Equipment and materials from stockroom:! DC Permanent-magnet Motor (If you can, get the same motor you used last time.)! Dual Power Amp!
|
|
|
- Dale Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Utah Electrical & Computer Engineering Department ECE 3510 Lab 5b Position Control Using a Proportional - Integral - Differential (PID) Controller Note: Bring the lab-2 handout to use as a dspace tutorial. M. Boson, A. Stolp, 2/19/08 rev,2/24/09, 2/23/17 B. Mukunda Objectives! Analyze a type of PID control system.! Modify the dspace programming to implement he PID control law.! Observe the step response with different zero locations (as set by the feedforward gain).! Compare the tuned PID response to the simple proportional response. Equipment and materials from stockroom:! DC Permanent-magnet Motor (If you can, get the same motor you used last time.)! Dual Power Amp! DSPACE kit Experiment 3, PID Position Control In this experiment you will construct a position controller, so you ll need to modify the model of the DC motor to be angular position over voltage rather than angular velocity over voltage. Write your motor transfer-function as: θ(s) k P(s) = = 1 V(s) s(s + a )(s + a ) 1 2 In lab 3 you used a proportional control law to control the motor position. v = k ( r θ) p In this experiment you will use a variation of the proportional-integral-derivative control law. d v = k ( r θ) + k r dt k r P I ( θ) + ( θ) D dt The integral term will minimize the steady state error as you saw with velocity control in experiment 2. The derivative term can be viewed as a proportional feedback acting on the velocity error. Responding to this additional error can increase the speed of the response-- a good thing. Ah, would that life were so simple... Think what would happen if you input a step response? What is the derivative of a step? Mathematically no big deal, the control system delivers an impulse to the motor which certainly speeds up the response. The problem arises with the limits of a system implemented with real parts. No real amplifier can deliver an impulse, so instead, it rails for a very short time and has a minimal impact on the p1 ECE 3510 PID Lab
2 response. (Actually, this might be a blessing in disguise, given that an impulse would mean an infinite voltage probably not too safe.) In practice, the control law is often modified in two ways. First, to avoid the problem with step inputs. the derivative action is applied only to the output (θ), and not to the reference input (r). This also eliminates a zero in the overall (closed-loop) transfer function. (No, I don t expect you to just see that, it takes a bit of math to show that that is the case.) Second, the reference input to the proportional gain is modified by a feedforward gain (k F ). This is not done to adjust the DC gain (as in experiment 1), but rather to gain control over the placement of the remaining zero of the closed-loop transfer function. Again, this is not obvious, but you will see it come out in the math. The modified control law is given by: d v = k ( k r θ) + k r dt k P F I ( θ) θ D dt Verify that the resulting closed-loop transfer function for the system is: H CL k I k1k Pk F( s + ) θ( s) k Pk F ( s) = = r( s) s + ( a + a ) s + ( a a + k k ) s + k k s + k k D 1 P 1 I Now again, set the poles somewhat like those of critical damping, that is, make all the poles the same, say at -p. That would make: s + ( a + a ) s + ( a a + k k ) s + k k s+ k k = ( s + p) D 1 P 1 I = s + 4ps + 6p s + 4p s+ p Find p, k D, k P, and k I. They should be about 180, 0.2, and respectively. Notice that the closed-loop transfer function has a zero at -k I /(k F k P ). With a neutral feedforward gain (k F = 1) the zero may have a small magnitude compared to the closed-loop poles, yielding overshoot in the step response even if the closed-loop poles are welldamped. (See page 37 in the text.) Find the position of the zero if k F = 1 then show that if k F <1, the zero will be further in the left-half plane and the step response will be better. Simulink Model Modifications Now you will need to modify the Simulink model and then the dspace layout to implement the PID controller. Open the Simulink model that you had previously downloaded for lab 5a. The following are the changes you will have to make: 4 p2 ECE 3510 PID Lab
3 1. Introduce kd (k D ) in the PI Controller block: >> Double click on the PI Controller block. You will see the function that was used for lab 5a. Consult the figure above and make the indicated changes to the input variable declaration and the function itself. Here dy will be the derivative of your reference signal y, y being the position and consequently dy being the speed. Once done, save and exit the function. You should be able to see an additional post for an input signal on the PI Controller block. 2. Create the section on model shown here. Note that the Switch block shown (found in the Simulink Library Browser, in the Signal Routing section has a >= threshold of 0.5. Here s how to set that: Once the block is dragged and dropped from the signal routing section, >> double click on the block >> in the Criteria for passing first input:, choose u2 >= Threshold >> in the Threshold section, enter 0.5 and hit OK. The kd, PID Controller and Contant3 blocks pictured below are just constant blocks you can find in the Commonly used blocks section of the Simulink library browser. You will need to double-click these blocks and enter the desired value (0 here) in the Constant value section to change their values. Name them (it is important to name kd and PID Controller) by clicking on the text under the blocks and changing it. 3. Once the section above is built, the output (red dotted connection) will be fed to the kd input on the PI Controller block. With this done, you will need to make a few minor modifications as shown. The Sum block can be found in the Simulink library browser under the Commonly used blocks, the Math Operations section or you may just type Sum into the search bar of the Simulink library browser. 4. For the final few edits, recall that lab 5a was designed with the intention of controlling velocity and not position. So the reference input signal (R) and the actual signal (y) were both velocity inputs. You will need to change this into position inputs. The dy input is then the velocity input. Shown below is a section of the PI Controller block with the changes explained. Note that the reference input (r) is a constant block named Pos_ref passed into a Gain block (found among the commonly used blocks) with its value changed to pi/180 (double click the dragged and dropped gain block and change the gain value to pi/180. The input you will be specifying reflects the Pos_ref p3 ECE 3510 PID Lab
4 block. Since you will be entering the reference position in degrees, the pi/180 gain block converts it into radians before it enters the PI Controller block. You probably noted that the y and dy inputs are fed by from blocks. Every Goto block can have one or more complementary From blocks. These can be found in the Signal Routing section and make the models much cleaner by eliminating winding connections. Note that there are already two Goto blocks with the tags th_rad and wm on the top right-hand section of the model. Now drag and drop two From blocks from the Simulink library. Double click the first one, under the Parameters, in the Goto dropdown list, where you can see all the tags assigned to Goto blocks. Select th_rad and click on update tags. Now this from block collects the signal from the Goto block with the same tag, in this case the position information in radians. Click on OK and connect the output of this block into y port of the PI Controller. Similarly, assign the tag wm to the second From block and connect the output to the dy port of the PI Controller block. The final form of the edited PI Controller block is provided for your reference in the appendix. Ensure that Ts, nd are defined in the model properties. Note that a Ts of 2e-3 s gives you the same resolution in data as a Ts of 1e-4 with a downsampling of 20 (in dspace). You can choose to do either. Make sure all the Model Configuration Parameters are defined appropriately, save and then build the model. Now in dspace: >> Open dspace > Click on Open Project+Experiment. This will allow you to open and existing project. Go on ahead and open the project that was created for lab 5a. You will be making a few adjustments to this layout. But before that, since new changes were built into the Simulink model, you will need to reload the variables into dspace. In the Project tab on the left side of the window, right click on the.sdf file and click on Reload Variable Description. All your new variables and changes should carry over to this experiment. You will now need two additional instruments, one for a control type selection (PID) and one to enter the value for kd. 1. Click on the Instrument Selector tab on the right side of the layout window. Choose a check button, click p4 ECE 3510 PID Lab
5 and drag it on the Control Type panel such that you now have three check boxes in the panel. In the Model Root, click on PID Controller, drag and drop the value into the new check box. 2. In the Instrument Selector again, select a Numeric Input instrument and draw it onto a comfortable spot on the layout. In the Model Root, click on kd, drag and drop the value into the new numeric input instrument. 3. Draw an On/Off button instrument for the encoder reset variable. You will notice that by default, there are two buttons. Right click on the instrument, and under the On/Off button settings, click on the browse option. Select button 2 on the left and click on the red X mark to remove it. Then, click on OK. The On/Off button window can be seen above. Map the RESET ENCODER value to this button. 4. In the Model Root, click on Pos_ref and map the value to the numeric instrument that contained Vel_ref in lab 5a. That instrument should now be blank since the model no longer has a constant named Vel_ref, but if there were a variable already mapped, to replace it with a new one, simply drag the new variable and drop it on the instrument. The previously mapped variable will be removed automatically (but the settings on that instrument will be retained, so make sure you reduce the increment size from1000 back to 1). The display instrument that sits beside this numeric input instrument will now be mapped to the Out1 signal from theta_deg, since this is what we will need to keep an eye on. 5. Also drag and drop Pos_ref and theta_deg on the small colored squares in the plotter, one in each. Your layout should now look something like the figure. Make sure you set all the data capture settings as instructed to in the previous labs. Set the data capture length to the same as that used in lab 3. Check your plots if you need to be sure. p5 ECE 3510 PID Lab
6 Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) Control Make sure to set up your recorder as you see fit. Once online, turn ON the simulation, hit Start, check the PID Controller in the Control Type panel and set the Feed-forward gain to 1 and all the other gains to your calculated values. The reference input is now the Pos_ref (degrees) and is angular position. Set this to 90 degrees. As soon as you enter this ref value, the motor should spin to 90 degrees and stop, giving you a step response with considerable overshoot due to the zero. The settling time should be about 100ms. You may run it again by simply unchecking the PID controller, the "start button", checking on the RESET ENCODER button to make sure the encoder position is at 0. Now check the start and PID controller buttons and re-enter the Pos_ref value. To shut the experiment down, uncheck the PID controller, zero out your Pos_ref, Uncheck Start, turn off the simulation and go offline to shut the experiment down. Adjust the parameter k F to get a better response (make k F smaller). Try several values of k F to get less than 5% overshoot and the fastest time to within 5% of the final position value. (Having trouble or don t have numbers yet? Use conservative values of 0.2, 30 and 1000 for k D, k P, and k I.) Use Matlab to plot the results for a few values of k F on a single graph (don t print it yet). If you still have the data from lab 3 (critical damp.) add that to the same plot. If not, make another run with k F =1, k P =3.66, and both k I =0 and k D =0. This should recreate that data and you can add it to the plot. Print the plot. Indicate what value of k F gives the best response and compare the PID response to the simple proportional response. Reset all your gains to your best values and make one last run, only this time don t hit Stop. Grab the coupler of the motor in such a way that if it unexpectedly begins to spin, it won t hurt you. If this worries you, temporarily remove the motor coupler. The naked shaft is pretty harmless. Try to turn the motor shaft. Can you feel (or see) the integral control fight the change and eliminate the steady-state error? Don t use too much force or do this too long. It seems that this can force the system into some weird state where it just keeps running. Conclusion Check-off and conclude as always. p6 ECE 3510 PID Lab
ECE 5671/6671 Lab 3. Impedance Measurement and Parameter Estimation of a DC Motor
 ECE 5671/6671 Lab 3 Impedance Measurement and Parameter Estimation of a DC Motor 1. Introduction The objective of this lab is to become more familiar with the hardware and software used in the Electric
ECE 5671/6671 Lab 3 Impedance Measurement and Parameter Estimation of a DC Motor 1. Introduction The objective of this lab is to become more familiar with the hardware and software used in the Electric
GE420 Laboratory Assignment 8 Positioning Control of a Motor Using PD, PID, and Hybrid Control
 GE420 Laboratory Assignment 8 Positioning Control of a Motor Using PD, PID, and Hybrid Control Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Design a PD discrete control algorithm to allow the closed-loop combination
GE420 Laboratory Assignment 8 Positioning Control of a Motor Using PD, PID, and Hybrid Control Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Design a PD discrete control algorithm to allow the closed-loop combination
ECE 5670/6670 Project. Brushless DC Motor Control with 6-Step Commutation. Objectives
 ECE 5670/6670 Project Brushless DC Motor Control with 6-Step Commutation Objectives The objective of the project is to build a circuit for 6-step commutation of a brushless DC motor and to implement control
ECE 5670/6670 Project Brushless DC Motor Control with 6-Step Commutation Objectives The objective of the project is to build a circuit for 6-step commutation of a brushless DC motor and to implement control
Ver. 4/5/2002, 1:11 PM 1
 Mechatronics II Laboratory Exercise 6 PID Design The purpose of this exercise is to study the effects of a PID controller on a motor-load system. Although not a second-order system, a PID controlled motor-load
Mechatronics II Laboratory Exercise 6 PID Design The purpose of this exercise is to study the effects of a PID controller on a motor-load system. Although not a second-order system, a PID controlled motor-load
E x p e r i m e n t 3 Characterization of DC Motor: Part 1
 E x p e r i m e n t 3 Characterization of DC Motor: Part 1 3.1 Introduction The output voltage control of a two-pole DC-Switch-mode-converter was implemented in realtime, in the last experiment. The purpose
E x p e r i m e n t 3 Characterization of DC Motor: Part 1 3.1 Introduction The output voltage control of a two-pole DC-Switch-mode-converter was implemented in realtime, in the last experiment. The purpose
Lab 2: Introduction to Real Time Workshop
 Lab 2: Introduction to Real Time Workshop 1 Introduction In this lab, you will be introduced to the experimental equipment. What you learn in this lab will be essential in each subsequent lab. Document
Lab 2: Introduction to Real Time Workshop 1 Introduction In this lab, you will be introduced to the experimental equipment. What you learn in this lab will be essential in each subsequent lab. Document
Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02. Rotary Experiment #02: Position Control. SRV02 Position Control using QuaRC. Student Manual
 Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02 Rotary Experiment #02: Position Control SRV02 Position Control using QuaRC Student Manual Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. PREREQUISITES...1 3. OVERVIEW OF FILES...2
Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02 Rotary Experiment #02: Position Control SRV02 Position Control using QuaRC Student Manual Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. PREREQUISITES...1 3. OVERVIEW OF FILES...2
 EC6405 - CONTROL SYSTEM ENGINEERING Questions and Answers Unit - II Time Response Analysis Two marks 1. What is transient response? The transient response is the response of the system when the system
EC6405 - CONTROL SYSTEM ENGINEERING Questions and Answers Unit - II Time Response Analysis Two marks 1. What is transient response? The transient response is the response of the system when the system
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points: Angular position control block diagram and fundamentals. Power amplifier 0.
 Exercise 6 Motor Shaft Angular Position Control EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to associate the pulses generated by a position sensing incremental encoder with
Exercise 6 Motor Shaft Angular Position Control EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to associate the pulses generated by a position sensing incremental encoder with
EE 4314 Lab 3 Handout Speed Control of the DC Motor System Using a PID Controller Fall Lab Information
 EE 4314 Lab 3 Handout Speed Control of the DC Motor System Using a PID Controller Fall 2012 IMPORTANT: This handout is common for all workbenches. 1. Lab Information a) Date, Time, Location, and Report
EE 4314 Lab 3 Handout Speed Control of the DC Motor System Using a PID Controller Fall 2012 IMPORTANT: This handout is common for all workbenches. 1. Lab Information a) Date, Time, Location, and Report
Root Locus Design. by Martin Hagan revised by Trevor Eckert 1 OBJECTIVE
 TAKE HOME LABS OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY Root Locus Design by Martin Hagan revised by Trevor Eckert 1 OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to design a feedback control system for a motor positioning
TAKE HOME LABS OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY Root Locus Design by Martin Hagan revised by Trevor Eckert 1 OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to design a feedback control system for a motor positioning
MAE106 Laboratory Exercises Lab # 5 - PD Control of DC motor position
 MAE106 Laboratory Exercises Lab # 5 - PD Control of DC motor position University of California, Irvine Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Goals Understand how to implement and tune a PD
MAE106 Laboratory Exercises Lab # 5 - PD Control of DC motor position University of California, Irvine Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Goals Understand how to implement and tune a PD
PID Control with Derivative Filtering and Integral Anti-Windup for a DC Servo
 PID Control with Derivative Filtering and Integral Anti-Windup for a DC Servo Nicanor Quijano and Kevin M. Passino The Ohio State University Department of Electrical Engineering 2015 Neil Avenue, Columbus
PID Control with Derivative Filtering and Integral Anti-Windup for a DC Servo Nicanor Quijano and Kevin M. Passino The Ohio State University Department of Electrical Engineering 2015 Neil Avenue, Columbus
E x p e r i m e n t 2 S i m u l a t i o n a n d R e a l - t i m e I m p l e m e n t a t i o n o f a S w i t c h - m o d e D C C o n v e r t e r
 E x p e r i m e n t 2 S i m u l a t i o n a n d R e a l - t i m e I m p l e m e n t a t i o n o f a S w i t c h - m o d e D C C o n v e r t e r IT IS PREFERED that students ANSWER THE QUESTION/S BEFORE
E x p e r i m e n t 2 S i m u l a t i o n a n d R e a l - t i m e I m p l e m e n t a t i o n o f a S w i t c h - m o d e D C C o n v e r t e r IT IS PREFERED that students ANSWER THE QUESTION/S BEFORE
5 Lab 5: Position Control Systems - Week 2
 5 Lab 5: Position Control Systems - Week 2 5.7 Introduction In this lab, you will convert the DC motor to an electromechanical positioning actuator by properly designing and implementing a proportional
5 Lab 5: Position Control Systems - Week 2 5.7 Introduction In this lab, you will convert the DC motor to an electromechanical positioning actuator by properly designing and implementing a proportional
Lab 1: Simulating Control Systems with Simulink and MATLAB
 Lab 1: Simulating Control Systems with Simulink and MATLAB EE128: Feedback Control Systems Fall, 2006 1 Simulink Basics Simulink is a graphical tool that allows us to simulate feedback control systems.
Lab 1: Simulating Control Systems with Simulink and MATLAB EE128: Feedback Control Systems Fall, 2006 1 Simulink Basics Simulink is a graphical tool that allows us to simulate feedback control systems.
ECE 5670/ Lab 5. Closed-Loop Control of a Stepper Motor. Objectives
 1. Introduction ECE 5670/6670 - Lab 5 Closed-Loop Control of a Stepper Motor Objectives The objective of this lab is to develop and test a closed-loop control algorithm for a stepper motor. First, field
1. Introduction ECE 5670/6670 - Lab 5 Closed-Loop Control of a Stepper Motor Objectives The objective of this lab is to develop and test a closed-loop control algorithm for a stepper motor. First, field
Experiment 9. PID Controller
 Experiment 9 PID Controller Objective: - To be familiar with PID controller. - Noting how changing PID controller parameter effect on system response. Theory: The basic function of a controller is to execute
Experiment 9 PID Controller Objective: - To be familiar with PID controller. - Noting how changing PID controller parameter effect on system response. Theory: The basic function of a controller is to execute
Lab 1: Steady State Error and Step Response MAE 433, Spring 2012
 Lab 1: Steady State Error and Step Response MAE 433, Spring 2012 Instructors: Prof. Rowley, Prof. Littman AIs: Brandt Belson, Jonathan Tu Technical staff: Jonathan Prévost Princeton University Feb. 14-17,
Lab 1: Steady State Error and Step Response MAE 433, Spring 2012 Instructors: Prof. Rowley, Prof. Littman AIs: Brandt Belson, Jonathan Tu Technical staff: Jonathan Prévost Princeton University Feb. 14-17,
LECTURE 2: PD, PID, and Feedback Compensation. ( ) = + We consider various settings for Zc when compensating the system with the following RL:
 LECTURE 2: PD, PID, and Feedback Compensation. 2.1 Ideal Derivative Compensation (PD) Generally, we want to speed up the transient response (decrease Ts and Tp). If we are lucky then a system s desired
LECTURE 2: PD, PID, and Feedback Compensation. 2.1 Ideal Derivative Compensation (PD) Generally, we want to speed up the transient response (decrease Ts and Tp). If we are lucky then a system s desired
Electric Drives Experiment 5 Four-Quadrant Operation of a PMDC Motor
 Electric Drives Experiment 5 Four-Quadrant Operation of a PMDC Motor 5.1 Objective The objective of this activity is to analyze the four-quadrant operation of a permanent-magnet DC (PMDC) motor. This activity
Electric Drives Experiment 5 Four-Quadrant Operation of a PMDC Motor 5.1 Objective The objective of this activity is to analyze the four-quadrant operation of a permanent-magnet DC (PMDC) motor. This activity
ANNA UNIVERSITY :: CHENNAI MODEL QUESTION PAPER(V-SEMESTER) B.E. ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC334 - CONTROL SYSTEMS
 ANNA UNIVERSITY :: CHENNAI - 600 025 MODEL QUESTION PAPER(V-SEMESTER) B.E. ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC334 - CONTROL SYSTEMS Time: 3hrs Max Marks: 100 Answer all Questions PART - A (10
ANNA UNIVERSITY :: CHENNAI - 600 025 MODEL QUESTION PAPER(V-SEMESTER) B.E. ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC334 - CONTROL SYSTEMS Time: 3hrs Max Marks: 100 Answer all Questions PART - A (10
Brushed DC Motor Microcontroller PWM Speed Control with Optical Encoder and H-Bridge
 Brushed DC Motor Microcontroller PWM Speed Control with Optical Encoder and H-Bridge L298 Full H-Bridge HEF4071B OR Gate Brushed DC Motor with Optical Encoder & Load Inertia Flyback Diodes Arduino Microcontroller
Brushed DC Motor Microcontroller PWM Speed Control with Optical Encoder and H-Bridge L298 Full H-Bridge HEF4071B OR Gate Brushed DC Motor with Optical Encoder & Load Inertia Flyback Diodes Arduino Microcontroller
1. Consider the closed loop system shown in the figure below. Select the appropriate option to implement the system shown in dotted lines using
 1. Consider the closed loop system shown in the figure below. Select the appropriate option to implement the system shown in dotted lines using op-amps a. b. c. d. Solution: b) Explanation: The dotted
1. Consider the closed loop system shown in the figure below. Select the appropriate option to implement the system shown in dotted lines using op-amps a. b. c. d. Solution: b) Explanation: The dotted
7 Lab: Motor control for orientation and angular speed
 Prelab Participation Lab Name: 7 Lab: Motor control for orientation and angular speed Control systems help satellites to track distant stars, airplanes to follow a desired trajectory, cars to travel at
Prelab Participation Lab Name: 7 Lab: Motor control for orientation and angular speed Control systems help satellites to track distant stars, airplanes to follow a desired trajectory, cars to travel at
Dr Ian R. Manchester Dr Ian R. Manchester Amme 3500 : Root Locus Design
 Week Content Notes 1 Introduction 2 Frequency Domain Modelling 3 Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 Block Diagrams 5 Feedback System Characteristics Assign 1 Due 6 Root Locus 7 Root Locus 2 Assign
Week Content Notes 1 Introduction 2 Frequency Domain Modelling 3 Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 Block Diagrams 5 Feedback System Characteristics Assign 1 Due 6 Root Locus 7 Root Locus 2 Assign
Sfwr Eng/TRON 3DX4, Lab 4 Introduction to Computer Based Control
 Announcements: Sfwr Eng/TRON 3DX4, Lab 4 Introduction to Computer Based Control First lab Week of: Mar. 10, 014 Demo Due Week of: End of Lab Period, Mar. 17, 014 Assignment #4 posted: Tue Mar. 0, 014 This
Announcements: Sfwr Eng/TRON 3DX4, Lab 4 Introduction to Computer Based Control First lab Week of: Mar. 10, 014 Demo Due Week of: End of Lab Period, Mar. 17, 014 Assignment #4 posted: Tue Mar. 0, 014 This
ECE 5670/ Lab 6. Parameter Estimation of a Brushless DC Motor. Objectives
 ECE 5670/6670 - Lab 6 Parameter Estimation of a Brushless DC Motor Objectives The objective of the lab is to determine the parameters of a brushless DC motor and to experiment with control strategies using
ECE 5670/6670 - Lab 6 Parameter Estimation of a Brushless DC Motor Objectives The objective of the lab is to determine the parameters of a brushless DC motor and to experiment with control strategies using
CDS 101/110: Lecture 8.2 PID Control
 CDS 11/11: Lecture 8.2 PID Control November 16, 216 Goals: Nyquist Example Introduce and review PID control. Show how to use loop shaping using PID to achieve a performance specification Discuss the use
CDS 11/11: Lecture 8.2 PID Control November 16, 216 Goals: Nyquist Example Introduce and review PID control. Show how to use loop shaping using PID to achieve a performance specification Discuss the use
Experiment 1 Introduction to Simulink
 1 Experiment 1 Introduction to Simulink 1.1 Objective The objective of Experiment #1 is to familiarize the students with simulation of power electronic circuits in Matlab/Simulink environment. Please follow
1 Experiment 1 Introduction to Simulink 1.1 Objective The objective of Experiment #1 is to familiarize the students with simulation of power electronic circuits in Matlab/Simulink environment. Please follow
Digital Control Lab Exp#8: PID CONTROLLER
 Digital Control Lab Exp#8: PID CONTROLLER we will design the velocity controller for a DC motor. For the sake of simplicity consider a basic transfer function for a DC motor where effects such as friction
Digital Control Lab Exp#8: PID CONTROLLER we will design the velocity controller for a DC motor. For the sake of simplicity consider a basic transfer function for a DC motor where effects such as friction
Frequency Response Analysis and Design Tutorial
 1 of 13 1/11/2011 5:43 PM Frequency Response Analysis and Design Tutorial I. Bode plots [ Gain and phase margin Bandwidth frequency Closed loop response ] II. The Nyquist diagram [ Closed loop stability
1 of 13 1/11/2011 5:43 PM Frequency Response Analysis and Design Tutorial I. Bode plots [ Gain and phase margin Bandwidth frequency Closed loop response ] II. The Nyquist diagram [ Closed loop stability
CSE 3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory Lab 5 Digital Control System
 Introduction CSE 3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory Lab 5 Digital Control System The purpose of this lab is to introduce you to digital control systems. The most basic function of a control system is to
Introduction CSE 3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory Lab 5 Digital Control System The purpose of this lab is to introduce you to digital control systems. The most basic function of a control system is to
Penn State Erie, The Behrend College School of Engineering
 Penn State Erie, The Behrend College School of Engineering EE BD 327 Signals and Control Lab Spring 2008 Lab 9 Ball and Beam Balancing Problem April 10, 17, 24, 2008 Due: May 1, 2008 Number of Lab Periods:
Penn State Erie, The Behrend College School of Engineering EE BD 327 Signals and Control Lab Spring 2008 Lab 9 Ball and Beam Balancing Problem April 10, 17, 24, 2008 Due: May 1, 2008 Number of Lab Periods:
EE 482 : CONTROL SYSTEMS Lab Manual
 University of Bahrain College of Engineering Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 482 : CONTROL SYSTEMS Lab Manual Dr. Ebrahim Al-Gallaf Assistance Professor of Intelligent Control and Robotics
University of Bahrain College of Engineering Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 482 : CONTROL SYSTEMS Lab Manual Dr. Ebrahim Al-Gallaf Assistance Professor of Intelligent Control and Robotics
Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02. Rotary Experiment #03: Speed Control. SRV02 Speed Control using QuaRC. Student Manual
 Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02 Rotary Experiment #03: Speed Control SRV02 Speed Control using QuaRC Student Manual Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. PREREQUISITES...1 3. OVERVIEW OF FILES...2
Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02 Rotary Experiment #03: Speed Control SRV02 Speed Control using QuaRC Student Manual Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. PREREQUISITES...1 3. OVERVIEW OF FILES...2
Figure 1: Unity Feedback System. The transfer function of the PID controller looks like the following:
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering department Control Systems Design Lab Eng. Mohammed S. Jouda Eng. Ola M. Skeik Experiment 3 PID Controller Overview This experiment
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering department Control Systems Design Lab Eng. Mohammed S. Jouda Eng. Ola M. Skeik Experiment 3 PID Controller Overview This experiment
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING BANGLADESH UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY EEE 402 : CONTROL SYSTEMS SESSIONAL
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING BANGLADESH UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY EEE 402 : CONTROL SYSTEMS SESSIONAL Experiment No. 1(a) : Modeling of physical systems and study of
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING BANGLADESH UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY EEE 402 : CONTROL SYSTEMS SESSIONAL Experiment No. 1(a) : Modeling of physical systems and study of
Course Outline. Time vs. Freq. Domain Analysis. Frequency Response. Amme 3500 : System Dynamics & Control. Design via Frequency Response
 Course Outline Amme 35 : System Dynamics & Control Design via Frequency Response Week Date Content Assignment Notes Mar Introduction 2 8 Mar Frequency Domain Modelling 3 5 Mar Transient Performance and
Course Outline Amme 35 : System Dynamics & Control Design via Frequency Response Week Date Content Assignment Notes Mar Introduction 2 8 Mar Frequency Domain Modelling 3 5 Mar Transient Performance and
MTE 360 Automatic Control Systems University of Waterloo, Department of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering
 MTE 36 Automatic Control Systems University of Waterloo, Department of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering Laboratory #1: Introduction to Control Engineering In this laboratory, you will become familiar
MTE 36 Automatic Control Systems University of Waterloo, Department of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering Laboratory #1: Introduction to Control Engineering In this laboratory, you will become familiar
Laboratory Assignment 5 Digital Velocity and Position control of a D.C. motor
 Laboratory Assignment 5 Digital Velocity and Position control of a D.C. motor 2.737 Mechatronics Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA0239 Topics Motor modeling
Laboratory Assignment 5 Digital Velocity and Position control of a D.C. motor 2.737 Mechatronics Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA0239 Topics Motor modeling
A M E M B E R O F T H E K E N D A L L G R O U P
 A M E M B E R O F T H E K E N D A L L G R O U P Basics of PID control in a Programmable Automation Controller Technology Summit September, 2018 Eric Paquette Definitions-PID A Proportional Integral Derivative
A M E M B E R O F T H E K E N D A L L G R O U P Basics of PID control in a Programmable Automation Controller Technology Summit September, 2018 Eric Paquette Definitions-PID A Proportional Integral Derivative
MCE441/541 Midterm Project Position Control of Rotary Servomechanism
 MCE441/541 Midterm Project Position Control of Rotary Servomechanism DUE: 11/08/2011 This project counts both as Homework 4 and 50 points of the second midterm exam 1 System Description A servomechanism
MCE441/541 Midterm Project Position Control of Rotary Servomechanism DUE: 11/08/2011 This project counts both as Homework 4 and 50 points of the second midterm exam 1 System Description A servomechanism
TF Electronics Throttle Controller
 TF Electronics Throttle Controller Software Installation: Double click on TFEsetup.exe file to start installation. After installation there will be a shortcut on your desktop. Connecting the USB cable
TF Electronics Throttle Controller Software Installation: Double click on TFEsetup.exe file to start installation. After installation there will be a shortcut on your desktop. Connecting the USB cable
CSMIO/IP-A motion controller and Mach4
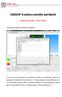 CSMIO/IP-A motion controller and Mach4 Quick start guide Axis tuning 1) We start the configuration with Motor axis assignment. As you can see in the picture above - the Motor0 was assign to X axis (the
CSMIO/IP-A motion controller and Mach4 Quick start guide Axis tuning 1) We start the configuration with Motor axis assignment. As you can see in the picture above - the Motor0 was assign to X axis (the
Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Lab 2: Characterization of Lab System Components
 OBJECTIVES Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering 2.004 System Dynamics and Control Fall Term 2007 Lab 2: Characterization of Lab System Components In the future lab
OBJECTIVES Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering 2.004 System Dynamics and Control Fall Term 2007 Lab 2: Characterization of Lab System Components In the future lab
Cantonment, Dhaka-1216, BANGLADESH
 International Conference on Mechanical, Industrial and Energy Engineering 2014 26-27 December, 2014, Khulna, BANGLADESH ICMIEE-PI-140153 Electro-Mechanical Modeling of Separately Excited DC Motor & Performance
International Conference on Mechanical, Industrial and Energy Engineering 2014 26-27 December, 2014, Khulna, BANGLADESH ICMIEE-PI-140153 Electro-Mechanical Modeling of Separately Excited DC Motor & Performance
Dr Ian R. Manchester
 Week Content Notes 1 Introduction 2 Frequency Domain Modelling 3 Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 Block Diagrams 5 Feedback System Characteristics Assign 1 Due 6 Root Locus 7 Root Locus 2 Assign
Week Content Notes 1 Introduction 2 Frequency Domain Modelling 3 Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 Block Diagrams 5 Feedback System Characteristics Assign 1 Due 6 Root Locus 7 Root Locus 2 Assign
Introduction to Simulink Assignment Companion Document
 Introduction to Simulink Assignment Companion Document Implementing a DSB-SC AM Modulator in Simulink The purpose of this exercise is to explore SIMULINK by implementing a DSB-SC AM modulator. DSB-SC AM
Introduction to Simulink Assignment Companion Document Implementing a DSB-SC AM Modulator in Simulink The purpose of this exercise is to explore SIMULINK by implementing a DSB-SC AM modulator. DSB-SC AM
Basic Tuning for the SERVOSTAR 400/600
 Basic Tuning for the SERVOSTAR 400/600 Welcome to Kollmorgen s interactive tuning chart. The first three sheets of this document provide a flow chart to describe tuning the servo gains of a SERVOSTAR 400/600.
Basic Tuning for the SERVOSTAR 400/600 Welcome to Kollmorgen s interactive tuning chart. The first three sheets of this document provide a flow chart to describe tuning the servo gains of a SERVOSTAR 400/600.
Lab 1: First Order CT Systems, Blockdiagrams, Introduction
 ECEN 3300 Linear Systems Spring 2010 1-18-10 P. Mathys Lab 1: First Order CT Systems, Blockdiagrams, Introduction to Simulink 1 Introduction Many continuous time (CT) systems of practical interest can
ECEN 3300 Linear Systems Spring 2010 1-18-10 P. Mathys Lab 1: First Order CT Systems, Blockdiagrams, Introduction to Simulink 1 Introduction Many continuous time (CT) systems of practical interest can
Chief Architect X3 Training Series. Layers and Layer Sets
 Chief Architect X3 Training Series Layers and Layer Sets Save time while creating more detailed plans Why do you need Layers? Setting up Layer Lets Adding items to layers Layers and Layout Pages Layer
Chief Architect X3 Training Series Layers and Layer Sets Save time while creating more detailed plans Why do you need Layers? Setting up Layer Lets Adding items to layers Layers and Layout Pages Layer
DEGREE: Biomedical Engineering YEAR: TERM: 1
 COURSE: Control Engineering DEGREE: Biomedical Engineering YEAR: TERM: 1 La asignatura tiene 14 sesiones que se distribuyen a lo largo de 7 semanas. Los dos laboratorios puede situarse en cualquiera de
COURSE: Control Engineering DEGREE: Biomedical Engineering YEAR: TERM: 1 La asignatura tiene 14 sesiones que se distribuyen a lo largo de 7 semanas. Los dos laboratorios puede situarse en cualquiera de
Practical Assignment 1: Arduino interface with Simulink
 !! Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Dharwad EE 303: Control Systems Practical Assignment - 1 Adapted from Take Home Labs, Oklahoma State University Practical Assignment
!! Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Dharwad EE 303: Control Systems Practical Assignment - 1 Adapted from Take Home Labs, Oklahoma State University Practical Assignment
Fundamentals of Servo Motion Control
 Fundamentals of Servo Motion Control The fundamental concepts of servo motion control have not changed significantly in the last 50 years. The basic reasons for using servo systems in contrast to open
Fundamentals of Servo Motion Control The fundamental concepts of servo motion control have not changed significantly in the last 50 years. The basic reasons for using servo systems in contrast to open
Introduction to Modeling of Switched Mode Power Converters Using MATLAB and Simulink
 Introduction to Modeling of Switched Mode Power Converters Using MATLAB and Simulink Extensive introductory tutorials for MATLAB and Simulink, including Control Systems Toolbox and Simulink Control Design
Introduction to Modeling of Switched Mode Power Converters Using MATLAB and Simulink Extensive introductory tutorials for MATLAB and Simulink, including Control Systems Toolbox and Simulink Control Design
ECE 5670/6670 Lab 7 Brushless DC Motor Control with 6-Step Commutation. Objectives
 ECE 5670/6670 Lab 7 Brushless DC Motor Control with 6-Step Commutation Objectives The objective of the lab is to implement a 6-step commutation scheme for a brushless DC motor in simulations, and to expand
ECE 5670/6670 Lab 7 Brushless DC Motor Control with 6-Step Commutation Objectives The objective of the lab is to implement a 6-step commutation scheme for a brushless DC motor in simulations, and to expand
SECTION 6: ROOT LOCUS DESIGN
 SECTION 6: ROOT LOCUS DESIGN MAE 4421 Control of Aerospace & Mechanical Systems 2 Introduction Introduction 3 Consider the following unity feedback system 3 433 Assume A proportional controller Design
SECTION 6: ROOT LOCUS DESIGN MAE 4421 Control of Aerospace & Mechanical Systems 2 Introduction Introduction 3 Consider the following unity feedback system 3 433 Assume A proportional controller Design
Open Loop Frequency Response
 TAKE HOME LABS OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY Open Loop Frequency Response by Carion Pelton 1 OBJECTIVE This experiment will reinforce your understanding of the concept of frequency response. As part of the
TAKE HOME LABS OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY Open Loop Frequency Response by Carion Pelton 1 OBJECTIVE This experiment will reinforce your understanding of the concept of frequency response. As part of the
ECE411 - Laboratory Exercise #1
 ECE411 - Laboratory Exercise #1 Introduction to Matlab/Simulink This laboratory exercise is intended to provide a tutorial introduction to Matlab/Simulink. Simulink is a Matlab toolbox for analysis/simulation
ECE411 - Laboratory Exercise #1 Introduction to Matlab/Simulink This laboratory exercise is intended to provide a tutorial introduction to Matlab/Simulink. Simulink is a Matlab toolbox for analysis/simulation
Motor Modeling and Position Control Lab 3 MAE 334
 Motor ing and Position Control Lab 3 MAE 334 Evan Coleman April, 23 Spring 23 Section L9 Executive Summary The purpose of this experiment was to observe and analyze the open loop response of a DC servo
Motor ing and Position Control Lab 3 MAE 334 Evan Coleman April, 23 Spring 23 Section L9 Executive Summary The purpose of this experiment was to observe and analyze the open loop response of a DC servo
EE 461 Experiment #1 Digital Control of DC Servomotor
 EE 461 Experiment #1 Digital Control of DC Servomotor 1 Objectives The objective of this lab is to introduce to the students the design and implementation of digital control. The digital control is implemented
EE 461 Experiment #1 Digital Control of DC Servomotor 1 Objectives The objective of this lab is to introduce to the students the design and implementation of digital control. The digital control is implemented
Switch Mode Power Conversion Prof. L. Umanand Department of Electronics System Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Switch Mode Power Conversion Prof. L. Umanand Department of Electronics System Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 30 Implementation on PID controller Good day to all of you. We
Switch Mode Power Conversion Prof. L. Umanand Department of Electronics System Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 30 Implementation on PID controller Good day to all of you. We
EEL 4350 Principles of Communication Project 2 Due Tuesday, February 10 at the Beginning of Class
 EEL 4350 Principles of Communication Project 2 Due Tuesday, February 10 at the Beginning of Class Description In this project, MATLAB and Simulink are used to construct a system experiment. The experiment
EEL 4350 Principles of Communication Project 2 Due Tuesday, February 10 at the Beginning of Class Description In this project, MATLAB and Simulink are used to construct a system experiment. The experiment
Engine Control Workstation Using Simulink / DSP. Platform. Mark Bright, Mike Donaldson. Advisor: Dr. Dempsey
 Engine Control Workstation Using Simulink / DSP Platform By Mark Bright, Mike Donaldson Advisor: Dr. Dempsey An Engine Control Workstation was designed to simulate the thermal environments found in liquid-based
Engine Control Workstation Using Simulink / DSP Platform By Mark Bright, Mike Donaldson Advisor: Dr. Dempsey An Engine Control Workstation was designed to simulate the thermal environments found in liquid-based
CHM 152 Lab 1: Plotting with Excel updated: May 2011
 CHM 152 Lab 1: Plotting with Excel updated: May 2011 Introduction In this course, many of our labs will involve plotting data. While many students are nerds already quite proficient at using Excel to plot
CHM 152 Lab 1: Plotting with Excel updated: May 2011 Introduction In this course, many of our labs will involve plotting data. While many students are nerds already quite proficient at using Excel to plot
Motomatic Servo Control
 Exercise 2 Motomatic Servo Control This exercise will take two weeks. You will work in teams of two. 2.0 Prelab Read through this exercise in the lab manual. Using Appendix B as a reference, create a block
Exercise 2 Motomatic Servo Control This exercise will take two weeks. You will work in teams of two. 2.0 Prelab Read through this exercise in the lab manual. Using Appendix B as a reference, create a block
Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies
 Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies S Prem Kumar 1 J V Pavan Chand 1 B Pangedaiah 1 1. Assistant professor of Laki Reddy Balireddy College Of Engineering, Mylavaram Abstract - As the
Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies S Prem Kumar 1 J V Pavan Chand 1 B Pangedaiah 1 1. Assistant professor of Laki Reddy Balireddy College Of Engineering, Mylavaram Abstract - As the
Software User Manual
 Software User Manual ElectroCraft CompletePower Plus Universal Servo Drive ElectroCraft Document Number: 198-0000021 2 Marin Way, Suite 3 Stratham, NH 03885-2578 www.electrocraft.com ElectroCraft 2018
Software User Manual ElectroCraft CompletePower Plus Universal Servo Drive ElectroCraft Document Number: 198-0000021 2 Marin Way, Suite 3 Stratham, NH 03885-2578 www.electrocraft.com ElectroCraft 2018
An Introduction to Proportional- Integral-Derivative (PID) Controllers
 An Introduction to Proportional- Integral-Derivative (PID) Controllers Stan Żak School of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 680 Fall 2017 1 Motivation Growing gap between real world control problems
An Introduction to Proportional- Integral-Derivative (PID) Controllers Stan Żak School of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 680 Fall 2017 1 Motivation Growing gap between real world control problems
User Guide IRMCS3041 System Overview/Guide. Aengus Murray. Table of Contents. Introduction
 User Guide 0607 IRMCS3041 System Overview/Guide By Aengus Murray Table of Contents Introduction... 1 IRMCF341 Application Circuit... 2 Sensorless Control Algorithm... 4 Velocity and Current Control...
User Guide 0607 IRMCS3041 System Overview/Guide By Aengus Murray Table of Contents Introduction... 1 IRMCF341 Application Circuit... 2 Sensorless Control Algorithm... 4 Velocity and Current Control...
Magnetic Levitation System
 Introduction Magnetic Levitation System There are two experiments in this lab. The first experiment studies system nonlinear characteristics, and the second experiment studies system dynamic characteristics
Introduction Magnetic Levitation System There are two experiments in this lab. The first experiment studies system nonlinear characteristics, and the second experiment studies system dynamic characteristics
Laboratory Tutorial#1
 Laboratory Tutorial#1 1.1. Objective: To become familiar with the modules and how they operate. 1.2. Equipment Required: Following equipment is required to perform above task. Quantity Apparatus 1 OU150A
Laboratory Tutorial#1 1.1. Objective: To become familiar with the modules and how they operate. 1.2. Equipment Required: Following equipment is required to perform above task. Quantity Apparatus 1 OU150A
Module 08 Controller Designs: Compensators and PIDs
 Module 08 Controller Designs: Compensators and PIDs Ahmad F. Taha EE 3413: Analysis and Desgin of Control Systems Email: ahmad.taha@utsa.edu Webpage: http://engineering.utsa.edu/ taha March 31, 2016 Ahmad
Module 08 Controller Designs: Compensators and PIDs Ahmad F. Taha EE 3413: Analysis and Desgin of Control Systems Email: ahmad.taha@utsa.edu Webpage: http://engineering.utsa.edu/ taha March 31, 2016 Ahmad
Servo Tuning Tutorial
 Servo Tuning Tutorial 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Servo system defined Why does a servo system need to be tuned Trajectory generator and velocity profiles The PID Filter Proportional gain Derivative
Servo Tuning Tutorial 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Servo system defined Why does a servo system need to be tuned Trajectory generator and velocity profiles The PID Filter Proportional gain Derivative
ECE 5671/6671 LAB 6. Wound-Field Synchronous Generators
 ECE 5671/6671 LAB 6 Wound-Field Synchronous Generators 1.0 Introduction This lab is designed to explore the characteristics of Wound Field Synchronous Generators (WFSG). The WFSG of this lab is obtained
ECE 5671/6671 LAB 6 Wound-Field Synchronous Generators 1.0 Introduction This lab is designed to explore the characteristics of Wound Field Synchronous Generators (WFSG). The WFSG of this lab is obtained
Assignment 5 due Monday, May 7
 due Monday, May 7 Simulations and the Law of Large Numbers Overview In both parts of the assignment, you will be calculating a theoretical probability for a certain procedure. In other words, this uses
due Monday, May 7 Simulations and the Law of Large Numbers Overview In both parts of the assignment, you will be calculating a theoretical probability for a certain procedure. In other words, this uses
SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 3. Ball & Beam. Student Handout
 SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 3 Ball & Beam Student Handout SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 3 Ball & Beam Student Handout 1. Objectives The objective in this experiment is to design a controller for
SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 3 Ball & Beam Student Handout SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 3 Ball & Beam Student Handout 1. Objectives The objective in this experiment is to design a controller for
Application Note CTAN #287
 Application Note CTAN #287 This Application Note is pertinent to the Commander SK Water Pressure PID Loop Control This application note will describe a way to utilize the Commander SK (note that the Unidrive
Application Note CTAN #287 This Application Note is pertinent to the Commander SK Water Pressure PID Loop Control This application note will describe a way to utilize the Commander SK (note that the Unidrive
Advanced Servo Tuning
 Advanced Servo Tuning Dr. Rohan Munasinghe Department of Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering University of Moratuwa Servo System Elements position encoder Motion controller (software) Desired
Advanced Servo Tuning Dr. Rohan Munasinghe Department of Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering University of Moratuwa Servo System Elements position encoder Motion controller (software) Desired
Lab 11. Speed Control of a D.C. motor. Motor Characterization
 Lab 11. Speed Control of a D.C. motor Motor Characterization Motor Speed Control Project 1. Generate PWM waveform 2. Amplify the waveform to drive the motor 3. Measure motor speed 4. Estimate motor parameters
Lab 11. Speed Control of a D.C. motor Motor Characterization Motor Speed Control Project 1. Generate PWM waveform 2. Amplify the waveform to drive the motor 3. Measure motor speed 4. Estimate motor parameters
Modelling for Temperature Non-Isothermal Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor Using Fuzzy Logic
 Modelling for Temperature Non-Isothermal Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor Using Fuzzy Logic Nasser Mohamed Ramli, Mohamad Syafiq Mohamad 1 Abstract Many types of controllers were applied on the continuous
Modelling for Temperature Non-Isothermal Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor Using Fuzzy Logic Nasser Mohamed Ramli, Mohamad Syafiq Mohamad 1 Abstract Many types of controllers were applied on the continuous
MEM01: DC-Motor Servomechanism
 MEM01: DC-Motor Servomechanism Interdisciplinary Automatic Controls Laboratory - ME/ECE/CHE 389 February 5, 2016 Contents 1 Introduction and Goals 1 2 Description 2 3 Modeling 2 4 Lab Objective 5 5 Model
MEM01: DC-Motor Servomechanism Interdisciplinary Automatic Controls Laboratory - ME/ECE/CHE 389 February 5, 2016 Contents 1 Introduction and Goals 1 2 Description 2 3 Modeling 2 4 Lab Objective 5 5 Model
GE423 Laboratory Assignment 6 Robot Sensors and Wall-Following
 GE423 Laboratory Assignment 6 Robot Sensors and Wall-Following Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Learn about the sensors available on the robot for environment sensing. 2. Learn about classical wall-following
GE423 Laboratory Assignment 6 Robot Sensors and Wall-Following Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Learn about the sensors available on the robot for environment sensing. 2. Learn about classical wall-following
MM7 Practical Issues Using PID Controllers
 MM7 Practical Issues Using PID Controllers Readings: FC textbook: Section 4.2.7 Integrator Antiwindup p.196-200 Extra reading: Hou Ming s lecture notes p.60-69 Extra reading: M.J. Willis notes on PID controler
MM7 Practical Issues Using PID Controllers Readings: FC textbook: Section 4.2.7 Integrator Antiwindup p.196-200 Extra reading: Hou Ming s lecture notes p.60-69 Extra reading: M.J. Willis notes on PID controler
Experiment Number 1. Revised: Fall 2018 Introduction to MATLAB Simulink and Simulink Resistor Simulations Preface:
 Experiment Number 1 Revised: Fall 2018 Introduction to MATLAB Simulink and Simulink Resistor Simulations Preface: Experiment number 1 will be held in CLC room 105, 106, or 107. Your TA will let you know
Experiment Number 1 Revised: Fall 2018 Introduction to MATLAB Simulink and Simulink Resistor Simulations Preface: Experiment number 1 will be held in CLC room 105, 106, or 107. Your TA will let you know
CHAPTER-III MODELING AND IMPLEMENTATION OF PMBLDC MOTOR DRIVE
 CHAPTER-III MODELING AND IMPLEMENTATION OF PMBLDC MOTOR DRIVE 3.1 GENERAL The PMBLDC motors used in low power applications (up to 5kW) are fed from a single-phase AC source through a diode bridge rectifier
CHAPTER-III MODELING AND IMPLEMENTATION OF PMBLDC MOTOR DRIVE 3.1 GENERAL The PMBLDC motors used in low power applications (up to 5kW) are fed from a single-phase AC source through a diode bridge rectifier
EMG Electrodes. Fig. 1. System for measuring an electromyogram.
 1270 LABORATORY PROJECT NO. 1 DESIGN OF A MYOGRAM CIRCUIT 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Electromyograms The gross muscle groups (e.g., biceps) in the human body are actually composed of a large number of parallel
1270 LABORATORY PROJECT NO. 1 DESIGN OF A MYOGRAM CIRCUIT 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Electromyograms The gross muscle groups (e.g., biceps) in the human body are actually composed of a large number of parallel
SignalCalc Drop Test Demo Guide
 SignalCalc Drop Test Demo Guide Introduction Most protective packaging for electronic and other fragile products use cushion materials in the packaging that are designed to deform in response to forces
SignalCalc Drop Test Demo Guide Introduction Most protective packaging for electronic and other fragile products use cushion materials in the packaging that are designed to deform in response to forces
Lesson number one. Operational Amplifier Basics
 What About Lesson number one Operational Amplifier Basics As well as resistors and capacitors, Operational Amplifiers, or Op-amps as they are more commonly called, are one of the basic building blocks
What About Lesson number one Operational Amplifier Basics As well as resistors and capacitors, Operational Amplifiers, or Op-amps as they are more commonly called, are one of the basic building blocks
Design of a Simulink-Based Control Workstation for Mobile Wheeled Vehicles with Variable-Velocity Differential Motor Drives
 Design of a Simulink-Based Control Workstation for Mobile Wheeled Vehicles with Variable-Velocity Differential Motor Drives Kevin Block, Timothy De Pasion, Benjamin Roos, Alexander Schmidt Gary Dempsey
Design of a Simulink-Based Control Workstation for Mobile Wheeled Vehicles with Variable-Velocity Differential Motor Drives Kevin Block, Timothy De Pasion, Benjamin Roos, Alexander Schmidt Gary Dempsey
Lab 2, Analysis and Design of PID
 Lab 2, Analysis and Design of PID Controllers IE1304, Control Theory 1 Goal The main goal is to learn how to design a PID controller to handle reference tracking and disturbance rejection. You will design
Lab 2, Analysis and Design of PID Controllers IE1304, Control Theory 1 Goal The main goal is to learn how to design a PID controller to handle reference tracking and disturbance rejection. You will design
CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR POWER CONVERSION SYSTEMS
 CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR POWER CONVERSION SYSTEMS Introduction A typical feedback system found in power converters Switched-mode power converters generally use PI, pz, or pz feedback compensators to regulate
CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR POWER CONVERSION SYSTEMS Introduction A typical feedback system found in power converters Switched-mode power converters generally use PI, pz, or pz feedback compensators to regulate
Chapter 3: Multi Domain - a servo mechanism
 Chapter 3: Multi Domain - a servo mechanism 11 This document is an excerpt from the book Introductory Examples, part of the MathModelica documentation. 2006-2009 MathCore Engineering AB. All rights reserved.
Chapter 3: Multi Domain - a servo mechanism 11 This document is an excerpt from the book Introductory Examples, part of the MathModelica documentation. 2006-2009 MathCore Engineering AB. All rights reserved.
Laboratory Project 1: Design of a Myogram Circuit
 1270 Laboratory Project 1: Design of a Myogram Circuit Abstract-You will design and build a circuit to measure the small voltages generated by your biceps muscle. Using your circuit and an oscilloscope,
1270 Laboratory Project 1: Design of a Myogram Circuit Abstract-You will design and build a circuit to measure the small voltages generated by your biceps muscle. Using your circuit and an oscilloscope,
Introduction to Servo Control & PID Tuning
 Introduction to Servo Control & PID Tuning Presented to: Agenda Introduction to Servo Control Theory PID Algorithm Overview Tuning & General System Characterization Oscillation Characterization Feed-forward
Introduction to Servo Control & PID Tuning Presented to: Agenda Introduction to Servo Control Theory PID Algorithm Overview Tuning & General System Characterization Oscillation Characterization Feed-forward
GE 320: Introduction to Control Systems
 GE 320: Introduction to Control Systems Laboratory Section Manual 1 Welcome to GE 320.. 1 www.softbankrobotics.com 1 1 Introduction This section summarizes the course content and outlines the general procedure
GE 320: Introduction to Control Systems Laboratory Section Manual 1 Welcome to GE 320.. 1 www.softbankrobotics.com 1 1 Introduction This section summarizes the course content and outlines the general procedure
Pre-lab Show that the filter shown at right has transfer function
 University of Utah Electrical & Computer Engineering Department ECE 3510 Lab 7 Advanced Phase - Locked Loop M. Bodson, A. Stolp, 3/5/06 rev,3/5/08, 3/24/19 Note : Bring circuit and lab handout from last
University of Utah Electrical & Computer Engineering Department ECE 3510 Lab 7 Advanced Phase - Locked Loop M. Bodson, A. Stolp, 3/5/06 rev,3/5/08, 3/24/19 Note : Bring circuit and lab handout from last
EC CONTROL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING
 1 YEAR / SEM: II / IV EC 1256. CONTROL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING UNIT I CONTROL SYSTEM MODELING PART-A 1. Define open loop and closed loop systems. 2. Define signal flow graph. 3. List the force-voltage analogous
1 YEAR / SEM: II / IV EC 1256. CONTROL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING UNIT I CONTROL SYSTEM MODELING PART-A 1. Define open loop and closed loop systems. 2. Define signal flow graph. 3. List the force-voltage analogous
Name: Date: Score: / (75)
 Name: Date: Score: / (75) This lab MUST be done in your normal lab time NO LATE LABS Bring Textbook to Lab. You don t need to use your lab notebook, just fill in the blanks, you ll be graded when you re
Name: Date: Score: / (75) This lab MUST be done in your normal lab time NO LATE LABS Bring Textbook to Lab. You don t need to use your lab notebook, just fill in the blanks, you ll be graded when you re
