate School, Shenzhen, , China
 6th International Conference on Machinery, Materials, Environment, Biotechnology and Computer (MMEBC 16) Precision Measurement of Displacement with Two Quasi-Orthogonal Signals for Linear Diffraction Grating
6th International Conference on Machinery, Materials, Environment, Biotechnology and Computer (MMEBC 16) Precision Measurement of Displacement with Two Quasi-Orthogonal Signals for Linear Diffraction Grating
OPTI 511L Fall (Part 1 of 2)
 Prof. R.J. Jones OPTI 511L Fall 2016 (Part 1 of 2) Optical Sciences Experiment 1: The HeNe Laser, Gaussian beams, and optical cavities (3 weeks total) In these experiments we explore the characteristics
Prof. R.J. Jones OPTI 511L Fall 2016 (Part 1 of 2) Optical Sciences Experiment 1: The HeNe Laser, Gaussian beams, and optical cavities (3 weeks total) In these experiments we explore the characteristics
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 20 at the start of class
 PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
Fabry-Perot Interferometer
 Experimental Optics Contact: Maximilian Heck (maximilian.heck@uni-jena.de) Ria Krämer (ria.kraemer@uni-jena.de) Last edition: Ria Krämer, March 2017 Fabry-Perot Interferometer Contents 1 Overview 3 2 Safety
Experimental Optics Contact: Maximilian Heck (maximilian.heck@uni-jena.de) Ria Krämer (ria.kraemer@uni-jena.de) Last edition: Ria Krämer, March 2017 Fabry-Perot Interferometer Contents 1 Overview 3 2 Safety
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Optics and Lasers. Matt Young. Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides
 Matt Young Optics and Lasers Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides Fourth Revised Edition With 188 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Matt Young Optics and Lasers Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides Fourth Revised Edition With 188 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP
 7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP Abstract: In this chapter we describe the use of a common path phase sensitive FDOCT set up. The phase measurements
7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP Abstract: In this chapter we describe the use of a common path phase sensitive FDOCT set up. The phase measurements
Waveguides and Optical Fibers
 Waveguides and Optical Fibers Dielectric Waveguides Light Light Light n n Light n > n A planar dielectric waveguide has a central rectangular region of higher refractive index n than the surrounding region
Waveguides and Optical Fibers Dielectric Waveguides Light Light Light n n Light n > n A planar dielectric waveguide has a central rectangular region of higher refractive index n than the surrounding region
Fiberoptic and Waveguide Sensors
 Fiberoptic and Waveguide Sensors Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mecahnical Engineering University of Washington Optical sensors Advantages: -immune from electromagnetic field interference (EMI) - extreme
Fiberoptic and Waveguide Sensors Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mecahnical Engineering University of Washington Optical sensors Advantages: -immune from electromagnetic field interference (EMI) - extreme
Optical Fiber Technology. Photonic Network By Dr. M H Zaidi
 Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
ADVANCED OPTICS LAB -ECEN Basic Skills Lab
 ADVANCED OPTICS LAB -ECEN 5606 Basic Skills Lab Dr. Steve Cundiff and Edward McKenna, 1/15/04 Revised KW 1/15/06, 1/8/10 Revised CC and RZ 01/17/14 The goal of this lab is to provide you with practice
ADVANCED OPTICS LAB -ECEN 5606 Basic Skills Lab Dr. Steve Cundiff and Edward McKenna, 1/15/04 Revised KW 1/15/06, 1/8/10 Revised CC and RZ 01/17/14 The goal of this lab is to provide you with practice
A Multiwavelength Interferometer for Geodetic Lengths
 A Multiwavelength Interferometer for Geodetic Lengths K. Meiners-Hagen, P. Köchert, A. Abou-Zeid, Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Braunschweig Abstract: Within the EURAMET joint research project
A Multiwavelength Interferometer for Geodetic Lengths K. Meiners-Hagen, P. Köchert, A. Abou-Zeid, Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Braunschweig Abstract: Within the EURAMET joint research project
ADVANCED OPTICS LAB -ECEN 5606
 ADVANCED OPTICS LAB -ECEN 5606 Basic Skills Lab Dr. Steve Cundiff and Edward McKenna, 1/15/04 rev KW 1/15/06, 1/8/10 The goal of this lab is to provide you with practice of some of the basic skills needed
ADVANCED OPTICS LAB -ECEN 5606 Basic Skills Lab Dr. Steve Cundiff and Edward McKenna, 1/15/04 rev KW 1/15/06, 1/8/10 The goal of this lab is to provide you with practice of some of the basic skills needed
Use of Computer Generated Holograms for Testing Aspheric Optics
 Use of Computer Generated Holograms for Testing Aspheric Optics James H. Burge and James C. Wyant Optical Sciences Center, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 http://www.optics.arizona.edu/jcwyant,
Use of Computer Generated Holograms for Testing Aspheric Optics James H. Burge and James C. Wyant Optical Sciences Center, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 http://www.optics.arizona.edu/jcwyant,
OPTICAL FIBER-BASED SENSING OF STRAIN AND TEMPERATURE
 OPTICAL FIBER-BASED SENSING OF STRAIN AND TEMPERATURE AT HIGH TEMPERATURE K. A. Murphy, C. Koob, M. Miller, S. Feth, and R. O. Claus Fiber & Electro-Optics Research Center Electrical Engineering Department
OPTICAL FIBER-BASED SENSING OF STRAIN AND TEMPERATURE AT HIGH TEMPERATURE K. A. Murphy, C. Koob, M. Miller, S. Feth, and R. O. Claus Fiber & Electro-Optics Research Center Electrical Engineering Department
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Design of a digital holographic interferometer for the. ZaP Flow Z-Pinch
 Design of a digital holographic interferometer for the M. P. Ross, U. Shumlak, R. P. Golingo, B. A. Nelson, S. D. Knecht, M. C. Hughes, R. J. Oberto University of Washington, Seattle, USA Abstract The
Design of a digital holographic interferometer for the M. P. Ross, U. Shumlak, R. P. Golingo, B. A. Nelson, S. D. Knecht, M. C. Hughes, R. J. Oberto University of Washington, Seattle, USA Abstract The
Fiber Optic Communications
 Fiber Optic Communications ( Chapter 2: Optics Review ) presented by Prof. Kwang-Chun Ho 1 Section 2.4: Numerical Aperture Consider an optical receiver: where the diameter of photodetector surface area
Fiber Optic Communications ( Chapter 2: Optics Review ) presented by Prof. Kwang-Chun Ho 1 Section 2.4: Numerical Aperture Consider an optical receiver: where the diameter of photodetector surface area
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit
 Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit Purpose 1. To understand the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction of light at a single slit and at a circular aperture; 2. To learn how to measure
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit Purpose 1. To understand the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction of light at a single slit and at a circular aperture; 2. To learn how to measure
The electric field for the wave sketched in Fig. 3-1 can be written as
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Light consists of an electric field and a magnetic field that oscillate at very high rates, of the order of 10 14 Hz. These fields travel in wavelike fashion at very high speeds.
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Light consists of an electric field and a magnetic field that oscillate at very high rates, of the order of 10 14 Hz. These fields travel in wavelike fashion at very high speeds.
Non-intrusive refractometer sensor
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 74, No. 4 journal of April 2010 physics pp. 661 668 Non-intrusive refractometer sensor PABITRA NATH 1,2 1 Department of Electronics Science, Gauhati University,
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 74, No. 4 journal of April 2010 physics pp. 661 668 Non-intrusive refractometer sensor PABITRA NATH 1,2 1 Department of Electronics Science, Gauhati University,
Experiment 19. Microwave Optics 1
 Experiment 19 Microwave Optics 1 1. Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Using a three centimeter microwave wavelength transforms the scale of the experiment. Microns
Experiment 19 Microwave Optics 1 1. Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Using a three centimeter microwave wavelength transforms the scale of the experiment. Microns
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
High-Power, Passively Q-switched Microlaser - Power Amplifier System
 High-Power, Passively Q-switched Microlaser - Power Amplifier System Yelena Isyanova Q-Peak, Inc.,135 South Road, Bedford, MA 01730 isyanova@qpeak.com Jeff G. Manni JGM Associates, 6 New England Executive
High-Power, Passively Q-switched Microlaser - Power Amplifier System Yelena Isyanova Q-Peak, Inc.,135 South Road, Bedford, MA 01730 isyanova@qpeak.com Jeff G. Manni JGM Associates, 6 New England Executive
Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating. Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel
 Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel Zhijun Yan *, Pouneh Saffari, Kaiming Zhou, Adedotun Adebay, Lin Zhang Photonic Research Group, Aston
Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel Zhijun Yan *, Pouneh Saffari, Kaiming Zhou, Adedotun Adebay, Lin Zhang Photonic Research Group, Aston
1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter
 8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA
 Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA Abstract: Speckle interferometry (SI) has become a complete technique over the past couple of years and is widely used in many branches of
Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA Abstract: Speckle interferometry (SI) has become a complete technique over the past couple of years and is widely used in many branches of
The Beam Characteristics of High Power Diode Laser Stack
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Beam Characteristics of High Power Diode Laser Stack To cite this article: Yuanyuan Gu et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Beam Characteristics of High Power Diode Laser Stack To cite this article: Yuanyuan Gu et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
Adaptive Optics for LIGO
 Adaptive Optics for LIGO Justin Mansell Ginzton Laboratory LIGO-G990022-39-M Motivation Wavefront Sensor Outline Characterization Enhancements Modeling Projections Adaptive Optics Results Effects of Thermal
Adaptive Optics for LIGO Justin Mansell Ginzton Laboratory LIGO-G990022-39-M Motivation Wavefront Sensor Outline Characterization Enhancements Modeling Projections Adaptive Optics Results Effects of Thermal
Fibre Optic Sensors: basic principles and most common applications
 SMR 1829-21 Winter College on Fibre Optics, Fibre Lasers and Sensors 12-23 February 2007 Fibre Optic Sensors: basic principles and most common applications (PART 2) Hypolito José Kalinowski Federal University
SMR 1829-21 Winter College on Fibre Optics, Fibre Lasers and Sensors 12-23 February 2007 Fibre Optic Sensors: basic principles and most common applications (PART 2) Hypolito José Kalinowski Federal University
The Lightwave Model 142 CW Visible Ring Laser, Beam Splitter, Model ATM- 80A1 Acousto-Optic Modulator, and Fiber Optic Cable Coupler Optics Project
 The Lightwave Model 142 CW Visible Ring Laser, Beam Splitter, Model ATM- 80A1 Acousto-Optic Modulator, and Fiber Optic Cable Coupler Optics Project Stephen W. Jordan Seth Merritt Optics Project PH 464
The Lightwave Model 142 CW Visible Ring Laser, Beam Splitter, Model ATM- 80A1 Acousto-Optic Modulator, and Fiber Optic Cable Coupler Optics Project Stephen W. Jordan Seth Merritt Optics Project PH 464
Industrial Instrumentation Prof. A. Barua Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Industrial Instrumentation Prof. A. Barua Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 29 Optoelectronic Sensor-II (Refer Slide Time: 00:36) Welcome to lesson
Industrial Instrumentation Prof. A. Barua Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 29 Optoelectronic Sensor-II (Refer Slide Time: 00:36) Welcome to lesson
Lab 12 Microwave Optics.
 b Lab 12 Microwave Optics. CAUTION: The output power of the microwave transmitter is well below standard safety levels. Nevertheless, do not look directly into the microwave horn at close range when the
b Lab 12 Microwave Optics. CAUTION: The output power of the microwave transmitter is well below standard safety levels. Nevertheless, do not look directly into the microwave horn at close range when the
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
Chapter 18 Optical Elements
 Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
OPSENS WHITE-LIGHT POLARIZATION INTERFEROMETRY TECHNOLOGY
 OPSENS WHITE-LIGHT POLARIZATION INTERFEROMETRY TECHNOLOGY 1. Introduction Fiber optic sensors are made up of two main parts: the fiber optic transducer (also called the fiber optic gauge or the fiber optic
OPSENS WHITE-LIGHT POLARIZATION INTERFEROMETRY TECHNOLOGY 1. Introduction Fiber optic sensors are made up of two main parts: the fiber optic transducer (also called the fiber optic gauge or the fiber optic
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Princeton University Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University ABSTRACT
 Phase and Amplitude Control Ability using Spatial Light Modulators and Zero Path Length Difference Michelson Interferometer Michael G. Littman, Michael Carr, Jim Leighton, Ezekiel Burke, David Spergel
Phase and Amplitude Control Ability using Spatial Light Modulators and Zero Path Length Difference Michelson Interferometer Michael G. Littman, Michael Carr, Jim Leighton, Ezekiel Burke, David Spergel
6.014 Lecture 6: Multipath, Arrays, and Frequency Reuse
 6.014 Lecture 6: Multipath, Arrays, and Frequency Reuse A. Superposition of phasors This lecture focuses on the superposition of duplicate waves at receivers, where the multiplicity of waves may have originated
6.014 Lecture 6: Multipath, Arrays, and Frequency Reuse A. Superposition of phasors This lecture focuses on the superposition of duplicate waves at receivers, where the multiplicity of waves may have originated
Analytical analysis of modulated signal in apertureless scanning near-field optical microscopy C. H. Chuang and Y. L. Lo *
 Research Express@NCKU Volume 5 Issue 10 - October 3, 2008 [ http://research.ncku.edu.tw/re/articles/e/20081003/2.html ] Analytical analysis of modulated signal in apertureless scanning near-field optical
Research Express@NCKU Volume 5 Issue 10 - October 3, 2008 [ http://research.ncku.edu.tw/re/articles/e/20081003/2.html ] Analytical analysis of modulated signal in apertureless scanning near-field optical
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017
 R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
PHYS2090 OPTICAL PHYSICS Laboratory Microwaves
 PHYS2090 OPTICAL PHYSICS Laboratory Microwaves Reference Hecht, Optics, (Addison-Wesley) 1. Introduction Interference and diffraction are commonly observed in the optical regime. As wave-particle duality
PHYS2090 OPTICAL PHYSICS Laboratory Microwaves Reference Hecht, Optics, (Addison-Wesley) 1. Introduction Interference and diffraction are commonly observed in the optical regime. As wave-particle duality
Applying of refractive beam shapers of circular symmetry to generate non-circular shapes of homogenized laser beams
 - 1 - Applying of refractive beam shapers of circular symmetry to generate non-circular shapes of homogenized laser beams Alexander Laskin a, Vadim Laskin b a MolTech GmbH, Rudower Chaussee 29-31, 12489
- 1 - Applying of refractive beam shapers of circular symmetry to generate non-circular shapes of homogenized laser beams Alexander Laskin a, Vadim Laskin b a MolTech GmbH, Rudower Chaussee 29-31, 12489
Multi-frequency and multiple phase-shift sinusoidal fringe projection for 3D profilometry
 Multi-frequency and multiple phase-shift sinusoidal fringe projection for 3D profilometry E. B. Li College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Tianjin Universit Tianjin 30007, P. R.
Multi-frequency and multiple phase-shift sinusoidal fringe projection for 3D profilometry E. B. Li College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Tianjin Universit Tianjin 30007, P. R.
Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes
 Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes Martin Booth Department of Engineering Science And Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour University of Oxford Outline Rays, wave fronts and
Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes Martin Booth Department of Engineering Science And Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour University of Oxford Outline Rays, wave fronts and
Jones matrix analysis of high-precision displacement measuring interferometers
 Jones matrix analysis of high-precision displacement measuring interferometers Peter de Groot, Laurel Brook Road, Middlefield, CT USA 06455 e-mail: peterd@zygo.com Abstract I analyze error sources in high-performance
Jones matrix analysis of high-precision displacement measuring interferometers Peter de Groot, Laurel Brook Road, Middlefield, CT USA 06455 e-mail: peterd@zygo.com Abstract I analyze error sources in high-performance
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry
 Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro Fourteenth NRAO Synthesis Imaging Summer School Socorro, NM Topics Why Interferometry? The Single Dish as an interferometer The Basic Interferometer
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro Fourteenth NRAO Synthesis Imaging Summer School Socorro, NM Topics Why Interferometry? The Single Dish as an interferometer The Basic Interferometer
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS
 UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
9. Microwaves. 9.1 Introduction. Safety consideration
 MW 9. Microwaves 9.1 Introduction Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths of the order of 1 mm to 1 m, or equivalently, with frequencies from 0.3 GHz to 0.3 THz, are commonly known as microwaves, sometimes
MW 9. Microwaves 9.1 Introduction Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths of the order of 1 mm to 1 m, or equivalently, with frequencies from 0.3 GHz to 0.3 THz, are commonly known as microwaves, sometimes
Mirrors and Lenses. Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses.
 Mirrors and Lenses Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses. Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object
Mirrors and Lenses Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses. Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object
Lecture 5: Polarisation of light 2
 Lecture 5: Polarisation of light 2 Lecture aims to explain: 1. Circularly and elliptically polarised light 2. Optical retarders - Birefringence - Quarter-wave plate, half-wave plate Circularly and elliptically
Lecture 5: Polarisation of light 2 Lecture aims to explain: 1. Circularly and elliptically polarised light 2. Optical retarders - Birefringence - Quarter-wave plate, half-wave plate Circularly and elliptically
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber. Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab
 Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
HIGH PRECISION OPERATION OF FIBER BRAGG GRATING SENSOR WITH INTENSITY-MODULATED LIGHT SOURCE
 HIGH PRECISION OPERATION OF FIBER BRAGG GRATING SENSOR WITH INTENSITY-MODULATED LIGHT SOURCE Nobuaki Takahashi, Hiroki Yokosuka, Kiyoyuki Inamoto and Satoshi Tanaka Department of Communications Engineering,
HIGH PRECISION OPERATION OF FIBER BRAGG GRATING SENSOR WITH INTENSITY-MODULATED LIGHT SOURCE Nobuaki Takahashi, Hiroki Yokosuka, Kiyoyuki Inamoto and Satoshi Tanaka Department of Communications Engineering,
Fiber Optic Communication Link Design
 Fiber Optic Communication Link Design By Michael J. Fujita, S.K. Ramesh, PhD, Russell L. Tatro Abstract The fundamental building blocks of an optical fiber transmission link are the optical source, the
Fiber Optic Communication Link Design By Michael J. Fujita, S.K. Ramesh, PhD, Russell L. Tatro Abstract The fundamental building blocks of an optical fiber transmission link are the optical source, the
3.0 Alignment Equipment and Diagnostic Tools:
 3.0 Alignment Equipment and Diagnostic Tools: Alignment equipment The alignment telescope and its use The laser autostigmatic cube (LACI) interferometer A pin -- and how to find the center of curvature
3.0 Alignment Equipment and Diagnostic Tools: Alignment equipment The alignment telescope and its use The laser autostigmatic cube (LACI) interferometer A pin -- and how to find the center of curvature
High Placement Effect of Fibre Bragg Grating Sensor
 High Placement Effect of Fibre Bragg Grating Sensor Suzairi Daud a,b*, Muhammad Safwan Abd Aziz a,b, Ahmad Fakhrurrazi Ahmad Noorden a and Jalil Ali a,b a Laser Center, Ibnu Sina Institute for Scientific
High Placement Effect of Fibre Bragg Grating Sensor Suzairi Daud a,b*, Muhammad Safwan Abd Aziz a,b, Ahmad Fakhrurrazi Ahmad Noorden a and Jalil Ali a,b a Laser Center, Ibnu Sina Institute for Scientific
APPLICATION NOTE POLARIZATION MEASUREMENTS
 OZ OPTICS LTD. APPLICATION NOTE POLARIZATION MEASUREMENTS OZ OPTICS FAMILY OF POLARIZATION MAINTAINING COMPONENTS, SOURCES, AND MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS The information/data furnished in this document shall
OZ OPTICS LTD. APPLICATION NOTE POLARIZATION MEASUREMENTS OZ OPTICS FAMILY OF POLARIZATION MAINTAINING COMPONENTS, SOURCES, AND MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS The information/data furnished in this document shall
Figure1. To construct a light pulse, the electric component of the plane wave should be multiplied with a bell shaped function.
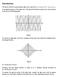 Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad.
 R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER III PAPER III OPTICS UNIT I: 1. MATRIX METHODS IN PARAXIAL OPTICS 2. ABERATIONS UNIT II
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER III PAPER III OPTICS UNIT I: 1. MATRIX METHODS IN PARAXIAL OPTICS 2. ABERATIONS UNIT II
