MULTIFUNCTIONAL circuits configured to realize
|
|
|
- Milton Tucker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 55, NO. 7, JULY A 5-GHz Subharmonic Injection-Locked Oscillator and Self-Oscillating Mixer Fotis C. Plessas, Member, IEEE, A. Papalambrou, Member, IEEE, and G. Kalivas, Member, IEEE Abstract This paper presents a multifunctional circuit realizing the functions of oscillation, mixing, amplification, and frequency multiplication at 5 GHz. A theoretical and experimental description of the circuit is given. The proposed circuit, which combines both the injection-locking and mixing processes, uses only one port where both the RF/intermediate frequency signal and the injection signal (IS) are applied. The IS, which is used to stabilize the oscillation, is at a subharmonic of the oscillation frequency ( osc 4) having a power level as low as 50 dbm. Calculations of the phase noise and measurements of the mixing properties are reported which indicate a noise improvement, and a high up-conversion gain. The implementation of the circuit exhibits an up-conversion gain of 14 db, a phase noise of 110 dbc/hz at 100-kHz offset, a P 1dB of 15 dbm, a third-order intercept point of 2 dbm, and a power consumption of 35 mw. Calculated and measured results are in good agreement for all cases, emphasizing the relevance of the proposed circuit. Index Terms Injection-locked oscillator (ILO), phase noise, self-oscillating mixer (SOM). I. INTRODUCTION MULTIFUNCTIONAL circuits configured to realize functions like oscillation, mixing, amplification, and frequency multiplication have become very attractive due to their smaller size, higher performance, improved reliability, reduced power consumption and lower cost. A number of different techniques and approaches could be used to build such a circuit, like injection locking or self-oscillating mixing. Injection locking [1] [3] is an approach to lock the state of a free-running oscillator by injecting an external signal of low phase noise. The frequency of the external signal must be within the operating frequency range of the oscillator at the fundamental or a subharmonic of the required output frequency [subharmonic injection-locked oscillator (ILO)] [4], [5]. Furthermore, self-oscillating mixers (SOMs) simultaneously implement both the oscillation and mixing functions [6] [8]. Their reduced size, cost and power consumption makes them an attractive choice for system designers. These circuits, however, lack the function of being tunable and have a reduced carrier-to-noise ratio, limited by the poor phase noise and Manuscript received August 14, 2007; revised November 11, First published May 2, 2008; last published July 16, 2008 (projected). This paper was recommended by Associate Editor A. Tasic. F. C. Plessas is with the Department of Telecommunications Science and Technology, University of Peloponnese, Tripoli 22100, Greece, and also with the Applied Electronics Laboratory, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Patras, Rio, Greece ( fplessas@uop.gr; plessas@ee.upatras.gr). A. Papalambrou and G. Kalivas are with the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Patras, Rio, Greece ( papalambrou@ieee.org; kalivas@ee.upatras.gr). Digital Object Identifier /TCSII Fig. 1. Functional block diagram of the proposed circuit. stability of the oscillation portion. In previous works, one more input port is used to apply a reference signal. In this way, an injection-locked SOM (ILSOM) is formed by the synchronization of the oscillation signal generated by the same active element [9] [11]. Subharmonic ILSOMs (s-ilsoms) combine both subharmonic injection-locked oscillation and mixing functions [12] [14]. Such devices operate typically as Doppler detectors, in fundamental or in subharmonic mode. Their reduced size and small consumption permits their use in applications such as active phased array antennas or in injection-locked phase-locked loops (ILPLLs) [15], where the same device may serve as VCO and phase detector. Earlier works described a 500-MHz SOM based on a push pull differential amplifier, using two inputs located at different points, one for the RF/intermediate frequency (IF) signals and one for the injection [6], and a 2.5-GHz cross-coupled SOM using two different inputs as well [7]. An optical injection locking SOM is presented in [9], whereas a subharmonic SOM for 60-GHz applications is reported in [13]. The generated local oscillator (LO) frequency is at 30 GHz while a doubling mechanism is introduced to generate the second harmonic. Finally, an s-ilsom used in a phase conjugation circuit is demonstrated in [14], where the SOM oscillates at its fundamental frequency, whereas the injected signal (IS) is at a subharmonic ( 2) frequency. In this work, we extend the work done in [12] where we presented a 1-GHz s-ilsom. Here, we propose a novel multifunctional circuit operating at 5 GHz, which provides injection-locked oscillation, self-oscillating mixing, and injectionlocked self oscillating mixing with high up-conversion gain and reduced carrier-to-noise ratio. Furthermore, it functions as a free-running oscillator and as a frequency multiplier ( 2, 4) and amplifier. Finally, the theoretical analysis of the proposed circuit is presented. In our approach, we use a 4 subharmonic signal, (s- stands for the 4) for stabilizing the oscillation signal by injection. In /$ IEEE
2 634 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 55, NO. 7, JULY 2008 Fig. 2. Proposed multifunctional circuit. this way, when the circuit operated as a s-ilsom for up-conversion the IF signal and the IS are close in frequency, requiring only one single matching network present at the input. Furthermore, and in contrast to previous works, both the IS and the RF/IF signals are applied at a common point (input) with a buffer isolating the load. Last but not least, the proposed circuit incorporates all functions reported separately by [5] [12]. A functional block diagram of the circuit illustrating all functions is shown in Fig. 1. At the input, the IS is applied (when injected), together with the IF signal when the circuit is used as an up-converter (UC), or the RF signal when is used as a down-converter (DC). Correspondingly, the IF signal appears at the output in the down-conversion process, while the RF signal is created at the output when the circuit is used for up-conversion. Calculated results using the derived formula for the locking range and phase noise are presented. In addition, detailed experimental results for phase noise, locking range, up- and down-conversion gain, noise-figure,, third-order intercept point (IP3), and power consumption are provided. Section II describes the proposed circuit including analysis and simulations, followed by implementation and measurement results in Section III. In Section IV summary and conclusions are presented. II. CIRCUIT AND SIMULATION The proposed multifunctional circuit is composed of three major building blocks, i.e., a preamplifier, an ILO/SOM, and a buffer, as shown in Fig. 2. The preamplifier in the first stage is implemented as a common source low-noise amplifier, providing sufficient gain for the ( 4 subharmonic) IS to synchronize the oscillator. The ILO and SOM block is a modified Colpitts oscillator functioning as: 1) a free-running oscillator; 2) an ILO; 3) an SOM; 4) an ILSOM; or 5) a frequency multiplier/amplifier depending on the applied signals at the input. Finally, the output buffer is a source follower added to isolate output loading from the oscillator/mixer. The oscillation signal can be tuned by using. Moreover, we apply the IS at the gate of the active device whereas we extract the stabilized signal from TABLE I CIRCUIT FUNCTIONS the drain. Table I summarizes the functions of the proposed circuit depending on the signals applied to the IS and RF/IF input. In agreement with Fig. 1, RF represents input for down-conversion operation and output for up-conversion operation, whereas, IF represents input for up-conversion operation and output for down-conversion operation. Most of the reported work for the phase noise analysis of oscillators and ILOs is based on the one port analytical model presented by Adler [2], Kurokawa [3] and extended by Razavi [1]. A two-port network, however, is the basis for our analysis. Considering operation of the circuit as an ILO or s-ilo (functions 2, 3, 4 of Table I), an external IS is used to stabilize the output frequency. The IS inserts an additional phase shift into the feedback loop of the oscillator. The tank can no longer oscillate at the free running frequency because the total phase shift at this frequency deviates from (Barkhausen criterion) by. If the amplitude and the frequency of the IS are
3 PLESSAS et al.: 5-GHz SUBHARMONIC ILO AND SOM 635 chosen properly the tank cancels the effect of by oscillating at the injection frequency and injection locking occurs. When injecting a sinusoid signal with a frequency of and an amplitude of, the nth harmonic with a frequency of and an amplitude of is inherently produced by the nonlinearities of the circuit. If, ( is half the locking range, [2]) the oscillator synchronizes with (the nth harmonic) and thus improves its phase noise characteristics. The total phase noise of the ILO originates from the free-running oscillator phase noise and the IS phase noise. Extending the analysis presented by Kurokawa [3] for the fundamental mode of operation, we calculate the total noise for the subharmonic ILO. Neglecting the phase noise of the IS the phase noise of the locked oscillator is calculated as (1) or Fig. 3. Phase noise of the 5-GHz s-ilsom. (2) If the IS contains noise then the output phase noise at a frequency offset of with respect to the input phase noise would be (3) or (4) Fig. 4. Output spectrum (up-conversion). We note that and that the total phase noise is given by times the phase noise of the free-running oscillator plus times the phase noise of the IS. Thus where and are the single-sideband spectral densities of the phase noise of the free-running oscillator and the IS, respectively. is the stationary phase difference between the free-running oscillator and the IS given by. In our case, is close to which means that the frequency of the IS is close to the edge of the locking range which represents the worst case in terms of phase noise. Fig. 3 shows the computed phase noise profile based on (3). For the computation, the measured phase noise of the free-running oscillator and the measured phase noise of the (5) 1.25-GHz reference signal have been used. The phase noise improvement is 30 db at 1 khz, 20 db at 5 khz, and 10 db at 10 khz. In the case that the IF or the RF signal at the input falls out of the locking range, it will intermodulate with the stabilized oscillation signal forming an s-ilsom (functions 6, 7 of Table I). The proposed s-ilsom uses only one input for both the IF/RF signal and the IS which contrasts previous work (for example [6] and [7]). Since a 4 subharmonic injection is used, the IF and the IS are adequately close in frequency. This fact allows us to design a single matching network at the input of the preamplifier. To analyze the mixing characteristics of the proposed circuit a harmonic balance simulation was performed. When used as an up-converter the output frequencies appearing at the RF/IF output port are at, whereas when used as a down-converter the output frequencies are at. As shown in Fig. 4 the generated oscillation signal is at 4156 MHz with 40-dBm output power. An IF signal at 988 MHz with a power level of 40 dbm is used, producing RF at 5144 MHz. The calculated IF/RF isolation is 28 db and the up-conversion gain is 14 db. Furthermore, simulation of down conversion showed a conversion gain of 2 db.
4 636 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 55, NO. 7, JULY 2008 TABLE II OSCILLATION PERFORMANCE Fig. 5. Phase noise of the reference. Fig. 7. Output spectrum (down-conversion). Fig. 6. Phase noise of the proposed circuit. III. MEASUREMENT RESULTS We designed a hybrid version of the circuit, using GaAs fieldeffect transistors (FETs) and a GaAs hyperabrupt tuning varactor, fabricated on polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) substrate with a relative dielectric constant of 6.15 and a thickness of 10 mils. This allows for rapid implementation and provides flexibility in design optimization. Phase noise of the free-running oscillation signal was measured at 72 dbc/hz at 5 khz. After applying an IS at 1250 MHz with a 50-dBm power level, produced from a synthesized source (Fig. 5), a considerable phase noise reduction of the proposed circuit was measured at low-frequency offsets as shown in Fig. 6. The calculations and measurements of the phase noise levels are in relatively good agreement. Some functions are performed simultaneously (i.e., sub-harmonic injection-locking and self-oscillating mixing resulting in an s-ilsom). The input of the ILO and SOM needs to be matched over a wide frequency range covering all the frequencies given in Table I. The inductive source-degeneration method along with a passband filter structure is a commonly used technique allowing the synthesis of a real part for the input impedance in a broadband range while resonating the reactive part of the input impedance over the whole band (wide-band matching). The measured S11 satisfies the condition of less than 10 db over the frequency spectrum of 900 MHz to 5.5 GHz. The measured locking range variation was from 3.7 khz for a subharmonic ( 4) IS of 45 dbm to 1000 khz for an IS of 10 dbm. In Table II we present the tuning range, tuning gain, output power, phase noise, and power consumption of the s-ilsom with and without IS. Regarding mixing characteristics of the SOM portion, up- and down-conversion gains are measured. An up-conversion gain of 14 db is measured whereas the down-conversion gain is 2 db. The output spectrum of the mixer when an RF signal of 30 dbm at 5150 MHz is applied at the RF/IF input is shown in Fig. 7. Furthermore an injection-locking signal of 50 dbm at 1250 MHz is applied at the IS port. The tone at the left-hand side of Fig. 7 corresponds to the produced IF signal of 25 dbm whereas the tone at the right-hand side of Fig. 7 corresponds to the harmonic ( 2) of the injection-locking signal. The output spectrum observed for the case of up-conversion is presented in Fig. 8. The IF signal of 43 dbm at 1000 MHz and the oscillation signal of 41 dbm tuned at 4150 MHz, produce an RF signal of 29 dbm at 5150 GHz. This results to a conversion gain of 14 db.
5 PLESSAS et al.: 5-GHz SUBHARMONIC ILO AND SOM 637 measured noise figure (NF) is 8.9 db and the power consumption is only 35 mw using a 3-V supply. Fig. 8. Output spectrum (up-conversion). IV. CONCLUSION In this work, a multifunctional circuit was proposed realizing a variety of operations. These include oscillation, fundamental and subharmonic injection-locked oscillation, fundamental and subharmonic injection-locked self-oscillating mixing, and frequency multiplication/amplification. Experimental results demonstrated high performance operation in all modes of the implemented circuit at 5 GHz. In contrast to previous works, only one input is used for both the injection and the IF/RF signals. Furthermore, in order to stabilize the oscillator and reduce the phase noise by 20 db at 5-kHz a subharmonic of the free-running oscillation frequency at 1250 MHz with 50 dbm of power level was used. When the circuit was used as s-ilsom, measurements of the mixing functions indicated an up-conversion gain of 14 db and a down-conversion gain of 2 db. The RF/IF isolation is 29 db, the phase noise 110 dbc/hz at 100-kHz offset, the is 15 dbm, the IP3 is 2 dbm, and the power consumption is only 35 mw. All the above demonstrate a novel, multifunction front-end component with low power consumption, suitable for integration in high-performance radio transceivers. Fig. 9. Output spectrum (frequency multiplier). TABLE III MIXING PERFORMANCE Fig. 9 shows the output spectrum of the proposed multifunctional circuit when it functions as a frequency doubler/amplifier. The input signal is at 2050 MHz with a power level of 52 dbm, while the output signal is at 4100 MHz with a power level of 40 dbm. Furthermore, the 1-dB compression point and the IP3 are also measured and the results are presented in Table III. Finally, the REFERENCES [1] B. Razavi, A Study of injection locking and pulling in oscillators, IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, vol. 39, no. 9, pp , Sep [2] R. Adler, A study of locking phenomena in oscillators, Proc. IEEE, vol. 61, no. 10, pp , Oct [3] K. Kurokawa, Noise in synchronized oscillators, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 16, no. 4, pp , Apr [4] A. S. Daryoush, T. Berceli, R. Saedi, P. R. Herczfeld, and A. Rosen, Theory of subharmonic synchronization of nonlinear oscillators, in Proc. IEEE MTT-S Int. Microwave Symp. Dig., Jun. 1989, pp [5] X. Zhang, X. Zhou, and A. Daryoush, A theoretical and experimental study of the noise behavior of subharmonic injection-locked local oscillators, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 40, no. 5, pp , May [6] M. Ghanevati and A. Daryoush, A low-power-consuming SOM for wireless communications, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 49, no. 7, pp , Jul [7] M.-R. Tofighi and A. Daryoush, A 2.5-GHz InGaP/GaAs differential cross-coupled self-oscillating mixer (SOM) IC, IEEE Microw. Wireless Compon. Lett., vol. 15, no. 4, pp , Apr [8] S. Ver Hoeye, L. Zurdo, and A. Suarez, New nonlinear design tools for self-oscillating mixers, IEEE Microw. Wireless Compon. Lett., vol. 11, no. 8, pp , Aug [9] P. Callaghan, N. J. Gomes, S. K. Suresh Babu, and A. K. Jastrzebski, Optical injection locking of a microwave monolithic self-oscillating mixer, Electron. Lett., vol. 33, pp , Jun [10] X. Zhou, Z. Zhan, and A. Daryoush, A new approach for a phase controlled self-oscillating mixer, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 45, no. 2, pp , Feb [11] S. Ver Hoeye, L. F. Herran, M. Fernandez, and F. Las Heras, Design and analysis of a microwave large-range variable phase-shifter based on an injection-locked harmonic self-oscillating mixer, IEEE Microw. Wireless Compon. Lett., vol. 16, no. 6, pp , Jun [12] F. Plessas, A. Papalambrou, and G. Kalivas, A subharmonic injectionlocked self-oscillating mixer, in Proc IEEE Int. Symp. Circuits Syst., New Orleans, LA, 2007, pp [13] M. Sironen, Y. Qian, and T. Itoh, A subharmonic self-oscillating mixer with integrated antenna for 60-GHz wireless applications, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 49, no. 4, pp , Mar [14] S. C. Yen and T. H. Chu, A retro-directive antenna array with phase conjuction circuit using subharmonically injection-locked self-oscillating mixers, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 52, no. 1, pp , Jan [15] F. Plessas and G. Kalivas, A subharmonically injected phased-locked loop for 5-GHz applications, Microw. Opt. Techn. Lett., vol. 48, pp , Aug
Design and Simulation of 5GHz Down-Conversion Self-Oscillating Mixer
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(12): 2595-2599, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Design and Simulation of 5GHz Down-Conversion Self-Oscillating Mixer 1 Alishir Moradikordalivand, 2 Sepideh Ebrahimi
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(12): 2595-2599, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Design and Simulation of 5GHz Down-Conversion Self-Oscillating Mixer 1 Alishir Moradikordalivand, 2 Sepideh Ebrahimi
PUSH-PUSH DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OSCILLATOR USING SUBSTRATE INTEGRATED WAVEGUIDE POW- ER COMBINER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 30, 105 113, 2012 PUSH-PUSH DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OSCILLATOR USING SUBSTRATE INTEGRATED WAVEGUIDE POW- ER COMBINER P. Su *, Z. X. Tang, and B. Zhang School
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 30, 105 113, 2012 PUSH-PUSH DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OSCILLATOR USING SUBSTRATE INTEGRATED WAVEGUIDE POW- ER COMBINER P. Su *, Z. X. Tang, and B. Zhang School
K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 34, 83 90, 2012 K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE Y. C. Du *, Z. X. Tang, B. Zhang, and P. Su School
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 34, 83 90, 2012 K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE Y. C. Du *, Z. X. Tang, B. Zhang, and P. Su School
Design of low phase noise InGaP/GaAs HBT-based differential Colpitts VCOs for interference cancellation system
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 17, February 2010, pp. 34-38 Design of low phase noise InGaP/GaAs HBT-based differential Colpitts VCOs for interference cancellation system Bhanu
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 17, February 2010, pp. 34-38 Design of low phase noise InGaP/GaAs HBT-based differential Colpitts VCOs for interference cancellation system Bhanu
NEW WIRELESS applications are emerging where
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 709 A Multiply-by-3 Coupled-Ring Oscillator for Low-Power Frequency Synthesis Shwetabh Verma, Member, IEEE, Junfeng Xu, and Thomas H. Lee,
IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 709 A Multiply-by-3 Coupled-Ring Oscillator for Low-Power Frequency Synthesis Shwetabh Verma, Member, IEEE, Junfeng Xu, and Thomas H. Lee,
HIGH-PERFORMANCE microwave oscillators require a
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 53, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 929 Injection-Locked Dual Opto-Electronic Oscillator With Ultra-Low Phase Noise and Ultra-Low Spurious Level Weimin Zhou,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 53, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 929 Injection-Locked Dual Opto-Electronic Oscillator With Ultra-Low Phase Noise and Ultra-Low Spurious Level Weimin Zhou,
A High Gain and Improved Linearity 5.7GHz CMOS LNA with Inductive Source Degeneration Topology
 A High Gain and Improved Linearity 5.7GHz CMOS LNA with Inductive Source Degeneration Topology Ch. Anandini 1, Ram Kumar 2, F. A. Talukdar 3 1,2,3 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering,
A High Gain and Improved Linearity 5.7GHz CMOS LNA with Inductive Source Degeneration Topology Ch. Anandini 1, Ram Kumar 2, F. A. Talukdar 3 1,2,3 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering,
CONVENTIONAL phase-locked loops (PLL s) use frequency
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 34, NO. 6, JUNE 1999 813 Superharmonic Injection-Locked Frequency Dividers Hamid R. Rategh, Student Member, IEEE, and Thomas H. Lee, Member, IEEE Abstract Injection-locked
IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 34, NO. 6, JUNE 1999 813 Superharmonic Injection-Locked Frequency Dividers Hamid R. Rategh, Student Member, IEEE, and Thomas H. Lee, Member, IEEE Abstract Injection-locked
A Push-Push Oscillator Array Using Resonator Type Coupling Circuits
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 54, 85 94, 214 A Push-Push Oscillator Array Using Resonator Type Coupling Circuits Takayuki Tanaka 1, *,KengoKawasaki 1, 2, Masayoshi Aikawa 1, 3, and Ichihiko
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 54, 85 94, 214 A Push-Push Oscillator Array Using Resonator Type Coupling Circuits Takayuki Tanaka 1, *,KengoKawasaki 1, 2, Masayoshi Aikawa 1, 3, and Ichihiko
Analysis and Design of Autonomous Microwave Circuits
 Analysis and Design of Autonomous Microwave Circuits ALMUDENA SUAREZ IEEE PRESS WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Contents Preface xiii 1 Oscillator Dynamics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Operational
Analysis and Design of Autonomous Microwave Circuits ALMUDENA SUAREZ IEEE PRESS WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Contents Preface xiii 1 Oscillator Dynamics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Operational
A study of superharmonic injection locking in multiband frequency dividers
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIRCUIT THEORY AND APPLICATIONS Int. J. Circ. Theor. Appl. (2010) Published online in Wiley Interscience (www.interscience.wiley.com)..644 A study of superharmonic injection locking
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIRCUIT THEORY AND APPLICATIONS Int. J. Circ. Theor. Appl. (2010) Published online in Wiley Interscience (www.interscience.wiley.com)..644 A study of superharmonic injection locking
Noise Reduction in Transistor Oscillators: Part 3 Noise Shifting Techniques. cross-coupled. over other topolo-
 From July 2005 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2005 Summit Technical Media Noise Reduction in Transistor Oscillators: Part 3 Noise Shifting Techniques By Andrei Grebennikov M/A-COM Eurotec Figure
From July 2005 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2005 Summit Technical Media Noise Reduction in Transistor Oscillators: Part 3 Noise Shifting Techniques By Andrei Grebennikov M/A-COM Eurotec Figure
An Area efficient structure for a Dual band Wilkinson power divider with flexible frequency ratios
 1 An Area efficient structure for a Dual band Wilkinson power divider with flexible frequency ratios Jafar Sadique, Under Guidance of Ass. Prof.K.J.Vinoy.E.C.E.Department Abstract In this paper a new design
1 An Area efficient structure for a Dual band Wilkinson power divider with flexible frequency ratios Jafar Sadique, Under Guidance of Ass. Prof.K.J.Vinoy.E.C.E.Department Abstract In this paper a new design
Quiz2: Mixer and VCO Design
 Quiz2: Mixer and VCO Design Fei Sun and Hao Zhong 1 Question1 - Mixer Design 1.1 Design Criteria According to the specifications described in the problem, we can get the design criteria for mixer design:
Quiz2: Mixer and VCO Design Fei Sun and Hao Zhong 1 Question1 - Mixer Design 1.1 Design Criteria According to the specifications described in the problem, we can get the design criteria for mixer design:
A Triple-Band Voltage-Controlled Oscillator Using Two Shunt Right-Handed 4 th -Order Resonators
 JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.16, NO.4, AUGUST, 2016 ISSN(Print) 1598-1657 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2016.16.4.506 ISSN(Online) 2233-4866 A Triple-Band Voltage-Controlled Oscillator
JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.16, NO.4, AUGUST, 2016 ISSN(Print) 1598-1657 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2016.16.4.506 ISSN(Online) 2233-4866 A Triple-Band Voltage-Controlled Oscillator
A 60-GHz Broad-Band Frequency Divider in 0.13-μm CMOS
 Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Instrumentation, Measurement, Circuits & Systems, Hangzhou, China, April 15-17, 2007 153 A 60-GHz Broad-Band Frequency Divider in 0.13-μm CMOS YUAN
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Instrumentation, Measurement, Circuits & Systems, Hangzhou, China, April 15-17, 2007 153 A 60-GHz Broad-Band Frequency Divider in 0.13-μm CMOS YUAN
A GHz HIGH IMAGE REJECTION RATIO SUB- HARMONIC MIXER. National Cheng-Kung University, Tainan 701, Taiwan
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 27, 197 207, 2012 A 20 31 GHz HIGH IMAGE REJECTION RATIO SUB- HARMONIC MIXER Y.-C. Lee 1, C.-H. Liu 2, S.-H. Hung 1, C.-C. Su 1, and Y.-H. Wang 1, 3, * 1 Institute
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 27, 197 207, 2012 A 20 31 GHz HIGH IMAGE REJECTION RATIO SUB- HARMONIC MIXER Y.-C. Lee 1, C.-H. Liu 2, S.-H. Hung 1, C.-C. Su 1, and Y.-H. Wang 1, 3, * 1 Institute
CMOS 120 GHz Phase-Locked Loops Based on Two Different VCO Topologies
 JOURNAL OF ELECTROMAGNETIC ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE, VOL. 17, NO. 2, 98~104, APR. 2017 http://dx.doi.org/10.5515/jkiees.2017.17.2.98 ISSN 2234-8395 (Online) ISSN 2234-8409 (Print) CMOS 120 GHz Phase-Locked
JOURNAL OF ELECTROMAGNETIC ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE, VOL. 17, NO. 2, 98~104, APR. 2017 http://dx.doi.org/10.5515/jkiees.2017.17.2.98 ISSN 2234-8395 (Online) ISSN 2234-8409 (Print) CMOS 120 GHz Phase-Locked
433MHz front-end with the SA601 or SA620
 433MHz front-end with the SA60 or SA620 AN9502 Author: Rob Bouwer ABSTRACT Although designed for GHz, the SA60 and SA620 can also be used in the 433MHz ISM band. The SA60 performs amplification of the
433MHz front-end with the SA60 or SA620 AN9502 Author: Rob Bouwer ABSTRACT Although designed for GHz, the SA60 and SA620 can also be used in the 433MHz ISM band. The SA60 performs amplification of the
A Novel Phase Conjugator for Active Retrodirective Array Applications
 A Novel Phase Conjugator for Active Retrodirective Array Applications Ryan Y. Miyamoto, Yongxi Qian and Tatsuo Itoh Department of Electrical Engineering University of California, Los Angeles 405 Hilgard
A Novel Phase Conjugator for Active Retrodirective Array Applications Ryan Y. Miyamoto, Yongxi Qian and Tatsuo Itoh Department of Electrical Engineering University of California, Los Angeles 405 Hilgard
Keywords Divide by-4, Direct injection, Injection locked frequency divider (ILFD), Low voltage, Locking range.
 Volume 6, Issue 4, April 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Design of CMOS
Volume 6, Issue 4, April 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Design of CMOS
THE LINEARIZATION TECHNIQUE FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS SYSTEMS WITH THE INJECTION OF THE SECOND HARMONICS
 THE LINEARIZATION TECHNIQUE FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS SYSTEMS WITH THE INJECTION OF THE SECOND HARMONICS N. Males-Ilic#, B. Milovanovic*, D. Budimir# #Wireless Communications Research Group, Department
THE LINEARIZATION TECHNIQUE FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS SYSTEMS WITH THE INJECTION OF THE SECOND HARMONICS N. Males-Ilic#, B. Milovanovic*, D. Budimir# #Wireless Communications Research Group, Department
WIDE-BAND HIGH ISOLATION SUBHARMONICALLY PUMPED RESISTIVE MIXER WITH ACTIVE QUASI- CIRCULATOR
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 18, 135 143, 2010 WIDE-BAND HIGH ISOLATION SUBHARMONICALLY PUMPED RESISTIVE MIXER WITH ACTIVE QUASI- CIRCULATOR W. C. Chien, C.-M. Lin, C.-H. Liu, S.-H.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 18, 135 143, 2010 WIDE-BAND HIGH ISOLATION SUBHARMONICALLY PUMPED RESISTIVE MIXER WITH ACTIVE QUASI- CIRCULATOR W. C. Chien, C.-M. Lin, C.-H. Liu, S.-H.
INJECTION locking of microwave oscillators [1] has been
![INJECTION locking of microwave oscillators [1] has been INJECTION locking of microwave oscillators [1] has been](/thumbs/84/90659524.jpg) IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 8, AUGUST 1999 1535 Analysis of Oscillators with External Feedback Loop for Improved Locking Range and Noise Reduction Heng-Chia Chang,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 47, NO. 8, AUGUST 1999 1535 Analysis of Oscillators with External Feedback Loop for Improved Locking Range and Noise Reduction Heng-Chia Chang,
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated RF Oscillator with Buffered Outputs. Typical Operating Circuit. 10nH 1000pF MAX2620 BIAS SUPPLY
 19-1248; Rev 1; 5/98 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small
19-1248; Rev 1; 5/98 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small
MIXERS AND their local oscillators are often designed
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 58, NO. 8, AUGUST 2011 1705 A Low-Noise Self-Oscillating Mixer Using a Balanced VCO Load Stanley S. K. Ho, Member, IEEE, and Carlos E.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 58, NO. 8, AUGUST 2011 1705 A Low-Noise Self-Oscillating Mixer Using a Balanced VCO Load Stanley S. K. Ho, Member, IEEE, and Carlos E.
GHz-band, high-accuracy SAW resonators and SAW oscillators
 The evolution of wireless communications and semiconductor technologies is spurring the development and commercialization of a variety of applications that use gigahertz-range frequencies. These new applications
The evolution of wireless communications and semiconductor technologies is spurring the development and commercialization of a variety of applications that use gigahertz-range frequencies. These new applications
2x2 QUASI-OPTICAL POWER COMBINER ARRAY AT 20 GHz
 Third International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 37 2x2 QUASI-OPTICAL POWER COMBINER ARRAY AT 20 GHz Shigeo Kawasaki and Tatsuo Itoh Department of Electrical Engineering University of California
Third International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 37 2x2 QUASI-OPTICAL POWER COMBINER ARRAY AT 20 GHz Shigeo Kawasaki and Tatsuo Itoh Department of Electrical Engineering University of California
Low-Power RF Integrated Circuit Design Techniques for Short-Range Wireless Connectivity
 Low-Power RF Integrated Circuit Design Techniques for Short-Range Wireless Connectivity Marvin Onabajo Assistant Professor Analog and Mixed-Signal Integrated Circuits (AMSIC) Research Laboratory Dept.
Low-Power RF Integrated Circuit Design Techniques for Short-Range Wireless Connectivity Marvin Onabajo Assistant Professor Analog and Mixed-Signal Integrated Circuits (AMSIC) Research Laboratory Dept.
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters
 High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
i. At the start-up of oscillation there is an excess negative resistance (-R)
 OSCILLATORS Andrew Dearn * Introduction The designers of monolithic or integrated oscillators usually have the available process dictated to them by overall system requirements such as frequency of operation
OSCILLATORS Andrew Dearn * Introduction The designers of monolithic or integrated oscillators usually have the available process dictated to them by overall system requirements such as frequency of operation
A 7-GHz 1.8-dB NF CMOS Low-Noise Amplifier
 852 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 37, NO. 7, JULY 2002 A 7-GHz 1.8-dB NF CMOS Low-Noise Amplifier Ryuichi Fujimoto, Member, IEEE, Kenji Kojima, and Shoji Otaka Abstract A 7-GHz low-noise amplifier
852 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 37, NO. 7, JULY 2002 A 7-GHz 1.8-dB NF CMOS Low-Noise Amplifier Ryuichi Fujimoto, Member, IEEE, Kenji Kojima, and Shoji Otaka Abstract A 7-GHz low-noise amplifier
RF Integrated Circuits
 Introduction and Motivation RF Integrated Circuits The recent explosion in the radio frequency (RF) and wireless market has caught the semiconductor industry by surprise. The increasing demand for affordable
Introduction and Motivation RF Integrated Circuits The recent explosion in the radio frequency (RF) and wireless market has caught the semiconductor industry by surprise. The increasing demand for affordable
Phase noise characterization of subharmonic injection locked oscillators
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIRCUIT THEORY AND APPLICATIONS Int. J. Circ. Theor. Appl. (2010) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com)..734 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Phase noise characterization
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIRCUIT THEORY AND APPLICATIONS Int. J. Circ. Theor. Appl. (2010) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com)..734 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Phase noise characterization
The Schottky Diode Mixer. Application Note 995
 The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
Design and Implementation of a Low Noise Block for Extended C-Band Earth Station
 THE INSTITUTE OF ELECTRONICS, VJMW 2015 INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERS Design and Implementation of a Low Noise Block for Extended C-Band Earth Station Khanh Duy NGUYEN 1, Doai Van NGUYEN 2, Duc
THE INSTITUTE OF ELECTRONICS, VJMW 2015 INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERS Design and Implementation of a Low Noise Block for Extended C-Band Earth Station Khanh Duy NGUYEN 1, Doai Van NGUYEN 2, Duc
/$ IEEE
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2006 1205 A Low-Phase Noise, Anti-Harmonic Programmable DLL Frequency Multiplier With Period Error Compensation for
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2006 1205 A Low-Phase Noise, Anti-Harmonic Programmable DLL Frequency Multiplier With Period Error Compensation for
DESIGN OF AN S-BAND TWO-WAY INVERTED ASYM- METRICAL DOHERTY POWER AMPLIFIER FOR LONG TERM EVOLUTION APPLICATIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 39, 73 80, 2013 DESIGN OF AN S-BAND TWO-WAY INVERTED ASYM- METRICAL DOHERTY POWER AMPLIFIER FOR LONG TERM EVOLUTION APPLICATIONS Hai-Jin Zhou * and Hua
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 39, 73 80, 2013 DESIGN OF AN S-BAND TWO-WAY INVERTED ASYM- METRICAL DOHERTY POWER AMPLIFIER FOR LONG TERM EVOLUTION APPLICATIONS Hai-Jin Zhou * and Hua
Exact Synthesis of Broadband Three-Line Baluns Hong-Ming Lee, Member, IEEE, and Chih-Ming Tsai, Member, IEEE
 140 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 57, NO. 1, JANUARY 2009 Exact Synthesis of Broadband Three-Line Baluns Hong-Ming Lee, Member, IEEE, and Chih-Ming Tsai, Member, IEEE Abstract
140 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 57, NO. 1, JANUARY 2009 Exact Synthesis of Broadband Three-Line Baluns Hong-Ming Lee, Member, IEEE, and Chih-Ming Tsai, Member, IEEE Abstract
Frequency Multipliers Design Techniques and Applications
 Frequency Multipliers Design Techniques and Applications Carlos E. Saavedra Associate Professor Electrical and Computer Engineering Queen s University Kingston, Ontario CANADA Outline Introduction applications
Frequency Multipliers Design Techniques and Applications Carlos E. Saavedra Associate Professor Electrical and Computer Engineering Queen s University Kingston, Ontario CANADA Outline Introduction applications
I. INTRODUCTION. Architecture of PLL-based integer-n frequency synthesizer. TABLE I DIVISION RATIO AND FREQUENCY OF ALL CHANNELS, N =16, P =16
 320 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 56, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2009 A 5-GHz CMOS Frequency Synthesizer With an Injection-Locked Frequency Divider and Differential Switched Capacitors
320 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 56, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2009 A 5-GHz CMOS Frequency Synthesizer With an Injection-Locked Frequency Divider and Differential Switched Capacitors
High Gain Low Noise Amplifier Design Using Active Feedback
 Chapter 6 High Gain Low Noise Amplifier Design Using Active Feedback In the previous two chapters, we have used passive feedback such as capacitor and inductor as feedback. This chapter deals with the
Chapter 6 High Gain Low Noise Amplifier Design Using Active Feedback In the previous two chapters, we have used passive feedback such as capacitor and inductor as feedback. This chapter deals with the
Low voltage LNA, mixer and VCO 1GHz
 DESCRIPTION The is a combined RF amplifier, VCO with tracking bandpass filter and mixer designed for high-performance low-power communication systems from 800-1200MHz. The low-noise preamplifier has a
DESCRIPTION The is a combined RF amplifier, VCO with tracking bandpass filter and mixer designed for high-performance low-power communication systems from 800-1200MHz. The low-noise preamplifier has a
WITH advancements in submicrometer CMOS technology,
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 53, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 881 A Complementary Colpitts Oscillator in CMOS Technology Choong-Yul Cha, Member, IEEE, and Sang-Gug Lee, Member, IEEE
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 53, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 881 A Complementary Colpitts Oscillator in CMOS Technology Choong-Yul Cha, Member, IEEE, and Sang-Gug Lee, Member, IEEE
1GHz low voltage LNA, mixer and VCO
 DESCRIPTION The is a combined RF amplifier, VCO with tracking bandpass filter and mixer designed for high-performance low-power communication systems from 800-1200MHz. The low-noise preamplifier has a
DESCRIPTION The is a combined RF amplifier, VCO with tracking bandpass filter and mixer designed for high-performance low-power communication systems from 800-1200MHz. The low-noise preamplifier has a
Highly linear common-gate mixer employing intrinsic second and third order distortion cancellation
 Highly linear common-gate mixer employing intrinsic second and third order distortion cancellation Mahdi Parvizi a), and Abdolreza Nabavi b) Microelectronics Laboratory, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran
Highly linear common-gate mixer employing intrinsic second and third order distortion cancellation Mahdi Parvizi a), and Abdolreza Nabavi b) Microelectronics Laboratory, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
A Low Phase Noise 24/77 GHz Dual-Band Sub-Sampling PLL for Automotive Radar Applications in 65 nm CMOS Technology
 A Low Phase Noise 24/77 GHz Dual-Band Sub-Sampling PLL for Automotive Radar Applications in 65 nm CMOS Technology Xiang Yi, Chirn Chye Boon, Junyi Sun, Nan Huang and Wei Meng Lim VIRTUS, Nanyang Technological
A Low Phase Noise 24/77 GHz Dual-Band Sub-Sampling PLL for Automotive Radar Applications in 65 nm CMOS Technology Xiang Yi, Chirn Chye Boon, Junyi Sun, Nan Huang and Wei Meng Lim VIRTUS, Nanyang Technological
WIDE tuning range is required in CMOS LC voltage-controlled
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 55, NO. 5, MAY 2008 399 A Wide-Band CMOS LC VCO With Linearized Coarse Tuning Characteristics Jongsik Kim, Jaewook Shin, Seungsoo Kim,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 55, NO. 5, MAY 2008 399 A Wide-Band CMOS LC VCO With Linearized Coarse Tuning Characteristics Jongsik Kim, Jaewook Shin, Seungsoo Kim,
Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance
 Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance Mixer Terms Defined Statistical Processing Applied to Mixers Today's stringent demands for precise electronic systems place a heavy burden
Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance Mixer Terms Defined Statistical Processing Applied to Mixers Today's stringent demands for precise electronic systems place a heavy burden
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent
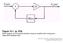 Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Optoelectronic Oscillator Topologies based on Resonant Tunneling Diode Fiber Optic Links
 Optoelectronic Oscillator Topologies based on Resonant Tunneling Diode Fiber Optic Links Bruno Romeira* a, José M. L Figueiredo a, Kris Seunarine b, Charles N. Ironside b, a Department of Physics, CEOT,
Optoelectronic Oscillator Topologies based on Resonant Tunneling Diode Fiber Optic Links Bruno Romeira* a, José M. L Figueiredo a, Kris Seunarine b, Charles N. Ironside b, a Department of Physics, CEOT,
INC. MICROWAVE. A Spectrum Control Business
 DRO Selection Guide DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OSCILLATORS Model Number Frequency Free Running, Mechanically Tuned Mechanical Tuning BW (MHz) +10 MDR2100 2.5-6.0 +10 6.0-21.0 +20 Free Running, Mechanically Tuned,
DRO Selection Guide DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OSCILLATORS Model Number Frequency Free Running, Mechanically Tuned Mechanical Tuning BW (MHz) +10 MDR2100 2.5-6.0 +10 6.0-21.0 +20 Free Running, Mechanically Tuned,
Introduction Introduction to radio frequencies p. 3 What are the 'radio frequencies'? p. 3 Why are radio frequencies different? p.
 Foreword p. xi Preface p. xiii Introduction Introduction to radio frequencies p. 3 What are the 'radio frequencies'? p. 3 Why are radio frequencies different? p. 3 What this book covers p. 3 Signals and
Foreword p. xi Preface p. xiii Introduction Introduction to radio frequencies p. 3 What are the 'radio frequencies'? p. 3 Why are radio frequencies different? p. 3 What this book covers p. 3 Signals and
Design of High Gain and Low Noise CMOS Gilbert Cell Mixer for Receiver Front End Design
 2016 International Conference on Information Technology Design of High Gain and Low Noise CMOS Gilbert Cell Mixer for Receiver Front End Design Shasanka Sekhar Rout Department of Electronics & Telecommunication
2016 International Conference on Information Technology Design of High Gain and Low Noise CMOS Gilbert Cell Mixer for Receiver Front End Design Shasanka Sekhar Rout Department of Electronics & Telecommunication
Above 200 GHz On-Chip CMOS Frequency Generation, Transmission and Receiving
 Above 200 GHz On-Chip CMOS Frequency Generation, Transmission and Receiving Bassam Khamaisi and Eran Socher Department of Physical Electronics Faculty of Engineering Tel-Aviv University Outline Background
Above 200 GHz On-Chip CMOS Frequency Generation, Transmission and Receiving Bassam Khamaisi and Eran Socher Department of Physical Electronics Faculty of Engineering Tel-Aviv University Outline Background
Low Power RF Transceivers
 Low Power RF Transceivers Mr. Zohaib Latif 1, Dr. Amir Masood Khalid 2, Mr. Uzair Saeed 3 1,3 Faculty of Computing and Engineering, Riphah International University Faisalabad, Pakistan 2 Department of
Low Power RF Transceivers Mr. Zohaib Latif 1, Dr. Amir Masood Khalid 2, Mr. Uzair Saeed 3 1,3 Faculty of Computing and Engineering, Riphah International University Faisalabad, Pakistan 2 Department of
Research Article A Parallel-Strip Balun for Wideband Frequency Doubler
 Microwave Science and Technology Volume 213, Article ID 8929, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.11/213/8929 Research Article A Parallel-Strip Balun for Wideband Frequency Doubler Leung Chiu and Quan Xue Department
Microwave Science and Technology Volume 213, Article ID 8929, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.11/213/8929 Research Article A Parallel-Strip Balun for Wideband Frequency Doubler Leung Chiu and Quan Xue Department
Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration
 22 Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration Jun-Hyuk Seo, and Woo-Young Choi Department of Electrical and
22 Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration Jun-Hyuk Seo, and Woo-Young Choi Department of Electrical and
Modified Wilkinson Compact Wide Band (2-12GHz) Equal Power Divider
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-03, Issue-10, pp-90-98 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Modified Wilkinson Compact Wide Band (2-12GHz)
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-03, Issue-10, pp-90-98 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Modified Wilkinson Compact Wide Band (2-12GHz)
10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated RF Oscillator with Buffered Outputs
 9-24; Rev 2; 2/02 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 0MHz to 050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small µmax
9-24; Rev 2; 2/02 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 0MHz to 050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small µmax
SP 22.3: A 12mW Wide Dynamic Range CMOS Front-End for a Portable GPS Receiver
 SP 22.3: A 12mW Wide Dynamic Range CMOS Front-End for a Portable GPS Receiver Arvin R. Shahani, Derek K. Shaeffer, Thomas H. Lee Stanford University, Stanford, CA At submicron channel lengths, CMOS is
SP 22.3: A 12mW Wide Dynamic Range CMOS Front-End for a Portable GPS Receiver Arvin R. Shahani, Derek K. Shaeffer, Thomas H. Lee Stanford University, Stanford, CA At submicron channel lengths, CMOS is
A COMPACT, AGILE, LOW-PHASE-NOISE FREQUENCY SOURCE WITH AM, FM AND PULSE MODULATION CAPABILITIES
 A COMPACT, AGILE, LOW-PHASE-NOISE FREQUENCY SOURCE WITH AM, FM AND PULSE MODULATION CAPABILITIES Alexander Chenakin Phase Matrix, Inc. 109 Bonaventura Drive San Jose, CA 95134, USA achenakin@phasematrix.com
A COMPACT, AGILE, LOW-PHASE-NOISE FREQUENCY SOURCE WITH AM, FM AND PULSE MODULATION CAPABILITIES Alexander Chenakin Phase Matrix, Inc. 109 Bonaventura Drive San Jose, CA 95134, USA achenakin@phasematrix.com
CMY210. Demonstration Board Documentation / Applications Note (V1.0) Ultra linear General purpose up/down mixer 1. DESCRIPTION
 Demonstration Board Documentation / (V1.0) Ultra linear General purpose up/down mixer Features: Very High Input IP3 of 24 dbm typical Very Low LO Power demand of 0 dbm typical; Wide input range Wide LO
Demonstration Board Documentation / (V1.0) Ultra linear General purpose up/down mixer Features: Very High Input IP3 of 24 dbm typical Very Low LO Power demand of 0 dbm typical; Wide input range Wide LO
Linearization of Three-Stage Doherty Amplifier
 Linearization of Three-Stage Doherty Amplifier NATAŠA MALEŠ ILIĆ, ALEKSANDAR ATANASKOVIĆ, BRATISLAV MILOVANOVIĆ Faculty of Electronic Engineering University of Niš, Aleksandra Medvedeva 14, Niš Serbia
Linearization of Three-Stage Doherty Amplifier NATAŠA MALEŠ ILIĆ, ALEKSANDAR ATANASKOVIĆ, BRATISLAV MILOVANOVIĆ Faculty of Electronic Engineering University of Niš, Aleksandra Medvedeva 14, Niš Serbia
Complex Impedance-Transformation Out-of-Phase Power Divider with High Power-Handling Capability
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 53, 13 19, 215 Complex Impedance-Transformation Out-of-Phase Power Divider with High Power-Handling Capability Lulu Bei 1, 2, Shen Zhang 2, *, and Kai
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 53, 13 19, 215 Complex Impedance-Transformation Out-of-Phase Power Divider with High Power-Handling Capability Lulu Bei 1, 2, Shen Zhang 2, *, and Kai
Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: Part 1
 From May 009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 009 Summit Technical Media, LLC Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: art 1 By Andrei Grebennikov Bell Labs Ireland In modern telecommunication
From May 009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 009 Summit Technical Media, LLC Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: art 1 By Andrei Grebennikov Bell Labs Ireland In modern telecommunication
Simple high sensitivity wireless transceiver
 Simple high sensitivity wireless transceiver Buchanan, N. B., & Fusco, V. (2014). Simple high sensitivity wireless transceiver. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 56(4), 790-792. DOI: 10.1002/mop.28205
Simple high sensitivity wireless transceiver Buchanan, N. B., & Fusco, V. (2014). Simple high sensitivity wireless transceiver. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 56(4), 790-792. DOI: 10.1002/mop.28205
small signal linear gain G s is: More realistically, oscillation occurs at frequencies where the G 2 Oscillation frequency is controlled by
 VOLTAGE CONTROLLED OSCILLATORS (VCOs) VCOs are RF oscillators whose actual output frequency can be controlled by the voltage present at a control (tuning) port. Barkhausen Criterion: Systems breaks into
VOLTAGE CONTROLLED OSCILLATORS (VCOs) VCOs are RF oscillators whose actual output frequency can be controlled by the voltage present at a control (tuning) port. Barkhausen Criterion: Systems breaks into
ACMOS RF up/down converter would allow a considerable
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 32, NO. 7, JULY 1997 1151 Low Voltage Performance of a Microwave CMOS Gilbert Cell Mixer P. J. Sullivan, B. A. Xavier, and W. H. Ku Abstract This paper demonstrates
IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 32, NO. 7, JULY 1997 1151 Low Voltage Performance of a Microwave CMOS Gilbert Cell Mixer P. J. Sullivan, B. A. Xavier, and W. H. Ku Abstract This paper demonstrates
WITH THE exploding growth of the wireless communication
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 60, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2012 387 0.6 3-GHz Wideband Receiver RF Front-End With a Feedforward Noise and Distortion Cancellation Resistive-Feedback
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 60, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2012 387 0.6 3-GHz Wideband Receiver RF Front-End With a Feedforward Noise and Distortion Cancellation Resistive-Feedback
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator. Advanced RF Circuit Simulation
 SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator Advanced RF Circuit Simulation SmartSpice RF Overview Uses harmonic balance approach to solve system equations in frequency domain Well suited for RF and
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator Advanced RF Circuit Simulation SmartSpice RF Overview Uses harmonic balance approach to solve system equations in frequency domain Well suited for RF and
WITH mobile communication technologies, such as longterm
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 63, NO. 6, JUNE 206 533 A Two-Stage Broadband Fully Integrated CMOS Linear Power Amplifier for LTE Applications Kihyun Kim, Jaeyong Ko,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 63, NO. 6, JUNE 206 533 A Two-Stage Broadband Fully Integrated CMOS Linear Power Amplifier for LTE Applications Kihyun Kim, Jaeyong Ko,
EECS-730 High-Power Inverted Doherty Power Amplifier for Broadband Application
 EECS-730 High-Power Inverted Doherty Power Amplifier for Broadband Application Jehyeon Gu* Mincheol Seo Hwiseob Lee Jinhee Kwon Junghyun Ham Hyungchul Kim and Youngoo Yang Sungkyunkwan University 300 Cheoncheon-dong
EECS-730 High-Power Inverted Doherty Power Amplifier for Broadband Application Jehyeon Gu* Mincheol Seo Hwiseob Lee Jinhee Kwon Junghyun Ham Hyungchul Kim and Youngoo Yang Sungkyunkwan University 300 Cheoncheon-dong
High Power Wideband AlGaN/GaN HEMT Feedback. Amplifier Module with Drain and Feedback Loop. Inductances
 High Power Wideband AlGaN/GaN HEMT Feedback Amplifier Module with Drain and Feedback Loop Inductances Y. Chung, S. Cai, W. Lee, Y. Lin, C. P. Wen, Fellow, IEEE, K. L. Wang, Fellow, IEEE, and T. Itoh, Fellow,
High Power Wideband AlGaN/GaN HEMT Feedback Amplifier Module with Drain and Feedback Loop Inductances Y. Chung, S. Cai, W. Lee, Y. Lin, C. P. Wen, Fellow, IEEE, K. L. Wang, Fellow, IEEE, and T. Itoh, Fellow,
A COMPACT DOUBLE-BALANCED STAR MIXER WITH NOVEL DUAL 180 HYBRID. National Cheng-Kung University, No. 1 University Road, Tainan 70101, Taiwan
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 24, 147 159, 2011 A COMPACT DOUBLE-BALANCED STAR MIXER WITH NOVEL DUAL 180 HYBRID Y.-A. Lai 1, C.-N. Chen 1, C.-C. Su 1, S.-H. Hung 1, C.-L. Wu 1, 2, and Y.-H.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 24, 147 159, 2011 A COMPACT DOUBLE-BALANCED STAR MIXER WITH NOVEL DUAL 180 HYBRID Y.-A. Lai 1, C.-N. Chen 1, C.-C. Su 1, S.-H. Hung 1, C.-L. Wu 1, 2, and Y.-H.
Recent Developments in RF Front Ends Based Upon Active Antenna Concepts
 Recent Developments in RF Front Ends Based Upon Active Antenna Concepts Abstract In this paper several developments in RF front end technology based upon the active antenna concept are presented. RF front
Recent Developments in RF Front Ends Based Upon Active Antenna Concepts Abstract In this paper several developments in RF front end technology based upon the active antenna concept are presented. RF front
Design and Characterization of a 10 Gb/s Clock and Data Recovery Circuit Implemented with Phase-Locked Loop
 Design and Characterization of a Clock and Recovery Implemented with -Locked Loop Jae Ho Song a), Tae Whan Yoo, Jeong Hoon Ko, Chang Soo Park, and Jae Keun Kim A clock and data recovery circuit with a
Design and Characterization of a Clock and Recovery Implemented with -Locked Loop Jae Ho Song a), Tae Whan Yoo, Jeong Hoon Ko, Chang Soo Park, and Jae Keun Kim A clock and data recovery circuit with a
Design of the Low Phase Noise Voltage Controlled Oscillator with On-Chip Vs Off- Chip Passive Components.
 3 rd International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology, Bhurban, Pakistan. June 07-12, 2004 Design of the Low Phase Noise Voltage Controlled Oscillator with On-Chip Vs Off- Chip Passive
3 rd International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology, Bhurban, Pakistan. June 07-12, 2004 Design of the Low Phase Noise Voltage Controlled Oscillator with On-Chip Vs Off- Chip Passive
A low noise amplifier with improved linearity and high gain
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1188 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 A low noise amplifier with improved linearity and high gain Ram Kumar, Jitendra
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1188 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 A low noise amplifier with improved linearity and high gain Ram Kumar, Jitendra
THE reference spur for a phase-locked loop (PLL) is generated
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 54, NO. 8, AUGUST 2007 653 Spur-Suppression Techniques for Frequency Synthesizers Che-Fu Liang, Student Member, IEEE, Hsin-Hua Chen, and
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 54, NO. 8, AUGUST 2007 653 Spur-Suppression Techniques for Frequency Synthesizers Che-Fu Liang, Student Member, IEEE, Hsin-Hua Chen, and
Negative Input Resistance and Real-time Active Load-pull Measurements of a 2.5GHz Oscillator Using a LSNA
 Negative Input Resistance and Real-time Active Load-pull Measurements of a.5ghz Oscillator Using a LSNA Inwon Suh*, Seok Joo Doo*, Patrick Roblin* #, Xian Cui*, Young Gi Kim*, Jeffrey Strahler +, Marc
Negative Input Resistance and Real-time Active Load-pull Measurements of a.5ghz Oscillator Using a LSNA Inwon Suh*, Seok Joo Doo*, Patrick Roblin* #, Xian Cui*, Young Gi Kim*, Jeffrey Strahler +, Marc
Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS. EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez. April 15, 2004
 Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez April 15, 2004 The University of Texas at El Paso Dr Tim S. Yao ABSTRACT Two circuits satisfying the
Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez April 15, 2004 The University of Texas at El Paso Dr Tim S. Yao ABSTRACT Two circuits satisfying the
A 2 4 GHz Octave Bandwidth GaN HEMT Power Amplifier with High Efficiency
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 63, 7 14, 216 A 2 4 GHz Octave Bandwidth GaN HEMT Power Amplifier with High Efficiency Hao Guo, Chun-Qing Chen, Hao-Quan Wang, and Ming-Li Hao * Abstract
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 63, 7 14, 216 A 2 4 GHz Octave Bandwidth GaN HEMT Power Amplifier with High Efficiency Hao Guo, Chun-Qing Chen, Hao-Quan Wang, and Ming-Li Hao * Abstract
Linearization of Broadband Microwave Amplifier
 SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 11, No. 1, February 2014, 111-120 UDK: 621.396:004.72.057.4 DOI: 10.2298/SJEE131130010D Linearization of Broadband Microwave Amplifier Aleksandra Đorić 1,
SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 11, No. 1, February 2014, 111-120 UDK: 621.396:004.72.057.4 DOI: 10.2298/SJEE131130010D Linearization of Broadband Microwave Amplifier Aleksandra Đorić 1,
PARALLEL coupled-line filters are widely used in microwave
 2812 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 53, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2005 Improved Coupled-Microstrip Filter Design Using Effective Even-Mode and Odd-Mode Characteristic Impedances Hong-Ming
2812 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 53, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2005 Improved Coupled-Microstrip Filter Design Using Effective Even-Mode and Odd-Mode Characteristic Impedances Hong-Ming
New Design Formulas for Impedance-Transforming 3-dB Marchand Baluns Hee-Ran Ahn, Senior Member, IEEE, and Sangwook Nam, Senior Member, IEEE
 2816 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 59, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2011 New Design Formulas for Impedance-Transforming 3-dB Marchand Baluns Hee-Ran Ahn, Senior Member, IEEE, and Sangwook
2816 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 59, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2011 New Design Formulas for Impedance-Transforming 3-dB Marchand Baluns Hee-Ran Ahn, Senior Member, IEEE, and Sangwook
Wideband and High Efficiency Feed-Forward Linear Power Amplifier for Base Stations
 Base Station Power Amplifier High Efficiency Wideband and High Efficiency Feed-Forward Linear Power Amplifier for Base Stations This paper presents a new feed-forward linear power amplifier configuration
Base Station Power Amplifier High Efficiency Wideband and High Efficiency Feed-Forward Linear Power Amplifier for Base Stations This paper presents a new feed-forward linear power amplifier configuration
Dual band planar hybrid coupler with enhanced bandwidth using particle swarm optimization technique
 Dual band planar hybrid coupler with enhanced bandwidth using particle swarm optimization technique Mahdi Yousefi a), Mohammad Mosalanejad b), Gholamreza Moradi c), and Abdolali Abdipour d) Wave Propagation
Dual band planar hybrid coupler with enhanced bandwidth using particle swarm optimization technique Mahdi Yousefi a), Mohammad Mosalanejad b), Gholamreza Moradi c), and Abdolali Abdipour d) Wave Propagation
Fully integrated CMOS transmitter design considerations
 Semiconductor Technology Fully integrated CMOS transmitter design considerations Traditionally, multiple IC chips are needed to build transmitters (Tx) used in wireless communications. The difficulty with
Semiconductor Technology Fully integrated CMOS transmitter design considerations Traditionally, multiple IC chips are needed to build transmitters (Tx) used in wireless communications. The difficulty with
Design technique of broadband CMOS LNA for DC 11 GHz SDR
 Design technique of broadband CMOS LNA for DC 11 GHz SDR Anh Tuan Phan a) and Ronan Farrell Institute of Microelectronics and Wireless Systems, National University of Ireland Maynooth, Maynooth,Co. Kildare,
Design technique of broadband CMOS LNA for DC 11 GHz SDR Anh Tuan Phan a) and Ronan Farrell Institute of Microelectronics and Wireless Systems, National University of Ireland Maynooth, Maynooth,Co. Kildare,
77 GHz VCO for Car Radar Systems T625_VCO2_W Preliminary Data Sheet
 77 GHz VCO for Car Radar Systems Preliminary Data Sheet Operating Frequency: 76-77 GHz Tuning Range > 1 GHz Output matched to 50 Ω Application in Car Radar Systems ESD: Electrostatic discharge sensitive
77 GHz VCO for Car Radar Systems Preliminary Data Sheet Operating Frequency: 76-77 GHz Tuning Range > 1 GHz Output matched to 50 Ω Application in Car Radar Systems ESD: Electrostatic discharge sensitive
PART MAX2605EUT-T MAX2606EUT-T MAX2607EUT-T MAX2608EUT-T MAX2609EUT-T TOP VIEW IND GND. Maxim Integrated Products 1
 19-1673; Rev 0a; 4/02 EVALUATION KIT MANUAL AVAILABLE 45MHz to 650MHz, Integrated IF General Description The are compact, high-performance intermediate-frequency (IF) voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs)
19-1673; Rev 0a; 4/02 EVALUATION KIT MANUAL AVAILABLE 45MHz to 650MHz, Integrated IF General Description The are compact, high-performance intermediate-frequency (IF) voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs)
A linearized amplifier using self-mixing feedback technique
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.5, 1 8 A linearized amplifier using self-mixing feedback technique Dong-Ho Lee a) Department of Information and Communication Engineering, Hanbat National University,
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.5, 1 8 A linearized amplifier using self-mixing feedback technique Dong-Ho Lee a) Department of Information and Communication Engineering, Hanbat National University,
MULTIPHASE voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs) are
 474 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 55, NO. 3, MARCH 2007 A 15/30-GHz Dual-Band Multiphase Voltage-Controlled Oscillator in 0.18-m CMOS Hsieh-Hung Hsieh, Student Member, IEEE,
474 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 55, NO. 3, MARCH 2007 A 15/30-GHz Dual-Band Multiphase Voltage-Controlled Oscillator in 0.18-m CMOS Hsieh-Hung Hsieh, Student Member, IEEE,
95GHz Receiver with Fundamental Frequency VCO and Static Frequency Divider in 65nm Digital CMOS
 95GHz Receiver with Fundamental Frequency VCO and Static Frequency Divider in 65nm Digital CMOS Ekaterina Laskin, Mehdi Khanpour, Ricardo Aroca, Keith W. Tang, Patrice Garcia 1, Sorin P. Voinigescu University
95GHz Receiver with Fundamental Frequency VCO and Static Frequency Divider in 65nm Digital CMOS Ekaterina Laskin, Mehdi Khanpour, Ricardo Aroca, Keith W. Tang, Patrice Garcia 1, Sorin P. Voinigescu University
A Folded SIR Cross Coupled WLAN Dual-Band Filter
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 45, 115 119, 2014 A Folded SIR Cross Coupled WLAN Dual-Band Filter Zi Jian Su *, Xi Chen, Long Li, Bian Wu, and Chang-Hong Liang Abstract A compact cross-coupled
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 45, 115 119, 2014 A Folded SIR Cross Coupled WLAN Dual-Band Filter Zi Jian Su *, Xi Chen, Long Li, Bian Wu, and Chang-Hong Liang Abstract A compact cross-coupled
HF Receivers, Part 3
 HF Receivers, Part 3 Introduction to frequency synthesis; ancillary receiver functions Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers Another link to receiver principles NSARC HF Operators HF
HF Receivers, Part 3 Introduction to frequency synthesis; ancillary receiver functions Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers Another link to receiver principles NSARC HF Operators HF
CMOS Design of Wideband Inductor-Less LNA
 IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 8, Issue 3, Ver. I (May.-June. 2018), PP 25-30 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 www.iosrjournals.org CMOS Design of Wideband Inductor-Less
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 8, Issue 3, Ver. I (May.-June. 2018), PP 25-30 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 www.iosrjournals.org CMOS Design of Wideband Inductor-Less
Intermodulation Distortion and Compression Point Measurement of Active Integrated Antennas Using a Radiative Method
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 54, 45 52, 207 Intermodulation Distortion and Compression Point Measurement of Active Integrated Antennas Using a Radiative Method Evgueni Kaverine, *, Sebastien
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 54, 45 52, 207 Intermodulation Distortion and Compression Point Measurement of Active Integrated Antennas Using a Radiative Method Evgueni Kaverine, *, Sebastien
