RMS Communications TECHNICAL BRIEF
|
|
|
- Giles Lawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TECHNICAL BRIEF BROADBAND CATV Coaxial Network Demands Today: Introducing Intermodulation: Its Role in Cable Modem and Reverse Path Operation RF Products Division A History of CATV Coaxial Network Design: Cable Television systems are designed for optimum forward path operation (in one direction only), allowing 6MHz analog video channels to move from the Headend to the home over a Hybrid Fiber/Coax medium. The products used in these networks, from amplifiers to passive's, were designed with forward transmission as the key requirement. As RF travels from the cable system Headend to the home, a number of things happen. For the purpose of understanding Intermodulation and why it occurs, the key thing to remember about RF signals passing through any medium is that they attenuate or loose strength. Cable systems are engineered to ensure that the RF signal present at the entry to every home is optimized to guarantee a minimum video level at the highest frequency of operation. To accomplish this, passive products are designed to attenuate RF signals that pass through them by varying degrees. Depending on how far away a particular home is from the last amplifier (distribution and drop cable length), the db value of a tap (coupling value) is chosen to ensure that the db level at all homes fed from that particular amplifier is constant. Homes fed from different taps at different distances from the amplifier should all receive the same signal level in order for the set-top box to work correctly (typically 7dB at the input to the home splitter). Consider the following example (See Figure 1, Page 2). Cable systems today are beginning to utilize their reverse paths extensively. The best example of this is the rapid deployment of cable modems, which allow customers high speed Internet access through their cable television networks. In order for cable modems to operate properly, they rely on being able to receive and transmit data from the home to the Headend over the cable network. As cable systems deploy cable modems, they are learning more about the limitations of passive products in this area. The limitations have primarily to do with the passive product s ability to pass high level RF signals in the reverse direction. From a fundamental design standpoint, RF passes freely through any passive product in either direction. The technical issues have more to do with what happens to the signal as it passes. More specifically, the Intermodulation issue relates to and results from the high RF signal level at which a cable modem must transmit a signal in order to ensure that it reaches the headend accurately and within an acceptable Bit Error Rate range. Just as a RF signal is attenuated through a passive devise in the forward direction, it is also attenuated by the same degree as it passes through that devise in the reverse direction. Consider the following example (See Figure 2): (continued on page 2)
2 (continued from page 1) Reverse Path Signal Level Budgeting: AMPLIFIER TAP #1 TAP #2 TAP #3 TAP #4 Let s now consider a signal originating at the cable modem and the obstacles it must overcome in order to reach the amplifier, at which point it can be amplified and continue its journey back towards the Headend. Consider the following example (See Figure 3): In this next example, let s look first at the forward direction. The output level of the amplifier is 50dBmV. This is attenuated by the following losses as it moves towards the home: 1.0dBmV Insertion Loss of the first Tap installed on the Amplifier output. 5.0dBmV loss of the distribution cable between Amplifier and Tap #2. 5.0dBmV loss of the drop cable between Tap #2 and Home B. AMPLIFIER -1dBmV -5dBmV TAP #1 TAP #2 TAP #3 AMPLIFIER OUTPUT LOAD = 50dBmV 50dBmV - 1dBmV - 5dBmV - 32dBmV* - 5dBmV = 7dBmV A Figure 1. The RF signal level at the entry point to each home must be approximately 7dBmV. The coupling values of Taps 1 through 4 are chosen to ensure this consistent RF level at each home entry port. * Coupling Value of Tap #2-5dBmV If a 7dBmV signal level is desired at the home entry point, a 32dB Tap must be selected in order to properly budget the available RF. Amplifier output (50dB), minus Insertion Loss of first Tap (-1dB) minus cable loss (-5dB) minus Tap db attenuation (-32dB), minus drop cable attenuation (-5dB), equals signal available at the home. [50dB minus 1dB, minus 5dB, minus 32dB, minus 5dB] equals 7dB. This RF budgeting has been carried out with only the forward path considered. Ba -7dBmV Desired Figure 2. This example shows typical attenuation losses, in the forward direction, of taps and drop cable for a desired 7dBmV at the home. B C D In this case, we are looking at a signal originating at the cable modem output. This signal must be transmitted at a level sufficient to overcome interference due to ingress (noise funneling from home appliances etc.), and the losses of passive devices and cable between the modem and AMPLIFIER -1dBmV -5dBmV TAP #1 TAP #2 TAP #3-5.5dBmV CUMULATIVE REVERSE PATH LOSS 3.5dBmV + 5.5dBmV dBmV + 5.0dBmV + 1.0dBmV the first amplifier upstream. These losses are the same as in Figure 2, with the addition of a loss through a 2-Way Splitter inside the home which was added to allow the cable modem to be connected, and the added cable between the entry point to the home and the Indoor Splitter. Beginning at the cable modem, the transmitted signal must overcome the following losses: 3.5dBmV loss of the 2-Way Splitter 5.5dBmV loss of the drop cable 32.0dBmV loss of the distribution tap 5.0dBmV loss of the distribution cable between tap and amplifier. 1.0dBmV insertion loss of the first tap on the amplifier output TOTAL LOSS = 47.0dBmV Let s assume that the reverse amplifier requires a minimum input signal level of 13dBmV in order to optimize the carrier to noise and dynamic range. The total output level of the cable modem must now be 60dBmV (47dBmV + SPLITTER MODEM SET-TOP = 47.0dBmV -3.5dBmV Desired Amplifier Reverse Path Input = + 16dBmV Required Modem Output = (43.5dBmV + 16dBmV) = 59.5dBmV Figure 3. This example shows added attenuation losses of 3.5dBmV due to 2-Way Splitter addition for connection of cable modem. PC TV (continued on page 3) 2 R M S C o m m u n i c a t i o n s
3 13dBmV) in order to overcome all losses along the way and still reach the amplifier with an acceptable signal strength. This extremely high cable modem output level of 60dBmV is the root cause of the intermodulation problem we will now discuss. What Is Intermodulation?: CATV Passive products are constructed using transformers with ferrite cores and various resistive/capacitive tuned circuits. These circuits function together to ensure that the RF signal is minimally compromised as it passes through the devise in order to redirect, split, reduce it in power by a predetermined factor, or combine it with other signals. The following circuit diagram depicts a typical 3-Way splitter circuit: IN OUT 1 OUT 3 OUT 2 Figure 4. A typical passive device circuit is designed to redirect, split, and/or reduce signal power by a predetermined factor, or to combine it with other signals. The ferrite core material is particularly sensitive in terms of its magnetic characteristics (linear magnetization curve) and how it allows a broadband ( MHz) RF signal to pass through it with minimum interference. It is used because of its ability to manage such a broadband signal while continuing to operate linearly or within a predictable and flat range across the entire 5 to 1000 MHz spectrum. The linear operation of a ferrite core is dependent on its magnetic properties remaining within a stable range (linear region). The stable magnetic range of a ferrite can be represented by what is known as a hysteresis curve. This curve depicts the stable operating range of the ferrite s magnetic property which occurs between the upper and lower hysteresis limits (linear region). The Problem: As we have demonstrated earlier, a cable modem must output signal levels over a wide dynamic range (25 to 60 dbmv typical) in order to overcome the losses it encounters on its way back to the amplifier. In fact, cable modems are designed to automatically increase their output level until they can verify the signal they are transmitting has been received at the headend within an acceptable bit error rate range. This adds an element of unpredictability to the actual output level of any given modem at any given time. Assuming the modem output level is a realistic 55 dbmv, the first passive device encountered is the 2-Way Splitter used to connect the cable modem to the CATV network. Depending on where the ferrite material is sitting about the hysteresis curve, the ferrite cores may no longer be capable of operating within their linear range when hit by such a high signal level. The high RF level changes the magnetic properties of the core, and results in operation of that core outside of its stable hysteresis range. This is referred to as saturation of the core (non-linear operation). When saturation occurs, undesired beats or signal sources are generated at harmonic's of the original frequency (fundamental frequency). For example, if the return path signal is being transmitted at 40 MHz and the ferrite saturates due to the high level being transmitted, a second harmonic beat will appear at 80 MHz (twice the fundamental frequency). This second harmonic beat now falls in the forward video band; its level is unpredictable and can distort the video channel being transmitted at 80MHz (causing severe interference on the TV picture). Other lower level beats may appear at higher harmonic frequencies depending on the level of the original beat. Detection of the problem will only occur when the cable modem is operating and a television set close to the modem is tuned to a channel which falls on one of the harmonic frequencies. This makes the interference itself intermittent and difficult to troubleshoot if not understood by the service technician. The following graph depicts this interaction (See Figure 5, Page 4): (continued on page 4) 3 R M S C o m m u n i c a t i o n s
4 Return Path 32MHz (60dBmV) Modem Signal 5MHz Intermod Distortion Forward Path 64 MHz Channel 4 TV 750MHz Figure 5. This example shows a return path signal that is being transmitted at 32MHz. As the ferrite saturates, due to the high level signal being transmitted, a second harmonic beat will appear at 64MHz (twice the fundamental frequency). Common Solutions to the Intermodulation Problem: Manufacturers have for some time known about this problem and have made some attempts to develop and implement a solution. However, the solutions commonly available all fall short in one fundamental manner. They do not address the problem at the root cause, which is the material composition and linear properties of the ferrite component itself. Other solutions attempt to make the ferrite less susceptible to saturation by merely increasing its size, improving the as produced magnetic properties of the ferrite by ensuring it is completely demagnetized on leaving the factory, or adding components which prevent or limit other sources of interference such as impulse noise or other forms of voltage spikes. Manufacturers are attempting to use combinations of the above in order to avoid fundamental redesigns of their staple, existing products. They then market the product as a Low Intermodulation, Modem/Digital Ready product. Let s look at these different solutions and identify some of their inherent drawbacks: Ferrite Size: By simply increasing the size of the ferrite, it can become more capable of handling higher signal levels before saturating. However, it is not only physical size that matters, the material composition also plays an important role. Merely increasing ferrite size has a direct negative impact on the broadband performance of the ferrite. In other words, as the size increases it becomes increasingly difficult to maintain desired return loss and frequency response characteristics across the 1000MHz band and the lower and upper portions of the band are most severely affected. Demagnetizing Ferrites in Production: This process is known as Degaussing and involves passing the final product through a degaussing chamber just before final packaging at the factory. The resulting ferrite is demagnetized and operating at optimum linearity on leaving the factory. The problem with this solution is that various things can happen in a standard network to re-magnetize the ferrite rendering the product susceptible once again to saturation. The most common re-magnetizing force is a voltage spike caused by impulse noise or lightening. It actually requires rather low voltage levels to change the magnetic properties of the ferrite once again rendering its intermodulation performance unpredictable. Changes in temperature can also vary the magnetization characteristic. Adding Components to Prevent Re-Magnetization of the Ferrite: Many manufacturers are now adding blocking capacitors with various voltage ratings to all ports of an indoor splitter. These blocking capacitors essentially reduce the level of the voltage spike reaching the ferrite, thereby preventing the ferrite from being re-magnetized. This method does help reduce the effects of low voltage spikes, but high voltage spikes can still induce enough magnetic change to cause the ferrite to operate nonlinearly. It is therefore at best only a partial solution or defensive measure against the problem. The RMS DigiTap Low Intermodulation Solution: The Low Intermodulation solution pioneered by Filtronic & over the past three years and now licensed exclusively to RMS centers on maintainingthe actual broadband linearity of the ferrite component itself. Through extensive experimentation and scientificresearch and development, Filtronic/RMS developed a unique multi-stage solution. The first is a new material composition, which when used with a specific manufacturing process, provides a guaranteed level of linear broadband performance greater than that ever achieved before. Unique circuit designs are used to optimize the broadband RF performance. In addition, some of the performance insurance measures presented above, such as optimizing the physical size of the ferrite and adding blocking capacitors, are incorporated into the final RMS DigiTap designs to provide redundant protection. (continued on back cover) 4
5 SPECIFICATIONS RMS DigiTap Low Intermodulation Splitters: Bandpass (MHz) MHz 1002DWSBSCTE 1003DWSBSCTE 1003UBDWSBSCTE 1004DWSB- Balanced Unbalanced SCTE Prt 2 Prt 3 Insertion Loss: (-db Max.) Isolation: (-db Min.) Return Loss Input: (-db Min.) Return Loss Output: (-db Min.) Tap Distortion (All Ports) (-dbc Min.) 60dBmV One Signal In Return Path Harmonic Second Order And Higher Second Order Beats 60dBmV One Signal In (-dbc Min.) Return Path EMC 30 KHz MHz 100 (db Min.) Environmental Operating Range: -20ºC to +70ºC Note: Intermodulation performance results are achieved without degaussing to provide spike immunity. 5
6 Isolation and It s Role in Cable Modem Operation: Isolation refers to the ability of a product to prevent a RF signal from coupling onto adjacent ports and interfering with other subscribers or other sets connected off the same passive product. For example, the signal transmitted by the cable modem, in an ideal situation, travels directly back to the headend and the isolation performance of the passives through which it must pass is sufficient to ensure that it does not interfere with adjacent ports. Unfortunately, once again the high output level of a cable modem places unusual isolation demands on particularly the first passive it encounters, since its signal level is highest at this point. This again will be the indoor splitter used to connect the modem into the CATV network. Because of this, it is not only necessary to prevent intermodulation in the design of the splitter, but also to increase the port-to-port isolation performance of the splitter to protect adjacent ports from the high level cable modem output signal. The DigiTap Splitter line also takes this into consideration in every detail of the design from the printed circuit board material, to tolerances of individual components, to production tuning methods. This has resulted in a significant improvement in the isolation specification of the product. This improvement is in the order of 10dB over conventional splitters in the market, particularly over the important reverse path frequency band where the high level cable modem signal enters the product. For additional product information, contact the office or distributor nearest you: Office Locations: UNITED STATES CANADA CANADA EUROPE Downs Road 4640 Lancelot Drive Telonix Communications TBA Pineville,NC Richmond,-BC-V7C4S Industrial-Parkway-South Auroro, Ontario L4G6X7 800/ / / Fax: Fax: Fax:
Frequency Division Multiplexing and Headend Combining Techniques
 Frequency Division Multiplexing and Headend Combining Techniques In the 3 rd quarter technical report for 2010, I mentioned that the next subject would be wireless link calculations and measurements; however,
Frequency Division Multiplexing and Headend Combining Techniques In the 3 rd quarter technical report for 2010, I mentioned that the next subject would be wireless link calculations and measurements; however,
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 145 2013 Test Method for Second Harmonic Distortion of ives Using a Single Carrier NOTICE The Society of Cable
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 145 2013 Test Method for Second Harmonic Distortion of ives Using a Single Carrier NOTICE The Society of Cable
Upstream Challenges With DOCSIS 3.1
 Upstream Challenges With DOCSIS 3.1 White Paper A Technical Paper prepared for SCTE/ISBE by Jan Ariesen Chief Technology Officer Technetix Inc 2017 SCTE-ISBE and NCTA. All rights reserved. Title Table
Upstream Challenges With DOCSIS 3.1 White Paper A Technical Paper prepared for SCTE/ISBE by Jan Ariesen Chief Technology Officer Technetix Inc 2017 SCTE-ISBE and NCTA. All rights reserved. Title Table
IMPROVEMENT OF THE HFC SYSTEM REVERSE PATH PERFORMANCE
 IMPROVEMENT OF THE HFC SYSTEM REVERSE PATH PERFORMANCE Lidia Totkova Jordanova, Dobri Mihajlov Dobrev Faculty of Communications and Communications Technologies, Technical University of Sofia, 8, Kl. Ohridski
IMPROVEMENT OF THE HFC SYSTEM REVERSE PATH PERFORMANCE Lidia Totkova Jordanova, Dobri Mihajlov Dobrev Faculty of Communications and Communications Technologies, Technical University of Sofia, 8, Kl. Ohridski
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 126 2013 Test Method for Distortion of 2-way Amplifiers Caused by Insufficient Isolation of Built in Diplex Filter
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 126 2013 Test Method for Distortion of 2-way Amplifiers Caused by Insufficient Isolation of Built in Diplex Filter
Features and Benefits
 Features and Benefits E-Option Plug-In Conditioner Conditioning at the Tap Antronix s patented E-Option conditioning multi-taps accommodate a variety of plug-in modules that provide signal conditioning
Features and Benefits E-Option Plug-In Conditioner Conditioning at the Tap Antronix s patented E-Option conditioning multi-taps accommodate a variety of plug-in modules that provide signal conditioning
UPSTREAM CHALLENGES WITH DOCSIS 3.1
 UPSTREAM CHALLENGES WITH DOCSIS 3.1 White Paper By Jan Ariesen Chief Technology Officer 24th August 2017 Aug/2017 Contents 1.0 Introduction... 1 2. Passive intermodulation (PIM) in in-home splitters...
UPSTREAM CHALLENGES WITH DOCSIS 3.1 White Paper By Jan Ariesen Chief Technology Officer 24th August 2017 Aug/2017 Contents 1.0 Introduction... 1 2. Passive intermodulation (PIM) in in-home splitters...
INSTALLATION MANUAL. CTA-30RK-550 Rack Mount Distribution Amplifier
 INSTALLATION MANUAL CTA-30RK-550 Rack Mount Distribution Amplifier 1 PACKAGE CONTENTS This package contains: One CTA-30RK-550 Rack Mount Distribution Amplifier One CTA-30RK-550 instruction manual PRODUCT
INSTALLATION MANUAL CTA-30RK-550 Rack Mount Distribution Amplifier 1 PACKAGE CONTENTS This package contains: One CTA-30RK-550 Rack Mount Distribution Amplifier One CTA-30RK-550 instruction manual PRODUCT
Application Note: PathTrak QAMTrak Analyzer Functionality. Overview
 Overview Increasing customer demand for upstream bandwidth is a welcomed challenge for MSO s as it often stems from growth in profitable bi-directional applications like VoIP and advanced video services.
Overview Increasing customer demand for upstream bandwidth is a welcomed challenge for MSO s as it often stems from growth in profitable bi-directional applications like VoIP and advanced video services.
Compact Model Fiber Deep Node 862 MHz with 42/54 MHz Split
 Optoelectronics Compact Model 90090 Fiber Deep Node 862 MHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The Scientific-Atlanta Compact Model 90090 Fiber Deep Node is a small, low-cost, 110V AC powered node that addresses
Optoelectronics Compact Model 90090 Fiber Deep Node 862 MHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The Scientific-Atlanta Compact Model 90090 Fiber Deep Node is a small, low-cost, 110V AC powered node that addresses
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 82 2012 Test Method for Low Frequency and Spurious Disturbances NOTICE The Society of Cable Telecommunications
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 82 2012 Test Method for Low Frequency and Spurious Disturbances NOTICE The Society of Cable Telecommunications
SmartScan. Application Note. Intelligent Frequency Response and Limits in Plant Distribution. VIAVI Solutions
 Application Note SmartScan Intelligent Frequency Response and Limits in Plant Distribution VIAVI Solutions As signals travel through the coaxial cable network they are attenuated more at higher frequencies.
Application Note SmartScan Intelligent Frequency Response and Limits in Plant Distribution VIAVI Solutions As signals travel through the coaxial cable network they are attenuated more at higher frequencies.
SCTE. San Diego Chapter March 19, 2014
 SCTE San Diego Chapter March 19, 2014 RFOG WHAT IS RFOG? WHY AND WHERE IS THIS TECHNOLOGY A CONSIDERATION? RFoG could be considered the deepest fiber version of HFC RFoG pushes fiber to the side of the
SCTE San Diego Chapter March 19, 2014 RFOG WHAT IS RFOG? WHY AND WHERE IS THIS TECHNOLOGY A CONSIDERATION? RFoG could be considered the deepest fiber version of HFC RFoG pushes fiber to the side of the
Understanding and Troubleshooting Linear Distortions: Micro-reflections, Amplitude Ripple/Tilt and Group Delay
 Understanding and Troubleshooting Linear Distortions: Micro-reflections, Amplitude Ripple/Tilt and Group Delay RON HRANAC 1 A Clean Upstream: Or Is It? Graphic courtesy of Sunrise Telecom 2 Transmission
Understanding and Troubleshooting Linear Distortions: Micro-reflections, Amplitude Ripple/Tilt and Group Delay RON HRANAC 1 A Clean Upstream: Or Is It? Graphic courtesy of Sunrise Telecom 2 Transmission
Application Note #60 Harmonic Measurement for IEC And other Radiated Immunity Standards
 Application Note #60 Harmonic Measurement for IEC 61000-4-3 And other Radiated Immunity Standards By: Applications Engineering In the rush to complete RF immunity testing on schedule, it is not all that
Application Note #60 Harmonic Measurement for IEC 61000-4-3 And other Radiated Immunity Standards By: Applications Engineering In the rush to complete RF immunity testing on schedule, it is not all that
AC3000 INTELLIGENT BROADBAND AMPLIFIER
 Kari Mäki 24.9.2012 1(7) AC3000 INTELLIGENT BROADBAND AMPLIFIER AC3000, the most advanced amplifier on the market, is the latest leading-edge addition to AC family with extended frequency and gain ranges
Kari Mäki 24.9.2012 1(7) AC3000 INTELLIGENT BROADBAND AMPLIFIER AC3000, the most advanced amplifier on the market, is the latest leading-edge addition to AC family with extended frequency and gain ranges
Agilent AN How to Characterize CATV Amplifiers Effectively
 Agilent AN 1288-4 How to Characterize CATV Amplifiers Effectively Application Note Using the Agilent 4396B RF Network/Spectrum/ Impedance Analyzer Page Contents 3 Introduction 3 1. CATV System Configuration
Agilent AN 1288-4 How to Characterize CATV Amplifiers Effectively Application Note Using the Agilent 4396B RF Network/Spectrum/ Impedance Analyzer Page Contents 3 Introduction 3 1. CATV System Configuration
XCOR TODAY S APPROACH TO DETECTING COMMON PATH DISTORTION
 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY XCOR TODAY S APPROACH TO DETECTING COMMON PATH DISTORTION 185 AINSLEY DRIVE SYRACUSE, NY 13210 800.448.1655 / WWW.ARCOMDIGITAL.COM A NEED FOR CHANGE ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY Cable networks
ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY XCOR TODAY S APPROACH TO DETECTING COMMON PATH DISTORTION 185 AINSLEY DRIVE SYRACUSE, NY 13210 800.448.1655 / WWW.ARCOMDIGITAL.COM A NEED FOR CHANGE ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY Cable networks
Broadband System - J
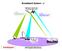 Broadband System - J Satellites are spaced every 2nd degrees above earth "C" Band Toward satellite 6.0 GHz Toward earth 4.0 GHz "L" Band Toward satellite 14.0 GHz Toward earth 12.0 GHz TV TRANSMITTER Headend
Broadband System - J Satellites are spaced every 2nd degrees above earth "C" Band Toward satellite 6.0 GHz Toward earth 4.0 GHz "L" Band Toward satellite 14.0 GHz Toward earth 12.0 GHz TV TRANSMITTER Headend
Transponder for GainMaker Optoelectronic Node
 Element Management Transponder for GainMaker Optoelectronic Node This full frequency agile transponder is designed to interface with Scientific-Atlanta s GainMaker Nodes. It is controlled by Scientific-Atlanta
Element Management Transponder for GainMaker Optoelectronic Node This full frequency agile transponder is designed to interface with Scientific-Atlanta s GainMaker Nodes. It is controlled by Scientific-Atlanta
IEEE p802.3bn EPoC. Channel Model Ad Hoc committee Baseline Channel Model
 IEEE p802.3bn EPoC Channel Model Ad Hoc committee Baseline Channel Model N-Way 2-Way Headend Baseline Topology Opt TRx HFC TAP TAP TAP TAP CLT CLT EPON OLT CLT CLT RG-6 (+) 150 Ft. (50M) max RG-6 < 6 Ft.
IEEE p802.3bn EPoC Channel Model Ad Hoc committee Baseline Channel Model N-Way 2-Way Headend Baseline Topology Opt TRx HFC TAP TAP TAP TAP CLT CLT EPON OLT CLT CLT RG-6 (+) 150 Ft. (50M) max RG-6 < 6 Ft.
MINIMIZING SITE INTERFERENCE
 MINIMIZING SITE INTERFERENCE CHAPTER 8 This chapter provides information on preventing radio frequency (RF) interference at a communications site. The following topics are included: Interference Protection
MINIMIZING SITE INTERFERENCE CHAPTER 8 This chapter provides information on preventing radio frequency (RF) interference at a communications site. The following topics are included: Interference Protection
16-?t R.S. S. Y \
 US 20170 155182A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0155182 A1 Rijssemus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2017 (54) CABLE TAP Publication Classification - - -
US 20170 155182A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0155182 A1 Rijssemus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2017 (54) CABLE TAP Publication Classification - - -
Interference & Suppression Page 59
 INTERFERENCE Interference & Suppression Page 59 Front-End Overload, Cross-Modulation What is meant by receiver overload? Interference caused by strong signals from a nearby transmitter What is one way
INTERFERENCE Interference & Suppression Page 59 Front-End Overload, Cross-Modulation What is meant by receiver overload? Interference caused by strong signals from a nearby transmitter What is one way
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 115 2011 Test Method for Reverse Path (Upstream) Intermodulation Using Two Carriers NOTICE The Society of Cable
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 115 2011 Test Method for Reverse Path (Upstream) Intermodulation Using Two Carriers NOTICE The Society of Cable
EFFECT OF SHIELDING ON CABLE RF INGRESS MEASUREMENTS LARRY COHEN
 EFFECT OF SHIELDING ON CABLE RF INGRESS MEASUREMENTS LARRY COHEN OVERVIEW Purpose: Examine the common-mode and differential RF ingress levels of 4-pair UTP, F/UTP, and F/FTP cables at an (RJ45) MDI port
EFFECT OF SHIELDING ON CABLE RF INGRESS MEASUREMENTS LARRY COHEN OVERVIEW Purpose: Examine the common-mode and differential RF ingress levels of 4-pair UTP, F/UTP, and F/FTP cables at an (RJ45) MDI port
GainMaker High Output Node 5-40/ MHz
 Optoelectronics GainMaker High Output Node 5-40/52-1002 MHz Description The GainMaker High Output Node is designed to serve as an integral part of today s network architectures, and combines the superior
Optoelectronics GainMaker High Output Node 5-40/52-1002 MHz Description The GainMaker High Output Node is designed to serve as an integral part of today s network architectures, and combines the superior
MODEL BLN GHz FIBER DEEP NODE STARLINE SERIES
 MODEL BLN100 1 1 GHz FIBER DEEP NODE STARLINE SERIES The BLN100 optical node is an essential building block in evolving Hybrid Fiber Coaxial (HFC) network architectures enabling amplifier to node conversions.
MODEL BLN100 1 1 GHz FIBER DEEP NODE STARLINE SERIES The BLN100 optical node is an essential building block in evolving Hybrid Fiber Coaxial (HFC) network architectures enabling amplifier to node conversions.
Distribution Amplifiers 1
 Distribution Amplifiers 1-30dB PUT 49-750 MHz 43 db GA POWER DOUBLED P/N: 1002705 REVERSE GA M MAX DESCRIPTION The R.L. DRAKE models DA8642, DA8632,, and DA7533, are broadband distribution amplifiers designed
Distribution Amplifiers 1-30dB PUT 49-750 MHz 43 db GA POWER DOUBLED P/N: 1002705 REVERSE GA M MAX DESCRIPTION The R.L. DRAKE models DA8642, DA8632,, and DA7533, are broadband distribution amplifiers designed
Improving Amplitude Accuracy with Next-Generation Signal Generators
 Improving Amplitude Accuracy with Next-Generation Signal Generators Generate True Performance Signal generators offer precise and highly stable test signals for a variety of components and systems test
Improving Amplitude Accuracy with Next-Generation Signal Generators Generate True Performance Signal generators offer precise and highly stable test signals for a variety of components and systems test
ALX. 870 MHz Line Extender
 ALX 870 MHz Line Extender Overview ALX 870 MHz 15 amp series of broadband RF amplifiers provide high quality RF distribution for fiber to fiber, HFC (hybrid fiber coaxial), or PDN (power domain node) architectures.
ALX 870 MHz Line Extender Overview ALX 870 MHz 15 amp series of broadband RF amplifiers provide high quality RF distribution for fiber to fiber, HFC (hybrid fiber coaxial), or PDN (power domain node) architectures.
Pa s s i v e s. 3 - way, 1 GHz Horizontal balanced splitter EA 200/ /6.2
 1 GHz Hi-Q Digital Sp l i t t e r s - Ho r i z o n t a l 2, 3 a n d 4 Po r t Se r i e s Ma r a t h o n series of splitters provides exceptional value, outstanding performance and high reliability for two-way
1 GHz Hi-Q Digital Sp l i t t e r s - Ho r i z o n t a l 2, 3 a n d 4 Po r t Se r i e s Ma r a t h o n series of splitters provides exceptional value, outstanding performance and high reliability for two-way
Case Study. Bryant Solutions. Evaluation of Intermodulation Products Displayed by Spectrum Analyzers. Expanding on Expectations F 1 F 2 -F 2 2F 1 -F 1
 Bryant Solutions RF Engineering & Training Services Expanding on Expectations Case Study Evaluation of Intermodulation s Displayed by Spectrum Analyzers F 1 F 2 2F 1 -F 2 2F 2 -F 1 3F 1-2F 2 3F 2-2F 1
Bryant Solutions RF Engineering & Training Services Expanding on Expectations Case Study Evaluation of Intermodulation s Displayed by Spectrum Analyzers F 1 F 2 2F 1 -F 2 2F 2 -F 1 3F 1-2F 2 3F 2-2F 1
Christen Rauscher NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number Filing Date Inventor 069.855 30 April 1998 Christen Rauscher NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE
Serial Number Filing Date Inventor 069.855 30 April 1998 Christen Rauscher NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits. Module 7
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters
 High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
Trees, vegetation, buildings etc.
 EMC Measurements Test Site Locations Open Area (Field) Test Site Obstruction Free Trees, vegetation, buildings etc. Chamber or Screened Room Smaller Equipments Attenuate external fields (about 100dB) External
EMC Measurements Test Site Locations Open Area (Field) Test Site Obstruction Free Trees, vegetation, buildings etc. Chamber or Screened Room Smaller Equipments Attenuate external fields (about 100dB) External
amplifiers Phoenix Communication Technologies AMPLIFIERS PAGE DROP AMPLIFIERS DISTRIBUTION AMPLIFIER
 Phoenix Communication Technologies AMPLIFIERS DROP AMPLIFIERS DISTRIBUTION AMPLIFIER PAGE C2 C7 07-2001 ANDES Industries, Inc. C2 drop f e a t u r e s 6 kv surge withstand on each port 1, 2, or 4-port
Phoenix Communication Technologies AMPLIFIERS DROP AMPLIFIERS DISTRIBUTION AMPLIFIER PAGE C2 C7 07-2001 ANDES Industries, Inc. C2 drop f e a t u r e s 6 kv surge withstand on each port 1, 2, or 4-port
Resistive components. Attenuators and terminators catalogue. Edition 2016
 Resistive components Attenuators and terminators catalogue Edition 2016 Be precise Fixed attenuators Low, medium and high power types up to 300 Watts 7 Terminators Low, medium and high power types up to
Resistive components Attenuators and terminators catalogue Edition 2016 Be precise Fixed attenuators Low, medium and high power types up to 300 Watts 7 Terminators Low, medium and high power types up to
Return Plant Issues SCTE Cascade Range Chapter. Micah Martin January 13, 2008
 Return Plant Issues SCTE Cascade Range Chapter Micah Martin January 13, 2008 1 1 Agenda Experience with DOCSIS upgrade Digital review & digital modulation Carrier to Noise issues Coaxial Plant Optical
Return Plant Issues SCTE Cascade Range Chapter Micah Martin January 13, 2008 1 1 Agenda Experience with DOCSIS upgrade Digital review & digital modulation Carrier to Noise issues Coaxial Plant Optical
Methods for Testing Impulse Noise Tolerance
 Methods for Testing Impulse Noise Tolerance May,6,2015 Larry Cohen Overview Purpose: Describe some potential test methods for impulse noise tolerance What we will cover in this presentation: Discuss need
Methods for Testing Impulse Noise Tolerance May,6,2015 Larry Cohen Overview Purpose: Describe some potential test methods for impulse noise tolerance What we will cover in this presentation: Discuss need
DStar Co-channel and Adjacent Channel Performance
 DStar Co-channel and Adjacent Channel Performance N5RFX 4/21/08 Introduction The purpose of this initial paper is to describe and show the results of DStar co-channel and adjacent channel interference
DStar Co-channel and Adjacent Channel Performance N5RFX 4/21/08 Introduction The purpose of this initial paper is to describe and show the results of DStar co-channel and adjacent channel interference
A Study OF RF INTERMODULATION BETWEEN TRANSMITTERS SHARING FILTERPLEXED OR CO-LOCATED ANTENNA SYSTEMS.
 A Study OF RF INTERMODULATION BETWEEN TRANSMITTERS SHARING FILTERPLEXED OR CO-LOCATED ANTENNA SYSTEMS. GEOFFREY N. MENDENHALL, P.E. PRESIDENT, ENGINEERING BROADCAST ELECTRONICS, INC. QUINCY, ILLINOIS "A
A Study OF RF INTERMODULATION BETWEEN TRANSMITTERS SHARING FILTERPLEXED OR CO-LOCATED ANTENNA SYSTEMS. GEOFFREY N. MENDENHALL, P.E. PRESIDENT, ENGINEERING BROADCAST ELECTRONICS, INC. QUINCY, ILLINOIS "A
HOW TO PROPERLY BUILD AN IN-BUILDING DAS SYSTEM Part 1 Use of Directional Couplers in DAS By J. Macias
 HOW TO PROPERLY BUILD AN IN-BUILDING DAS SYSTEM Part 1 Use of Directional Couplers in DAS By J. Macias RF in-building coverage has become a fast growing market in recent years. Commercial wireless users
HOW TO PROPERLY BUILD AN IN-BUILDING DAS SYSTEM Part 1 Use of Directional Couplers in DAS By J. Macias RF in-building coverage has become a fast growing market in recent years. Commercial wireless users
Application Note 5477
 Push-Pull Amplifier Design for CATV Application using Avago Technologies MGA-30x89 Amplifier Series Application Note 5477 Introduction The Avago MGA-30689 and MGA-30889 are innovative wideband, flat gain,
Push-Pull Amplifier Design for CATV Application using Avago Technologies MGA-30x89 Amplifier Series Application Note 5477 Introduction The Avago MGA-30689 and MGA-30889 are innovative wideband, flat gain,
ACI SDLA. Miniflex Line Extender 1002 MHz
 ACI SDLA Miniflex Line Extender 1002 MHz Overview SDLA 1002 MHz 15 amp series of broadband RF amplifiers provide high quality RF distribution for fiber-to fiber, HFC (hybrid fiber coaxial), or PDN (power
ACI SDLA Miniflex Line Extender 1002 MHz Overview SDLA 1002 MHz 15 amp series of broadband RF amplifiers provide high quality RF distribution for fiber-to fiber, HFC (hybrid fiber coaxial), or PDN (power
Measurement of Distortion in Multi-tone Modulation Fiber-based analog CATV Transmission System
 5 th SASTech 011, Khavaran Higher-education Institute, Mashhad, Iran. May 1-14. 1 Measurement of Distortion in Multi-tone Modulation Fiber-based analog CATV Transmission System Morteza Abdollahi Sharif
5 th SASTech 011, Khavaran Higher-education Institute, Mashhad, Iran. May 1-14. 1 Measurement of Distortion in Multi-tone Modulation Fiber-based analog CATV Transmission System Morteza Abdollahi Sharif
How will the third edition of IEC affect your test facility?
 How will the third edition of IEC 61000-4-3 affect your test facility? Changes in the standard could mean that your amplifier is no longer powerful enough Introduction The third edition of IEC 61000-4-3
How will the third edition of IEC 61000-4-3 affect your test facility? Changes in the standard could mean that your amplifier is no longer powerful enough Introduction The third edition of IEC 61000-4-3
rf link 870 mhz mini-bridger
 application ANTEC s 870 MHz Mini-Bridger is deployed in the RF network as either a two or three output device. The Mini-Bridger provides a flexible high gain and high level PHD platform that is cost-effective
application ANTEC s 870 MHz Mini-Bridger is deployed in the RF network as either a two or three output device. The Mini-Bridger provides a flexible high gain and high level PHD platform that is cost-effective
Receiver Design. Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21
 Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
Diamond Line 3 Single Output Amplifiers
 Diamond Line 3 Single Output Amplifiers About this Section In this section, you will find the following reference information about the Diamond Line 3 single output amplifiers: Item...Page Equipment Description...9
Diamond Line 3 Single Output Amplifiers About this Section In this section, you will find the following reference information about the Diamond Line 3 single output amplifiers: Item...Page Equipment Description...9
FMC664CC FM BAND CONVERTER
 FMC664CC FM BAND CONVERTER INSTRUCTION BOOK IB6225/6226-01 COPYRIGHT 1995 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED NO PART OF THIS BOOK MAY BE REPRODUCED OR UTILIZED IN ANY FORM OR BY ANY MEANS, ELECTRONIC OR MECHANICAL, INCLUDING
FMC664CC FM BAND CONVERTER INSTRUCTION BOOK IB6225/6226-01 COPYRIGHT 1995 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED NO PART OF THIS BOOK MAY BE REPRODUCED OR UTILIZED IN ANY FORM OR BY ANY MEANS, ELECTRONIC OR MECHANICAL, INCLUDING
Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: Part 1
 From May 009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 009 Summit Technical Media, LLC Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: art 1 By Andrei Grebennikov Bell Labs Ireland In modern telecommunication
From May 009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 009 Summit Technical Media, LLC Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: art 1 By Andrei Grebennikov Bell Labs Ireland In modern telecommunication
LIMITATIONS IN MAKING AUDIO BANDWIDTH MEASUREMENTS IN THE PRESENCE OF SIGNIFICANT OUT-OF-BAND NOISE
 LIMITATIONS IN MAKING AUDIO BANDWIDTH MEASUREMENTS IN THE PRESENCE OF SIGNIFICANT OUT-OF-BAND NOISE Bruce E. Hofer AUDIO PRECISION, INC. August 2005 Introduction There once was a time (before the 1980s)
LIMITATIONS IN MAKING AUDIO BANDWIDTH MEASUREMENTS IN THE PRESENCE OF SIGNIFICANT OUT-OF-BAND NOISE Bruce E. Hofer AUDIO PRECISION, INC. August 2005 Introduction There once was a time (before the 1980s)
Agilent Highly Accurate Amplifier ACLR and ACPR Testing with the Agilent N5182A MXG Vector Signal Generator. Application Note
 Agilent Highly Accurate Amplifier ACLR and ACPR Testing with the Agilent N5182A MXG Vector Signal Generator Application Note Introduction 1 0 0 1 Symbol encoder I Q Baseband filters I Q IQ modulator Other
Agilent Highly Accurate Amplifier ACLR and ACPR Testing with the Agilent N5182A MXG Vector Signal Generator Application Note Introduction 1 0 0 1 Symbol encoder I Q Baseband filters I Q IQ modulator Other
Shively Labs. Spectral Regrowth
 Shively Labs Spectral Regrowth Abstract Intermodulation products, or spurs, can develop within the analog and digital transmitters in combined systems using high-level injection. In some cases, spurs can
Shively Labs Spectral Regrowth Abstract Intermodulation products, or spurs, can develop within the analog and digital transmitters in combined systems using high-level injection. In some cases, spurs can
ACI SDAF MHz Miniflex Configurable Bridger Amplifier
 ACI SDAF MHz Miniflex Configurable Bridger Amplifier Overview SDAF MHz 15 amp series of broadband RF amplifiers provide high quality RF distribution for fiber-to fiber, HFC (hybrid fiber coaxial), or PDN
ACI SDAF MHz Miniflex Configurable Bridger Amplifier Overview SDAF MHz 15 amp series of broadband RF amplifiers provide high quality RF distribution for fiber-to fiber, HFC (hybrid fiber coaxial), or PDN
Diamond Line Type 1 and Type 2 Amplifiers
 TM Diamond Line Type 1 and Type 2 Amplifiers Reference & Installation Manual Part Number: 2244001 Rev. D 06/03 Diamond Line Series Type 1 and Type 2 Amplifiers Reference and Installation Manual 2244001
TM Diamond Line Type 1 and Type 2 Amplifiers Reference & Installation Manual Part Number: 2244001 Rev. D 06/03 Diamond Line Series Type 1 and Type 2 Amplifiers Reference and Installation Manual 2244001
GainMaker Unbalanced Triple System Amplifier 1 GHz with 42/54 MHz Split
 Optoelectronics GainMaker Unbalanced Triple System Amplifier 1 GHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The GainMaker Broadband Amplifier Platform includes a variety of RF amplifiers that address the divergent
Optoelectronics GainMaker Unbalanced Triple System Amplifier 1 GHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The GainMaker Broadband Amplifier Platform includes a variety of RF amplifiers that address the divergent
POSITIVE JAMMING CARRIER SCRAMBLING SYSTEM MODEL--EE-2002 INSTALLATION MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENTS
 POSITIVE JAMMING CARRIER SCRAMBLING SYSTEM MODEL--EE-2002 INSTALLATION MANUAL WRITTEN BY: DALE MARLAND PREPARED BY: PATRICK M. CONWAY TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0--GENERAL DESCRIPTION 2.0--FRONT PANEL DESCRIPTION
POSITIVE JAMMING CARRIER SCRAMBLING SYSTEM MODEL--EE-2002 INSTALLATION MANUAL WRITTEN BY: DALE MARLAND PREPARED BY: PATRICK M. CONWAY TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0--GENERAL DESCRIPTION 2.0--FRONT PANEL DESCRIPTION
CX380X Advanced Spectrum and Burst QAM Analyzer
 Advanced Spectrum and Burst QAM Analyzer Preventative Network Monitoring With VeEX s VeSion system, the advanced Spectrum Analyzer and Bursty Demodulator captures rogue cable modems and provides proactive
Advanced Spectrum and Burst QAM Analyzer Preventative Network Monitoring With VeEX s VeSion system, the advanced Spectrum Analyzer and Bursty Demodulator captures rogue cable modems and provides proactive
Keysight Technologies 8 Hints for Making Better Measurements Using RF Signal Generators. Application Note
 Keysight Technologies 8 Hints for Making Better Measurements Using RF Signal Generators Application Note 02 Keysight 8 Hints for Making Better Measurements Using RF Signal Generators - Application Note
Keysight Technologies 8 Hints for Making Better Measurements Using RF Signal Generators Application Note 02 Keysight 8 Hints for Making Better Measurements Using RF Signal Generators - Application Note
RangeStud Professional Grade FM Transmitter
 RangeStud Professional Grade FM Transmitter Package Contents: 1-20W RangeStud FM Transmitter 1-12V 4 A Power Adapter 1-Power Cord 1-Amateur Grade Tunable ¼ Wave FM Antenna + 30 Amateur Grade BNC Male x
RangeStud Professional Grade FM Transmitter Package Contents: 1-20W RangeStud FM Transmitter 1-12V 4 A Power Adapter 1-Power Cord 1-Amateur Grade Tunable ¼ Wave FM Antenna + 30 Amateur Grade BNC Male x
Measuring ACPR of W-CDMA signals with a spectrum analyzer
 Measuring ACPR of W-CDMA signals with a spectrum analyzer When measuring power in the adjacent channels of a W-CDMA signal, requirements for the dynamic range of a spectrum analyzer are very challenging.
Measuring ACPR of W-CDMA signals with a spectrum analyzer When measuring power in the adjacent channels of a W-CDMA signal, requirements for the dynamic range of a spectrum analyzer are very challenging.
CXE202 UNIVERSAL AMPLIFIER
 Broadband Cable Networks / Kari Mäki November 23, 2006 1(7) CXE202 UNIVERSAL AMPLIFIER The CXE202 is a dual output amplifier. It has two gain modes in one product. Gain can be selected on the field according
Broadband Cable Networks / Kari Mäki November 23, 2006 1(7) CXE202 UNIVERSAL AMPLIFIER The CXE202 is a dual output amplifier. It has two gain modes in one product. Gain can be selected on the field according
GainMaker Optoelectronic Node 1 GHz with 42/54 MHz Split
 Optoelectronics GainMaker Optoelectronic Node 1 GHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The GainMaker Node is designed to serve as the cornerstone of today s emerging fiber deeper network architectures. The
Optoelectronics GainMaker Optoelectronic Node 1 GHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The GainMaker Node is designed to serve as the cornerstone of today s emerging fiber deeper network architectures. The
GainMaker Unbalanced Triple System Amplifier 870 MHz with 40/52 MHz Split
 RF Electronics GainMaker Unbalanced Triple System Amplifier 870 MHz with 40/52 MHz Split Description The GainMaker Broadband Amplifier Platform includes a variety of RF amplifiers that address the divergent
RF Electronics GainMaker Unbalanced Triple System Amplifier 870 MHz with 40/52 MHz Split Description The GainMaker Broadband Amplifier Platform includes a variety of RF amplifiers that address the divergent
TELESTE AC AMPLIFIER MODULES
 TELESTE AC AMPLIFIER MODULES AC 6110 INPUT MODULE AC6110 is an input module with 0 db attenuation. Supports frequencies up to 1.2 GHz. 0 db jumper module to be used as an input module in AC-amplifier platform
TELESTE AC AMPLIFIER MODULES AC 6110 INPUT MODULE AC6110 is an input module with 0 db attenuation. Supports frequencies up to 1.2 GHz. 0 db jumper module to be used as an input module in AC-amplifier platform
Predicting Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) in ADSL Transformers using Behavioural Modeling
 Predicting Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) in ADSL Transformers using Behavioural Modeling, J. Neil Ross & Andrew D. Brown S 1 Outline Introduction ADSL Where is the need for the transformer? What are
Predicting Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) in ADSL Transformers using Behavioural Modeling, J. Neil Ross & Andrew D. Brown S 1 Outline Introduction ADSL Where is the need for the transformer? What are
Model 6940 Collector/Terminator Three Port Unbalanced Optoelectronic Node 870 MHz with 65/86 MHz Split
 Optoelectronics Model 6940 Collector/Terminator Three ort Unbalanced Optoelectronic Node 870 MHz with 65/86 MHz Split Description The Model 6940 Collector/Terminator Node is a three port unbalanced node
Optoelectronics Model 6940 Collector/Terminator Three ort Unbalanced Optoelectronic Node 870 MHz with 65/86 MHz Split Description The Model 6940 Collector/Terminator Node is a three port unbalanced node
SMD Pulse Transformer for Ethernet Applications. The New Reference LAN Pulse Transformer
 Fascinating, Fast, Accurate Communication SMD Pulse Transformer for Ethernet Applications ALT Series The New Reference Pulse Transformer In recent years, connectors have become standard equipment not only
Fascinating, Fast, Accurate Communication SMD Pulse Transformer for Ethernet Applications ALT Series The New Reference Pulse Transformer In recent years, connectors have become standard equipment not only
PDi COMMUNICATIONS, INC.
 12 in 1 MULTI MOD SAW FILTERED FIXED CHANNEL MODULATOR SYSTEM PDI-50121CM RF SECTION AUDIO SECTION Frequency Range Channel 2-134 (54 to 860MHz) Input Level 250mV minimum for Channels VHF, CATV (STD) 25kHz
12 in 1 MULTI MOD SAW FILTERED FIXED CHANNEL MODULATOR SYSTEM PDI-50121CM RF SECTION AUDIO SECTION Frequency Range Channel 2-134 (54 to 860MHz) Input Level 250mV minimum for Channels VHF, CATV (STD) 25kHz
A COMPACT HIGH POWER UHF COMBINER FOR MULTIPLE CHANNELS OVER A WIDE FREQUENCY SPAN
 A COMPACT HIGH POWER UHF COMBINER FOR MULTIPLE CHANNELS OVER A WIDE FREQUENCY SPAN Lewis Steer Radio Frequency Systems, Melbourne, Australia Abstract Conventional UHF high power balanced combiners are
A COMPACT HIGH POWER UHF COMBINER FOR MULTIPLE CHANNELS OVER A WIDE FREQUENCY SPAN Lewis Steer Radio Frequency Systems, Melbourne, Australia Abstract Conventional UHF high power balanced combiners are
CXE180 UNIVERSAL AMPLIFIER
 Kari Mäki 20.9.2012 1(6) CXE180 UNIVERSAL AMPLIFIER The CXE180 is a compact dual output amplifier. It has two gain modes in one product. Gain can be selected on the field according to wanted operation.
Kari Mäki 20.9.2012 1(6) CXE180 UNIVERSAL AMPLIFIER The CXE180 is a compact dual output amplifier. It has two gain modes in one product. Gain can be selected on the field according to wanted operation.
GainMaker High Output Reverse Segmentable Node with 40/52 MHz Split
 Data Sheet GainMaker High Output Reverse Segmentable Node with 40/52 MHz Split The GainMaker High Output Reverse Segmentable (RS) Node is designed to serve as an integral part of today s network architectures.
Data Sheet GainMaker High Output Reverse Segmentable Node with 40/52 MHz Split The GainMaker High Output Reverse Segmentable (RS) Node is designed to serve as an integral part of today s network architectures.
RFPD2650 GaAs/GaN Power Doubler Hybrid 45MHz to 1003MHz
 GaAs/GaN Power Doubler Hybrid 45MHz to 1003MHz The RFPD2650 is a Hybrid Power Doubler amplifier module. The part employs GaAs phemt die and GaN HEMT die, has extremely high output capability, and is operated
GaAs/GaN Power Doubler Hybrid 45MHz to 1003MHz The RFPD2650 is a Hybrid Power Doubler amplifier module. The part employs GaAs phemt die and GaN HEMT die, has extremely high output capability, and is operated
OBSOLETE. Active RF Splitter ADA FEATURES FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM APPLICATIONS GENERAL DESCRIPTION
 FEATURES Single V supply 4 MHz to 86 MHz CATV operating range 4.6 db of gain per output channel 4.4 db noise figure 2 db isolation between output channels 16 db input return loss CSO of 73 dbc (13 channels,
FEATURES Single V supply 4 MHz to 86 MHz CATV operating range 4.6 db of gain per output channel 4.4 db noise figure 2 db isolation between output channels 16 db input return loss CSO of 73 dbc (13 channels,
Frequency-Dependent Distortion Mechanism in a Broadband Amplifier
 Frequency-Dependent Distortion Mechanism in a Broadband Amplifier Jodi Steel, Anthony Parker Electronics Department, Macquarie University, Australia jodis, tonyp@ieee.org March 25, 1999 Abstract Investigation
Frequency-Dependent Distortion Mechanism in a Broadband Amplifier Jodi Steel, Anthony Parker Electronics Department, Macquarie University, Australia jodis, tonyp@ieee.org March 25, 1999 Abstract Investigation
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
HEADEND SYSTEM PLANAR-SG24
 HEADEND SYSTEM PLANAR-SG24 HEADEND SYSTEM MODULES ARE MADE AS PROGRAMMABLE SUCH AS FIXED (UPON SEPARATE REQUEST) CHANNELS. HIGH SELECTIVITY OF CHANNEL AMPLIFIERS AND CONVERTERS. HIGH LINEARITY AND INTERFERENCE
HEADEND SYSTEM PLANAR-SG24 HEADEND SYSTEM MODULES ARE MADE AS PROGRAMMABLE SUCH AS FIXED (UPON SEPARATE REQUEST) CHANNELS. HIGH SELECTIVITY OF CHANNEL AMPLIFIERS AND CONVERTERS. HIGH LINEARITY AND INTERFERENCE
Keysight Technologies Vector Network Analyzer Receiver Dynamic Accuracy
 Specifications and Uncertainties Keysight Technologies Vector Network Analyzer Receiver Dynamic Accuracy (Linearity Over Its Specified Dynamic Range) Notices Keysight Technologies, Inc. 2011-2016 No part
Specifications and Uncertainties Keysight Technologies Vector Network Analyzer Receiver Dynamic Accuracy (Linearity Over Its Specified Dynamic Range) Notices Keysight Technologies, Inc. 2011-2016 No part
ODN4P. Optical Distribution Node, Four Ports. About the Product
 About the Product The Light Link Series 2, deep-fibre Optical Distribution Node ODN4P is a prime building block for highperformance networks, designed for adaptability, scalability and optional return-path
About the Product The Light Link Series 2, deep-fibre Optical Distribution Node ODN4P is a prime building block for highperformance networks, designed for adaptability, scalability and optional return-path
Electromagnetic Compatibility
 Electromagnetic Compatibility Introduction to EMC International Standards Measurement Setups Emissions Applications for Switch-Mode Power Supplies Filters 1 What is EMC? A system is electromagnetic compatible
Electromagnetic Compatibility Introduction to EMC International Standards Measurement Setups Emissions Applications for Switch-Mode Power Supplies Filters 1 What is EMC? A system is electromagnetic compatible
GainMaker Optoelectronic Node 1 GHz with 42/54 MHz Split
 Optoelectronics GainMaker Optoelectronic Node 1 GHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The GainMaker Node is designed to serve as the cornerstone of today s emerging fiber deeper network architectures. The
Optoelectronics GainMaker Optoelectronic Node 1 GHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The GainMaker Node is designed to serve as the cornerstone of today s emerging fiber deeper network architectures. The
The design of Ruthroff broadband voltage transformers M. Ehrenfried G8JNJ
 The design of Ruthroff broadband voltage transformers M. Ehrenfried G8JNJ Introduction I started investigating balun construction as a result of various observations I made whilst building HF antennas.
The design of Ruthroff broadband voltage transformers M. Ehrenfried G8JNJ Introduction I started investigating balun construction as a result of various observations I made whilst building HF antennas.
AC2000 AMPLIFIER PLATFORM
 Broadband Cable Networks / Kari Mäki June 26, 2008 1(6) 2000 AMPLIFIER PLATFORM The 2000 is a dual active output amplifier with 2 x 39 of gain. The input and output amplifier stages are both based on high
Broadband Cable Networks / Kari Mäki June 26, 2008 1(6) 2000 AMPLIFIER PLATFORM The 2000 is a dual active output amplifier with 2 x 39 of gain. The input and output amplifier stages are both based on high
GainMaker 1 GHz High Output 4-Port Node with 40/52 MHz Split
 Data Sheet GainMaker 1 GHz High Output 4-Port Node with 40/52 MHz Split The Cisco GainMaker High Output 4-Port Node with 40/52 MHz Split is designed to serve as an integral part of today s network architectures.
Data Sheet GainMaker 1 GHz High Output 4-Port Node with 40/52 MHz Split The Cisco GainMaker High Output 4-Port Node with 40/52 MHz Split is designed to serve as an integral part of today s network architectures.
Introduction to Same Band Combining of UMTS & GSM
 Introduction to Same Band Combining of UMTS & GSM Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Non-Filter Based Combining Options 2 3. Type 1 Combiners 2 4. Type 2 Combiners 3 5. Overview of Active & Passive
Introduction to Same Band Combining of UMTS & GSM Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Non-Filter Based Combining Options 2 3. Type 1 Combiners 2 4. Type 2 Combiners 3 5. Overview of Active & Passive
GainMaker Low Gain Dual System Amplifier 1 GHz with 55/70 MHz Split
 RF Electronics GainMaker Low Gain Dual System Amplifier 1 GHz with 55/70 MHz Split Description The GainMaker Broadband Amplifier Platform includes a variety of RF amplifiers that address the divergent
RF Electronics GainMaker Low Gain Dual System Amplifier 1 GHz with 55/70 MHz Split Description The GainMaker Broadband Amplifier Platform includes a variety of RF amplifiers that address the divergent
Understanding Power Splitters
 Understanding Power Splitters How they work, what parameters are critical, and how to select the best value for your application. Basically, a 0 splitter is a passive device which accepts an input signal
Understanding Power Splitters How they work, what parameters are critical, and how to select the best value for your application. Basically, a 0 splitter is a passive device which accepts an input signal
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Hybrid Management Sub-Layer Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Hybrid Management Sub-Layer Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 25-1 2008 Hybrid Fiber Coax Outside Plant Status Monitoring Physical (PHY) Layer Specification v1. NOTICE
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Hybrid Management Sub-Layer Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 25-1 2008 Hybrid Fiber Coax Outside Plant Status Monitoring Physical (PHY) Layer Specification v1. NOTICE
 RSS-2R RF-Broadband Automatic Switch The RSS-2R is a Broadband Automatic Switch, designed for the redundancy of CATV feeds in Headend and Hub sites. It monitors the RF Broadband feeds of the main and backup
RSS-2R RF-Broadband Automatic Switch The RSS-2R is a Broadband Automatic Switch, designed for the redundancy of CATV feeds in Headend and Hub sites. It monitors the RF Broadband feeds of the main and backup
R&S CLGD DOCSIS Cable Load Generator Multichannel signal generator for DOCSIS 3.1 downstream and upstream
 CLGD_bro_en_3607-0123-12_v0200.indd 1 Product Brochure 02.00 Broadcast & Media Test & Measurement R&S CLGD DOCSIS Cable Load Generator Multichannel signal generator for downstream and upstream 24.07.2015
CLGD_bro_en_3607-0123-12_v0200.indd 1 Product Brochure 02.00 Broadcast & Media Test & Measurement R&S CLGD DOCSIS Cable Load Generator Multichannel signal generator for downstream and upstream 24.07.2015
Screening Attenuation When enough is enough
 Screening Attenuation When enough is enough Anders Møller-Larsen, Ph.D. M.Sc. E.E. Product Manager, Coax Network Introduction This white paper describes the requirements to screening attenuation of cables
Screening Attenuation When enough is enough Anders Møller-Larsen, Ph.D. M.Sc. E.E. Product Manager, Coax Network Introduction This white paper describes the requirements to screening attenuation of cables
Optical Modulation and Frequency of Operation
 Optical Modulation and Frequency of Operation Developers AB Overby Objectives Preparation Background The objectives of this experiment are to describe and illustrate the differences between frequency of
Optical Modulation and Frequency of Operation Developers AB Overby Objectives Preparation Background The objectives of this experiment are to describe and illustrate the differences between frequency of
Broadband Power Amplifier
 601L Broadband Power Amplifier HIGH RF VOLTAGES MAY BE PRESENT AT THE OUTPUT OF THIS UNIT. All operating personnel should use extreme caution in handling these voltages and be thoroughly familiar with
601L Broadband Power Amplifier HIGH RF VOLTAGES MAY BE PRESENT AT THE OUTPUT OF THIS UNIT. All operating personnel should use extreme caution in handling these voltages and be thoroughly familiar with
Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specifications Technical Reports. Midsplit Migration Implications on the HFC Network Technical Report
 Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specifications Midsplit Migration Implications on the HFC Network Technical Report Released Notice This DOCSIS technical report is the result of a cooperative effort undertaken
Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specifications Midsplit Migration Implications on the HFC Network Technical Report Released Notice This DOCSIS technical report is the result of a cooperative effort undertaken
Co-Existence of UMTS900 and GSM-R Systems
 Asdfadsfad Omnitele Whitepaper Co-Existence of UMTS900 and GSM-R Systems 30 August 2011 Omnitele Ltd. Tallberginkatu 2A P.O. Box 969, 00101 Helsinki Finland Phone: +358 9 695991 Fax: +358 9 177182 E-mail:
Asdfadsfad Omnitele Whitepaper Co-Existence of UMTS900 and GSM-R Systems 30 August 2011 Omnitele Ltd. Tallberginkatu 2A P.O. Box 969, 00101 Helsinki Finland Phone: +358 9 695991 Fax: +358 9 177182 E-mail:
Design Considerations
 Design Considerations APPLICATION NOTES: Multi-hole cores provide specialized shapes that are sometimes more useful than single hole devices. One example is wide band transformers where good coupling between
Design Considerations APPLICATION NOTES: Multi-hole cores provide specialized shapes that are sometimes more useful than single hole devices. One example is wide band transformers where good coupling between
A statistical survey of common-mode noise
 A statistical survey of common-mode noise By Jerry Gaboian Characterization Engineer, High Performance Linear Department Introduction In today s high-tech world, one does not have to look very far to find
A statistical survey of common-mode noise By Jerry Gaboian Characterization Engineer, High Performance Linear Department Introduction In today s high-tech world, one does not have to look very far to find
