Chapter 6 Passband Data Transmission
|
|
|
- Lynne Small
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 6 Passband Data Transmission Passband Data Transmission concerns the Transmission of the Digital Data over the real Passband channel. 6.1 Introduction Categories of digital communications (ASK/PSK/FSK) o Three basic signaling schemes in digital communications Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) Phase-shift keying (PSK) Frequency-shift keying (FSK) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter 6-2 1
2 6.1 Introduction Categories of M-ary digital communications (ASK/PSK/FSK) o Three basic signaling schemes in M-ary digital communications ary Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) T T b 4-ary Phase-shift keying (PSK) 4-ary Frequency-shift keying (FSK) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Introduction Categories of M-ary digital communications (Constant Envelope versus Non-Constant Envelope) o Constant envelope: A necessity for non-linear channels Non-constant envelope (ASK) T T b Constant envelope (PSK) Constant evnelope (FSK) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter 6-4 2
3 6.1 Introduction Categories of digital communications (Coherent versus Non-Coherent) o Coherent technique n The transmitter and receiver are required to be synchronized in both carrier phase and bit timing. o Non-Coherent technique n The transmitter and receiver are not required to be synchronized in both carrier phase and bit timing. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Introduction Roadmap o In this chapter, we will focus on n Power : A resource in communication o Power Spectra n The relation between passband signal and baseband signal is easier to identify in spectra view n Bandwidth: Another resource in communication o Bandwidth efficiency : The ratio of data rate in bits per second to the effectively utilized bandwidth. (Bits/Second/Hz) n Probability of M-ary symbol error (Union bound) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter 6-6 3
4 6.1 Introduction Relation between passband and baseband signals o Math relation between passband and baseband signals (spectrum view) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Introduction Relation between passband and baseband signals Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter 6-8 4
5 6.1 Introduction Relation between passband and baseband signals Signal Spectrum Po-Ning Chapter Introduction Relation between passband and baseband signals o Math relation between passband and baseband signals (power spectrum view subject to wise-sense stationarity) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
6 6.1 Introduction Relation between passband and baseband signals o Let o Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Introduction Relation between passband and baseband signals Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
7 6.1 Introduction Relation between passband signal and baseband signal Po-Ning Chapter Introduction Relation between passband signal and baseband signal Po-Ning Chapter
8 6.1 Introduction Relation between passband signal and baseband signal Power Spectral Density Po-Ning Chapter Introduction Relation between passband signal and baseband signal o Integration of the Power Spectral Density gives the Power. n Integration of the Prabability Density gives the Prabability. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
9 6.2 Passband transmission model Message source Po-Ning Chapter Passband transmission model Signal space analysis Recall Chapter 5: Signal Space Analysis 2-dimensional vector codeword (N=2) N-dimensional vector codeword Po-Ning Chapter
10 6.2 Passband transmission model Signal space analysis Recall Chapter 5: Signal Space Analysis Po-Ning Chapter Passband transmission model Signal space analysis o n What is an energy signal? Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
11 6.2 Passband transmission model Signal space analysis Po-Ning Chapter Passband transmission model Signal space analysis o Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
12 6.2 Passband transmission model Signal space analysis o Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Passband transmission model Communication channel o Communication channel n Linear: Principle of superposition n n Sufficient bandwidth AWGN Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
13 6.2 Passband transmission model Signal space analysis o Detector Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Passband transmission model Decoder o Signal transmission decoder Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
14 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying o Binary PSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Antipodal signal o Vector space analysis of binary PSK n Antipodal signal Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
15 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Signal space analysis Signal-space diagram Po-Ning Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Optimal decision region o Error probability of binary PSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
16 Recall: Po-Ning Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Error probability o Error probability of binary PSK n Based on the decision rule Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
17 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Block diagram o Block diagram for PSK transmitter and (coherent) receiver (coherent) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Baseband signal o (Complex) Baseband signal of binary PSK passband signal Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
18 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Sequential baseband signal o Sequence of complex baseband signals n No autocorrelation function for one-shot single random variable n Calculation of autocorrelation function requires a random process. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Autocorrelation function Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
19 Po-Ning Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Autocorrelation function o Power spectrum of binary PSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
20 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Autocorrelation function o Power spectrum of binary PSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Quadriphaseshift keying o QPSK E is the transmitted energy per QPSK symbol, and T is the symbol duration. o Vector space analysis of QPSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
21 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Quadriphaseshift keying o Two-dimensional signal space diagram of QPSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Quadriphaseshift keying o Example 6.1 Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
22 o Error probability of QPSK Po-Ning Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Error probability of QPSK o Following the same derivation as that in Slide 6-32 Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
23 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Error probability of QPSK o Symbol error rate of QPSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Error probability of QPSK o Alternative approach to derive the symbol error rate of QPSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
24 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Summary o Partial summary n QPSK (with Gray code mapping) and BPSK have the same BER under the same E b /N 0. n QPSK however doubles the transmission bit rate per second (or uses half the bandwidth under the same bit rate) by introducing another quadrature. n In its implementation, QPSK is more complex since it involves two quadratures. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phaseshift keying QPSK diagram o Block diagram of QPSK transmitter and receiver coherent Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
25 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Sequential baseband signal o Sequence of complex baseband signals n No autocorrelation function of one-shot (namely, single) random variable. n Calculation of autocorrelation function requires a random process. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Sequential baseband signal Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
26 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Autocorrelation function o Power spectrum of BPSK and QPSK under the same E b and T b QPSK BPSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter 6-51 Single sign change = 90 degree shift Double sign change = 180 degree shift 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Offset QPSK o Example 6.1: n QPSK 90 degree 0 degree 90 degree 90 degree 90+90=180 degree phase shift 90+0=90 degree phase shift Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
27 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Offset QPSK o Example 6.1: n Offset QPSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu 90 degree phase shift 90 degree phase shift 90 degree phase shift Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Offset QPSK o Offset QPSK n By offseting the quadrature component by half a symbol interval with respect to the in-phase component, Offset QPSK limits the amplitude fluctuation to 90 degree. n The 90 degree phase transition in OQPSK occurs twice as frequently encountered in QPSK. n o Personal comment: One 180 degree phase transition in QPSK becomes two 90 degree phase transitions in OQPSK. Hence, twice is an over-estimate. Under AWGN and coherent receiver, the error rate of OQPSK is exactly the same as that of QPSK. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
28 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying p/4-shifted DQPSK o p/4-shifted DQPSK (D=Differential) n The input dibit does not determine the absolute phase, but the phase change. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying p/4-shifted DQPSK o p/4-shifted DQPSK n The phase transition is restricted to either 45 or 135 degree. o No 0 degree phase transition occurs now! n Noncoherent receiver is feasible. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
29 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Detection of p/4-shifted DQPSK o Noncoherent receiver n Differential detector Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying M-ary PSK o M-ary PSK E is the transmitted energy per M-ary PSK symbol, and T is the symbol duration. o Vector space analysis of M-ary PSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
30 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying M-ary PSK o Example 8PSK (Octaphase-shift keying) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Union bound of M-ary PSK error Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
31 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Union bound of M-ary PSK error o If the signal constellation is symmetric in the sense that then Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Union bound of M-ary PSK error o Example 8PSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
32 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Union bound of M-ary PSK error This is the lower bound of the upper bound. So it is not really an upper bound! Po-Ning Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Power spectra of M-ary PSK signals o Same as Slide 6-50 Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
33 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Power spectra of M-ary PSK signals Po-Ning Chapter Coherent phase-shift keying Bandwidth efficiency o Bandwidth efficiency of M-ary PSK signals n Null-to-null bandwidth n Bandwidth efficiency Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
34 6.3 Coherent phase-shift keying Bandwidth efficiency o Final note n There is a trade-off between symbol error rate and bandwidth efficiency for M-ary PSK signals. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes o For M-ary PSK signals, the in-phase and quadrature components are dependent. n How about making them independent (to increase the data rate)? n Answer: M-ary quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
35 6.4 Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes o Square constellation PSK n Gray-encoded quadbits o Gray-encode the first two bits by quadrants (PSK) o Gray-encode the remaining two bits within quadrants (ASK) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes o Symbol error rate of square QAM o Symbol error rate of equal-prior L-ary ASK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
36 o Symbol error rate of equal-prior L-ary ASK Po-Ning Chapter Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes o Average transmitted energy of M-ary QAM Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
37 6.4 Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes o Square constellation QAM n M is usually even power of two. n For example, M = 2 2, 2 4, 2 6, 2 8, (in such case L = 2, 2 2, 2 3, 2 4, ) o Question: How about M = 2 3, 2 5, 2 7, n Answer: Cross constellation QAM Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes o Symbol error rate of cross-constellation QAM Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
38 6.4 Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes Carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) o QAM can be viewed as one of the family members in carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter 6-75 o Re-express QAM into CAP form Carrierless since no carrier f c appears in this formula. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
39 6.4 Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes Carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) o Properties of the passband in-phase and quadrature pulses in CAP n Property 1: Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes Carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
40 A2.3 Hilbert transform o Let P(f) be the spectrum of a real function p(t). n By convention, denote by u(f) the unit step function, i.e., Multiply by 2 to unchange the area. o Put g + (t) to be the function corresponding to 2u(f)P(f). Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter A2.3 Hilbert transform o How to obtain g + (t)? o Answer: Hilbert Transformer. Proof: Observe that Then by the next slide, we learn that Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
41 By extended Fourier transform, Po-Ning Chapter A2.3 Hilbert transform Po-Ning Chapter
42 A2.3 Hilbert transform 1 h( t ) = pt Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes Carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
43 A2.3 Hilbert transform n Hence, Hilbert transform is basically a 90 degree phase shifter. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter A2.3 Hilbert transform 1 h( t ) = pt 1 h( t ) = pt Ä -1 Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
44 A2.3 Hilbert Transform o An important property of Hilbert transform is that: (Examples of Hilbert transform pairs can be found in Table A6.4.) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
45 6.4 Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes Carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) o Properties of the passband in-phase and quadrature pulses in CAP n Property 2: n Property 3: o This is similar to use another pulse shaping function as g(t)*l(t). o One is thus free to choose the pulse shaping function (to, e.g., improve the bandwidth efficiency) without affecting the orthogonality of two quadratures. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter 6-89 o Example 6.4: Bandwidthefficient spectral shaping n a = 0.2 Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
46 6.4 Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes Carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) o Block diagram of CAP transmitter (See Slide 6-76) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes Carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) o Block diagram of CAP receiver Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
47 6.4 Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes Carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) o How about channels with intersymbol interferences, in addition to AWGN? s(t) Linear time-variant filter h(t) + x(t) Channel w(t) Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter 6-93 o Recall in Section 4.9: Optimum linear receiver. Recall the below terms: 1. Zero-forcing equalizer 2. Nyquist criterion/isi 3. Noise enhancement 4. MMSE equalizer n Design of receiver c(t) as an MMSE equalizer Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
48 6.4 Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes Carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) o This leads to Fig in text. o Can we implement the above structure in digital form? Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes Carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) Combine into one FIR filter May be adaptive when required Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
49 6.4 Hybrid amplitude/phase modulation schemes Carrierless amplitude/phase modulation (CAP) o Applications of CAP n Passband transmission of digital data over twisted-pair wiring of lengths less than 100m. n Data rates may range from 51 upto 155 Mbps with bandwidth being strictly limited to 30 MHz. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter Coherent frequency-shift keying o (M-ary) ASK, (M-ary) PSK and (M-ary) FSK are three major categories of digital modulations, in which QAM can be viewed/analyzed similarly to (M-ary) PSK. o In this section, the last one, i.e., (M-ary) FSK, will be introduced and discussed. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
50 6.5 Coherent frequency-shift keying o Binary FSK E b is the transmitted energy per bit, and T b is the bit duration. o Vector space analysis of binary FSK Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter 6-99 E. D. Sunde, "Ideal binary pulse transmission by AM and FM," Bell Labs Technical Journal, 38, pp , November With this multiple-(1/t b ) restriction, it becomes continuous-phase in every inter-bit transition. Such kind of forced continuous-phase signals, known as Sunde s FSK, surely belongs to the general continuous-phase FSK (CPFSK) family. Po-Ning Chen@cm.nctu Chapter
Thus there are three basic modulation techniques: 1) AMPLITUDE SHIFT KEYING 2) FREQUENCY SHIFT KEYING 3) PHASE SHIFT KEYING
 CHAPTER 5 Syllabus 1) Digital modulation formats 2) Coherent binary modulation techniques 3) Coherent Quadrature modulation techniques 4) Non coherent binary modulation techniques. Digital modulation formats:
CHAPTER 5 Syllabus 1) Digital modulation formats 2) Coherent binary modulation techniques 3) Coherent Quadrature modulation techniques 4) Non coherent binary modulation techniques. Digital modulation formats:
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS. MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications
 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
Digital modulation techniques
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Digital Modulation Schemes
 Digital Modulation Schemes 1. In binary data transmission DPSK is preferred to PSK because (a) a coherent carrier is not required to be generated at the receiver (b) for a given energy per bit, the probability
Digital Modulation Schemes 1. In binary data transmission DPSK is preferred to PSK because (a) a coherent carrier is not required to be generated at the receiver (b) for a given energy per bit, the probability
Content. Chapter 6 PASSBAND DATA TRANSMISSION. Dr. Samir Alghadhban 11/22/13
 Chapter 6 PASSBAND DATA TRANSMISSION Dr. Samir Alghadhban 1 Content Different methods of digital modula3on, namely, phase- shi8 keying, quadrature- amplitude modula3on, and frequency- shi8 keying, and
Chapter 6 PASSBAND DATA TRANSMISSION Dr. Samir Alghadhban 1 Content Different methods of digital modula3on, namely, phase- shi8 keying, quadrature- amplitude modula3on, and frequency- shi8 keying, and
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61)
 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
Lecture 3: Wireless Physical Layer: Modulation Techniques. Mythili Vutukuru CS 653 Spring 2014 Jan 13, Monday
 Lecture 3: Wireless Physical Layer: Modulation Techniques Mythili Vutukuru CS 653 Spring 2014 Jan 13, Monday Modulation We saw a simple example of amplitude modulation in the last lecture Modulation how
Lecture 3: Wireless Physical Layer: Modulation Techniques Mythili Vutukuru CS 653 Spring 2014 Jan 13, Monday Modulation We saw a simple example of amplitude modulation in the last lecture Modulation how
Objectives. Presentation Outline. Digital Modulation Revision
 Digital Modulation Revision Professor Richard Harris Objectives To identify the key points from the lecture material presented in the Digital Modulation section of this paper. What is in the examination
Digital Modulation Revision Professor Richard Harris Objectives To identify the key points from the lecture material presented in the Digital Modulation section of this paper. What is in the examination
Communication Systems
 Electrical Engineering Communication Systems Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near
Electrical Engineering Communication Systems Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near
EC 6501 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION UNIT - IV PART A
 EC 6501 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION UNIT - IV PART A 1. Distinguish coherent vs non coherent digital modulation techniques. [N/D-16] a. Coherent detection: In this method the local carrier generated at the receiver
EC 6501 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION UNIT - IV PART A 1. Distinguish coherent vs non coherent digital modulation techniques. [N/D-16] a. Coherent detection: In this method the local carrier generated at the receiver
Communication Systems
 Electronics Engineering Communication Systems Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near
Electronics Engineering Communication Systems Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 121 FINAL EXAM
 Name: UNIVERSIY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Professor David se EECS 121 FINAL EXAM 21 May 1997, 5:00-8:00 p.m. Please write answers on
Name: UNIVERSIY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Professor David se EECS 121 FINAL EXAM 21 May 1997, 5:00-8:00 p.m. Please write answers on
Wireless Communication Fading Modulation
 EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS
 EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
Principles of Communications
 Principles of Communications Meixia Tao Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 8: Digital Modulation Techniques Textbook: Ch 8.4 8.5, Ch 10.1-10.5 1 Topics to be Covered data baseband Digital modulator
Principles of Communications Meixia Tao Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 8: Digital Modulation Techniques Textbook: Ch 8.4 8.5, Ch 10.1-10.5 1 Topics to be Covered data baseband Digital modulator
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering 1
 UNIT I SAMPLING AND QUANTIZATION Pulse Modulation 1. Explain in detail the generation of PWM and PPM signals (16) (M/J 2011) 2. Explain in detail the concept of PWM and PAM (16) (N/D 2012) 3. What is the
UNIT I SAMPLING AND QUANTIZATION Pulse Modulation 1. Explain in detail the generation of PWM and PPM signals (16) (M/J 2011) 2. Explain in detail the concept of PWM and PAM (16) (N/D 2012) 3. What is the
Theory of Telecommunications Networks
 Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
UNIT I Source Coding Systems
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: DC (16EC421) Year & Sem: III-B. Tech & II-Sem Course & Branch: B. Tech
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: DC (16EC421) Year & Sem: III-B. Tech & II-Sem Course & Branch: B. Tech
Digital Modulation Lecture 01. Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris
 Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Objectives. Presentation Outline. Digital Modulation Lecture 01
 Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Chapter 6 Passband Data Transmission
 Chapter 6 Passband Data ransmission Different methods of digital modulation Outline PSK(Phase-shift keying), QAM(Quad. amp. mod), FSK(Phase-shift keying) Coherent detection of modulated signals in AWGN
Chapter 6 Passband Data ransmission Different methods of digital modulation Outline PSK(Phase-shift keying), QAM(Quad. amp. mod), FSK(Phase-shift keying) Coherent detection of modulated signals in AWGN
OptiSystem applications: Digital modulation analysis (PSK)
 OptiSystem applications: Digital modulation analysis (PSK) 7 Capella Court Nepean, ON, Canada K2E 7X1 +1 (613) 224-4700 www.optiwave.com 2009 Optiwave Systems, Inc. Introduction PSK modulation Digital
OptiSystem applications: Digital modulation analysis (PSK) 7 Capella Court Nepean, ON, Canada K2E 7X1 +1 (613) 224-4700 www.optiwave.com 2009 Optiwave Systems, Inc. Introduction PSK modulation Digital
Modulation and Coding Tradeoffs
 0 Modulation and Coding Tradeoffs Contents 1 1. Design Goals 2. Error Probability Plane 3. Nyquist Minimum Bandwidth 4. Shannon Hartley Capacity Theorem 5. Bandwidth Efficiency Plane 6. Modulation and
0 Modulation and Coding Tradeoffs Contents 1 1. Design Goals 2. Error Probability Plane 3. Nyquist Minimum Bandwidth 4. Shannon Hartley Capacity Theorem 5. Bandwidth Efficiency Plane 6. Modulation and
Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 2: Wireless Transmission (2/2)
 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 2: Wireless Transmission (2/2) [Schiller, Section 2.6 & 2.7] [Reader Part 1: OFDM: An architecture for the fourth generation] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 2: Wireless Transmission (2/2) [Schiller, Section 2.6 & 2.7] [Reader Part 1: OFDM: An architecture for the fourth generation] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture
Amplitude Frequency Phase
 Chapter 4 (part 2) Digital Modulation Techniques Chapter 4 (part 2) Overview Digital Modulation techniques (part 2) Bandpass data transmission Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) Frequency
Chapter 4 (part 2) Digital Modulation Techniques Chapter 4 (part 2) Overview Digital Modulation techniques (part 2) Bandpass data transmission Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) Frequency
Chapter 4. Part 2(a) Digital Modulation Techniques
 Chapter 4 Part 2(a) Digital Modulation Techniques Overview Digital Modulation techniques Bandpass data transmission Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Quadrature
Chapter 4 Part 2(a) Digital Modulation Techniques Overview Digital Modulation techniques Bandpass data transmission Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Quadrature
Detection and Estimation of Signals in Noise. Dr. Robert Schober Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia
 Detection and Estimation of Signals in Noise Dr. Robert Schober Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia Vancouver, August 24, 2010 2 Contents 1 Basic Elements
Detection and Estimation of Signals in Noise Dr. Robert Schober Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia Vancouver, August 24, 2010 2 Contents 1 Basic Elements
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 4TH EDITION Simon Hayhin McMaster University JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Ш.! [ BACKGROUND AND PREVIEW 1. The Communication Process 1 2. Primary Communication Resources 3 3. Sources of
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 4TH EDITION Simon Hayhin McMaster University JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Ш.! [ BACKGROUND AND PREVIEW 1. The Communication Process 1 2. Primary Communication Resources 3 3. Sources of
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES
 COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES Encoding Coding is the process of embedding clocks into a given data stream and producing a signal that can be transmitted over a selected medium.
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES Encoding Coding is the process of embedding clocks into a given data stream and producing a signal that can be transmitted over a selected medium.
Principles of Communications
 Principles of Communications Weiyao Lin Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 8: Digital Modulation Techniques Textbook: Ch 8.4.8.7 2009/2010 Meixia Tao @ SJTU 1 Topics to be Covered data baseband Digital
Principles of Communications Weiyao Lin Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 8: Digital Modulation Techniques Textbook: Ch 8.4.8.7 2009/2010 Meixia Tao @ SJTU 1 Topics to be Covered data baseband Digital
3/26/18. Lecture 3 EITN STRUCTURE OF A WIRELESS COMMUNICATION LINK
 Lecture 3 EITN75 208 STRUCTURE OF A WIRELESS COMMUNICATION LINK 2 A simple structure Speech Data A/D Speech encoder Encrypt. Chann. encoding Modulation Key Speech D/A Speech decoder Decrypt. Chann. decoding
Lecture 3 EITN75 208 STRUCTURE OF A WIRELESS COMMUNICATION LINK 2 A simple structure Speech Data A/D Speech encoder Encrypt. Chann. encoding Modulation Key Speech D/A Speech decoder Decrypt. Chann. decoding
MODULATION AND MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES
 1 MODULATION AND MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES Networks and Communication Department Dr. Marwah Ahmed Outlines 2 Introduction Digital Transmission Digital Modulation Digital Transmission of Analog Signal
1 MODULATION AND MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES Networks and Communication Department Dr. Marwah Ahmed Outlines 2 Introduction Digital Transmission Digital Modulation Digital Transmission of Analog Signal
EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035)
 EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June 2007 101902 COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035) Official Reading Time: Writing Time: Total Duration: 10 mins 120 mins 130 mins Instructions: This is a closed
EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June 2007 101902 COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035) Official Reading Time: Writing Time: Total Duration: 10 mins 120 mins 130 mins Instructions: This is a closed
Receiver Designs for the Radio Channel
 Receiver Designs for the Radio Channel COS 463: Wireless Networks Lecture 15 Kyle Jamieson [Parts adapted from C. Sodini, W. Ozan, J. Tan] Today 1. Delay Spread and Frequency-Selective Fading 2. Time-Domain
Receiver Designs for the Radio Channel COS 463: Wireless Networks Lecture 15 Kyle Jamieson [Parts adapted from C. Sodini, W. Ozan, J. Tan] Today 1. Delay Spread and Frequency-Selective Fading 2. Time-Domain
ECE 4600 Communication Systems
 ECE 4600 Communication Systems Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Course Topics Course Introduction
ECE 4600 Communication Systems Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Course Topics Course Introduction
3. 3. Noncoherent Binary Modulation Techniques
 3. 3. Noncoherent Binary Modulation Techniques A digital communication receiver with no provision make for carrier phase recovery is said to be noncoherent. A. Noncoherent Orthogonal Modulation Scheme.
3. 3. Noncoherent Binary Modulation Techniques A digital communication receiver with no provision make for carrier phase recovery is said to be noncoherent. A. Noncoherent Orthogonal Modulation Scheme.
Outline. EECS 3213 Fall Sebastian Magierowski York University. Review Passband Modulation. Constellations ASK, FSK, PSK.
 EECS 3213 Fall 2014 L12: Modulation Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline Review Passband Modulation ASK, FSK, PSK Constellations 2 1 Underlying Idea Attempting to send a sequence of digits through
EECS 3213 Fall 2014 L12: Modulation Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline Review Passband Modulation ASK, FSK, PSK Constellations 2 1 Underlying Idea Attempting to send a sequence of digits through
QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold
 QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold circuit 2. What is the difference between natural sampling
QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold circuit 2. What is the difference between natural sampling
Digital Modulators & Line Codes
 Digital Modulators & Line Codes Professor A. Manikas Imperial College London EE303 - Communication Systems An Overview of Fundamental Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial College) EE303: Dig. Mod. and Line Codes
Digital Modulators & Line Codes Professor A. Manikas Imperial College London EE303 - Communication Systems An Overview of Fundamental Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial College) EE303: Dig. Mod. and Line Codes
ON SYMBOL TIMING RECOVERY IN ALL-DIGITAL RECEIVERS
 ON SYMBOL TIMING RECOVERY IN ALL-DIGITAL RECEIVERS 1 Ali A. Ghrayeb New Mexico State University, Box 30001, Dept 3-O, Las Cruces, NM, 88003 (e-mail: aghrayeb@nmsu.edu) ABSTRACT Sandia National Laboratories
ON SYMBOL TIMING RECOVERY IN ALL-DIGITAL RECEIVERS 1 Ali A. Ghrayeb New Mexico State University, Box 30001, Dept 3-O, Las Cruces, NM, 88003 (e-mail: aghrayeb@nmsu.edu) ABSTRACT Sandia National Laboratories
Digital Communication
 Digital Communication (ECE4058) Electronics and Communication Engineering Hanyang University Haewoon Nam Lecture 1 1 Digital Band Pass Modulation echnique Digital and-pass modulation techniques Amplitude-shift
Digital Communication (ECE4058) Electronics and Communication Engineering Hanyang University Haewoon Nam Lecture 1 1 Digital Band Pass Modulation echnique Digital and-pass modulation techniques Amplitude-shift
Table of Contents. Acknowledgments... XVII Prologue... 1
 Introduction to Spread-Spectrum Communications By Roger L. Peterson (Motorola), Rodger E. Ziemer (University of Co. at Colorado Springs), and David E. Borth (Motorola) Prentice Hall, 1995 (Navtech order
Introduction to Spread-Spectrum Communications By Roger L. Peterson (Motorola), Rodger E. Ziemer (University of Co. at Colorado Springs), and David E. Borth (Motorola) Prentice Hall, 1995 (Navtech order
Real and Complex Modulation
 Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Revision of Lecture 3
 Revision of Lecture 3 Modulator/demodulator Basic operations of modulation and demodulation Complex notations for modulation and demodulation Carrier recovery and timing recovery This lecture: bits map
Revision of Lecture 3 Modulator/demodulator Basic operations of modulation and demodulation Complex notations for modulation and demodulation Carrier recovery and timing recovery This lecture: bits map
CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION
 2.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION Referring to Equation (2.1), if the information signal is digital and the amplitude (lv of the carrier is varied proportional to the information signal, a
2.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION Referring to Equation (2.1), if the information signal is digital and the amplitude (lv of the carrier is varied proportional to the information signal, a
MSK has three important properties. However, the PSD of the MSK only drops by 10log 10 9 = 9.54 db below its midband value at ft b = 0.
 Gaussian MSK MSK has three important properties Constant envelope (why?) Relatively narrow bandwidth Coherent detection performance equivalent to that of QPSK However, the PSD of the MSK only drops by
Gaussian MSK MSK has three important properties Constant envelope (why?) Relatively narrow bandwidth Coherent detection performance equivalent to that of QPSK However, the PSD of the MSK only drops by
Swedish College of Engineering and Technology Rahim Yar Khan
 PRACTICAL WORK BOOK Telecommunication Systems and Applications (TL-424) Name: Roll No.: Batch: Semester: Department: Swedish College of Engineering and Technology Rahim Yar Khan Introduction Telecommunication
PRACTICAL WORK BOOK Telecommunication Systems and Applications (TL-424) Name: Roll No.: Batch: Semester: Department: Swedish College of Engineering and Technology Rahim Yar Khan Introduction Telecommunication
ISHIK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Information Technology Fall Course Name: Wireless Networks
 ISHIK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Information Technology 2017-2018 Fall Course Name: Wireless Networks Agenda Lecture 4 Multiple Access Techniques: FDMA, TDMA, SDMA and CDMA 1. Frequency
ISHIK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Information Technology 2017-2018 Fall Course Name: Wireless Networks Agenda Lecture 4 Multiple Access Techniques: FDMA, TDMA, SDMA and CDMA 1. Frequency
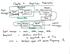 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
EC6501 Digital Communication
 EC6501 Digital Communication UNIT -1 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Digital Communication system 1) Write the advantages and disadvantages of digital communication. [A/M 11] The advantages of digital communication
EC6501 Digital Communication UNIT -1 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Digital Communication system 1) Write the advantages and disadvantages of digital communication. [A/M 11] The advantages of digital communication
Outline / Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 5: Physical Layer Signal Propagation and Modulation
 Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 5: Physical Layer Signal Propagation and Modulation Peter Steenkiste Carnegie Mellon University Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17/
Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 5: Physical Layer Signal Propagation and Modulation Peter Steenkiste Carnegie Mellon University Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17/
ENSC327 Communication Systems 27: Digital Bandpass Modulation. (Ch. 7) Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC37 Communication Systems 7: Digital Bandpass Modulation (Ch. 7) Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline 7.1 Preliminaries 7. Binary Amplitude-Shift Keying (BASK) 7.3
ENSC37 Communication Systems 7: Digital Bandpass Modulation (Ch. 7) Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline 7.1 Preliminaries 7. Binary Amplitude-Shift Keying (BASK) 7.3
Spread Spectrum (SS) is a means of transmission in which the signal occupies a
 SPREAD-SPECTRUM SPECTRUM TECHNIQUES: A BRIEF OVERVIEW SS: AN OVERVIEW Spread Spectrum (SS) is a means of transmission in which the signal occupies a bandwidth in excess of the minimum necessary to send
SPREAD-SPECTRUM SPECTRUM TECHNIQUES: A BRIEF OVERVIEW SS: AN OVERVIEW Spread Spectrum (SS) is a means of transmission in which the signal occupies a bandwidth in excess of the minimum necessary to send
CHAPTER 2. Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication ( )
 CHAPTER 2 Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication (2170710) Syllabus Chapter-2.3 Modulation Techniques Reasons for Choosing Encoding Techniques Digital data,
CHAPTER 2 Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication (2170710) Syllabus Chapter-2.3 Modulation Techniques Reasons for Choosing Encoding Techniques Digital data,
Mobile Communication An overview Lesson 03 Introduction to Modulation Methods
 Mobile Communication An overview Lesson 03 Introduction to Modulation Methods Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Modulation The process of varying one signal, called carrier, according
Mobile Communication An overview Lesson 03 Introduction to Modulation Methods Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Modulation The process of varying one signal, called carrier, according
Chapter 3 Communication Concepts
 Chapter 3 Communication Concepts 1 Sections to be covered 3.1 General Considerations 3.2 Analog Modulation 3.3 Digital Modulation 3.4 Spectral Regrowth 3.7 Wireless Standards 2 Chapter Outline Modulation
Chapter 3 Communication Concepts 1 Sections to be covered 3.1 General Considerations 3.2 Analog Modulation 3.3 Digital Modulation 3.4 Spectral Regrowth 3.7 Wireless Standards 2 Chapter Outline Modulation
Chapter 14 MODULATION INTRODUCTION
 Chapter 14 MODULATION INTRODUCTION As we have seen in previous three chapters, different types of media need different types of electromagnetic signals to carry information from the source to the destination.
Chapter 14 MODULATION INTRODUCTION As we have seen in previous three chapters, different types of media need different types of electromagnetic signals to carry information from the source to the destination.
Lab 3.0. Pulse Shaping and Rayleigh Channel. Faculty of Information Engineering & Technology. The Communications Department
 Faculty of Information Engineering & Technology The Communications Department Course: Advanced Communication Lab [COMM 1005] Lab 3.0 Pulse Shaping and Rayleigh Channel 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Summary...
Faculty of Information Engineering & Technology The Communications Department Course: Advanced Communication Lab [COMM 1005] Lab 3.0 Pulse Shaping and Rayleigh Channel 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Summary...
Chapter 2 Direct-Sequence Systems
 Chapter 2 Direct-Sequence Systems A spread-spectrum signal is one with an extra modulation that expands the signal bandwidth greatly beyond what is required by the underlying coded-data modulation. Spread-spectrum
Chapter 2 Direct-Sequence Systems A spread-spectrum signal is one with an extra modulation that expands the signal bandwidth greatly beyond what is required by the underlying coded-data modulation. Spread-spectrum
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER GCE@Bodi_ SCIENCE GCE@Bodi_ AND ENIGNEERING GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ Analog and Digital Communication GCE@Bodi_ DEPARTMENT OF CsE Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER GCE@Bodi_ SCIENCE GCE@Bodi_ AND ENIGNEERING GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ Analog and Digital Communication GCE@Bodi_ DEPARTMENT OF CsE Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication
Digital to Digital Encoding
 MODULATION AND ENCODING Data must be transformed into signals to send them from one place to another Conversion Schemes Digital-to-Digital Analog-to-Digital Digital-to-Analog Analog-to-Analog Digital to
MODULATION AND ENCODING Data must be transformed into signals to send them from one place to another Conversion Schemes Digital-to-Digital Analog-to-Digital Digital-to-Analog Analog-to-Analog Digital to
CSE4214 Digital Communications. Bandpass Modulation and Demodulation/Detection. Bandpass Modulation. Page 1
 CSE414 Digital Communications Chapter 4 Bandpass Modulation and Demodulation/Detection Bandpass Modulation Page 1 1 Bandpass Modulation n Baseband transmission is conducted at low frequencies n Passband
CSE414 Digital Communications Chapter 4 Bandpass Modulation and Demodulation/Detection Bandpass Modulation Page 1 1 Bandpass Modulation n Baseband transmission is conducted at low frequencies n Passband
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject Name: Digital Communication Techniques
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject Code: EC1351 Year/Sem: III/IV Subject Name: Digital Communication Techniques UNIT I PULSE MODULATION
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject Code: EC1351 Year/Sem: III/IV Subject Name: Digital Communication Techniques UNIT I PULSE MODULATION
Chapter 7. Multiple Division Techniques
 Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
Wireless Communication Systems Laboratory Lab#1: An introduction to basic digital baseband communication through MATLAB simulation Objective
 Wireless Communication Systems Laboratory Lab#1: An introduction to basic digital baseband communication through MATLAB simulation Objective The objective is to teach students a basic digital communication
Wireless Communication Systems Laboratory Lab#1: An introduction to basic digital baseband communication through MATLAB simulation Objective The objective is to teach students a basic digital communication
Spread Spectrum Techniques
 0 Spread Spectrum Techniques Contents 1 1. Overview 2. Pseudonoise Sequences 3. Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Systems 4. Frequency Hopping Systems 5. Synchronization 6. Applications 2 1. Overview Basic
0 Spread Spectrum Techniques Contents 1 1. Overview 2. Pseudonoise Sequences 3. Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Systems 4. Frequency Hopping Systems 5. Synchronization 6. Applications 2 1. Overview Basic
COSC 3213: Computer Networks I: Chapter 3 Handout #4. Instructor: Dr. Marvin Mandelbaum Department of Computer Science York University Section A
 COSC 3213: Computer Networks I: Chapter 3 Handout #4 Instructor: Dr. Marvin Mandelbaum Department of Computer Science York University Section A Topics: 1. Line Coding: Unipolar, Polar,and Inverted ; Bipolar;
COSC 3213: Computer Networks I: Chapter 3 Handout #4 Instructor: Dr. Marvin Mandelbaum Department of Computer Science York University Section A Topics: 1. Line Coding: Unipolar, Polar,and Inverted ; Bipolar;
C06a: Digital Modulation
 CISC 7332X T6 C06a: Digital Modulation Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 10/2/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Digital modulation Baseband transmission Line
CISC 7332X T6 C06a: Digital Modulation Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 10/2/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Digital modulation Baseband transmission Line
ECE 4203: COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 4203: COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2017/2018 DIGITAL MODULATIONS INTRODUCTION In many digital communication systems, cable (as for data
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 4203: COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2017/2018 DIGITAL MODULATIONS INTRODUCTION In many digital communication systems, cable (as for data
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 3: Modulation (II) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 3: Modulation (II) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques chapter 3.3.2 3.3.6 2 Constellation Diagram (3.3.2) Quadrature Modulation Higher Order
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 3: Modulation (II) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques chapter 3.3.2 3.3.6 2 Constellation Diagram (3.3.2) Quadrature Modulation Higher Order
Chapter 6 Modulation Techniques for Mobile Radio
 Chapter 6. Modulation Techniques for Mobile Radio - 1-2 nd Semester, 2010 Chapter 6 Modulation Techniques for Mobile Radio Text. [1] T. S. Rappaport, Wireless Communications - Principles and Practice,
Chapter 6. Modulation Techniques for Mobile Radio - 1-2 nd Semester, 2010 Chapter 6 Modulation Techniques for Mobile Radio Text. [1] T. S. Rappaport, Wireless Communications - Principles and Practice,
Performance Evaluation of ½ Rate Convolution Coding with Different Modulation Techniques for DS-CDMA System over Rician Channel
 Performance Evaluation of ½ Rate Convolution Coding with Different Modulation Techniques for DS-CDMA System over Rician Channel Dilip Mandloi PG Scholar Department of ECE, IES, IPS Academy, Indore [India]
Performance Evaluation of ½ Rate Convolution Coding with Different Modulation Techniques for DS-CDMA System over Rician Channel Dilip Mandloi PG Scholar Department of ECE, IES, IPS Academy, Indore [India]
WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS PRELIMINARIES
 WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS Preliminaries Radio Environment Modulation Performance PRELIMINARIES db s and dbm s Frequency/Time Relationship Bandwidth, Symbol Rate, and Bit Rate 1 DECIBELS Relative signal strengths
WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS Preliminaries Radio Environment Modulation Performance PRELIMINARIES db s and dbm s Frequency/Time Relationship Bandwidth, Symbol Rate, and Bit Rate 1 DECIBELS Relative signal strengths
21. Orthonormal Representation of Signals
 1. Orthonormal Representation of Signals Introduction An analogue communication system is designed for the transmission of information in analogue form. he source information is in analogue form. In practice,
1. Orthonormal Representation of Signals Introduction An analogue communication system is designed for the transmission of information in analogue form. he source information is in analogue form. In practice,
Physical Layer: Modulation, FEC. Wireless Networks: Guevara Noubir. S2001, COM3525 Wireless Networks Lecture 3, 1
 Wireless Networks: Physical Layer: Modulation, FEC Guevara Noubir Noubir@ccsneuedu S, COM355 Wireless Networks Lecture 3, Lecture focus Modulation techniques Bit Error Rate Reducing the BER Forward Error
Wireless Networks: Physical Layer: Modulation, FEC Guevara Noubir Noubir@ccsneuedu S, COM355 Wireless Networks Lecture 3, Lecture focus Modulation techniques Bit Error Rate Reducing the BER Forward Error
Bit Error Probability Computations for M-ary Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
 KING ABDULLAH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Bit Error Probability Computations for M-ary Quadrature Amplitude Modulation Ronell B. Sicat ID: 4000217 Professor Tareq
KING ABDULLAH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Bit Error Probability Computations for M-ary Quadrature Amplitude Modulation Ronell B. Sicat ID: 4000217 Professor Tareq
Optical Coherent Receiver Analysis
 Optical Coherent Receiver Analysis 7 Capella Court Nepean, ON, Canada K2E 7X1 +1 (613) 224-4700 www.optiwave.com 2009 Optiwave Systems, Inc. Introduction (1) Coherent receiver analysis Optical coherent
Optical Coherent Receiver Analysis 7 Capella Court Nepean, ON, Canada K2E 7X1 +1 (613) 224-4700 www.optiwave.com 2009 Optiwave Systems, Inc. Introduction (1) Coherent receiver analysis Optical coherent
KINGS DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING DIGITAL COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUES YEAR/SEM: III / VI BRANCH : ECE PULSE MODULATION
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUB.NAME : EC1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUES BRANCH : ECE YEAR/SEM: III / VI UNIT I PULSE MODULATION PART A (2
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUB.NAME : EC1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUES BRANCH : ECE YEAR/SEM: III / VI UNIT I PULSE MODULATION PART A (2
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications
 ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
Lecture #11 Overview. Vector representation of signal waveforms. Two-dimensional signal waveforms. 1 ENGN3226: Digital Communications L#
 Lecture #11 Overview Vector representation of signal waveforms Two-dimensional signal waveforms 1 ENGN3226: Digital Communications L#11 00101011 Geometric Representation of Signals We shall develop a geometric
Lecture #11 Overview Vector representation of signal waveforms Two-dimensional signal waveforms 1 ENGN3226: Digital Communications L#11 00101011 Geometric Representation of Signals We shall develop a geometric
 UNIT 2 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION DIGITAL COMMUNICATION-Introduction The techniques used to modulate digital information so that it can be transmitted via microwave, satellite or down a cable pair is different
UNIT 2 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION DIGITAL COMMUNICATION-Introduction The techniques used to modulate digital information so that it can be transmitted via microwave, satellite or down a cable pair is different
EE 460L University of Nevada, Las Vegas ECE Department
 EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
EITG05 Digital Communications
 Fourier transform EITG05 Digital Communications Lecture 4 Bandwidth of Transmitted Signals Michael Lentmaier Thursday, September 3, 08 X(f )F{x(t)} x(t) e jπ ft dt X Re (f )+jx Im (f ) X(f ) e jϕ(f ) x(t)f
Fourier transform EITG05 Digital Communications Lecture 4 Bandwidth of Transmitted Signals Michael Lentmaier Thursday, September 3, 08 X(f )F{x(t)} x(t) e jπ ft dt X Re (f )+jx Im (f ) X(f ) e jϕ(f ) x(t)f
Chapter 7 Spread-Spectrum Modulation
 Chapter 7 Spread-Spectrum Modulation Spread Spectrum Technique simply consumes spectrum in excess of the minimum spectrum necessary to send the data. 7.1 Introduction Definition of spread-spectrum modulation
Chapter 7 Spread-Spectrum Modulation Spread Spectrum Technique simply consumes spectrum in excess of the minimum spectrum necessary to send the data. 7.1 Introduction Definition of spread-spectrum modulation
AN INTRODUCTION OF ANALOG AND DIGITAL MODULATION TECHNIQUES IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
 AN INTRODUCTION OF ANALOG AND DIGITAL MODULATION TECHNIQUES IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Rashmi Pandey Vedica Institute of Technology, Bhopal Department of Electronics & Communication rashmipandey07@rediffmail.com
AN INTRODUCTION OF ANALOG AND DIGITAL MODULATION TECHNIQUES IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Rashmi Pandey Vedica Institute of Technology, Bhopal Department of Electronics & Communication rashmipandey07@rediffmail.com
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON ELEC6014W1 SEMESTER II EXAMINATIONS 2007/08 RADIO COMMUNICATION NETWORKS AND SYSTEMS Duration: 120 mins Answer THREE questions out of FIVE. University approved calculators may
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON ELEC6014W1 SEMESTER II EXAMINATIONS 2007/08 RADIO COMMUNICATION NETWORKS AND SYSTEMS Duration: 120 mins Answer THREE questions out of FIVE. University approved calculators may
Theory of Telecommunications Networks
 Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 Introduction... 6. Mathematical models for communication channels...
Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 Introduction... 6. Mathematical models for communication channels...
Fund. of Digital Communications Ch. 3: Digital Modulation
 Fund. of Digital Communications Ch. 3: Digital Modulation Klaus Witrisal witrisal@tugraz.at Signal Processing and Speech Communication Laboratory www.spsc.tugraz.at Graz University of Technology November
Fund. of Digital Communications Ch. 3: Digital Modulation Klaus Witrisal witrisal@tugraz.at Signal Processing and Speech Communication Laboratory www.spsc.tugraz.at Graz University of Technology November
Exercise 3-2. Digital Modulation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. PSK digital modulation
 Exercise 3-2 Digital Modulation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with PSK digital modulation and with a typical QPSK modulator and demodulator. DISCUSSION
Exercise 3-2 Digital Modulation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with PSK digital modulation and with a typical QPSK modulator and demodulator. DISCUSSION
College of information Technology Department of Information Networks Telecommunication & Networking I Chapter 5. Analog Transmission
 Analog Transmission 5.1 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION Digital-to-analog conversion is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal based on the information in digital data. The
Analog Transmission 5.1 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION Digital-to-analog conversion is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal based on the information in digital data. The
Exercises for chapter 2
 Exercises for chapter Digital Communications A baseband PAM system uses as receiver filter f(t) a matched filter, f(t) = g( t), having two choices for transmission filter g(t) g a (t) = ( ) { t Π =, t,
Exercises for chapter Digital Communications A baseband PAM system uses as receiver filter f(t) a matched filter, f(t) = g( t), having two choices for transmission filter g(t) g a (t) = ( ) { t Π =, t,
END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time.
 END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS 2005 Unit: Day and Time: Time Allowed: ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time. Total Number of Questions:
END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS 2005 Unit: Day and Time: Time Allowed: ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time. Total Number of Questions:
comparasion to BPSK, to distinguish those symbols, therefore, the error performance is degraded. Fig 2 QPSK signal constellation
 Study of Digital Modulation Schemes using DDS 1. Introduction Phase shift keying(psk) is a simple form of data modulation scheme in which the phase of the transmitted signal is varied to convey information.
Study of Digital Modulation Schemes using DDS 1. Introduction Phase shift keying(psk) is a simple form of data modulation scheme in which the phase of the transmitted signal is varied to convey information.
a) Abasebanddigitalcommunicationsystemhasthetransmitterfilterg(t) thatisshowninthe figure, and a matched filter at the receiver.
 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS PART A (Time: 60 minutes. Points 4/0) Last Name(s):........................................................ First (Middle) Name:.................................................
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS PART A (Time: 60 minutes. Points 4/0) Last Name(s):........................................................ First (Middle) Name:.................................................
EE3723 : Digital Communications
 EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
Wireless Communication
 Wireless Communication Systems @CS.NCTU Lecture 2: Modulation and Demodulation Reference: Chap. 5 in Goldsmith s book Instructor: Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) 1 Modulation From Wikipedia: The process of varying
Wireless Communication Systems @CS.NCTU Lecture 2: Modulation and Demodulation Reference: Chap. 5 in Goldsmith s book Instructor: Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) 1 Modulation From Wikipedia: The process of varying
(Refer Slide Time: 01:45)
 Digital Communication Professor Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module 01 Lecture 21 Passband Modulations for Bandlimited Channels In our discussion
Digital Communication Professor Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module 01 Lecture 21 Passband Modulations for Bandlimited Channels In our discussion
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F , KARUR DT.
 CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Analog & Digital
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Analog & Digital
March, 2003 IEEE P /131r0. IEEE P Wireless Personal Area Networks
 Project Title IEEE P802.15 Wireless Personal rea Networks IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal rea Networks (WPNs) PHY Proposal Using Dual Independent Single Sideband, Non-coherent M and Defined
Project Title IEEE P802.15 Wireless Personal rea Networks IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal rea Networks (WPNs) PHY Proposal Using Dual Independent Single Sideband, Non-coherent M and Defined
