Bit error rate and cross talk performance in optical cross connect with wavelength converter
|
|
|
- Walter Lester
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
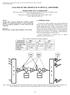
1 Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 295 Bit error rate and cross talk performance in optical cross connect with wavelength converter M. S. Islam and S. P. Majumder Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh mdsaifulislam@iict.buet.ac.bd Received September 5, 2006; revised December 12, 2006; accepted January 19, 2007; published February 28, 2007 Doc. ID An analytical approach is presented for modeling cross talk and evaluating the bit error rate (BER) performance in a WDM network for link with optical cross connect (OXC). Factors affecting the magnitude of cross talk in the OXC are investigated and identified. The effects of OXC induced cross talk on the BER performance is evaluated at a bit rate of 10 Gbits/s by optimizing different parameters. The results show that for optimized values of gate extinction ratio, filter transmission factor, and number of wavelengths and input fibers, the minimum input power is approximately 10 to 8 dbm to maintain a BER of Optical Society of America OCIS codes: , , , , Introduction WDM is a technique to increase the information capacity of a fiber by transmitting a number of optical signals of different wavelengths simultaneously over the same fiber. WDM networks are very promising due to their flexibility and possibility of upgrading the existing optical fiber networks to WDM networks [1]. The optical cross connect (OXC) is an essential network element enabling reconfigurable optical networks, where lightpaths can be set up and taken down as needed [2 4]. It offers routing scalability, bit rate and protocol independence, power saving, and increased transport capacity to WDM networks [5,6]. Propagation through the switching elements that are part of the OXC results in signal degradation both due to the device intrinsic losses and their imperfect operation. Imperfect switching gives a leakage signal, the wavelength of which can be equal to or different from the signal wavelength. The cross-talk induced power penalties could also be caused by various nonlinear mechanisms including four-wave mixing (FWM). The effect of this cross talk would be smaller for spectrum-sliced light sources since these light sources are relatively insensitive to the nonlinear cross talk caused by FWM [7]. The build-up of cross talk noise on a certain optical channel due to interference with other signals while propagating through the different elements of the WDM network could result in serious problems. Cross talk due to the OXC is one of the basic criteria that characterize the performance of the WDM network [8 11]. Since optical cross talk is a major limiting factor, the commercial use of an all-optical OXC is so far prevented in WDM networks. In this paper, we present an analytical approach to identify and determine the optimum values of parameters that induce cross talk in the OXC with a wavelength converter and its influence on the overall bit error rate (BER) performance for spectral-sliced light sources at a bit rate of 10 Gbits/s. 2. Optical Cross-Connect Topology The block diagram of a WDM transmission link with an OXC is shown in Fig. 1. The OXC is based on the gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier (GC-SOA) and wavelength converter (WC). It uses a combination of space and wavelength switching. The wavelength channel to be transmitted is multiplexed by a WDM multiplexer and fed to an incoming fiber. At the input of OXC the incoming signals are split by a first array of power splitters followed by a second array of power splitters. At the input of GC-SOA gates, all channels are present. The gate selects the wavelength that carries /07/ /$ Optical Society of America
2 Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 296 Fig. 1. Block diagram of a WDM transmission link with an OXC based on GC-SOA and wavelength. the desired channel. A wavelength converter is used to convert the channel wavelength from one wavelength to the other wavelength. The OXC enables any wavelength channel from any input fiber to be cross-connected to any output fiber, on the condition that no two channels in the output fiber have the same wavelength. In Fig. 1, fiber a carries wavelength channels a1, a2,..., am and fiber b carries wavelength channels b1, b2,..., bm. Given that N is the number of input fiber and M is the number of different wavelengths, there are a total of N M wavelength channels. The N M wavelength channels passed through first array of power splitters. There are N power splitters for all the N input fibers. All the different wavelength channels appear at the output of the power splitter at lesser power due to power splitting. Wavelengths a1, a2,..., am are then fed to another array of M power splitters. There is a total of N M power splitters at the second array. The output of the second array of power splitters are fed to gates made from GC-SOA, which allows only specific wavelengths to pass through. The combiner at first output fiber, such as combiner 1, receives its inputs from a1, b1,..., 1. The output of N M combiners is fed to N M filters and wavelength converter. The second array of N combiners, combine all cross-connected wavelength channels and output them to N output fibers. The desired wavelength channel of an outgoing fiber is demultiplexed by a WDM demultiplexer and is received by a direct detection receiver. 3. Cross Talk and the Bit Error Rate Model An analytical model of cross talk due to the OXC is presented in this section and used to evaluate the BER performance of the WDM link with the OXC. Analytical expressions are given that describe the output power of the OXC as a function of input powers and component parameters. Here, P jo io is the input power of a channel, P out io1 is defined as the output power of wavelength channel i o with cross talk contributions added (with all wavelength channels carrying bit 1). T F is the filter transmission factor, R gate is the gate extinction ratio, X gate is gate cross talk, N is the number of input fiber into the OXC, and M is the number of wavelengths per input fiber. P jo i is the signal power at fiber j o with another wavelength i. P j io is the signal power at another fiber j that carries the wavelength under consideration, i o. P j i is the signal power at another fiber j with other wavelengths, i. We assume that all wavelength channels including P jo io carry bit 1. P out io1 at any output fiber may be just 1/N of the output power, due to division of power before entering the GC-SOA. However, in this paper, it is also assumed that the GC-SOA is set with gain of N times to compensate for the division of output optical power. X gate is a parameter that measures the gate s imperfection in gain clamping and is given by, X gate =P gate ref /P gate ; where P gate is the power output from the GC-SOA gate. P gate ref is the reference output power of the GC-SOA gate. T F is derived from the filter suppression of wavelength channel, T 1 F.
3 Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 297 In the OXC with wavelength converter, there is one gate in the ON state for every group of N gates. Hence there are NM gates in the ON state at any time for a total of NM 2 gates. The calculation is done for worst-case situation, where the OXC is handling full traffic and also the amplitudes of the beat term are assumed to be maximum. Extinction ratio is defined as, R gate =P off /P on. P in is defined as the input power through each gate. The expression for output power with cross talk of wavelength channel i 0 is given by Eq. (1) based on [1] based on the assumption that all channels carry bit 1. P io out = P io jo + P io jo X gate M 1 P i jo + P io jo + P io j N 1 R gate 1+X gate MP i j + M 1 T F 1+X gate MP i j + N 1 M 1 2 T F R gate 2 P io jo Pio j N 1 R gate + M 1 T F + N 1 M 1 R gate T F 2P io j N 1 M 1 R gate T F + N N M 1 R gate T F + N 1 M 1 2 R gate T F 2P io j R gate M 1 N R gate T F t. M 2 t + T F t 1 P jo io is defined as N times of P in since there is one gate in the ON state for every group of gates. P out ref io is the output power of wavelength channel i o when the OXC is carrying only wavelength channel i o, such as when there is no cross talk. P io is out ref given by, P out ref io =P jo io +X gate P jo io 2. Since wavelength channel i o may carry bit 1 or bit 0 at any instant of time, Eq. (1) has to be modified. If wavelength channel i o carries bit 0, then Eq. (1) reduces to Eq. (2). P io0 out = P io j N 1 R gate 1+X gate MP i j + M 1 T F 1+X gate MP i j + N 1 M 1 2 T F R gate 2P io j N 1 M 1 R gate T F + N 1 2 M N 2 1 R gate T F + N 1 M 1 2 R gate T F 2P io j R gate M 1 N R gate T F t. M 2 t + T F t 2 P io out ref when wavelength channel i o carries bit 0 can be written as, P io out ref =0. The cross talk is calculated for a certain wavelength channel, which is called the channel under study. The expression for relative cross talk is given by P out ref io P out io1 cross talk =. 3 P io out ref To evaluate the BER of a WDM system, the cross talk model for the OXC with a wavelength converter is used to derive the BER model for the OXC with a wavelength converter. The expression for the BER of a WDM network with a wavelength converter in an IM-DD system can be given by Eq. (4). This equation assumes the scenario when a bit 1 is interfered with by a cross talk bit 1, bit 0 is interfered with by cross talk bit 0, bit 1 is interfered with by cross talk bit 0, and bit 0 is interfered with by cross talk bit 1 as reported by [9]. where BER worse case = 1 8 erfc 1 + erfc i 1 + i CT0 i D i 1 + i CT1 i D erfc 1 i D i 0 i CT erfc 1 i D i 0 i CT , = th 2 +2eR d P S + P sp + P CT0 B + S sp 2 + CT0 sp 2 + sp sp 2 + S CT0 2, 5
4 Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING = th 2 +2eR d P sp + P CT0 B + CT0 sp 2 + sp sp 2, = th 2 +2eR d P S + P sp + P CT1 B + S sp 2 + CT1 sp 2 + sp sp 2 + S CT1 2, = th 2 +2eR d P sp + P CT1 B + CT0 sp 2 + sp sp 2. 8 The variance of the interference is given in Eqs. (5) (8) where is the variance when signal bit 1 is interfered with by cross talk due to bit 0 and is the variance when signal bit 0 is interfered with by cross talk due to bit is the variance when signal bit 1 is interfered with by cross talk due to bit 1, and is the variance when signal bit 0 is interfered with by cross talk due to bit 1. th 2 is the power of thermal noise, R d is the receiver responsivity, B is the bandwidth of the receiver low-pass filter, and P S is signal power. The photocurrent for a transmitted bit 1 is given by i 1 =2R d P S. For transmitted bit 0, the photocurrent is i 0 =0, with P S assumed to be zero, and i D is the threshold current. The expression for amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) power P sp is given by P sp =hff G 1 B. The amount of cross talk power due to bit 1 is P CT1 = P io1 out ref P io1 out, and cross talk power due to bit 0 can be expressed as P CT0 = P io0 out. The threshold current, i D, is shown in Eq. (9). S sp 2 is the power of the beating of signal and ASE, shown in Eq. (10). CT sp 2 is the power of the beating of cross talk and ASE, shown in Eqs. (11) and (12) for cross talk due to bits 1 and 0, respectively. S CT 2 is the power of the beating of signal and cross talk, shown in Eqs. (13) and (14) for cross talk due to bits 1 and 0, respectively. sp sp 2 is the power of the beating of ASE and ASE, shown in Eq. (15). S sp f is the power spectral density of ASE noise, S CT1 f is the power spectral density of cross talk due to bit 1, S CT0 f is the power spectral density of cross talk due to bit 0, and S S f is the power spectral density of the signal. i D = 0 1i i , 9 S sp 2 = R d S S f S sp f H f 2 df, 10 CT1 sp 2 = R d S sp f S CT1 f H f 2 df, 11 CT0 sp 2 = R d S sp f S CT0 f H f 2 df, 12 S CT1 2 = R d S S f S CT1 f H f 2 df, 13 S CT0 2 = R d S S f S CT0 f H f 2 df, 14 sp sp 2 = R d S sp f S sp f H f 2 df Bit Error Rate and Cross Talk Results Following the analytical approach presented in Section 3, the BER performance results are evaluated at a bit rate of 10 Gbits/s. We determine the relation between filter transmission T F and the number of wavelength M under certain computation conditions such as varying R gate, N, and P in. The same models are used to determine the relation between R gate and N using selected set of T F, M, and P in parameters.
5 Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 299 Fig. 2. Plot of BER versus filter transmission factor T F with optimized parameters. (N=13, M=16, R gate = 46.6 db, P in = 6.88 dbm). The plot of BER versus filter transmission factor T F is shown in Fig. 2. It is observed that for a certain number of wavelengths passing through the OXC, the quality of T F needs to be better than a value determined by setting BER to be at least As the number of wavelengths passing through an OXC increases, the wavelength suppression capability of the filter has to be improved to maintain a specific BER. A plot of the BER versus number of wavelength M is shown in Fig. 3. Figure 2 also shows a relationship between T F and M. This means that for a number of wavelengths BER is less than 10 9 if the filter transmission factor T F is chosen to be smaller than the value of T F at BER=10 9. It is confirmed in Fig. 3 and seen that the BER is successfully maintained below The plot of the number of wavelength M versus filter transmission factor T F (Fig. 5) shows that the BER increases as T F quality is decreased (larger value). The plot of cross talk versus number of wavelength, M, in Fig. 4 shows an almost linear relationship between cross talk and number of wavelength, M. It is evident that there is an inverse relationship between the filter transmission factor, T F, and M as shown in Fig. 5. It is discovered that increasing the suppression ratio T 1 F reduces the requirement for better gate extinction ratio R gate and vice versa. However, there is a minimum practical value of T F beyond which a requirement for better R gate will be impractical. Fig. 3. Plot of BER versus number of wavelength, M, with optimized parameters. (N=13, M=16, R gate = 46.6 db, P in = 6.88 dbm).
6 Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 300 Fig. 4. Cross talk versus number of wavelength, M, with optimized parameters. (N=13, M=16, R gate = 46.6 db, P in = 6.88 dbm). The penalty for increasing M in terms of the need to increase the wavelength suppression capability of the OXC is decreasing as M is increased. From the plot in Fig. 5, it is evident that the slope of the plot increases as M increases. This means that the penalty for increasing M can be minimized by decreasing N and can also be optimized to minimize the BER. There is a minimum BER for the plot of input fiber, N, versus BER for different R gate. For a particular R gate (for which the corresponding T F had been determined from Fig. 5), N should be chosen from the minimum point of Fig. 6. The corresponding N versus cross talk plot shows a maximum at around N=4. The plot of cross talk versus input fibers, N, is shown in Fig. 7. It is found that for N larger than 4, cross talk in the OXC decreases; this does not reflect improvement in the BER because the BER is not only influenced by cross talk in the OXC but also on the signal power compared to the cross talk power, noise power, and variance of signal cross-talk noise. Figure 8 shows the plot of the BER versus input power, P in, for different values of filter transmission factor, T F. From the plot, we found that the input power, P in, corresponding to the minimum BER is approximately 10 to 8 dbm for the filter transmission factor T F that is approximately 80 to 30 db. Increasing the input power P in reduces the requirement for better suppression ratio T F 1 and vice versa. The plot of cross talk versus input power P in is depicted in Fig. 5. Plot of number of wavelength, M, versus filter transmission factor, T F.
7 Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 301 Fig. 6. Plot of the BER versus gate extinction ratio, R gate, with optimized parameters. (N=13, M=16, T f = 37 db, P in = 6.88 dbm). Fig. 7. Plot of cross talk versus input fibers, N, with optimized parameters. (N=13, M=16, T f = 37 db, P in = 6.88 dbm). Fig. 8. Plot of the BER versus input power, P in, with optimized parameters. (N=13, M=16, T f = 37 db, R gate = 46.6 db).
8 Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 302 Fig. 9. Plot of cross talk versus input power P in. (N=13, M=16, T f = 37 db, R gate = 46.6 db). Table 1. Optimized Parameters Parameters Values Unit Number of wavelength M 16 Unitless Filter transmission T f 37 db Number of input fiber N 13 Unitless Gate extinction ratio R gate 46.6 db Input power per gate Pin 6.88 dbm Gate cross talk X gate 0.1 mw Table 2. Assumptions Parameters Values Unit Temperature T 300 K Bandwidth B 10 GHz Receiver load R L 50 Ohm Receiver responsivity R d 1 A/W Inversion factor F Unitless Amplifier gain G 250 Unitless Operating frequency f Hz Fig. 9. It is found that cross talk decreases tremendously at high P in after achieving maximum point at approximately 10 dbm. From the above discussion, we observed that to operate the OXC at minimum input power, the values of the filter transmission factor, T F, and gate extinction ratio, R gate, should be slightly better than the optimized value. This is to take into account of possible variation of input power P in. The optimized parameters for M=16 and N=13 are as shown in Table 1. The assumptions used in computing the optimized parameters are as shown in Table Conclusion In this paper cross talk and the BER performance of a WDM network with an OXC with a WC are analytically determined, and different factors that affect the magnitude of cross talk and the BER in the OXC are investigated in detail. The OXC parameters that play an important role in determining the magnitude of cross talk and the BER are identified, and parameters that result in minimum BER in the OXC are evaluated.
9 Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 303 References 1. T. Gyselings, G. Morthier, and R. Baets, Crosstalk analysis of multiwavelength optical cross connect, J. Lightwave Technol. 17, (1999). 2. S. P. Majumder and S. Dey, BER performance degradation due to component crosstalk of an arrayed waveguide grating and FBG-OC based WDM cross-connect, in IEEE, INDICON 2005 International Conference (IEEE, 2005), pp T. Song, H. Zhang, Y. Guo, and X. Zheng, Statistical study of crosstalk accumulation in WDM optical network with different topology, in Proceedings of 2002 IEEE Region 10 Conference on Computers, Communications, Control and Power Engineering (TENCON 02) (IEEE, 2002), pp E. Iannone and R. Sabella, Optical path technologies: A comparison among different cross-connect architectures, J. Lightwave Technol. 14, (1996). 5. R. Ramaswami, Using all-optical crossconnect in the transport network, in Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exhibit, 2001 (OFC 2001), (IEEE, 2001), Vol. 3, pp. WZ1 WZ1. 6. Y. W. Song, Z. Pan, D. Starodubov, V. Grubsky, E. Salik, S. A. Havstad, Y. Xie, A. E. Willner, and J. Feinberg, All-optical cross connect using ultrastrong widely tunable FBGs, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 10, (2001). 7. R. D. Feldman, Crosstalk and loss in wavelength division multiplexed systems employing spectral slicing, J. Lightwave Technol. 10, (1997). 8. Y. Shen, K. Lu, and W. Gu, Coherent and incoherent crosstalk in WDM optical networks, J. Lightwave Technol. 17, (1999). 9. T. Y. Chai, H. Chen, S. K. Bose, and C. Lu, Crosstalk analysis for limited wavelength interchanging cross connects, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 14, (2002). 10. J. Zhou, E. Casaccia Cavazzoni, and M. J. O Mahony, Crosstalk in multiwavelength OXC networks, J. Lightwave Technol. 14, (1996). 11. Y. S. Jang, C.-H. Lee, and Y. C. Chung, Effects of crosstalk in WDM systems using spectrum-sliced light sources, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 10, (1999).
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique
 S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
2015 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER)
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-4, Issue-8, pp-01-08 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Performance Analysis of DWDM System Considering
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-4, Issue-8, pp-01-08 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Performance Analysis of DWDM System Considering
Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks.
 Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks. Hercules Simos * National and Kapodistrian University
Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks. Hercules Simos * National and Kapodistrian University
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion
 Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source
 JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. X, NO. XX, XXXX XXX 1 Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source Jérôme Vasseur, Jianjun Yu Senior Member,
JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. X, NO. XX, XXXX XXX 1 Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source Jérôme Vasseur, Jianjun Yu Senior Member,
High bit-rate combined FSK/IM modulated optical signal generation by using GCSR tunable laser sources
 High bit-rate combined FSK/IM modulated optical signal generation by using GCSR tunable laser sources J. J. Vegas Olmos, I. Tafur Monroy, A. M. J. Koonen COBRA Research Institute, Eindhoven University
High bit-rate combined FSK/IM modulated optical signal generation by using GCSR tunable laser sources J. J. Vegas Olmos, I. Tafur Monroy, A. M. J. Koonen COBRA Research Institute, Eindhoven University
Concatenated Error Control Coding Applied to WDM Optical Communication Systems for Performance Enhancement
 73 Concatenated Error Control Coding Applied to WDM Optical Communication Systems for Performance Enhancement H.S. Mruthyunjaya *a, G. Umesh b, M. Sathish Kumar a, a Reader, Department of Electronics &
73 Concatenated Error Control Coding Applied to WDM Optical Communication Systems for Performance Enhancement H.S. Mruthyunjaya *a, G. Umesh b, M. Sathish Kumar a, a Reader, Department of Electronics &
Performance Improvement of All Optical WDM Systems on Binary Asymmetric Channel
 Performance Improvement of All Optical WDM Systems on Binary Asymmetric Channel H.S. Mruthyunjaya Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal, India.
Performance Improvement of All Optical WDM Systems on Binary Asymmetric Channel H.S. Mruthyunjaya Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal, India.
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF GB/S BIDIRECTIONAL DWDM PASSIVE OPTICAL NETWORK BASED ON CYCLIC AWG
 http:// PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF 1.25 16 GB/S BIDIRECTIONAL DWDM PASSIVE OPTICAL NETWORK BASED ON CYCLIC AWG Arashdeep Kaur 1, Ramandeep Kaur 2 1 Student, M.Tech, Department of Electronics and Communication
http:// PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF 1.25 16 GB/S BIDIRECTIONAL DWDM PASSIVE OPTICAL NETWORK BASED ON CYCLIC AWG Arashdeep Kaur 1, Ramandeep Kaur 2 1 Student, M.Tech, Department of Electronics and Communication
Colorless Amplified WDM-PON Employing Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources and Channel-by-Channel Dispersion Compensators for >100 km Reach
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 18, No. 5, October 014, pp. 46-441 ISSN: 16-4776(Print) / ISSN: 09-6885(Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.807/josk.014.18.5.46 Colorless Amplified WDM-PON Employing
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 18, No. 5, October 014, pp. 46-441 ISSN: 16-4776(Print) / ISSN: 09-6885(Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.807/josk.014.18.5.46 Colorless Amplified WDM-PON Employing
An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources and a Novel Bidirectional Reach Extender
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 15, No. 3, September 2011, pp. 222-226 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2011.15.3.222 An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 15, No. 3, September 2011, pp. 222-226 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2011.15.3.222 An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources
Design and Performance Evaluation of 20 GB/s Bidirectional DWDM Passive Optical Network Based on Array Waveguide Gratings
 ISSN: 2278 909X International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJARECE) Volume 2, Issue 9, September 2013 Design and Performance Evaluation of 20 GB/s Bidirectional
ISSN: 2278 909X International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJARECE) Volume 2, Issue 9, September 2013 Design and Performance Evaluation of 20 GB/s Bidirectional
Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators. by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings
 Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings Paper no: 1471 S. Y. Set, H. Geiger, R. I. Laming, M. J. Cole and L. Reekie Optoelectronics Research
Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings Paper no: 1471 S. Y. Set, H. Geiger, R. I. Laming, M. J. Cole and L. Reekie Optoelectronics Research
Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter
 Research Online ECU Publications 29 Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter Feng Xiao Mingya Shen Budi Juswardy Kamal Alameh This article was originally published as: Xiao, F., Shen, M., Juswardy,
Research Online ECU Publications 29 Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter Feng Xiao Mingya Shen Budi Juswardy Kamal Alameh This article was originally published as: Xiao, F., Shen, M., Juswardy,
Optical Fiber Technology
 Optical Fiber Technology 18 (2012) 29 33 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Optical Fiber Technology www.elsevier.com/locate/yofte A novel WDM passive optical network architecture supporting
Optical Fiber Technology 18 (2012) 29 33 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Optical Fiber Technology www.elsevier.com/locate/yofte A novel WDM passive optical network architecture supporting
Minimization of amplified spontaneous emission noise in upstream SuperPON 512 ONU, 10 Gbit/s.
 Minimization of amplified spontaneous emission noise in upstream SuperPON 512, 10 Gbit/s. A.J. Sakena* a, M.Y. Jamro b and J.M. Senior b a Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Sarawak, 94300, Kota
Minimization of amplified spontaneous emission noise in upstream SuperPON 512, 10 Gbit/s. A.J. Sakena* a, M.Y. Jamro b and J.M. Senior b a Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Sarawak, 94300, Kota
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber
 Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis
 EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis Narruvala Lokesh, kranthi Kumar Katam,Prof. Jabeena A Vellore Institute of Technology VIT University, Vellore, India Abstract : Optical network that apply wavelength division
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis Narruvala Lokesh, kranthi Kumar Katam,Prof. Jabeena A Vellore Institute of Technology VIT University, Vellore, India Abstract : Optical network that apply wavelength division
To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks
 289 To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks Areet Aulakh 1, Kulwinder Singh Malhi 2 1 Student, M.Tech, ECE department, Punjabi University,
289 To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks Areet Aulakh 1, Kulwinder Singh Malhi 2 1 Student, M.Tech, ECE department, Punjabi University,
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor
 Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
Spectrally Compact Optical Subcarrier Multiplexing with 42.6 Gbit/s AM-PSK Payload and 2.5Gbit/s NRZ Labels
 Spectrally Compact Optical Subcarrier Multiplexing with 42.6 Gbit/s AM-PSK Payload and 2.5Gbit/s NRZ Labels A.K. Mishra (1), A.D. Ellis (1), D. Cotter (1),F. Smyth (2), E. Connolly (2), L.P. Barry (2)
Spectrally Compact Optical Subcarrier Multiplexing with 42.6 Gbit/s AM-PSK Payload and 2.5Gbit/s NRZ Labels A.K. Mishra (1), A.D. Ellis (1), D. Cotter (1),F. Smyth (2), E. Connolly (2), L.P. Barry (2)
A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation
 A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer & Communications Research Laboratories,
A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer & Communications Research Laboratories,
PH-7. Understanding of FWM Behavior in 2-D Time-Spreading Wavelength- Hopping OCDMA Systems. Abstract. Taher M. Bazan Egyptian Armed Forces
 PH-7 Understanding of FWM Behavior in 2-D Time-Spreading Wavelength- Hopping OCDMA Systems Taher M. Bazan Egyptian Armed Forces Abstract The behavior of four-wave mixing (FWM) in 2-D time-spreading wavelength-hopping
PH-7 Understanding of FWM Behavior in 2-D Time-Spreading Wavelength- Hopping OCDMA Systems Taher M. Bazan Egyptian Armed Forces Abstract The behavior of four-wave mixing (FWM) in 2-D time-spreading wavelength-hopping
A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs
 A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs Yue Tian, Qingjiang Chang, and Yikai Su * State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department
A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs Yue Tian, Qingjiang Chang, and Yikai Su * State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department
UNIT - 7 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS
 UNIT - 7 LECTURE-1 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS WDM concepts, overview of WDM operation principles, WDM standards, Mach-Zehender interferometer, multiplexer, Isolators and circulators, direct thin film
UNIT - 7 LECTURE-1 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS WDM concepts, overview of WDM operation principles, WDM standards, Mach-Zehender interferometer, multiplexer, Isolators and circulators, direct thin film
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 26
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 26 Wavelength Division Multiplexed (WDM) Systems Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 26 Wavelength Division Multiplexed (WDM) Systems Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
A proposal for two-input arbitrary Boolean logic gates using single semiconductor optical amplifier by picosecond pulse injection
 A proposal for two-input arbitrary Boolean logic gates using single semiconductor optical amplifier by picosecond pulse injection Jianji Dong,,* Xinliang Zhang, and Dexiu Huang Wuhan National Laboratory
A proposal for two-input arbitrary Boolean logic gates using single semiconductor optical amplifier by picosecond pulse injection Jianji Dong,,* Xinliang Zhang, and Dexiu Huang Wuhan National Laboratory
Impact of Double Cavity Fabry-Perot Demultiplexers on the Performance of. Dispersion Supported Transmission of Three 10 Gbit/s
 Impact of Double Cavity Fabry-Perot Demultiplexers on the Performance of Dispersion Supported Transmission of Three 10 Gbit/s WDM Channels Separated 1 nm Mário M. Freire and José A. R. Pacheco de Carvalho
Impact of Double Cavity Fabry-Perot Demultiplexers on the Performance of Dispersion Supported Transmission of Three 10 Gbit/s WDM Channels Separated 1 nm Mário M. Freire and José A. R. Pacheco de Carvalho
Simultaneous Four-Wave Mixing and Cross-Gain Modulation for Implementing All Optical Full Adder without Assist Light
 Simultaneous Four-Wave Mixing and Cross-Gain Modulation for Implementing All Optical Full Adder without Assist Light Jaspreet Kaur 1, Naveen Dhillon 2, Rupinder Kaur 3 1 Lecturer, ECE, LPU, Punjab, India
Simultaneous Four-Wave Mixing and Cross-Gain Modulation for Implementing All Optical Full Adder without Assist Light Jaspreet Kaur 1, Naveen Dhillon 2, Rupinder Kaur 3 1 Lecturer, ECE, LPU, Punjab, India
Module 12 : System Degradation and Power Penalty
 Module 12 : System Degradation and Power Penalty Lecture : System Degradation and Power Penalty Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Degradation during Propagation Modal Noise Dispersion
Module 12 : System Degradation and Power Penalty Lecture : System Degradation and Power Penalty Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Degradation during Propagation Modal Noise Dispersion
Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window
 Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2,3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer and Communications Research Laboratories,
Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2,3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer and Communications Research Laboratories,
Eye-Diagram-Based Evaluation of RZ and NRZ Modulation Methods in a 10-Gb/s Single-Channel and a 160-Gb/s WDM Optical Networks
 International Journal of Optics and Applications 2017, 7(2): 31-36 DOI: 10.5923/j.optics.20170702.01 Eye-Diagram-Based Evaluation of RZ and NRZ Modulation Methods in a 10-Gb/s Single-Channel and a 160-Gb/s
International Journal of Optics and Applications 2017, 7(2): 31-36 DOI: 10.5923/j.optics.20170702.01 Eye-Diagram-Based Evaluation of RZ and NRZ Modulation Methods in a 10-Gb/s Single-Channel and a 160-Gb/s
International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) ISSN: Vol. 2 Issue 9, September
 Performance Enhancement of WDM-ROF Networks With SOA-MZI Shalu (M.Tech), Baljeet Kaur (Assistant Professor) Department of Electronics and Communication Guru Nanak Dev Engineering College, Ludhiana Abstract
Performance Enhancement of WDM-ROF Networks With SOA-MZI Shalu (M.Tech), Baljeet Kaur (Assistant Professor) Department of Electronics and Communication Guru Nanak Dev Engineering College, Ludhiana Abstract
Module 19 : WDM Components
 Module 19 : WDM Components Lecture : WDM Components - II Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following OADM Optical Circulators Bidirectional OADM using Optical Circulators and FBG Optical Cross
Module 19 : WDM Components Lecture : WDM Components - II Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following OADM Optical Circulators Bidirectional OADM using Optical Circulators and FBG Optical Cross
Performance Analysis of WDM RoF-EPON Link with and without DCF and FBG
 Optics and Photonics Journal, 2013, 3, 163-168 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2013.32027 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/opj) Performance Analysis of WDM RoF-EPON Link with and
Optics and Photonics Journal, 2013, 3, 163-168 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2013.32027 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/opj) Performance Analysis of WDM RoF-EPON Link with and
All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration
 1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
CHAPTER 5 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM
 61 CHAPTER 5 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM 5.1 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM Due to the ever-expanding Internet data traffic, telecommunication networks are witnessing a demand for high-speed data transfer.
61 CHAPTER 5 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM 5.1 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM Due to the ever-expanding Internet data traffic, telecommunication networks are witnessing a demand for high-speed data transfer.
SOA-PIN performance. Rene Bonk, Dora van Veen, Vincent Houtsma, Bell Labs Ed Harstead, member Fixed Networks CTO. January 2017
 SOA-PIN performance Rene Bonk, Dora van Veen, Vincent Houtsma, Bell Labs Ed Harstead, member Fixed Networks CTO January 2017 1 Receiver Model for SOA+Filter+PIN / APD Analytical Rx model for SOA+filter+PIN
SOA-PIN performance Rene Bonk, Dora van Veen, Vincent Houtsma, Bell Labs Ed Harstead, member Fixed Networks CTO January 2017 1 Receiver Model for SOA+Filter+PIN / APD Analytical Rx model for SOA+filter+PIN
Linear cavity erbium-doped fiber laser with over 100 nm tuning range
 Linear cavity erbium-doped fiber laser with over 100 nm tuning range Xinyong Dong, Nam Quoc Ngo *, and Ping Shum Network Technology Research Center, School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Nanyang
Linear cavity erbium-doped fiber laser with over 100 nm tuning range Xinyong Dong, Nam Quoc Ngo *, and Ping Shum Network Technology Research Center, School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Nanyang
REDUCTION OF CROSSTALK IN WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXED FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 77, 367 378, 2007 REDUCTION OF CROSSTALK IN WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXED FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS R. Tripathi Northern India Engineering College
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 77, 367 378, 2007 REDUCTION OF CROSSTALK IN WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXED FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS R. Tripathi Northern India Engineering College
ISSN (ONLINE): , ISSN (PRINT):
 Volume-7, Issue-3, May-June 2017 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 227-237 Simulative Evaluations of in Band and Out of Band Crosstalk Penalties for Advanced Modulation
Volume-7, Issue-3, May-June 2017 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 227-237 Simulative Evaluations of in Band and Out of Band Crosstalk Penalties for Advanced Modulation
1 Introduction. Keywords: modified double weight (MDW) code, SAC- OCDMA, WDM and FBG
 N. Ahmed*, S. A. Aljunid, R. B. Ahmad, Nizam Uddin Ahamed and Matiur Rahman Performance Analysis of Hybrid OCDMA/WDM System for Metro Area Network Abstract: In this study a hybrid spectral amplitude coding
N. Ahmed*, S. A. Aljunid, R. B. Ahmad, Nizam Uddin Ahamed and Matiur Rahman Performance Analysis of Hybrid OCDMA/WDM System for Metro Area Network Abstract: In this study a hybrid spectral amplitude coding
SOA-BASED NOISE SUPPRESSION IN SPECTRUM-SLICED PONs: IMPACT OF BIT-RATE AND SOA GAIN RECOVERY TIME
 SOA-BASED NOISE SUPPRESSION IN SPECTRUM-SLICED PONs: IMPACT OF BIT-RATE AND SOA GAIN RECOVERY TIME Francesco Vacondio, Walid Mathlouthi, Pascal Lemieux, Leslie Ann Rusch Centre d optique photonique et
SOA-BASED NOISE SUPPRESSION IN SPECTRUM-SLICED PONs: IMPACT OF BIT-RATE AND SOA GAIN RECOVERY TIME Francesco Vacondio, Walid Mathlouthi, Pascal Lemieux, Leslie Ann Rusch Centre d optique photonique et
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 15, 37 48, 2010 TEMPERATURE INSENSITIVE BROAD AND FLAT GAIN C-BAND EDFA BASED ON MACRO-BENDING
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 15, 37 48, 2010 TEMPERATURE INSENSITIVE BROAD AND FLAT GAIN C-BAND EDFA BASED ON MACRO-BENDING P. Hajireza Optical Fiber Devices Group Multimedia University
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 15, 37 48, 2010 TEMPERATURE INSENSITIVE BROAD AND FLAT GAIN C-BAND EDFA BASED ON MACRO-BENDING P. Hajireza Optical Fiber Devices Group Multimedia University
Performance Analysis of Direct Detection-Based Modulation Formats for WDM Long-Haul Transmission Systems Abstract 1.0 Introduction
 Performance Analysis of Direct Detection-Based Modulation Formats for WDM Long-Haul Transmission Systems PRLightCOM Broadband Solutions Pvt. Ltd. Bangalore, Karnataka, INDIA Abstract During the last decade,
Performance Analysis of Direct Detection-Based Modulation Formats for WDM Long-Haul Transmission Systems PRLightCOM Broadband Solutions Pvt. Ltd. Bangalore, Karnataka, INDIA Abstract During the last decade,
Nonlinear Effect of Four Wave Mixing for WDM in Radio-over-Fiber Systems
 Quest Journals Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Research Volume ~ Issue 4 (014) pp: 01-06 ISSN(Online) : 31-5941 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Nonlinear Effect of Four Wave Mixing
Quest Journals Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Research Volume ~ Issue 4 (014) pp: 01-06 ISSN(Online) : 31-5941 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Nonlinear Effect of Four Wave Mixing
from ocean to cloud SEAMLESS OADM FUNCTIONALITY FOR SUBMARINE BU
 SEAMLESS OADM FUNCTIONALITY FOR SUBMARINE BU Shigui Zhang, Yan Wang, Hongbo Sun, Wendou Zhang and Liping Ma sigurd.zhang@huaweimarine.com Huawei Marine Networks, Hai-Dian District, Beijing, P.R. China,
SEAMLESS OADM FUNCTIONALITY FOR SUBMARINE BU Shigui Zhang, Yan Wang, Hongbo Sun, Wendou Zhang and Liping Ma sigurd.zhang@huaweimarine.com Huawei Marine Networks, Hai-Dian District, Beijing, P.R. China,
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF TWO-CHANNEL DISPERSION SUPPORTED TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS USING SINGLE AND DOUBLE-CAVITY FABRY-PEROT FILTERS AS DEMULTIPLEXERS
 PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF TWO-CHANNEL DISPERSION SUPPORTED TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS USING SINGLE AND DOUBLE-CAVITY FABRY-PEROT FILTERS AS DEMULTIPLEXERS Mário M. Freire Department of Mathematics and Information
PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF TWO-CHANNEL DISPERSION SUPPORTED TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS USING SINGLE AND DOUBLE-CAVITY FABRY-PEROT FILTERS AS DEMULTIPLEXERS Mário M. Freire Department of Mathematics and Information
FI..,. HEWLETT. High-Frequency Photodiode Characterization using a Filtered Intensity Noise Technique
 FI..,. HEWLETT ~~ PACKARD High-Frequency Photodiode Characterization using a Filtered Intensity Noise Technique Doug Baney, Wayne Sorin, Steve Newton Instruments and Photonics Laboratory HPL-94-46 May,
FI..,. HEWLETT ~~ PACKARD High-Frequency Photodiode Characterization using a Filtered Intensity Noise Technique Doug Baney, Wayne Sorin, Steve Newton Instruments and Photonics Laboratory HPL-94-46 May,
Devices for all-optical wavelength conversion and spectral inversion
 Devices for all-optical wavelength conversion and spectral inversion Antonio Mecozzi Fondazione Ugo Bordoni, via B. Castiglione 59,1-00142 Roma, Italy Phone: +39 (6) 5480--2232 Fax: +39 (6) 5480--4402
Devices for all-optical wavelength conversion and spectral inversion Antonio Mecozzi Fondazione Ugo Bordoni, via B. Castiglione 59,1-00142 Roma, Italy Phone: +39 (6) 5480--2232 Fax: +39 (6) 5480--4402
Fiber Parametric Amplifiers for Wavelength Band Conversion
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 8, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2002 527 Fiber Parametric Amplifiers for Wavelength Band Conversion Mohammed N. Islam and Özdal Boyraz, Student Member, IEEE
IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 8, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2002 527 Fiber Parametric Amplifiers for Wavelength Band Conversion Mohammed N. Islam and Özdal Boyraz, Student Member, IEEE
Strictly Non-Blocking Optical Cross Connect for WDM Wavelength Path Networks
 Strictly Non-Blocking Optical Cross Connect for WDM Wavelength Path Networks P. S. André 1, 2, J. Pinto 1, A. J. Teixeira 1,3, T. Almeida 1, 4, A. Nolasco Pinto 1, 3, J. L. Pinto 1, 2, F. Morgado 4 and
Strictly Non-Blocking Optical Cross Connect for WDM Wavelength Path Networks P. S. André 1, 2, J. Pinto 1, A. J. Teixeira 1,3, T. Almeida 1, 4, A. Nolasco Pinto 1, 3, J. L. Pinto 1, 2, F. Morgado 4 and
Mahendra Kumar1 Navneet Agrawal2
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 9, September-2015 1202 Performance Enhancement of DCF Based Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network (WDM-PON)
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 9, September-2015 1202 Performance Enhancement of DCF Based Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network (WDM-PON)
OPTICAL NETWORKS. Building Blocks. A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005
 OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 3, ISSUE 06 34 Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System Meenakshi,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 3, ISSUE 06 34 Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System Meenakshi,
Gain-clamping techniques in two-stage double-pass L-band EDFA
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 66, No. 3 journal of March 2006 physics pp. 539 545 Gain-clamping techniques in two-stage double-pass L-band EDFA S W HARUN 1, N Md SAMSURI 2 and H AHMAD 2 1 Faculty
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 66, No. 3 journal of March 2006 physics pp. 539 545 Gain-clamping techniques in two-stage double-pass L-band EDFA S W HARUN 1, N Md SAMSURI 2 and H AHMAD 2 1 Faculty
SEMICONDUCTOR lasers and amplifiers are important
 240 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 28, NO. 3, FEBRUARY 1, 2010 Temperature-Dependent Saturation Characteristics of Injection Seeded Fabry Pérot Laser Diodes/Reflective Optical Amplifiers Hongyun
240 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 28, NO. 3, FEBRUARY 1, 2010 Temperature-Dependent Saturation Characteristics of Injection Seeded Fabry Pérot Laser Diodes/Reflective Optical Amplifiers Hongyun
Chapter 8. Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM) Part II: Amplifiers
 Chapter 8 Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM) Part II: Amplifiers Introduction Traditionally, when setting up an optical link, one formulates a power budget and adds repeaters when the path loss exceeds
Chapter 8 Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM) Part II: Amplifiers Introduction Traditionally, when setting up an optical link, one formulates a power budget and adds repeaters when the path loss exceeds
Performance of A Multicast DWDM Network Applied to the Yemen Universities Network using Quality Check Algorithm
 Performance of A Multicast DWDM Network Applied to the Yemen Universities Network using Quality Check Algorithm Khaled O. Basulaim, Samah Ali Al-Azani Dept. of Information Technology Faculty of Engineering,
Performance of A Multicast DWDM Network Applied to the Yemen Universities Network using Quality Check Algorithm Khaled O. Basulaim, Samah Ali Al-Azani Dept. of Information Technology Faculty of Engineering,
Multiwavelength Single-Longitudinal-Mode Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Laser. Citation IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 2013, v. 25, p.
 Title Multiwavelength Single-Longitudinal-Mode Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Laser Author(s) ZHOU, Y; Chui, PC; Wong, KKY Citation IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 2013, v. 25, p. 385-388 Issued Date 2013 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/189009
Title Multiwavelength Single-Longitudinal-Mode Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Laser Author(s) ZHOU, Y; Chui, PC; Wong, KKY Citation IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 2013, v. 25, p. 385-388 Issued Date 2013 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/189009
4x25-Gb/s 40-km 1310-nm PMD with SOA Pre-Amplifier: Impact of Channel Spacing
 4x25-Gb/s 40-km 1310-nm PMD with SOA Pre-Amplifier: Impact of Channel Spacing Ramón Gutiérrez-Castrejón, email: RGutierrezC@ii.unam.mx Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico-UNAM (collaboration with Marcus
4x25-Gb/s 40-km 1310-nm PMD with SOA Pre-Amplifier: Impact of Channel Spacing Ramón Gutiérrez-Castrejón, email: RGutierrezC@ii.unam.mx Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico-UNAM (collaboration with Marcus
An integrated recirculating optical buffer
 An integrated recirculating optical buffer Hyundai Park, John P. Mack, Daniel J. Blumenthal, and John E. Bowers* University of California, Santa Barbara, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
An integrated recirculating optical buffer Hyundai Park, John P. Mack, Daniel J. Blumenthal, and John E. Bowers* University of California, Santa Barbara, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Application Instruction 001. The Enhanced Functionalities of Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and their Role in Advanced Optical Networking
 The Enhanced Functionalities of Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and their Role in Advanced Optical Networking I. Introduction II. III. IV. SOA Fundamentals Wavelength Conversion based on SOAs The Role
The Enhanced Functionalities of Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and their Role in Advanced Optical Networking I. Introduction II. III. IV. SOA Fundamentals Wavelength Conversion based on SOAs The Role
1.25 Gb/s Broadcast Signal Transmission in WDM-PON Based on Mutually Injected Fabry-Perot Laser Diodes
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 16, No. 2, June 2012, pp. 101-106 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2012.16.2.101 1.25 Gb/s Broadcast Signal Transmission in WDM-PON Based on Mutually Injected
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 16, No. 2, June 2012, pp. 101-106 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2012.16.2.101 1.25 Gb/s Broadcast Signal Transmission in WDM-PON Based on Mutually Injected
Spectral Response of FWM in EDFA for Long-haul Optical Communication
 Spectral Response of FWM in EDFA for Long-haul Optical Communication Lekshmi.S.R 1, Sindhu.N 2 1 P.G.Scholar, Govt. Engineering College, Wayanad, Kerala, India 2 Assistant Professor, Govt. Engineering
Spectral Response of FWM in EDFA for Long-haul Optical Communication Lekshmi.S.R 1, Sindhu.N 2 1 P.G.Scholar, Govt. Engineering College, Wayanad, Kerala, India 2 Assistant Professor, Govt. Engineering
Optical phase-locked loop for coherent transmission over 500 km using heterodyne detection with fiber lasers
 Optical phase-locked loop for coherent transmission over 500 km using heterodyne detection with fiber lasers Keisuke Kasai a), Jumpei Hongo, Masato Yoshida, and Masataka Nakazawa Research Institute of
Optical phase-locked loop for coherent transmission over 500 km using heterodyne detection with fiber lasers Keisuke Kasai a), Jumpei Hongo, Masato Yoshida, and Masataka Nakazawa Research Institute of
Performance Improvement of 40-Gb/s Capacity Four-Channel WDM. Dispersion-Supported Transmission by Using Broadened Passband
 Performance Improvement of 40-Gb/s Capacity Four-Channel WDM Dispersion-Supported Transmission by Using Broadened Passband Arrayed-Waveguide Grating Demultiplexers Mário M. Freire Department of Mathematics
Performance Improvement of 40-Gb/s Capacity Four-Channel WDM Dispersion-Supported Transmission by Using Broadened Passband Arrayed-Waveguide Grating Demultiplexers Mário M. Freire Department of Mathematics
Lecture 8 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 8, Slide 1
 Lecture 8 Bit error rate The Q value Receiver sensitivity Sensitivity degradation Extinction ratio RIN Timing jitter Chirp Forward error correction Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 8, Slide Bit error
Lecture 8 Bit error rate The Q value Receiver sensitivity Sensitivity degradation Extinction ratio RIN Timing jitter Chirp Forward error correction Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 8, Slide Bit error
Prabhjeet Singh a, Narwant Singh b, Amandeep Singh c
 ISSN : 2250-3021 Investigation of DWDM System for Different Modulation Formats Prabhjeet Singh a, Narwant Singh b, Amandeep Singh c a B.G.I.E.T. Sangrur, India b G.N.D.E.C. Ludhiana, India c R.I.E.T, Ropar,
ISSN : 2250-3021 Investigation of DWDM System for Different Modulation Formats Prabhjeet Singh a, Narwant Singh b, Amandeep Singh c a B.G.I.E.T. Sangrur, India b G.N.D.E.C. Ludhiana, India c R.I.E.T, Ropar,
Emerging Subsea Networks
 EVALUATION OF NONLINEAR IMPAIRMENT FROM NARROW- BAND UNPOLARIZED IDLERS IN COHERENT TRANSMISSION ON DISPERSION-MANAGED SUBMARINE CABLE SYSTEMS Masashi Binkai, Keisuke Matsuda, Tsuyoshi Yoshida, Naoki Suzuki,
EVALUATION OF NONLINEAR IMPAIRMENT FROM NARROW- BAND UNPOLARIZED IDLERS IN COHERENT TRANSMISSION ON DISPERSION-MANAGED SUBMARINE CABLE SYSTEMS Masashi Binkai, Keisuke Matsuda, Tsuyoshi Yoshida, Naoki Suzuki,
A novel 3-stage structure for a low-noise, high-gain and gain-flattened L-band erbium doped fiber amplifier *
 Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE ISSN 9-9 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn A novel -stage structure for a low-noise, high-gain and gain-flattened L-band erbium doped fiber amplifier
Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE ISSN 9-9 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn A novel -stage structure for a low-noise, high-gain and gain-flattened L-band erbium doped fiber amplifier
EDFA TRANSIENT REDUCTION USING POWER SHAPING
 Proceedings of the Eighth IASTED International Conference WIRELESS AND OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS (WOC 2008) May 26-28, 2008 Quebec City, Quebec, Canada EDFA TRANSIENT REDUCTION USING POWER SHAPING Trent Jackson
Proceedings of the Eighth IASTED International Conference WIRELESS AND OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS (WOC 2008) May 26-28, 2008 Quebec City, Quebec, Canada EDFA TRANSIENT REDUCTION USING POWER SHAPING Trent Jackson
Performance of Digital Optical Communication Link: Effect of In-Line EDFA Parameters
 PCS-7 766 CSDSP 00 Performance of Digital Optical Communication Link: Effect of n-line EDFA Parameters Ahmed A. Elkomy, Moustafa H. Aly, Member of SOA, W. P. g 3, Senior Member, EEE, Z. Ghassemlooy 3,
PCS-7 766 CSDSP 00 Performance of Digital Optical Communication Link: Effect of n-line EDFA Parameters Ahmed A. Elkomy, Moustafa H. Aly, Member of SOA, W. P. g 3, Senior Member, EEE, Z. Ghassemlooy 3,
MODELING AND EVALUATION OF CHIP-TO-CHIP SCALE SILICON PHOTONIC NETWORKS
 1 MODELING AND EVALUATION OF CHIP-TO-CHIP SCALE SILICON PHOTONIC NETWORKS Robert Hendry, Dessislava Nikolova, Sébastien Rumley, Keren Bergman Columbia University HOTI 2014 2 Chip-to-chip optical networks
1 MODELING AND EVALUATION OF CHIP-TO-CHIP SCALE SILICON PHOTONIC NETWORKS Robert Hendry, Dessislava Nikolova, Sébastien Rumley, Keren Bergman Columbia University HOTI 2014 2 Chip-to-chip optical networks
OBSERVATION AND MITIGATION OF POWER TRANSIENTS IN 160Gbps OPTICAL BACKHAUL NETWORKS
 OBSERVATION AND MITIGATION OF POWER TRANSIENTS IN 160Gbps OPTICAL BACKHAUL NETWORKS Vikrant Sharma Anurag Sharma Electronics and Communication Engineering, CT Group of Institutions, Jalandhar Dalveer Kaur
OBSERVATION AND MITIGATION OF POWER TRANSIENTS IN 160Gbps OPTICAL BACKHAUL NETWORKS Vikrant Sharma Anurag Sharma Electronics and Communication Engineering, CT Group of Institutions, Jalandhar Dalveer Kaur
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Design System
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 53 ( 2013 ) 294 302 Malaysian Technical Universities Conference on Engineering & Technology 2012, MUCET 2012 Part -1 Electronic and Electrical
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 53 ( 2013 ) 294 302 Malaysian Technical Universities Conference on Engineering & Technology 2012, MUCET 2012 Part -1 Electronic and Electrical
Optical monitoring technique based on scanning the gain profiles of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers for WDM networks
 Optics Communications () 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Optical monitoring technique based on scanning the gain profiles of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers for WDM networks Chien-Hung Yeh *, Chien-Chung
Optics Communications () 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Optical monitoring technique based on scanning the gain profiles of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers for WDM networks Chien-Hung Yeh *, Chien-Chung
SIMULATION OF FIBER LOOP BUFFER MEMORY OF ALL-OPTICAL PACKET SWITCH. Mandar Naik, Yatindra Nath Singh
 SIMULATION OF FIBER LOOP BUFFER MEMORY ABSTRACT OF ALL-OPTICAL PACKET SWITCH Mandar Naik, Yatindra Nath Singh Center for Laser Technology Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur - 28 16 India {mandy,ynsingh}@iitk.ac.in
SIMULATION OF FIBER LOOP BUFFER MEMORY ABSTRACT OF ALL-OPTICAL PACKET SWITCH Mandar Naik, Yatindra Nath Singh Center for Laser Technology Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur - 28 16 India {mandy,ynsingh}@iitk.ac.in
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. 4.1 Introduction
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Introduction In this chapter focus are given more on WDM system. The results which are obtained mainly from the simulation work are presented. In simulation analysis, the study will
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Introduction In this chapter focus are given more on WDM system. The results which are obtained mainly from the simulation work are presented. In simulation analysis, the study will
Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET
 Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET 1 Outlines of the Class Principles of WDM DWDM, CWDM, Bidirectional WDM Components of WDM AWG, filter Problems with WDM Four-wave mixing Stimulated Brillouin scattering WDM Network
Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET 1 Outlines of the Class Principles of WDM DWDM, CWDM, Bidirectional WDM Components of WDM AWG, filter Problems with WDM Four-wave mixing Stimulated Brillouin scattering WDM Network
CSO/CTB PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT BY USING FABRY-PEROT ETALON AT THE RECEIVING SITE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 107 113, 2009 CSO/CTB PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT BY USING FABRY-PEROT ETALON AT THE RECEIVING SITE S.-J. Tzeng, H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, K.-H. Chang,and C.-H.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 107 113, 2009 CSO/CTB PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT BY USING FABRY-PEROT ETALON AT THE RECEIVING SITE S.-J. Tzeng, H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, K.-H. Chang,and C.-H.
RZ BASED DISPERSION COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE IN DWDM SYSTEM FOR BROADBAND SPECTRUM
 RZ BASED DISPERSION COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE IN DWDM SYSTEM FOR BROADBAND SPECTRUM Prof. Muthumani 1, Mr. Ayyanar 2 1 Professor and HOD, 2 UG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
RZ BASED DISPERSION COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE IN DWDM SYSTEM FOR BROADBAND SPECTRUM Prof. Muthumani 1, Mr. Ayyanar 2 1 Professor and HOD, 2 UG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers
 ECE 6323 Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers Semiconductor optical amplifier Others: stimulated Raman, optical parametric Advanced application:
ECE 6323 Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers Semiconductor optical amplifier Others: stimulated Raman, optical parametric Advanced application:
ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS
 MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
Optical Transport Tutorial
 Optical Transport Tutorial 4 February 2015 2015 OpticalCloudInfra Proprietary 1 Content Optical Transport Basics Assessment of Optical Communication Quality Bit Error Rate and Q Factor Wavelength Division
Optical Transport Tutorial 4 February 2015 2015 OpticalCloudInfra Proprietary 1 Content Optical Transport Basics Assessment of Optical Communication Quality Bit Error Rate and Q Factor Wavelength Division
4x100GE through 2 and 10km SMF Using DMT and 1.3mm LAN-WDM EMLs. Winston Way, Trevor Chan, NeoPhotonics, USA
 4x100GE through 2 and 10km SMF Using and 1.3mm LAN-WDM EMLs Winston Way, Trevor Chan, NeoPhotonics, USA IEEE802.3 400GbE Study Group, November 2013 Objectives Study the technical feasibility of using to
4x100GE through 2 and 10km SMF Using and 1.3mm LAN-WDM EMLs Winston Way, Trevor Chan, NeoPhotonics, USA IEEE802.3 400GbE Study Group, November 2013 Objectives Study the technical feasibility of using to
22-Channel Capacity of 2.5Gbit/s DWDM-PON ONU Transmitter by Direct-Modularly Side-Mode Injection Locked FPLD
 22-Channel Capacity of 2.5Gbit/s DWDM-PON ONU Transmitter by Direct-Modularly Side-Mode Injection Locked FPLD Yu-Sheng Liao a, Yung-Jui Chen b, and Gong-Ru Lin c* a Department of Photonics & Institute
22-Channel Capacity of 2.5Gbit/s DWDM-PON ONU Transmitter by Direct-Modularly Side-Mode Injection Locked FPLD Yu-Sheng Liao a, Yung-Jui Chen b, and Gong-Ru Lin c* a Department of Photonics & Institute
Chapter 3 Metro Network Simulation
 Chapter 3 Metro Network Simulation 3.1 Photonic Simulation Tools Simulation of photonic system has become a necessity due to the complex interactions within and between components. Tools have evolved from
Chapter 3 Metro Network Simulation 3.1 Photonic Simulation Tools Simulation of photonic system has become a necessity due to the complex interactions within and between components. Tools have evolved from
Optical Local Area Networking
 Optical Local Area Networking Richard Penty and Ian White Cambridge University Engineering Department Trumpington Street, Cambridge, CB2 1PZ, UK Tel: +44 1223 767029, Fax: +44 1223 767032, e-mail:rvp11@eng.cam.ac.uk
Optical Local Area Networking Richard Penty and Ian White Cambridge University Engineering Department Trumpington Street, Cambridge, CB2 1PZ, UK Tel: +44 1223 767029, Fax: +44 1223 767032, e-mail:rvp11@eng.cam.ac.uk
SOA preamp performance: theoretical modeling
 SOA preamp performance: theoretical modeling ene Bonk, Dora van Veen, Vincent Houtsma, Bell Labs Ed Harstead, member Fixed Networks CTO January 2017 1 eceiver Model for SOA+Filter+PIN / APD Analytical
SOA preamp performance: theoretical modeling ene Bonk, Dora van Veen, Vincent Houtsma, Bell Labs Ed Harstead, member Fixed Networks CTO January 2017 1 eceiver Model for SOA+Filter+PIN / APD Analytical
ASEMICONDUCTOR optical amplifier (SOA) that is linear
 1162 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 3, NO. 5, OCTOBER 1997 Numerical and Theoretical Study of the Crosstalk in Gain Clamped Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers Jinying Sun, Geert
1162 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 3, NO. 5, OCTOBER 1997 Numerical and Theoretical Study of the Crosstalk in Gain Clamped Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers Jinying Sun, Geert
Vol. 6, No. 9 / September 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 1105
 Vol. 6, No. 9 / September 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 1105 Electronic equalization of 10 Gbit/ s upstream signals for asynchronous-modulation and chromatic-dispersion compensation in a high-speed
Vol. 6, No. 9 / September 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 1105 Electronic equalization of 10 Gbit/ s upstream signals for asynchronous-modulation and chromatic-dispersion compensation in a high-speed
Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber
 Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber I. H. M. Nadzar 1 and N. A.Awang 1* 1 Faculty of Science, Technology and Human Development, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor,
Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber I. H. M. Nadzar 1 and N. A.Awang 1* 1 Faculty of Science, Technology and Human Development, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor,
The wavelength division multiplexing passive optical
 Lee et al. VOL., NO. 6/JUNE 010/J. OPT. COMMUN. NETW. 381 Decision Threshold Control Method for the Optical Receiver of a WDM-PON Hoon-Keun Lee, Jung-Hyung Moon, Sil-Gu Mun, Ki-Man Choi, and Chang-Hee
Lee et al. VOL., NO. 6/JUNE 010/J. OPT. COMMUN. NETW. 381 Decision Threshold Control Method for the Optical Receiver of a WDM-PON Hoon-Keun Lee, Jung-Hyung Moon, Sil-Gu Mun, Ki-Man Choi, and Chang-Hee
Enhanced 10 Gb/s operations of directly modulated reflective semiconductor optical amplifiers without electronic equalization
 Enhanced Gb/s operations of directly modulated reflective semiconductor optical amplifiers without electronic equalization M. Presi, 1, A. Chiuchiarelli, 1 R. Corsini, 1 P. Choudury, 1 F. Bottoni, 1, L.
Enhanced Gb/s operations of directly modulated reflective semiconductor optical amplifiers without electronic equalization M. Presi, 1, A. Chiuchiarelli, 1 R. Corsini, 1 P. Choudury, 1 F. Bottoni, 1, L.
Microwave and Optical Technology Letters. Minhui Yan, Qing-Yang Xu 1, Chih-Hung Chen, Wei-Ping Huang, and Xiaobin Hong
 Page of 0 0 0 0 0 0 Schemes of Optical Power Splitter Nodes for Direct ONU-ONU Intercommunication Minhui Yan, Qing-Yang Xu, Chih-Hung Chen, Wei-Ping Huang, and Xiaobin Hong Department of Electrical and
Page of 0 0 0 0 0 0 Schemes of Optical Power Splitter Nodes for Direct ONU-ONU Intercommunication Minhui Yan, Qing-Yang Xu, Chih-Hung Chen, Wei-Ping Huang, and Xiaobin Hong Department of Electrical and
Technical Feasibility of 4x25 Gb/s PMD for 40km at 1310nm using SOAs
 Technical Feasibility of 4x25 Gb/s PMD for 40km at 1310nm using SOAs Ramón Gutiérrez-Castrejón RGutierrezC@ii.unam.mx Tel. +52 55 5623 3600 x8824 Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico Introduction A
Technical Feasibility of 4x25 Gb/s PMD for 40km at 1310nm using SOAs Ramón Gutiérrez-Castrejón RGutierrezC@ii.unam.mx Tel. +52 55 5623 3600 x8824 Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico Introduction A
Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise
 Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise Ben Wu, * Zhenxing Wang, Bhavin J. Shastri, Matthew P. Chang, Nicholas A. Frost, and Paul R. Prucnal
Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise Ben Wu, * Zhenxing Wang, Bhavin J. Shastri, Matthew P. Chang, Nicholas A. Frost, and Paul R. Prucnal
