SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS
|
|
|
- Lee Jordan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Volume Issue January 04, ISSN SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS Gyan Prakash Pal, Manishankar Gupta,,, Assistant Professor, Electronics & Communication Engineering Department, Shanti Institute of Technology, Meerut, India ABSTRACT Dispersion is the spreading of a light pulse as it propagates down the fiber. Since optical fiber is a waveguide, light can propagate in a number of modes. If a fiber is of large diameter, light entering at different angles will excite different modes while narrow fiber may only excite one mode. Multimode propagation will cause dispersion, which results in the spreading of pulses and limits the usable bandwidth. Single-mode fiber has much less dispersion but is more expensive to produce. Its small size, together with the fact that its numerical aperture is smaller than that of multimode fiber, makes it more difficult to couple to light sources. Dispersion distorts both pulse and analog modulation signals. known as inter symbol interference (ISI). The error rate is also a function of the signal attenuation on the link and the subsequent signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at the receiver. For no overlapping of light pulses down on an optical fiber link the digital bit rate B T must be less than the reciprocal of the broadened (through dispersion) pulse duration (τ). Hence: B T / τ The maximum bit rate for an optical channel with dispersion may be obtained by considering the light pulses at the output to have a Gaussian shape with an rms width of σ. Keywords: Modal Dispersion, Intramodal Dispersion or Chromatic Dispersion, Material Dispersion, Waveguide Dispersion I. Introduction Dispersion results when some components of the input signal spend more time traversing the fiber than other components. In a pulse modulated system, this causes the received pulse to be spread out over a longer period. It is noted that actually no power is lost to dispersion; the spreading effect reduces the peak power. In step-index fibers, the index of refraction changes radically between the core and the cladding. Graded-index fiber is a compromise multimode fiber, but the index of refraction gradually decreases away from the center of the core. Graded-index fiber has less dispersion than a multimode step-index fiber. Dispersion mechanisms within the fiber cause broadening of the transmitted light pulses as they travel along the channel. The phenomenon is illustrated in Figure () where it may be observed that each pulse broadens and overlaps with its neighbors, eventually becoming indistinguishable at the receiver input. The effect is Figure : An illustration using the digital bit pattern 0 of the broadening of light pulses as they are transmitted along a fiber: (a) fiber input; (b) fiber output at a distance L; (c) fiber output at a distance L > L Dispersion of optical energy within an optical fiber falls into following categories: Intermodal Delay or Modal Delay and Intramodal Dispersion or Chromatic Dispersion. Material Dispersion. Waveguide Dispersion 3. Polarization Mode Dispersion 5
2 Volume Issue January 04, ISSN II. Modal (Intermodal Delay) Dispersion The temporal spreading of a pulse in an optical waveguide caused by modal effects. Intermodal, or modal, dispersion occurs only in multimode fibers. Contributes to pulse broadening. Intermodal distortion or modal delay appears only in multimode fibers. This signal distortion mechanism is a result of each mode having a different value of the group velocity at a single frequency. The amount of spreading that occurs in a fiber is a function of the number of modes propagated by the fiber and length of the fiber. [] The delay differences may be caused by the dispersive properties of the waveguide material (material dispersion) and also guidance effects within the fiber structure (waveguide dispersion). Intramodal dispersion depends on the wavelength, its effect on signal distortion increases with the spectral width of the light source. Spectral width is approximately 4 to 9 percent of a central wavelength. Intramodal Dispersion depends on the following three factors. Material dispersion. waveguide dispersion 3. Cross product dispersion 3. Material dispersion Material dispersion occurs because the spreading of a light pulse is dependent on the wavelengths' interaction with the refractive index of the fiber core. Material dispersion is a function of the source spectral width, which specifies the range of wavelengths that can propagate in the fiber. Material dispersion is less at longer wavelengths. Pulse broadening due to material dispersion results from the different group velocities of the various spectral components launched into the fiber from the optical source. It occurs when the phase velocity of a plane wave propagating in the dielectric medium varies on linearly with wavelength, and a material is said to exhibit material dispersion when the second differential of the refractive index with respect to wavelength is not zero i.e. d n/dλ 0). [] Fig : Schematic diagram showing a multimode step index fiber, multimode graded index fiber and single-mode step index fiber, and illustrating the pulse broadening due to intermodal dispersion in each fiber type III. Intramodal Dispersion or Chromatic Dispersion: Intramodal dispersion may occur in all types of optical fiber and results from the finite spectral line width of the optical source. Since optical sources do not emit just a single frequency but a band of frequencies, then there may be propagation delay differences between the different spectral components of the transmitted signal. The pulse spread due to material dispersion may be obtained by considering the group delay τ g in the optical fiber which is the reciprocal of the group velocity υ g Hence the group delay is given by: Where n is the refractive index of the core material. The pulse delay τ m due to material dispersion in a fiber of length L is therefore For a source with rms spectral width σ λ and a mean wavelength λ, the rms pulse broadening due to material dispersion σm may be obtained from the 6
3 Volume Issue January 04, ISSN above expansion of Eq. in a Taylor series about λ where: As the first term in Eq. (3) usual ly dominates, especially for sources operating over the 0.8 to 0.9 μm wavelength range, then Hence the pulse spread may be evaluated by considering the dependence of τ m on λ, where from Eq. (): Therefore, substituting the expression obtained in Eq. (5) into Eq. (4), the rms pulse broadening due to material dispersion is given by: The material dispersion for optical fibers is sometimes quoted as a value for λ/( d n /dλ ) or simply d n /dλ. However, it may be given in terms of a material dispersion parameter M which is defined as: and expressed in units of ps nm- km-. Transmission characteristics of optical fibers Figure 3: The material dispersion parameter for silica as a function of wavelength 3. Waveguide dispersion Waveguide dispersion occurs because the mode propagation constant is a function of the size of the fiber's core relative to the wavelength of operation. Waveguide dispersion also occurs because light propagates differently in the core than in the cladding. Waveguide dispersion occurs when the speed of a wave in a waveguide, such as a coaxial cable or optical fiber depends on its frequency. This type of dispersion leads to signal degradation in telecommunications because the varying delay in arrival time between different components of a signal "smears out" the signal in time. It causes pulse spreading because only part of the optical power propagation along a fiber is confined to core. Dispersion arises because the fraction of light power propagating in the cladding travels faster than the light confined to core. The amount of waveguide dispersion depends on the fiber design. Single mode fiber confines only 80 percent of the power in the core for V values around. Waveguide dispersion is due to the dependency of the group velocity of the fundamental mode as well as other modes on the V number. In order to calculate waveguide dispersion, we consider that n is not dependent on wavelength. Defining the normalized propagation constant b as: / k b n n n solving for propagation constant: nk( b) Using V number / k n n n V ka( n ) / n kan Delay time due to waveguide dispersion can then be expressed as: L d( Vb) wg n n 3.3 Signal Distortion c in single mode dv fibers 7
4 Volume Issue January 04, ISSN For single mode fibers, waveguide dispersion is in the same order of material dispersion. The pulse spread can be well approximated as d wg n L d ( Vb wg L Dwg( ) V d c dv ) Figure 4: The waveguide parameter Vd (Vb)/dV as a function of the normalized frequency V for the LP 0 mode. 3.4 Overall fiber dispersion. Multimode fibers: The overall dispersion in multimode fibers comprises both chromatic and intermodal terms. The total rms pulse broadening σ T is given by: Where σ C is the intramodal or chromatic broadening and σ n is the intermodal broadening caused by delay differences between the modes (i.e. σ C for multimode step index fiber and σ g for multimode graded index fiber) The chromatic term σ c consists of pulse broadening due to both material and waveguide dispersion. However, since waveguide dispersion is generally negligible compared with material dispersion in multimode fibers, then σ c = σ m Total dispersion within single-mode fibers: The total first-order dispersion DT in a practical single-mode fiber as comprising: DT = DM + DW + DP (ps nm km ) which is simply the addition of the material dispersion DM, the waveguide dispersion DW and the profile dispersion DP components. In standard single-mode fibers the total dispersion tends to be dominated by the material dispersion of fused silica Figure 5: The material dispersion parameter (DM), the waveguide dispersion parameter (DW) and the total dispersion parameter (D T) as functions of wavelength for a conventional single-mode fiber Figure 6: The total first order intramodal dispersion as a function of wavelength for single-mode fibers with core diameters of 4, 5, and 6 μm Transmission characteristics of optical fibers Figure 7: The pulse dispersion as a function of wavelength in km single-mode fiber showing the major contributing dispersion mechanisms (dashed 8
5 Volume Issue January 04, ISSN and dotted curves) and the overall dispersion (solid curve) 3.5 The total chromatic dispersion: The variation of the chromatic dispersion with wavelength is usually characterized by the secondorder dispersion parameter or dispersion slope S which may be written as: Whereas the first-order dispersion parameter DT may be seen to be related only to the second derivative of the propagation constant β with respect to angular frequency the dispersion slope can be shown to be related to both the second and third derivatives. Higher order chromatic effects impose limitations on the possible bandwidths that may be achieved with single-mode fibers. By contrast the minimum pulse spread at a wavelength of 0.85 μm is around 00 ps nm km. An important value of the dispersion slope S(λ) is obtained at the wavelength of minimum chromatic dispersion λ 0 such that, S 0 = S(λ 0 ). S 0 is called the zero-dispersion slope which is determined only by the third derivative of β. Typical values for the dispersion slope for standard single-mode fiber at λ 0 are in the region to ps nm km. [3] The total chromatic dispersion at an arbitrary wavelength can be estimated when the two parameters λ 0 and S 0 are specified as: References [] John M. Senior Optical Fiber Communications Principles and Practice, 3 rd edition, Pearson Pentice Hall 009 [] B.C. YADAV, R.C. YADAV and G.C. DUBEY, Optical humidity sensing behavior of sol gel processed nano structured ZnO films, Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXIX, No. 3, 009 [3] Monir Hossen, Md. Asaduzzaman, Gour Chand Sarkar, Analysis of Dispersion of Single Mode Optical Fiber, published in National Conference on Communication and Information Security, Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh, pp , November 007 [4] Pallavi Gupta, Rahul Sharma, Manoj Kumar Chauhan, Lavi Agarwal, Optical Fibre Communication: Optimiztion Using Simulation, IJSRET, Volume Issue 5, pp , August, 0 IV. Conclusion Signal degradation in optical fibers due to dispersion is shown in this paper. Intermodal distortion or modal delay appears only in multimode fibers but Intramodal dispersion occurs in all types of optical fiber and results from the finite spectral line width of the optical source. Material dispersion caused by second differential of the refractive index with respect to wavelength is not zero i.e. d n/dλ 0). Waveguide dispersion occurs because light propagates differently in the core than in the cladding. 9
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS
 UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
Analysis of Dispersion of Single Mode Optical Fiber
 Daffodil International University Institutional Repository Proceedings of NCCIS November 007 007-11-4 Analysis of Dispersion of Single Mode Optical Fiber Hossen, Monir Daffodil International University
Daffodil International University Institutional Repository Proceedings of NCCIS November 007 007-11-4 Analysis of Dispersion of Single Mode Optical Fiber Hossen, Monir Daffodil International University
Chapter 3 Signal Degradation in Optical Fibers
 What about the loss in optical fiber? Why and to what degree do optical signals gets distorted as they propagate along a fiber? Fiber links are limited by in path length by attenuation and pulse distortion.
What about the loss in optical fiber? Why and to what degree do optical signals gets distorted as they propagate along a fiber? Fiber links are limited by in path length by attenuation and pulse distortion.
Lecture 10. Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers
 Lecture 10 Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide Dispersions Step-Index Fiber, Multimode and Single Mode Fibers Numerical Aperture, Coupling
Lecture 10 Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide Dispersions Step-Index Fiber, Multimode and Single Mode Fibers Numerical Aperture, Coupling
Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology Supplementary Article Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation R. Udayakumar 1 *, V. Khanaa 2 and T. Saravanan
Indian Journal of Science and Technology Supplementary Article Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation R. Udayakumar 1 *, V. Khanaa 2 and T. Saravanan
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber. Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab
 Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber
 Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic wave Ray Theory Light
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic wave Ray Theory Light
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber. Xavier Fernando Ryerson University
 Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson University The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson University The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Section B Lecture 5 FIBER CHARACTERISTICS
 Section B Lecture 5 FIBER CHARACTERISTICS Material absorption Losses Material absorption is a loss mechanism related to material composition and fabrication process for the fiber. This results in dissipation
Section B Lecture 5 FIBER CHARACTERISTICS Material absorption Losses Material absorption is a loss mechanism related to material composition and fabrication process for the fiber. This results in dissipation
DIELECTRIC WAVEGUIDES and OPTICAL FIBERS
 DIELECTRIC WAVEGUIDES and OPTICAL FIBERS Light Light Light n 2 n 2 Light n 1 > n 2 A planar dielectric waveguide has a central rectangular region of higher refractive index n 1 than the surrounding region
DIELECTRIC WAVEGUIDES and OPTICAL FIBERS Light Light Light n 2 n 2 Light n 1 > n 2 A planar dielectric waveguide has a central rectangular region of higher refractive index n 1 than the surrounding region
τ mod = T modal = longest ray path shortest ray path n 1 L 1 = L n 2 1
 S. Blair February 15, 2012 23 2.2. Pulse dispersion Pulse dispersion is the spreading of a pulse as it propagates down an optical fiber. Pulse spreading is an obvious detrimental effect that limits the
S. Blair February 15, 2012 23 2.2. Pulse dispersion Pulse dispersion is the spreading of a pulse as it propagates down an optical fiber. Pulse spreading is an obvious detrimental effect that limits the
UNIT Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion?
 UNIT 3 1. Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion? Ans: The dispersion of the transmitted optical signal causes distortion for both digital and analog transmission along optical fibers.
UNIT 3 1. Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion? Ans: The dispersion of the transmitted optical signal causes distortion for both digital and analog transmission along optical fibers.
Fiber Optic Communication Systems. Unit-05: Types of Fibers. https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif
 Unit-05: Types of Fibers https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro 1 Optical Fiber Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro
Unit-05: Types of Fibers https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro 1 Optical Fiber Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro
Module 12 : System Degradation and Power Penalty
 Module 12 : System Degradation and Power Penalty Lecture : System Degradation and Power Penalty Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Degradation during Propagation Modal Noise Dispersion
Module 12 : System Degradation and Power Penalty Lecture : System Degradation and Power Penalty Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Degradation during Propagation Modal Noise Dispersion
Waveguides and Optical Fibers
 Waveguides and Optical Fibers Dielectric Waveguides Light Light Light n n Light n > n A planar dielectric waveguide has a central rectangular region of higher refractive index n than the surrounding region
Waveguides and Optical Fibers Dielectric Waveguides Light Light Light n n Light n > n A planar dielectric waveguide has a central rectangular region of higher refractive index n than the surrounding region
Optical Fiber Technology. Photonic Network By Dr. M H Zaidi
 Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
Study of Optical Fiber Design Parameters in Fiber Optics Communications
 Kurdistan Journal of Applied Research (KJAR) Print-ISSN: 2411-7684 Electronic-ISSN: 2411-7706 kjar.spu.edu.iq Volume 2 Issue 3 August 2017 DOI: 10.24017/science.2017.3.52 Study of Optical Fiber Design
Kurdistan Journal of Applied Research (KJAR) Print-ISSN: 2411-7684 Electronic-ISSN: 2411-7706 kjar.spu.edu.iq Volume 2 Issue 3 August 2017 DOI: 10.24017/science.2017.3.52 Study of Optical Fiber Design
Photonics and Optical Communication
 Photonics and Optical Communication (Course Number 300352) Spring 2007 Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/dknipp/ 1 Photonics and Optical Communication
Photonics and Optical Communication (Course Number 300352) Spring 2007 Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/dknipp/ 1 Photonics and Optical Communication
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Optical Fiber Communication
 A Seminar report On Optical Fiber Communication Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of Mechanical SUBMITTED TO: www.studymafia.org SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org
A Seminar report On Optical Fiber Communication Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of Mechanical SUBMITTED TO: www.studymafia.org SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org
NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE of TECHNOLOGY
 NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE of TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Course : Prepared by: TCET 4102 Fiber-optic communications Module
NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE of TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Course : Prepared by: TCET 4102 Fiber-optic communications Module
2. The Basic principle of optical fibre (Or) Working principle of optical fibre (or) Total internal reflection
 Introduction Fibre optics deals with the light propagation through thin glass fibres. Fibre optics plays an important role in the field of communication to transmit voice, television and digital data signals
Introduction Fibre optics deals with the light propagation through thin glass fibres. Fibre optics plays an important role in the field of communication to transmit voice, television and digital data signals
Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS. Unit-03
 Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS Unit-03 INTRODUCTION FUNDAMENTAL IDEAS ABOUT OPTICAL FIBRE Multimode Fibres Multimode Step Index Fibres Multimode Graded Index Fibres INTRODUCTION In communication systems, there
Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS Unit-03 INTRODUCTION FUNDAMENTAL IDEAS ABOUT OPTICAL FIBRE Multimode Fibres Multimode Step Index Fibres Multimode Graded Index Fibres INTRODUCTION In communication systems, there
1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems
 OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-I : OPTICAL FIBERS STRUCTURE: 1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems The operating range of optical fiber system term and the characteristics of the four key components of
OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-I : OPTICAL FIBERS STRUCTURE: 1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems The operating range of optical fiber system term and the characteristics of the four key components of
Dispersion Pre-Compensation for a Multi-wavelength Erbium Doped Fiber Laser Using Cascaded Fiber Bragg Gratings
 Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 5(10): 1744749, 009 009, INSInet Publication Dispersion Pre-Compensation for a Multi-wavelength Erbium Doped Fiber Laser Using Cascaded Fiber Bragg Gratings 1 1 1
Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 5(10): 1744749, 009 009, INSInet Publication Dispersion Pre-Compensation for a Multi-wavelength Erbium Doped Fiber Laser Using Cascaded Fiber Bragg Gratings 1 1 1
Multimode Optical Fiber
 Multimode Optical Fiber 1 OBJECTIVE Determine the optical modes that exist for multimode step index fibers and investigate their performance on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB The backbone of optical systems
Multimode Optical Fiber 1 OBJECTIVE Determine the optical modes that exist for multimode step index fibers and investigate their performance on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB The backbone of optical systems
Characterization of Fiber Bragg Grating for Dispersion Compensation
 Instituto de Engenharia de Sistemas e Computadores do Porto Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Licenciatura em Engenharia Electrotécnica e de Computadores Characterization of Fiber Bragg
Instituto de Engenharia de Sistemas e Computadores do Porto Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Licenciatura em Engenharia Electrotécnica e de Computadores Characterization of Fiber Bragg
The absorption of the light may be intrinsic or extrinsic
 Attenuation Fiber Attenuation Types 1- Material Absorption losses 2- Intrinsic Absorption 3- Extrinsic Absorption 4- Scattering losses (Linear and nonlinear) 5- Bending Losses (Micro & Macro) Material
Attenuation Fiber Attenuation Types 1- Material Absorption losses 2- Intrinsic Absorption 3- Extrinsic Absorption 4- Scattering losses (Linear and nonlinear) 5- Bending Losses (Micro & Macro) Material
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 25 Aug 2003
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 25 Aug 2003 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 25 Aug 2003](/thumbs/84/90868967.jpg) arxiv:physics/0308087v1 [physics.optics] 25 Aug 2003 Multi-mode photonic crystal fibers for VCSEL based data transmission N. A. Mortensen, 1 M. Stach, 2 J. Broeng, 1 A. Petersson, 1 H. R. Simonsen, 1 and
arxiv:physics/0308087v1 [physics.optics] 25 Aug 2003 Multi-mode photonic crystal fibers for VCSEL based data transmission N. A. Mortensen, 1 M. Stach, 2 J. Broeng, 1 A. Petersson, 1 H. R. Simonsen, 1 and
Single Mode Optical Fiber - Dispersion
 Single Mode Optical Fiber - Dispersion 1 OBJECTIVE Characterize analytically and through simulation the effects of dispersion on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB A single mode fiber, as the name implies, supports
Single Mode Optical Fiber - Dispersion 1 OBJECTIVE Characterize analytically and through simulation the effects of dispersion on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB A single mode fiber, as the name implies, supports
Lecture 8 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 8, Slide 1
 Lecture 8 Bit error rate The Q value Receiver sensitivity Sensitivity degradation Extinction ratio RIN Timing jitter Chirp Forward error correction Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 8, Slide Bit error
Lecture 8 Bit error rate The Q value Receiver sensitivity Sensitivity degradation Extinction ratio RIN Timing jitter Chirp Forward error correction Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 8, Slide Bit error
Fiber Optic Principles. Oct-09 1
 Fiber Optic Principles Oct-09 1 Fiber Optic Basics Optical fiber Active components Attenuation Power budget Bandwidth Oct-09 2 Reference www.flukenetworks.com/fiber Handbook Fiber Optic Technologies (Vivec
Fiber Optic Principles Oct-09 1 Fiber Optic Basics Optical fiber Active components Attenuation Power budget Bandwidth Oct-09 2 Reference www.flukenetworks.com/fiber Handbook Fiber Optic Technologies (Vivec
Total care for networks. Introduction to Dispersion
 Introduction to Dispersion Introduction to PMD Version1.0- June 01, 2000 Copyright GN Nettest 2000 Introduction To Dispersion Contents Definition of Dispersion Chromatic Dispersion Polarization Mode Dispersion
Introduction to Dispersion Introduction to PMD Version1.0- June 01, 2000 Copyright GN Nettest 2000 Introduction To Dispersion Contents Definition of Dispersion Chromatic Dispersion Polarization Mode Dispersion
Fiber Optic Communications Communication Systems
 INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates
 Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates Simarpreet Kaur Gill 1, Gurinder Kaur 2 1Mtech Student, ECE Department, Rayat- Bahra University,
Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates Simarpreet Kaur Gill 1, Gurinder Kaur 2 1Mtech Student, ECE Department, Rayat- Bahra University,
Fiber Optic Communication Systems. Unit-04: Theory of Light. https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif
 Unit-04: Theory of Light https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro 1 Limitations of Ray theory Ray theory describes only the direction
Unit-04: Theory of Light https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro 1 Limitations of Ray theory Ray theory describes only the direction
There are lots of problems or challenges with fiber, Attenuation, Reflections, Dispersion and so on. So here we will look at these problems.
 The Hard theory The Hard Theory An introduction to fiber, should also include a section with some of the difficult theory. So if everything else in the book was very easily understood, then this section
The Hard theory The Hard Theory An introduction to fiber, should also include a section with some of the difficult theory. So if everything else in the book was very easily understood, then this section
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 4
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 4 Modal Propagation of Light in an Optical Fiber Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 4 Modal Propagation of Light in an Optical Fiber Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
WHITE PAPER LINK LOSS BUDGET ANALYSIS TAP APPLICATION NOTE LINK LOSS BUDGET ANALYSIS
 TAP APPLICATION NOTE LINK LOSS BUDGET ANALYSIS WHITE PAPER JULY 2017 1 Table of Contents Basic Information... 3 Link Loss Budget Analysis... 3 Singlemode vs. Multimode... 3 Dispersion vs. Attenuation...
TAP APPLICATION NOTE LINK LOSS BUDGET ANALYSIS WHITE PAPER JULY 2017 1 Table of Contents Basic Information... 3 Link Loss Budget Analysis... 3 Singlemode vs. Multimode... 3 Dispersion vs. Attenuation...
Design of a double clad optical fiber with particular consideration of leakage losses
 Vol. (4), pp. 7-62 October, 23 DOI.897/JEEER23.467 ISSN 993 822 23 Academic Journals http://www.academicjournals.org/jeeer Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Research Full Length Research
Vol. (4), pp. 7-62 October, 23 DOI.897/JEEER23.467 ISSN 993 822 23 Academic Journals http://www.academicjournals.org/jeeer Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Research Full Length Research
ECE 6323 Ridge Waveguide Laser homework
 ECE 633 Ridge Waveguide Laser homework Introduction This is a slide from a lecture we will study later on. It is about diode lasers. Although we haven t studied diode lasers, there is one aspect about
ECE 633 Ridge Waveguide Laser homework Introduction This is a slide from a lecture we will study later on. It is about diode lasers. Although we haven t studied diode lasers, there is one aspect about
Chapter 18: Fiber Optic and Laser Technology
 Chapter 18: Fiber Optic and Laser Technology Chapter 18 Objectives At the conclusion of this chapter, the reader will be able to: Describe the construction of fiber optic cable. Describe the propagation
Chapter 18: Fiber Optic and Laser Technology Chapter 18 Objectives At the conclusion of this chapter, the reader will be able to: Describe the construction of fiber optic cable. Describe the propagation
PH-7. Understanding of FWM Behavior in 2-D Time-Spreading Wavelength- Hopping OCDMA Systems. Abstract. Taher M. Bazan Egyptian Armed Forces
 PH-7 Understanding of FWM Behavior in 2-D Time-Spreading Wavelength- Hopping OCDMA Systems Taher M. Bazan Egyptian Armed Forces Abstract The behavior of four-wave mixing (FWM) in 2-D time-spreading wavelength-hopping
PH-7 Understanding of FWM Behavior in 2-D Time-Spreading Wavelength- Hopping OCDMA Systems Taher M. Bazan Egyptian Armed Forces Abstract The behavior of four-wave mixing (FWM) in 2-D time-spreading wavelength-hopping
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI - 621213 DEPARTMENT : ECE SUBJECT NAME : OPTICAL COMMUNICATION & NETWORKS SUBJECT CODE : EC 2402 UNIT II: TRANSMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF OPTICAL FIBERS PART
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI - 621213 DEPARTMENT : ECE SUBJECT NAME : OPTICAL COMMUNICATION & NETWORKS SUBJECT CODE : EC 2402 UNIT II: TRANSMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF OPTICAL FIBERS PART
The electric field for the wave sketched in Fig. 3-1 can be written as
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Light consists of an electric field and a magnetic field that oscillate at very high rates, of the order of 10 14 Hz. These fields travel in wavelike fashion at very high speeds.
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Light consists of an electric field and a magnetic field that oscillate at very high rates, of the order of 10 14 Hz. These fields travel in wavelike fashion at very high speeds.
Simulated Design and Analysis of PMD-induced Broadening of Ultra-Short Pulses in Optical Fiber Communication System
 Simulated Design and Analysis of PMD-induced Broadening of Ultra-Short Pulses in Optical Fiber Communication System H.V.Rajurkar Dept. of Electronics & Telecommunication Shri Sant Gajanan Maharaj College
Simulated Design and Analysis of PMD-induced Broadening of Ultra-Short Pulses in Optical Fiber Communication System H.V.Rajurkar Dept. of Electronics & Telecommunication Shri Sant Gajanan Maharaj College
Fiber Optic Communication Link Design
 Fiber Optic Communication Link Design By Michael J. Fujita, S.K. Ramesh, PhD, Russell L. Tatro Abstract The fundamental building blocks of an optical fiber transmission link are the optical source, the
Fiber Optic Communication Link Design By Michael J. Fujita, S.K. Ramesh, PhD, Russell L. Tatro Abstract The fundamental building blocks of an optical fiber transmission link are the optical source, the
Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks
 363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
Broadcast and distribution networks
 4/7/06 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURES Point-to-point links Point-to-point links constitute the simplest kind of lightwave systems The link length can vary from less than a kilometer (short haul) to thousands of
4/7/06 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURES Point-to-point links Point-to-point links constitute the simplest kind of lightwave systems The link length can vary from less than a kilometer (short haul) to thousands of
Dispersion Measurements of High-Speed Lightwave Systems
 Lightwave Symposium Dispersion Measurements of Presented by Johann L. Fernando, Product Manager 3-1 Topics Chromatic dispersion concepts Agilent 86037C Chromatic Dispersion Measurement System Polarization
Lightwave Symposium Dispersion Measurements of Presented by Johann L. Fernando, Product Manager 3-1 Topics Chromatic dispersion concepts Agilent 86037C Chromatic Dispersion Measurement System Polarization
SKP Engineering College
 SKP Engineering College Tiruvannamalai 606611 A Course Material on Optical Communication and Networks By M.Mageshbabu Assistant Professor Electronics and Communication Engineering Department Electronics
SKP Engineering College Tiruvannamalai 606611 A Course Material on Optical Communication and Networks By M.Mageshbabu Assistant Professor Electronics and Communication Engineering Department Electronics
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL FIBERS
 UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL FIBERS 9 Evolution of fiber optic system Element of an Optical Fiber Transmission link Total internal reflection Acceptance angle Numerical aperture Skew rays Ray Optics
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL FIBERS 9 Evolution of fiber optic system Element of an Optical Fiber Transmission link Total internal reflection Acceptance angle Numerical aperture Skew rays Ray Optics
Types of losses in optical fiber cable are: Due to attenuation, the power of light wave decreases exponentially with distance.
 UNIT-II TRANSMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF OPTICAL FIBERS SIGNAL ATTENUATION: Signal attenuation in an optical fiber is defined as the decrease in light power during light propagation along an optical fiber.
UNIT-II TRANSMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF OPTICAL FIBERS SIGNAL ATTENUATION: Signal attenuation in an optical fiber is defined as the decrease in light power during light propagation along an optical fiber.
EENG473 Mobile Communications Module 3 : Week # (12) Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Path Loss
 EENG473 Mobile Communications Module 3 : Week # (12) Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Path Loss Introduction Small-scale fading is used to describe the rapid fluctuation of the amplitude of a radio
EENG473 Mobile Communications Module 3 : Week # (12) Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Path Loss Introduction Small-scale fading is used to describe the rapid fluctuation of the amplitude of a radio
Teaching fiber-optic communications in engineering technology programs by virtual collaboration with industry
 Teaching fiber-optic communications in engineering technology programs by virtual collaboration with industry Djafar K. Mynbaev New York City College of Technology of the City University of New York, 300
Teaching fiber-optic communications in engineering technology programs by virtual collaboration with industry Djafar K. Mynbaev New York City College of Technology of the City University of New York, 300
UNIT - 7 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS
 UNIT - 7 LECTURE-1 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS WDM concepts, overview of WDM operation principles, WDM standards, Mach-Zehender interferometer, multiplexer, Isolators and circulators, direct thin film
UNIT - 7 LECTURE-1 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS WDM concepts, overview of WDM operation principles, WDM standards, Mach-Zehender interferometer, multiplexer, Isolators and circulators, direct thin film
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER
 CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic
 is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. The
is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. The
Chapter 8. Digital Links
 Chapter 8 Digital Links Point-to-point Links Link Power Budget Rise-time Budget Power Penalties Dispersions Noise Content Photonic Digital Link Analysis & Design Point-to-Point Link Requirement: - Data
Chapter 8 Digital Links Point-to-point Links Link Power Budget Rise-time Budget Power Penalties Dispersions Noise Content Photonic Digital Link Analysis & Design Point-to-Point Link Requirement: - Data
Fiber Optics IV - Testing
 PDHonline Course E311 (3 PDH) Fiber Optics IV - Testing Instructor: Lee Layton, PE 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org
PDHonline Course E311 (3 PDH) Fiber Optics IV - Testing Instructor: Lee Layton, PE 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org
10Gbps Optical Line Using Electronic Equalizer and its Cost Effectiveness
 10Gbps Optical Line Using Electronic Equalizer and its Cost Effectiveness Dr. Pulidindi Venugopal #1, Y.S.V.S.R.Karthik *2, Jariwala Rudra A #3 #1 VIT Business School, VIT University Vellore, Tamilnadu,
10Gbps Optical Line Using Electronic Equalizer and its Cost Effectiveness Dr. Pulidindi Venugopal #1, Y.S.V.S.R.Karthik *2, Jariwala Rudra A #3 #1 VIT Business School, VIT University Vellore, Tamilnadu,
Optical networking. Emilie CAMISARD GIP RENATER Optical technologies engineer Advanced IP Services
 Optical networking Emilie CAMISARD GIP RENATER Optical technologies engineer Advanced IP Services Agenda Optical fibre principle Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
Optical networking Emilie CAMISARD GIP RENATER Optical technologies engineer Advanced IP Services Agenda Optical fibre principle Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG)
 Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 35. Self-Phase-Modulation
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
2 in the multipath dispersion of the optical fibre. (b) Discuss the merits and drawbacks of cut bouls method of measurement of alternation.
 B.TECH IV Year I Semester (R09) Regular Examinations, November 2012 1 (a) Derive an expression for multiple time difference tt 2 in the multipath dispersion of the optical fibre. (b) Discuss the merits
B.TECH IV Year I Semester (R09) Regular Examinations, November 2012 1 (a) Derive an expression for multiple time difference tt 2 in the multipath dispersion of the optical fibre. (b) Discuss the merits
1. Explain in detail with necessary circuit diagram and advantages of trans impedance amplifier. [M/J-16] 10MARKS Transimpedance Preamplifier:
![1. Explain in detail with necessary circuit diagram and advantages of trans impedance amplifier. [M/J-16] 10MARKS Transimpedance Preamplifier: 1. Explain in detail with necessary circuit diagram and advantages of trans impedance amplifier. [M/J-16] 10MARKS Transimpedance Preamplifier:](/thumbs/89/99807561.jpg) 1. Explain in detail with necessary circuit diagram and advantages of trans impedance amplifier. [M/J-16] 10MARKS Transimpedance Preamplifier: Figure 4.11 Equivalent Circuit of the Transimpedance Receiver
1. Explain in detail with necessary circuit diagram and advantages of trans impedance amplifier. [M/J-16] 10MARKS Transimpedance Preamplifier: Figure 4.11 Equivalent Circuit of the Transimpedance Receiver
RZ BASED DISPERSION COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE IN DWDM SYSTEM FOR BROADBAND SPECTRUM
 RZ BASED DISPERSION COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE IN DWDM SYSTEM FOR BROADBAND SPECTRUM Prof. Muthumani 1, Mr. Ayyanar 2 1 Professor and HOD, 2 UG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
RZ BASED DISPERSION COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE IN DWDM SYSTEM FOR BROADBAND SPECTRUM Prof. Muthumani 1, Mr. Ayyanar 2 1 Professor and HOD, 2 UG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
3. Design of single-channel IM/DD systems
 3. Design of single-channel IM/DD systems Optical Communication Systems and Networks 2/38 BIBLIOGRAPHY Theory: Fiber-Optic Communications Systems Govind P. Agrawal, Chapter 5, Lightwave Systems, John Wiley
3. Design of single-channel IM/DD systems Optical Communication Systems and Networks 2/38 BIBLIOGRAPHY Theory: Fiber-Optic Communications Systems Govind P. Agrawal, Chapter 5, Lightwave Systems, John Wiley
Introduction to Fiber Optics
 Introduction to Fiber Optics Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior Milestones in Electrical Communication 1838 Samuel F.B. Morse
Introduction to Fiber Optics Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior Milestones in Electrical Communication 1838 Samuel F.B. Morse
Signal Conditioning Parameters for OOFDM System
 Chapter 4 Signal Conditioning Parameters for OOFDM System 4.1 Introduction The idea of SDR has been proposed for wireless transmission in 1980. Instead of relying on dedicated hardware, the network has
Chapter 4 Signal Conditioning Parameters for OOFDM System 4.1 Introduction The idea of SDR has been proposed for wireless transmission in 1980. Instead of relying on dedicated hardware, the network has
Unit-5. Lecture -4. Power Penalties,
 Unit-5 Lecture -4 Power Penalties, Power Penalties When any signal impairments are present, a lower optical power level arrives at the receiver compared to the ideal reception case. This lower power results
Unit-5 Lecture -4 Power Penalties, Power Penalties When any signal impairments are present, a lower optical power level arrives at the receiver compared to the ideal reception case. This lower power results
Lecture 3 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1
 Lecture 3 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion Limitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Lecture 3 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion Limitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Comparative Performance Analysis of Single Mode Fiber over Different Channels Using Matlab
 International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-0869 (O) 2454-4698 (P) Volume-8, Issue-3, March 2018 Comparative Performance Analysis of Single Mode Fiber over Different
International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-0869 (O) 2454-4698 (P) Volume-8, Issue-3, March 2018 Comparative Performance Analysis of Single Mode Fiber over Different
Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion
 36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
Index of refraction varies significantly for broadband pulses
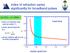 Index of refraction varies significantly for broadband pulses Δt=10 fs Δλ =90nm index of refraction may vary by nearly 1% phase speed depends on n v φ (λ) = c n(λ) n phase relations will be lost as pulse
Index of refraction varies significantly for broadband pulses Δt=10 fs Δλ =90nm index of refraction may vary by nearly 1% phase speed depends on n v φ (λ) = c n(λ) n phase relations will be lost as pulse
OPTICAL NETWORKS. Building Blocks. A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005
 OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
DEPARTMENT OF CSE QUESTION BANK
 DEPARTMENT OF CSE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: CS6304 SUBJECT NAME: ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Part-A UNIT-I ANALOG COMMUNICATION 1.Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics
DEPARTMENT OF CSE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: CS6304 SUBJECT NAME: ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Part-A UNIT-I ANALOG COMMUNICATION 1.Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics
Attenuation and Time Dispersion Measurements of Graded Index Polymer Optical Fiber for. Indoor Cellular Coverage
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 2, 2009, no. 2, 47-58 Attenuation and Time Dispersion Measurements of Graded Index Polymer Optical Fiber for Indoor Cellular Coverage S. Louvros and I. E. Kougias
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 2, 2009, no. 2, 47-58 Attenuation and Time Dispersion Measurements of Graded Index Polymer Optical Fiber for Indoor Cellular Coverage S. Louvros and I. E. Kougias
SYLLABUS Optical Fiber Communication
 SYLLABUS Optical Fiber Communication Subject Code : IA Marks : 25 No. of Lecture Hrs/Week : 04 Exam Hours : 03 Total no. of Lecture Hrs. : 52 Exam Marks : 100 UNIT - 1 PART - A OVERVIEW OF OPTICAL FIBER
SYLLABUS Optical Fiber Communication Subject Code : IA Marks : 25 No. of Lecture Hrs/Week : 04 Exam Hours : 03 Total no. of Lecture Hrs. : 52 Exam Marks : 100 UNIT - 1 PART - A OVERVIEW OF OPTICAL FIBER
Concepts of optical signal processing and optical communications
 Concepts of optical signal processing and optical communications Electronic components allowing to control electric currents with electric currents (or voltages) and integration of a large number of such
Concepts of optical signal processing and optical communications Electronic components allowing to control electric currents with electric currents (or voltages) and integration of a large number of such
End Capped High Power Assemblies
 Fiberguide s end capped fiber optic assemblies allow the user to achieve higher coupled power into a fiber core by reducing the power density at the air/ silica interface, commonly the point of laser damage.
Fiberguide s end capped fiber optic assemblies allow the user to achieve higher coupled power into a fiber core by reducing the power density at the air/ silica interface, commonly the point of laser damage.
Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks))
 Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks)) Lesson 3... Transmission Media, Part 1 Abstract The successful transmission of data depends principally on two factors: the quality of the signal being transmitted
Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks)) Lesson 3... Transmission Media, Part 1 Abstract The successful transmission of data depends principally on two factors: the quality of the signal being transmitted
Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications by Stuart M. Wentworth Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
 Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information S1. Theory of TPQI in a lossy directional coupler Following Barnett, et al. [24], we start with the probability of detecting one photon in each output of a lossy, symmetric beam
Supplementary Information S1. Theory of TPQI in a lossy directional coupler Following Barnett, et al. [24], we start with the probability of detecting one photon in each output of a lossy, symmetric beam
for SWL and LWL Fiber Systems Chromatic Dispersion Limited Link Lengths David Cunningham, Leonid Kazovsky* and M. Nowell
 Chromatic Dispersion Limited Link Lengths for SWL and LWL Fiber Systems IEEE 802 Plenary Meeting Vancouver, BC November 11-15, 1996 David Cunningham, Leonid Kazovsky* and M. Nowell Hewlett-Packard Laboratories
Chromatic Dispersion Limited Link Lengths for SWL and LWL Fiber Systems IEEE 802 Plenary Meeting Vancouver, BC November 11-15, 1996 David Cunningham, Leonid Kazovsky* and M. Nowell Hewlett-Packard Laboratories
Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating
 International Journal of Computational Engineering & Management, Vol. 15 Issue 5, September 2012 www..org 16 Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating P. K. Raghav 1,
International Journal of Computational Engineering & Management, Vol. 15 Issue 5, September 2012 www..org 16 Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating P. K. Raghav 1,
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance
 Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Keywords: Photonic crystal fibers (PCFs), Chromatic dispersion, Confinement losses, SVEI Method. Linear waveguide.
 Volume 3, Issue 11, November 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Analysis of
Volume 3, Issue 11, November 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Analysis of
Multi-Path Fading Channel
 Instructor: Prof. Dr. Noor M. Khan Department of Electronic Engineering, Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Campus, Islamabad, PAKISTAN Ph: +9 (51) 111-878787, Ext. 19 (Office), 186 (Lab) Fax: +9
Instructor: Prof. Dr. Noor M. Khan Department of Electronic Engineering, Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Campus, Islamabad, PAKISTAN Ph: +9 (51) 111-878787, Ext. 19 (Office), 186 (Lab) Fax: +9
EE 233. LIGHTWAVE. Chapter 2. Optical Fibers. Instructor: Ivan P. Kaminow
 EE 233. LIGHTWAVE SYSTEMS Chapter 2. Optical Fibers Instructor: Ivan P. Kaminow PLANAR WAVEGUIDE (RAY PICTURE) Agrawal (2004) Kogelnik PLANAR WAVEGUIDE a = (n s 2 - n c2 )/ (n f 2 - n s2 ) = asymmetry;
EE 233. LIGHTWAVE SYSTEMS Chapter 2. Optical Fibers Instructor: Ivan P. Kaminow PLANAR WAVEGUIDE (RAY PICTURE) Agrawal (2004) Kogelnik PLANAR WAVEGUIDE a = (n s 2 - n c2 )/ (n f 2 - n s2 ) = asymmetry;
UNIT-1. Basic signal processing operations in digital communication
 UNIT-1 Lecture-1 Basic signal processing operations in digital communication The three basic elements of every communication systems are Transmitter, Receiver and Channel. The Overall purpose of this system
UNIT-1 Lecture-1 Basic signal processing operations in digital communication The three basic elements of every communication systems are Transmitter, Receiver and Channel. The Overall purpose of this system
Sanjeev Kumar Raghuwanshi * andb.m.azizurrahman
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 62, 255 275, 2015 Propagation and Characterization of Novel Graded and Linearly Chirped Type s of Refractive Index Profile Symmetric Planar Slab Waveguide
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 62, 255 275, 2015 Propagation and Characterization of Novel Graded and Linearly Chirped Type s of Refractive Index Profile Symmetric Planar Slab Waveguide
Fiberoptic and Waveguide Sensors
 Fiberoptic and Waveguide Sensors Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mecahnical Engineering University of Washington Optical sensors Advantages: -immune from electromagnetic field interference (EMI) - extreme
Fiberoptic and Waveguide Sensors Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mecahnical Engineering University of Washington Optical sensors Advantages: -immune from electromagnetic field interference (EMI) - extreme
Objectives of transmission lines
 Introduction to Transmission Lines Applications Telephone Cable TV (CATV, or Community Antenna Television) Broadband network High frequency (RF) circuits, e.g., circuit board, RF circuits, etc. Microwave
Introduction to Transmission Lines Applications Telephone Cable TV (CATV, or Community Antenna Television) Broadband network High frequency (RF) circuits, e.g., circuit board, RF circuits, etc. Microwave
Differential Mode Group Delay (DMGD) in Few Mode Fibers (FMF)
 Differential Mode Group Delay (DMGD) in Few Mode Fibers (FMF) Microwave Interferometric Technique for Characterizing Few Mode Fibers Abstract We propose and experimentally demonstrate a simple and accurate
Differential Mode Group Delay (DMGD) in Few Mode Fibers (FMF) Microwave Interferometric Technique for Characterizing Few Mode Fibers Abstract We propose and experimentally demonstrate a simple and accurate
Optical Fiber. n 2. n 1. θ 2. θ 1. Critical Angle According to Snell s Law
 ECE 271 Week 10 Critical Angle According to Snell s Law n 1 sin θ 1 = n 1 sin θ 2 θ 1 and θ 2 are angle of incidences The angle of incidence is measured with respect to the normal at the refractive boundary
ECE 271 Week 10 Critical Angle According to Snell s Law n 1 sin θ 1 = n 1 sin θ 2 θ 1 and θ 2 are angle of incidences The angle of incidence is measured with respect to the normal at the refractive boundary
Fiber Optics Dr. Vipul Rastogi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee. Lecture - 04 Salient features of optical fiber II
 Fiber Optics Dr. Vipul Rastogi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture - 04 Salient features of optical fiber II In the last lecture we had understood the propagation characteristics
Fiber Optics Dr. Vipul Rastogi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture - 04 Salient features of optical fiber II In the last lecture we had understood the propagation characteristics
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. 4.1 Introduction
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Introduction In this chapter focus are given more on WDM system. The results which are obtained mainly from the simulation work are presented. In simulation analysis, the study will
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Introduction In this chapter focus are given more on WDM system. The results which are obtained mainly from the simulation work are presented. In simulation analysis, the study will
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016
 ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 016 Lecture 7: Transmitter Analysis Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Optical Modulation Techniques
ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 016 Lecture 7: Transmitter Analysis Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Optical Modulation Techniques
