DEEP FOUNDATION TYPES DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION ISSUES
|
|
|
- Elinor Watkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEEP FOUNDATION TYPES DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION ISSUES OFFICE OF STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING OHIO DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION JAWDAT SIDDIQI P.E. ASSISTANT ADMINISTRATOR
2 Reliability Index #&! #&!!" # $%!" # $% The LRFD philosophy provides a more uniform, systematic, and rational approach to the selection of load factors and resistance factors than LFD.
3 LRFD: Load & Resistance Factor Design For Safety: η γ Q φ R = R i i i n r Q i - Load Effect R n - Component Resistance γ i - Load Factor φ - Resistance Factor i - Load Modifier (Ductility, Redundancy and Operational Importance) R n - Factored Resistance
4 Variability of Loads and Resistances '()&*%+(
5 Variability of Loads and Resistances σ = σ + σ 2 2 ( R Q) R Q β = Mean R Q σ ( ) ( R Q)
6 Reliability Index β P(Failure) % % % % %
7 Reliability Index AISC: β D+(L or S) D+L+W D+L+E Members Connections AASHTO: β = 3.5 Super/Sub Structures β = 2.3 Foundations
8 LRFD: Load & Resistance Factor Design For Safety: η γ Q φ R = R i i i n r Q i - Load Effect R n - Component Resistance γ i - Load Factor φ - Resistance Factor i - Load Modifier (Ductility, Redundancy and Operational Importance) R n - Factored Resistance
9 LRFD: Load & Resistance Factor Design Table Load Combinations and Load Factors. Load Combination Limit State DC DD DW EH EV ES EL LL IM CE BR PL LS WA WS WL FR TU CR SH TG SE Use One of These at a Time EQ IC CT CV STRENGTH I (unless noted) p /1.20 TG SE STRENGTH II p /1.20 TG SE STRENGTH III p /1.20 TG SE STRENGTH IV p /1.20 STRENGTH V p /1.20 TG SE EXTREME EVENT I EXTREME EVENT II p EQ p SERVICE I /1.20 TG SE SERVICE II /1.20 SERVICE III /1.20 TG SE SERVICE IV / FATIGUE LL, IM & CE ONLY 0.75
10 LRFD: Load & Resistance Factor Design Table Load Combinations and Load Factors. DC DD LL Use One of These at DW IM a Time EH CE Load Combination Limit State EV ES EL BR PL LS WA WS WL FR TU CR SH TG SE EQ IC CT CV STRENGTH I (unless noted) STRENGTH II STRENGTH III STRENGTH IV STRENGTH V p /1.2 TG SE p /1.2 TG SE p /1.2 TG SE p /1.2 p /1.2 TG SE
11 LRFD: Load & Resistance Factor Design Table Load Combinations and Load Factors. Load Combinatio n Limit State EXTREME EVENT I EXTREME EVENT II FATIGUE LL, IM & CE ONLY DC DD DW EH EV ES EL LL IM CE BR PL LS WA WS WL FR Use One of These at a Time TU CR SH TG SE EQ IC CT CV p EQ p
12 LRFD: Load & Resistance Factor Design Table Load Combinations and Load Factors. Load Combinati on Limit State SERVICE I SERVICE II SERVICE III SERVICE IV DC DD DW EH EV ES EL LL IM CE BR PL LS WA WS W L FR TU CR SH TG SE E Q Use One of These at a Time /1.20 TG SE / /1.20 TG SE / I C C T C V
13 Resistance Factors Table Resistance Factors for Geotechnical Resistance of Shallow Foundations at the Strength Limit State. Method/Soil/Condition Resistance Factor Theoretical method (Munfakh et al., 2001), in clay 0.50 Theoretical method (Munfakh et al., 2001), in sand, using CPT 0.50 Bearing Resistance ϕ b Theoretical method (Munfakh et al., 2001), in sand, using SPT 0.45 Semi-empirical methods (Meyerhof, 1957), all soils 0.45 Footings on rock 0.45 Plate Load Test 0.55 Precast concrete placed on sand 0.90 Sliding ϕ τ Cast-in-Place Concrete on sand 0.80 Cast-in-Place or precast Concrete on Clay 0.85 Soil on soil 0.90 ϕ ep Passive earth pressure component of sliding resistance 0.50
14 Resistance Factors Table Resistance Factors for Driven Piles. Condition/Resistance Determination Method Driving criteria established by static load test(s); quality control by dynamic testing and/or calibrated wave equation, or minimum driving resistance combined with minimum delivered hammer energy from the load test(s). For the last case, the hammer used for the test pile(s) shall be used for the production piles. Resistance Factor Values in Table 2 Nominal Resistance of Single Pile in Axial Compression Dynamic Analysis and Static Load Test Methods, ϕ dyn Driving criteria established by dynamic test with signal matching at beginning of redrive conditions only of at least one production pile per pier, but no less than the number of tests per site provided in Table 3. Quality control of remaining piles by calibrated wave equation and/or dynamic testing. Wave equation analysis, without pile dynamic measurements or load test, at end of drive conditions only FHWA-modified Gates dynamic pile formula (End of Drive condition only) Engineering News Record (as defined in Article ) dynamic pile formula (End of Drive condition only)
15 Resistance Factors Table Resistance Factors for Driven Piles (continued). Nominal Resistance of Single Pile in Axial Compression Static Analysis Methods, ϕ stat Condition/Resistance Determination Method Skin Friction and End Bearing: Clay and Mixed Soils α-method (Tomlinson, 1987; Skempton, 1951) β-method (Esrig & Kirby, 1979; Skempton, 1951) λ-method (Vijayvergiya & Focht, 1972; Skempton, 1951) Skin Friction and End Bearing: Sand Nordlund/Thurman Method (Hannigan et al., 2005) SPT-method (Meyerhof) CPT-method (Schmertmann) End bearing in rock (Canadian Geotech. Society, 1985) Resistance Factor Block Failure, ϕ b1 Clay 0.60 Uplift Resistance of Single Piles, ϕ up Nordlund Method α-method β-method λ-method SPT-method CPT-method Load test Group Uplift Resistance, ϕ ug Sand and clay 0.50 Horizontal Geotechnical Resistance of Single Pile or Pile Group Structural Limit State Pile Drivability Analysis, ϕ da All soils and rock 1.0 Steel piles See the provisions of Article Concrete piles See the provisions of Article Timber piles See the provisions of Article and Steel piles See the provisions of Article Concrete piles See the provisions of Article Timber piles See the provisions of Article In all three Articles identified above, use ϕ identified as resistance during pile driving
16 Resistance Factors Table Resistance Factors for Driven Piles (continued). Nominal Resistance of Single Pile in Axial Compression Static Analysis Methods, ϕ stat Condition/Resistance Determination Method Skin Friction and End Bearing: Clay and Mixed Soils α-method (Tomlinson, 1987; Skempton, 1951) β-method (Esrig & Kirby, 1979; Skempton, 1951) λ-method (Vijayvergiya & Focht, 1972; Skempton, 1951) Skin Friction and End Bearing: Sand Nordlund/Thurman Method (Hannigan et al., 2005) SPT-method (Meyerhof) CPT-method (Schmertmann) End bearing in rock (Canadian Geotech. Society, 1985) Resistance Factor
17 Resistance Factors ϕ dyn x R n = ϕ stat x R nstat (C ) where: ϕ dyn = the resistance factor for the dynamic method used to verify pile bearing resistance during driving specified in Table R n = the nominal pile bearing resistance (kips) ϕ stat = the resistance factor for the static analysis method used to estimate the pile penetration depth required to achieve the desired bearing resistance specified in Table R nstat = the predicted nominal resistance from the static analysis method used to estimate the penetration depth required (kips)
18 Resistance Factors The Ultimate Bearing Value for each pile to be shown in the plans shall be determined as follows: R ndr i i = η γ φ DYN Q i Where: Rndr = Ultimate Bearing Value (Kips) ηiγ iq i = Total factored load for highest loaded pile at each substructure unit (Kips) DYN = Resistance factor for driven piles DYN = 0.70 for piles installed according to CMS 507 and CMS 523.
19 Resistance Factors Table Resistance Factors for Driven Piles (continued). Condition/Resistance Determination Method Resistance Factor Block Failure, ϕ b1 Clay 0.60 Uplift Resistance of Single Piles, ϕ up Nordlund Method α-method β-method λ-method SPT-method CPT-method Load test Group Uplift Sand and clay 0.50 Resistance, ϕ ug
20 Resistance Factors Table Resistance Factors for Driven Piles (continued). Structural Limit State Condition/Resistance Determination Method Resistance Factor Steel piles See the provisions of Article Concrete piles See the provisions of Article Timber piles See the provisions of Article and Pile Drivability Analysis, ϕ da Steel piles See the provisions of Article Concrete piles See the provisions of Article Timber piles See the provisions of Article In all three Articles identified above, use ϕ identified as resistance during pile driving
21 Resistance Factors Resistance Factors For axial resistance of piles in compression and subject to damage due to severe driving conditions where use of a pile tip is necessary: H-piles φ c = 0.50 pipe piles φ c = 0.60 For axial resistance of piles in compression under good driving conditions where use of a pile tip is not necessary: H-piles φ c = 0.60 pipe piles φ c = 0.70 For combined axial and flexural resistance of undamaged piles: axial resistance for H-piles φ c = 0.70 axial resistance for pipe piles φ c = 0.80 Flexural resistance φ f = 1.00
22 Resistance Factors Table Relationship between Number of Static Load Tests Conducted per Site and ϕ (after Paikowsky et al., 2004). Number of Static Load Tests per Site Resistance Factor, ϕ Site Variability a Low a Medium a High a >
23 Resistance Factors Table Number of Dynamic Tests with Signal Matching Analysis per Site to Be Conducted During Production Pile Driving (after Paikowsky et al., 2004). Site Variability a Low a Medium a High a Number of Piles Located Within Site Number of Piles with Dynamic Tests and Signal Matching Analysis Required (BOR) < >
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 Resistance Factors Table Resistance Factors for Geotechnical Resistance of Drilled Shafts. Method/Soil/Condition Resistance Factor Side resistance in clay α-method (O Neill and Reese, 1999) 0.45 Tip resistance in clay Total Stress (O Neill and Reese, 1999) 0.40 Side resistance in sand β-method O Neill and Reese, 1999) 0.55 Tip resistance in sand O Neill and Reese (1999) 0.50 Nominal Axial Compressive Resistance of Single-Drilled Shafts, ϕ stat Side resistance in IGMs O Neill and Reese (1999) 0.60 Tip resistance in IGMs O Neill and Reese (1999) 0.55 Side resistance in rock Horvath and Kenney (1979) O Neill and Reese (1999) 0.55 Side resistance in rock Carter and Kulhawy (1988) 0.50 Tip resistance in rock Canadian Geotechnical Society (1985) Pressuremeter Method (Canadian Geotechnical Society, 1985) O Neill and Reese (1999) 0.50 Block Failure, ϕ b1 Clay 0.55 Uplift Resistance of Single-Drilled Shafts, ϕ up Clay α-method (O Neill and Reese, 1999) 0.35 Sand β-method (O Neill and Reese, 1999) 0.45 Rock Horvath and Kenney (1979) Carter and Kulhawy (1988) 0.40 Group Uplift Resistance, ϕ ug Sand and clay 0.45 Horizontal Geotechnical Resistance of Single Shaft or Shaft Group All materials 1.0 Static Load Test (compression), ϕ load All Materials Values in Table , but no greater than 0.70 Static Load Test (uplift), ϕ upload All Materials 0.60
33 Resistance Factors Table Resistance Factors for Geotechnical Resistance of Drilled Shafts. Method/Soil/Condition Resistance Factor Side resistance in clay α-method (O Neill and Reese, 1999) 0.45 Tip resistance in clay Total Stress (O Neill and Reese, 1999) 0.40 Nominal Axial Compressive Resistance of Single- Drilled Shafts, ϕ stat Side resistance in sand β-method O Neill and Reese, 1999) 0.55 Tip resistance in sand O Neill and Reese (1999) 0.50 Side resistance in IGMs O Neill and Reese (1999) 0.60 Tip resistance in IGMs O Neill and Reese (1999) 0.55 Side resistance in rock Horvath and Kenney (1979) O Neill and Reese (1999) 0.55 Side resistance in rock Carter and Kulhawy (1988) 0.50 Tip resistance in rock Canadian Geotechnical Society (1985) Pressuremeter Method (Canadian Geotechnical Society, 1985) O Neill and Reese (1999) 0.50 Block Clay 0.55 Failure, ϕ b1
34 Resistance Factors Table Resistance Factors for Geotechnical Resistance of Drilled Shafts. Uplift Resistance of Single-Drilled Shafts, ϕ up Group Uplift Resistance, ϕ ug Method/Soil/Condition Clay Sand α-method (O Neill and Reese, 1999) β-method (O Neill and Reese, 1999) Rock Horvath and Kenney (1979) Carter and Kulhawy (1988) Sand and clay Resistance Factor
35 Resistance Factors Table Resistance Factors for Geotechnical Resistance of Drilled Shafts. Horizontal Geotechnical Resistance of Single Shaft or Shaft Group Static Load Test (compression), ϕ load Method/Soil/Condition Resistance Factor All materials 1.0 All Materials Values in Table , but no greater than 0.70 Static Load Test (uplift), ϕ upload All Materials 0.60
36 Intermediate Geo Materials Intermediate Geo Materials (IGMs) For detailed settlement estimation of shafts in IGMs, the procedures provided by O Neill and Reese (1999) should be used. C IGMs are defined by O Neill and Reese (1999) as follows: Cohesive IGM clay shales or mudstones with an S u of 5 to 50 ksf, and Cohesionless granular tills or granular residual soils with N1 60 greater than 50 blows/ft.
37 Intermediate Geo Material (IGM) b Side Resistance q = σ 4.0 for ( b-1) s in which, for sandy soils: for N 60 15: v β = z ( b-2) for N 60 < 15: N 60 β = ( z ) ( b-3) 15 in which, for IGM s: for N 60 50: β = ( z) 0.75 ( b-4)
38 Intermediate Geo Material (IGM) c Tip Resistance for sandy soils: for N 60 < 50: q p = 1.2 N 60 ( c-1) for IGM s: for N 60 50: p 0.8 a q p = 0.59N 60 σv σ ' v ( c-2)
39 Scour Assessment of Rocks Bridges on aggressive steams and waterways
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52 Thank You
Piles Capacity Reference Manual
 Piles Capacity Reference Manual hetge hetge geotechnics on the go Piles Capacity Reference Manual May 22, 2012 Version: PC-1.2.120728b hetge LLC Moscow Virginia Istanbul E info@hetge.com W www.hetge.com
Piles Capacity Reference Manual hetge hetge geotechnics on the go Piles Capacity Reference Manual May 22, 2012 Version: PC-1.2.120728b hetge LLC Moscow Virginia Istanbul E info@hetge.com W www.hetge.com
Case Histories LRFD Procedures for Design of Deep Foundations
 Case Histories LRFD Procedures for Design of Deep Foundations Paul Axtell, P.E. ASCE Geotechnical Conference, Ames, IA March 3, 2011 www.danbrownandassociates.com paxtell@danbrownandassociates.com 913
Case Histories LRFD Procedures for Design of Deep Foundations Paul Axtell, P.E. ASCE Geotechnical Conference, Ames, IA March 3, 2011 www.danbrownandassociates.com paxtell@danbrownandassociates.com 913
DEEP FOUNDATIONS PILES
 DEEP FOUNDATIONS PILES Pile foundation used to support structure when poor quality soil bearing capacity failure excessive settlement piles END BEARING PILES SKIN FRICTION PILES End bearing pile rests
DEEP FOUNDATIONS PILES Pile foundation used to support structure when poor quality soil bearing capacity failure excessive settlement piles END BEARING PILES SKIN FRICTION PILES End bearing pile rests
Module 5 : Design of Deep Foundations. Lecture 20 : Introduction [ Section 20.1 : Introduction ]
![Module 5 : Design of Deep Foundations. Lecture 20 : Introduction [ Section 20.1 : Introduction ] Module 5 : Design of Deep Foundations. Lecture 20 : Introduction [ Section 20.1 : Introduction ]](/thumbs/82/86090197.jpg) Lecture 20 : Introduction [ Section 20.1 : Introduction ] Objectives In this section you will learn the following Introduction Lecture 20 : Introduction [ Section 20.1 : Introduction ] INTRODUCTION The
Lecture 20 : Introduction [ Section 20.1 : Introduction ] Objectives In this section you will learn the following Introduction Lecture 20 : Introduction [ Section 20.1 : Introduction ] INTRODUCTION The
SKIN FRICTION OF PILES COATED WITH BITUMINOUS COATS Makarand G. Khare 1 and Shailesh R. Gandhi 2
 SKIN FRICTION OF PILES COATED WITH BITUMINOUS COATS Makarand G. Khare 1 and Shailesh R. Gandhi 2 1 Ph.D Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Tech. Madras, Chennai, India-600036 Email:
SKIN FRICTION OF PILES COATED WITH BITUMINOUS COATS Makarand G. Khare 1 and Shailesh R. Gandhi 2 1 Ph.D Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Tech. Madras, Chennai, India-600036 Email:
STABILITY. SECURITY. INTEGRITY.
 MODEL 150 HELICAL ANCHOR SYSTEM PN #MBHAT STABILITY. SECURITY. INTEGRITY. 150 Helical Anchor System About Foundation Supportworks is a network of the most experienced and knowledgeable foundation repair
MODEL 150 HELICAL ANCHOR SYSTEM PN #MBHAT STABILITY. SECURITY. INTEGRITY. 150 Helical Anchor System About Foundation Supportworks is a network of the most experienced and knowledgeable foundation repair
Module 9 Lecture 35 to 40 DRILLED-SHAFT AND CAISSON FOUNDATIONS
 Topics Module 9 Lecture 35 to 40 DRILLED-SHAFT AND CAISSON FOUNDATIONS 35.1 INTRODUCTION 35.2 DRILLED SHAFTS 35.3 TYPES OF DRILLED SHAFTS 35.4 CONSTRUCTION PROCEDURES Use of Casings and Drilling Mud Inspection
Topics Module 9 Lecture 35 to 40 DRILLED-SHAFT AND CAISSON FOUNDATIONS 35.1 INTRODUCTION 35.2 DRILLED SHAFTS 35.3 TYPES OF DRILLED SHAFTS 35.4 CONSTRUCTION PROCEDURES Use of Casings and Drilling Mud Inspection
Experimental Study on Pile Groups Settlement and Efficiency in Cohesionless Soil
 Experimental Study on Pile Groups Settlement and Efficiency in Cohesionless Soil Elsamny, M.K. 1, Ibrahim, M.A. 2, Gad S.A. 3 and Abd-Mageed, M.F. 4 1, 2, 3 & 4- Civil Engineering Department Faculty of
Experimental Study on Pile Groups Settlement and Efficiency in Cohesionless Soil Elsamny, M.K. 1, Ibrahim, M.A. 2, Gad S.A. 3 and Abd-Mageed, M.F. 4 1, 2, 3 & 4- Civil Engineering Department Faculty of
transmit foundation loads
 PILES Long, slender members that transmit foundation loads through soil strata of low bearing capacity or through water to deeper soil or rock strata having a high bearing capacity. End bearing piles End
PILES Long, slender members that transmit foundation loads through soil strata of low bearing capacity or through water to deeper soil or rock strata having a high bearing capacity. End bearing piles End
Sixth Cycle Celebration of His Majesty the King of Thailand and 40 th Anniversary of the Asian Institute of Technology
 Under the Royal Patronage of His Majesty King Bhumibol Adulyadej Sixth Cycle Celebration of His Majesty the King of Thailand and 40 th Anniversary of the Asian Institute of Technology Civil and Environmental
Under the Royal Patronage of His Majesty King Bhumibol Adulyadej Sixth Cycle Celebration of His Majesty the King of Thailand and 40 th Anniversary of the Asian Institute of Technology Civil and Environmental
ANALYSIS OF PILE-RAFT FOUNDATIONS NON- RESTED AND DIRECTLY RESTED ON SOIL
 ANALYSIS OF PILE-RAFT FOUNDATIONS NON- RESTED AND DIRECTLY RESTED ON SOIL Elsamny M. Kassem1, Abd EL Samee W. Nashaat2 and Essa. Tasneem.A1 1 Civil Engineering Department, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
ANALYSIS OF PILE-RAFT FOUNDATIONS NON- RESTED AND DIRECTLY RESTED ON SOIL Elsamny M. Kassem1, Abd EL Samee W. Nashaat2 and Essa. Tasneem.A1 1 Civil Engineering Department, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
Information Systems and Artificial Intelligence Technology Applied in Pile Design
 Information Systems and Artificial Intelligence Technology Applied in Pile Design Erhan Burak PANCAR Yapi Isleri ve Teknik Daire Baskanligi Ondokuz Mayıs University Samsun/TURKEY erhanpancar @hotmail.com
Information Systems and Artificial Intelligence Technology Applied in Pile Design Erhan Burak PANCAR Yapi Isleri ve Teknik Daire Baskanligi Ondokuz Mayıs University Samsun/TURKEY erhanpancar @hotmail.com
EXPERIENCES OF HIGH STRAIN DYNAMICS PILE TESTING (HSDPT) IN ACCORDANCE WITH EC7 IN SWEDEN
 EXPERIENCES OF HIGH STRAIN DYNAMICS PILE TESTING (HSDPT) IN ACCORDANCE WITH EC7 IN SWEDEN Mattias Grävare 1, Ingemar Hermansson 1, Thomas Bjerendal 1, Carl-John Grävare 1 1 Pålanalys i Göteborg AB Sweden,
EXPERIENCES OF HIGH STRAIN DYNAMICS PILE TESTING (HSDPT) IN ACCORDANCE WITH EC7 IN SWEDEN Mattias Grävare 1, Ingemar Hermansson 1, Thomas Bjerendal 1, Carl-John Grävare 1 1 Pålanalys i Göteborg AB Sweden,
Dimension Effect on P-y Model Used for Design of Laterally Loaded Piles
 Procedia Engineering Volume 143, 2016, Pages 598 606 Advances in Transportation Geotechnics 3. The 3rd International Conference on Transportation Geotechnics (ICTG 2016) Dimension Effect on P-y Model Used
Procedia Engineering Volume 143, 2016, Pages 598 606 Advances in Transportation Geotechnics 3. The 3rd International Conference on Transportation Geotechnics (ICTG 2016) Dimension Effect on P-y Model Used
Embedded Data Collectors
 Florida Experience with Embedded Data Collectors Rodrigo Herrera, PE Florida Department of Transportation Asst. State Geotechnical Engineer July 25, 2013 Embedded Data Collectors Rodrigo Herrera, PE FDOT
Florida Experience with Embedded Data Collectors Rodrigo Herrera, PE Florida Department of Transportation Asst. State Geotechnical Engineer July 25, 2013 Embedded Data Collectors Rodrigo Herrera, PE FDOT
Helical Pier Frequently Asked Questions
 Helical Pier Basics Q: What is a Helical Pier? A: A helical pier or pile is an extendable deep foundation system with helical bearing plates welded to a central steel shaft. Load is transferred from the
Helical Pier Basics Q: What is a Helical Pier? A: A helical pier or pile is an extendable deep foundation system with helical bearing plates welded to a central steel shaft. Load is transferred from the
DENTAL IMPLANT NUMERICAL MODELING USING PILE MODLEING SCHEME IN CIVIL ENGINEERING FIELD
 VI International Conference on Computational Bioengineering ICCB 2015 M. Cerrolaza and S.Oller (Eds) DENTAL IMPLANT NUMERICAL MODELING USING PILE MODLEING SCHEME IN CIVIL ENGINEERING FIELD YUN MOOK LIM
VI International Conference on Computational Bioengineering ICCB 2015 M. Cerrolaza and S.Oller (Eds) DENTAL IMPLANT NUMERICAL MODELING USING PILE MODLEING SCHEME IN CIVIL ENGINEERING FIELD YUN MOOK LIM
INFLUENCE OF PILES ON LOAD- SETTLEMENT BEHAVIOUR OF RAFT FOUNDATION
 INFLUENCE OF PILES ON LOAD- SETTLEMENT BEHAVIOUR OF RAFT FOUNDATION BALESHWAR SINGH Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 78139, India NINGOMBAM THOIBA SINGH
INFLUENCE OF PILES ON LOAD- SETTLEMENT BEHAVIOUR OF RAFT FOUNDATION BALESHWAR SINGH Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 78139, India NINGOMBAM THOIBA SINGH
SCOUR: EVALUATION AND RIPRAP. John G. Delphia, P.E. TxDOT Bridge Division Geotechnical Branch
 SCOUR: EVALUATION AND RIPRAP John G. Delphia, P.E. TxDOT Bridge Division Geotechnical Branch IMPORTANCE OF SCOUR The most common cause of bridge failures is from floods scouring bed material from around
SCOUR: EVALUATION AND RIPRAP John G. Delphia, P.E. TxDOT Bridge Division Geotechnical Branch IMPORTANCE OF SCOUR The most common cause of bridge failures is from floods scouring bed material from around
Some Innovations for Offshore and Harbor Berths Construction
 Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 5 (2015) 115-122 10.17265/2159-5879/2015.03.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Some Innovations for Offshore and Harbor Berths Construction Doubrovsky Michael 1, Kaluzhnaya
Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 5 (2015) 115-122 10.17265/2159-5879/2015.03.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Some Innovations for Offshore and Harbor Berths Construction Doubrovsky Michael 1, Kaluzhnaya
With time, the evolution of anchors have led to different designs More than one anchor type may be suitable for a particular purpose Thus there are
 Supreme range of Soil & rock anchors Introduction Used to anchor into concrete, masonry, stone With time, the evolution of anchors have led to different designs More than one anchor type may be suitable
Supreme range of Soil & rock anchors Introduction Used to anchor into concrete, masonry, stone With time, the evolution of anchors have led to different designs More than one anchor type may be suitable
Title. Author(s) P. WULANDARI. Issue Date Doc URLhttp://hdl.handle.net/2115/ Type. Note. File Information AND ANALYTICAL METHODS
 Title ANALYSIS OF PILED RAFT FOUNDATIONS IN CLAYEY S AND ANALYTICAL METHODS Author(s) P. WULANDARI Issue Date 2013-09-11 Doc URLhttp://hdl.handle.net/2115/54231 Type proceedings Note The Thirteenth East
Title ANALYSIS OF PILED RAFT FOUNDATIONS IN CLAYEY S AND ANALYTICAL METHODS Author(s) P. WULANDARI Issue Date 2013-09-11 Doc URLhttp://hdl.handle.net/2115/54231 Type proceedings Note The Thirteenth East
SImulation of MONopile installation - JIP SIMON
 SImulation of MONopile installation - JIP SIMON Ahmed Elkadi Deltares 14 February 2019 MOTIVATION Vanbeekimages.com 14 februari 2019 Matchmaking Day 2019 2 Global substructure statistics/trends 2016 Offshore
SImulation of MONopile installation - JIP SIMON Ahmed Elkadi Deltares 14 February 2019 MOTIVATION Vanbeekimages.com 14 februari 2019 Matchmaking Day 2019 2 Global substructure statistics/trends 2016 Offshore
Pile Driving Homework Quiz Questions Transcript
 Pile Driving Homework Quiz Questions Transcript In this section there are additional exercises and questions that will help you prepare for the exam. In a classroom environment these exercises may be assigned
Pile Driving Homework Quiz Questions Transcript In this section there are additional exercises and questions that will help you prepare for the exam. In a classroom environment these exercises may be assigned
Geotechnical Investigation November 2016 Kampala, Uganda 02-JUN-16
 07-10 November 2016 Kampala, Uganda 02-JUN-16 This course is Designed, Developed, and will be Delivered under ISO 29990:2010 Standards & ISO 9001:2015 Why Choose this Training Course? What are the Goals?
07-10 November 2016 Kampala, Uganda 02-JUN-16 This course is Designed, Developed, and will be Delivered under ISO 29990:2010 Standards & ISO 9001:2015 Why Choose this Training Course? What are the Goals?
Comparison of the Behavior for Free Standing Pile Group and Piles of Piled Raft
 Engineering and Technology Journal Vol. 36, Part A, No.4, 218 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.3684/etj.36.4a.3 Awf A. Al-Kaisi Building & Const. Eng. Dept. University of Technology, Baghdad, Iraq Comparison of
Engineering and Technology Journal Vol. 36, Part A, No.4, 218 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.3684/etj.36.4a.3 Awf A. Al-Kaisi Building & Const. Eng. Dept. University of Technology, Baghdad, Iraq Comparison of
Investigation of the Behavior of Piled Raft Foundations in Sand by Numerical Modeling
 Investigation of the Behavior of Piled Raft Foundations in Sand by Numerical Modeling Author Oh, Erwin, Bui, Quan-Minh, Surarak, Chanaton, Balasubramaniam, Bala Published 29 Conference Title Proceedings
Investigation of the Behavior of Piled Raft Foundations in Sand by Numerical Modeling Author Oh, Erwin, Bui, Quan-Minh, Surarak, Chanaton, Balasubramaniam, Bala Published 29 Conference Title Proceedings
ISO 29990:2010 Standards
 07-10 November 2016 Kampala, Uganda 24-MAR-16 This course is Designed, Developed, and will be Delivered under ISO 29990:2010 Standards Why Choose this Course? What are the Goals? This training course provides
07-10 November 2016 Kampala, Uganda 24-MAR-16 This course is Designed, Developed, and will be Delivered under ISO 29990:2010 Standards Why Choose this Course? What are the Goals? This training course provides
Effect of Pile Bending Stiffness on Static Lateral Behavior of a Short Monopile in Dry Sand
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COASTAL & OFFSHORE ENGINEERING JCOE No. 5/ Winter 217 (25-32) Effect of Pile Bending Stiffness on Static Lateral Behavior of a Short Monopile in Dry Sand Saeed Darvishi Alamouti
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COASTAL & OFFSHORE ENGINEERING JCOE No. 5/ Winter 217 (25-32) Effect of Pile Bending Stiffness on Static Lateral Behavior of a Short Monopile in Dry Sand Saeed Darvishi Alamouti
This document is a preview generated by EVS
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 19901-4 Second edition 2016-07-15 Petroleum and natural gas industries Specific requirements for offshore structures Part 4: Geotechnical and foundation design considerations
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 19901-4 Second edition 2016-07-15 Petroleum and natural gas industries Specific requirements for offshore structures Part 4: Geotechnical and foundation design considerations
Numerical simulation of screw piles under axial loads in a cohesive soil
 Numerical simulation of screw piles under axial loads in a cohesive soil Yan Cui EBA Engineering Consultants Ltd., Nanaimo, British Columbia, Canada Steve D Zou Dept of Civil and Resource Engineering Dalhousie
Numerical simulation of screw piles under axial loads in a cohesive soil Yan Cui EBA Engineering Consultants Ltd., Nanaimo, British Columbia, Canada Steve D Zou Dept of Civil and Resource Engineering Dalhousie
Parametric Study on Piled Raft Foundation in Sand Using Numerical Modelling
 Parametric Study on Piled Raft Foundation in Using Numerical Modelling Author Oh, Erwin, Bui, Quan-Minh, Surarak, Chanaton, Adamec, Richard, Balasubramaniam, Bala Published 28 Conference Title Futures
Parametric Study on Piled Raft Foundation in Using Numerical Modelling Author Oh, Erwin, Bui, Quan-Minh, Surarak, Chanaton, Adamec, Richard, Balasubramaniam, Bala Published 28 Conference Title Futures
METHODOLOGY TO DEMONSTRATE PILE CAPACITY IN RELAXING GROUND
 286 METHODOLOGY TO DEMONSTRATE PILE CAPACITY IN RELAXING GROUND T. A. Peiris 1, B. Morris 2, R. Kelly 1, K. Chan 3 1 Coffey Geotechnics, Sydney, Australia 1 E-mail: Ashok.Peiris@leicon.com.au, Ashok_Peiris@coffey.com
286 METHODOLOGY TO DEMONSTRATE PILE CAPACITY IN RELAXING GROUND T. A. Peiris 1, B. Morris 2, R. Kelly 1, K. Chan 3 1 Coffey Geotechnics, Sydney, Australia 1 E-mail: Ashok.Peiris@leicon.com.au, Ashok_Peiris@coffey.com
The DFI Institute is organized to serve as a primary means through which members of the Institute may participate in improvement of the planning,
 The DFI Institute is organized to serve as a primary means through which members of the Institute may participate in improvement of the planning, design and construction aspects of deep foundations and
The DFI Institute is organized to serve as a primary means through which members of the Institute may participate in improvement of the planning, design and construction aspects of deep foundations and
INTERPRETATION OF SCREW PILE LOAD TEST DATA USING EXTRAPOLATION METHOD IN DENSE SAND
 Geotech., Const. Mat. and Env., ISSN: 2186-2982(P), 2186-2990(O), Japan INTERPRETATION OF SCREW PILE LOAD TEST DATA USING EXTRAPOLATION METHOD IN DENSE SAND Adnan Anwar Malik 1, Jiro Kuwano 2, Shinya Tachibana
Geotech., Const. Mat. and Env., ISSN: 2186-2982(P), 2186-2990(O), Japan INTERPRETATION OF SCREW PILE LOAD TEST DATA USING EXTRAPOLATION METHOD IN DENSE SAND Adnan Anwar Malik 1, Jiro Kuwano 2, Shinya Tachibana
NALYSIS OF STABILIZING SLOPES USING VERTICAL PILES
 NALYSIS OF STABILIZING SLOPES USING VERTICAL PILES Mahmoud S. Abdelbaki: Lecturer, Gehan E. Abdelrahman: Lecturer, Youssef G. Youssef :Assis.Lecturer, Civil Eng. Dep., Faculty of Eng., Cairo University,
NALYSIS OF STABILIZING SLOPES USING VERTICAL PILES Mahmoud S. Abdelbaki: Lecturer, Gehan E. Abdelrahman: Lecturer, Youssef G. Youssef :Assis.Lecturer, Civil Eng. Dep., Faculty of Eng., Cairo University,
Effect of Tie Beam Dimensions on Vertical and Horizontal Displacement of Isolated Footing
 http:// Effect of Tie Beam Dimensions on Vertical and Horizontal Displacement of Isolated Footing El-samny, M.K. (1), Ezz-Eldeen, H.A. (1), Elbatal, S.A. (1) and Kamar,A.M. (2) (1) Al-Azhar University,
http:// Effect of Tie Beam Dimensions on Vertical and Horizontal Displacement of Isolated Footing El-samny, M.K. (1), Ezz-Eldeen, H.A. (1), Elbatal, S.A. (1) and Kamar,A.M. (2) (1) Al-Azhar University,
Safety Concepts and Calibration of Partial Factors in European. and North American Codes of Practice. 30/11 01/12/2011, TU Delft, The Netherlands
 Safety Concepts and Calibration of Partial Factors in European and North American Codes of Practice 30/11 01/12/2011, TU Delft, The Netherlands The objective of this workshop was to transfer knowledge
Safety Concepts and Calibration of Partial Factors in European and North American Codes of Practice 30/11 01/12/2011, TU Delft, The Netherlands The objective of this workshop was to transfer knowledge
FB-PIER VALIDATION SET
 FB-PIER VALIDATION SET Dynamics February 2004 FB-Pier Dynamics Validation Manual 1 Example 1 Single Pile Subject to a Pulse Load at the Pile Head Problem: The single 24 square prestressed concrete pile
FB-PIER VALIDATION SET Dynamics February 2004 FB-Pier Dynamics Validation Manual 1 Example 1 Single Pile Subject to a Pulse Load at the Pile Head Problem: The single 24 square prestressed concrete pile
Application of Advanced Materials and New Detailing for ABC Column Connections
 Application of Advanced Materials and New Detailing for ABC Column Connections Mostafa Tazarv, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering South Dakota State University (SDSU)
Application of Advanced Materials and New Detailing for ABC Column Connections Mostafa Tazarv, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering South Dakota State University (SDSU)
ENGINEERING JUDGMENT IN THE EVOLUTION FROM DETERMINISTIC TO RELIABILITY-BASED FOUNDATION DESIGN
 Proceedings of Uncertainty 96, Uncertainty in the Geologic Environment - From Theory to Practice (GSP 58), Eds. C. D. Shackelford, P. P. Nelson & M. J. S. Roth, ASCE, New York, 1996 ENGINEERING JUDGMENT
Proceedings of Uncertainty 96, Uncertainty in the Geologic Environment - From Theory to Practice (GSP 58), Eds. C. D. Shackelford, P. P. Nelson & M. J. S. Roth, ASCE, New York, 1996 ENGINEERING JUDGMENT
Integrity testing of a very large number of piles
 Integrity testing of a very large number of piles Klingmueller, O. & Mayer, C. GSP mbh, Mannheim Germany Keywords: low- strain integrity testing, classification system, coring, wave velocity ABSTRACT:
Integrity testing of a very large number of piles Klingmueller, O. & Mayer, C. GSP mbh, Mannheim Germany Keywords: low- strain integrity testing, classification system, coring, wave velocity ABSTRACT:
VIBRATIONAL TESTING OF A FULL-SCALE PILE GROUP IN SOFT CLAY
 VIBRATIONAL TESTING OF A FULL-SCALE PILE GROUP IN SOFT CLAY Marvin W HALLING 1, Kevin C WOMACK 2, Ikhsan MUHAMMAD 3 And Kyle M ROLLINS 4 SUMMARY A 3 x 3 pile group and pile cap were constructed in a soft
VIBRATIONAL TESTING OF A FULL-SCALE PILE GROUP IN SOFT CLAY Marvin W HALLING 1, Kevin C WOMACK 2, Ikhsan MUHAMMAD 3 And Kyle M ROLLINS 4 SUMMARY A 3 x 3 pile group and pile cap were constructed in a soft
European Technical Assessment ETA 15/0029 of 12/06/2017
 RISE Research Institutes of Sweden AB RISE Certifiering Box 553 SE-371 23 Karlskrona Sweden Member of www.eota.eu Tel: +46 10 516 63 00 Web: www.ri.se Mail: certifiering@ri.se European of 12/06/2017 General
RISE Research Institutes of Sweden AB RISE Certifiering Box 553 SE-371 23 Karlskrona Sweden Member of www.eota.eu Tel: +46 10 516 63 00 Web: www.ri.se Mail: certifiering@ri.se European of 12/06/2017 General
Piled raft foundation for the W-TOWER Tel Aviv
 Piled raft foundation for the W-TOWER Tel Aviv Prepared by A. Lehrer, S. Bar. 1. Introduction. Development of the world's largest cities dictated the need for high building housing in different soil conditions,
Piled raft foundation for the W-TOWER Tel Aviv Prepared by A. Lehrer, S. Bar. 1. Introduction. Development of the world's largest cities dictated the need for high building housing in different soil conditions,
Perma-Column Design and Use Guide for PC6300, PC6400, PC6600, PC8300, and PC8400 Models
 Perma-Column Design and Use Guide for PC6300, PC6400, PC6600, PC300, and PC400 Models by Brent Leatherman, P.E. Timber Tech Engineering, Inc E-Mail: bl@timbertecheng.com April 1, 2005 East: 22 Denver Road,
Perma-Column Design and Use Guide for PC6300, PC6400, PC6600, PC300, and PC400 Models by Brent Leatherman, P.E. Timber Tech Engineering, Inc E-Mail: bl@timbertecheng.com April 1, 2005 East: 22 Denver Road,
Perma-Column Design and Use Guide for PC6300, PC6400, PC6600, PC8300, and PC8400 Models
 Perma-Column Design and Use Guide for PC6300, PC6400, PC6600, PC300, and PC400 Models by Brent Leatherman, P.E. Timber Tech Engineering, Inc E-Mail: bl@timbertecheng.com April 1, 2005 East: 22 Denver Road,
Perma-Column Design and Use Guide for PC6300, PC6400, PC6600, PC300, and PC400 Models by Brent Leatherman, P.E. Timber Tech Engineering, Inc E-Mail: bl@timbertecheng.com April 1, 2005 East: 22 Denver Road,
Manual. Pile Design [NEN method]
![Manual. Pile Design [NEN method] Manual. Pile Design [NEN method]](/thumbs/75/72745348.jpg) Manual Pile Design [NEN method] The information contained in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part of this document may be reproduced, transmitted or stored in a data retrieval
Manual Pile Design [NEN method] The information contained in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part of this document may be reproduced, transmitted or stored in a data retrieval
B422 - PRECAST REINFORCED CONCRETE BOX CULVERTS AND BOX SEWERS - OPSS 422
 B422 - PRECAST REINFORCED CONCRETE BOX CULVERTS AND BOX SEWERS - OPSS 422 422.1 GENERAL The work under these tender items consists of the fabrication and installation in open cut of precast reinforced
B422 - PRECAST REINFORCED CONCRETE BOX CULVERTS AND BOX SEWERS - OPSS 422 422.1 GENERAL The work under these tender items consists of the fabrication and installation in open cut of precast reinforced
Finite Element Study of Using Concrete Tie Beams to Reduce Differential Settlement Between Footings
 Finite Element Study of Using Concrete Tie Beams to Reduce Differential Settlement Between Footings AMIN H. ALMASRI* AND ZIAD N. TAQIEDDIN** *Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Jordan
Finite Element Study of Using Concrete Tie Beams to Reduce Differential Settlement Between Footings AMIN H. ALMASRI* AND ZIAD N. TAQIEDDIN** *Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Jordan
Interference Fits Interference Fits Reference Lecture 15 Notes
 Interference Fits Interference Fits Hole is undersized and part is heated to allow it to slide over shaft. Compressive interface pressure develops when part cools. Reference Lecture 15 Notes. Keys and
Interference Fits Interference Fits Hole is undersized and part is heated to allow it to slide over shaft. Compressive interface pressure develops when part cools. Reference Lecture 15 Notes. Keys and
Module 10 : Improvement of rock mass responses. Content
 IMPROVEMENT OF ROCK MASS RESPONSES Content 10.1 INTRODUCTION 10.2 ROCK REINFORCEMENT Rock bolts, dowels and anchors 10.3 ROCK BOLTING MECHANICS Suspension theory Beam building theory Keying theory 10.4
IMPROVEMENT OF ROCK MASS RESPONSES Content 10.1 INTRODUCTION 10.2 ROCK REINFORCEMENT Rock bolts, dowels and anchors 10.3 ROCK BOLTING MECHANICS Suspension theory Beam building theory Keying theory 10.4
Simplified analysis of timber rivet connections
 Simplified analysis of timber rivet connections Stahl, Douglas C., 1 Begel, Marshall, 2 and Wolfe, Ronald W. 3 ABSTRACT Timber rivets, fasteners for glulam and heavy timber construction, have been used
Simplified analysis of timber rivet connections Stahl, Douglas C., 1 Begel, Marshall, 2 and Wolfe, Ronald W. 3 ABSTRACT Timber rivets, fasteners for glulam and heavy timber construction, have been used
CIVIL CONSTRUCTION PRODUCT CATALOG VOL. I
 CIVIL CONSTRUCTION PRODUCT CATALOG VOL. I Table of Contents Section Description A page CHANCE Helical Round Corner Square Shaft Products Introduction to Round and Square Shaft 3 Square Shaft (SS) Product
CIVIL CONSTRUCTION PRODUCT CATALOG VOL. I Table of Contents Section Description A page CHANCE Helical Round Corner Square Shaft Products Introduction to Round and Square Shaft 3 Square Shaft (SS) Product
Synopsis. Civil Engineering Construction Chapter 3 TYPES OF FOUNDATIONS 7/22/2011. Deep Foundation. 1. Shallow foundations. 2.
 Synopsis Civil Engineering Construction Chapter 3 Introduction to substructure: foundation and piles. Deep Foundation Dr Mohamad Syazli Fathi Department of Civil Engineering UTM RAZAK School of Engineering
Synopsis Civil Engineering Construction Chapter 3 Introduction to substructure: foundation and piles. Deep Foundation Dr Mohamad Syazli Fathi Department of Civil Engineering UTM RAZAK School of Engineering
Curriculum Vitae: Academic and Practical Experience. Married and have four children
 Curriculum Vitae: Academic and Practical Experience 1- Personality data: Name Abdel-Aziz Ahmed Ali Hassan Date of Birth 28/7/1964 Position Status Address Tel. Associate professor Married and have four
Curriculum Vitae: Academic and Practical Experience 1- Personality data: Name Abdel-Aziz Ahmed Ali Hassan Date of Birth 28/7/1964 Position Status Address Tel. Associate professor Married and have four
GENERAL NOTES ABBREVIATIONS DRAWING THEME STRUCTURAL DRAWING LIST SUBMITTALS S101 GENERAL NOTES SOUTH DYKE RIVERFRONT WALKWAY
 GENERAL NOTES ABBREVIATIONS DRAWING THEME SUBMITTALS STRUCTURAL DRAWING LIST GENERAL NOTES S0 LETTERS OF ASSURANCE TENDER DOCUMENTS DESIGN BY CONTRACTORS TEMPORARY AND ANCILLARY WORKS AND SITE SAFETY FIELD
GENERAL NOTES ABBREVIATIONS DRAWING THEME SUBMITTALS STRUCTURAL DRAWING LIST GENERAL NOTES S0 LETTERS OF ASSURANCE TENDER DOCUMENTS DESIGN BY CONTRACTORS TEMPORARY AND ANCILLARY WORKS AND SITE SAFETY FIELD
Construction Tolerances - The following tolerances apply to cast-in-place structures:
 00540.40(b) Construction 00540.40 Tolerances - The following tolerances apply to cast-in-place structures: (a) Foundation Footings: (1) Lateral Alignment: Actual (as cast) location of the center of gravity:
00540.40(b) Construction 00540.40 Tolerances - The following tolerances apply to cast-in-place structures: (a) Foundation Footings: (1) Lateral Alignment: Actual (as cast) location of the center of gravity:
Connection Philosophy. p NDS Chapter-by-chapter description Changes from previous editions Examples. Part 1: Member Design Webinar.
 Outline ASD and LRFD with the 2005 NDS Part 2 Connection Design Presented by: John Buddy Showalter, P.E. Vice President, Technology Transfer Connection philosophy p NDS Chapter-by-chapter description Changes
Outline ASD and LRFD with the 2005 NDS Part 2 Connection Design Presented by: John Buddy Showalter, P.E. Vice President, Technology Transfer Connection philosophy p NDS Chapter-by-chapter description Changes
BER Case 95-5 Approved December 7, 1995 FAILURE TO INCLUDE INFORMATION IN ENGINEERING REPORT
 Approved December 7, 1995 II.3.a. II.3.b. II.3.c. III.1.a. III.1.b. III.1.f. III.3.a. FACTS: FAILURE TO INCLUDE INFORMATION IN ENGINEERING REPORT Engineer A was retained by a municipality to design a dock
Approved December 7, 1995 II.3.a. II.3.b. II.3.c. III.1.a. III.1.b. III.1.f. III.3.a. FACTS: FAILURE TO INCLUDE INFORMATION IN ENGINEERING REPORT Engineer A was retained by a municipality to design a dock
3. Existing uncertainties
 Fig. 1. Cumulative and annual offshore wind installations [1]. sector, some uncertainties have not been identified yet; these will be discussed in the paper with the aim of achieving an adequate and sustainable
Fig. 1. Cumulative and annual offshore wind installations [1]. sector, some uncertainties have not been identified yet; these will be discussed in the paper with the aim of achieving an adequate and sustainable
1. Enumerate the most commonly used engineering materials and state some important properties and their engineering applications.
 Code No: R05310305 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Production Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks:
Code No: R05310305 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Production Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks:
SEA SELF DRILLING, THREADED, HOLLOW BAR / GROUT-ABLE SOIL NAILS / ANCHORS
 SEA SELF DRILLING, THREADED, HOLLOW BAR / GROUT-ABLE SOIL NAILS / ANCHORS THE SEA SYSTEM SEA hollow T threaded bar Rock Anchors / Soil Nails provide the ultimate solution for securing unstable embankments
SEA SELF DRILLING, THREADED, HOLLOW BAR / GROUT-ABLE SOIL NAILS / ANCHORS THE SEA SYSTEM SEA hollow T threaded bar Rock Anchors / Soil Nails provide the ultimate solution for securing unstable embankments
Settlement Analysis of Piled Raft System in Soft Stratified Soils
 Settlement Analysis of Piled Raft System in Soft Stratified Soils Srinivasa Reddy Ayuluri 1, Dr. M. Kameswara Rao 2 1 (PG Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, Malla Reddy Engineering College, Hyderabad,
Settlement Analysis of Piled Raft System in Soft Stratified Soils Srinivasa Reddy Ayuluri 1, Dr. M. Kameswara Rao 2 1 (PG Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, Malla Reddy Engineering College, Hyderabad,
Numerical Modeling of Grouted Soil Nails
 Numerical Modeling of Grouted Soil Nails Dr. Haider S. Al -Jubair Department of Civil Engineering University of Basrah-College of Engineering Basrah, Iraq Afaf A. Maki Department of Civil Engineering University
Numerical Modeling of Grouted Soil Nails Dr. Haider S. Al -Jubair Department of Civil Engineering University of Basrah-College of Engineering Basrah, Iraq Afaf A. Maki Department of Civil Engineering University
Welded connections Welded connections are basically the same design in AISI as in AISC. Minor differences are present and outlined below.
 Cold-Formed Steel Design for the Student E. CONNECTIONS AND JOINTS E1 General Provisions Connections shall be designed to transmit the maximum design forces acting on the connected members. Proper regard
Cold-Formed Steel Design for the Student E. CONNECTIONS AND JOINTS E1 General Provisions Connections shall be designed to transmit the maximum design forces acting on the connected members. Proper regard
Moment Resisting Connections for Load Bearing Walls
 PRECAST: MOMENT RESISTING CONNECTIONS Moment Resisting Connections for Load Bearing Walls Manish Khandelwal Sr. Structural Engineer, Building Structures, Sweco India Private Limited Design philosophy for
PRECAST: MOMENT RESISTING CONNECTIONS Moment Resisting Connections for Load Bearing Walls Manish Khandelwal Sr. Structural Engineer, Building Structures, Sweco India Private Limited Design philosophy for
Limit Equilibrium including Shear Capacity for Launched Soil Nails. Matthew Birchmier, P.E.
 Limit Equilibrium including Shear Capacity for Launched Soil Nails Matthew Birchmier, P.E. The Soil Nail Launcher Declassified British Military Cannon modified to Launch Soil Nails War on shallow landslides
Limit Equilibrium including Shear Capacity for Launched Soil Nails Matthew Birchmier, P.E. The Soil Nail Launcher Declassified British Military Cannon modified to Launch Soil Nails War on shallow landslides
Research on Deformation of Soil Nailing Structure with Flexible Facing
 2017 International Conference on Transportation Infrastructure and Materials (ICTIM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-442-4 Research on Deformation of Soil Nailing Structure with Flexible Facing Tao Sun 1, Yanfeng
2017 International Conference on Transportation Infrastructure and Materials (ICTIM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-442-4 Research on Deformation of Soil Nailing Structure with Flexible Facing Tao Sun 1, Yanfeng
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17610 15116 4 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17610 15116 4 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
Appendix C Construction Details
 7172 Kennedy Road Warrenton, Virginia 20187 Appendix C Construction Details November 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS THRUST BLOCKS Anchorage for 11 1/4 o, 22 1/2 o & 45 o Upper Vertical Bends... AV 01 Buttresses
7172 Kennedy Road Warrenton, Virginia 20187 Appendix C Construction Details November 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS THRUST BLOCKS Anchorage for 11 1/4 o, 22 1/2 o & 45 o Upper Vertical Bends... AV 01 Buttresses
Load-Displacement behavior of passive piles in cohesive soils
 3 r d International Conference on New Developments in Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Load-Displacement behavior of passive piles in cohesive soils Mehmet Rifat Kahyaoğlu Asst.Prof.Dr., Muğla
3 r d International Conference on New Developments in Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Load-Displacement behavior of passive piles in cohesive soils Mehmet Rifat Kahyaoğlu Asst.Prof.Dr., Muğla
1. ANSI/ASME Standard B , Square and Hex Bolts and Screws, Inch Series
 SECTION 31 66 13 HELICAL PILES AND HELICAL ANCHORS PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION A. This work pertains to furnishing and installing Helical Piles and Bracket Assemblies shown in the Contract in accordance
SECTION 31 66 13 HELICAL PILES AND HELICAL ANCHORS PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION A. This work pertains to furnishing and installing Helical Piles and Bracket Assemblies shown in the Contract in accordance
This document downloaded from vulcanhammer.net vulcanhammer.info Chet Aero Marine
 This document downloaded from vulcanhammer.net vulcanhammer.info Chet Aero Marine Don t forget to visit our companion site http://www.vulcanhammer.org Use subject to the terms and conditions of the respective
This document downloaded from vulcanhammer.net vulcanhammer.info Chet Aero Marine Don t forget to visit our companion site http://www.vulcanhammer.org Use subject to the terms and conditions of the respective
Continuing Education. Michelle Kam-Biron, S.E. Wood Products Council WoodWorks!
 WOOD CONNECTIONS II Michelle Kam-Biron, S.E. Wood Products Council WoodWorks! Continuing Education Wood Products Council is a Registered Provider with The American Institute of Architects Continuing Education
WOOD CONNECTIONS II Michelle Kam-Biron, S.E. Wood Products Council WoodWorks! Continuing Education Wood Products Council is a Registered Provider with The American Institute of Architects Continuing Education
James Luebke, PE Structural Development Engineer WisDOT Bureau of Structures
 James Luebke, PE Structural Development Engineer WisDOT Bureau of Structures 1 Highlights WisDOT s ABC Development of PBES Piers Road of Development, Implementation, and Institutionalization Lessons Learned
James Luebke, PE Structural Development Engineer WisDOT Bureau of Structures 1 Highlights WisDOT s ABC Development of PBES Piers Road of Development, Implementation, and Institutionalization Lessons Learned
Helical News. Welcome to ISHF NEWSLETTER OF THE INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR HELICAL FOUNDATIONS. January, Volume 1, Issue 1
 NEWSLETTER OF THE INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR HELICAL FOUNDATIONS Helical News Volume 1, Issue 1 January, 011 Welcome to ISHF Inside this issue: Catalog New Publications in 010 News Items 4 History Lesson
NEWSLETTER OF THE INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR HELICAL FOUNDATIONS Helical News Volume 1, Issue 1 January, 011 Welcome to ISHF Inside this issue: Catalog New Publications in 010 News Items 4 History Lesson
Double rotary drilling
 Double rotary drilling The ideal drilling machine for double rotary drilling 1 basic machine 1 drive 3 drilling methods Flushing head Sliding cylinder for relative adjustment Gear I Gear II Sheave head
Double rotary drilling The ideal drilling machine for double rotary drilling 1 basic machine 1 drive 3 drilling methods Flushing head Sliding cylinder for relative adjustment Gear I Gear II Sheave head
British Columbia Carpenter Apprenticeship Program
 British Columbia Carpenter Apprenticeship Program Level 2 Line G Competency G-8 Use Pile Foundations and Shoring 7960003564 Ordering Crown Publications, Queen s Printer PO Box 9452 Stn Prov Govt 563 Superior
British Columbia Carpenter Apprenticeship Program Level 2 Line G Competency G-8 Use Pile Foundations and Shoring 7960003564 Ordering Crown Publications, Queen s Printer PO Box 9452 Stn Prov Govt 563 Superior
Foundation Specifications for 5.6-Meter Modular Earth Station Antennas
 Installation Instructions Bulletin 237029 Foundation Specifications for 5.6-Meter Modular Earth Station Antennas Revision A Introduction This document specifies typical foundation characteristics, designs,
Installation Instructions Bulletin 237029 Foundation Specifications for 5.6-Meter Modular Earth Station Antennas Revision A Introduction This document specifies typical foundation characteristics, designs,
INDEX PAGE RELEASE SECTION NUMBER DATE
 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS For Wind Zone 1 (other Wind Zones available on request) Version 11/20/2002 INDEX PAGE RELEASE SECTION NUMBER DATE Approval INTRODUCTION 2 2/26/2001 GENERAL INSTALLATION 3 2/26/2001
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS For Wind Zone 1 (other Wind Zones available on request) Version 11/20/2002 INDEX PAGE RELEASE SECTION NUMBER DATE Approval INTRODUCTION 2 2/26/2001 GENERAL INSTALLATION 3 2/26/2001
PART MATERIALS. Section Fencing Materials. Description
 PART 03000 - MATERIALS Section 03010 - Fencing Materials Description 03010.00 Scope - This section consists of the test requirements, specifications and tolerances for barbed wire, woven wire and chain
PART 03000 - MATERIALS Section 03010 - Fencing Materials Description 03010.00 Scope - This section consists of the test requirements, specifications and tolerances for barbed wire, woven wire and chain
INSTALLATION GUIDE PermaTrak. Patented Product: U.S. Patent #5,906,084 #8,302,362 #8,522,505 #8,839,588 #9,096,975
 INSTALLATION GUIDE 2009-2017 PermaTrak. Patented Product: U.S. Patent #5,906,084 #8,302,362 #8,522,505 #8,839,588 #9,096,975 Table of Contents Project Overview Forward, Acceptability Criteria, Safety,
INSTALLATION GUIDE 2009-2017 PermaTrak. Patented Product: U.S. Patent #5,906,084 #8,302,362 #8,522,505 #8,839,588 #9,096,975 Table of Contents Project Overview Forward, Acceptability Criteria, Safety,
Foundation Specifications for 7.6-Meter Modular Earth Station Antennas
 Installation Instructions Foundation Specifications for 7.6-Meter Modular Earth Station Antennas Bulletin 237186A Revision A Introduction This document specifies typical foundation characteristics, designs,
Installation Instructions Foundation Specifications for 7.6-Meter Modular Earth Station Antennas Bulletin 237186A Revision A Introduction This document specifies typical foundation characteristics, designs,
Ground Improvement Prof. G. L. Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. Lecture No.
 Ground Improvement Prof. G. L. Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 33 Soil Nailing So, what I do is, now I talk about soil nail wall. This
Ground Improvement Prof. G. L. Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 33 Soil Nailing So, what I do is, now I talk about soil nail wall. This
Design of structural connections for precast concrete buildings
 BE2008 Encontro Nacional Betão Estrutural 2008 Guimarães 5, 6, 7 de Novembro de 2008 Design of structural connections for precast concrete buildings Björn Engström 1 ABSTRACT A proper design of structural
BE2008 Encontro Nacional Betão Estrutural 2008 Guimarães 5, 6, 7 de Novembro de 2008 Design of structural connections for precast concrete buildings Björn Engström 1 ABSTRACT A proper design of structural
Appendix A. Steel Deck Details & Calculations
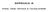 Appendix A Steel Deck Details & Calculations Composite Steel Deck Load Calculations: DL = 45 psf LL = 100 psf TL = 1.(45)+1.6(100) = 14 psf Total slab depth = 4 + 1.5 = 5.5 Slab Reinforcing: 4 Slab w/
Appendix A Steel Deck Details & Calculations Composite Steel Deck Load Calculations: DL = 45 psf LL = 100 psf TL = 1.(45)+1.6(100) = 14 psf Total slab depth = 4 + 1.5 = 5.5 Slab Reinforcing: 4 Slab w/
363. Fellenius, B.H., The unified design of piled foundations. The Sven Hansbo Lecture. Geotechnics for Sustainable Infrastructure Development
 363. Fellenius, B.H., 216. The unified design of piled foundations. The Sven Hansbo Lecture. Geotechnics for Sustainable Infrastructure Development Geotec Hanoi 216, edited by Phung Duc Long, Hanoi, November
363. Fellenius, B.H., 216. The unified design of piled foundations. The Sven Hansbo Lecture. Geotechnics for Sustainable Infrastructure Development Geotec Hanoi 216, edited by Phung Duc Long, Hanoi, November
GT4800 Ground Vibration Measurements near Impact Pile Driving
 GT4800 Ground Vibration Measurements near Impact Pile Driving Athina Grizi, S.M. ASCE 1, Adda Athanasopoulos-Zekkos, A.M. ASCE 2 and Richard D. Woods, P.E., D.GE, Dist.M. ASCE 3 Abstract: Pile driving
GT4800 Ground Vibration Measurements near Impact Pile Driving Athina Grizi, S.M. ASCE 1, Adda Athanasopoulos-Zekkos, A.M. ASCE 2 and Richard D. Woods, P.E., D.GE, Dist.M. ASCE 3 Abstract: Pile driving
Underwater Investigations Standard Practice >>>CLICK HERE<<<
 Underwater Investigations Standard Practice Manual Asce 2001 American Society of Civil Engineers' Manual No. 101 Underwater Investigations Standard Practice Manual(Link). American Society of Civil Engineers.
Underwater Investigations Standard Practice Manual Asce 2001 American Society of Civil Engineers' Manual No. 101 Underwater Investigations Standard Practice Manual(Link). American Society of Civil Engineers.
Advancement simulation of parallel tunnels and their interchange with two other subway lines using a new FEM approach, a case study
 Geotechnics for Sustainable Development - Geotec Hanoi 0, Phung (edt). Construction Publisher. ISBN 978-60-8-00-8 Advancement simulation of parallel tunnels and their interchange with two other subway
Geotechnics for Sustainable Development - Geotec Hanoi 0, Phung (edt). Construction Publisher. ISBN 978-60-8-00-8 Advancement simulation of parallel tunnels and their interchange with two other subway
nineteen Wood Construction 1 and design APPLIED ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: DR. ANNE NICHOLS FALL 2016 lecture STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS ARCH 631
 APPLIED ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS DR. ANNE NICHOLS FALL 2016 lecture nineteen wood construction and design Wood Construction 1 Timber Construction all-wood framing systems
APPLIED ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS DR. ANNE NICHOLS FALL 2016 lecture nineteen wood construction and design Wood Construction 1 Timber Construction all-wood framing systems
712 - STRUCTURAL STEEL CONSTRUCTION SECTION 712 STRUCTURAL STEEL CONSTRUCTION
 SECTION 712 STRUCTURAL STEEL CONSTRUCTION 712.1 DESCRIPTION Fabricate and erect the structural steel as designated in the Contract Documents. See SECTION 705 for fabrication of structural steel. Provide
SECTION 712 STRUCTURAL STEEL CONSTRUCTION 712.1 DESCRIPTION Fabricate and erect the structural steel as designated in the Contract Documents. See SECTION 705 for fabrication of structural steel. Provide
Formulae for calculations A) Nomenclature
 Formulae for calculations A) Nomenclature do= Nominal diameter {Outside diameter of screw} dc= Core diameter of screw d= Mean Diameter of the screw p= Pitch of the screw. ) Thread angle ( α) α = tan 1
Formulae for calculations A) Nomenclature do= Nominal diameter {Outside diameter of screw} dc= Core diameter of screw d= Mean Diameter of the screw p= Pitch of the screw. ) Thread angle ( α) α = tan 1
LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY OF METAL DOWEL TYPE CONNECTIONS OF TIMBER STRUCTURES
 Vol. 10, Issue /014, 51-60 DOI: 10.478/cee-014-0011 LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY OF METAL DOWEL TYPE CONNECTIONS OF TIMBER STRUCTURES Jozef GOCÁL 1,* 1 Department of Structures and Bridges, Faculty of Civil
Vol. 10, Issue /014, 51-60 DOI: 10.478/cee-014-0011 LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY OF METAL DOWEL TYPE CONNECTIONS OF TIMBER STRUCTURES Jozef GOCÁL 1,* 1 Department of Structures and Bridges, Faculty of Civil
ABC and Innovative Bridge Construction for Minnesota Local Roads
 ABC and Innovative Bridge Construction for Minnesota Local Roads May 23, 2013 To box the cha of t unl qua gra ma all g You ma add Tex Chris Werner, PE Senior Bridge Engineer HDR Engineering, Inc. 763-278-5918
ABC and Innovative Bridge Construction for Minnesota Local Roads May 23, 2013 To box the cha of t unl qua gra ma all g You ma add Tex Chris Werner, PE Senior Bridge Engineer HDR Engineering, Inc. 763-278-5918
Study on embedded length of piles for slope reinforced with one row of piles
 Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering. 11, 3 (2): 7 17 Study on embedded length of piles for slope reinforced with one row of piles Shikou Yang, Xuhua Ren, Jixun Zhang College of Water
Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering. 11, 3 (2): 7 17 Study on embedded length of piles for slope reinforced with one row of piles Shikou Yang, Xuhua Ren, Jixun Zhang College of Water
2016 AASHTO BRIDGE COMMITTEE AGENDA ITEM: 24 (REVISION 1) SUBJECT: LRFD Bridge Design Specifications: Section 6, Various Articles (2)
 2016 AASHTO BRIDGE COMMITTEE AGENDA ITEM: 24 (REVISION 1) SUBJECT: LRFD Bridge Design Specifications: Section 6, Various Articles (2) TECHNICAL COMMITTEE: T-14 Steel REVISION ADDITION NEW DOCUMENT DESIGN
2016 AASHTO BRIDGE COMMITTEE AGENDA ITEM: 24 (REVISION 1) SUBJECT: LRFD Bridge Design Specifications: Section 6, Various Articles (2) TECHNICAL COMMITTEE: T-14 Steel REVISION ADDITION NEW DOCUMENT DESIGN
Correction for CPT f s errors due to variation in sleeve diameter
 Geotechnical and Geophysical Site Characterisation 5 Lehane, Acosta-Martínez & Kelly (Eds) 2016 Australian Geomechanics Society, Sydney, Australia, ISBN 978-0-9946261-1-0 Correction for CPT f s errors
Geotechnical and Geophysical Site Characterisation 5 Lehane, Acosta-Martínez & Kelly (Eds) 2016 Australian Geomechanics Society, Sydney, Australia, ISBN 978-0-9946261-1-0 Correction for CPT f s errors
MAKING REMAINING LIFE PREDICTIONS FOR POWER CABLES USING RELIABILITY ANALYSES
 MAKING REMAINING LIFE PREDICTIONS FOR POWER CABLES USING RELIABILITY ANALYSES Jey K. JEYAPALAN, Dr. Jeyapalan & Associates, (USA), jkjeyapalan@earthlink.net ABSTRACT Most underground cable owners would
MAKING REMAINING LIFE PREDICTIONS FOR POWER CABLES USING RELIABILITY ANALYSES Jey K. JEYAPALAN, Dr. Jeyapalan & Associates, (USA), jkjeyapalan@earthlink.net ABSTRACT Most underground cable owners would
