Voltage-Mode Grid-Tie Inverter with Active Power Factor Correction
|
|
|
- Toby Burke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Voltage-Mode Grid-Tie Inverter with Active Power Factor Correction Kasemsan Siri Electronics and Power Systems Department, Engineering and Technology Group, The Aerospace Corporation, Tel: he Aerospace Corporation 2009 Patent-Pending
2 Motivation for Voltage-Mode Grid-Tie Inverter Conventional grid-tie inverter operates in a current-source mode: Require fast response of the innermost control loop that regulates the waveform of the inverter s output current, Not easy to compensate the current-mode control loop to be stable, Be susceptible to interactions with the back-end EMI filter and the grid s non-ideal voltage source characteristics. Conventional grid-tie inverter for solar array does not provide active power factor correction (APFC): Only allowed to operate during sunlight periods, Deliver the in-phase output current with respect to the grid voltage, Not fully utilized the capability of active power factor correction particularly during the periods of no sunlight. Voltage-Mode grid-tie inverter for solar array potentially offers APFC function without increasing the power component count. Page 2 Patent-Pending
3 Motivation for Active Power Factor Correction Conventional grid-tie inverter only works during sunlight (day time): Only designed for power transfer from the solar array to a utility grid, Controlled to deliver an in-phase current into the grid, Controlled to provide 0-A reactive current, No active power correction for a reactive load across the grid voltage. Grid-tie inverters should be fully utilized during both day time and night time: Optionally providing active power factor correction which maximizes the power factor for a given set of AC loads sharing the same utilitygrid voltage across the inverter s output. Page 3 Patent-Pending
4 Difficulties of Conventional Current-Mode Inverter (1) Distortion of current waveform, particularly when the utility grid voltage crosses 0-V. (2) As inverter current increases, the system performance decreases toward an instability of the innermost control loop. localized bursts of high frequency oscillation superimposed on the AC current waveform of the utility frequency. (3) Difficult to design the back-end EMI filter that minimizes or avoids undesirable interactions with the inverter response. Higher control crossover frequency is needed for the fidelity of the sinusoidal waveform of the inverter output current, resulting in a potential interaction with the resonant frequency of the EMI filter. Page 4 Patent-Pending
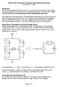
5 INVERTER SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM Convert DC power from solar array to an AC inverter output current, Provide a proper phase control of the inverter output voltage to remove the reactive component from the utility grid current, Track peak power delivered by the solar array at night, Maintain 0-a reactive component in the utility grid current during both daytime and night-time periods. Page 5 Patent-Pending
6 INVERTER SYSTEM CONTROL CONCEPT Six basic blocks work together for reliable DC-to-AC power conversion: 1. SINE-WAVE Regulation Controller with PWM Output 2. Active Power Factor Correction and Harmonic Cancellation Controller 3. 0-ADC Regulation Controller 4. Maximum Power Tacking (MPT) & Input Voltage Regulation Controller 5. Non-MPT Mode Controller 6. Protection Controller Page 6 Patent-Pending
7 Phase-Shift Control & Sinusoidal Profile Regulation Active power factor correction is achieved by the phaseshift control. Being equivalent to Independent MPT Sharing only one common MPT controller Actively performing an MPT control for one power source at a time while holding the most recently tracked source voltages of the remaining power sources After proper phase-shifting of the sinusoidal reference signal, it is multiplied with the DC command signal V CON Forming a sinusoidal profile for production of the inverter output voltage through a voltage-mode PWM scheme, Fulfilling other control objectives such as Maximum Power Tracking and/or Inverter Input Voltage Regulation Page 7 Patent-Pending
8 Harmonic Cancellation Method To achieve the AC grid current having 0-A harmonic or negligible harmonic content, a harmonic cancellation term, v INac (t)/v IN (t), is inserted and the dutyratio can be expressed as d PWM ( t ) = 0. 5 B + k sin( w t + f ) 1 - v V INac IN ( t ) ( t ) where v INac (t) is all of the AC components that are superimposed on the DC component V INdc of the inverter input voltage, V IN (t), and V IN (t) = V INdc + v INac (t). Block 210 shown in Fig. 1 also accepts the inverter input voltage V IN (t) from which the harmonic cancellation term is derived and superimposed onto the ideal sinusoidal reference waveform such that the composite reference signal SINE_AC leads to the duty-ratio signal that satisfies the equation above. Page 8 Patent-Pending
9 0-ADC Regulation Controller The 0-ADC regulation controller 260 ensures the 0-ADC average value of the inverter output current during steady state. providing an integral-lead compensation to the feedback inverter output current signal I O and delivering the counter balance signal V OFF to be added to the composite sinusoidal signal within the controller block 200. Page 9 Patent-Pending
10 VOLTAGE-MODE SINE-WAVE REGULATION CONTROLLER WITH PWM OUTPUT Each of the three source voltages: V1, V2, and V3 is actively controlled by the common MPT controller one voltage at a time, while holding their most recently tracked source voltages of the remaining sources. Page 10 Patent-Pending
11 PWM CONTROL FOR SINE-WAVE VOLTAGE V GS1 = VGS 4 = PWM SD V where GS 2 d PWM = VGS 3 = PWM SD d ( t) = k sin( wt) PWM Ton = + and k 0.5 T Page 11 Patent-Pending
12 SIMULATED INVERTER RESPONSE Amplitude of the capacitive load current (60-degree lead) was varied from 10 ma to 14 A while the inverter output power is kept constant at 200 W. When the load current, I LOAD, is zero or small (i.e. 10 ma), nearly all of the inverter output power is transferred to the utility grid and the amplitude of grid current I AC is around 3.6 A at time = 4s. As I LOAD increases, I AC is decreased as more inverter power is transferred to the load and less inverter power to the grid while the inverter transferred power P IN of 200 W is sustained. Five following plots of the detailed responses from top to bottom (in the lower plot area) are revealed: V IN : the inverter input voltage, I IN : the inverter input current, P IN : the inverter input power (its moving-average), I LOAD : the load current, and I AC : the grid current being paired with V AC The bottom left plot: I AC and V AC are in-phase, signifying that the excess inverter power above the load demand is absorbed by the utility grid. The bottom right plot: I AC and V AC are out-of-phase, signifying that the grid provides an extra power above the inverter 200-W output power to fulfill the heavy load demand. Page 12 Patent-Pending
13 Inverter Response (Inductive Load) without Harmonic Cancellation V LOAD, I LOAD, P IN, P LOAD, and I AC are simulated at around time t = 11s for an inductive load (60-degree lag). For 10.95s < t < 11.05s, the inductive load consumes the same power as that delivered by the inverter output P IN, consequently causing I AC at the utility frequency to be reduced to nearly 0 A. Due to distributed imperfections in the inverter power stage and control, the grid current exhibits the third harmonic frequency (180-Hz) with respect to the grid frequency (without the harmonic cancellation). Page 13 Patent-Pending
14 Inverter Response (Capacitive Load) without harmonic Cancellation V LOAD, I LOAD, P IN, P LOAD, and I AC are simulated at around time t = 11s for a capacitive load (60-degree lead). For 11.15s < t < 11.25s, the capacitive load consumes the same power as that delivered by the inverter output P IN, consequently causing I AC at the utility frequency to be reduced to nearly 0 A. Due to distributed imperfections in the inverter power stage and control, the grid current exhibits the third harmonic frequency (180-Hz) with respect to the grid frequency (without the harmonic cancellation). Page 14 Patent-Pending
15 Inverter Response Before and After Harmonic Cancellation Before After Before the harmonic cancellation is included, the peak-to-peak grid current is ma which mostly contains the third harmonic frequency (180 Hz) as shown on the bottom left plot. After the harmonic cancellation term is included as shown in chart #6, the third harmonic content is almost totally eliminated, leaving only the less than 100-mA peak-topeak current which occurs at the fundamental frequency (60 Hz) as shown on the bottom right plot of the figure. Page 15 Patent-Pending
16 Maximum Power Tracking Controller Two Major Operational Modes (MPT and Non-MPT): In MPT mode, Input Voltage Regulation (IVR) regulates the inverter input voltage at the solar array peak power voltage. In Non-MPT mode, the inverter input voltage is above the solar array peak power voltage to reduce the solar array power as needed. Page 16 Patent-Pending
17 Change in Peak Power Voltage (Between 20 V and 30 V) Inductive load of A (RMS) or 8A (amplitude), utility grid absorbs excess array power, i.e. I AC and V AC are in-phase. Inductive load of slightly below 200 W, leaving about 100 W of the excess inverter output power to be absorbed by the utility grid. The array peak power of 300 W is continuously tracked despite the change in the peak power voltage between 20V and 30V. Page 17 Patent-Pending
18 Change in Peak Power Voltage (Between 20 V and 30 V) Inductive load 14A, utility grid fulfills the load demand while the array peak power (300 W) is tracked and delivered to the load. Grid voltage and current are out of phase, revealing that the utility grid provides extra power to fulfill the load demand which exceeds the 300-W solar array peak power. Page 18 Patent-Pending
19 Simulation of the Grid-Tie Inverter Power System With MPT Control and Active Power Factor Correction PSPICE simulation verifies that the following novel features of the inverter system control: The proper phase-shift method that results in the unity power factor regardless of the load type being terminated across the inverter output (resistive, inductive, or capacitive). The harmonic cancellation method that effectively eliminates or significantly reduces harmonic content from the inverter output voltage and current, particularly at the third or higher harmonic frequencies. The 0-ADC regulation control which ensures that the inverter output current possesses no DC component, thus preventing magnetic saturation from occurring in the inverter isolation transformer. Page 19 Patent-Pending
20 CONCLUSION PSPICE simulation has validated the novel system controller for a voltagemode grid-tie inverter with active power factor correction (APFC). APFC between the grid voltage and current was achieved by a proper phase-shift control method regardless of the inverter load type The harmonic cancellation circuit has demonstrated the control ability to eliminate or significantly reduce harmonic content from the grid voltage and current, particularly at the third or higher harmonic frequencies. Under the non-linear characteristics of the input power source and the non-ideal impedance characteristics of the utility grid, The voltage-mode inverter is much easier to be implemented than the current-mode inverter, particularly for obtaining the unity power factor being observed by the utility grid. Finally, the 0-ADC regulation controller was also validated, preventing magnetic saturation from occurring at the inverter isolation transformer. Page 20 Patent-Pending
21 Maximum Power Tracking Controller Two Major Operational Modes (MPT and Non-MPT): In MPT mode, Input Voltage Regulation (IVR) regulates the inverter input voltage at the solar array peak power voltage. In Non-MPT mode, the inverter input voltage is above the solar array peak power voltage to reduce the solar array power as needed. Page 21 Patent-Pending ISIE 2015
22 TYPICAL I-V & P-V CHARACTERISTICS OF SOLAR ARRAY Page 22 Patent-Pending
23 THREE MAJOR STATES OF SOLAR ARRAY POWER Page 23 Patent-Pending
24 APPENDIX B: MPT Controller Page 24 Patent-Pending ISIE 2015
25 AC ARRAY VOTLAGE AND POWER RIPPLE WITH RESPECT TO UTILITY FREQUENCY Page 25 Patent-Pending
26 MPT CONCEPTUAL BLOCK DIAGRAM Page 26 Patent-Pending
27 MPT IMPLEMENTATION DIAGRAM BASED ON DISCRETE LOGIC Page 27 Patent-Pending
28 Change in Peak Power Voltage (Between 20 V and 30 V) Inductive load of A (RMS) or 8A (amplitude), utility grid absorbs excess array power, i.e. I AC and V AC are in-phase. Inductive load of slightly below 200 W, leaving about 100 W of the excess inverter output power to be absorbed by the utility grid. The array peak power of 300 W is continuously tracked despite the change in the peak power voltage between 20V and 30V. Page 28 Patent-Pending ISIE 2015
29 Change in Peak Power Voltage (Between 20 V and 30 V) Inductive load 14A, utility grid fulfills the load demand while the array peak power (300 W) is tracked and delivered to the load. Grid voltage and current are out of phase, revealing that the utility grid provides extra power to fulfill the load demand which exceeds the 300-W solar array peak power. Page 29 Patent-Pending ISIE 2015
30 Page 30 Patent-Pending
31 Simplified Concept of Inverter Model Page 31 Patent-Pending
32 The Simplest System of Closed-Loop Controlled Inverter Page 32 Patent-Pending
33 Simplified Phasor Diagram with Inductive Load Page 33 Patent-Pending
34 Simplified Phasor Diagram with Capacitive Load Page 34 Patent-Pending
35 Model of Strong-Power Inverter and Utility Grid Simplified equivalent circuit consisting of an inverter, load, and a utility grid with two phasor diagrams of AC voltages and currents when excess inverter power above the load demand is absorbed by the utility grid; the lower-left phasor diagram for an inductive load and the lowerright phasor diagram for a capacitive load. Page 35 Patent-Pending
36 Model of Weak-Power Inverter and Utility Grid Simplified equivalent circuit consisting of an inverter, load, and a utility grid with two phasor diagrams of AC voltages and currents when extra power is provided by the utility grid to fulfill the load demand above the inverter output power; the lower-left phasor diagram for an inductive load and the lower-right phasor diagram for a capacitive load. Page 36 Patent-Pending
37 PHASE-SHIFT CONTROL Page 37 Patent-Pending
38 Extraction of Harmonic Cancellation Term Page 38 Patent-Pending
39 Average Model of the Bridge Switching Network Q1 and Q4 are concurrently switched with their identical ON time, T ON, which is proportionally to the modulation duty ratio D = T ON /T, whereas Q2 and Q3 are always switched in a complementary fashion with Q1 and Q4. <V(VOP)> = D*V IN <V(VON)> = (1-D)*V IN <V(VOP) V(VON)> = (2*D 1)*V IN Page 39 Patent-Pending
40 Large-Signal Average Model of the Bridge Switching Ckt. Page 40 Patent-Pending
41 Average Model of BI-POLAR PWM Modulator d(t) = V CPWM / VR d(t) = T ON (t) / T Where V CPWM = V CON sin(wt) *( 1 - v inac (t) / V IN (t) ) Page 41 Patent-Pending
42 Average Model of SINGLE POLAR PWM Modulator d(t) = V CPWM / VR d(t) = T ON (t) / T Where V CPWM = V CON sin(wt) *( 1 - v inac (t) / V IN (t) ) Page 42 Patent-Pending
43 Homework: (1) Prove that V(VOP, VON) contains no product term sin(wt)*sin(2wt) with harmonic cancellation. (2) Prove that sin(wt)*sin(2wt) contains two frequencies (w 1 and w 2 ) and (3) What are the values of w 1 and w 2? where v inac (t) = V m sin(2wt) V IN (t) = V INDC + V m sin(2wt) V CPWM = V CON * V(SINE_AC) V(SINE_AC) = sin(wt) *( 1 - V m sin(2wt)/ V IN (t) ) Page 43 Patent-Pending
44 PWM SWITCHING SIGNAL BASED ON BI-POLAR MODULATION V GS1 = VGS 4 = PWM SD V where GS 2 d PWM = VGS 3 = PWM SD d ( t) = k sin( wt) PWM Ton = + and k 0.5 T Page 44 Patent-Pending ISIE 2015
45 Large Signal Average Model of Power Switching Bridge (Bi-Polar Modulation Scheme) Page 45 Patent-Pending
46 PWM SWITCHING SIGNAL BASED ON SINGLE POLAR MODULATION V GS 1 V GS 2 = ( PWM * SQW) SD = PWM + SQW SD V GS 3 V GS 4 = ( PWM * SQW) SD = PWM + SQW SD d PWM ( t) = k sin( w t) Page 46 Patent-Pending ISIE 2015 where d PWM Ton = + and k T 1.0
47 ALTERNATIVE PWM SWITCHING SIGNAL BASED ON SINGLE POLAR MODULATION Page 47 Patent-Pending ISIE 2015 PWM A = PWM + SQ2T PWM B = PWM + SQ2T PWM 1 = PWM A SQ _ 60 PWM 2 = PWM B SQ _ 60 V V where = PWM SD V = PWM 1 GS1 1, d PWM GS 2 SD = PWM 2 SD and VGS 4 = PWM 2 GS3, Ton = + and k T SD 1.0
48 Large Signal Average Model of Power Switching Bridge Single Polar Modulation Page 48 Patent-Pending
Oscillators. An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier.
 Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
CHAPTER 5 MODIFIED SINUSOIDAL PULSE WIDTH MODULATION (SPWM) TECHNIQUE BASED CONTROLLER
 74 CHAPTER 5 MODIFIED SINUSOIDAL PULSE WIDTH MODULATION (SPWM) TECHNIQUE BASED CONTROLLER 5.1 INTRODUCTION Pulse Width Modulation method is a fixed dc input voltage is given to the inverters and a controlled
74 CHAPTER 5 MODIFIED SINUSOIDAL PULSE WIDTH MODULATION (SPWM) TECHNIQUE BASED CONTROLLER 5.1 INTRODUCTION Pulse Width Modulation method is a fixed dc input voltage is given to the inverters and a controlled
Chapter 2 Shunt Active Power Filter
 Chapter 2 Shunt Active Power Filter In the recent years of development the requirement of harmonic and reactive power has developed, causing power quality problems. Many power electronic converters are
Chapter 2 Shunt Active Power Filter In the recent years of development the requirement of harmonic and reactive power has developed, causing power quality problems. Many power electronic converters are
CHAPTER 3. SINGLE-STAGE PFC TOPOLOGY GENERALIZATION AND VARIATIONS
 CHAPTER 3. SINGLE-STAGE PFC TOPOLOG GENERALIATION AND VARIATIONS 3.1. INTRODUCTION The original DCM S 2 PFC topology offers a simple integration of the DCM boost rectifier and the PWM DC/DC converter.
CHAPTER 3. SINGLE-STAGE PFC TOPOLOG GENERALIATION AND VARIATIONS 3.1. INTRODUCTION The original DCM S 2 PFC topology offers a simple integration of the DCM boost rectifier and the PWM DC/DC converter.
Chapter 6. Small signal analysis and control design of LLC converter
 Chapter 6 Small signal analysis and control design of LLC converter 6.1 Introduction In previous chapters, the characteristic, design and advantages of LLC resonant converter were discussed. As demonstrated
Chapter 6 Small signal analysis and control design of LLC converter 6.1 Introduction In previous chapters, the characteristic, design and advantages of LLC resonant converter were discussed. As demonstrated
CHAPTER 2 GENERAL STUDY OF INTEGRATED SINGLE-STAGE POWER FACTOR CORRECTION CONVERTERS
 CHAPTER 2 GENERAL STUDY OF INTEGRATED SINGLE-STAGE POWER FACTOR CORRECTION CONVERTERS 2.1 Introduction Conventional diode rectifiers have rich input harmonic current and cannot meet the IEC PFC regulation,
CHAPTER 2 GENERAL STUDY OF INTEGRATED SINGLE-STAGE POWER FACTOR CORRECTION CONVERTERS 2.1 Introduction Conventional diode rectifiers have rich input harmonic current and cannot meet the IEC PFC regulation,
CHAPTER 6 UNIT VECTOR GENERATION FOR DETECTING VOLTAGE ANGLE
 98 CHAPTER 6 UNIT VECTOR GENERATION FOR DETECTING VOLTAGE ANGLE 6.1 INTRODUCTION Process industries use wide range of variable speed motor drives, air conditioning plants, uninterrupted power supply systems
98 CHAPTER 6 UNIT VECTOR GENERATION FOR DETECTING VOLTAGE ANGLE 6.1 INTRODUCTION Process industries use wide range of variable speed motor drives, air conditioning plants, uninterrupted power supply systems
Module 5. DC to AC Converters. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 DC to AC Converters Version EE II, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 34 Analysis of 1-Phase, Square - Wave Voltage Source Inverter Version EE II, Kharagpur After completion of this lesson the reader will be
Module 5 DC to AC Converters Version EE II, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 34 Analysis of 1-Phase, Square - Wave Voltage Source Inverter Version EE II, Kharagpur After completion of this lesson the reader will be
Lecture 6 ECEN 4517/5517
 Lecture 6 ECEN 4517/5517 Experiment 4: inverter system Battery 12 VDC HVDC: 120-200 VDC DC-DC converter Isolated flyback DC-AC inverter H-bridge v ac AC load 120 Vrms 60 Hz d d Feedback controller V ref
Lecture 6 ECEN 4517/5517 Experiment 4: inverter system Battery 12 VDC HVDC: 120-200 VDC DC-DC converter Isolated flyback DC-AC inverter H-bridge v ac AC load 120 Vrms 60 Hz d d Feedback controller V ref
Minimizing Input Filter Requirements In Military Power Supply Designs
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, MIL-STD-461, input filter design, open loop gain, voltage feedback loop, AC-DC, transfer function, feedback control loop, maximize attenuation output, impedance,
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, MIL-STD-461, input filter design, open loop gain, voltage feedback loop, AC-DC, transfer function, feedback control loop, maximize attenuation output, impedance,
Lecture 19 - Single-phase square-wave inverter
 Lecture 19 - Single-phase square-wave inverter 1. Introduction Inverter circuits supply AC voltage or current to a load from a DC supply. A DC source, often obtained from an AC-DC rectifier, is converted
Lecture 19 - Single-phase square-wave inverter 1. Introduction Inverter circuits supply AC voltage or current to a load from a DC supply. A DC source, often obtained from an AC-DC rectifier, is converted
Lecture 4 ECEN 4517/5517
 Lecture 4 ECEN 4517/5517 Experiment 3 weeks 2 and 3: interleaved flyback and feedback loop Battery 12 VDC HVDC: 120-200 VDC DC-DC converter Isolated flyback DC-AC inverter H-bridge v ac AC load 120 Vrms
Lecture 4 ECEN 4517/5517 Experiment 3 weeks 2 and 3: interleaved flyback and feedback loop Battery 12 VDC HVDC: 120-200 VDC DC-DC converter Isolated flyback DC-AC inverter H-bridge v ac AC load 120 Vrms
Testing Power Sources for Stability
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, oscillator, power source, stability testing, feedback loop, error amplifier compensation, impedance, output voltage, transfer function, gain crossover, bode
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, oscillator, power source, stability testing, feedback loop, error amplifier compensation, impedance, output voltage, transfer function, gain crossover, bode
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF FEEDBACK CONTROLLERS FOR A DC BUCK-BOOST CONVERTER
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF FEEDBACK CONTROLLERS FOR A DC BUCK-BOOST CONVERTER Murdoch University: The Murdoch School of Engineering & Information Technology Author: Jason Chan Supervisors: Martina Calais &
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF FEEDBACK CONTROLLERS FOR A DC BUCK-BOOST CONVERTER Murdoch University: The Murdoch School of Engineering & Information Technology Author: Jason Chan Supervisors: Martina Calais &
ATYPICAL high-power gate-turn-off (GTO) currentsource
 1278 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 34, NO. 6, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 1998 A Novel Power Factor Control Scheme for High-Power GTO Current-Source Converter Yuan Xiao, Bin Wu, Member, IEEE,
1278 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 34, NO. 6, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 1998 A Novel Power Factor Control Scheme for High-Power GTO Current-Source Converter Yuan Xiao, Bin Wu, Member, IEEE,
Lecture Note. DC-AC PWM Inverters. Prepared by Dr. Oday A Ahmed Website: https://odayahmeduot.wordpress.com
 Lecture Note 10 DC-AC PWM Inverters Prepared by Dr. Oday A Ahmed Website: https://odayahmeduot.wordpress.com Email: 30205@uotechnology.edu.iq Scan QR DC-AC PWM Inverters Inverters are AC converters used
Lecture Note 10 DC-AC PWM Inverters Prepared by Dr. Oday A Ahmed Website: https://odayahmeduot.wordpress.com Email: 30205@uotechnology.edu.iq Scan QR DC-AC PWM Inverters Inverters are AC converters used
Grid-Tied Home Energy Production Using a Solar or Wind Power Inverter without DC-to-DC Converter
 Exercise 3 Grid-Tied Home Energy Production Using a Solar or Wind Power Inverter without DC-to-DC Converter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with grid-tied
Exercise 3 Grid-Tied Home Energy Production Using a Solar or Wind Power Inverter without DC-to-DC Converter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with grid-tied
Figure 1: Closed Loop System
 SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
Parallel-Connected Converters with Maximum Power Tracking
 Parallel-Connected Converters with Maximum Power Tracking Kasemsan Siri and Kenneth A. Conner Power and Analog Engineering Section, Electrical and Electronic Systems Department The Aerospace Corporation
Parallel-Connected Converters with Maximum Power Tracking Kasemsan Siri and Kenneth A. Conner Power and Analog Engineering Section, Electrical and Electronic Systems Department The Aerospace Corporation
Pulse width modulated (PWM) inverters are mostly used power electronic circuits in
 2.1 Introduction Pulse width modulated (PWM) inverters are mostly used power electronic circuits in practical applications. These inverters are able to produce ac voltages of variable magnitude and frequency.
2.1 Introduction Pulse width modulated (PWM) inverters are mostly used power electronic circuits in practical applications. These inverters are able to produce ac voltages of variable magnitude and frequency.
ELEC387 Power electronics
 ELEC387 Power electronics Jonathan Goldwasser 1 Power electronics systems pp.3 15 Main task: process and control flow of electric energy by supplying voltage and current in a form that is optimally suited
ELEC387 Power electronics Jonathan Goldwasser 1 Power electronics systems pp.3 15 Main task: process and control flow of electric energy by supplying voltage and current in a form that is optimally suited
A Fuzzy Controlled PWM Current Source Inverter for Wind Energy Conversion System
 7 International Journal of Smart Electrical Engineering, Vol.3, No.2, Spring 24 ISSN: 225-9246 pp.7:2 A Fuzzy Controlled PWM Current Source Inverter for Wind Energy Conversion System Mehrnaz Fardamiri,
7 International Journal of Smart Electrical Engineering, Vol.3, No.2, Spring 24 ISSN: 225-9246 pp.7:2 A Fuzzy Controlled PWM Current Source Inverter for Wind Energy Conversion System Mehrnaz Fardamiri,
A Novel Control Method for Input Output Harmonic Elimination of the PWM Boost Type Rectifier Under Unbalanced Operating Conditions
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 16, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 2001 603 A Novel Control Method for Input Output Harmonic Elimination of the PWM Boost Type Rectifier Under Unbalanced Operating Conditions
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 16, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 2001 603 A Novel Control Method for Input Output Harmonic Elimination of the PWM Boost Type Rectifier Under Unbalanced Operating Conditions
Chapter 13 Oscillators and Data Converters
 Chapter 13 Oscillators and Data Converters 13.1 General Considerations 13.2 Ring Oscillators 13.3 LC Oscillators 13.4 Phase Shift Oscillator 13.5 Wien-Bridge Oscillator 13.6 Crystal Oscillators 13.7 Chapter
Chapter 13 Oscillators and Data Converters 13.1 General Considerations 13.2 Ring Oscillators 13.3 LC Oscillators 13.4 Phase Shift Oscillator 13.5 Wien-Bridge Oscillator 13.6 Crystal Oscillators 13.7 Chapter
CHAPTER 9. Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 CHAPTER 9 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 9.1 The Sinusoidal Source A sinusoidal voltage source (independent or dependent) produces a voltage that varies sinusoidally with time. A sinusoidal current source
CHAPTER 9 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 9.1 The Sinusoidal Source A sinusoidal voltage source (independent or dependent) produces a voltage that varies sinusoidally with time. A sinusoidal current source
A New Small-Signal Model for Current-Mode Control Raymond B. Ridley
 A New Small-Signal Model for Current-Mode Control Raymond B. Ridley Copyright 1999 Ridley Engineering, Inc. A New Small-Signal Model for Current-Mode Control By Raymond B. Ridley Before this book was written
A New Small-Signal Model for Current-Mode Control Raymond B. Ridley Copyright 1999 Ridley Engineering, Inc. A New Small-Signal Model for Current-Mode Control By Raymond B. Ridley Before this book was written
CHAPTER 2 A SERIES PARALLEL RESONANT CONVERTER WITH OPEN LOOP CONTROL
 14 CHAPTER 2 A SERIES PARALLEL RESONANT CONVERTER WITH OPEN LOOP CONTROL 2.1 INTRODUCTION Power electronics devices have many advantages over the traditional power devices in many aspects such as converting
14 CHAPTER 2 A SERIES PARALLEL RESONANT CONVERTER WITH OPEN LOOP CONTROL 2.1 INTRODUCTION Power electronics devices have many advantages over the traditional power devices in many aspects such as converting
CHAPTER 3 COMBINED MULTIPULSE MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM
 CHAPTER 3 COMBINED MULTIPULSE MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM 3.1 INTRODUCTION Static synchronous compensator is a shunt connected reactive power compensation device that is capable of generating or
CHAPTER 3 COMBINED MULTIPULSE MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM 3.1 INTRODUCTION Static synchronous compensator is a shunt connected reactive power compensation device that is capable of generating or
Positive Feedback and Oscillators
 Physics 3330 Experiment #5 Fall 2011 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
Physics 3330 Experiment #5 Fall 2011 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
SHUNT ACTIVE POWER FILTER
 75 CHAPTER 4 SHUNT ACTIVE POWER FILTER Abstract A synchronous logic based Phase angle control method pulse width modulation (PWM) algorithm is proposed for three phase Shunt Active Power Filter (SAPF)
75 CHAPTER 4 SHUNT ACTIVE POWER FILTER Abstract A synchronous logic based Phase angle control method pulse width modulation (PWM) algorithm is proposed for three phase Shunt Active Power Filter (SAPF)
Module 5. DC to AC Converters. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 DC to AC Converters Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 37 Sine PWM and its Realization Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 After completion of this lesson, the reader shall be able to: 1. Explain
Module 5 DC to AC Converters Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 37 Sine PWM and its Realization Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 After completion of this lesson, the reader shall be able to: 1. Explain
DUAL BRIDGE LLC RESONANT CONVERTER WITH FREQUENCY ADAPTIVE PHASE-SHIFT MODULATION CONTROL FOR WIDE VOLTAGE GAIN RANGE
 DUAL BRIDGE LLC RESONANT CONVERTER WITH FREQUENCY ADAPTIVE PHASE-SHIFT MODULATION CONTROL FOR WIDE VOLTAGE GAIN RANGE S M SHOWYBUL ISLAM SHAKIB ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITI OF MALAYA KUALA LUMPUR,
DUAL BRIDGE LLC RESONANT CONVERTER WITH FREQUENCY ADAPTIVE PHASE-SHIFT MODULATION CONTROL FOR WIDE VOLTAGE GAIN RANGE S M SHOWYBUL ISLAM SHAKIB ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITI OF MALAYA KUALA LUMPUR,
CHAPTER 6 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE HYBRID SCHEME WITH VIENNA RECTIFIER USING PV ARRAY AND WIND DRIVEN INDUCTION GENERATORS
 73 CHAPTER 6 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE HYBRID SCHEME WITH VIENNA RECTIFIER USING PV ARRAY AND WIND DRIVEN INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Hybrid distributed generators are gaining prominence over the
73 CHAPTER 6 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE HYBRID SCHEME WITH VIENNA RECTIFIER USING PV ARRAY AND WIND DRIVEN INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Hybrid distributed generators are gaining prominence over the
=. This will typically be less
 Pulse Width Modulated Inverters In a pulse width modulated inverter the desired sine-wave output (the modulation) is modulated onto a high frequency square wave (the carrier). This can be done using a
Pulse Width Modulated Inverters In a pulse width modulated inverter the desired sine-wave output (the modulation) is modulated onto a high frequency square wave (the carrier). This can be done using a
EE 560 Electric Machines and Drives. Autumn 2014 Final Project. Contents
 EE 560 Electric Machines and Drives. Autumn 2014 Final Project Page 1 of 53 Prof. N. Nagel December 8, 2014 Brian Howard Contents Introduction 2 Induction Motor Simulation 3 Current Regulated Induction
EE 560 Electric Machines and Drives. Autumn 2014 Final Project Page 1 of 53 Prof. N. Nagel December 8, 2014 Brian Howard Contents Introduction 2 Induction Motor Simulation 3 Current Regulated Induction
A Novel FPGA based PWM Active Power Filter for Harmonics Elimination in Power System
 International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 5, Number 7 (2012), pp. 853-862 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com A Novel FPGA based PWM Active Power
International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 5, Number 7 (2012), pp. 853-862 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com A Novel FPGA based PWM Active Power
Power Factor Pre-regulator Using Constant Tolerance Band Control Scheme
 Power Factor Pre-regulator Using Constant Tolerance Band Control Scheme Akanksha Mishra, Anamika Upadhyay Akanksha Mishra is a lecturer ABIT, Cuttack, India (Email: misakanksha@gmail.com) Anamika Upadhyay
Power Factor Pre-regulator Using Constant Tolerance Band Control Scheme Akanksha Mishra, Anamika Upadhyay Akanksha Mishra is a lecturer ABIT, Cuttack, India (Email: misakanksha@gmail.com) Anamika Upadhyay
Field Programmable Gate Array-Based Pulse-Width Modulation for Single Phase Active Power Filter
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (9): 1742-1747, 2009 ISSN 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Field Programmable Gate Array-Based Pulse-Width Modulation for Single Phase Active Power Filter N.A.
American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (9): 1742-1747, 2009 ISSN 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Field Programmable Gate Array-Based Pulse-Width Modulation for Single Phase Active Power Filter N.A.
Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Lesson Four Lesson Five PREVIEW COPY
 Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
ANALYSIS OF EFFECTS OF VECTOR CONTROL ON TOTAL CURRENT HARMONIC DISTORTION OF ADJUSTABLE SPEED AC DRIVE
 ANALYSIS OF EFFECTS OF VECTOR CONTROL ON TOTAL CURRENT HARMONIC DISTORTION OF ADJUSTABLE SPEED AC DRIVE KARTIK TAMVADA Department of E.E.E, V.S.Lakshmi Engineering College for Women, Kakinada, Andhra Pradesh,
ANALYSIS OF EFFECTS OF VECTOR CONTROL ON TOTAL CURRENT HARMONIC DISTORTION OF ADJUSTABLE SPEED AC DRIVE KARTIK TAMVADA Department of E.E.E, V.S.Lakshmi Engineering College for Women, Kakinada, Andhra Pradesh,
Single-Phase Grid-Tied Inverter (PWM Rectifier/Inverter)
 Exercise 2 Single-Phase Grid-Tied Inverter (PWM Rectifier/Inverter) EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the singlephase grid-tied inverter. DISCUSSION OUTLINE
Exercise 2 Single-Phase Grid-Tied Inverter (PWM Rectifier/Inverter) EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the singlephase grid-tied inverter. DISCUSSION OUTLINE
LC Resonant Circuits Dr. Roger King June Introduction
 LC Resonant Circuits Dr. Roger King June 01 Introduction Second-order systems are important in a wide range of applications including transformerless impedance-matching networks, frequency-selective networks,
LC Resonant Circuits Dr. Roger King June 01 Introduction Second-order systems are important in a wide range of applications including transformerless impedance-matching networks, frequency-selective networks,
EE362L, Power Electronics, Powering the Grid with Renewable Energy Version Feb. 21, 2009
 Introduction You have successfully built a DC-AC erter. You will now use your erter to convert DC to AC and send power back into the AC. Your access point is a 10 wall outlet. Make sure that your erter
Introduction You have successfully built a DC-AC erter. You will now use your erter to convert DC to AC and send power back into the AC. Your access point is a 10 wall outlet. Make sure that your erter
Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019
 Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019 Objective: The objective of this experiment is to develop methods for characterizing key properties of operational amplifiers Note: We will be using
Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019 Objective: The objective of this experiment is to develop methods for characterizing key properties of operational amplifiers Note: We will be using
3. Discrete and Continuous-Time Analysis of Current-Mode Cell
 3. Discrete and Continuous-Time Analysis of Current-Mode Cell 3.1 ntroduction Fig. 3.1 shows schematics of the basic two-state PWM converters operating with current-mode control. The sensed current waveform
3. Discrete and Continuous-Time Analysis of Current-Mode Cell 3.1 ntroduction Fig. 3.1 shows schematics of the basic two-state PWM converters operating with current-mode control. The sensed current waveform
Renewable Energy Systems
 Renewable Energy Systems 6 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd Chapter Outline The Charge Controller and Inverter 6 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd 6-1 BATTERY CHARGERS 6-2 THE PWM CHARGE CONTROLLER 6-3 THE MPPT CHARGE CONTROLLER
Renewable Energy Systems 6 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd Chapter Outline The Charge Controller and Inverter 6 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd 6-1 BATTERY CHARGERS 6-2 THE PWM CHARGE CONTROLLER 6-3 THE MPPT CHARGE CONTROLLER
Lecture 18 Stability of Feedback Control Systems
 16.002 Lecture 18 Stability of Feedback Control Systems May 9, 2008 Today s Topics Stabilizing an unstable system Stability evaluation using frequency responses Take Away Feedback systems stability can
16.002 Lecture 18 Stability of Feedback Control Systems May 9, 2008 Today s Topics Stabilizing an unstable system Stability evaluation using frequency responses Take Away Feedback systems stability can
Lecture 41 SIMPLE AVERAGING OVER T SW to ACHIEVE LOW FREQUENCY MODELS
 Lecture 41 SIMPLE AVERAGING OVER T SW to ACHIEVE LOW FREQUENCY MODELS. Goals and Methodology to Get There 0. Goals 0. Methodology. BuckBoost and Other Converter Models 0. Overview of Methodology 0. Example
Lecture 41 SIMPLE AVERAGING OVER T SW to ACHIEVE LOW FREQUENCY MODELS. Goals and Methodology to Get There 0. Goals 0. Methodology. BuckBoost and Other Converter Models 0. Overview of Methodology 0. Example
Sample Question Paper
 Scheme G Sample Question Paper Course Name : Electrical Engineering Group Course Code : EE/EP Semester : Third Subject Title : Electrical Circuit and Network 17323 Marks : 100 Time: 3 hrs Instructions:
Scheme G Sample Question Paper Course Name : Electrical Engineering Group Course Code : EE/EP Semester : Third Subject Title : Electrical Circuit and Network 17323 Marks : 100 Time: 3 hrs Instructions:
ELG4139: DC to AC Converters
 ELG4139: DC to AC Converters Converts DC to AC power by switching the DC input voltage (or current) in a pre-determined sequence so as to generate AC voltage (or current) output. I DC I ac + + V DC V ac
ELG4139: DC to AC Converters Converts DC to AC power by switching the DC input voltage (or current) in a pre-determined sequence so as to generate AC voltage (or current) output. I DC I ac + + V DC V ac
Testing Power Factor Correction Circuits For Stability
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, switching power supply, PFC, boost converter, flyback converter,
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, switching power supply, PFC, boost converter, flyback converter,
Bidirectional Ac/Dc Converter with Reduced Switching Losses using Feed Forward Control
 Bidirectional Ac/Dc Converter with Reduced Switching Losses using Feed Forward Control Lakkireddy Sirisha Student (power electronics), Department of EEE, The Oxford College of Engineering, Abstract: The
Bidirectional Ac/Dc Converter with Reduced Switching Losses using Feed Forward Control Lakkireddy Sirisha Student (power electronics), Department of EEE, The Oxford College of Engineering, Abstract: The
Applied Electronics II
 Applied Electronics II Chapter 3: Operational Amplifier Part 1- Op Amp Basics School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Addis Ababa Institute of Technology Addis Ababa University Daniel D./Getachew
Applied Electronics II Chapter 3: Operational Amplifier Part 1- Op Amp Basics School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Addis Ababa Institute of Technology Addis Ababa University Daniel D./Getachew
P. Sivakumar* 1 and V. Rajasekaran 2
 IJESC: Vol. 4, No. 1, January-June 2012, pp. 1 5 P. Sivakumar* 1 and V. Rajasekaran 2 Abstract: This project describes the design a controller for PWM boost Rectifier. This regulates the output voltage
IJESC: Vol. 4, No. 1, January-June 2012, pp. 1 5 P. Sivakumar* 1 and V. Rajasekaran 2 Abstract: This project describes the design a controller for PWM boost Rectifier. This regulates the output voltage
Filter Considerations for the IBC
 APPLICATION NOTE AN:202 Filter Considerations for the IBC Mike DeGaetano Application Engineering Contents Page Introduction 1 IBC Attributes 1 Input Filtering Considerations 2 Damping and Converter Bandwidth
APPLICATION NOTE AN:202 Filter Considerations for the IBC Mike DeGaetano Application Engineering Contents Page Introduction 1 IBC Attributes 1 Input Filtering Considerations 2 Damping and Converter Bandwidth
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
PV System Components: Inverters and Charge Controllers. EE 495/695 Spring 2011
 PV System Components: Inverters and Charge Controllers EE 495/695 Spring 2011 Maximum Power Point Tracker (MPPT) Each DC load has its own I-V Curve. When connecting a DC load directly to a PV system, the
PV System Components: Inverters and Charge Controllers EE 495/695 Spring 2011 Maximum Power Point Tracker (MPPT) Each DC load has its own I-V Curve. When connecting a DC load directly to a PV system, the
Advances in Averaged Switch Modeling
 Advances in Averaged Switch Modeling Robert W. Erickson Power Electronics Group University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado USA 80309-0425 rwe@boulder.colorado.edu http://ece-www.colorado.edu/~pwrelect 1
Advances in Averaged Switch Modeling Robert W. Erickson Power Electronics Group University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado USA 80309-0425 rwe@boulder.colorado.edu http://ece-www.colorado.edu/~pwrelect 1
POWER FACTOR CORRECTION AND HARMONIC CURRENT REDUCTION IN DUAL FEEDBACK PWM CONTROLLED AC/DC DRIVES.
 POWER FACTOR CORRECTION AND HARMONIC CURRENT REDUCTION IN DUAL FEEDBACK PWM CONTROLLED AC/DC DRIVES. 1 RAJENDRA PANDAY, 2 C.VEERESH,ANIL KUMAR CHAUDHARY 1, 2 Mandsaur Institute of Techno;ogy,Mandsaur,
POWER FACTOR CORRECTION AND HARMONIC CURRENT REDUCTION IN DUAL FEEDBACK PWM CONTROLLED AC/DC DRIVES. 1 RAJENDRA PANDAY, 2 C.VEERESH,ANIL KUMAR CHAUDHARY 1, 2 Mandsaur Institute of Techno;ogy,Mandsaur,
Chapter 33. Alternating Current Circuits
 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits Alternating Current Circuits Electrical appliances in the house use alternating current (AC) circuits. If an AC source applies an alternating voltage to a series
Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits Alternating Current Circuits Electrical appliances in the house use alternating current (AC) circuits. If an AC source applies an alternating voltage to a series
Power supplies are one of the last holdouts of true. The Purpose of Loop Gain DESIGNER SERIES
 DESIGNER SERIES Power supplies are one of the last holdouts of true analog feedback in electronics. For various reasons, including cost, noise, protection, and speed, they have remained this way in the
DESIGNER SERIES Power supplies are one of the last holdouts of true analog feedback in electronics. For various reasons, including cost, noise, protection, and speed, they have remained this way in the
Module 4. AC to AC Voltage Converters. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 4 AC to AC Voltage Converters Version EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 9 Introduction to Cycloconverters Version EE IIT, Kharagpur Instructional Objectives Study of the following: The cyclo-converter
Module 4 AC to AC Voltage Converters Version EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 9 Introduction to Cycloconverters Version EE IIT, Kharagpur Instructional Objectives Study of the following: The cyclo-converter
INVESTIGATION AND DESIGN OF HIGH CURRENT SOURCES FOR B-H LOOP MEASUREMENTS
 INVESTIGATION AND DESIGN OF HIGH CURRENT SOURCES FOR B-H LOOP MEASUREMENTS Boyanka Marinova Nikolova, Georgi Todorov Nikolov Faculty of Electronics and Technologies, Technical University of Sofia, Studenstki
INVESTIGATION AND DESIGN OF HIGH CURRENT SOURCES FOR B-H LOOP MEASUREMENTS Boyanka Marinova Nikolova, Georgi Todorov Nikolov Faculty of Electronics and Technologies, Technical University of Sofia, Studenstki
A Novel Control Method to Minimize Distortion in AC Inverters. Dennis Gyma
 A Novel Control Method to Minimize Distortion in AC Inverters Dennis Gyma Hewlett-Packard Company 150 Green Pond Road Rockaway, NJ 07866 ABSTRACT In PWM AC inverters, the duty-cycle modulator transfer
A Novel Control Method to Minimize Distortion in AC Inverters Dennis Gyma Hewlett-Packard Company 150 Green Pond Road Rockaway, NJ 07866 ABSTRACT In PWM AC inverters, the duty-cycle modulator transfer
Solar-based Single-stage High-efficiency Gridconnected
 University of Central Florida Electronic Theses and Dissertations Masters Thesis (Open Access) Solar-based Single-stage High-efficiency Gridconnected Inverter 2005 Feng Tian University of Central Florida
University of Central Florida Electronic Theses and Dissertations Masters Thesis (Open Access) Solar-based Single-stage High-efficiency Gridconnected Inverter 2005 Feng Tian University of Central Florida
Micro-controller Based Three-phase Voltage Source Inverter for Alternative Energy Source. Abstract
 Micro-controller Based Three-phase Voltage Source Inverter for Alternative Energy Source M.M. A. Rahman, Kurt Hammons, Phillip Beemer, Marcia Isserstedt, and Matt Trommater School of Engineering Padnos
Micro-controller Based Three-phase Voltage Source Inverter for Alternative Energy Source M.M. A. Rahman, Kurt Hammons, Phillip Beemer, Marcia Isserstedt, and Matt Trommater School of Engineering Padnos
Investigations on Reactive Power and Dead Time Compensation for a Double Active Bridge with a Planar Transformer. Javier Gómez-Aleixandre Tiemblo
 Investigations on Reactive Power and Dead Time Compensation for a Double Active Bridge with a Planar Transformer by Javier Gómez-Aleixandre Tiemblo Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering,
Investigations on Reactive Power and Dead Time Compensation for a Double Active Bridge with a Planar Transformer by Javier Gómez-Aleixandre Tiemblo Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering,
Dr.Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth Class. 3-Phase Voltage Source Inverter With Square Wave Output
 3-Phase Voltage Source Inverter With Square Wave Output ١ fter completion of this lesson the reader will be able to: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Explain the operating principle of a three-phase square wave inverter.
3-Phase Voltage Source Inverter With Square Wave Output ١ fter completion of this lesson the reader will be able to: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Explain the operating principle of a three-phase square wave inverter.
High Voltage DC Transmission 2
 High Voltage DC Transmission 2 1.0 Introduction Interconnecting HVDC within an AC system requires conversion from AC to DC and inversion from DC to AC. We refer to the circuits which provide conversion
High Voltage DC Transmission 2 1.0 Introduction Interconnecting HVDC within an AC system requires conversion from AC to DC and inversion from DC to AC. We refer to the circuits which provide conversion
Specify Gain and Phase Margins on All Your Loops
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, power supply, gain and phase margins, feedback loop, open-loop gain, output capacitance, stability margins, oscillator, power electronics circuits, voltmeter,
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, power supply, gain and phase margins, feedback loop, open-loop gain, output capacitance, stability margins, oscillator, power electronics circuits, voltmeter,
A Thyristor Controlled Three Winding Transformer as a Static Var Compensator
 Abstract: A Thyristor Controlled Three Winding Transformer as a Static Var Compensator Vijay Bendre, Prof. Pat Bodger, Dr. Alan Wood. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, The University of
Abstract: A Thyristor Controlled Three Winding Transformer as a Static Var Compensator Vijay Bendre, Prof. Pat Bodger, Dr. Alan Wood. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, The University of
Investigation of negative sequence injection capability in H-bridge Multilevel STATCOM
 Investigation of negative sequence injection capability in H-bridge Multilevel STATCOM Ehsan Behrouzian 1, Massimo Bongiorno 1, Hector Zelaya De La Parra 1,2 1 CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY SE-412
Investigation of negative sequence injection capability in H-bridge Multilevel STATCOM Ehsan Behrouzian 1, Massimo Bongiorno 1, Hector Zelaya De La Parra 1,2 1 CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY SE-412
SINGLE STAGE LOW FREQUENCY ELECTRONIC BALLAST FOR HID LAMPS
 SINGLE STAGE LOW FREQUENCY ELECTRONIC BALLAST FOR HID LAMPS SUMAN TOLANUR 1 & S.N KESHAVA MURTHY 2 1,2 EEE Dept., SSIT Tumkur E-mail : sumantolanur@gmail.com Abstract - The paper presents a single-stage
SINGLE STAGE LOW FREQUENCY ELECTRONIC BALLAST FOR HID LAMPS SUMAN TOLANUR 1 & S.N KESHAVA MURTHY 2 1,2 EEE Dept., SSIT Tumkur E-mail : sumantolanur@gmail.com Abstract - The paper presents a single-stage
2020 P a g e. Figure.2: Line diagram of series active power filter.
 Power Quality Improvement By UPQC Using ANN Controller Saleha Tabassum 1, B.Mouli Chandra 2 (Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering KSRM College of Engineering, Kadapa.) (Asst. Professor Dept
Power Quality Improvement By UPQC Using ANN Controller Saleha Tabassum 1, B.Mouli Chandra 2 (Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering KSRM College of Engineering, Kadapa.) (Asst. Professor Dept
Grid Connected photovoltaic system based on Chain cell converter Using Simulink
 Grid Connected photovoltaic system based on Chain cell converter Using Simulink Problem statement To prove Chain cell converter performance superior when compared with the traditional Pulse width modulation
Grid Connected photovoltaic system based on Chain cell converter Using Simulink Problem statement To prove Chain cell converter performance superior when compared with the traditional Pulse width modulation
Exercise 9: inductor-resistor-capacitor (LRC) circuits
 Exercise 9: inductor-resistor-capacitor (LRC) circuits Purpose: to study the relationship of the phase and resonance on capacitor and inductor reactance in a circuit driven by an AC signal. Introduction
Exercise 9: inductor-resistor-capacitor (LRC) circuits Purpose: to study the relationship of the phase and resonance on capacitor and inductor reactance in a circuit driven by an AC signal. Introduction
Harmonics White Paper
 Harmonics White Paper New Breakthrough In PWM Drives Technology Reduces Input Line Harmonics Without the Use of Filtering Devices Harmonic Distortion Damages Equipment and Creates a Host of Other Problems
Harmonics White Paper New Breakthrough In PWM Drives Technology Reduces Input Line Harmonics Without the Use of Filtering Devices Harmonic Distortion Damages Equipment and Creates a Host of Other Problems
IMPORTANCE OF VSC IN HVDC
 IMPORTANCE OF VSC IN HVDC Snigdha Sharma (Electrical Department, SIT, Meerut) ABSTRACT The demand of electrical energy has been increasing day by day. To meet these high demands, reliable and stable transmission
IMPORTANCE OF VSC IN HVDC Snigdha Sharma (Electrical Department, SIT, Meerut) ABSTRACT The demand of electrical energy has been increasing day by day. To meet these high demands, reliable and stable transmission
Lab 4: Transmission Line
 1 Introduction Lab 4: Transmission Line In this experiment we will study the properties of a wave propagating in a periodic medium. Usually this takes the form of an array of masses and springs of the
1 Introduction Lab 4: Transmission Line In this experiment we will study the properties of a wave propagating in a periodic medium. Usually this takes the form of an array of masses and springs of the
Compensation of Distribution Feeder Loading With Power Factor Correction by Using D-STATCOM
 Compensation of Distribution Feeder Loading With Power Factor Correction by Using D-STATCOM N.Shakeela Begum M.Tech Student P.V.K.K Institute of Technology. Abstract This paper presents a modified instantaneous
Compensation of Distribution Feeder Loading With Power Factor Correction by Using D-STATCOM N.Shakeela Begum M.Tech Student P.V.K.K Institute of Technology. Abstract This paper presents a modified instantaneous
CHAPTER 4 MODIFIED H- BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER USING MPD-SPWM TECHNIQUE
 58 CHAPTER 4 MODIFIED H- BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER USING MPD-SPWM TECHNIQUE 4.1 INTRODUCTION Conventional voltage source inverter requires high switching frequency PWM technique to obtain a quality output
58 CHAPTER 4 MODIFIED H- BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER USING MPD-SPWM TECHNIQUE 4.1 INTRODUCTION Conventional voltage source inverter requires high switching frequency PWM technique to obtain a quality output
EMT212 Analog Electronic II. Chapter 4. Oscillator
 EMT Analog Electronic II Chapter 4 Oscillator Objectives Describe the basic concept of an oscillator Discuss the basic principles of operation of an oscillator Analyze the operation of RC, LC and crystal
EMT Analog Electronic II Chapter 4 Oscillator Objectives Describe the basic concept of an oscillator Discuss the basic principles of operation of an oscillator Analyze the operation of RC, LC and crystal
CHAPTER 4 A NEW CARRIER BASED PULSE WIDTH MODULATION STRATEGY FOR VSI
 52 CHAPTER 4 A NEW CARRIER BASED PULSE WIDTH MODULATION STRATEGY FOR VSI 4.1 INTRODUCTION The present day applications demand ac power with adjustable amplitude and frequency. A well defined mode of operation
52 CHAPTER 4 A NEW CARRIER BASED PULSE WIDTH MODULATION STRATEGY FOR VSI 4.1 INTRODUCTION The present day applications demand ac power with adjustable amplitude and frequency. A well defined mode of operation
Electronics II. Previous Lecture
 Fall 2014 (Rev. 3.0) Lecture 22 Oscillators I Muhammad Tilal Department of Electrical Engineering CIIT Attock Campus The theme of this presentation is an inspiration from the one used in S2 Department
Fall 2014 (Rev. 3.0) Lecture 22 Oscillators I Muhammad Tilal Department of Electrical Engineering CIIT Attock Campus The theme of this presentation is an inspiration from the one used in S2 Department
CHAPTER 4 PV-UPQC BASED HARMONICS REDUCTION IN POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
 66 CHAPTER 4 PV-UPQC BASED HARMONICS REDUCTION IN POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The use of electronic controllers in the electric power supply system has become very common. These electronic
66 CHAPTER 4 PV-UPQC BASED HARMONICS REDUCTION IN POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The use of electronic controllers in the electric power supply system has become very common. These electronic
CHAPTER 7 MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING USING HILL CLIMBING ALGORITHM
 100 CHAPTER 7 MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING USING HILL CLIMBING ALGORITHM 7.1 INTRODUCTION An efficient Photovoltaic system is implemented in any place with minimum modifications. The PV energy conversion
100 CHAPTER 7 MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING USING HILL CLIMBING ALGORITHM 7.1 INTRODUCTION An efficient Photovoltaic system is implemented in any place with minimum modifications. The PV energy conversion
Current Rebuilding Concept Applied to Boost CCM for PF Correction
 Current Rebuilding Concept Applied to Boost CCM for PF Correction Sindhu.K.S 1, B. Devi Vighneshwari 2 1, 2 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, The Oxford College of Engineering, Bangalore-560068,
Current Rebuilding Concept Applied to Boost CCM for PF Correction Sindhu.K.S 1, B. Devi Vighneshwari 2 1, 2 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, The Oxford College of Engineering, Bangalore-560068,
Study of Centralized Anti-Islanding Method on Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants
 4th International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Information Technology Applications (ICMMITA 2016) Study of Centralized Anti-Islanding Method on Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants Chen-Xin
4th International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Information Technology Applications (ICMMITA 2016) Study of Centralized Anti-Islanding Method on Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants Chen-Xin
CHAPTER 5 POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BY USING POWER ACTIVE FILTERS
 86 CHAPTER 5 POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BY USING POWER ACTIVE FILTERS 5.1 POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT This chapter deals with the harmonic elimination in Power System by adopting various methods. Due to the
86 CHAPTER 5 POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BY USING POWER ACTIVE FILTERS 5.1 POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT This chapter deals with the harmonic elimination in Power System by adopting various methods. Due to the
Matrix Drives Boost Power Quality and Energy Savings
 Matrix Drives Boost Power Quality and Energy Savings How It s Done: An Overview of Matrix Drive Technology yaskawa.com Introduction Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) are electronic devices used to regulate
Matrix Drives Boost Power Quality and Energy Savings How It s Done: An Overview of Matrix Drive Technology yaskawa.com Introduction Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) are electronic devices used to regulate
B.Tech II SEM Question Bank. Electronics & Electrical Engg UNIT-1
 UNIT-1 1. State & Explain Superposition theorem & Thevinin theorem with example? 2. Calculate the current in the 400Ωm resistor of below figure by Superposition theorem. 3. State & Explain node voltage
UNIT-1 1. State & Explain Superposition theorem & Thevinin theorem with example? 2. Calculate the current in the 400Ωm resistor of below figure by Superposition theorem. 3. State & Explain node voltage
Background (What Do Line and Load Transients Tell Us about a Power Supply?)
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Power-Supply Circuits > APP 3443 Keywords: line transient, load transient, time domain, frequency domain APPLICATION NOTE 3443 Line and
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Power-Supply Circuits > APP 3443 Keywords: line transient, load transient, time domain, frequency domain APPLICATION NOTE 3443 Line and
Type of loads Active load torque: - Passive load torque :-
 Type of loads Active load torque: - Active torques continues to act in the same direction irrespective of the direction of the drive. e.g. gravitational force or deformation in elastic bodies. Passive
Type of loads Active load torque: - Active torques continues to act in the same direction irrespective of the direction of the drive. e.g. gravitational force or deformation in elastic bodies. Passive
The measurement of loop gain in feedback seismometers Brett M. Nordgren April 9, 1999 Rev.
 Introduction The measurement of loop gain in feedback seismometers Brett M. Nordgren http://bnordgren.org/contactb.html April 9, 1999 Rev. October 5, 2004 In reading the messages coming through PSN-L,
Introduction The measurement of loop gain in feedback seismometers Brett M. Nordgren http://bnordgren.org/contactb.html April 9, 1999 Rev. October 5, 2004 In reading the messages coming through PSN-L,
Tutorial 5 - Isolated DC-DC Converters and Inverters
 University of New South Wales School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications Tutorial 5 - Isolated DC-DC Converters and Inverters Flyback Converter N2 3 1. A dc-dc flyback converter has a turns
University of New South Wales School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications Tutorial 5 - Isolated DC-DC Converters and Inverters Flyback Converter N2 3 1. A dc-dc flyback converter has a turns
Source Transformation
 HW Chapter 0: 4, 20, 26, 44, 52, 64, 74, 92. Source Transformation Source transformation in frequency domain involves transforming a voltage source in series with an impedance to a current source in parallel
HW Chapter 0: 4, 20, 26, 44, 52, 64, 74, 92. Source Transformation Source transformation in frequency domain involves transforming a voltage source in series with an impedance to a current source in parallel
HVDC CAPACITOR COMMUTATED CONVERTERS IN WEAK NETWORKS GUNNAR PERSSON, VICTOR F LESCALE, ALF PERSSON ABB AB, HVDC SWEDEN
 HVDC CAPACITOR COMMUTATED CONVERTERS IN WEAK NETWORKS GUNNAR PERSSON, VICTOR F LESCALE, ALF PERSSON ABB AB, HVDC SWEDEN Summary Capacitor Commutated Converters (CCC) were introduced to the HVDC market
HVDC CAPACITOR COMMUTATED CONVERTERS IN WEAK NETWORKS GUNNAR PERSSON, VICTOR F LESCALE, ALF PERSSON ABB AB, HVDC SWEDEN Summary Capacitor Commutated Converters (CCC) were introduced to the HVDC market
Power Quality improvement of a three phase four wire system using UPQC
 International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: 2395-56 Volume: 2 Issue: 4 July-215 www.irjet.net p-issn: 2395-72 Power Quality improvement of a three phase four wire system
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: 2395-56 Volume: 2 Issue: 4 July-215 www.irjet.net p-issn: 2395-72 Power Quality improvement of a three phase four wire system
Highly-Reliable Fly-back-based PV Micro-inverter Applying Power Decoupling Capability without Additional Components
 Highly-Reliable Fly-back-based P Micro-inverter Applying Power Decoupling Capability without Additional Components Hiroki Watanabe, Nagaoka University of technology, Japan, hwatanabe@stn.nagaopkaut.ac.jp
Highly-Reliable Fly-back-based P Micro-inverter Applying Power Decoupling Capability without Additional Components Hiroki Watanabe, Nagaoka University of technology, Japan, hwatanabe@stn.nagaopkaut.ac.jp
APPLICATION NOTE 6609 HOW TO OPTIMIZE USE OF CONTROL ALGORITHMS IN SWITCHING REGULATORS
 Keywords: switching regulators, control algorithms, loop compensation, constant on-time, voltage mode, current mode, control methods, isolated converters, buck converter, boost converter, buck-boost converter
Keywords: switching regulators, control algorithms, loop compensation, constant on-time, voltage mode, current mode, control methods, isolated converters, buck converter, boost converter, buck-boost converter
