Estimation of the Earth s Impulse Response: Deconvolution and Beyond. Gary Pavlis Indiana University Rick Aster New Mexico Tech
|
|
|
- Sherilyn Tucker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Estimation of the Earth s Impulse Response: Deconvolution and Beyond Gary Pavlis Indiana University Rick Aster New Mexico Tech Presentation for Imaging Science Workshop Washington University, November 1, 2006
2 Outline Guiding principle: This talk is mainly for students, post-docs, and those new to this area. For the experts it is mostly review. Fundamentals Impulse response concept Geometry Scattering assumptions Conventional deconvolution Single station methods [Tutorial 1] Frequency domain methods Time domain methods Multichannel methods Receiver array methods [Tutorial 2: f-k filtering] Common receiver gather methods [Tutorial 3: pseudostation stacking] Discussion of some fundamental assumptions Beyond receiver functions Baig and Bostock s blind deconvolution conjecture Weglein,, Fan et al. s inverse scattering series [Tutorial 4] Model-based approach Next steps
3 What is an impulse response? M=6.5, intermediate depth event from Fiji (2006) recorded on M=8 event Tonga, 2006, recorded on USArray USArray. Here the recorded data are a fair approximation to the impulse response. P Pmp pp
4 Why is the impulse response fundamental to wavefield imaging? Imaging Manipulates full seismogram to construct image If not impulse, image distorted by source wavelet Most imaging assumes primaries only? How does this differ from seismic tomography? Classic inversion methods Extract parameters as data (e.g. arrival times) Invert for model using parametric data Regularization always leads to smoothed models while imaging methods focus on discontinuities From Forel et al (2005)
5 Teleseismic Imaging Geometry Fan et al, 2006
6 Receiver function concept Focuses on P to S conversions Rotation to L,R,T Standard deconvolution method discards P Demonstrated success in many papers Impedance Contrast
7 Conventional Theory for Impulse Response and Receiver Functions
8 P-SV-SH SH wavefield separation
9 Forms of matrix F Single rotation to R,T,Z Double rotation to R,T,L Free Surface Transformation operator (Kennett, 1991) NOT an orthogonal transformation A key point commonly misunderstood: this is NEVER a complete wavefield separation. Even in a 1d earth with homogenous layers separation is incomplete except at normal incidence.
10 The Receiver Function (subject of Tutorial 1)
11 Frequency-domain RF Estimate Issues Divide by zero or nearly so Small values magnify noise (????) Methods Water level Other regularizations Multitaper algorithm (robust spectral estimator)
12 Time Domain Methods Cast problem as linear equations d=si Some have preferred this approach to frequency domain methods because: Full machinery of linear inverse theory available More flexibility in regularization (e.g. Tikhonov regularization) Very high computational cost compared to frequency domain methods For this workshop provide useful insight and familiar framework for some
13 Convolution Fundamentals s i d
14 Convolution as a Matrix Operation S i d
15 Time Domain Decon and Inversion
16 Time or Frequency Domain? Frequency domain method MUCH faster to compute (NlogN( versus N 3 algorithm) Multitaper method (Park and Levin, 2000) is probably the best FD method Time domain approach likely has more unexplored options
17 Some Fundamental Receiver Function Assumptions Incident wavefield is a pure P wave Requires very weak scattering in lower mantle to be true; otherwise incident wavefield would not be pure P waves. S wave receiver functions require a comparable assumption Single phase incident as a plane wave Reason for focus on degree distance What happens between degrees? What happens beyond 90? Limits time window for some intermediate depth events Limits time window in 90+ range where PcP-P P small Scattering in imaging volume is weak More on this one later.
18 Inversion strategy for receiver function interpretation Approach of earliest paper using this technique Approach Nonlinear inversion Compute synthetics and synthetic receiver function Minimize misfit between data and synthetic receiver functions Variable minimization strategies (standard inversion issues) Key point: uses RF as data, NOT the impulse response Actual and Predicted rf Velocity models Ammon et al. (1990)
19 Receiver Functions and Direct Imaging Harder problem than inversion approach because Multiples are a BIG problem that is not an issue for inversion approach A receiver function is NOT the radial impulse response treating it as such is at best an approximation Conventional rf decon discards P wavefield data.
20 P wave and Conventional RF Estimates force P component to delta at zero lag This example shows the RF is NOT the radial impulse response Imaging methods will treat residual as noise Deconvolution
21 Multichannel Methods Why multichannel? Emergence of broadband array data (e.g. IRIS PASSCAL) in the past 15 years Aim to exploit data redundancy Learn from experience of reflection seismology Some versions provide estimates of P impulse response Types: Common receiver gathers Common event gathers
22 Common receiver gather methods Most common approach: average moveout corrected RF estimates for each station Simultaneous time-domain deconvolution (Gurrola et al, 1995) Wilson and Aster (2005) f-k filtering (Subject of tutorial 2)
23 Receiver Function Imaging: Receiver functions are obtained for all earthquakes recorded at all stations. Sets of receiver functions arriving from various angles of incidence are jointly filtered to remove noise using array (FK) processing techniques. Wilson and Aster, 2005
24 Common Event Gather Methods Li and Nabalek (1999) method Principal component method (Bostock and Rondenay,, 1999) Pseudostation stacking method (Neal and Pavlis,, 1999,2000)
25 Common Event Gather Methods Common to all Align to actual P arrival time (how?) Use the stack for deconvolution (stack?) Differences What defines the array? Stacking algorithm Simple mean Principal component Robust stack Full Array Methods Pseudostation Stack Method (Subject of Tutorial 3)
26 Common Event Gather Methods Common to all Align to actual P arrival time Use the stack for deconvolution Differences What defines the array? Stacking algorithm Simple mean Principal component Robust stack Nth root Coherence method
27 Beyond Receiver Functions Issues with receiver functions Complicated by P multiples Experience is the approach simply doesn t always work All except array methods make estimating P reflection response impossible Multiples/other modes can obscure structure and/or complicate interpretation (but can also be exploited). General approaches Statistical approaches Inverse scattering series Model-based correction
28 Statistical Method Baig and Bostock (2005), Mercier et al. (2006) Blind convolution conjecture Assume wavelet is smooth Assume impulse response functions to be estimated are minimum phase A common receiver gather method (some common ground with Gurrola et al, 1995)
29 Example: Mercier et al (2006) SV P
30 Inverse Scattering Series Approach Does not require earth model to be estimated at all Uses free-surface transformation operator to get backscattered P response Remove multiple with inverse scattering series Requires an accurate wavelet estimate
31 Example: Fan et al (2006) Synthetic Data Transmission response Reflection Response Basic idea: free surface bounce removal maps to reflection primary
32 Model-based Approach: Convolutional Model Theory KEY CONCEPT: the source wavelet is unknown AND a fundamental part of the problem data = source * impulse_response The source wavelet has a nonlinear relationship to the real Earth s velocity and density structure through the unknown impulse response function
33 How would we do this if we knew Data=d=s*i k (i=1,2,3) s est =i -1 k *d (i=1,2,3) Use s est to estimate impulse response BIG PROBLEM IN REAL WORLD: Don t know i k which has to be computed from Earth structure the answer?
34 Inversion issues for discussion KEY POINT: The source wavelet is an unknown we need to estimate as a fundamental part of the problem Optimization conditions(?) Single station: minimize difference between individual component wavelet estimates Arrays: minimize difference between wavelet estimates from ALL components of ALL stations foreach event gather OR difference over a finite aperture Earth model parameterization? Station by station 1d models Fixed number of layers of variable thickness (1D synthetics foreach station) Fully 3D models Construction strategy? Linearize? Directed search (e.g. genetic algorithms)? Inverse scattering series?
35 Model-based approach: Theory for General Elastic Media Using the elastic wave representation theorem it can be shown (Pavlis, in preparation) Propagator Plane wave source
36 Plane wave source Wavefront Propagating Line Source
37 Forward Modeling and Imaging 3D modeling problem requires plane wave synthetics Needed badly to explore limits of current impulse generation capabilities Needed badly to explore limits of current imaging methods
38 Summary of Key Points Receiver function estimation is a form of deconvolution Receiver functions are never the impulse response of the medium Not a problem for 1D model inversion because RFs are data for inversion Treating RFs as the impulse response will cause artifacts in all wavefield imaging AND limit resolution Approaches to do better Multichannel methods Common receiver methods Common event methods Statistical methods Multiple removal Solving for the source wavelet as part of the problem Denser data Assertion: doing this right is one of the biggest barrier to progress with most data
39 Discussion points on forward modeling: What do we need to test imaging algorithms? What do we need to improve impulse response estimates? Can global synthetics provide a workable source wavelet? Requires implementation of a plane-wave source condition Feasible? How should it be done (sum G sources or produce family of plane waves?) Implementing a community model?
40 Other Discussion Points Questions for previous speakers? What are the key unsolved theoretical problems that limit what we can do in wavefield imaging? What are the main practical bottlenecks to progress for you?
Broadband Signal Enhancement of Seismic Array Data: Application to Long-period Surface Waves and High-frequency Wavefields
 Broadband Signal Enhancement of Seismic Array Data: Application to Long-period Surface Waves and High-frequency Wavefields Frank Vernon and Robert Mellors IGPP, UCSD La Jolla, California David Thomson
Broadband Signal Enhancement of Seismic Array Data: Application to Long-period Surface Waves and High-frequency Wavefields Frank Vernon and Robert Mellors IGPP, UCSD La Jolla, California David Thomson
Coda Waveform Correlations
 Chapter 5 Coda Waveform Correlations 5.1 Cross-Correlation of Seismic Coda 5.1.1 Introduction In the previous section, the generation of the surface wave component of the Green s function by the correlation
Chapter 5 Coda Waveform Correlations 5.1 Cross-Correlation of Seismic Coda 5.1.1 Introduction In the previous section, the generation of the surface wave component of the Green s function by the correlation
Global Broadband Arrays a View from NORSAR
 Global Broadband Arrays a View from NORSAR Johannes Schweitzer and NORSAR s Array Seismology Group Workshop on Arrays in Global Seismology May 15 16, 2013 Raleigh, North Carolina NORSAR Array Until 1976
Global Broadband Arrays a View from NORSAR Johannes Schweitzer and NORSAR s Array Seismology Group Workshop on Arrays in Global Seismology May 15 16, 2013 Raleigh, North Carolina NORSAR Array Until 1976
Digital Imaging and Deconvolution: The ABCs of Seismic Exploration and Processing
 Digital Imaging and Deconvolution: The ABCs of Seismic Exploration and Processing Enders A. Robinson and Sven Treitcl Geophysical References Series No. 15 David V. Fitterman, managing editor Laurence R.
Digital Imaging and Deconvolution: The ABCs of Seismic Exploration and Processing Enders A. Robinson and Sven Treitcl Geophysical References Series No. 15 David V. Fitterman, managing editor Laurence R.
28th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 SEISMIC SOURCE LOCATIONS AND PARAMETERS FOR SPARSE NETWORKS BY MATCHING OBSERVED SEISMOGRAMS TO SEMI-EMPIRICAL SYNTHETIC SEISMOGRAMS: IMPROVEMENTS TO THE PHASE SPECTRUM PARAMETERIZATION David. Salzberg
SEISMIC SOURCE LOCATIONS AND PARAMETERS FOR SPARSE NETWORKS BY MATCHING OBSERVED SEISMOGRAMS TO SEMI-EMPIRICAL SYNTHETIC SEISMOGRAMS: IMPROVEMENTS TO THE PHASE SPECTRUM PARAMETERIZATION David. Salzberg
PR No. 119 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING XVIII. Academic Research Staff. Prof. Alan V. Oppenheim Prof. James H. McClellan.
 XVIII. DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Academic Research Staff Prof. Alan V. Oppenheim Prof. James H. McClellan Graduate Students Bir Bhanu Gary E. Kopec Thomas F. Quatieri, Jr. Patrick W. Bosshart Jae S. Lim
XVIII. DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Academic Research Staff Prof. Alan V. Oppenheim Prof. James H. McClellan Graduate Students Bir Bhanu Gary E. Kopec Thomas F. Quatieri, Jr. Patrick W. Bosshart Jae S. Lim
SPNA 2.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2177
 SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
Th ELI1 08 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data
 Th ELI1 8 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data P. Edme* (Schlumberger Gould Research), E. Muyzert (Sclumberger Gould Research) & E. Kragh (Schlumberger Gould Research) SUMMARY
Th ELI1 8 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data P. Edme* (Schlumberger Gould Research), E. Muyzert (Sclumberger Gould Research) & E. Kragh (Schlumberger Gould Research) SUMMARY
Module 2 WAVE PROPAGATION (Lectures 7 to 9)
 Module 2 WAVE PROPAGATION (Lectures 7 to 9) Lecture 9 Topics 2.4 WAVES IN A LAYERED BODY 2.4.1 One-dimensional case: material boundary in an infinite rod 2.4.2 Three dimensional case: inclined waves 2.5
Module 2 WAVE PROPAGATION (Lectures 7 to 9) Lecture 9 Topics 2.4 WAVES IN A LAYERED BODY 2.4.1 One-dimensional case: material boundary in an infinite rod 2.4.2 Three dimensional case: inclined waves 2.5
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 5c: Array Signal Processing and Parametric Estimation Techniques
 Antennas and Propagation : Array Signal Processing and Parametric Estimation Techniques Introduction Time-domain Signal Processing Fourier spectral analysis Identify important frequency-content of signal
Antennas and Propagation : Array Signal Processing and Parametric Estimation Techniques Introduction Time-domain Signal Processing Fourier spectral analysis Identify important frequency-content of signal
Analyzing Velocity Structure and Scattering in Homestake Area
 Analyzing Velocity Structure and Scattering in Homestake Area Zhi Li 1, Gabriel Gribler 2, Lee M. Liberty 2, Daniel C. Bowden 3, Victor C. Tsai 3 1 School of Earth and Space Sciences, University of Science
Analyzing Velocity Structure and Scattering in Homestake Area Zhi Li 1, Gabriel Gribler 2, Lee M. Liberty 2, Daniel C. Bowden 3, Victor C. Tsai 3 1 School of Earth and Space Sciences, University of Science
Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion
 P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
CDP noise attenuation using local linear models
 CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010.
 This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010. The information herein remains the property of Mustagh
This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010. The information herein remains the property of Mustagh
Low wavenumber reflectors
 Low wavenumber reflectors Low wavenumber reflectors John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT A numerical modelling environment was created to accurately evaluate reflections from a D interface that has a smooth transition
Low wavenumber reflectors Low wavenumber reflectors John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT A numerical modelling environment was created to accurately evaluate reflections from a D interface that has a smooth transition
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas
 Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data
 Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
AVO compliant spectral balancing
 Summary AVO compliant spectral balancing Nirupama Nagarajappa CGGVeritas, Calgary, Canada pam.nagarajappa@cggveritas.com Spectral balancing is often performed after surface consistent deconvolution to
Summary AVO compliant spectral balancing Nirupama Nagarajappa CGGVeritas, Calgary, Canada pam.nagarajappa@cggveritas.com Spectral balancing is often performed after surface consistent deconvolution to
A COMPARISON OF SITE-AMPLIFICATION ESTIMATED FROM DIFFERENT METHODS USING A STRONG MOTION OBSERVATION ARRAY IN TANGSHAN, CHINA
 A COMPARISON OF SITE-AMPLIFICATION ESTIMATED FROM DIFFERENT METHODS USING A STRONG MOTION OBSERVATION ARRAY IN TANGSHAN, CHINA Wenbo ZHANG 1 And Koji MATSUNAMI 2 SUMMARY A seismic observation array for
A COMPARISON OF SITE-AMPLIFICATION ESTIMATED FROM DIFFERENT METHODS USING A STRONG MOTION OBSERVATION ARRAY IN TANGSHAN, CHINA Wenbo ZHANG 1 And Koji MATSUNAMI 2 SUMMARY A seismic observation array for
P and S wave separation at a liquid-solid interface
 and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface Maria. Donati and Robert R. tewart ABTRACT and seismic waves impinging on a liquid-solid interface give rise
and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface Maria. Donati and Robert R. tewart ABTRACT and seismic waves impinging on a liquid-solid interface give rise
AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan
 AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan Zimin Zhang, Robert R. Stewart, and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT The AVO processing and analysis of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake
AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan Zimin Zhang, Robert R. Stewart, and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT The AVO processing and analysis of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake
EXPLOITING AMBIENT NOISE FOR SOURCE CHARACTERIZATION OF REGIONAL SEISMIC EVENTS
 EXPLOITING AMBIENT NOISE FOR SOURCE CHARACTERIZATION OF REGIONAL SEISMIC EVENTS ABSTRACT Michael H. Ritzwoller, Anatoli L. Levshin, and Mikhail P. Barmin University of Colorado at Boulder Sponsored by
EXPLOITING AMBIENT NOISE FOR SOURCE CHARACTERIZATION OF REGIONAL SEISMIC EVENTS ABSTRACT Michael H. Ritzwoller, Anatoli L. Levshin, and Mikhail P. Barmin University of Colorado at Boulder Sponsored by
Frequency extrapolation to enhance the deconvolution of transmitted seismic waves
 IOP PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS AND ENGINEERING J. Geophys. Eng. 5 (2008) 118 127 doi:10.1088/1742-2132/5/1/012 Frequency extrapolation to enhance the deconvolution of transmitted seismic waves Saptarshi
IOP PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS AND ENGINEERING J. Geophys. Eng. 5 (2008) 118 127 doi:10.1088/1742-2132/5/1/012 Frequency extrapolation to enhance the deconvolution of transmitted seismic waves Saptarshi
2012 SEG SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
Summary. Theory. Introduction
 round motion through geophones and MEMS accelerometers: sensor comparison in theory modeling and field data Michael Hons* Robert Stewart Don Lawton and Malcolm Bertram CREWES ProjectUniversity of Calgary
round motion through geophones and MEMS accelerometers: sensor comparison in theory modeling and field data Michael Hons* Robert Stewart Don Lawton and Malcolm Bertram CREWES ProjectUniversity of Calgary
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data
 Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain
 Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG)
 Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
=, (1) Summary. Theory. Introduction
 Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Seismic Reflection Method
 1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
WS15-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise
 WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results
 Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data
 Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Stan J. Gorek, Robert R. Stewart, and Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT During early July, 1995, a large
Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Stan J. Gorek, Robert R. Stewart, and Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT During early July, 1995, a large
Mel Spectrum Analysis of Speech Recognition using Single Microphone
 International Journal of Engineering Research in Electronics and Communication Mel Spectrum Analysis of Speech Recognition using Single Microphone [1] Lakshmi S.A, [2] Cholavendan M [1] PG Scholar, Sree
International Journal of Engineering Research in Electronics and Communication Mel Spectrum Analysis of Speech Recognition using Single Microphone [1] Lakshmi S.A, [2] Cholavendan M [1] PG Scholar, Sree
Geophysical Journal International. Empirically determined finite frequency sensitivity kernels for surface waves
 Empirically determined finite frequency sensitivity kernels for surface waves Journal: Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Research Paper Date Submitted by the Author: Complete List of Authors: Lin,
Empirically determined finite frequency sensitivity kernels for surface waves Journal: Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Research Paper Date Submitted by the Author: Complete List of Authors: Lin,
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION MOTIVATION
 Isabella Masoni, Total E&P, R. Brossier, University Grenoble Alpes, J. L. Boelle, Total E&P, J. Virieux, University Grenoble Alpes SUMMARY In this study, an innovative layer stripping approach for FWI
Isabella Masoni, Total E&P, R. Brossier, University Grenoble Alpes, J. L. Boelle, Total E&P, J. Virieux, University Grenoble Alpes SUMMARY In this study, an innovative layer stripping approach for FWI
Spectral Detection of Attenuation and Lithology
 Spectral Detection of Attenuation and Lithology M S Maklad* Signal Estimation Technology Inc., Calgary, AB, Canada msm@signalestimation.com and J K Dirstein Total Depth Pty Ltd, Perth, Western Australia,
Spectral Detection of Attenuation and Lithology M S Maklad* Signal Estimation Technology Inc., Calgary, AB, Canada msm@signalestimation.com and J K Dirstein Total Depth Pty Ltd, Perth, Western Australia,
SCATTERING POLARIMETRY PART 1. Dr. A. Bhattacharya (Slide courtesy Prof. E. Pottier and Prof. L. Ferro-Famil)
 SCATTERING POLARIMETRY PART 1 Dr. A. Bhattacharya (Slide courtesy Prof. E. Pottier and Prof. L. Ferro-Famil) 2 That s how it looks! Wave Polarisation An electromagnetic (EM) plane wave has time-varying
SCATTERING POLARIMETRY PART 1 Dr. A. Bhattacharya (Slide courtesy Prof. E. Pottier and Prof. L. Ferro-Famil) 2 That s how it looks! Wave Polarisation An electromagnetic (EM) plane wave has time-varying
Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update
 Q-estimation Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update Peng Cheng and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT In this article, three methods of Q estimation are compared: a complex spectral ratio method, the centroid
Q-estimation Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update Peng Cheng and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT In this article, three methods of Q estimation are compared: a complex spectral ratio method, the centroid
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation
 WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis
 Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Noise Attenuation in Seismic Data Iterative Wavelet Packets vs Traditional Methods Lionel J. Woog, Igor Popovic, Anthony Vassiliou, GeoEnergy, Inc.
 Noise Attenuation in Seismic Data Iterative Wavelet Packets vs Traditional Methods Lionel J. Woog, Igor Popovic, Anthony Vassiliou, GeoEnergy, Inc. Summary In this document we expose the ideas and technologies
Noise Attenuation in Seismic Data Iterative Wavelet Packets vs Traditional Methods Lionel J. Woog, Igor Popovic, Anthony Vassiliou, GeoEnergy, Inc. Summary In this document we expose the ideas and technologies
Tu SRS3 06 Wavelet Estimation for Broadband Seismic Data
 Tu SRS3 06 Wavelet Estimation for Broadband Seismic Data E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), J. Gunning (CSIRO), R. White (Birkbeck University of London) & P. Spaans (Woodside) SUMMARY The volumes of broadband
Tu SRS3 06 Wavelet Estimation for Broadband Seismic Data E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), J. Gunning (CSIRO), R. White (Birkbeck University of London) & P. Spaans (Woodside) SUMMARY The volumes of broadband
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. Anelastic attenuation in seismic data: modeling, measurement, and correction. Peng Cheng A THESIS
 Important Notice This copy may be used only for the purposes of research and private study, and any use of the copy for a purpose other than research or private study may require the authorization of the
Important Notice This copy may be used only for the purposes of research and private study, and any use of the copy for a purpose other than research or private study may require the authorization of the
Understanding Seismic Amplitudes
 Understanding Seismic Amplitudes The changing amplitude values that define the seismic trace are typically explained using the convolutional model. This model states that trace amplitudes have three controlling
Understanding Seismic Amplitudes The changing amplitude values that define the seismic trace are typically explained using the convolutional model. This model states that trace amplitudes have three controlling
Spectral analysis of seismic signals using Burg algorithm V. Ravi Teja 1, U. Rakesh 2, S. Koteswara Rao 3, V. Lakshmi Bharathi 4
 Volume 114 No. 1 217, 163-171 ISSN: 1311-88 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Spectral analysis of seismic signals using Burg algorithm V. avi Teja
Volume 114 No. 1 217, 163-171 ISSN: 1311-88 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Spectral analysis of seismic signals using Burg algorithm V. avi Teja
Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements
 Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements David C. Henley Radial traces revisited ABSTRACT Filtering seismic data in the radial trace (R-T) domain is an effective technique for
Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements David C. Henley Radial traces revisited ABSTRACT Filtering seismic data in the radial trace (R-T) domain is an effective technique for
2D field data applications
 Chapter 5 2D field data applications In chapter 4, using synthetic examples, I showed how the regularized joint datadomain and image-domain inversion methods developed in chapter 3 overcome different time-lapse
Chapter 5 2D field data applications In chapter 4, using synthetic examples, I showed how the regularized joint datadomain and image-domain inversion methods developed in chapter 3 overcome different time-lapse
Downloaded 09/04/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Enhanced subsurface response for marine CSEM surveying Frank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA
 rank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA Summary A new robust method for enhancing marine CSEM subsurface response is presented. The method is demonstrated to enhance resolution and depth penetration
rank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA Summary A new robust method for enhancing marine CSEM subsurface response is presented. The method is demonstrated to enhance resolution and depth penetration
REGIONAL WAVEFIELD ANALYSIS USING THREE-COMPONENT SEISMIC ARRAY DATA
 REGIONAL WAVEFIELD ANALYSIS USING THREE-COMPONENT SEISMIC ARRAY DATA Gregory S. Wagner & Thomas J. Owens Department of Geological Sciences University of South Carolina Columbia, SC 29208 AFOSR Contract
REGIONAL WAVEFIELD ANALYSIS USING THREE-COMPONENT SEISMIC ARRAY DATA Gregory S. Wagner & Thomas J. Owens Department of Geological Sciences University of South Carolina Columbia, SC 29208 AFOSR Contract
Retrieving Focal Mechanism of Earthquakes Using the CAP Method
 Retrieving Focal Mechanism of Earthquakes Using the CAP Method Hongfeng Yang April 11, 2013 1 Introduction Waveforms recorded at a seismic station, W (t), compose of three components: W (t) = S(t) G(t)
Retrieving Focal Mechanism of Earthquakes Using the CAP Method Hongfeng Yang April 11, 2013 1 Introduction Waveforms recorded at a seismic station, W (t), compose of three components: W (t) = S(t) G(t)
New Metrics Developed for a Complex Cepstrum Depth Program
 T3.5-05 Robert C. Kemerait Ileana M. Tibuleac Jose F. Pascual-Amadeo Michael Thursby Chandan Saikia Nuclear Treaty Monitoring, Geophysics Division New Metrics Developed for a Complex Cepstrum Depth Program
T3.5-05 Robert C. Kemerait Ileana M. Tibuleac Jose F. Pascual-Amadeo Michael Thursby Chandan Saikia Nuclear Treaty Monitoring, Geophysics Division New Metrics Developed for a Complex Cepstrum Depth Program
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency
 25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
27th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 ADVANCES IN MIXED SIGNAL PROCESSING FOR REGIONAL AND TELESEISMIC ARRAYS Robert H. Shumway Department of Statistics, University of California, Davis Sponsored by Air Force Research Laboratory Contract No.
ADVANCES IN MIXED SIGNAL PROCESSING FOR REGIONAL AND TELESEISMIC ARRAYS Robert H. Shumway Department of Statistics, University of California, Davis Sponsored by Air Force Research Laboratory Contract No.
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo
 Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
Digital Signal Processing
 Digital Signal Processing Fourth Edition John G. Proakis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University Boston, Massachusetts Dimitris G. Manolakis MIT Lincoln Laboratory Lexington,
Digital Signal Processing Fourth Edition John G. Proakis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University Boston, Massachusetts Dimitris G. Manolakis MIT Lincoln Laboratory Lexington,
Image Denoising Using Different Filters (A Comparison of Filters)
 International Journal of Emerging Trends in Science and Technology Image Denoising Using Different Filters (A Comparison of Filters) Authors Mr. Avinash Shrivastava 1, Pratibha Bisen 2, Monali Dubey 3,
International Journal of Emerging Trends in Science and Technology Image Denoising Using Different Filters (A Comparison of Filters) Authors Mr. Avinash Shrivastava 1, Pratibha Bisen 2, Monali Dubey 3,
Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring
 Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring Michael Thornton*, MicroSeismic Inc., Houston,Texas mthornton@microseismic.com Summary While related concepts, resolution and uncertainty
Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring Michael Thornton*, MicroSeismic Inc., Houston,Texas mthornton@microseismic.com Summary While related concepts, resolution and uncertainty
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 EM wave transport through a 150 bend. (a) Bend of our PEC-PMC waveguide. (b) Bend of the conventional PEC waveguide. Waves are incident from the lower left
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 EM wave transport through a 150 bend. (a) Bend of our PEC-PMC waveguide. (b) Bend of the conventional PEC waveguide. Waves are incident from the lower left
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 6b: Path Models Rayleigh, Rician Fading, MIMO
 Antennas and Propagation b: Path Models Rayleigh, Rician Fading, MIMO Introduction From last lecture How do we model H p? Discrete path model (physical, plane waves) Random matrix models (forget H p and
Antennas and Propagation b: Path Models Rayleigh, Rician Fading, MIMO Introduction From last lecture How do we model H p? Discrete path model (physical, plane waves) Random matrix models (forget H p and
SHF Communication Technologies AG
 SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 2277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 0 Fax ++49 30 / 753 0 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz Tutorial
SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 2277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 0 Fax ++49 30 / 753 0 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz Tutorial
A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical
 A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical Summary Here we present a method of robust seismic data deghosting for
A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical Summary Here we present a method of robust seismic data deghosting for
The fast marching method in Spherical coordinates: SEG/EAGE salt-dome model
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 97, July 8, 1998, pages 251 264 The fast marching method in Spherical coordinates: SEG/EAGE salt-dome model Tariq Alkhalifah 1 keywords: traveltimes, finite difference
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 97, July 8, 1998, pages 251 264 The fast marching method in Spherical coordinates: SEG/EAGE salt-dome model Tariq Alkhalifah 1 keywords: traveltimes, finite difference
Northing (km)
 Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
Shallow shear wave velocity structure in two sites of Khartoum, Sudan using methods of seismic dispersion and ambient noise.
 Norwegian National Seismic Network Technical Report No. 25 Shallow shear wave velocity structure in two sites of Khartoum, Sudan using methods of seismic dispersion and ambient noise. Prepared by Miguel
Norwegian National Seismic Network Technical Report No. 25 Shallow shear wave velocity structure in two sites of Khartoum, Sudan using methods of seismic dispersion and ambient noise. Prepared by Miguel
Some observations of data quality at global seismic stations
 Some observations of data quality at global seismic stations Meredith Nettles and Göran Ekström Global CMT Project Waveform Quality Center SITS, 2009/11/10 1. Data quality control using signals 1a. Sensor
Some observations of data quality at global seismic stations Meredith Nettles and Göran Ekström Global CMT Project Waveform Quality Center SITS, 2009/11/10 1. Data quality control using signals 1a. Sensor
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 103, April 27, 2000, pages
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 103, April 27, 2000, pages 205 231 204 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 103, April 27, 2000, pages 205 231 Ground roll and the Radial Trace Transform revisited
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 103, April 27, 2000, pages 205 231 204 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 103, April 27, 2000, pages 205 231 Ground roll and the Radial Trace Transform revisited
Attenuation compensation for georadar data by Gabor deconvolution
 Attenuation compensation for georadar data by Gabor deconvolution Robert J. Ferguson and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Attenuation compensation It has been shown through previous data examples that nonstationary
Attenuation compensation for georadar data by Gabor deconvolution Robert J. Ferguson and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Attenuation compensation It has been shown through previous data examples that nonstationary
Analysis of PS-to-PP amplitude ratios for seismic reflector characterisation: method and application
 Analysis of PS-to-PP amplitude ratios for seismic reflector characterisation: method and application N. Maercklin, A. Zollo RISSC, Italy Abstract: Elastic parameters derived from seismic reflection data
Analysis of PS-to-PP amplitude ratios for seismic reflector characterisation: method and application N. Maercklin, A. Zollo RISSC, Italy Abstract: Elastic parameters derived from seismic reflection data
TOWARD A RAYLEIGH WAVE ATTENUATION MODEL FOR EURASIA AND CALIBRATING A NEW M S FORMULA
 TOWARD A RAYLEIGH WAVE ATTENUATION MODEL FOR EURASIA AND CALIBRATING A NEW M S FORMULA Xiaoning (David) Yang 1, Anthony R. Lowry 2, Anatoli L. Levshin 2 and Michael H. Ritzwoller 2 1 Los Alamos National
TOWARD A RAYLEIGH WAVE ATTENUATION MODEL FOR EURASIA AND CALIBRATING A NEW M S FORMULA Xiaoning (David) Yang 1, Anthony R. Lowry 2, Anatoli L. Levshin 2 and Michael H. Ritzwoller 2 1 Los Alamos National
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion
 Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal
 Seismic processing for coherent noise suppression Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal Patricia E. Gavotti and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT Two different
Seismic processing for coherent noise suppression Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal Patricia E. Gavotti and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT Two different
Amplitude and Phase Distortions in MIMO and Diversity Systems
 Amplitude and Phase Distortions in MIMO and Diversity Systems Christiane Kuhnert, Gerd Saala, Christian Waldschmidt, Werner Wiesbeck Institut für Höchstfrequenztechnik und Elektronik (IHE) Universität
Amplitude and Phase Distortions in MIMO and Diversity Systems Christiane Kuhnert, Gerd Saala, Christian Waldschmidt, Werner Wiesbeck Institut für Höchstfrequenztechnik und Elektronik (IHE) Universität
High-Frequency Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization
 High-Frequency Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization Kevin D. Heaney Lockheed-Martin ORINCON Corporation, 4350 N. Fairfax Dr., Arlington VA 22203 Abstract. The Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization (RGC) algorithm
High-Frequency Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization Kevin D. Heaney Lockheed-Martin ORINCON Corporation, 4350 N. Fairfax Dr., Arlington VA 22203 Abstract. The Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization (RGC) algorithm
Multicomponent seismic polarization analysis
 Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Effect of Frequency and Migration Aperture on Seismic Diffraction Imaging
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of Frequency and Migration Aperture on Seismic Diffraction Imaging To cite this article: Y. Bashir et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of Frequency and Migration Aperture on Seismic Diffraction Imaging To cite this article: Y. Bashir et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
Corresponding Author William Menke,
 Waveform Fitting of Cross-Spectra to Determine Phase Velocity Using Aki s Formula William Menke and Ge Jin Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Corresponding Author William Menke, MENKE@LDEO.COLUMBIA.EDU,
Waveform Fitting of Cross-Spectra to Determine Phase Velocity Using Aki s Formula William Menke and Ge Jin Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Corresponding Author William Menke, MENKE@LDEO.COLUMBIA.EDU,
( ) ( ) (1) GeoConvention 2013: Integration 1
 Regular grids travel time calculation Fast marching with an adaptive stencils approach Zhengsheng Yao, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada zyao2@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, Randy Kolesar, WesternGeco,
Regular grids travel time calculation Fast marching with an adaptive stencils approach Zhengsheng Yao, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada zyao2@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, Randy Kolesar, WesternGeco,
IMAGE FORMATION. Light source properties. Sensor characteristics Surface. Surface reflectance properties. Optics
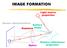 IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
Site Response from Incident Pnl Waves
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 1, pp. 357 362, February 2004 Site Response from Incident Pnl Waves by Brian Savage and Don V. Helmberger Abstract We developed a new method
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 1, pp. 357 362, February 2004 Site Response from Incident Pnl Waves by Brian Savage and Don V. Helmberger Abstract We developed a new method
Image Simulator for One Dimensional Synthetic Aperture Microwave Radiometer
 524 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 25, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 Image Simulator for One Dimensional Synthetic Aperture Microwave Radiometer Qiong Wu, Hao Liu, and Ji Wu Center for
524 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 25, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 Image Simulator for One Dimensional Synthetic Aperture Microwave Radiometer Qiong Wu, Hao Liu, and Ji Wu Center for
System analysis and signal processing
 System analysis and signal processing with emphasis on the use of MATLAB PHILIP DENBIGH University of Sussex ADDISON-WESLEY Harlow, England Reading, Massachusetts Menlow Park, California New York Don Mills,
System analysis and signal processing with emphasis on the use of MATLAB PHILIP DENBIGH University of Sussex ADDISON-WESLEY Harlow, England Reading, Massachusetts Menlow Park, California New York Don Mills,
On Determination of Focal Laws for Linear Phased Array Probes as to the Active and Passive Element Size
 19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 On Determination of Focal Laws for Linear Phased Array Probes as to the Active and Passive Element Size Andreas GOMMLICH 1, Frank SCHUBERT 2 1 Institute
19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 On Determination of Focal Laws for Linear Phased Array Probes as to the Active and Passive Element Size Andreas GOMMLICH 1, Frank SCHUBERT 2 1 Institute
Deconvolution , , Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 12
 Deconvolution http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 12 Course announcements Homework 3 is out. - Due October 12 th. - Any questions?
Deconvolution http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 12 Course announcements Homework 3 is out. - Due October 12 th. - Any questions?
Detection of Obscured Targets
 Detection of Obscured Targets Waymond R. Scott, Jr. and James Mcclellan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30332-0250 waymond.scott@ece.gatech.edu
Detection of Obscured Targets Waymond R. Scott, Jr. and James Mcclellan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30332-0250 waymond.scott@ece.gatech.edu
Chapter 2 Channel Equalization
 Chapter 2 Channel Equalization 2.1 Introduction In wireless communication systems signal experiences distortion due to fading [17]. As signal propagates, it follows multiple paths between transmitter and
Chapter 2 Channel Equalization 2.1 Introduction In wireless communication systems signal experiences distortion due to fading [17]. As signal propagates, it follows multiple paths between transmitter and
A033 Combination of Multi-component Streamer Pressure and Vertical Particle Velocity - Theory and Application to Data
 A33 Combination of Multi-component Streamer ressure and Vertical article Velocity - Theory and Application to Data.B.A. Caprioli* (Westerneco), A.K. Ödemir (Westerneco), A. Öbek (Schlumberger Cambridge
A33 Combination of Multi-component Streamer ressure and Vertical article Velocity - Theory and Application to Data.B.A. Caprioli* (Westerneco), A.K. Ödemir (Westerneco), A. Öbek (Schlumberger Cambridge
This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems.
 This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems. This is a general treatment of the subject and applies to I/O System
This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems. This is a general treatment of the subject and applies to I/O System
Short Notes Characterization of a Continuous, Very Narrowband Seismic Signal near 2.08 Hz
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 91, 6, pp. 1910 1916, December 2001 Short Notes Characterization of a Continuous, Very Narrowband Seismic Signal near 2.08 Hz by Kelly H. Liu and Stephen
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 91, 6, pp. 1910 1916, December 2001 Short Notes Characterization of a Continuous, Very Narrowband Seismic Signal near 2.08 Hz by Kelly H. Liu and Stephen
Coherent noise attenuation: A synthetic and field example
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 108, April 29, 2001, pages 1?? Coherent noise attenuation: A synthetic and field example Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT Noise attenuation using either a filtering or a
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 108, April 29, 2001, pages 1?? Coherent noise attenuation: A synthetic and field example Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT Noise attenuation using either a filtering or a
Group Velocity Measurement
 Group Velocity Measurement Distance Travelled (8.3) Group Velocity Time It Took Group Velocity Measurement Distance Travelled (8.3) Group Velocity Time It Took station Earthquake t time d distance earthquake
Group Velocity Measurement Distance Travelled (8.3) Group Velocity Time It Took Group Velocity Measurement Distance Travelled (8.3) Group Velocity Time It Took station Earthquake t time d distance earthquake
Surface wave analysis for P- and S-wave velocity models
 Distinguished Lectures in Earth Sciences, Napoli, 24 Maggio 2018 Surface wave analysis for P- and S-wave velocity models Laura Valentina Socco, Farbod Khosro Anjom, Cesare Comina, Daniela Teodor POLITECNICO
Distinguished Lectures in Earth Sciences, Napoli, 24 Maggio 2018 Surface wave analysis for P- and S-wave velocity models Laura Valentina Socco, Farbod Khosro Anjom, Cesare Comina, Daniela Teodor POLITECNICO
ENHANCEMENT OF SYNTHETIC APERTURE FOCUSING TECHNIQUE (SAFT) BY ADVANCED SIGNAL PROCESSING
 ENHANCEMENT OF SYNTHETIC APERTURE FOCUSING TECHNIQUE (SAFT) BY ADVANCED SIGNAL PROCESSING M. Jastrzebski, T. Dusatko, J. Fortin, F. Farzbod, A.N. Sinclair; University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada; M.D.C.
ENHANCEMENT OF SYNTHETIC APERTURE FOCUSING TECHNIQUE (SAFT) BY ADVANCED SIGNAL PROCESSING M. Jastrzebski, T. Dusatko, J. Fortin, F. Farzbod, A.N. Sinclair; University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada; M.D.C.
Recent Advances in Acoustic Signal Extraction and Dereverberation
 Recent Advances in Acoustic Signal Extraction and Dereverberation Emanuël Habets Erlangen Colloquium 2016 Scenario Spatial Filtering Estimated Desired Signal Undesired sound components: Sensor noise Competing
Recent Advances in Acoustic Signal Extraction and Dereverberation Emanuël Habets Erlangen Colloquium 2016 Scenario Spatial Filtering Estimated Desired Signal Undesired sound components: Sensor noise Competing
Interpretational applications of spectral decomposition in reservoir characterization
 Interpretational applications of spectral decomposition in reservoir characterization GREG PARTYKA, JAMES GRIDLEY, and JOHN LOPEZ, Amoco E&P Technology Group, Tulsa, Oklahoma, U.S. Figure 1. Thin-bed spectral
Interpretational applications of spectral decomposition in reservoir characterization GREG PARTYKA, JAMES GRIDLEY, and JOHN LOPEZ, Amoco E&P Technology Group, Tulsa, Oklahoma, U.S. Figure 1. Thin-bed spectral
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution
 Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
3/15/2010. Distance Distance along the ground (km) Time, (sec)
 GG45 March 16, 21 Introduction to Seismic Exploration and Elementary Digital Analysis Some of the material I will cover today can be found in the book on pages 19-2 and 122-13. 13. However, much of what
GG45 March 16, 21 Introduction to Seismic Exploration and Elementary Digital Analysis Some of the material I will cover today can be found in the book on pages 19-2 and 122-13. 13. However, much of what
Spatial coherency of earthquake-induced ground accelerations recorded by 100-Station of Istanbul Rapid Response Network
 Spatial coherency of -induced ground accelerations recorded by 100-Station of Istanbul Rapid Response Network Ebru Harmandar, Eser Cakti, Mustafa Erdik Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute,
Spatial coherency of -induced ground accelerations recorded by 100-Station of Istanbul Rapid Response Network Ebru Harmandar, Eser Cakti, Mustafa Erdik Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute,
