White-light interferometry, Hilbert transform, and noise
|
|
|
- Hilda Hoover
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 White-light interferometry, Hilbert transform, and noise Pavel Pavlíček *a, Václav Michálek a a Institute of Physics of Academy of Science of the Czech Republic, Joint Laboratory of Optics, 17. listopadu 50a, Olomouc, , Czech Republic; ABSTRACT White-light interferometry is an established and proved method for the measurement of the geometrical shape of objects. The advantage of white-light interferometry is that it is suitable for the measurement of the shape of objects with smooth as well as rough surface. The information about the longitudinal coordinate of the surface of the measured object is obtained from the white-light interferogram. The interferogram is the intensity at the detector expressed as the function of the position of the object. (The object is moved along the optical axis during the measurement process.) If the shape of an object with rough surface is measured, the phase of the interferogram is not evaluated because it is a random value. The information about the longitudinal coordinate is obtained from the center of the interferogram envelope. A classical method for the calculation of the envelope of white-light interferogram is the demodulation by means of Hilbert transform. However, the electric signal at the output of the camera is influenced by the noise. Therefore, as expected, the calculated envelope is also influenced by the noise. The result is that the measured longitudinal coordinate of the surface of the object is affected by an error. In our contribution, we look for the answer on following questions: How does the noise of the evaluated envelope differ from the noise of the interferogram? What is the minimal measurement uncertainty that can be achieved? Keywords: White-light interferometry, Hilbert transform, noise, measurement uncertainty 1. INTRODUCTION White-light interferometry is used to measure the geometrical shape of objects. The height variations of the measured object can be found in range from nanometers up to millimeters. White-light interferometry can be used for the measurement of the shape of objects with smooth as well as with rough surface. In this paper, we will deal with whitelight interferometry on rough surfaces [1]. The experimental setup of white-light interferometry is illustrated in Fig. 1. Usually a Michelson interferometer is used. The light source has a broadband spectrum. Suitable light sources for white-light interferometry are light-emitting diode, superluminescent diode or an incandescent lamp. The measured object is placed in one arm of the interferometer. The other arm is terminated by reference mirror. The light from the light source passes the beam-splitter and is reflected from the measured object as well as from the reference mirror. The reflected light from both interferometer arms is transmitted through an imaging system to a CCD camera. During the measurement, the object is moved along the optical axis as indicated by the arrow in Fig. 1. The intensity in each pixel is recorded as a function of the longitudinal position of the measured object. Such a record is called interferogram. An example of the interferogram is shown in Fig. 2(a). White-light interferometry on rough surfaces is based on interferometry in individual speckles. Therefore it is important that the speckle size corresponds roughly with the size of the pixel of the camera. The speckle size can be controlled by the stop in the imaging system. Thus, an interferogram is acquired for each individual speckle. The longitudinal coordinate of an object point is determined from the position of the center of the interferogram. The center of the interferogram is denoted by letter C in Fig. 2(a). As the measured surface is rough, the phase of the interferogram is a random value [1]. Therefore it has no significance to evaluate the phase of the interferogram. The longitudinal coordinate of the object surface is determined from the interferogram envelope only. The envelope of the * Pavel.Pavlicek@upol.cz; phone ; fax ; jointlab.upol.cz
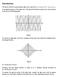
2 interferogram from Fig. 2(a) is depicted in Fig. 2(b). The process of extracting the envelope from the interferogram is called demodulation. A classical method for the demodulation of the interferogram is the detection by means of Hilbert transform [2]. Figure 1. The schematic of the experimental setup of white-light interferometry. Figure 2. (a) Example of white-light interferogram - the original signal. (b) The envelope of white-light interferogram the signal after demodulation. (c) The noise extracted from the original signal. (d) The noise extracted from the signal after demodulation. In the real measurement, the interferogram is corrupted by the noise. Therefore, as one can expect, the interferogram envelope is also corrupted by the noise. Our goal is to determine how the noise of the interferogram affects the interferogram envelope. We investigate the influence of the noise on the measurement uncertainty of white-light interferometry on rough surfaces.
3 2. MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTY The measurement uncertainty of white-light interferometry on rough surface is given by the ability of the evaluation algorithm to find the center of the interferogram envelope. The center of the interferogram envelope cannot be found absolutely accurately because the interferogram is affected by the noise. The theoretical limit of the evaluation algorithm can be calculated by means of Cramer-Rao inequality [3]. It shows that the theoretical limit of the search for the center of a modulated signal with a Gaussian envelope is given by 2 I δz = 2 4 l z, A where σ is the standard deviation of the noise, I A is the amplitude of the signal, l c is the coherence length of the used light and z is the sampling step. The meaning of the amplitude I A, the coherence length l c and the sampling step z is illustrated in Fig. 3. Coherence length is defined as the distance from the center of the interferogram to the value of longitudinal coordinate at which the envelope of the interferogram is equal to 1/e of its maximal value. c (1) Figure 3. The meaning of the amplitude I A, the coherence length l c, the sampling step Δz, and the wavelength λ. The marks indicate the sampled values. 3. CORRELATION OF THE NOISE The noise extracted from the interferogram is shown in Fig. 2(c). We assume that the noise of the interferogram is an uncorrelated noise with standard deviation equal to σ. The noise of the interferogram may be assumed to be uncorrelated because the individual intensities measured in one pixel of the camera for various positions of the measured object are independent. Figures 4(a) and (c) show the noise of the interferogram and its spectral density. Because the noise is uncorrelated, its spectral density is constant and equal to the variance σ 2 of the noise [4]. The envelope of the interferogram is calculated by means of Hilbert transform. The demodulation by Hilbert transform changes the form of the spectral density of the noise as shown in Fig. 4(d). The spatial frequency shift ν 0 that is observed in Fig. 4(d) is given by the wavelength λ of the used light source: ν 0 = 2/λ. Because of the Michelson arrangement of the interferometer, the period of the modulation of the interferogram is equal to λ/2 as shown in Fig. 3. The maximal spatial frequency ν max is determined by the sampling step: ν max = 2/z. The noise extracted from the envelope is shown in Fig. 4(b). The variance of the noise is equal to the mean value of the spectral density [4]. It is apparent from Fig. 4(d) that the variance of the noise of the envelope is equal to σ 2. This means that the standard deviation of the noise of the envelope is the same as that of the noise of the interferogram. Further, it is apparent from Fig. 4(d) that the noise of the envelope is no more uncorrelated because its spectral density is not constant. The process of demodulation by means of Hilbert transform conserves the variance of the noise but causes the correlation of the noise. The correlation of the noise is also apparent in Fig. 4(b).
4 The autocovariance function of the noise is calculated as the inverse Fourier transform of the spectral density of the noise. The noise of the interferogram is uncorrelated, its spectral density is a constant function with the value σ 2. Accordingly, the autocovariance function of the noise of the interferogram has the value σ 2 at 0 and the value 0 elsewhere. The spectral density of the noise of the interferogram and the corresponding autocovariance function are shown in Fig. 5(a) and (c), respectively. The spectral density of the noise of the envelope is shown in Fig. 5(b). The autocovariance function of the noise of the envelope is shown in Fig. 5(d). The variance of the noise is equal to σ 2 in both cases: the noise of the interferogram and the noise of the envelope. (The variance of the noise is equal to the autocovariance function at 0.) For both cases, the noise of the interferogram and the noise of the envelope, the variance of the noise (which is equal to the autocovariance function at 0) is equal to σ 2. Figure 4. (a) The noise extracted from the original signal. (b) The noise extracted from the signal after demodulation. (c) Spectral density of the noise of the original signal. (d) Spectral density of the noise of the signal after demodulation. In this example λ/δz = 10 (10 samples within the distance of one wavelength). Figure 5. (a) Spectral density of the original signal noise. (b) Spectral density of the noise of the signal after demodulation. (c) Autocovariance function of the noise of the original signal. (d) Autocovariance function of the noise of the signal after demodulation.
5 4. INFLUENCE OF THE CORRELATION OF THE NOISE The noise of the envelope is correlated. Therefore, if the minimal achievable measurement uncertainty is calculated from the envelope by means of Cramer-Rao inequality, the inverse of the correlation matrix must be involved. The correlation matrix r k,l of the noise can be constructed from the autocovariance function j kl kl 0 r kl = (2) 2 shown in Figs. 5(c) and (d). The construction of the correlation matrix is illustrated in Fig. 6. Figure 6. The construction of the correlation matrix from the autocovariance function. For the uncorrelated noise, 0 = (0) = 2 and i = (iz) = 0 for all i > 0. Therefore, the correlation matrix of an uncorrelated noise is an identity matrix. According to Eq. (2), the correlation depends only on the distance between two points. Therefore the correlation matrix of the noise extracted from the interferogram envelope is a symmetric Toeplitz matrix. A Toeplitz matrix is a matrix in which each descending diagonal from left to right is constant as can be seen in Fig. 6 [5]. The inverse of a Toeplitz matrix is generally not a Toeplitz matrix. However, for large dimensions, the inverse correlation matrix has nearly Toeplitz form and can be easily expressed [4]. The inverse k,l of the correlation matrix is calculated from function j 2 kl = k l. (3) The autocovariance function is the inverse Fourier transform of the spectral density () = 1 FT (4) and the function is the inverse Fourier transform of the reciprocal of the spectral density = 1 1 FT (5). By inserting of the inverse correlation matrix into Cramer-Rao inequality, the measurement uncertainty is by a factor of square root of two (1.414) higher than that for the uncorrelated noise [3]. This is an important result. The measurement uncertainty of the interferogram is by factor square root of two higher than the measurement uncertainty of a signal with the same form as the interferogram envelope. The reason is the correlated noise of the envelope of the interferogram. The increase factor does not depend on the coherence length l c, wavelength and step size z.
6 5. CONCLUSIONS The envelope detection by means of Hilbert transform transforms the noise of the interferogram. If the interferogram is affected by a normally distributed uncorrelated noise, the envelope noise has the same standard deviation but it is correlated. The autocovariance function of the envelope noise depends on the ratio between the mean wavelength of the used light and the sampling step. The correlation of the noise causes that the measurement uncertainty is by factor of square root of two higher than it would be for a signal with the same form but without modulation. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This research was supported financially by the project TA REFERENCES [1] Dresel, T., Häusler, G., and Venzke, H., "Three-dimensional sensing of rough surfaces by coherence radar," Appl. Opt. 31, (1992). [2] Larkin, K. G., "Efficient nonlinear algorithm for envelope detection in white light interferometry," J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 13, (1996). [3] Pavliček, P. and Michalek, V., "White-light interferometry Envelope detection by Hilbert transform and influence of noise," Opt. Lasers. Eng. 50, (2012). [4] Helstrom, C. W., [Elements of signal detection & estimation], PTR Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1995). [5] Golub, G. H. and van Loan, C. F., [Matrix computation], The John Hopkins University Press, London (1996).
Coherence radar - new modifications of white-light interferometry for large object shape acquisition
 Coherence radar - new modifications of white-light interferometry for large object shape acquisition G. Ammon, P. Andretzky, S. Blossey, G. Bohn, P.Ettl, H. P. Habermeier, B. Harand, G. Häusler Chair for
Coherence radar - new modifications of white-light interferometry for large object shape acquisition G. Ammon, P. Andretzky, S. Blossey, G. Bohn, P.Ettl, H. P. Habermeier, B. Harand, G. Häusler Chair for
Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA
 Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA Abstract: Speckle interferometry (SI) has become a complete technique over the past couple of years and is widely used in many branches of
Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA Abstract: Speckle interferometry (SI) has become a complete technique over the past couple of years and is widely used in many branches of
of surface microstructure
 Invited Paper Computerized interferometric measurement of surface microstructure James C. Wyant WYKO Corporation, 2650 E. Elvira Road Tucson, Arizona 85706, U.S.A. & Optical Sciences Center University
Invited Paper Computerized interferometric measurement of surface microstructure James C. Wyant WYKO Corporation, 2650 E. Elvira Road Tucson, Arizona 85706, U.S.A. & Optical Sciences Center University
Modifications of the coherence radar for in vivo profilometry in dermatology
 Modifications of the coherence radar for in vivo profilometry in dermatology P. Andretzky, M. W. Lindner, G. Bohn, J. Neumann, M. Schmidt, G. Ammon, and G. Häusler Physikalisches Institut, Lehrstuhl für
Modifications of the coherence radar for in vivo profilometry in dermatology P. Andretzky, M. W. Lindner, G. Bohn, J. Neumann, M. Schmidt, G. Ammon, and G. Häusler Physikalisches Institut, Lehrstuhl für
University of Huddersfield Repository
 University of Huddersfield Repository Gao, F., Muhamedsalih, Hussam and Jiang, Xiang In process fast surface measurement using wavelength scanning interferometry Original Citation Gao, F., Muhamedsalih,
University of Huddersfield Repository Gao, F., Muhamedsalih, Hussam and Jiang, Xiang In process fast surface measurement using wavelength scanning interferometry Original Citation Gao, F., Muhamedsalih,
Temporal coherence characteristics of a superluminescent diode system with an optical feedback mechanism
 VI Temporal coherence characteristics of a superluminescent diode system with an optical feedback mechanism Fang-Wen Sheu and Pei-Ling Luo Department of Applied Physics, National Chiayi University, Chiayi
VI Temporal coherence characteristics of a superluminescent diode system with an optical feedback mechanism Fang-Wen Sheu and Pei-Ling Luo Department of Applied Physics, National Chiayi University, Chiayi
Optical coherence tomography
 Optical coherence tomography Peter E. Andersen Optics and Plasma Research Department Risø National Laboratory E-mail peter.andersen@risoe.dk Outline Part I: Introduction to optical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography Peter E. Andersen Optics and Plasma Research Department Risø National Laboratory E-mail peter.andersen@risoe.dk Outline Part I: Introduction to optical coherence tomography
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Princeton University Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University ABSTRACT
 Phase and Amplitude Control Ability using Spatial Light Modulators and Zero Path Length Difference Michelson Interferometer Michael G. Littman, Michael Carr, Jim Leighton, Ezekiel Burke, David Spergel
Phase and Amplitude Control Ability using Spatial Light Modulators and Zero Path Length Difference Michelson Interferometer Michael G. Littman, Michael Carr, Jim Leighton, Ezekiel Burke, David Spergel
(51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 ( ) G01B 11/24 ( ) G01N 21/47 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 939 581 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.07.2008 Bulletin 2008/27 (21) Application number: 07405346.3 (51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 (2006.01) G01B 11/24 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 939 581 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.07.2008 Bulletin 2008/27 (21) Application number: 07405346.3 (51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 (2006.01) G01B 11/24 (2006.01)
Spatial-Phase-Shift Imaging Interferometry Using Spectrally Modulated White Light Source
 Spatial-Phase-Shift Imaging Interferometry Using Spectrally Modulated White Light Source Shlomi Epshtein, 1 Alon Harris, 2 Igor Yaacobovitz, 1 Garrett Locketz, 3 Yitzhak Yitzhaky, 4 Yoel Arieli, 5* 1AdOM
Spatial-Phase-Shift Imaging Interferometry Using Spectrally Modulated White Light Source Shlomi Epshtein, 1 Alon Harris, 2 Igor Yaacobovitz, 1 Garrett Locketz, 3 Yitzhak Yitzhaky, 4 Yoel Arieli, 5* 1AdOM
Optical Characterization and Defect Inspection for 3D Stacked IC Technology
 Minapad 2014, May 21 22th, Grenoble; France Optical Characterization and Defect Inspection for 3D Stacked IC Technology J.Ph.Piel, G.Fresquet, S.Perrot, Y.Randle, D.Lebellego, S.Petitgrand, G.Ribette FOGALE
Minapad 2014, May 21 22th, Grenoble; France Optical Characterization and Defect Inspection for 3D Stacked IC Technology J.Ph.Piel, G.Fresquet, S.Perrot, Y.Randle, D.Lebellego, S.Petitgrand, G.Ribette FOGALE
Imaging Systems Laboratory II. Laboratory 8: The Michelson Interferometer / Diffraction April 30 & May 02, 2002
 1051-232 Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 8: The Michelson Interferometer / Diffraction April 30 & May 02, 2002 Abstract. In the last lab, you saw that coherent light from two different locations
1051-232 Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 8: The Michelson Interferometer / Diffraction April 30 & May 02, 2002 Abstract. In the last lab, you saw that coherent light from two different locations
Frequency-stepping interferometry for accurate metrology of rough components and assemblies
 Frequency-stepping interferometry for accurate metrology of rough components and assemblies Thomas J. Dunn, Chris A. Lee, Mark J. Tronolone Corning Tropel, 60 O Connor Road, Fairport NY, 14450, ABSTRACT
Frequency-stepping interferometry for accurate metrology of rough components and assemblies Thomas J. Dunn, Chris A. Lee, Mark J. Tronolone Corning Tropel, 60 O Connor Road, Fairport NY, 14450, ABSTRACT
In-line digital holographic interferometry
 In-line digital holographic interferometry Giancarlo Pedrini, Philipp Fröning, Henrik Fessler, and Hans J. Tiziani An optical system based on in-line digital holography for the evaluation of deformations
In-line digital holographic interferometry Giancarlo Pedrini, Philipp Fröning, Henrik Fessler, and Hans J. Tiziani An optical system based on in-line digital holography for the evaluation of deformations
A 3D Profile Parallel Detecting System Based on Differential Confocal Microscopy. Y.H. Wang, X.F. Yu and Y.T. Fei
 Key Engineering Materials Online: 005-10-15 ISSN: 166-9795, Vols. 95-96, pp 501-506 doi:10.408/www.scientific.net/kem.95-96.501 005 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A 3D Profile Parallel Detecting
Key Engineering Materials Online: 005-10-15 ISSN: 166-9795, Vols. 95-96, pp 501-506 doi:10.408/www.scientific.net/kem.95-96.501 005 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A 3D Profile Parallel Detecting
New Phase Shifting Algorithms Insensitive to Linear Phase Shift Errors J. Novák
 New Phase Shifting Algorithms Insensitive to Linear Phase Shift Errors J. Novák This article describes and analyses multistep algorithms for evaluating of the wave field phase in interferometric measurements
New Phase Shifting Algorithms Insensitive to Linear Phase Shift Errors J. Novák This article describes and analyses multistep algorithms for evaluating of the wave field phase in interferometric measurements
Gerhard K. Ackermann and Jurgen Eichler. Holography. A Practical Approach BICENTENNIAL. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA
 Gerhard K. Ackermann and Jurgen Eichler Holography A Practical Approach BICENTENNIAL BICENTENNIAL WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XVII Part 1 Fundamentals of Holography 1 1 Introduction
Gerhard K. Ackermann and Jurgen Eichler Holography A Practical Approach BICENTENNIAL BICENTENNIAL WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XVII Part 1 Fundamentals of Holography 1 1 Introduction
Figure1. To construct a light pulse, the electric component of the plane wave should be multiplied with a bell shaped function.
 Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
S.R.Taplin, A. Gh.Podoleanu, D.J.Webb, D.A.Jackson AB STRACT. Keywords: fibre optic sensors, white light, channeled spectra, ccd, signal processing.
 White-light displacement sensor incorporating signal analysis of channeled spectra S.R.Taplin, A. Gh.Podoleanu, D.J.Webb, D.A.Jackson Applied Optics Group, Physics Department, University of Kent, Canterbury,
White-light displacement sensor incorporating signal analysis of channeled spectra S.R.Taplin, A. Gh.Podoleanu, D.J.Webb, D.A.Jackson Applied Optics Group, Physics Department, University of Kent, Canterbury,
Experimental Test of an Alignment Sensing Scheme for a Gravitational-wave Interferometer
 Experimental Test of an Alignment Sensing Scheme for a Gravitational-wave Interferometer Nergis Mavalvala *, Daniel Sigg and David Shoemaker LIGO Project Department of Physics and Center for Space Research,
Experimental Test of an Alignment Sensing Scheme for a Gravitational-wave Interferometer Nergis Mavalvala *, Daniel Sigg and David Shoemaker LIGO Project Department of Physics and Center for Space Research,
LightGage Frequency Scanning Technology
 Corning Tropel Metrology Instruments LightGage Frequency Scanning Technology Thomas J. Dunn 6 October 007 Introduction Presentation Outline Introduction Review of Conventional Interferometry FSI Technology
Corning Tropel Metrology Instruments LightGage Frequency Scanning Technology Thomas J. Dunn 6 October 007 Introduction Presentation Outline Introduction Review of Conventional Interferometry FSI Technology
some aspects of Optical Coherence Tomography
 some aspects of Optical Coherence Tomography SSOM Lectures, Engelberg 17.3.2009 Ch. Meier 1 / 34 Contents 1. OCT - basic principles (Time Domain Frequency Domain) 2. Performance and limiting factors 3.
some aspects of Optical Coherence Tomography SSOM Lectures, Engelberg 17.3.2009 Ch. Meier 1 / 34 Contents 1. OCT - basic principles (Time Domain Frequency Domain) 2. Performance and limiting factors 3.
Rotation/ scale invariant hybrid digital/optical correlator system for automatic target recognition
 Rotation/ scale invariant hybrid digital/optical correlator system for automatic target recognition V. K. Beri, Amit Aran, Shilpi Goyal, and A. K. Gupta * Photonics Division Instruments Research and Development
Rotation/ scale invariant hybrid digital/optical correlator system for automatic target recognition V. K. Beri, Amit Aran, Shilpi Goyal, and A. K. Gupta * Photonics Division Instruments Research and Development
Development of innovative fringe locking strategies for vibration-resistant white light vertical scanning interferometry (VSI)
 Development of innovative fringe locking strategies for vibration-resistant white light vertical scanning interferometry (VSI) Liang-Chia Chen 1), Abraham Mario Tapilouw 1), Sheng-Lih Yeh 2), Shih-Tsong
Development of innovative fringe locking strategies for vibration-resistant white light vertical scanning interferometry (VSI) Liang-Chia Chen 1), Abraham Mario Tapilouw 1), Sheng-Lih Yeh 2), Shih-Tsong
Contouring aspheric surfaces using two-wavelength phase-shifting interferometry
 OPTICA ACTA, 1985, VOL. 32, NO. 12, 1455-1464 Contouring aspheric surfaces using two-wavelength phase-shifting interferometry KATHERINE CREATH, YEOU-YEN CHENG and JAMES C. WYANT University of Arizona,
OPTICA ACTA, 1985, VOL. 32, NO. 12, 1455-1464 Contouring aspheric surfaces using two-wavelength phase-shifting interferometry KATHERINE CREATH, YEOU-YEN CHENG and JAMES C. WYANT University of Arizona,
Instructions for the Experiment
 Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
771 Series LASER SPECTRUM ANALYZER. The Power of Precision in Spectral Analysis. It's Our Business to be Exact! bristol-inst.com
 771 Series LASER SPECTRUM ANALYZER The Power of Precision in Spectral Analysis It's Our Business to be Exact! bristol-inst.com The 771 Series Laser Spectrum Analyzer combines proven Michelson interferometer
771 Series LASER SPECTRUM ANALYZER The Power of Precision in Spectral Analysis It's Our Business to be Exact! bristol-inst.com The 771 Series Laser Spectrum Analyzer combines proven Michelson interferometer
9. Microwaves. 9.1 Introduction. Safety consideration
 MW 9. Microwaves 9.1 Introduction Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths of the order of 1 mm to 1 m, or equivalently, with frequencies from 0.3 GHz to 0.3 THz, are commonly known as microwaves, sometimes
MW 9. Microwaves 9.1 Introduction Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths of the order of 1 mm to 1 m, or equivalently, with frequencies from 0.3 GHz to 0.3 THz, are commonly known as microwaves, sometimes
Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film
 Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film Hisashi Akiyama 1, Osami Sasaki 2, and Takamasa Suzuki
Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film Hisashi Akiyama 1, Osami Sasaki 2, and Takamasa Suzuki
Sub-nanometer Interferometry Aspheric Mirror Fabrication
 UCRL-JC- 134763 PREPRINT Sub-nanometer Interferometry Aspheric Mirror Fabrication for G. E. Sommargren D. W. Phillion E. W. Campbell This paper was prepared for submittal to the 9th International Conference
UCRL-JC- 134763 PREPRINT Sub-nanometer Interferometry Aspheric Mirror Fabrication for G. E. Sommargren D. W. Phillion E. W. Campbell This paper was prepared for submittal to the 9th International Conference
Isolator-Free 840-nm Broadband SLEDs for High-Resolution OCT
 Isolator-Free 840-nm Broadband SLEDs for High-Resolution OCT M. Duelk *, V. Laino, P. Navaretti, R. Rezzonico, C. Armistead, C. Vélez EXALOS AG, Wagistrasse 21, CH-8952 Schlieren, Switzerland ABSTRACT
Isolator-Free 840-nm Broadband SLEDs for High-Resolution OCT M. Duelk *, V. Laino, P. Navaretti, R. Rezzonico, C. Armistead, C. Vélez EXALOS AG, Wagistrasse 21, CH-8952 Schlieren, Switzerland ABSTRACT
Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing
 Journal of Computer Science 2 (): 09-3, 2006 ISSN 549-3636 Science Publications, 2006 Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing Yas A. Alsultanny Computer Science Department, Amman Arab University for
Journal of Computer Science 2 (): 09-3, 2006 ISSN 549-3636 Science Publications, 2006 Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing Yas A. Alsultanny Computer Science Department, Amman Arab University for
Dynamic Phase-Shifting Electronic Speckle Pattern Interferometer
 Dynamic Phase-Shifting Electronic Speckle Pattern Interferometer Michael North Morris, James Millerd, Neal Brock, John Hayes and *Babak Saif 4D Technology Corporation, 3280 E. Hemisphere Loop Suite 146,
Dynamic Phase-Shifting Electronic Speckle Pattern Interferometer Michael North Morris, James Millerd, Neal Brock, John Hayes and *Babak Saif 4D Technology Corporation, 3280 E. Hemisphere Loop Suite 146,
Large Field of View, High Spatial Resolution, Surface Measurements
 Large Field of View, High Spatial Resolution, Surface Measurements James C. Wyant and Joanna Schmit WYKO Corporation, 2650 E. Elvira Road Tucson, Arizona 85706, USA jcwyant@wyko.com and jschmit@wyko.com
Large Field of View, High Spatial Resolution, Surface Measurements James C. Wyant and Joanna Schmit WYKO Corporation, 2650 E. Elvira Road Tucson, Arizona 85706, USA jcwyant@wyko.com and jschmit@wyko.com
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT
 CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
Basics of INTERFEROMETRY
 Basics of INTERFEROMETRY P Hariharan CSIRO Division of Applied Sydney, Australia Physics ACADEMIC PRESS, INC. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Publishers Boston San Diego New York London Sydney Tokyo Toronto
Basics of INTERFEROMETRY P Hariharan CSIRO Division of Applied Sydney, Australia Physics ACADEMIC PRESS, INC. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Publishers Boston San Diego New York London Sydney Tokyo Toronto
Understanding Digital Signal Processing
 Understanding Digital Signal Processing Richard G. Lyons PRENTICE HALL PTR PRENTICE HALL Professional Technical Reference Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 www.photr,com Contents Preface xi 1 DISCRETE
Understanding Digital Signal Processing Richard G. Lyons PRENTICE HALL PTR PRENTICE HALL Professional Technical Reference Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 www.photr,com Contents Preface xi 1 DISCRETE
The Henryk Niewodniczański INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS Polish Academy of Sciences ul. Radzikowskiego 152, Kraków, Poland.
 The Henryk Niewodniczański INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS Polish Academy of Sciences ul. Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland. www.ifj.edu.pl/reports/2003.html Kraków, grudzień 2003 Report No 1931/PH
The Henryk Niewodniczański INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS Polish Academy of Sciences ul. Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland. www.ifj.edu.pl/reports/2003.html Kraków, grudzień 2003 Report No 1931/PH
Optical Coherence: Recreation of the Experiment of Thompson and Wolf
 Optical Coherence: Recreation of the Experiment of Thompson and Wolf David Collins Senior project Department of Physics, California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo June 2010 Abstract The purpose
Optical Coherence: Recreation of the Experiment of Thompson and Wolf David Collins Senior project Department of Physics, California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo June 2010 Abstract The purpose
SPECKLE INTERFEROMETRY WITH TEMPORAL PHASE EVALUATION: INFLUENCE OF DECORRELATION, SPECKLE SIZE, AND NON-LINEARITY OF THE CAMERA
 SPECKLE INTERFEROMETRY WITH TEMPORAL PHASE EVALUATION: INFLUENCE OF DECORRELATION, SPECKLE SIZE, AND NON-LINEARITY OF THE CAMERA C. Joenathan*, P. Haible, B. Franze, and H. J. Tiziani Universitaet Stuttgart,
SPECKLE INTERFEROMETRY WITH TEMPORAL PHASE EVALUATION: INFLUENCE OF DECORRELATION, SPECKLE SIZE, AND NON-LINEARITY OF THE CAMERA C. Joenathan*, P. Haible, B. Franze, and H. J. Tiziani Universitaet Stuttgart,
Supplementary Figure S1. Schematic representation of different functionalities that could be
 Supplementary Figure S1. Schematic representation of different functionalities that could be obtained using the fiber-bundle approach This schematic representation shows some example of the possible functions
Supplementary Figure S1. Schematic representation of different functionalities that could be obtained using the fiber-bundle approach This schematic representation shows some example of the possible functions
SENSOR+TEST Conference SENSOR 2009 Proceedings II
 B8.4 Optical 3D Measurement of Micro Structures Ettemeyer, Andreas; Marxer, Michael; Keferstein, Claus NTB Interstaatliche Hochschule für Technik Buchs Werdenbergstr. 4, 8471 Buchs, Switzerland Introduction
B8.4 Optical 3D Measurement of Micro Structures Ettemeyer, Andreas; Marxer, Michael; Keferstein, Claus NTB Interstaatliche Hochschule für Technik Buchs Werdenbergstr. 4, 8471 Buchs, Switzerland Introduction
High stability multiplexed fibre interferometer and its application on absolute displacement measurement and on-line surface metrology
 High stability multiplexed fibre interferometer and its application on absolute displacement measurement and on-line surface metrology Dejiao Lin, Xiangqian Jiang and Fang Xie Centre for Precision Technologies,
High stability multiplexed fibre interferometer and its application on absolute displacement measurement and on-line surface metrology Dejiao Lin, Xiangqian Jiang and Fang Xie Centre for Precision Technologies,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information S1. Theory of TPQI in a lossy directional coupler Following Barnett, et al. [24], we start with the probability of detecting one photon in each output of a lossy, symmetric beam
Supplementary Information S1. Theory of TPQI in a lossy directional coupler Following Barnett, et al. [24], we start with the probability of detecting one photon in each output of a lossy, symmetric beam
Final Year Projects 2016/7 Integrated Photonics Group
 Final Year Projects 2016/7 Integrated Photonics Group Overview: This year, a number of projects have been created where the student will work with researchers in the Integrated Photonics Group. The projects
Final Year Projects 2016/7 Integrated Photonics Group Overview: This year, a number of projects have been created where the student will work with researchers in the Integrated Photonics Group. The projects
Focal Plane Speckle Patterns for Compressive Microscopic Imaging in Laser Spectroscopy
 Focal Plane Speckle Patterns for Compressive Microscopic Imaging in Laser Spectroscopy Karel Žídek Regional Centre for Special Optics and Optoelectronic Systems (TOPTEC) Institute of Plasma Physics, Academy
Focal Plane Speckle Patterns for Compressive Microscopic Imaging in Laser Spectroscopy Karel Žídek Regional Centre for Special Optics and Optoelectronic Systems (TOPTEC) Institute of Plasma Physics, Academy
Single Photon Interference Laboratory
 Single Photon Interference Laboratory Renald Dore Institute of Optics University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, U.S.A Abstract The purpose of our laboratories was to observe the wave-particle duality
Single Photon Interference Laboratory Renald Dore Institute of Optics University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, U.S.A Abstract The purpose of our laboratories was to observe the wave-particle duality
Experimental Competition
 37 th International Physics Olympiad Singapore 8 17 July 2006 Experimental Competition Wed 12 July 2006 Experimental Competition Page 2 List of apparatus and materials Label Component Quantity Label Component
37 th International Physics Olympiad Singapore 8 17 July 2006 Experimental Competition Wed 12 July 2006 Experimental Competition Page 2 List of apparatus and materials Label Component Quantity Label Component
Advances in Direction-of-Arrival Estimation
 Advances in Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Sathish Chandran Editor ARTECH HOUSE BOSTON LONDON artechhouse.com Contents Preface xvii Acknowledgments xix Overview CHAPTER 1 Antenna Arrays for Direction-of-Arrival
Advances in Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Sathish Chandran Editor ARTECH HOUSE BOSTON LONDON artechhouse.com Contents Preface xvii Acknowledgments xix Overview CHAPTER 1 Antenna Arrays for Direction-of-Arrival
7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP
 7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP Abstract: In this chapter we describe the use of a common path phase sensitive FDOCT set up. The phase measurements
7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP Abstract: In this chapter we describe the use of a common path phase sensitive FDOCT set up. The phase measurements
Module 5: Experimental Modal Analysis for SHM Lecture 36: Laser doppler vibrometry. The Lecture Contains: Laser Doppler Vibrometry
 The Lecture Contains: Laser Doppler Vibrometry Basics of Laser Doppler Vibrometry Components of the LDV system Working with the LDV system file:///d /neha%20backup%20courses%2019-09-2011/structural_health/lecture36/36_1.html
The Lecture Contains: Laser Doppler Vibrometry Basics of Laser Doppler Vibrometry Components of the LDV system Working with the LDV system file:///d /neha%20backup%20courses%2019-09-2011/structural_health/lecture36/36_1.html
A Multiwavelength Interferometer for Geodetic Lengths
 A Multiwavelength Interferometer for Geodetic Lengths K. Meiners-Hagen, P. Köchert, A. Abou-Zeid, Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Braunschweig Abstract: Within the EURAMET joint research project
A Multiwavelength Interferometer for Geodetic Lengths K. Meiners-Hagen, P. Köchert, A. Abou-Zeid, Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Braunschweig Abstract: Within the EURAMET joint research project
Testing Aspheric Lenses: New Approaches
 Nasrin Ghanbari OPTI 521 - Synopsis of a published Paper November 5, 2012 Testing Aspheric Lenses: New Approaches by W. Osten, B. D orband, E. Garbusi, Ch. Pruss, and L. Seifert Published in 2010 Introduction
Nasrin Ghanbari OPTI 521 - Synopsis of a published Paper November 5, 2012 Testing Aspheric Lenses: New Approaches by W. Osten, B. D orband, E. Garbusi, Ch. Pruss, and L. Seifert Published in 2010 Introduction
Be aware that there is no universal notation for the various quantities.
 Fourier Optics v2.4 Ray tracing is limited in its ability to describe optics because it ignores the wave properties of light. Diffraction is needed to explain image spatial resolution and contrast and
Fourier Optics v2.4 Ray tracing is limited in its ability to describe optics because it ignores the wave properties of light. Diffraction is needed to explain image spatial resolution and contrast and
Sensitive measurement of partial coherence using a pinhole array
 1.3 Sensitive measurement of partial coherence using a pinhole array Paul Petruck 1, Rainer Riesenberg 1, Richard Kowarschik 2 1 Institute of Photonic Technology, Albert-Einstein-Strasse 9, 07747 Jena,
1.3 Sensitive measurement of partial coherence using a pinhole array Paul Petruck 1, Rainer Riesenberg 1, Richard Kowarschik 2 1 Institute of Photonic Technology, Albert-Einstein-Strasse 9, 07747 Jena,
Is imaging with millimetre waves the same as optical imaging?
 Is imaging with millimetre waves the same as optical imaging? Bart Nauwelaers 13 March 2008 K.U.Leuven Div. ESAT-TELEMIC Kasteelpark Arenberg 10, B-3001 Leuven-Heverlee, Belgium Bart.Nauwelaers@esat.kuleuven.be
Is imaging with millimetre waves the same as optical imaging? Bart Nauwelaers 13 March 2008 K.U.Leuven Div. ESAT-TELEMIC Kasteelpark Arenberg 10, B-3001 Leuven-Heverlee, Belgium Bart.Nauwelaers@esat.kuleuven.be
Heterodyne Interferometry with a Supercontinuum Local Oscillator. Pavel Gabor Vatican Observatory, 933 N Cherry Ave., Tucson AZ 85721, USA
 **Volume Title** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **Volume Number** **Author** c **Copyright Year** Astronomical Society of the Pacific Heterodyne Interferometry with a Supercontinuum Local Oscillator Pavel
**Volume Title** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **Volume Number** **Author** c **Copyright Year** Astronomical Society of the Pacific Heterodyne Interferometry with a Supercontinuum Local Oscillator Pavel
Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI)
 Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI) Liang-Chia Chen 1#, Chao-Nan Chen 1 and Yi-Wei Chang 1 1. Institute of Automation Technology,
Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI) Liang-Chia Chen 1#, Chao-Nan Chen 1 and Yi-Wei Chang 1 1. Institute of Automation Technology,
Thomas G. Cleary Building and Fire Research Laboratory National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, MD U.S.A.
 Thomas G. Cleary Building and Fire Research Laboratory National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, MD 20899 U.S.A. Video Detection and Monitoring of Smoke Conditions Abstract Initial tests
Thomas G. Cleary Building and Fire Research Laboratory National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, MD 20899 U.S.A. Video Detection and Monitoring of Smoke Conditions Abstract Initial tests
Detection of Partially Coherent Optical Emission Sources
 Detection of Partially Coherent Optical Emission Sources Ricardo C. Coutinho a,b, David R. Selviah a and Herbert A. French a a University College London, Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering,
Detection of Partially Coherent Optical Emission Sources Ricardo C. Coutinho a,b, David R. Selviah a and Herbert A. French a a University College London, Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering,
A STUDY ON THE VIBRATION CHARACTERISTICS OF CFRP COMPOSITE MATERIALS USING TIME- AVERAGE ESPI
 A STUDY ON THE VIBRATION CHARACTERISTICS OF CFRP COMPOSITE MATERIALS USING TIME- AVERAGE ESPI Authors: K.-M. Hong, Y.-J. Kang, S.-J. Kim, A. Kim, I.-Y. Choi, J.-H. Park, C.-W. Cho DOI: 10.12684/alt.1.66
A STUDY ON THE VIBRATION CHARACTERISTICS OF CFRP COMPOSITE MATERIALS USING TIME- AVERAGE ESPI Authors: K.-M. Hong, Y.-J. Kang, S.-J. Kim, A. Kim, I.-Y. Choi, J.-H. Park, C.-W. Cho DOI: 10.12684/alt.1.66
Technical Brief #2. Depolarizers
 Technical Brief #2 Depolarizers What is a depolarizer?...2 Principle of operation...2 Source coherence function dependence...2 Depolarizer realization...3 Input linear polarization state definition...4
Technical Brief #2 Depolarizers What is a depolarizer?...2 Principle of operation...2 Source coherence function dependence...2 Depolarizer realization...3 Input linear polarization state definition...4
Wave Front Detection for Virgo
 Wave Front Detection for Virgo L.L.Richardson University of Arizona, Steward Observatory, 933 N. Cherry ave, Tucson Arizona 8575, USA E-mail: zimlance@email.arizona.edu Abstract. The use of phase cameras
Wave Front Detection for Virgo L.L.Richardson University of Arizona, Steward Observatory, 933 N. Cherry ave, Tucson Arizona 8575, USA E-mail: zimlance@email.arizona.edu Abstract. The use of phase cameras
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore.
 This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Some new developments in optical dynamic testing Author(s) Fu, Yu; Phua, Poh Boon Citation Fu, Y., &
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Some new developments in optical dynamic testing Author(s) Fu, Yu; Phua, Poh Boon Citation Fu, Y., &
Diffractive optical elements for high gain lasers with arbitrary output beam profiles
 Diffractive optical elements for high gain lasers with arbitrary output beam profiles Adam J. Caley, Martin J. Thomson 2, Jinsong Liu, Andrew J. Waddie and Mohammad R. Taghizadeh. Heriot-Watt University,
Diffractive optical elements for high gain lasers with arbitrary output beam profiles Adam J. Caley, Martin J. Thomson 2, Jinsong Liu, Andrew J. Waddie and Mohammad R. Taghizadeh. Heriot-Watt University,
Transport and Aerospace Engineering. Deniss Brodņevs 1, Igors Smirnovs 2. Riga Technical University, Latvia
 ISSN 2255-9876 (online) ISSN 2255-968X (print) December 2016, vol. 3, pp. 52 61 doi: 10.1515/tae-2016-0007 https://www.degruyter.com/view/j/tae Experimental Proof of the Characteristics of Short-Range
ISSN 2255-9876 (online) ISSN 2255-968X (print) December 2016, vol. 3, pp. 52 61 doi: 10.1515/tae-2016-0007 https://www.degruyter.com/view/j/tae Experimental Proof of the Characteristics of Short-Range
MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER & FOURIER TRANSFORM SPECTROMETRY
 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER & FOURIER TRANSFORM SPECTROMETRY REFERENCES Revised October 18, 217. 1. Hecht, Optics (4th ed.), Fourier transforms and coherence basics, pp. 39 316; Michelson interferometer and
MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER & FOURIER TRANSFORM SPECTROMETRY REFERENCES Revised October 18, 217. 1. Hecht, Optics (4th ed.), Fourier transforms and coherence basics, pp. 39 316; Michelson interferometer and
Optics and Lasers. Matt Young. Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides
 Matt Young Optics and Lasers Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides Fourth Revised Edition With 188 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Matt Young Optics and Lasers Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides Fourth Revised Edition With 188 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Measurement of the group refractive index of air and glass
 Application Note METROLOGY Czech Metrology Institute (CMI), Prague Menlo Systems, Martinsried Measurement of the group refractive index of air and glass Authors: Petr Balling (CMI), Benjamin Sprenger (Menlo
Application Note METROLOGY Czech Metrology Institute (CMI), Prague Menlo Systems, Martinsried Measurement of the group refractive index of air and glass Authors: Petr Balling (CMI), Benjamin Sprenger (Menlo
A laser speckle reduction system
 A laser speckle reduction system Joshua M. Cobb*, Paul Michaloski** Corning Advanced Optics, 60 O Connor Road, Fairport, NY 14450 ABSTRACT Speckle degrades the contrast of the fringe patterns in laser
A laser speckle reduction system Joshua M. Cobb*, Paul Michaloski** Corning Advanced Optics, 60 O Connor Road, Fairport, NY 14450 ABSTRACT Speckle degrades the contrast of the fringe patterns in laser
Section 2 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS
 Section 2 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS 2.A High-Power Laser Interferometry Central to the uniformity issue is the need to determine the factors that control the target-plane intensity distribution
Section 2 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS 2.A High-Power Laser Interferometry Central to the uniformity issue is the need to determine the factors that control the target-plane intensity distribution
Optical phase-coherent link between an optical atomic clock. and 1550 nm mode-locked lasers
 Optical phase-coherent link between an optical atomic clock and 1550 nm mode-locked lasers Kevin W. Holman, David J. Jones, Steven T. Cundiff, and Jun Ye* JILA, National Institute of Standards and Technology
Optical phase-coherent link between an optical atomic clock and 1550 nm mode-locked lasers Kevin W. Holman, David J. Jones, Steven T. Cundiff, and Jun Ye* JILA, National Institute of Standards and Technology
COMPOSITE MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES TESTING BY ELECTRONIC HOLOGRAPHY
 COMPOSITE MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES TESTING BY ELECTRONIC HOLOGRAPHY Dan N. Borza 1 1 Laboratoire de Mécanique de Rouen, Institut National des Sciences Appliquées de Rouen Place Blondel, BP 08, Mont-Saint-Aignan,
COMPOSITE MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES TESTING BY ELECTRONIC HOLOGRAPHY Dan N. Borza 1 1 Laboratoire de Mécanique de Rouen, Institut National des Sciences Appliquées de Rouen Place Blondel, BP 08, Mont-Saint-Aignan,
Multi aperture coherent imaging IMAGE testbed
 Multi aperture coherent imaging IMAGE testbed Nick Miller, Joe Haus, Paul McManamon, and Dave Shemano University of Dayton LOCI Dayton OH 16 th CLRC Long Beach 20 June 2011 Aperture synthesis (part 1 of
Multi aperture coherent imaging IMAGE testbed Nick Miller, Joe Haus, Paul McManamon, and Dave Shemano University of Dayton LOCI Dayton OH 16 th CLRC Long Beach 20 June 2011 Aperture synthesis (part 1 of
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Student Name Date MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161 Modern Optics Project Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 6 Fall 2010 Solid-State
Student Name Date MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161 Modern Optics Project Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 6 Fall 2010 Solid-State
Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength Holography
 Reprinted from APPLIED OPTICS. Vol. 10, page 2113, September 1971 Copyright 1971 by the Optical Society of America and reprinted by permission of the copyright owner Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength
Reprinted from APPLIED OPTICS. Vol. 10, page 2113, September 1971 Copyright 1971 by the Optical Society of America and reprinted by permission of the copyright owner Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings
 A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014
 PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014 Laboratory #1 Week of January 13 Read: Handout (Introduction & Projects #2 & 3 from Newport Project in Optics Workbook), pp.150-170 of Optics by Hecht Do: 1. Experiment
PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014 Laboratory #1 Week of January 13 Read: Handout (Introduction & Projects #2 & 3 from Newport Project in Optics Workbook), pp.150-170 of Optics by Hecht Do: 1. Experiment
Diffractive interferometer for visualization and measurement of optical inhomogeneities
 Diffractive interferometer for visualization and measurement of optical inhomogeneities Irina G. Palchikova,2, Ivan А. Yurlagin 2 Technological Design Institute of Scientific Instrument Engineering (TDI
Diffractive interferometer for visualization and measurement of optical inhomogeneities Irina G. Palchikova,2, Ivan А. Yurlagin 2 Technological Design Institute of Scientific Instrument Engineering (TDI
Frequency-estimation-based signal-processing algorithm for white-light optical fiber Fabry Perot interferometers
 Frequency-estimation-based signal-processing algorithm for white-light optical fiber Fabry Perot interferometers Fabin Shen and Anbo Wang A novel signal-processing algorithm based on frequency estimation
Frequency-estimation-based signal-processing algorithm for white-light optical fiber Fabry Perot interferometers Fabin Shen and Anbo Wang A novel signal-processing algorithm based on frequency estimation
Single-shot areal profilometry using hyperspectral interferometry with a microlens array
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Single-shot areal profilometry using hyperspectral interferometry with a microlens array This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Single-shot areal profilometry using hyperspectral interferometry with a microlens array This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Improvements for determining the modulation transfer function of charge-coupled devices by the speckle method
 Improvements for determining the modulation transfer function of charge-coupled devices by the speckle method A. M. Pozo 1, A. Ferrero 2, M. Rubiño 1, J. Campos 2 and A. Pons 2 1 Departamento de Óptica,
Improvements for determining the modulation transfer function of charge-coupled devices by the speckle method A. M. Pozo 1, A. Ferrero 2, M. Rubiño 1, J. Campos 2 and A. Pons 2 1 Departamento de Óptica,
Automation of Fingerprint Recognition Using OCT Fingerprint Images
 Journal of Signal and Information Processing, 2012, 3, 117-121 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jsip.2012.31015 Published Online February 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jsip) 117 Automation of Fingerprint
Journal of Signal and Information Processing, 2012, 3, 117-121 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jsip.2012.31015 Published Online February 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jsip) 117 Automation of Fingerprint
Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16
 Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16 9 Pulse Characterization 9.1 Intensity Autocorrelation 9.2 Interferometric Autocorrelation (IAC) 9.3 Frequency Resolved Optical Gating (FROG)
Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16 9 Pulse Characterization 9.1 Intensity Autocorrelation 9.2 Interferometric Autocorrelation (IAC) 9.3 Frequency Resolved Optical Gating (FROG)
Interference [Hecht Ch. 9]
![Interference [Hecht Ch. 9] Interference [Hecht Ch. 9]](/thumbs/79/79365345.jpg) Interference [Hecht Ch. 9] Note: Read Ch. 3 & 7 E&M Waves and Superposition of Waves and Meet with TAs and/or Dr. Lai if necessary. General Consideration 1 2 Amplitude Splitting Interferometers If a lightwave
Interference [Hecht Ch. 9] Note: Read Ch. 3 & 7 E&M Waves and Superposition of Waves and Meet with TAs and/or Dr. Lai if necessary. General Consideration 1 2 Amplitude Splitting Interferometers If a lightwave
OPSENS WHITE-LIGHT POLARIZATION INTERFEROMETRY TECHNOLOGY
 OPSENS WHITE-LIGHT POLARIZATION INTERFEROMETRY TECHNOLOGY 1. Introduction Fiber optic sensors are made up of two main parts: the fiber optic transducer (also called the fiber optic gauge or the fiber optic
OPSENS WHITE-LIGHT POLARIZATION INTERFEROMETRY TECHNOLOGY 1. Introduction Fiber optic sensors are made up of two main parts: the fiber optic transducer (also called the fiber optic gauge or the fiber optic
Swept Wavelength Testing:
 Application Note 13 Swept Wavelength Testing: Characterizing the Tuning Linearity of Tunable Laser Sources In a swept-wavelength measurement system, the wavelength of a tunable laser source (TLS) is swept
Application Note 13 Swept Wavelength Testing: Characterizing the Tuning Linearity of Tunable Laser Sources In a swept-wavelength measurement system, the wavelength of a tunable laser source (TLS) is swept
Off-axis negative-branch unstable resonator in rectangular geometry
 Off-axis negative-branch unstable resonator in rectangular geometry Carsten Pargmann, 1, * Thomas Hall, 2 Frank Duschek, 1 Karin Maria Grünewald, 1 and Jürgen Handke 1 1 German Aerospace Center (DLR),
Off-axis negative-branch unstable resonator in rectangular geometry Carsten Pargmann, 1, * Thomas Hall, 2 Frank Duschek, 1 Karin Maria Grünewald, 1 and Jürgen Handke 1 1 German Aerospace Center (DLR),
Introduction to Interferometry. Michelson Interferometer. Fourier Transforms. Optics: holes in a mask. Two ways of understanding interferometry
 Introduction to Interferometry P.J.Diamond MERLIN/VLBI National Facility Jodrell Bank Observatory University of Manchester ERIS: 5 Sept 005 Aim to lay the groundwork for following talks Discuss: General
Introduction to Interferometry P.J.Diamond MERLIN/VLBI National Facility Jodrell Bank Observatory University of Manchester ERIS: 5 Sept 005 Aim to lay the groundwork for following talks Discuss: General
Optical Isolation Can Occur in Linear and Passive Silicon Photonic Structures
 Optical Isolation Can Occur in Linear and Passive Silicon Photonic Structures Chen Wang and Zhi-Yuan Li Laboratory of Optical Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, P. O. Box 603,
Optical Isolation Can Occur in Linear and Passive Silicon Photonic Structures Chen Wang and Zhi-Yuan Li Laboratory of Optical Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, P. O. Box 603,
OPSENS WHITE-LIGHT POLARIZATION INTERFEROMETRY TECHNOLOGY
 OPSENS WHITE-LIGHT POLARIZATION INTERFEROMETRY TECHNOLOGY 1. Introduction Fiber optic sensors are made up of two main parts: the fiber optic transducer (also called the fiber optic gauge or the fiber optic
OPSENS WHITE-LIGHT POLARIZATION INTERFEROMETRY TECHNOLOGY 1. Introduction Fiber optic sensors are made up of two main parts: the fiber optic transducer (also called the fiber optic gauge or the fiber optic
Long distance measurement with femtosecond pulses using a dispersive interferometer
 Long distance measurement with femtosecond pulses using a dispersive interferometer M. Cui, 1, M. G. Zeitouny, 1 N. Bhattacharya, 1 S. A. van den Berg, 2 and H. P. Urbach 1 1 Optics Research Group, Department
Long distance measurement with femtosecond pulses using a dispersive interferometer M. Cui, 1, M. G. Zeitouny, 1 N. Bhattacharya, 1 S. A. van den Berg, 2 and H. P. Urbach 1 1 Optics Research Group, Department
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION
 FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
Development of a Low Cost 3x3 Coupler. Mach-Zehnder Interferometric Optical Fibre Vibration. Sensor
 Development of a Low Cost 3x3 Coupler Mach-Zehnder Interferometric Optical Fibre Vibration Sensor Kai Tai Wan Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering, Brunel University London, UB8 3PH,
Development of a Low Cost 3x3 Coupler Mach-Zehnder Interferometric Optical Fibre Vibration Sensor Kai Tai Wan Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering, Brunel University London, UB8 3PH,
Absolute distance interferometer in LaserTracer geometry
 Absolute distance interferometer in LaserTracer geometry Corresponding author: Karl Meiners-Hagen Abstract 1. Introduction 1 In this paper, a combination of variable synthetic and two-wavelength interferometry
Absolute distance interferometer in LaserTracer geometry Corresponding author: Karl Meiners-Hagen Abstract 1. Introduction 1 In this paper, a combination of variable synthetic and two-wavelength interferometry
Phase Modulation Characteristics of Spatial Light Modulator and the System for Its Calibration
 Journal of Electrical Engineering 6 (2018) 193-205 doi: 10.17265/2328-2223/2018.04.001 D DAVID PUBLISHING Phase Modulation Characteristics of Spatial Light Modulator and the System for Its Calibration
Journal of Electrical Engineering 6 (2018) 193-205 doi: 10.17265/2328-2223/2018.04.001 D DAVID PUBLISHING Phase Modulation Characteristics of Spatial Light Modulator and the System for Its Calibration
Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
Comparison of Fourier transform methods for calculating MTF Joseph D. LaVeigne a, Stephen D. Burks b, Brian Nehring a
 Comparison of Fourier transform methods for calculating Joseph D. LaVeigne a, Stephen D. Burks b, Brian Nehring a a Santa Barbara Infrared, Inc., 30 S Calle Cesar Chavez, Santa Barbara, CA, USA 93103;
Comparison of Fourier transform methods for calculating Joseph D. LaVeigne a, Stephen D. Burks b, Brian Nehring a a Santa Barbara Infrared, Inc., 30 S Calle Cesar Chavez, Santa Barbara, CA, USA 93103;
Simple interferometric fringe stabilization by CCD-based feedback control
 Simple interferometric fringe stabilization by CCD-based feedback control Preston P. Young and Purnomo S. Priambodo, Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Texas at Arlington, P.O. Box 19016,
Simple interferometric fringe stabilization by CCD-based feedback control Preston P. Young and Purnomo S. Priambodo, Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Texas at Arlington, P.O. Box 19016,
Introduction to interferometry with bolometers: Bob Watson and Lucio Piccirillo
 Introduction to interferometry with bolometers: Bob Watson and Lucio Piccirillo Paris, 19 June 2008 Interferometry (heterodyne) In general we have i=1,...,n single dishes (with a single or dual receiver)
Introduction to interferometry with bolometers: Bob Watson and Lucio Piccirillo Paris, 19 June 2008 Interferometry (heterodyne) In general we have i=1,...,n single dishes (with a single or dual receiver)
