Low-Driving-Voltage Silicon DP-IQ Modulator
|
|
|
- Anthony Howard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Low-Driving-Voltage Silicon DP-IQ Modulator Kazuhiro Goi, 1 Norihiro Ishikura, 1 Haike Zhu, 1 Kensuke Ogawa, 1 Yuki Yoshida, 2 Ken-ichi Kitayama, 2, 3 Tsung-Yang Liow, 4 Xiaoguang Tu, 4 Guo-Qiang Lo, 4 and Dim-Lee Kwong 4 Silicon photonics is a promising technology to bring drastic reduction in cost and size for various kinds of optical devices. In this paper, we report a low-driving-voltage silicon dual polarization (DP) in-phase quadrature modulator especially for a digital coherent transmission system requiring low power consumption. The modulator includes a newly developed phase shifter and polarization multiplexing waveguide. The phase shifter employs a p-n junction formed in vertical direction, which enhances modulation efficiency and provides a low Vp of 2.5 V. The polarization multiplexing waveguide enables polarization rotation and combination at a low insertion loss of less than.5 db in a broad wavelength range of C- and L-bands. A packaged modulator has exhibited high-speed modulations such as DP 16- and 32-quadrature amplitude modulations, and achieved 2-km standard SMF transmission in DP quadrature phases shift keying well used in commercial optical fiber networks. 1. Introduction Worldwide spread of cloud services with high-speed IT equipment has generated huge amount of traffic in telecommunication networks. Led by these demands, digital coherent transmission has been introduced to long-haul networks and upgraded its capacity to 1 Gb/s/l. This technology is now expected to be applied to shorter reach networks such as metro and datacenter interconnects, where a coherent transceiver for the digital coherent transmission needs to be operated in small space with low power consumption 1). The standardization organization Optical Internetworking Forum, for example, published the specification for compact pluggable form-factor of coherent transceiver CFP2-ACO (C-form factor pluggable analog coherent optics), and announced that they were undertaking standardization of next-generation form-factors 2). A coherent transceiver for the digital coherent transmission uses complicated optical devices to deal with both amplitude and phase of light. For the nextgeneration coherent transceiver, the optical devices need to be improved in size and power consumption as well as electrical devices. Silicon photonics attracts attention as a promising technology giving drastic improvement to such optical devices. A high refractive index contrast waveguides made of silicon and silica confines optical light in small region, allowing high-density deployment of waveguide 1 Optical Device Research Department of Advanced Technology Laboratory 2 National Institute of Information and Communications Technology 3 The Graduate School for the Creation of New Photonics Industries 4 Institute of Microelectronics, Agency for Science, Technology and Research based optical devices. As silicon is semiconductor material, its optical characteristics can be varied by electrical signals. This technology realizes integration of various kinds of optical functions to a small chip of just a few square millimeters. Moreover, the chip can be fabricated at a low cost using a production process well-developed for electronic integrated circuits. We applied this technology to an optical modulator for the digital coherent transmission. The fabricated silicon DP-IQ modulator includes monolithically integrated high-speed phase shifters, a polarization multiplexing waveguide, and monitor PDs, achieving a small footprint of approximately one tenth of a conventional lithium niobate modulator 3) 4). Recently, we further focused on increasing modulation efficiency of the phase shifter and developed a low-driving-voltage silicon DP-IQ modulator package 5). This paper firstly describes details of major functions of the modulator: the phase shifter and the polarization multiplexing waveguide. And then, it shows demonstration of highspeed modulation including DP 16- and 32- quadrature amplitude modulations (QAMs) and long distance fiber transmission in DP- quadrature phases shift keying (QPSK) format widely used in commercial optical fiber networks. 2. Structure of DP-IQ modulator for digital coherent transmission Optical signals in the digital coherent transmission are generated using a DP-IQ modulator. This section describes a structure and modulation formats of the DP-IQ modulator with its fundamental elements: a Mach-Zehnder (MZ) modulator and an IQ modulator. 1
2 Panel 1. Abbreviations, Acronyms, and Terms. OIF Optical Internetworking Forum CFP C Form-factor Pluggable DSP Digital Signal Processing IQ In-phase Quadrature OOK On-Off Keying BPSK Binary Phase Shift Keying QPSK Quadrature Phase Shift Keying QAM Quadrature Amplitude Modulation DP Dual Polarization MZ Mach-Zehnder Vp Half wave voltage TE Transverse Electric TM Transverse Magnetic TEC Thermoelectric Cooler PAM Pulse Amplitude Modulation AWG Arbitrary Waveform Generator VOA Variable Optical Attenuator EDFA Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier BPF Band Pass Filter BER Bit Error Rate FEC Forward Error Correction Figure 1 illustrates a configurations of modulators with their typical modulation formats. The top row shows a MZ modulator, which consists of a single MZ interferometer with phase shifters on its two arms. In the phase shifter, an applied electrical signal changes velocity of propagating light, giving phase and amplitude modulation to an output light from the MZ interferometer. The modulated optical signals can be expressed in a constellation, in which electric fields of modulated signals are mapped onto symbols on a Structure Modulation Format MZ mod. CW Input electrical signals DATA: Mod. signals out. (DATA: ) Phase shifter Amplitude: OOK (On off keying) Im 1 BPSK (Binary phase shift keying) Im 1 Re Re Amplitude: Electric field Time Electric field Time MZ mod. 1 QPSK (Quadrature phase shift keying) xqam (Quadrature amplitude modulation) IQ mod. 9 MZ mod. 2 9 Phase shifter (16QAM) (32QAM) Pol. mux. waveguide DP-QPSK (Dual polarizatoin quadrature phase shift keying) DP-IQ mod. IQ mod. 1 IQ mod. 2 X-pol. Y-pol. Fig. 1. Modulator structures and modulation formats. Fujikura Technical Review,
3 complex field. The MZ modulator can generate on-off keying (OOK) or binary phase shift keying (BPSK), in which symbols are located on single axis in the constellation. The second row shows an IQ modulator, which is composed of two MZ modulators and a 9-degree phase shifter. This IQ modulator supports QPSK in which data is allotted to phase states differing by 9 degrees and QAM in which data is allotted to states differing in both phase and amplitude. In the bottom row, DP-IQ modulator was described. This modulator includes two IQ modulators and a polarization multiplexing waveguide. The polarization multiplexing waveguide combines two modulated signals from the two IQ modulators with controlling their polarization states to be orthogonal to each other. The modulator generates DP-QPSK or DP-QAM. The DP-IQ modulator thus has complicated structure including four conventional MZ modulators and additional functional elements such as the polarization multiplexing waveguide. In the early products, those elements are realized based on combination of plural materials and technologies, e.g. lithium niobate for the phase shifter, III-V materials for PD, and micro-optics for the polarization multiplexing function. The modulator tends to become considerably large and costly. Novel technology for the nextgeneration DP-IQ modulator is now emerging. 3. Functional elements for silicon DP-IQ modulator Silicon photonics provides integration of the various optical functions for the DP-IQ modulator to a single silicon chip 3) 4). In this section, we describe the two key functional elements: the phase shifter newly introduced for reduction of driving voltage and the polarization multiplexing waveguide providing high conversion efficiency over a broad wavelength range. 3.1 silicon phase shifter for low driving voltage operation A phase shifter controls phase of propagating light by electrical signals. A silicon modulator usually functions through carrier plasma dispersion, which is the phenomenon that a refractive index for light passing through silicon medium is affected by existence of free carriers 6). In C- and L-bands used for telecommunications, an increase in free carrier density decreases the refractive index; a decrease in free carrier density increases the refractive index 7). A change of the refractive index, i.e. a change of velocity of light propagating in a transmission medium, results in a change of phase of light output from the phase shifter. A structure for controlling free carrier density thereby provides function of a phase shifter. Figure 2 illustrates a schematic of a designed silicon phase shifter. The optical waveguide is a silicon-based rib-type waveguide that has a thick rib region at center of the core. In the silicon core, the p-n diode structure is formed and connected to the electrode located on the top of the waveguide through p+ and n+ regions. The electrode is patterned to be a coplanar-type traveling-wave electrode, in which electrical signals propagate with light in parallel to allow high-speed modulation. At the same time, operation under a reverse bias condition also helps the high-speed modulation because it does not include slow minority carrier recombination caused under a normal bias condition. In this design, the p-n junction is located in vertical direction. This implementation contributes to reduction of driving voltage due to following reasons. When the p-n junction is reversely biased, the depletion layer broadens and the free carrier density decreases. The broadening depletion layer covers major center area of the rib region as indicated in the simulated results in Fig. 3(a). On the other hand, as Fig. 3(b) shows, an optical field of light propagating in the silicon rib waveguide also localizes in the rib region. The vertical p-n junction structure thus causes the p+ Silisa(SiO 2 ) Electrode n Silicon substrate (a) Silicon p n+ Depletion layer Ground (b) Fig. 2. Schematics of silicon phase shifter : (a) cross section and (b) electrodes. No bias n p Rib region Depletion layer (a) (b) p Signal Reverse bias(-3v) Fig. 3. (a) Carrier distribution and (b) optical mode field. n 12
4 large overlaps between the depletion layer and the optical field. That is because a small driving voltage is allowed to shift optical phase. Figure 4 indicates transmission characteristics of the fabricated MZ modulator with the vertical p-n junction phase shifter. Vp is defined as a difference of voltage from where the output power is minimum to where the output power is maximum. This parameter named half-wave voltage is one of the major indicators for efficiency of an optical modulator and represents a voltage required for 18-degree phase shift. The obtained Vp is as low as 2.5 V, which is less than a half of our previous design based on a conventional lateral 8) p-n junction. Figure 5 shows dependence on Transmittance (5dB/div) Vp (V) V p ~2.5V Applied bias (V) Fig. 4. Applied bias vs. output power in MZ modulator Wavelength (nm) wavelength and temperature. No significant degradation of Vp was observed in the broad wavelength range over C- and L-bands, as well in the wide temperature range up to 15 degrees Celsius. These results conclude that the silicon modulator can be used in the broad wavelength range without a thermo-optic cooler consuming considerable electric power. 3.2 Polarization multiplexing waveguide for C- and L-bands A silicon waveguide devices formed on a silicon wafer is asymmetric between horizontal structure and vertical structure, causing birefringence; characteristics for transverse electric (TE) polarized light and that for transverse magnetic (TM) polarized light differ. The waveguide device is usually designed to function properly only for one polarization state. The modulator mentioned above affects TE polarized light and generates optical signals with TE polarization. For generating polarization multiplexed signals, a polarization multiplexing waveguide should have a function to rotate TE polarized light from a modulator to TM polarized light and combine the TM polarized light to the other TE polarized light from the other modulator. Our previous design of a polarization multiplexing waveguide utilized a directional coupler for the function of the combination. Since the directional coupler had wavelength dependence and it was optimized to C-band, the integrated DP-IQ modulator had limited characteristics in L-band 4) 9). In the new design of the polarization multiplexing waveguide, mode-evolution-type conversion is employed instead, bringing low wavelength dependence 1). Figure 6 illustrates the polarization multiplexing waveguide. The structure of the waveguide is like a transformation from a silicon rib waveguide. Because the two heights are designed to be the same as those of the silicon rib waveguide in the phase shifter, the polarization multiplexing waveguide can be fabricated at the same time with the phase shifter without any additional fabrication process. 3 Port 1 Region A Region B Vp (V) 2 1 TE Port 2 TE Cross section TE TE Port 3 TM+TE Temperature (deg C) Fig. 5. Wavelength and temperature dependence of Vp. SiO 2 Si SiO 2 Si Fig. 6. Schematic view of polarization multiplexing waveguide. Fujikura Technical Review,
5 When TE polarized light is input from Port 1, it is converted to the first order TE polarization (TE ) in adjacent waveguide in Region A and then further converted to TM polarization in Region B. On the other hand, when TE polarized light is input from Port 2, it propagates as a TE polarized light in the waveguide and reaches to Port 3. This waveguide thus functions as both of a polarization rotator and a combiner. By connecting Ports 1 and 2 to two IQ modulators, polarization multiplexed modulated signals can be output from Port 3. Through this conversion process, the propagating lights stay in only single eigen mode at the waveguide; the lights do not split to the plural of eigen modes. This is mode-evolution-type conversion that has an advantage of low wavelength dependence. Measurement results of a fabricated device are shown in Fig. 7. The remarkable low conversion losses less than.5 db were observed in the broad wavelength range over C- and L-bands. 4. High-speed modulation demonstrations with low-driving-voltage operation We evaluated high-speed modulations and fiber transmissions under low-driving-voltage operation conditions using the silicon DP-IQ modulator package shown in Fig. 8. Figure 9 shows the experimental setup. In the transmitter side, an arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) was used to supply electrical signals in pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) required for QAM generation. The output amplitudes were 1.4 Vppd or 2. Vppd (.7 Vpp or 1. Vpp for each of positive and negative ports) and applied directly to the modulator package without any driver amplifier. The line width of the light source was less than 1 khz and the wavelength was 155 nm. In the receiver side, the modulated signals were detected with the coherent receiver and real-time oscilloscope, and recovered by offline digital signal processing (DSP). In the transmission experiment, the circulating loop Transmittance (db) Input Port1(TE) Output Port(TM) Input Port2(TE) Output Port(TE) Wavelength (nm) Fig. 7. Transmission spectra of polarization multiplexing waveguide. Fig. 8. Silicon DP-IQ modulator package. CW laser BPF AWG EDFA back to back transmission SW SW 3-dB coupler EDFA 1-km SMF VOA EDFA BPF Coherent receiver EDFA: Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier BPF: Band Pass Filter SW: Switch DSP: Digital Signal Processing Real-time oscilloscope Offline DSP Fig. 9. Experimental setup for fiber transmission. 14
6 16 Gbaud 32-QAM 32 Gbaud 16-QAM 32 Gbaud QPSK 48 Gbaud QPSK Back to back 1 km 2 km X-pol. X-pol. Y-pol. Y-pol. BER 5.9x x1-2 ~1x x1-3 BER < x x1-3 Fig.1. Constellations in various modulation formats. Fig.11. Constellations in 128-Gb/s DP-QPSK format. configuration was employed. Firstly, high-speed modulation formats including QAM were evaluated in the back-to-back configuration. Driving voltage applied from the AWG was 1.4 Vppd. Figure 1 shows constellations in various modulation formats. Symbols are aligned in line with no distortion, indicating that MZ modulator worked appropriately with the low-voltage differential drive. In each constellation, the bit error rate (BER) was less than forward error correction (FEC) limit of ). We thus confirmed that the modulator provides highspeed modulations over 1 Gb/s with low driving voltage directly applied from the AWG. We next confirmed the long-distance transmission in 128-Gb/s DP-QPSK which is widely used in commercial networks. The driving voltage was 2 Vppd in this experiment. Signal degradation by chromatic dispersion of the fiber was compensated in the DSP. Figure 11 shows constellations in the back-to-back and after transmission. The noise in the constellation increases with an increase of the transmission length. However, even in after transmission of 2 km, the BER of , less than the FEC limit, was obtained. The 2-km SMF long distance transmission is also confirmed under the low-driving-voltage operation condition. 5. Conclusion We developed a low-driving-voltage silicon DP-IQ modulator for digital coherent transmission. The phase shifter with the vertical p-n junction structure increases modulation efficiency, achieving the low Vp of 2.5 V. In addition, the characteristics are stable in broad wavelength and temperature ranges. The integrated polarization multiplexing waveguide uses adiabatic conversion to enable low conversion loss of less than.5 db also in the broad wavelength range. Using the silicon DP-IQ modulator with low-drivingvoltage less than 2 Vppd, we demonstrated high-speed modulation such as in DP 16- and 32- QAM, and long distance SMF transmission in 2 km with 128 Gb/s DP-QPSK format. Reduction of a driving voltage of a DP-IQ modulator allows a direct drive from DSP-LSI, which facilitates large reduction both in space and power consumption currently used for a driver amplifier. The low-drivingvoltage silicon DP-IQ modulator will be an indispensable component for coherent transceivers applied to various optical communication fields. References 1) T. Saida, Emerging integrated devices for coherent transmission - digitally assisted analog optics, in Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exhibition, Th3B.4, 217 2) Optical Networking Forum: 3) K. Goi et al., 128-Gb/s DP-QPSK using low-loss monolithic silicon IQ modulator integrated with partial-rib polarization rotator, in Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exhibition, W1I.2, 214 4) K. Goi et al., 128-Gb/s Monolithic Silicon Optical Modulator for Digital Coherent Communication, Fujikura Technical Review, No.44, pp.33 4, 215 5) N. Ishikura et al., Transmission characteristics of 32-Gbaud PDM IQ monolithic silicon modulator operating with 2-Vppd drive voltage, in 42nd European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication, W.2.E.4, 216 6) G. T. Reed et al., Silicon optical modulators, Nature Photonics, Vol.4, No.8, pp , 21 7) R. A. Soref and B. R. Bennett, Electrooptical effects in silicon, IEEE J. Quantum Electron., Vol.23, No.1, pp , ) K. Goi et al., Low-loss high-speed silicon IQ modulator for QPSK/DQPSK in C and L bands, Optics Express, Vol.22, No.9, pp , 214 9) K. Goi et al., Low-loss partial rib polarization rotator consisting only of silicon core and silica cladding, Optics Letters, Vol.4, No.7, pp , 215 1) A. Oka et al., Low-loss all-adiabatic silicon-waveguide polarization-division multiplexer in C and L bands, in OptoElectronics and Communication Conference and Australian Conference on Optical Fibre Technology 214, WE7E 1, ) G. Tzimpragos et al., A survey on FEC codes for 1G and beyond optical networks, IEEE Communication Surveys & Tutorials, Vol.18, No.1, pp , 216 Fujikura Technical Review,
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide
 Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
PLC-based integrated devices for advanced modulation formats
 ECOC 2009 workshop 7-5 Sep. 20, 2009 PLC-based integrated devices for advanced modulation formats Y. Inoue NTT Photonics Labs. NTT Corporation NTT Photonics Laboratories Hybrid integration of photonics
ECOC 2009 workshop 7-5 Sep. 20, 2009 PLC-based integrated devices for advanced modulation formats Y. Inoue NTT Photonics Labs. NTT Corporation NTT Photonics Laboratories Hybrid integration of photonics
ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016
 ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016 Lecture 9: Mach-Zehnder Modulator Transmitters Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Mach-Zehnder
ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016 Lecture 9: Mach-Zehnder Modulator Transmitters Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Mach-Zehnder
Low Power DSP and Photonic Integration in Optical Networks. Atul Srivastava CTO, NTT Electronics - America. Market Focus ECOC 2014
 Low Power DSP and Photonic Integration in Optical Networks Atul Srivastava CTO, NTT Electronics - America Market Focus ECOC 2014 Outline 100G Deployment Rapid Growth in Long Haul Role of Modules New Low
Low Power DSP and Photonic Integration in Optical Networks Atul Srivastava CTO, NTT Electronics - America Market Focus ECOC 2014 Outline 100G Deployment Rapid Growth in Long Haul Role of Modules New Low
Module 16 : Integrated Optics I
 Module 16 : Integrated Optics I Lecture : Integrated Optics I Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Electro-Optic Effect Optical Phase Modulator Optical Amplitude Modulator
Module 16 : Integrated Optics I Lecture : Integrated Optics I Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Electro-Optic Effect Optical Phase Modulator Optical Amplitude Modulator
White Paper. 100G beyond 10km A global study coherent and PAM4 Technology. Date: By Ambroise Thirion
 White Paper Date: 100G beyond 10km A global study coherent and PAM4 Technology By Ambroise Thirion Contents I. II. III. IV. The challenge of going beyond 10km on 100G links...3 Long reach technologies
White Paper Date: 100G beyond 10km A global study coherent and PAM4 Technology By Ambroise Thirion Contents I. II. III. IV. The challenge of going beyond 10km on 100G links...3 Long reach technologies
Performance Analysis Of Hybrid Optical OFDM System With High Order Dispersion Compensation
 Performance Analysis Of Hybrid Optical OFDM System With High Order Dispersion Compensation Manpreet Singh Student, University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India. Abstract Orthogonal
Performance Analysis Of Hybrid Optical OFDM System With High Order Dispersion Compensation Manpreet Singh Student, University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India. Abstract Orthogonal
Phase Modulator for Higher Order Dispersion Compensation in Optical OFDM System
 Phase Modulator for Higher Order Dispersion Compensation in Optical OFDM System Manpreet Singh 1, Karamjit Kaur 2 Student, University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India 1. Assistant
Phase Modulator for Higher Order Dispersion Compensation in Optical OFDM System Manpreet Singh 1, Karamjit Kaur 2 Student, University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India 1. Assistant
Optical IQ modulators for coherent 100G and beyond
 for coherent 1G and beyond By GARY WANG Indium phosphide can overcome the limitations of LiNbO3, opening the door to the performance tomorrow s coherent transmission systems will require. T HE CONTINUED
for coherent 1G and beyond By GARY WANG Indium phosphide can overcome the limitations of LiNbO3, opening the door to the performance tomorrow s coherent transmission systems will require. T HE CONTINUED
50-Gb/s silicon optical modulator with travelingwave
 5-Gb/s silicon optical modulator with travelingwave electrodes Xiaoguang Tu, 1, * Tsung-Yang Liow, 1 Junfeng Song, 1,2 Xianshu Luo, 1 Qing Fang, 1 Mingbin Yu, 1 and Guo-Qiang Lo 1 1 Institute of Microelectronics,
5-Gb/s silicon optical modulator with travelingwave electrodes Xiaoguang Tu, 1, * Tsung-Yang Liow, 1 Junfeng Song, 1,2 Xianshu Luo, 1 Qing Fang, 1 Mingbin Yu, 1 and Guo-Qiang Lo 1 1 Institute of Microelectronics,
Low-voltage, high speed, compact silicon modulator for BPSK modulation
 Low-voltage, high speed, compact silicon modulator for BPSK modulation Tiantian Li, 1 Junlong Zhang, 1 Huaxiang Yi, 1 Wei Tan, 1 Qifeng Long, 1 Zhiping Zhou, 1,2 Xingjun Wang, 1,* and Hequan Wu 1 1 State
Low-voltage, high speed, compact silicon modulator for BPSK modulation Tiantian Li, 1 Junlong Zhang, 1 Huaxiang Yi, 1 Wei Tan, 1 Qifeng Long, 1 Zhiping Zhou, 1,2 Xingjun Wang, 1,* and Hequan Wu 1 1 State
Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p.
 Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Electro-Optic Crosstalk in Parallel Silicon Photonic Mach-Zehnder Modulators
 > REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < 1 Electro-Optic Crosstalk in Parallel Silicon Photonic Mach-Zehnder Modulators Lingjun Jiang, Xi Chen, Kwangwoong
> REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < 1 Electro-Optic Crosstalk in Parallel Silicon Photonic Mach-Zehnder Modulators Lingjun Jiang, Xi Chen, Kwangwoong
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER
 CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
Compact Low-power-consumption Optical Modulator
 Compact Low-power-consumption Modulator Eiichi Yamada, Ken Tsuzuki, Nobuhiro Kikuchi, and Hiroshi Yasaka Abstract modulators are indispensable devices for optical fiber communications. They turn light
Compact Low-power-consumption Modulator Eiichi Yamada, Ken Tsuzuki, Nobuhiro Kikuchi, and Hiroshi Yasaka Abstract modulators are indispensable devices for optical fiber communications. They turn light
L évolution des systèmes de transmission optique très haut débit et l impact de la photonique sur silicium
 L évolution des systèmes de transmission optique très haut débit et l impact de la photonique sur silicium G. Charlet 27-November-2017 1 Introduction Evolution of long distance transmission systems: from
L évolution des systèmes de transmission optique très haut débit et l impact de la photonique sur silicium G. Charlet 27-November-2017 1 Introduction Evolution of long distance transmission systems: from
Next-Generation Optical Fiber Network Communication
 Next-Generation Optical Fiber Network Communication Naveen Panwar; Pankaj Kumar & manupanwar46@gmail.com & chandra.pankaj30@gmail.com ABSTRACT: In all over the world, much higher order off modulation formats
Next-Generation Optical Fiber Network Communication Naveen Panwar; Pankaj Kumar & manupanwar46@gmail.com & chandra.pankaj30@gmail.com ABSTRACT: In all over the world, much higher order off modulation formats
Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides
 Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides Yaming Li, Chong Li, Chuanbo Li, Buwen Cheng, * and Chunlai Xue State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics,
Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides Yaming Li, Chong Li, Chuanbo Li, Buwen Cheng, * and Chunlai Xue State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics,
SEVENTH FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME THEME [ICT ] [Photonics]
![SEVENTH FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME THEME [ICT ] [Photonics] SEVENTH FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME THEME [ICT ] [Photonics]](/thumbs/91/106870333.jpg) SEVENTH FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME THEME [ICT-2013.3.2] [Photonics] Software-defined energy-efficient Photonic transceivers IntRoducing Intelligence and dynamicity in Terabit superchannels for flexible optical
SEVENTH FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME THEME [ICT-2013.3.2] [Photonics] Software-defined energy-efficient Photonic transceivers IntRoducing Intelligence and dynamicity in Terabit superchannels for flexible optical
40Gb/s Optical Transmission System Testbed
 The University of Kansas Technical Report 40Gb/s Optical Transmission System Testbed Ron Hui, Sen Zhang, Ashvini Ganesh, Chris Allen and Ken Demarest ITTC-FY2004-TR-22738-01 January 2004 Sponsor: Sprint
The University of Kansas Technical Report 40Gb/s Optical Transmission System Testbed Ron Hui, Sen Zhang, Ashvini Ganesh, Chris Allen and Ken Demarest ITTC-FY2004-TR-22738-01 January 2004 Sponsor: Sprint
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING. FINAL EXAMINATION, April 2017 DURATION: 2.5 hours
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING ECE4691-111 S - FINAL EXAMINATION, April 2017 DURATION: 2.5 hours Optical Communication and Networks Calculator Type: 2 Exam Type: X Examiner:
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING ECE4691-111 S - FINAL EXAMINATION, April 2017 DURATION: 2.5 hours Optical Communication and Networks Calculator Type: 2 Exam Type: X Examiner:
10Gbit/s error-free DPSK modulation using a push-pull dual-drive silicon modulator
 10Gbit/s error-free DPSK modulation using a push-pull dual-drive silicon modulator M. Aamer, 1,* D. J. Thomson, 2 A. M. Gutiérrez, 1 A. Brimont, 1 F. Y. Gardes, 2 G. T. Reed, 2 J.M. Fedeli, 3 A. Hakansson,
10Gbit/s error-free DPSK modulation using a push-pull dual-drive silicon modulator M. Aamer, 1,* D. J. Thomson, 2 A. M. Gutiérrez, 1 A. Brimont, 1 F. Y. Gardes, 2 G. T. Reed, 2 J.M. Fedeli, 3 A. Hakansson,
Lecture 7 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 7, Slide 1
 Dispersion management Lecture 7 Dispersion compensating fibers (DCF) Fiber Bragg gratings (FBG) Dispersion-equalizing filters Optical phase conjugation (OPC) Electronic dispersion compensation (EDC) Fiber
Dispersion management Lecture 7 Dispersion compensating fibers (DCF) Fiber Bragg gratings (FBG) Dispersion-equalizing filters Optical phase conjugation (OPC) Electronic dispersion compensation (EDC) Fiber
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WDM AND EDFA IN C-BAND FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol13issue1/ijrras_13_1_26.pdf PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WDM AND EDFA IN C-BAND FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM M.M. Ismail, M.A. Othman, H.A. Sulaiman, M.H. Misran & M.A. Meor
www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol13issue1/ijrras_13_1_26.pdf PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WDM AND EDFA IN C-BAND FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM M.M. Ismail, M.A. Othman, H.A. Sulaiman, M.H. Misran & M.A. Meor
Index. Cambridge University Press Silicon Photonics Design Lukas Chrostowski and Michael Hochberg. Index.
 absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
Electronic-Photonic ICs for Low Cost and Scalable Datacenter Solutions
 Electronic-Photonic ICs for Low Cost and Scalable Datacenter Solutions Christoph Theiss, Director Packaging Christoph.Theiss@sicoya.com 1 SEMICON Europe 2016, October 27 2016 Sicoya Overview Spin-off from
Electronic-Photonic ICs for Low Cost and Scalable Datacenter Solutions Christoph Theiss, Director Packaging Christoph.Theiss@sicoya.com 1 SEMICON Europe 2016, October 27 2016 Sicoya Overview Spin-off from
Optical Transmission Fundamentals
 Optical Transmission Fundamentals F. Vasey, CERN-EP-ESE Context Technology HEP Specifics 12 Nov 2018 0 Context: Bandwidth Demand Internet traffic is growing at ~Moore s law Global interconnection bandwidth
Optical Transmission Fundamentals F. Vasey, CERN-EP-ESE Context Technology HEP Specifics 12 Nov 2018 0 Context: Bandwidth Demand Internet traffic is growing at ~Moore s law Global interconnection bandwidth
Emerging Highly Compact Amplification Solutions for Coherent Transmission
 Emerging Highly Compact Amplification Solutions for Coherent Transmission Market Focus ECOC 2017 Sep 20, 2017 Dr. Sanjai Parthasarathi Vice President, Product Marketing & Strategy II-VI Photonics Outline
Emerging Highly Compact Amplification Solutions for Coherent Transmission Market Focus ECOC 2017 Sep 20, 2017 Dr. Sanjai Parthasarathi Vice President, Product Marketing & Strategy II-VI Photonics Outline
Phase Noise Compensation for Coherent Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing in Optical Fiber Communications Systems
 Jassim K. Hmood Department of Laser and Optoelectronic Engineering, University of Technology, Baghdad, Iraq Phase Noise Compensation for Coherent Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing in Optical Fiber
Jassim K. Hmood Department of Laser and Optoelectronic Engineering, University of Technology, Baghdad, Iraq Phase Noise Compensation for Coherent Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing in Optical Fiber
Emerging Subsea Networks
 Optimization of Pulse Shaping Scheme and Multiplexing/Demultiplexing Configuration for Ultra-Dense WDM based on mqam Modulation Format Takanori Inoue, Yoshihisa Inada, Eduardo Mateo, Takaaki Ogata (NEC
Optimization of Pulse Shaping Scheme and Multiplexing/Demultiplexing Configuration for Ultra-Dense WDM based on mqam Modulation Format Takanori Inoue, Yoshihisa Inada, Eduardo Mateo, Takaaki Ogata (NEC
A Fully Integrated 20 Gb/s Optoelectronic Transceiver Implemented in a Standard
 A Fully Integrated 20 Gb/s Optoelectronic Transceiver Implemented in a Standard 0.13 µm CMOS SOI Technology School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Yonsei University 이슬아 1. Introduction 2. Architecture
A Fully Integrated 20 Gb/s Optoelectronic Transceiver Implemented in a Standard 0.13 µm CMOS SOI Technology School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Yonsei University 이슬아 1. Introduction 2. Architecture
Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers with Low Noise Figure
 Hideaki Hasegawa *, Masaki Funabashi *, Kazuomi Maruyama *, Kazuaki Kiyota *, and Noriyuki Yokouchi * In the multilevel phase modulation which is expected to provide the nextgeneration modulation format
Hideaki Hasegawa *, Masaki Funabashi *, Kazuomi Maruyama *, Kazuaki Kiyota *, and Noriyuki Yokouchi * In the multilevel phase modulation which is expected to provide the nextgeneration modulation format
Optical Polarization Filters and Splitters Based on Multimode Interference Structures using Silicon Waveguides
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume No. 7, July, 01 Optical Polarization Filters and Splitters Based on Multimode Interference Structures using Silicon Waveguides 1 Trung-Thanh Le,
International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume No. 7, July, 01 Optical Polarization Filters and Splitters Based on Multimode Interference Structures using Silicon Waveguides 1 Trung-Thanh Le,
Emerging Subsea Networks
 EVALUATION OF NONLINEAR IMPAIRMENT FROM NARROW- BAND UNPOLARIZED IDLERS IN COHERENT TRANSMISSION ON DISPERSION-MANAGED SUBMARINE CABLE SYSTEMS Masashi Binkai, Keisuke Matsuda, Tsuyoshi Yoshida, Naoki Suzuki,
EVALUATION OF NONLINEAR IMPAIRMENT FROM NARROW- BAND UNPOLARIZED IDLERS IN COHERENT TRANSMISSION ON DISPERSION-MANAGED SUBMARINE CABLE SYSTEMS Masashi Binkai, Keisuke Matsuda, Tsuyoshi Yoshida, Naoki Suzuki,
Integrated TOSA with High-Speed EML Chips for up to 400 Gbit/s Communication
 FEATURED TOPIC Integrated TOSA with High-Speed EML Chips for up to 4 Gbit/s Communication Ryota TERANISHI*, Hidetoshi NAITO, Masahiro HIRAYAMA, Masahiro HONDA, Shuichi KUBOTA, and Takayuki MIYAHARA ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FEATURED TOPIC Integrated TOSA with High-Speed EML Chips for up to 4 Gbit/s Communication Ryota TERANISHI*, Hidetoshi NAITO, Masahiro HIRAYAMA, Masahiro HONDA, Shuichi KUBOTA, and Takayuki MIYAHARA ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Project: IEEE P Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs)
 Project: IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) Title: 30-Gbps-class terahertz transmission using optical sub-harmonic IQ mixer for backhaul/fronthaul directly connected
Project: IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) Title: 30-Gbps-class terahertz transmission using optical sub-harmonic IQ mixer for backhaul/fronthaul directly connected
Performance Analysis of SOA-MZI based All-Optical AND & XOR Gate
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Utkarsh
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Utkarsh
Multi-format all-optical-3r-regeneration technology
 Multi-format all-optical-3r-regeneration technology Masatoshi Kagawa Hitoshi Murai Amount of information flowing through the Internet is growing by about 40% per year. In Japan, the monthly average has
Multi-format all-optical-3r-regeneration technology Masatoshi Kagawa Hitoshi Murai Amount of information flowing through the Internet is growing by about 40% per year. In Japan, the monthly average has
CodeSScientific OCSim Modules Modern Fiber Optic Communication Systems Simulations With Advanced Level Matlab Modules APPLICATIONS
 CodeSScientific OCSim Modules Modern Fiber Optic Communication Systems Simulations With Advanced Level Matlab Modules APPLICATIONS OCSim Modules** Modern Fiber Optic Communication Systems Simulations with
CodeSScientific OCSim Modules Modern Fiber Optic Communication Systems Simulations With Advanced Level Matlab Modules APPLICATIONS OCSim Modules** Modern Fiber Optic Communication Systems Simulations with
from ocean to cloud WELCOME TO 400GB/S & 1TB/S ERA FOR HIGH SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY UNDERSEA SYSTEMS
 WELCOME TO 400GB/S & 1TB/S ERA FOR HIGH SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY UNDERSEA SYSTEMS G. Charlet, O. Bertran-Pardo, M. Salsi, J. Renaudier, P. Tran, H. Mardoyan, P. Brindel, A. Ghazisaeidi, S. Bigo (Alcatel-Lucent
WELCOME TO 400GB/S & 1TB/S ERA FOR HIGH SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY UNDERSEA SYSTEMS G. Charlet, O. Bertran-Pardo, M. Salsi, J. Renaudier, P. Tran, H. Mardoyan, P. Brindel, A. Ghazisaeidi, S. Bigo (Alcatel-Lucent
Lecture 2 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 2, Slide 1
 Lecture 2 General concepts Digital modulation in general Optical modulation Direct modulation External modulation Modulation formats Differential detection Coherent detection Fiber Optical Communication
Lecture 2 General concepts Digital modulation in general Optical modulation Direct modulation External modulation Modulation formats Differential detection Coherent detection Fiber Optical Communication
Hybrid Integration Technology of Silicon Optical Waveguide and Electronic Circuit
 Hybrid Integration Technology of Silicon Optical Waveguide and Electronic Circuit Daisuke Shimura Kyoko Kotani Hiroyuki Takahashi Hideaki Okayama Hiroki Yaegashi Due to the proliferation of broadband services
Hybrid Integration Technology of Silicon Optical Waveguide and Electronic Circuit Daisuke Shimura Kyoko Kotani Hiroyuki Takahashi Hideaki Okayama Hiroki Yaegashi Due to the proliferation of broadband services
Key Features for OptiSystem 12
 12 New Features Created to address the needs of research scientists, optical telecom engineers, professors and students, OptiSystem satisfies the demand of users who are searching for a powerful yet easy
12 New Features Created to address the needs of research scientists, optical telecom engineers, professors and students, OptiSystem satisfies the demand of users who are searching for a powerful yet easy
Modulators. Digital Intensity Modulators. Analogue Intensity Modulators. 2.5Gb/sec...Page Gb/sec Small Form Factor...Page 3
 Date Created: 1/12/4 Modulators Digital Intensity Modulators Modulators 2.Gb/sec.....................Page 2 2.Gb/sec Small Form Factor.......Page 3 2.Gb/sec with Attenuator.........Page 4 12.Gb/sec Integrated
Date Created: 1/12/4 Modulators Digital Intensity Modulators Modulators 2.Gb/sec.....................Page 2 2.Gb/sec Small Form Factor.......Page 3 2.Gb/sec with Attenuator.........Page 4 12.Gb/sec Integrated
Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University
 Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Last Lecture Topics Course introduction Ray optics & optical
Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Last Lecture Topics Course introduction Ray optics & optical
Coherent Receivers: A New Paradigm For Optical Components. ECOC Market Focus September 20, 2010
 Photonic Integrated Circuit Based Coherent Receivers: A New Paradigm For Optical Components G. Ferris Lipscomb ECOC Market Focus September 20, 2010 Agenda Advanced Coding Schemes Use Phase Encoding To
Photonic Integrated Circuit Based Coherent Receivers: A New Paradigm For Optical Components G. Ferris Lipscomb ECOC Market Focus September 20, 2010 Agenda Advanced Coding Schemes Use Phase Encoding To
Optical Networks emerging technologies and architectures
 Optical Networks emerging technologies and architectures Faculty of Computer Science, Electronics and Telecommunications Department of Telecommunications Artur Lasoń 100 Gb/s PM-QPSK (DP-QPSK) module Hot
Optical Networks emerging technologies and architectures Faculty of Computer Science, Electronics and Telecommunications Department of Telecommunications Artur Lasoń 100 Gb/s PM-QPSK (DP-QPSK) module Hot
A HIGH SPEED WDM PON FOR DOWNSTREAM DPSK ASK SIGNALS AND UPSTREAM OOK SIGNAL WITH BROADCAST CAPABILTY
 A HIGH SPEED WDM PON FOR DOWNSTREAM DPSK ASK SIGNALS AND UPSTREAM OOK SIGNAL WITH BROADCAST CAPABILTY 1 AAMIR KHAN, 2 ANITA CHOPRA 1 Department of Information Technology, Suresh Gyan Vihar University,
A HIGH SPEED WDM PON FOR DOWNSTREAM DPSK ASK SIGNALS AND UPSTREAM OOK SIGNAL WITH BROADCAST CAPABILTY 1 AAMIR KHAN, 2 ANITA CHOPRA 1 Department of Information Technology, Suresh Gyan Vihar University,
Key Features for OptiSystem 14
 14.0 New Features Created to address the needs of research scientists, photonic engineers, professors and students; OptiSystem satisfies the demand of users who are searching for a powerful yet easy to
14.0 New Features Created to address the needs of research scientists, photonic engineers, professors and students; OptiSystem satisfies the demand of users who are searching for a powerful yet easy to
A 3.9 ns 8.9 mw 4 4 Silicon Photonic Switch Hybrid-Integrated with CMOS Driver
 A 3.9 ns 8.9 mw 4 4 Silicon Photonic Switch Hybrid-Integrated with CMOS Driver A. Rylyakov, C. Schow, B. Lee, W. Green, J. Van Campenhout, M. Yang, F. Doany, S. Assefa, C. Jahnes, J. Kash, Y. Vlasov IBM
A 3.9 ns 8.9 mw 4 4 Silicon Photonic Switch Hybrid-Integrated with CMOS Driver A. Rylyakov, C. Schow, B. Lee, W. Green, J. Van Campenhout, M. Yang, F. Doany, S. Assefa, C. Jahnes, J. Kash, Y. Vlasov IBM
CodeSScientific. OCSim Modules 2018 version 2.0. Fiber Optic Communication System Simulations Software Modules with Matlab
 CodeSScientific OCSim Modules 2018 version 2.0 Fiber Optic Communication System Simulations Software Modules with Matlab Use the Existing Modules for Research Papers, Research Projects and Theses Modify
CodeSScientific OCSim Modules 2018 version 2.0 Fiber Optic Communication System Simulations Software Modules with Matlab Use the Existing Modules for Research Papers, Research Projects and Theses Modify
Semiconductor Optical Communication Components and Devices Lecture 39: Optical Modulators
 Semiconductor Optical Communication Components and Devices Lecture 39: Optical Modulators Prof. Utpal Das Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering, Laser Technology Program, Indian Institute of
Semiconductor Optical Communication Components and Devices Lecture 39: Optical Modulators Prof. Utpal Das Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering, Laser Technology Program, Indian Institute of
Utilizing Self-Seeding RSOA with Faraday Rotator Mirror for Colorless Access Network
 Utilizing Self-Seeding RSOA with Faraday Rotator Mirror for Colorless Access Network Yu-Fu Wu a, Jinu-Yu Sung a, and Chi-Wai Chow a, and Chien-Hung Yeh* b,c a Department of Photonics and Institute of Electro-Optical
Utilizing Self-Seeding RSOA with Faraday Rotator Mirror for Colorless Access Network Yu-Fu Wu a, Jinu-Yu Sung a, and Chi-Wai Chow a, and Chien-Hung Yeh* b,c a Department of Photonics and Institute of Electro-Optical
ISSCC 2006 / SESSION 13 / OPTICAL COMMUNICATION / 13.7
 13.7 A 10Gb/s Photonic Modulator and WDM MUX/DEMUX Integrated with Electronics in 0.13µm SOI CMOS Andrew Huang, Cary Gunn, Guo-Liang Li, Yi Liang, Sina Mirsaidi, Adithyaram Narasimha, Thierry Pinguet Luxtera,
13.7 A 10Gb/s Photonic Modulator and WDM MUX/DEMUX Integrated with Electronics in 0.13µm SOI CMOS Andrew Huang, Cary Gunn, Guo-Liang Li, Yi Liang, Sina Mirsaidi, Adithyaram Narasimha, Thierry Pinguet Luxtera,
Single- versus Dual-Carrier Transmission for Installed Submarine Cable Upgrades
 Single- versus Dual-Carrier Transmission for Installed Submarine Cable Upgrades L. Molle, M. Nölle, C. Schubert (Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, HHI) W. Wong, S. Webb, J. Schwartz (Xtera Communications)
Single- versus Dual-Carrier Transmission for Installed Submarine Cable Upgrades L. Molle, M. Nölle, C. Schubert (Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, HHI) W. Wong, S. Webb, J. Schwartz (Xtera Communications)
UNIT - 7 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS
 UNIT - 7 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS WDM concepts, overview of WDM operation principles, WDM standards, Mach-Zehender interferometer, multiplexer, Isolators and circulators, direct thin film filters, active
UNIT - 7 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS WDM concepts, overview of WDM operation principles, WDM standards, Mach-Zehender interferometer, multiplexer, Isolators and circulators, direct thin film filters, active
Introduction and concepts Types of devices
 ECE 6323 Introduction and concepts Types of devices Passive splitters, combiners, couplers Wavelength-based devices for DWDM Modulator/demodulator (amplitude and phase), compensator (dispersion) Others:
ECE 6323 Introduction and concepts Types of devices Passive splitters, combiners, couplers Wavelength-based devices for DWDM Modulator/demodulator (amplitude and phase), compensator (dispersion) Others:
ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016
 ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016 Lecture 10: Electroabsorption Modulator Transmitters Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements
ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016 Lecture 10: Electroabsorption Modulator Transmitters Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements
1 COPYRIGHT 2011 ALCATEL-LUCENT. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
 1 ECOC 2011 WORKSHOP Space-Division Multiplexed Transmission in Strongly Coupled Few-Mode and Multi-Core Fibers Roland Ryf September 18 th 2011 CONTENTS 1. THE CAPACITY CRUNCH 2. SPACE DIVISION MULTIPLEXING
1 ECOC 2011 WORKSHOP Space-Division Multiplexed Transmission in Strongly Coupled Few-Mode and Multi-Core Fibers Roland Ryf September 18 th 2011 CONTENTS 1. THE CAPACITY CRUNCH 2. SPACE DIVISION MULTIPLEXING
Full-duplex bidirectional transmission of 10-Gb/s millimeter-wave QPSK signal in E-band optical wireless link
 Full-duplex bidirectional transmission of 10-Gb/s millimeter-wave QPSK signal in E-band optical wireless link Yuan Fang, 1 Jianjun Yu, 1,* Nan Chi, 1 and Jiangnan Xiao 1 1 Department of Communication Science
Full-duplex bidirectional transmission of 10-Gb/s millimeter-wave QPSK signal in E-band optical wireless link Yuan Fang, 1 Jianjun Yu, 1,* Nan Chi, 1 and Jiangnan Xiao 1 1 Department of Communication Science
Performance Analysis of dispersion compensation using Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) in Optical Communication
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347-5161 214 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Performance
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347-5161 214 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Performance
Real-time transmission of 16 Tb/s over 1020km using 200Gb/s CFP2-DCO
 Vol. 26, No. 6 19 Mar 2018 OPTICS EXPRESS 6943 Real-time transmission of 16 Tb/s over 1020km using 200Gb/s CFP2-DCO H. ZHANG,1,* B. ZHU,2 S. PARK,1 C. DOERR,1 M. AYDINLIK,1 J. GEYER,1 T. PFAU,1 G. PENDOCK,1
Vol. 26, No. 6 19 Mar 2018 OPTICS EXPRESS 6943 Real-time transmission of 16 Tb/s over 1020km using 200Gb/s CFP2-DCO H. ZHANG,1,* B. ZHU,2 S. PARK,1 C. DOERR,1 M. AYDINLIK,1 J. GEYER,1 T. PFAU,1 G. PENDOCK,1
Silicon photonics on 3 and 12 μm thick SOI for optical interconnects Timo Aalto VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland
 Silicon photonics on 3 and 12 μm thick SOI for optical interconnects Timo Aalto VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland 5th International Symposium for Optical Interconnect in Data Centres in ECOC, Gothenburg,
Silicon photonics on 3 and 12 μm thick SOI for optical interconnects Timo Aalto VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland 5th International Symposium for Optical Interconnect in Data Centres in ECOC, Gothenburg,
Lecture: Integration of silicon photonics with electronics. Prepared by Jean-Marc FEDELI CEA-LETI
 Lecture: Integration of silicon photonics with electronics Prepared by Jean-Marc FEDELI CEA-LETI Context The goal is to give optical functionalities to electronics integrated circuit (EIC) The objectives
Lecture: Integration of silicon photonics with electronics Prepared by Jean-Marc FEDELI CEA-LETI Context The goal is to give optical functionalities to electronics integrated circuit (EIC) The objectives
MICRO RING MODULATOR. Dae-hyun Kwon. High-speed circuits and Systems Laboratory
 MICRO RING MODULATOR Dae-hyun Kwon High-speed circuits and Systems Laboratory Paper preview Title of the paper Low Vpp, ultralow-energy, compact, high-speed silicon electro-optic modulator Publication
MICRO RING MODULATOR Dae-hyun Kwon High-speed circuits and Systems Laboratory Paper preview Title of the paper Low Vpp, ultralow-energy, compact, high-speed silicon electro-optic modulator Publication
Direct Demodulation of Optical BPSK/QPSK Signal without Digital Signal Processing
 942 THUY HATRONG, SEO DONGSUN, DIRECT DEMODULATION OF OPTICAL BPSK/QPSK SIGNALS Direct Demodulation of Optical BPSK/QPSK Signal without Digital Signal Processing TrongThuy HA, DongSun SEO Dept. of Electronics,
942 THUY HATRONG, SEO DONGSUN, DIRECT DEMODULATION OF OPTICAL BPSK/QPSK SIGNALS Direct Demodulation of Optical BPSK/QPSK Signal without Digital Signal Processing TrongThuy HA, DongSun SEO Dept. of Electronics,
All-optical clock division at 40 GHz using a semiconductor amplifier. nonlinear interferometer
 All-optical clock division at 40 GHz using a semiconductor amplifier nonlinear interferometer R. J. Manning, I. D. Phillips, A. D. Ellis, A. E. Kelly, A. J. Poustie, K.J. Blow BT Laboratories, Martlesham
All-optical clock division at 40 GHz using a semiconductor amplifier nonlinear interferometer R. J. Manning, I. D. Phillips, A. D. Ellis, A. E. Kelly, A. J. Poustie, K.J. Blow BT Laboratories, Martlesham
Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications by Stuart M. Wentworth Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
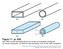 Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Polarization Optimized PMD Source Applications
 PMD mitigation in 40Gb/s systems Polarization Optimized PMD Source Applications As the bit rate of fiber optic communication systems increases from 10 Gbps to 40Gbps, 100 Gbps, and beyond, polarization
PMD mitigation in 40Gb/s systems Polarization Optimized PMD Source Applications As the bit rate of fiber optic communication systems increases from 10 Gbps to 40Gbps, 100 Gbps, and beyond, polarization
SYLLABUS Optical Fiber Communication
 SYLLABUS Optical Fiber Communication Subject Code : IA Marks : 25 No. of Lecture Hrs/Week : 04 Exam Hours : 03 Total no. of Lecture Hrs. : 52 Exam Marks : 100 UNIT - 1 PART - A OVERVIEW OF OPTICAL FIBER
SYLLABUS Optical Fiber Communication Subject Code : IA Marks : 25 No. of Lecture Hrs/Week : 04 Exam Hours : 03 Total no. of Lecture Hrs. : 52 Exam Marks : 100 UNIT - 1 PART - A OVERVIEW OF OPTICAL FIBER
Fiber-based components. by: Khanh Kieu
 Fiber-based components by: Khanh Kieu Projects 1. Handling optical fibers, numerical aperture 2. Measurement of fiber attenuation 3. Connectors and splices 4. Free space coupling of laser into fibers 5.
Fiber-based components by: Khanh Kieu Projects 1. Handling optical fibers, numerical aperture 2. Measurement of fiber attenuation 3. Connectors and splices 4. Free space coupling of laser into fibers 5.
100G Coherent Transceiver Technologies for DWDM Metro Applications: Key Requirements and Design Trends
 100G Coherent Transceiver Technologies for DWDM Metro Applications: Key Requirements and Design Trends Benny Mikkelsen benny.mikkelsen@acacia-inc.com ECOC, 2012 Market Focus Optical Networks Advances Outline
100G Coherent Transceiver Technologies for DWDM Metro Applications: Key Requirements and Design Trends Benny Mikkelsen benny.mikkelsen@acacia-inc.com ECOC, 2012 Market Focus Optical Networks Advances Outline
Semiconductor Optoelectronics Prof. M. R. Shenoy Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Semiconductor Optoelectronics Prof. M. R. Shenoy Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 26 Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (SOA) (Refer Slide Time: 00:39) Welcome to this
Semiconductor Optoelectronics Prof. M. R. Shenoy Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 26 Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (SOA) (Refer Slide Time: 00:39) Welcome to this
COHERENT DETECTION OPTICAL OFDM SYSTEM
 342 COHERENT DETECTION OPTICAL OFDM SYSTEM Puneet Mittal, Nitesh Singh Chauhan, Anand Gaurav B.Tech student, Electronics and Communication Engineering, VIT University, Vellore, India Jabeena A Faculty,
342 COHERENT DETECTION OPTICAL OFDM SYSTEM Puneet Mittal, Nitesh Singh Chauhan, Anand Gaurav B.Tech student, Electronics and Communication Engineering, VIT University, Vellore, India Jabeena A Faculty,
Lecture 9 External Modulators and Detectors
 Optical Fibres and Telecommunications Lecture 9 External Modulators and Detectors Introduction Where are we? A look at some real laser diodes. External modulators Mach-Zender Electro-absorption modulators
Optical Fibres and Telecommunications Lecture 9 External Modulators and Detectors Introduction Where are we? A look at some real laser diodes. External modulators Mach-Zender Electro-absorption modulators
Ross Saunders GM, Next-gen Transport Opnext Subsystems Inc. 100G Cost/Performance Optimization
 Ross Saunders GM, Next-gen Transport Opnext Subsystems Inc. 100G Cost/Performance Optimization Contents Historical vs Future Optical Transport Challenges What we did at 40G lessons learned Electronic and
Ross Saunders GM, Next-gen Transport Opnext Subsystems Inc. 100G Cost/Performance Optimization Contents Historical vs Future Optical Transport Challenges What we did at 40G lessons learned Electronic and
Photonic Generation of Millimeter-Wave Signals With Tunable Phase Shift
 Photonic Generation of Millimeter-Wave Signals With Tunable Phase Shift Volume 4, Number 3, June 2012 Weifeng Zhang, Student Member, IEEE Jianping Yao, Fellow, IEEE DOI: 10.1109/JPHOT.2012.2199481 1943-0655/$31.00
Photonic Generation of Millimeter-Wave Signals With Tunable Phase Shift Volume 4, Number 3, June 2012 Weifeng Zhang, Student Member, IEEE Jianping Yao, Fellow, IEEE DOI: 10.1109/JPHOT.2012.2199481 1943-0655/$31.00
Silicon photonics with low loss and small polarization dependency. Timo Aalto VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland
 Silicon photonics with low loss and small polarization dependency Timo Aalto VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland EPIC workshop in Tokyo, 9 th November 2017 VTT Technical Research Center of Finland
Silicon photonics with low loss and small polarization dependency Timo Aalto VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland EPIC workshop in Tokyo, 9 th November 2017 VTT Technical Research Center of Finland
High-speed silicon-based microring modulators and electro-optical switches integrated with grating couplers
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series High-speed silicon-based microring modulators and electro-optical switches integrated with grating couplers To cite this article: Xi Xiao et al 2011 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series High-speed silicon-based microring modulators and electro-optical switches integrated with grating couplers To cite this article: Xi Xiao et al 2011 J. Phys.: Conf.
Transmitting Light: Fiber-optic and Free-space Communications Holography
 1 Lecture 9 Transmitting Light: Fiber-optic and Free-space Communications Holography 2 Wireless Phone Calls http://havilandtelconews.com/2011/10/the-reality-behind-wireless-networks/ 3 Undersea Cable and
1 Lecture 9 Transmitting Light: Fiber-optic and Free-space Communications Holography 2 Wireless Phone Calls http://havilandtelconews.com/2011/10/the-reality-behind-wireless-networks/ 3 Undersea Cable and
Silicon Carrier-Depletion-Based Mach-Zehnder and Ring Modulators with Different Doping Patterns for Telecommunication and Optical Interconnect
 Silicon Carrier-Depletion-Based Mach-Zehnder and Ring Modulators with Different Doping Patterns for Telecommunication and Optical Interconnect Hui Yu, Marianna Pantouvaki*, Joris Van Campenhout*, Katarzyna
Silicon Carrier-Depletion-Based Mach-Zehnder and Ring Modulators with Different Doping Patterns for Telecommunication and Optical Interconnect Hui Yu, Marianna Pantouvaki*, Joris Van Campenhout*, Katarzyna
Wavelength Interleaving Based Dispersion Tolerant RoF System with Double Sideband Carrier Suppression
 Wavelength Interleaving Based Dispersion Tolerant RoF System with Double Sideband Carrier Suppression Hilal Ahmad Sheikh 1, Anurag Sharma 2 1 (Dept. of Electronics & Communication, CTITR, Jalandhar, India)
Wavelength Interleaving Based Dispersion Tolerant RoF System with Double Sideband Carrier Suppression Hilal Ahmad Sheikh 1, Anurag Sharma 2 1 (Dept. of Electronics & Communication, CTITR, Jalandhar, India)
Schematic image of multi-core transmission line composed of different vendors and its loss characteristics
 8 August, 2017 Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation KDDI Research, Inc. Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. Fujikura Ltd. Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. NEC Corporation Chiba Institute of Technology
8 August, 2017 Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation KDDI Research, Inc. Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. Fujikura Ltd. Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. NEC Corporation Chiba Institute of Technology
NEXT GENERATION SILICON PHOTONICS FOR COMPUTING AND COMMUNICATION PHILIPPE ABSIL
 NEXT GENERATION SILICON PHOTONICS FOR COMPUTING AND COMMUNICATION PHILIPPE ABSIL OUTLINE Introduction Platform Overview Device Library Overview What s Next? Conclusion OUTLINE Introduction Platform Overview
NEXT GENERATION SILICON PHOTONICS FOR COMPUTING AND COMMUNICATION PHILIPPE ABSIL OUTLINE Introduction Platform Overview Device Library Overview What s Next? Conclusion OUTLINE Introduction Platform Overview
RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #4 is due today, HW #5 is assigned (due April 8)
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #4 is due today, HW #5 is assigned (due April 8)
from ocean to cloud THE FUTURE IS NOW - MAXIMIZING SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY AND CAPACITY USING MODERN COHERENT TRANSPONDER TECHNIQUES
 Required OSNR (db/0.1nm RBW) @ 10-dB Q-factor THE FUTURE IS NOW - MAXIMIZING SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY AND CAPACITY USING MODERN COHERENT TRANSPONDER TECHNIQUES Neal S. Bergano, Georg Mohs, and Alexei Pilipetskii
Required OSNR (db/0.1nm RBW) @ 10-dB Q-factor THE FUTURE IS NOW - MAXIMIZING SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY AND CAPACITY USING MODERN COHERENT TRANSPONDER TECHNIQUES Neal S. Bergano, Georg Mohs, and Alexei Pilipetskii
Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks
 363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
Cisco PONC Pavan Voruganti Senior Product Manager. March 2015
 Cisco PONC 2015 Pavan Voruganti Senior Product Manager March 2015 Bandwidth Explosion With a progressive uptake of video, IP, audio and cloud the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of IP traffic is above
Cisco PONC 2015 Pavan Voruganti Senior Product Manager March 2015 Bandwidth Explosion With a progressive uptake of video, IP, audio and cloud the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of IP traffic is above
Photonics and Optical Communication Spring 2005
 Photonics and Optical Communication Spring 2005 Final Exam Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp, Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering Name: Mat. -Nr.: Guidelines: Duration of the Final Exam: 2 hour You
Photonics and Optical Communication Spring 2005 Final Exam Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp, Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering Name: Mat. -Nr.: Guidelines: Duration of the Final Exam: 2 hour You
Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology Supplementary Article Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation R. Udayakumar 1 *, V. Khanaa 2 and T. Saravanan
Indian Journal of Science and Technology Supplementary Article Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation R. Udayakumar 1 *, V. Khanaa 2 and T. Saravanan
A review on optical time division multiplexing (OTDM)
 International Journal of Academic Research and Development ISSN: 2455-4197 Impact Factor: RJIF 5.22 www.academicsjournal.com Volume 3; Issue 1; January 2018; Page No. 520-524 A review on optical time division
International Journal of Academic Research and Development ISSN: 2455-4197 Impact Factor: RJIF 5.22 www.academicsjournal.com Volume 3; Issue 1; January 2018; Page No. 520-524 A review on optical time division
Development of Vertical Spot Size Converter (SSC) with Low Coupling Loss Using 2.5%Δ Silica-Based Planar Lightwave Circuit
 Development of Vertical Spot Size Converter (SSC) with Low Coupling Loss Using 2.5%Δ Silica-Based Planar Lightwave Circuit Yasuyoshi Uchida *, Hiroshi Kawashima *, and Kazutaka Nara * Recently, new planar
Development of Vertical Spot Size Converter (SSC) with Low Coupling Loss Using 2.5%Δ Silica-Based Planar Lightwave Circuit Yasuyoshi Uchida *, Hiroshi Kawashima *, and Kazutaka Nara * Recently, new planar
Network Challenges for Coherent Systems. Mike Harrop Technical Sales Engineering, EXFO
 Network Challenges for Coherent Systems Mike Harrop Technical Sales Engineering, EXFO Agenda 1. 100G Transmission Technology 2. Non Linear effects 3. RAMAN Amplification 1. Optimsing gain 2. Keeping It
Network Challenges for Coherent Systems Mike Harrop Technical Sales Engineering, EXFO Agenda 1. 100G Transmission Technology 2. Non Linear effects 3. RAMAN Amplification 1. Optimsing gain 2. Keeping It
Optical Transport Tutorial
 Optical Transport Tutorial 4 February 2015 2015 OpticalCloudInfra Proprietary 1 Content Optical Transport Basics Assessment of Optical Communication Quality Bit Error Rate and Q Factor Wavelength Division
Optical Transport Tutorial 4 February 2015 2015 OpticalCloudInfra Proprietary 1 Content Optical Transport Basics Assessment of Optical Communication Quality Bit Error Rate and Q Factor Wavelength Division
Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering
 Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering Technical Report MECSE-4-2005 DWDM Optically Amplified Transmission Systems - SIMULINK Models and Test-Bed: Part III DPSK L.N. Binh and Y.L.Cheung
Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering Technical Report MECSE-4-2005 DWDM Optically Amplified Transmission Systems - SIMULINK Models and Test-Bed: Part III DPSK L.N. Binh and Y.L.Cheung
OPTICAL NETWORKS. Building Blocks. A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005
 OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
IBM T. J. Watson Research Center IBM Corporation
 Broadband Silicon Photonic Switch Integrated with CMOS Drive Electronics B. G. Lee, J. Van Campenhout, A. V. Rylyakov, C. L. Schow, W. M. J. Green, S. Assefa, M. Yang, F. E. Doany, C. V. Jahnes, R. A.
Broadband Silicon Photonic Switch Integrated with CMOS Drive Electronics B. G. Lee, J. Van Campenhout, A. V. Rylyakov, C. L. Schow, W. M. J. Green, S. Assefa, M. Yang, F. E. Doany, C. V. Jahnes, R. A.
High-Power Highly Linear Photodiodes for High Dynamic Range LADARs
 High-Power Highly Linear Photodiodes for High Dynamic Range LADARs Shubhashish Datta and Abhay Joshi th June, 6 Discovery Semiconductors, Inc. 9 Silvia Street, Ewing, NJ - 868, USA www.discoverysemi.com
High-Power Highly Linear Photodiodes for High Dynamic Range LADARs Shubhashish Datta and Abhay Joshi th June, 6 Discovery Semiconductors, Inc. 9 Silvia Street, Ewing, NJ - 868, USA www.discoverysemi.com
Development of LiNbO 3 for CATV Transmission Systems
 Development of LiNbO 3 Modulators for CATV Transmission Systems Norikazu Miyazaki, Takashi Noguchi, and Toshio Sakane (Optoelectronics Research Div., New Technology Research Laboratory) ABSTRACT We have
Development of LiNbO 3 Modulators for CATV Transmission Systems Norikazu Miyazaki, Takashi Noguchi, and Toshio Sakane (Optoelectronics Research Div., New Technology Research Laboratory) ABSTRACT We have
