LAB VII. TRANSIENT SIGNALS OF PN DIODES
|
|
|
- Kimberly Sutton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LAB VII. TRANSIENT SIGNALS OF PN DIODES 1. OBJECTIVE In his lab, you will sudy he ransien effecs in a -n juncion diode due o a sudden change in curren. Secifically, you will sudy he urn-on, urn-off, and reverse-recovery ransien behaviors of a -n juncion diode. One of he more ineresing henomena of he las ransien behavior is he charge sorage delay ha allows large reverse-bias currens o flow hrough a diode for shor eriods of ime, which is an imoran figure of meri in swiching alicaions. 2. OVERVIEW For small signals, we assume ha he sored charge densiy in he n-side and -side regions of our diode do no change significanly, i.e. we assume ha he diode is very close o seady-sae. However, his is no he case when larger volages are alied. In his lab, we will vary he magniudes of he alied volages from small o large and observe he resuling ransien behavior of he diodes. Nex we will use charge conrol analysis o make a firs order aroximaion of he curren and volage values of he diode as a funcion of ime. From hese analyses we can begin o undersand he ransien behavior, and hus he swiching rocesses, of a -n juncion diode. Informaion essenial o your undersanding of his lab: 1. Carrier injecion and sorage (Sreeman secion 5.3.2) 2. Transien and AC condiions (Sreeman secions ) Maerials necessary for his Exerimen: 1. You mus bring your own USB FLASH MEMORY. 2. Sandard esing saion 3. One recifier diode (Par: 1N4002) Ω, 2W resisor Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 1
2 3. BACKGROUND INFORMATION 3.1 CHART OF SYMBOLS Here is a char of symbols used in his lab manual. This lis is no all inclusive; however, i does conain he mos common symbols and heir unis used in his Lab. Table 1. Char of he symbols used in his lab. Symbol Symbol Name Unis h + hole Posiive charge aricle e - elecron Negaive charge aricle q magniude of elecronic charge 1.6 x C hole densiy (number h + / cm 2 ) n elecron densiy (number e - / cm 2 ) n i inrinsic elecron densiy (number e - / cm 2 ) hole concenraion a deleion edge (number h + / cm 2 ) n elecron concenraion a deleion edge (number e - / cm 2 ) k b Bolzmann's consan 1.38 x joules / K T Temeraure K E g energy ga of semiconducor ev A juncion area cm 2 g general carrier lifeime sec hole lifeime sec n elecron lifeime sec L diffusion lengh of holes cm Ln diffusion lengh of elecrons cm x x-axis for -ye maerial cm xn x-axis for n-ye maerial cm I0 reverse sauraion curren A I change in DC curren A VD DC diode volage V vd AC diode volage V vd oal diode volage V fr forward recovery ime sec rd relaxaion delay ime sec sd sorage delay ime sec rr reverse recovery ime sec Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 2
3 3.2 CHART OF EQUATIONS All of he equaions from he background orion of he manual are shown in he able below. Equaion Name Table 2. Char of he equaions used in his lab. Formula 1 Ideal Diode Equaion ( qvd ( ) / nkt ) I ( ) I e 1 D 0 2 Hole curren in a + n juncion as a funcion of he sored charge Q i Q ( ) dq ( ) ( ) d 3 Sored charge in he n-side as a funcion of ime Q ( ) I e F qal n 4 Excess charge carrier concenraion a he edge of he deleion region in he n-side 5 Volage across he + n juncion assuming quasi-seady sae condiions qv Q kt n ( ) n0 e 1 qal v( ) kt q I F ln qal n0 e 1 Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 3
4 3.3 TIME DEPENDANCE OF THE IDEAL DIODE EQUATION When ime-varying volages are alied across a -n juncion diode, he diode curren, execedly, are also ime-varying. When he ime-variaion is slower han he diffusion of minoriy carriers, he carriers have ime o equilibrae in resonse o he fields. Thus, he diode remains in a quasi-seady sae condiion and he sandard I-V relaion of he -n juncion diode under equilibrium can be assumed: ( qvd ( ) / nkt ) i ( ) I e 1. (1) D 0 If he ime-variaion of he curren and volage signals become much faser han he ime i akes for he minoriy carrier o equilibrae, he I-V characerisic can no longer be reresened by (1). Figure 1 shows how he minoriy carrier disribuion changes over ime (and as a funcion of he osiion in he n-side) when he curren flow hrough a + -n juncion diode suddenly sos (a urn-off ransien.) As soon as he curren so flowing, here will be no more hole diffusion from he -side and he sored charge disribuion decays exonenially in ime. However, is decay in sace becomes non-exonenial, which is due o he charge densiy a he deleion edge being roorional o he curren flow. Thus, when he curren flow is zero, he sloe of he charge densiy a he deleion edge mus also be zero (Figure 1). I D δ(x n) I forward Noice how he sloe is zero a he deleion edge. DC seady sae charge densiy level x n Figure 1. A urn-off ransien: curren as a funcion of ime (lef) and minoriy carrier re-disribuion over ime as a funcion of osiion in he n-side (righ). Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 4
5 This non-exonenial saial decay makes i difficul o direcly calculae he sored charge as a funcion of ime. Therefore, a quasi-seady sae aroximaion is used o simlify calculaions which in his case is simly assuming ha he decay of a sored charge highly resembles an exonenial rofile in sace as he seady sae condiion (see Figure 2). Using his aroximaion, we can calculae raher simly he sored charge in ime and find he volage across he juncion. Le s now use Figure 3 o beer undersand he quasi-seady sae aroximaion and deermine he oal diode curren. Consider a urn-on ransien signal across a -n juncion (Figure 3, lef). In his case, he curren is suddenly seed u from zero o I F. For > 0 +, he increased hole injecion curren will firs cause an increase in he excess hole densiy a he edge (x n=0) of he deleion region. Shorly afer, he excess holes will have had ime o diffuse ino he neural region of he n-side, hus increasing he charge sored in he n-side as ime rogresses from 0 o 1 o 2 o seady sae, as shown in Figure 3. The diffusion rocess akes ime and he build-u of charge wihin he n-region will always lag he build-u of he charge near x n = 0. During his ransien rocess, he oal diode curren is he sum of he recombinaion curren and he charge build-u curren, yielding: i Q ( ) dq ( ) ( ). (2) d δ(x n) Seady sae condiion excess charge carrier disribuion. Noice he difference in he doed lines(acual charge densiies) and he solid lines (quasiseady sae aroximaions) x n quasi-seady sae aroximaions Figure 2. Excess carrier concenraion as a funcion of osiion in ime: he doed lines are he acual carrier disribuions while he solid lines are quasi-seady sae charge aroximaions. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 5
6 I F I D δ(x n) Noice how he sloe of he blue line is he same as ha of he line for ime less han zero. a seady sae x n Figure 3. A urn-on ransien: curren as a funcion of ime (lef) and minoriy carrier redisribuion over ime as a funcion of osiion in he n-side (righ). 3.4 CHARGE CONTROL ANALYSIS In many cases, we will know he curren running hrough a diode and can use i o find he sored charge in a -n juncion diode. Afer finding he sored charge, i is ossible o find he charge densiy a he deleion region edge, which in urn can be used o calculae he volage across he juncion as a funcion of ime. To find he sored charge we will use Lalace ransforms on he equaion (2) o solve for he sored charge Q(). For generaliy, we are going o use I F + ΔI as our curren a =0. I F is he iniial curren which esablishes a seady sae charge; and ΔI is he change in curren, which can be a osiive or negaive ime varying funcion. Afer aking he Lalace ransform of equaion (8), one can use he iniial condiions for he charge densiy (i.e., Q(=0) = Iτ ) o solve he equaion. A bi of algebraic maniulaion and a reverse Lalace ransform will give us: Q ( ) I e qal (3) Solving for he excess charge carrier concenraion a he edge of he deleion region and equaing i o (1), we ge: qv Q kt ( ) n n0 e 1 (4) qal Solving for v(), we ge: kt I F v( ) ln e 1 (5) q qal n0 F n Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 6
7 3.5 SWITCHING TRANSIENTS Le s ake a look a he swiching ransiens in he ideal diode s I-V characerisic curves. When a diode is suddenly urned on (urn on ransien), he swiching rajecory is sraigh u he curren axis and hen across he volage axis in ime (Figure 4). I D I V D Noice where he volage is every seconds Noice he curren change is insananeous Normal I-V swiching rajecory of a diode Key Ideal Diode Trajecory V Charge Conrol Trajecory Figure 4. A urn-on ransien of a diode: he boom grah illusraes he swiching rajecory derived from our charge conrol modeling agains an ideal diode rajecory. If he curren changes less abruly, hen he swiching rajecory will more closely follow he ideal diode characerisic as shown in Figure 5. Figure 5. The swiching rajecory for differen urn-on ransien condiions. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 7
8 3.6 TIME DELAYS INCURRED BY SWITCHING Now ha you have some idea of wha a swiching rajecory is and how i works, we are going o look a a slighly more comlex circui wih a volage signal, a series resisance, and a diode configured as shown in Figure 6. The urose of his analysis is o find ou how long i akes for our swiching oeraion reach seady-sae (i.e. recover ). Since diodes are used more in AC alicaions han in DC alicaions, swiching seeds of a diode becomes a very imoran diode feaure. R VS() + - id() + + vd() Figure 6. A circui diagram for he ime delay measuremen. When a se-on volage is alied o a -n juncion wih a series resisance you should have an ouu similar o Figure 7. Noice ha he volage across he juncion sikes and hen seles down o a seady-sae volage level. When he volage across he diode has droed o wihin 10% of he seady-sae value he juncion is said o have recovered. The forward recovery ime, fr is he ime from he swiching-on of he volage source o he ime ha diode has recovered. When a volage source is urned off, he sored charge is resen unil i recombines or is dissiaed over he resisor in he circui. We will give his ye of charge sorage delay a secial name, he relaxaion delay ime, rd (see Figure 8). We sae ha he sysem is relaxed if i s curren value is wihin 10% of he seady-sae value. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 8
9 V S() V Can grow o he se on volage V Diode Charge builds unil he Diode urns on Volage Peak V = 0.1(Volage Peak Seady Sae Volage) Seady-Sae Volage fr Figure 7. A urn on ransien: he grah above shows alied volage waveform (se funcion) from he funcion generaor and he boom grah shows corresonding volage signal across he diode. Noe how o deermine he fr. V S() Cu off oin for volage signal V whole circui 0 Volage droed over he resisor. rd Seady sae volage Volage (off) Figure 8. A urn off ransien: he grah above shows alied volage waveform from he funcion generaor and he boom grah shows corresonding volage signal across he diode. Noe how o deermine he rd. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 9
10 When you swich from forward o reverse bias ( a osiive o negaive ransien or a reverse recovery ransien ) reverse recovery swiching will occur as shown in Figure 9. Figure 9-a deics he case of an ideal curren source which is seed from a forward biasing curren I F o a curren of oosie olariy. Since I F is assumed o be flowing for quie some ime we should exec o see a seady sae charge densiy a =0. Noe ha when =0 +, he sloe of he charge disribuion (i.e. ime rae of charge disribuion) mus mach he curren ha is flowing. The reverse curren consiss of minoriy carrier being drawn back across juncion ino he -ye maerial. The charge densiy in n-side is shown in Figure 10 below. Figure 9. Reverse recovery swiching rajecories for a curren source (a) and a volage source (b). Δ(xn) Figure 10. Changes in he excess charge carrier disribuion over ime. Noe he osiive sloes near he edge of he deleion region. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 10
11 When he sored charge densiy on boh sides of he juncion reaches zero, he sorage delay orion of he ransien is over. The curren source will hen raidly drive he diode owards reverse breakdown. In he case of a volage source, deiced in Figure 9-b, he curren sulied o he circui can be aroximaed as he volage sulied by he source over he series resisance. This means ha he curren sourced is deenden on he volage droed across he resisor. Afer he sorage delay ime ( sd), he diode urns off changing he diodes role in he circui from ha of a simle volage dro o imedance many orders of magniude larger han ha of he series resisance; his causes nearly all of he volage o fall across he -n juncion. Noe ha he volage droed across he resisor decays exonenially in ime (Figure 9-b, 11). Since he curren for he circui is he same as ha flowing hrough he resisor, he exonenial decay in volage causes he reverse curren o saurae o he reverse sauraion curren (Figure 9-b). The oal reverse recovery ime ( rr) is he ime i akes he volage signal across he diode o reach 10% of he seady-sae value from he reverse volage exerienced by he diode during he sorage delay eriod. Figure 11 demonsraes boh he sorage delay ime sd, and he reverse recovery ime, rr. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 11
12 V S() v F v R v Resisor() Seady Sae Volage (a some reverse-bias curren) V = 0.1( Volage Peak Seady Sae Volage ) rd sd Volage Peak rr Figure 11. A reverse recovery ransien of a diode. Noe he ime eriod of each delay on he ime axis. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 12
13 4. PREPARATION 1. Make sure you undersand how o roerly oerae he oscilloscoe by reading he secion 3.3 of he Lab 1 manual. Ouline secion 3.3 of he Lab 1 manual. 2. Ouline secions 3.3 o 3.6 of his Lab 7 manual. Take noe of key assumions and main conces conained in each secion. 5. PROCEDURE The following measuremens will be made using your recifier diode (1N4002). Since here will be subsanial currens flowing a various imes in he exerimen be sure o use a 10 Ω, 2W resisor for his exerimen. In his lab, you will manually conrol he funcion generaor and he oscilloscoe o ge he daa. 5.1 TURN-ON TRANSIENT In his secion, you will measure he forward recovery ransien of he diode volage as he ulsed curren is swiched on from I = 0 o I = I F as a funcion of I F. 1. Measure he exac value of your ~10 Ω resisor using he Keiheley SMU and record i in he Table 3. You will need exac resisance value o accuraely analyze he daa. 2. Consruc he circui as shown in Figure 12. Figure 12. Circui used o make he urn on and urn off ransien measuremens. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 13
14 3. Funcion Generaor seings: In his lab, we ll use he High-Level and Low-Level seings on he funcion generaor raher han he Amliude and Offse seings. Se he funcion generaor o ouu a square wave. Nex, se he funcion generaor o have a high-level volage of 1 V and a low-level volage of 0 V. We choose he low-level o be 0 V because we need a se funcion raher han a square wave in his ar of he exerimen. This generaes a 1V se funcion ouu from he funcion generaor. (Laer, you will increase his volage; see Table 3.) Se he frequency of he funcion generaor a 20 khz. Do no change he duy cycle (defaul value is 50 %). 4. Oscilloscoe Seings: If you are no sure how o oerae he oscilloscoe, go back o he Lab 1 manual and read more on he oscilloscoe oeraion. Adjus he waveform seings of he oscilloscoe o oimally dislay he urn-on ransien signals. Your dislayed waveforms should be similar o hose in Figure Save he waveform o your USBG o collec CH1 (diode) and CH2 (whole circui) daa searaely as.csv files. 6. Using cursors (or imor.csv files ino EXCEL sreadshee), calculae he forward curren (I F) as follows (be sure o record your values in Table 3): I VCh2, ss VCh 1, ss F, Rmeasured Here he subscri ss means seady-sae. If using cursors, be sure he robe signals are a same ground on he screen. 7. Nex, leave only he Channel across he diode (CH1) on. Use he cursors for boh volage and ime o measure he Vk - Vss and he forward recovery ime ( fr) as shown in Figure 7. Record he forward recovery ime in he Table Again, save your waveform o USB o collec daa. You can use his daa o recheck se 7 if needed. 9. Reea Ses 5-7 for he oher volages given in Table 3 and be sure o record he corresonding I F and fr. Remember o also save your waveforms. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 14
15 Table 3. Measured daa for he urn on and urn off ransien. V High-Level V Low-Level R I F V k-vss fr V ss-voff rd 1 V V 2.5 V V 5 V V 5.2 TURN-OFF TRANSIENT Nex, you will measure he urn-off characerisics of he -n juncion diode. 1. Use he same circui and he same inu as used in he revious secion (5.1), bu his ime adjus he oscilloscoe o see he close u view of he waveforms similar o he Figure 8. In oher words, you ve invesigaed he firs half, he se u orion of he signals, now scroll over (in ime) o invesigae he se down orion of he signals. 2. Use he Channel across he diode (CH1) o measure he V ss V off and relaxaion delay ime ( rd) and record i in Table 3 above; use Figure 8 as a guide o making he measuremens for all se volages shown in he Table 3. Do no forge o save waveforms o USB o collec daa for grahs for each rd measuremen (similar o se 8). You may no see a significan volage dro as noed in Figure REVERSE RECOVERY TRANSIENT Nex, you will measure he reverse recovery ransien of he diode as he ulsed curren is swiched from I F o I R. 1. Consruc he circui as shown in Figure 13. You will need only one oscilloscoe robe, se across he resisor, and aached o CH1. 2. Program he funcion generaor o: Ouu a square wave. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 15
16 Se he funcion generaor o have a high-level volage of 0.9 V and a low-level volage of 0 V (his is he firs enry of Table 9; you will be adjusing hese volages as noed in he Table). Se he frequency of he funcion generaor o 20 khz. Do no change he duy cycle (defaul value is 50 %). 3. Measure he forward curren (I F) and he reverse curren (I R) as follows and record hem in he Table 4; Use he equaion given below. You would se u he oscilloscoe o show he close u view of he waveforms similar o he Figure 11. V. R Ch1 I measured Noe: he ransien signals may no be erfecly fla. Esimae a middle region. 4. Now use he cursors for boh volage and ime o find he sorage delay ime ( sd) and he oal reverse recovery ime ( rr) as shown in Figure 11 and record hem in he Table Save waveforms o USB o collec daa; you may use his daa o verify Se 4 in case here were any errors done in lab. 6. Reea ses 3-5 for he several volage seings lised in Table 4 and record he corresonding sd and rr. 1N4002 Figure 13. Circui used o make he reverse recovery ransien measuremens. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 16
17 Table 4. Measured daa for he reverse recovery ransien. V High-Level V Low-Level V F I F V R I R sd rr 0.9 V 0.0 V 0.9 V V 0.9 V -1 V 0.9 V -2 V 0.9 V -4 V 0.5 V -1 V 0.1 V -1 V 1.4 V -1 V 1.8 V -1 V 6. LAB REPORT Tye a lab reor wih a cover shee conaining your ile, name, your lab arner s name, class, secion number, dae he lab was erformed and he dae he reor is due. Use he following ouline o draf your lab reor: ABSTRACT: Briefly describe he conens of your reor. DATA PRESENTATION: o Creae a well formaed able resening he daa from Table 3. o Creae a well formaed able resening he daa from Table 4. ANALYSIS: o Turn ON Transien Using any one aricular daa se from Table 3 (e.g., 1V High- Level and 0V Low-Level), and roerly lo he volage waveforms from boh channels and show how you calculaed he forward curren I F. You should imor your grah ino your reor and use labels o show Vch1,ss and Vch2,ss, ec. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 17
18 o o Again, using any one aricular daa se, roerly lo he Ch2 volage waveform and show how you calculaed he forward recovery ime fr. Be sure o use labels o show V eak and V ss. In your own words, briefly exlain wha is haening in he diode during his urn on ransien. Turn OFF Transien Presen all scoegrab.vi acquired daa los for his secion in one grah. Make sure i is iled, boh axes are labeled, and he los are disinguishable and have aroriae legends. Using any one aricular daa se (e.g., 1V High-Level and 0V Low-Level), roerly lo he CH2 volage waveform and show how you calculaed he relaxaion delay ime rd. Be sure o use labels o show V ss and V off. In your own words, briefly exlain wha is haening in he diode during his urn-off ransien. Reverse Recovery Transien Using any one aricular daa se (e.g., 0.9V High-Level and - 0.5V Low-Level), roerly lo he volage waveform from CH1 and show how you calculaed sd and rr. Be sure o clearly label V F, V R, sd, and rr. In your own words, briefly exlain wha is haening in he diode during his reverse recovery ransien. CONCLUSION: Describe how your analyses corresond wih he heory described in BACKGROUND secion and he exbook. Aach: Signed insrucor verificaion form. Lab VII: Transien Signals of PN Juncion Diodes Page 18
ECEN325: Electronics Spring 2017
 ECEN325: Elecronics Srg 207 Semiconducor n Juncion Diode Sam alermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Cener Texas A&M Universiy Announcemens & eadg HW5 due Mar. 9 azavi Ch2 (oional) Basic semiconducor device hysics,
ECEN325: Elecronics Srg 207 Semiconducor n Juncion Diode Sam alermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Cener Texas A&M Universiy Announcemens & eadg HW5 due Mar. 9 azavi Ch2 (oional) Basic semiconducor device hysics,
Diodes. Diodes, Page 1
 Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characerisics signal diode Measure he volage-curren characerisic of a sandard signal diode, he 1N914, using he circui shown below. The purpose of he back-o-back power supplies
Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characerisics signal diode Measure he volage-curren characerisic of a sandard signal diode, he 1N914, using he circui shown below. The purpose of he back-o-back power supplies
EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER
 EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER INTRODUCTION: Being able o ransmi a radio frequency carrier across space is of no use unless we can place informaion or inelligence upon i. This las ransmier
EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER INTRODUCTION: Being able o ransmi a radio frequency carrier across space is of no use unless we can place informaion or inelligence upon i. This las ransmier
Explanation of Maximum Ratings and Characteristics for Thyristors
 8 Explanaion of Maximum Raings and Characerisics for Thyrisors Inroducion Daa shees for s and riacs give vial informaion regarding maximum raings and characerisics of hyrisors. If he maximum raings of
8 Explanaion of Maximum Raings and Characerisics for Thyrisors Inroducion Daa shees for s and riacs give vial informaion regarding maximum raings and characerisics of hyrisors. If he maximum raings of
Table of Contents. 3.0 SMPS Topologies. For Further Research. 3.1 Basic Components. 3.2 Buck (Step Down) 3.3 Boost (Step Up) 3.4 Inverter (Buck/Boost)
 Table of Conens 3.0 SMPS Topologies 3.1 Basic Componens 3.2 Buck (Sep Down) 3.3 Boos (Sep Up) 3.4 nverer (Buck/Boos) 3.5 Flyback Converer 3.6 Curren Boosed Boos 3.7 Curren Boosed Buck 3.8 Forward Converer
Table of Conens 3.0 SMPS Topologies 3.1 Basic Componens 3.2 Buck (Sep Down) 3.3 Boos (Sep Up) 3.4 nverer (Buck/Boos) 3.5 Flyback Converer 3.6 Curren Boosed Boos 3.7 Curren Boosed Buck 3.8 Forward Converer
Lab 3 Acceleration. What You Need To Know: Physics 211 Lab
 b Lab 3 Acceleraion Wha You Need To Know: The Physics In he previous lab you learned ha he velociy of an objec can be deermined by finding he slope of he objec s posiion vs. ime graph. x v ave. = v ave.
b Lab 3 Acceleraion Wha You Need To Know: The Physics In he previous lab you learned ha he velociy of an objec can be deermined by finding he slope of he objec s posiion vs. ime graph. x v ave. = v ave.
P. Bruschi: Project guidelines PSM Project guidelines.
 Projec guidelines. 1. Rules for he execuion of he projecs Projecs are opional. Their aim is o improve he sudens knowledge of he basic full-cusom design flow. The final score of he exam is no affeced by
Projec guidelines. 1. Rules for he execuion of he projecs Projecs are opional. Their aim is o improve he sudens knowledge of he basic full-cusom design flow. The final score of he exam is no affeced by
EE201 Circuit Theory I Fall
 EE1 Circui Theory I 17 Fall 1. Basic Conceps Chaper 1 of Nilsson - 3 Hrs. Inroducion, Curren and Volage, Power and Energy. Basic Laws Chaper &3 of Nilsson - 6 Hrs. Volage and Curren Sources, Ohm s Law,
EE1 Circui Theory I 17 Fall 1. Basic Conceps Chaper 1 of Nilsson - 3 Hrs. Inroducion, Curren and Volage, Power and Energy. Basic Laws Chaper &3 of Nilsson - 6 Hrs. Volage and Curren Sources, Ohm s Law,
ORDER INFORMATION TO pin 320 ~ 340mV AMC7150DLF
 www.addmek.com DESCRIPTI is a PWM power ED driver IC. The driving curren from few milliamps up o 1.5A. I allows high brighness power ED operaing a high efficiency from 4Vdc o 40Vdc. Up o 200KHz exernal
www.addmek.com DESCRIPTI is a PWM power ED driver IC. The driving curren from few milliamps up o 1.5A. I allows high brighness power ED operaing a high efficiency from 4Vdc o 40Vdc. Up o 200KHz exernal
EE 40 Final Project Basic Circuit
 EE 0 Spring 2006 Final Projec EE 0 Final Projec Basic Circui Par I: General insrucion 1. The final projec will coun 0% of he lab grading, since i s going o ake lab sessions. All oher individual labs will
EE 0 Spring 2006 Final Projec EE 0 Final Projec Basic Circui Par I: General insrucion 1. The final projec will coun 0% of he lab grading, since i s going o ake lab sessions. All oher individual labs will
10. The Series Resistor and Inductor Circuit
 Elecronicsab.nb 1. he Series esisor and Inducor Circui Inroducion he las laboraory involved a resisor, and capacior, C in series wih a baery swich on or off. I was simpler, as a pracical maer, o replace
Elecronicsab.nb 1. he Series esisor and Inducor Circui Inroducion he las laboraory involved a resisor, and capacior, C in series wih a baery swich on or off. I was simpler, as a pracical maer, o replace
AN5028 Application note
 Applicaion noe Calculaion of urn-off power losses generaed by an ulrafas diode Inroducion This applicaion noe explains how o calculae urn-off power losses generaed by an ulrafas diode, by aking ino accoun
Applicaion noe Calculaion of urn-off power losses generaed by an ulrafas diode Inroducion This applicaion noe explains how o calculae urn-off power losses generaed by an ulrafas diode, by aking ino accoun
4.5 Biasing in BJT Amplifier Circuits
 4/5/011 secion 4_5 Biasing in MOS Amplifier Circuis 1/ 4.5 Biasing in BJT Amplifier Circuis eading Assignmen: 8086 Now le s examine how we C bias MOSFETs amplifiers! f we don bias properly, disorion can
4/5/011 secion 4_5 Biasing in MOS Amplifier Circuis 1/ 4.5 Biasing in BJT Amplifier Circuis eading Assignmen: 8086 Now le s examine how we C bias MOSFETs amplifiers! f we don bias properly, disorion can
EXPERIMENT #9 FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS LINK
 EXPERIMENT #9 FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS LINK INTRODUCTION: Much of daa communicaions is concerned wih sending digial informaion hrough sysems ha normally only pass analog signals. A elephone line is such
EXPERIMENT #9 FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS LINK INTRODUCTION: Much of daa communicaions is concerned wih sending digial informaion hrough sysems ha normally only pass analog signals. A elephone line is such
THE OSCILLOSCOPE AND NOISE. Objectives:
 -26- Preparaory Quesions. Go o he Web page hp://www.ek.com/measuremen/app_noes/xyzs/ and read a leas he firs four subsecions of he secion on Trigger Conrols (which iself is a subsecion of he secion The
-26- Preparaory Quesions. Go o he Web page hp://www.ek.com/measuremen/app_noes/xyzs/ and read a leas he firs four subsecions of he secion on Trigger Conrols (which iself is a subsecion of he secion The
Lecture 5: DC-DC Conversion
 1 / 31 Lecure 5: DC-DC Conversion ELEC-E845 Elecric Drives (5 ECTS) Mikko Rouimo (lecurer), Marko Hinkkanen (slides) Auumn 217 2 / 31 Learning Oucomes Afer his lecure and exercises you will be able o:
1 / 31 Lecure 5: DC-DC Conversion ELEC-E845 Elecric Drives (5 ECTS) Mikko Rouimo (lecurer), Marko Hinkkanen (slides) Auumn 217 2 / 31 Learning Oucomes Afer his lecure and exercises you will be able o:
DATA SHEET. 1N914; 1N916 High-speed diodes DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS Sep 03
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET M3D176 Supersedes daa of April 1996 File under Discree Semiconducors, SC01 1996 Sep 03 FEATURES Hermeically sealed leaded glass SOD27 (DO-35) package High swiching speed:
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET M3D176 Supersedes daa of April 1996 File under Discree Semiconducors, SC01 1996 Sep 03 FEATURES Hermeically sealed leaded glass SOD27 (DO-35) package High swiching speed:
<Diode Modules> RM200CY-24S HIGH POWER SWITCHING USE INSULATED TYPE
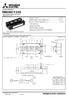 dual swich (Cahode Common) Forward curren...... 2 0 0 A Repeiive peak reverse volage V RRM... 1 2 0 0 V Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 1 5 0 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive
dual swich (Cahode Common) Forward curren...... 2 0 0 A Repeiive peak reverse volage V RRM... 1 2 0 0 V Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 1 5 0 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive
MEASUREMENTS OF VARYING VOLTAGES
 MEASUREMENTS OF ARYING OLTAGES Measuremens of varying volages are commonly done wih an oscilloscope. The oscilloscope displays a plo (graph) of volage versus imes. This is done by deflecing a sream of
MEASUREMENTS OF ARYING OLTAGES Measuremens of varying volages are commonly done wih an oscilloscope. The oscilloscope displays a plo (graph) of volage versus imes. This is done by deflecing a sream of
GaN-HEMT Dynamic ON-state Resistance characterisation and Modelling
 GaN-HEMT Dynamic ON-sae Resisance characerisaion and Modelling Ke Li, Paul Evans, Mark Johnson Power Elecronics, Machine and Conrol group Universiy of Noingham, UK Email: ke.li@noingham.ac.uk, paul.evans@noingham.ac.uk,
GaN-HEMT Dynamic ON-sae Resisance characerisaion and Modelling Ke Li, Paul Evans, Mark Johnson Power Elecronics, Machine and Conrol group Universiy of Noingham, UK Email: ke.li@noingham.ac.uk, paul.evans@noingham.ac.uk,
Memorandum on Impulse Winding Tester
 Memorandum on Impulse Winding Teser. Esimaion of Inducance by Impulse Response When he volage response is observed afer connecing an elecric charge sored up in he capaciy C o he coil L (including he inside
Memorandum on Impulse Winding Teser. Esimaion of Inducance by Impulse Response When he volage response is observed afer connecing an elecric charge sored up in he capaciy C o he coil L (including he inside
Programmable DC Electronic Load 8600 Series
 Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Load The programmable DC elecronic loads provide he performance of modular sysem DC elecronic loads in a compac benchop form facor. Wih fas ransien operaion speeds and
Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Load The programmable DC elecronic loads provide he performance of modular sysem DC elecronic loads in a compac benchop form facor. Wih fas ransien operaion speeds and
Primary Side Control SMPS with Integrated MOSFET
 General Descripion GG64 is a primary side conrol SMPS wih an inegraed MOSFET. I feaures programmable cable drop compensaion and a peak curren compensaion funcion, PFM echnology, and a CV/CC conrol loop
General Descripion GG64 is a primary side conrol SMPS wih an inegraed MOSFET. I feaures programmable cable drop compensaion and a peak curren compensaion funcion, PFM echnology, and a CV/CC conrol loop
Pulse Train Controlled PCCM Buck-Boost Converter Ming Qina, Fangfang Lib
 5h Inernaional Conference on Environmen, Maerials, Chemisry and Power Elecronics (EMCPE 016 Pulse Train Conrolled PCCM Buck-Boos Converer Ming Qina, Fangfang ib School of Elecrical Engineering, Zhengzhou
5h Inernaional Conference on Environmen, Maerials, Chemisry and Power Elecronics (EMCPE 016 Pulse Train Conrolled PCCM Buck-Boos Converer Ming Qina, Fangfang ib School of Elecrical Engineering, Zhengzhou
EE 330 Lecture 24. Amplification with Transistor Circuits Small Signal Modelling
 EE 330 Lecure 24 Amplificaion wih Transisor Circuis Small Signal Modelling Review from las ime Area Comparison beween BJT and MOSFET BJT Area = 3600 l 2 n-channel MOSFET Area = 168 l 2 Area Raio = 21:1
EE 330 Lecure 24 Amplificaion wih Transisor Circuis Small Signal Modelling Review from las ime Area Comparison beween BJT and MOSFET BJT Area = 3600 l 2 n-channel MOSFET Area = 168 l 2 Area Raio = 21:1
16.5 ADDITIONAL EXAMPLES
 16.5 ADDITIONAL EXAMPLES For reiew purposes, more examples of boh piecewise linear and incremenal analysis are gien in he following subsecions. No new maerial is presened, so readers who do no need addiional
16.5 ADDITIONAL EXAMPLES For reiew purposes, more examples of boh piecewise linear and incremenal analysis are gien in he following subsecions. No new maerial is presened, so readers who do no need addiional
GG6005. General Description. Features. Applications DIP-8A Primary Side Control SMPS with Integrated MOSFET
 General Descripion GG65 is a primary side conrol PSR SMPS wih an inegraed MOSFET. I feaures a programmable cable drop compensaion funcion, PFM echnology, and a CV/CC conrol loop wih high reliabiliy and
General Descripion GG65 is a primary side conrol PSR SMPS wih an inegraed MOSFET. I feaures a programmable cable drop compensaion funcion, PFM echnology, and a CV/CC conrol loop wih high reliabiliy and
Programmable DC Electronic Loads 8600 Series
 Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Loads The programmable DC elecronic loads provide he performance of modular sysem DC elecronic loads in a compac benchop form facor. Wih fas ransien operaion speeds and
Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Loads The programmable DC elecronic loads provide he performance of modular sysem DC elecronic loads in a compac benchop form facor. Wih fas ransien operaion speeds and
Experiment 6: Transmission Line Pulse Response
 Eperimen 6: Transmission Line Pulse Response Lossless Disribued Neworks When he ime required for a pulse signal o raverse a circui is on he order of he rise or fall ime of he pulse, i is no longer possible
Eperimen 6: Transmission Line Pulse Response Lossless Disribued Neworks When he ime required for a pulse signal o raverse a circui is on he order of he rise or fall ime of he pulse, i is no longer possible
Application Note 5324
 Desauraion Faul Deecion Opocoupler Gae Drive Producs wih Feaure: PLJ, PL0J, PLJ, PL1J and HCPLJ Applicaion Noe 1. Inroducion A desauraion faul deecion circui provides proecion for power semiconducor swiches
Desauraion Faul Deecion Opocoupler Gae Drive Producs wih Feaure: PLJ, PL0J, PLJ, PL1J and HCPLJ Applicaion Noe 1. Inroducion A desauraion faul deecion circui provides proecion for power semiconducor swiches
Parameters Affecting Lightning Backflash Over Pattern at 132kV Double Circuit Transmission Lines
 Parameers Affecing Lighning Backflash Over Paern a 132kV Double Circui Transmission Lines Dian Najihah Abu Talib 1,a, Ab. Halim Abu Bakar 2,b, Hazlie Mokhlis 1 1 Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering, Faculy
Parameers Affecing Lighning Backflash Over Paern a 132kV Double Circui Transmission Lines Dian Najihah Abu Talib 1,a, Ab. Halim Abu Bakar 2,b, Hazlie Mokhlis 1 1 Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering, Faculy
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #8 C-T Sysems: Frequency-Domain Analysis of Sysems Reading Assignmen: Secion 5.2 of Kamen and Heck /2 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual
EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #8 C-T Sysems: Frequency-Domain Analysis of Sysems Reading Assignmen: Secion 5.2 of Kamen and Heck /2 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual
PI90LV9637. LVDS High-Speed Differential Line Receivers. Features. Description. Applications PI90LV9637
 LVDS High-Speed Differenial Line Receivers Feaures Signaling Raes >400Mbps (200 MHz) Single 3.3V Power Supply Design Acceps ±350mV (ypical) Differenial Swing Maximum Differenial Skew of 0.35ns Maximum
LVDS High-Speed Differenial Line Receivers Feaures Signaling Raes >400Mbps (200 MHz) Single 3.3V Power Supply Design Acceps ±350mV (ypical) Differenial Swing Maximum Differenial Skew of 0.35ns Maximum
AN303 APPLICATION NOTE
 AN303 APPLICATION NOTE LATCHING CURRENT INTRODUCTION An imporan problem concerning he uilizaion of componens such as hyrisors or riacs is he holding of he componen in he conducing sae afer he rigger curren
AN303 APPLICATION NOTE LATCHING CURRENT INTRODUCTION An imporan problem concerning he uilizaion of componens such as hyrisors or riacs is he holding of he componen in he conducing sae afer he rigger curren
Programmable DC Electronic Loads 8600 Series
 Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Loads 99 Washingon Sree Melrose, MA 02176 Phone 781-665-1400 Toll Free 1-800-517-8431 Visi us a www.tesequipmendepo.com 2U half-rack 3U 6U USB RS232 GPIB The programmable
Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Loads 99 Washingon Sree Melrose, MA 02176 Phone 781-665-1400 Toll Free 1-800-517-8431 Visi us a www.tesequipmendepo.com 2U half-rack 3U 6U USB RS232 GPIB The programmable
Anomalous oscillations with an IMP ATT diode
 Philips ech. Rev. 32, 361-369,1971, No. 9/10/11/12 361 Anomalous oscillaions wih an IMP ATT diode P. J. de Waard Inrodueion In 1967 i was discovered ha an IMPATT-diode oscillaor can have a mode of oscillaion
Philips ech. Rev. 32, 361-369,1971, No. 9/10/11/12 361 Anomalous oscillaions wih an IMP ATT diode P. J. de Waard Inrodueion In 1967 i was discovered ha an IMPATT-diode oscillaor can have a mode of oscillaion
AK8777B. Overview. Features
 AK8777B Hall Effec IC for Pulse Encoders Overview The AK8777B is a Hall effec lach which deecs boh verical and horizonal (perpendicular and parallel o he marking side of he package) magneic field a he
AK8777B Hall Effec IC for Pulse Encoders Overview The AK8777B is a Hall effec lach which deecs boh verical and horizonal (perpendicular and parallel o he marking side of he package) magneic field a he
M2 3 Introduction to Switching Regulators. 1. What is a switching power supply? 2. What types of switchers are available?
 M2 3 Inroducion o Swiching Regulaors Objecive is o answerhe following quesions: 1. Wha is a swiching power supply? 2. Wha ypes of swichers are available? 3. Why is a swicher needed? 4. How does a swicher
M2 3 Inroducion o Swiching Regulaors Objecive is o answerhe following quesions: 1. Wha is a swiching power supply? 2. Wha ypes of swichers are available? 3. Why is a swicher needed? 4. How does a swicher
Synchronization of single-channel stepper motor drivers reduces noise and interference
 hronizaion of single-channel sepper moor drivers reduces noise and inerference n mos applicaions, a non-synchronized operaion causes no problems. However, in some cases he swiching of he wo channels inerfere,
hronizaion of single-channel sepper moor drivers reduces noise and inerference n mos applicaions, a non-synchronized operaion causes no problems. However, in some cases he swiching of he wo channels inerfere,
CoolMOS 1) Power MOSFET ISOPLUS - electrically isolated surface to heatsink Surface Mount Power Device
 CoolMOS 1) Power MOSFET ISOPLUS - elecrically isolaed surface o heasink Surface Moun Power Device S = V 25 = R DS(on) max = 45 mw Preliminary daa G KS D T D K Isolaed surface o heasink D K 3x S G KS nc
CoolMOS 1) Power MOSFET ISOPLUS - elecrically isolaed surface o heasink Surface Moun Power Device S = V 25 = R DS(on) max = 45 mw Preliminary daa G KS D T D K Isolaed surface o heasink D K 3x S G KS nc
A1 K. 12V rms. 230V rms. 2 Full Wave Rectifier. Fig. 2.1: FWR with Transformer. Fig. 2.2: Transformer. Aim: To Design and setup a full wave rectifier.
 2 Full Wave Recifier Aim: To Design and seup a full wave recifier. Componens Required: Diode(1N4001)(4),Resisor 10k,Capacior 56uF,Breadboard,Power Supplies and CRO and ransformer 230V-12V RMS. + A1 K B1
2 Full Wave Recifier Aim: To Design and seup a full wave recifier. Componens Required: Diode(1N4001)(4),Resisor 10k,Capacior 56uF,Breadboard,Power Supplies and CRO and ransformer 230V-12V RMS. + A1 K B1
(This lesson plan assumes the students are using an air-powered rocket as described in the Materials section.)
 The Mah Projecs Journal Page 1 PROJECT MISSION o MArs inroducion Many sae mah sandards and mos curricula involving quadraic equaions require sudens o solve "falling objec" or "projecile" problems, which
The Mah Projecs Journal Page 1 PROJECT MISSION o MArs inroducion Many sae mah sandards and mos curricula involving quadraic equaions require sudens o solve "falling objec" or "projecile" problems, which
Impacts of the dv/dt Rate on MOSFETs Outline:
 Ouline: A high dv/d beween he drain and source of he MOSFET may cause problems. This documen describes he cause of his phenomenon and is counermeasures. Table of Conens Ouline:... 1 Table of Conens...
Ouline: A high dv/d beween he drain and source of he MOSFET may cause problems. This documen describes he cause of his phenomenon and is counermeasures. Table of Conens Ouline:... 1 Table of Conens...
MODEL: M6SXF1. POWER INPUT DC Power R: 24 V DC
 Tension-Clamp Ulra-Slim Signal Condiioners M6S Series FUNCTION MODULE (PC programmable) Funcions & Feaures Mainenance-free ension clamp connecion Single inpu filer and funcion module 12 ypes of funcions
Tension-Clamp Ulra-Slim Signal Condiioners M6S Series FUNCTION MODULE (PC programmable) Funcions & Feaures Mainenance-free ension clamp connecion Single inpu filer and funcion module 12 ypes of funcions
Signal Characteristics
 Signal Characerisics Analog Signals Analog signals are always coninuous (here are no ime gaps). The signal is of infinie resoluion. Discree Time Signals SignalCharacerisics.docx 8/28/08 10:41 AM Page 1
Signal Characerisics Analog Signals Analog signals are always coninuous (here are no ime gaps). The signal is of infinie resoluion. Discree Time Signals SignalCharacerisics.docx 8/28/08 10:41 AM Page 1
MODEL: M6NXF1. POWER INPUT DC Power R: 24 V DC
 Screw Terminal Ulra-Slim Signal Condiioners M6N Series FUNCTION MODULE (PC programmable) Funcions & Feaures Single inpu filer and funcion module 12 ypes of funcions are PC programmable 7.5-mm wide ulra-slim
Screw Terminal Ulra-Slim Signal Condiioners M6N Series FUNCTION MODULE (PC programmable) Funcions & Feaures Single inpu filer and funcion module 12 ypes of funcions are PC programmable 7.5-mm wide ulra-slim
Lecture #7: Discrete-time Signals and Sampling
 EEL335: Discree-Time Signals and Sysems Lecure #7: Discree-ime Signals and Sampling. Inroducion Lecure #7: Discree-ime Signals and Sampling Unlike coninuous-ime signals, discree-ime signals have defined
EEL335: Discree-Time Signals and Sysems Lecure #7: Discree-ime Signals and Sampling. Inroducion Lecure #7: Discree-ime Signals and Sampling Unlike coninuous-ime signals, discree-ime signals have defined
ECMA st Edition / June Near Field Communication Wired Interface (NFC-WI)
 ECMA-373 1 s Ediion / June 2006 Near Field Communicaion Wired Inerface (NFC-WI) Sandard ECMA-373 1 s Ediion / June 2006 Near Field Communicaion Wired Inerface (NFC-WI) Ecma Inernaional Rue du Rhône 114
ECMA-373 1 s Ediion / June 2006 Near Field Communicaion Wired Inerface (NFC-WI) Sandard ECMA-373 1 s Ediion / June 2006 Near Field Communicaion Wired Inerface (NFC-WI) Ecma Inernaional Rue du Rhône 114
BOUNCER CIRCUIT FOR A 120 MW/370 KV SOLID STATE MODULATOR
 BOUNCER CIRCUIT FOR A 120 MW/370 KV SOLID STATE MODULATOR D. Gerber, J. Biela Laboraory for High Power Elecronic Sysems ETH Zurich, Physiksrasse 3, CH-8092 Zurich, Swizerland Email: gerberdo@ehz.ch This
BOUNCER CIRCUIT FOR A 120 MW/370 KV SOLID STATE MODULATOR D. Gerber, J. Biela Laboraory for High Power Elecronic Sysems ETH Zurich, Physiksrasse 3, CH-8092 Zurich, Swizerland Email: gerberdo@ehz.ch This
Noise properties in the ideal Kirchhoff-Law-Johnson-Noise. secure communication system
 Noise roeries in he ideal Kirchhoff-aw-Johnson-Noise secure communicaion sysem Zolan Gingl and ober Mingesz Dearmen of Technical Informaics, Universiy of Szeged, ungary bsrac In his aer we deermine he
Noise roeries in he ideal Kirchhoff-aw-Johnson-Noise secure communicaion sysem Zolan Gingl and ober Mingesz Dearmen of Technical Informaics, Universiy of Szeged, ungary bsrac In his aer we deermine he
Notes on the Fourier Transform
 Noes on he Fourier Transform The Fourier ransform is a mahemaical mehod for describing a coninuous funcion as a series of sine and cosine funcions. The Fourier Transform is produced by applying a series
Noes on he Fourier Transform The Fourier ransform is a mahemaical mehod for describing a coninuous funcion as a series of sine and cosine funcions. The Fourier Transform is produced by applying a series
Phase-Shifting Control of Double Pulse in Harmonic Elimination Wei Peng1, a*, Junhong Zhang1, Jianxin gao1, b, Guangyi Li1, c
 Inernaional Symposium on Mechanical Engineering and Maerial Science (ISMEMS 016 Phase-Shifing Conrol of Double Pulse in Harmonic Eliminaion Wei Peng1, a*, Junhong Zhang1, Jianxin gao1, b, Guangyi i1, c
Inernaional Symposium on Mechanical Engineering and Maerial Science (ISMEMS 016 Phase-Shifing Conrol of Double Pulse in Harmonic Eliminaion Wei Peng1, a*, Junhong Zhang1, Jianxin gao1, b, Guangyi i1, c
COMBITRON Program Schedule
 OMBITRO Program Schedule OMBITRO are supply and acuaor modules for he elecromagne cluches and brakes. As power supply for D- or A-side swiching differen single-wave and bridge recifiers as well as rapid
OMBITRO Program Schedule OMBITRO are supply and acuaor modules for he elecromagne cluches and brakes. As power supply for D- or A-side swiching differen single-wave and bridge recifiers as well as rapid
Answer Key for Week 3 Homework = 100 = 140 = 138
 Econ 110D Fall 2009 K.D. Hoover Answer Key for Week 3 Homework Problem 4.1 a) Laspeyres price index in 2006 = 100 (1 20) + (0.75 20) Laspeyres price index in 2007 = 100 (0.75 20) + (0.5 20) 20 + 15 = 100
Econ 110D Fall 2009 K.D. Hoover Answer Key for Week 3 Homework Problem 4.1 a) Laspeyres price index in 2006 = 100 (1 20) + (0.75 20) Laspeyres price index in 2007 = 100 (0.75 20) + (0.5 20) 20 + 15 = 100
Control and Protection Strategies for Matrix Converters. Control and Protection Strategies for Matrix Converters
 Conrol and Proecion Sraegies for Marix Converers Dr. Olaf Simon, Siemens AG, A&D SD E 6, Erlangen Manfred Bruckmann, Siemens AG, A&D SD E 6, Erlangen Conrol and Proecion Sraegies for Marix Converers To
Conrol and Proecion Sraegies for Marix Converers Dr. Olaf Simon, Siemens AG, A&D SD E 6, Erlangen Manfred Bruckmann, Siemens AG, A&D SD E 6, Erlangen Conrol and Proecion Sraegies for Marix Converers To
Chapter 2 Introduction: From Phase-Locked Loop to Costas Loop
 Chaper 2 Inroducion: From Phase-Locked Loop o Cosas Loop The Cosas loop can be considered an exended version of he phase-locked loop (PLL). The PLL has been invened in 932 by French engineer Henri de Belleszice
Chaper 2 Inroducion: From Phase-Locked Loop o Cosas Loop The Cosas loop can be considered an exended version of he phase-locked loop (PLL). The PLL has been invened in 932 by French engineer Henri de Belleszice
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Second ediion ober W. Erickson Dragan Maksimovic Universiy of Colorado, Boulder.. Inroducion o power processing.. Some applicaions of power elecronics.3. Elemens of power elecronics Summary of he course.
Second ediion ober W. Erickson Dragan Maksimovic Universiy of Colorado, Boulder.. Inroducion o power processing.. Some applicaions of power elecronics.3. Elemens of power elecronics Summary of he course.
Three phase full Bridge with Trench MOSFETs in DCB isolated high current package
 MTI2WX75GD Three phase full Bridge wih Trench MOSFETs in DCB isolaed high curren package S = 75 V 25 = 255 R DSon yp. = 1.1 mw Par number MTI2WX75GD G1 L1+ L2+ T1 T3 T5 G3 G5 L3+ Surface Moun Device S1
MTI2WX75GD Three phase full Bridge wih Trench MOSFETs in DCB isolaed high curren package S = 75 V 25 = 255 R DSon yp. = 1.1 mw Par number MTI2WX75GD G1 L1+ L2+ T1 T3 T5 G3 G5 L3+ Surface Moun Device S1
 Disribued by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The conen and copyrighs of he aached maerial are he propery of is owner. 16K-Bi CMOS PARALLEL E 2 PROM FEATURES Fas Read Access Times: 200 ns Low Power CMOS
Disribued by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The conen and copyrighs of he aached maerial are he propery of is owner. 16K-Bi CMOS PARALLEL E 2 PROM FEATURES Fas Read Access Times: 200 ns Low Power CMOS
Photo Modules for PCM Remote Control Systems
 Phoo Modules for PCM Remoe Conrol Sysems Descripion The HS38B series are miniaurized receivers for infrared remoe conrol sysems. PIN diode and preamplifier are assembled on lead frame, he epoxy package
Phoo Modules for PCM Remoe Conrol Sysems Descripion The HS38B series are miniaurized receivers for infrared remoe conrol sysems. PIN diode and preamplifier are assembled on lead frame, he epoxy package
Dead Zone Compensation Method of H-Bridge Inverter Series Structure
 nd Inernaional Conference on Elecrical, Auomaion and Mechanical Engineering (EAME 7) Dead Zone Compensaion Mehod of H-Bridge Inverer Series Srucure Wei Li Insiue of Elecrical Engineering and Informaion
nd Inernaional Conference on Elecrical, Auomaion and Mechanical Engineering (EAME 7) Dead Zone Compensaion Mehod of H-Bridge Inverer Series Srucure Wei Li Insiue of Elecrical Engineering and Informaion
f t 2cos 2 Modulator Figure 21: DSB-SC modulation.
 4.5 Ampliude modulaion: AM 4.55. DSB-SC ampliude modulaion (which is summarized in Figure 21) is easy o undersand and analyze in boh ime and frequency domains. However, analyical simpliciy is no always
4.5 Ampliude modulaion: AM 4.55. DSB-SC ampliude modulaion (which is summarized in Figure 21) is easy o undersand and analyze in boh ime and frequency domains. However, analyical simpliciy is no always
A New Voltage Sag and Swell Compensator Switched by Hysteresis Voltage Control Method
 Proceedings of he 8h WSEAS Inernaional Conference on ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS, HIGH VOLTAGES, ELECTRIC MACHINES (POWER '8) A New Volage Sag and Swell Compensaor Swiched by Hyseresis Volage Conrol Mehod AMIR
Proceedings of he 8h WSEAS Inernaional Conference on ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS, HIGH VOLTAGES, ELECTRIC MACHINES (POWER '8) A New Volage Sag and Swell Compensaor Swiched by Hyseresis Volage Conrol Mehod AMIR
CURRENT MODE PWM+PFM CONTROLLER WITH BUILT-IN HIGH VOLTAGE MOSFET
 CURRENT MODE PWM+PFM CONTROLLER WITH BUILT-IN HIGH VOLTAGE MOSFET DESCRIPTION SD6835 is curren mode PWM+PFM conroller used for SMPS wih buil-in high-volage MOSFET and exernal sense resisor. I feaures low
CURRENT MODE PWM+PFM CONTROLLER WITH BUILT-IN HIGH VOLTAGE MOSFET DESCRIPTION SD6835 is curren mode PWM+PFM conroller used for SMPS wih buil-in high-volage MOSFET and exernal sense resisor. I feaures low
BELECTRIC: Enhanced Frequency Control Capability
 BELECTRIC: Enhanced Frequency Conrol Capabiliy Tim Müller, CTO 28/03/2018 0 Company profile Yearly oal revenue of 550M EUR 84 MW / 95 MWh energy sorage sysems insalled or under consrucion Over 120 paens
BELECTRIC: Enhanced Frequency Conrol Capabiliy Tim Müller, CTO 28/03/2018 0 Company profile Yearly oal revenue of 550M EUR 84 MW / 95 MWh energy sorage sysems insalled or under consrucion Over 120 paens
DISCONTINUED MODEL Replaced with Model JPS3
 Plug-in Signal Condiioners M-UNIT PUSE ADDER (field-programmable) MODE MODE & SUFFIX CODE SEECTI MODE A : Dry conac B :Volage pulse (Specify sensiiviy) C : V pulse (sensiiviy V) D : V/V pulse (sensiiviy
Plug-in Signal Condiioners M-UNIT PUSE ADDER (field-programmable) MODE MODE & SUFFIX CODE SEECTI MODE A : Dry conac B :Volage pulse (Specify sensiiviy) C : V pulse (sensiiviy V) D : V/V pulse (sensiiviy
Communications II Lecture 7: Performance of digital modulation
 Communicaions II Lecure 7: Performance of digial modulaion Professor Kin K. Leung EEE and Compuing Deparmens Imperial College London Copyrigh reserved Ouline Digial modulaion and demodulaion Error probabiliy
Communicaions II Lecure 7: Performance of digial modulaion Professor Kin K. Leung EEE and Compuing Deparmens Imperial College London Copyrigh reserved Ouline Digial modulaion and demodulaion Error probabiliy
Transmission Lines. Transmission Lines :: Topics. Introduction Wave Propagation Termination Reflections Summary. Introduction.
 Transmission Lines Digial Design and Compuer Archiecure David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Transmission Lines :: Topics Inroducion Wave Propagaion Terminaion Reflecions Summary TL- TL- Inroducion
Transmission Lines Digial Design and Compuer Archiecure David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Transmission Lines :: Topics Inroducion Wave Propagaion Terminaion Reflecions Summary TL- TL- Inroducion
Design and Simulation of Remotely Power Controller
 Inernaional Journal of Alied Engineering Research ISSN 973-456 olume 1, Number 1 (15. 369-366 Research India Publicaions h://www.riublicaion.com Design and Simulaion of Remoely Power Conroller Hussain
Inernaional Journal of Alied Engineering Research ISSN 973-456 olume 1, Number 1 (15. 369-366 Research India Publicaions h://www.riublicaion.com Design and Simulaion of Remoely Power Conroller Hussain
Three phase full Bridge with Trench MOSFETs in DCB-isolated high-current package
 MTI145WX1GD Three phase full Bridge wih Trench MOSFETs in DCB-isolaed high-curren package S = 1 V 5 = 19 R DSon yp. = 1.7 mw Par number MTI145WX1GD L1+ L+ L3+ G1 G3 G5 Surface Moun Device S1 S3 S5 L1 L
MTI145WX1GD Three phase full Bridge wih Trench MOSFETs in DCB-isolaed high-curren package S = 1 V 5 = 19 R DSon yp. = 1.7 mw Par number MTI145WX1GD L1+ L+ L3+ G1 G3 G5 Surface Moun Device S1 S3 S5 L1 L
AM Demodulation (peak detect.)
 AM Deodulaion (peak deec.) Deodulaion is abou recovering he original signal--crysal Radio Exaple Anenna = Long Wire FM AM Tuning Circui A siple Diode! Deodulaion Circui (envelop of AM Signal) Filer (Mechanical)
AM Deodulaion (peak deec.) Deodulaion is abou recovering he original signal--crysal Radio Exaple Anenna = Long Wire FM AM Tuning Circui A siple Diode! Deodulaion Circui (envelop of AM Signal) Filer (Mechanical)
Power losses in pulsed voltage source inverters/rectifiers with sinusoidal currents
 ree-wheeling diode Turn-off power dissipaion: off/d = f s * E off/d (v d, i LL, T j/d ) orward power dissipaion: fw/t = 1 T T 1 v () i () d Neglecing he load curren ripple will resul in: fw/d = i Lavg
ree-wheeling diode Turn-off power dissipaion: off/d = f s * E off/d (v d, i LL, T j/d ) orward power dissipaion: fw/t = 1 T T 1 v () i () d Neglecing he load curren ripple will resul in: fw/d = i Lavg
< IGBT MODULES > CM100DY-34A HIGH POWER SWITCHING USE INSULATED TYPE APPLICATION
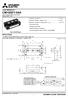 CMDY-34A Dual (Half-Bridge) Collecor curren I C...... A Collecor-emier volage CES... 7 Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 5 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive complian UL Recognized under
CMDY-34A Dual (Half-Bridge) Collecor curren I C...... A Collecor-emier volage CES... 7 Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 5 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive complian UL Recognized under
ANALOG AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS : CHAPTER 3
 Laboraory # Chap 3 Objecives Linear Sysem Response: general case Undersand he difference and he relaionship beween a sep and impulse response. Deermine he limis of validiy of an approximaed impulse response.
Laboraory # Chap 3 Objecives Linear Sysem Response: general case Undersand he difference and he relaionship beween a sep and impulse response. Deermine he limis of validiy of an approximaed impulse response.
= f 8 f 2 L C. i C. 8 f C. Q1 open Q2 close (1+D)T DT 2. i C = i L. Figure 2: Typical Waveforms of a Step-Down Converter.
 Inroducion Oupu Volage ipple in Sep-Down and Sep-Up Swiching egulaors Oupu volage ripple is always an imporan performance parameer wih DC-DC converers. For inducor-based swiching regulaors, several key
Inroducion Oupu Volage ipple in Sep-Down and Sep-Up Swiching egulaors Oupu volage ripple is always an imporan performance parameer wih DC-DC converers. For inducor-based swiching regulaors, several key
Photo Modules for PCM Remote Control Systems
 Phoo Modules for PCM Remoe Conrol Sysems Available ypes for differen carrier frequencies Type fo Type fo TSOP223 3 khz TSOP2233 33 khz TSOP2236 36 khz TSOP2237 36.7 khz TSOP2238 38 khz TSOP224 4 khz TSOP2256
Phoo Modules for PCM Remoe Conrol Sysems Available ypes for differen carrier frequencies Type fo Type fo TSOP223 3 khz TSOP2233 33 khz TSOP2236 36 khz TSOP2237 36.7 khz TSOP2238 38 khz TSOP224 4 khz TSOP2256
MODELING OF CROSS-REGULATION IN MULTIPLE-OUTPUT FLYBACK CONVERTERS
 MODELING OF CROSS-REGULATION IN MULTIPLE-OUTPUT FLYBACK CONVERTERS Dragan Maksimovićand Rober Erickson Colorado Power Elecronics Cener Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Universiy of Colorado,
MODELING OF CROSS-REGULATION IN MULTIPLE-OUTPUT FLYBACK CONVERTERS Dragan Maksimovićand Rober Erickson Colorado Power Elecronics Cener Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Universiy of Colorado,
APPLICATION. CM150DUS-12F - 4 th generation Fast switching IGBT module - MITSUBISHI IGBT MODULES CM150DUS-12F HIGH POWER SWITCHING USE INSULATED TYPE
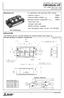 CM5DUS-2F CM5DUS-2F - 4 h generaion Fas swiching IGBT module - Collecor curren I C...... 5A Collecor-emier volage CES... 6 Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 5 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive
CM5DUS-2F CM5DUS-2F - 4 h generaion Fas swiching IGBT module - Collecor curren I C...... 5A Collecor-emier volage CES... 6 Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 5 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive
Time Control Technique
 Time Conrol Technique muliimer Mulifuncion Relay MK 785N/2 23928 Your Advanages Up o 1 funcions in one uni Simplified sorage Increased flexibiliy Quick seing of long ime values Opions wih Pluggable Terminal
Time Conrol Technique muliimer Mulifuncion Relay MK 785N/2 23928 Your Advanages Up o 1 funcions in one uni Simplified sorage Increased flexibiliy Quick seing of long ime values Opions wih Pluggable Terminal
Communication Systems. Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering
 COMM 704: Communicaion Lecure : Analog Mulipliers Dr Mohamed Abd El Ghany Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Mohamed.abdel-ghany@guc.edu.eg nroducion Nonlinear operaions on coninuous-valued analog signals are ofen
COMM 704: Communicaion Lecure : Analog Mulipliers Dr Mohamed Abd El Ghany Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Mohamed.abdel-ghany@guc.edu.eg nroducion Nonlinear operaions on coninuous-valued analog signals are ofen
TSOP322.. IR Receiver Modules for Remote Control Systems VISHAY. Vishay Semiconductors
 TSOP3.. IR Receiver Modules for Remoe Conrol Sysems Descripion The TSOP3.. - series are miniaurized receivers for infrared remoe conrol sysems. PIN diode and preamplifier are assembled on lead frame, he
TSOP3.. IR Receiver Modules for Remoe Conrol Sysems Descripion The TSOP3.. - series are miniaurized receivers for infrared remoe conrol sysems. PIN diode and preamplifier are assembled on lead frame, he
Proceedings of International Conference on Mechanical, Electrical and Medical Intelligent System 2017
 on Mechanical, Elecrical and Medical Inelligen Sysem 7 Consan On-ime Conrolled Four-phase Buck Converer via Saw-oohwave Circui and is Elemen Sensiiviy Yi Xiong a, Koyo Asaishi b, Nasuko Miki c, Yifei Sun
on Mechanical, Elecrical and Medical Inelligen Sysem 7 Consan On-ime Conrolled Four-phase Buck Converer via Saw-oohwave Circui and is Elemen Sensiiviy Yi Xiong a, Koyo Asaishi b, Nasuko Miki c, Yifei Sun
Time Control Technique
 Time Conrol Technique MULTITIMER Mulifuncion Relay MK 785N/2 23928 Your Advanages Up o 1 funcions in one uni Simplified sorage Increased flexibiliy Quick seing of long ime values Circui Diagrams B1 22
Time Conrol Technique MULTITIMER Mulifuncion Relay MK 785N/2 23928 Your Advanages Up o 1 funcions in one uni Simplified sorage Increased flexibiliy Quick seing of long ime values Circui Diagrams B1 22
TSOP12.. IR Receiver Modules for Remote Control Systems VISHAY. Vishay Semiconductors
 TSOP1.. IR Receiver Modules for Remoe Conrol Sysems Descripion The TSOP1.. - series are miniaurized receivers for infrared remoe conrol sysems. PIN diode and preamplifier are assembled on lead frame, he
TSOP1.. IR Receiver Modules for Remoe Conrol Sysems Descripion The TSOP1.. - series are miniaurized receivers for infrared remoe conrol sysems. PIN diode and preamplifier are assembled on lead frame, he
FROM ANALOG TO DIGITAL
 FROM ANALOG TO DIGITAL OBJECTIVES The objecives of his lecure are o: Inroduce sampling, he Nyquis Limi (Shannon s Sampling Theorem) and represenaion of signals in he frequency domain Inroduce basic conceps
FROM ANALOG TO DIGITAL OBJECTIVES The objecives of his lecure are o: Inroduce sampling, he Nyquis Limi (Shannon s Sampling Theorem) and represenaion of signals in he frequency domain Inroduce basic conceps
<IGBT Modules> CM900DUC-24S HIGH POWER SWITCHING USE INSULATED TYPE
 dual swich (Half-Bridge) Collecor curren I C...... 9 A Collecor-emier volage CES... 1 2 Maximum juncion emperaure T j m a x... 1 7 5 C Fla base Type Copper base plae (non-plaing) RoHS Direcive complian
dual swich (Half-Bridge) Collecor curren I C...... 9 A Collecor-emier volage CES... 1 2 Maximum juncion emperaure T j m a x... 1 7 5 C Fla base Type Copper base plae (non-plaing) RoHS Direcive complian
AN UVLO (Under Voltage Lock Out) FUNCTION Calculation of Minimum Value of IGBT external Gate Resistance RG. Table 2-1.
 A p p l i c a i o n Noe AN318 IGBT/Power MOSFET Gae Drive Phoocoupler Technical Markeing Deparmen Compound Semiconducor Devices Business Division Analog & Power Devices Business Uni Renesas Elecronics
A p p l i c a i o n Noe AN318 IGBT/Power MOSFET Gae Drive Phoocoupler Technical Markeing Deparmen Compound Semiconducor Devices Business Division Analog & Power Devices Business Uni Renesas Elecronics
Control circuit for a Self-Oscillating Power Supply (SOPS) TDA8385
 FEATURES Bandgap reference generaor Slow-sar circuiry Low-loss peak curren sensing Over-volage proecion Hyseresis conrolled sand-by funcion Error amplifier wih gain seing Programmable ransfer characer
FEATURES Bandgap reference generaor Slow-sar circuiry Low-loss peak curren sensing Over-volage proecion Hyseresis conrolled sand-by funcion Error amplifier wih gain seing Programmable ransfer characer
Active Filters - 1. Active Filters - 2
 PHY35 - Elecronics Laboraory, all Term (K rong) Acie ilers - By combining op-amps wih energy-sorage elemens, circuis can be designed o gie frequency-dependen op-amp responses Acie filers are hose ha use
PHY35 - Elecronics Laboraory, all Term (K rong) Acie ilers - By combining op-amps wih energy-sorage elemens, circuis can be designed o gie frequency-dependen op-amp responses Acie filers are hose ha use
< IGBT MODULES > CM450DY-24S HIGH POWER SWITCHING USE INSULATED TYPE APPLICATION
 Dual (Half-Bridge) Collecor curren I C...... 4A * Collecor-emier volage CES... 2 Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 75 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive compliance UL Recognized under UL557,
Dual (Half-Bridge) Collecor curren I C...... 4A * Collecor-emier volage CES... 2 Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 75 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive compliance UL Recognized under UL557,
PRELIMINARY N-CHANNEL MOSFET 1 P-CHANNEL MOSFET. Top View
 HEXFET Power MOSFET dvanced Process Technology Ulra Low On-Resisance ual N and P Channel Mosfe Surface Moun vailable in Tape & Reel ynamic dv/d Raing Fas Swiching escripion PRELIMINRY N-CHNNEL MOSFET 8
HEXFET Power MOSFET dvanced Process Technology Ulra Low On-Resisance ual N and P Channel Mosfe Surface Moun vailable in Tape & Reel ynamic dv/d Raing Fas Swiching escripion PRELIMINRY N-CHNNEL MOSFET 8
MX629. DELTA MODULATION CODEC meets Mil-Std DATA BULLETIN. Military Communications Multiplexers, Switches, & Phones
 DATA BULLETIN MX629 DELTA MODULATION CODEC mees Mil-Sd-188-113 Feaures Mees Mil-Sd-188-113 Single Chip Full Duplex CVSD CODEC On-chip Inpu and Oupu Filers Programmable Sampling Clocks 3- or 4-bi Companding
DATA BULLETIN MX629 DELTA MODULATION CODEC mees Mil-Sd-188-113 Feaures Mees Mil-Sd-188-113 Single Chip Full Duplex CVSD CODEC On-chip Inpu and Oupu Filers Programmable Sampling Clocks 3- or 4-bi Companding
A-LEVEL Electronics. ELEC4 Programmable Control Systems Mark scheme June Version: 1.0 Final
 A-LEVEL Elecronics ELEC4 Programmable Conrol Sysems scheme 243 June 26 Version:. Final schemes are prepared by he Lead Assessmen Wrier and considered, ogeher wih he relevan quesions, by a panel of subjec
A-LEVEL Elecronics ELEC4 Programmable Conrol Sysems scheme 243 June 26 Version:. Final schemes are prepared by he Lead Assessmen Wrier and considered, ogeher wih he relevan quesions, by a panel of subjec
IXBN42N170A V CES = 1700V. = 21A V CE(sat) 6.0V t fi. = 20ns. High Voltage, High Gain BIMOSFET TM Monolithic Bipolar MOS Transistor
 Preliminary Technical Informaion High Volage, High Gain BIMOSFET TM Monolihic Bipolar MOS Transisor IXBNN7A S = 7V 9 = A (sa).v fi = ns E SOT-7B, minibloc E33 Symbol Tes Condiions Maximum Raings S = C
Preliminary Technical Informaion High Volage, High Gain BIMOSFET TM Monolihic Bipolar MOS Transisor IXBNN7A S = 7V 9 = A (sa).v fi = ns E SOT-7B, minibloc E33 Symbol Tes Condiions Maximum Raings S = C
PI90LV022, PI90LVB022
 PI9LV, PI9LVB 456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789 LVDS Mux/Repeaer Feaures Mees or Exceeds he Requiremens of ANSI TIA/ EIA-644-995 Designed for Signaling Raes
PI9LV, PI9LVB 456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789456789 LVDS Mux/Repeaer Feaures Mees or Exceeds he Requiremens of ANSI TIA/ EIA-644-995 Designed for Signaling Raes
< IGBT MODULES > CM600DU-12NFH HIGH POWER HIGH FREQUENTLY SWITCHING USE INSULATED TYPE
 Dual (Half-Bridge) Collecor curren I C...... 6A Collecor-emier volage CES... 6 Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 5 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive complian UL Recognized under UL557, File
Dual (Half-Bridge) Collecor curren I C...... 6A Collecor-emier volage CES... 6 Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 5 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive complian UL Recognized under UL557, File
ECE-517 Reinforcement Learning in Artificial Intelligence
 ECE-517 Reinforcemen Learning in Arificial Inelligence Lecure 11: Temporal Difference Learning (con.), Eligibiliy Traces Ocober 8, 2015 Dr. Iamar Arel College of Engineering Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering
ECE-517 Reinforcemen Learning in Arificial Inelligence Lecure 11: Temporal Difference Learning (con.), Eligibiliy Traces Ocober 8, 2015 Dr. Iamar Arel College of Engineering Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering
<IGBT Modules> CM450DY-24S HIGH POWER SWITCHING USE INSULATED TYPE
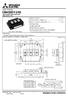 dual swich (Half-Bridge) Collecor curren I C...... 4 1 A * Collecor-emier volage CES... 1 2 Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 1 7 5 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive complian UL Recognized
dual swich (Half-Bridge) Collecor curren I C...... 4 1 A * Collecor-emier volage CES... 1 2 Maximum juncion emperaure T jmax... 1 7 5 C Fla base Type Copper base plae RoHS Direcive complian UL Recognized
HS0038B5. IR Receiver Modules for Remote Control Systems. Vishay Semiconductors
 IR Receiver Modules for Remoe Conrol Sysems Descripion The - series are miniaurized receivers for infrared remoe conrol sysems. PIN diode and preamplifier are assembled on lead frame, he epoxy package
IR Receiver Modules for Remoe Conrol Sysems Descripion The - series are miniaurized receivers for infrared remoe conrol sysems. PIN diode and preamplifier are assembled on lead frame, he epoxy package
 - MPD series using 5 h Generaion IGBT and FWDi - I C.... 4 A CES....... 2 Fla base Type Copper (non-plaing) base plae RoHS Direcive complian Dual swich (Half-Bridge) UL Recognized under UL557, File E323585
- MPD series using 5 h Generaion IGBT and FWDi - I C.... 4 A CES....... 2 Fla base Type Copper (non-plaing) base plae RoHS Direcive complian Dual swich (Half-Bridge) UL Recognized under UL557, File E323585
