Ultra-fast all-optical wavelength conversion in silicon waveguides using femtosecond pulses
|
|
|
- Maurice Erick Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ultra-fast all-optical wavelength conversion in silicon waveguides using femtosecond pulses R.Dekker a, J. Niehusmann b, M. Först b, and A. Driessen a a Integrated Optical Micro Systems, Mesa+, University of Twente, P.O. Box 217, 7500 AE Enschede, The Netherlands. Phone: ; R.Dekker@utwente.nl. b RWTH Aachen University, Institut für Halbleitertechnik, Aachen, Germany. In this work, the propagation of 300 femtosecond optical pulses in Silicon-on Insulator waveguides has been studied by means of a pump-probe set-up. Large Cross Phase Modulation (XPM) induced red and blue shifts (9nm and 15nm, respectively) of the probe signal have been observed depending on the delay between pump (1554nm) and probe (1683nm) pulses. A numerical model taking into account Two Photon Absorption (TPA) and Free Carrier Absorption (FCA) in the semiconductor waveguide is presented and provides good agreement with the experimental data. Our model reveals that the wavelength conversion is dominated by the instantaneous optical Kerr effect, enabling ultra-fast all-optical functionalities. Furthermore, the importance of waveguide dispersion on the wavelength conversion efficiency will be treated in the case of femtosecond pulses. Introduction Silicon photonics is receiving increasingly attention, especially because of its potential for integration with microelectronics (1). In recent years many new types of nonlinear active silicon-based photonic devices have been developed. Substantial progress has been achieved in the field of Raman amplification, in both continuous-wave (2) and pulsed pump-probe (3,4) experiments. Other nonlinear effects like two-photon absorption (TPA) (5), self-phase modulation (SPM) (6,7), cross-phase modulation (XPM) and continuum generation (8), four-wave mixing (FWM) (9) and the Kerr coefficient (10) have been successfully demonstrated and thoroughly investigated. In this paper, we present both theoretical and experimental results of femtosecond pump-probe experiments in Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) waveguides. Large Kerr-induced wavelength shifts of the probe signal have been observed, whereas the free carrier contribution did not substantially contribute. Since the ultra-fast Kerr effect is the dominating mechanism, this method of wavelength conversion is suitable for ultra-fast all-optical switching. Finally, the importance of waveguide dispersion on the conversion efficiency will be discussed Experimental setup Figure 1 shows a schematic representation of our experimental setup. Both the pump (1554nm) and probe (1683nm) pulses with a FWHM pulse duration of 300fs are generated using an optical parametric oscillator (OPO), while their beam shapes are being modified by optical beam formers (OBF) in order to optimize the fiber coupling
2 efficiency. The time delay between pump and probe pulses is controlled with an optical delay line (ODL) with 6 femtosecond accuracy. Both beams are combined using a beam splitter (BS), polarized (Pol) and coupled into a 10cm piece of polarization maintaining fiber (PMF) using a microscope objective (MO). The output of the PMF is used to couple TM polarized light pulses into our SOI waveguides that have a 450nm 300nm (w h) cross section (by design) and a length of 7mm. The transmitted pulses are coupled out using a single mode fiber, which is attached to an optical spectrum analyzer (OSA). Folding mirrors (FM) are used to tap the pump and probe signals to detect their power levels using an optical detector (OD). The pump intensity can be controlled using a neutral density filter (FW). Figure 1. Schematic representation of the femtosecond pump-probe setup used in the experiments. Theory When strong pump pulses (I max ~10TW/m 2 ) propagate through a SOI waveguide, the refractive index of the material is changed mainly by two nonlinear effects. The first one is the instantaneous Kerr effect, inducing an ultra-fast refractive index increase of (10): n Kerr ( = n2. I( [1] Secondly, by TPA, free carriers (FCs) are generated that cause a refractive index decrease according to [4]: ( = ( N ( N ( ) [2] n FC with N the free carrier density. Since both refractive index changes are intensity dependent, they both change with the envelope of the pulse and induce a temporal phase shift:
3 2πL n( φ( = [3] λ Here, L is the interaction length of pump and probe pulses. Consequently, this temporal phase shift causes a frequency shift ω(=d φ(/dt, which is the basis for SPM and cross phase modulation (XPM). In turn, the frequency shift causes the wavelength to shift, according to: λ0 λ s = [4] Lint n( 1 c dt with λ s the center wavelength of the frequency converted probe pulse, λ 0 the center wavelength of the original probe spectrum and c is the speed of light in vacuum. The intensity of the pulse and the amount of generated free carriers as function of the propagation distance of the pulse in the SOI waveguide can be calculated by numerically solving the following set of coupled differential equations (3): di( t, 2 = αi ( t, β I ( t, σ N( t, I( t, [5] dz dn( t, β 2 N( t, = I ( t, [6] dt 2hv τ where α is the linear absorption, β is the two photon absorption coefficient and σ is the free carrier absorption cross section, hv the photon energy and τ the free carrier lifetime. TABLE I. Overview of values used in the numerical simulations Property Symbol Value Waveguide cross section w h nm Mode area A eff ~0.15µm 2 Waveguide length L 7mm Free Carrier lifetime τ 5ns Peak intensity I max ~10TW/m 2 Pulse repetition rate F rep 80MHz Center wavelength of the pump λ p 1554nm Center wavelength of the probe signal λ s 1683nm linear absorption α 0m -1 TPA coefficient β m/w free carrier absorption cross section σ (λ/1.55) m 2 Kerr nonlinearity n m 2 /W Pulse shape Gaussian - In Table II some numerical results of Equations [1-6] are presented at several propagation distances using the parameters from Table I. It can be concluded from the first graph in Table II that the pulse intensity decreases mainly due to TPA, since the pulse keeps its Gaussian shape. This is in contrast to pulses with a longer pulse duration (> 1ps), where the trailing edge experiences stronger absorption due to the generated free carriers, distorting the pulse shape. It can also be seen in the third graph that the Kerr induced refractive index change is the dominant mechanism. Even though the intensities are very high, a relatively low amount of free carriers are generated since the pulses are very short.
4 TABLE II. Simulation results of 300fs pulse propagation in SOI waveguides Simulation results Pulse shape: I [W/m 2 ] 0 11x10 12 z=0mm z=3.5mm z=7mm Time [fs] Free carrier density: Refractive index change: N [1/m 3 ] 0 550x10 18 n [-] 0 50x10-6 z=0mm z=3.5mm z=7mm Time [fs] n Kerr n FC n Total Time [fs] 1690 Wavelength shift: λ probe [nm] Time delay [fs]
5 Experimental results In Figure 2 the experimentally observed center wavelength of the probe pulses are plotted as function of delay time. Here a negative delay time means that the probe pulses are running ahead of the pump pulses, i.e. are overlapping with the leading edge of the pump pulse. The discrepancy between the experimental results and the simulations is caused by the fact that dispersion effects are not included in the previously discussed model. We observed a 10nm redshift at negative delay times, indicating that the nonlinearities are dominated by the Kerr effect in case of femtosecond pulses. This is in contrast to the blueshift that is normally observed in pump-probe experiments with longer ps pulses [1], where the free carrier dispersion effect is dominant due to the fact that ps pulses are long enough to build up a sufficient amount of free carriers. Figure 2: Center wavelength vs. delay time. Waveguide dispersion The geometry induced waveguide dispersion will dominate the material dispersion in case the SOI waveguide dimensions are in the submicron range [12]. The distance over which the pump and probe pulses pass through each other s envelope is called the walkoff length L w and is defined as [12]: L w( 1 λ) = T0 β1p ( λ) β s ( λ) [7] where T 0 is the half width of the pulse, and β 1p and β 1s are the first order dispersion coefficients of the pump and probe, respectively. In Figure 3 the first order dispersion coefficients and walkoff lengths between the 1554nm pump and 1683nm probe pulses (T 0 =300fs) are plotted for a SOI waveguide with a height of 300nm and the width as varying parameter. It can be seen that the waveguide width is a critical parameter that strongly affects the pump-probe interaction and therefore the maximum attainable wavelength conversion as the conversion efficiency increases with L w.
6 Figure 3: (lef First order dispersion β 1 as a function of wavelength and waveguide width. (righ Walkoff length vs. waveguide width. To achieve efficient wavelength conversion, the pump and probe wavelengths need to be chosen such that both their first order dispersion values are on the same contour line, as can be seen in the left chart of Figure 3. The interaction length could easily be increased by increasing the pulse lengths, since the walkoff length scales linearly with the pulse length (see Equation [7]). However, at longer pulse lengths, the pulse envelope is less steep resulting in weaker wavelength conversion. The walkoff length can in principle go to infinity when the first order dispersion coefficients are exactly the same (right chart in Figure 3, around w=458nm). This ideal case can be achieved by tuning the pump and/or probe wavelengths or with extremely accurate control of the waveguide fabrication. We believe that the observed large wavelength shifts in short SOI waveguides can only be achieved with sub-picosecond pulses, combined with precise control of the waveguide dispersion. Conclusions We have shown that both 10nm blue and red shifts in SOI waveguides using a pumpprobe setup with 300fs pulses are feasible. The XPM is dominated by the Kerr effect, since the pulses in the femtosecond regime are too short to accumulate a sufficient amount of free carriers to have considerable free carrier dispersion. This means that the temporal refractive index changes are mainly caused by the instantaneous Kerr effect and thus both the wavelength up and down-conversion takes place in a sub-picosecond timeframe. We have shown the importance of waveguide dispersion management on the wavelength conversion efficiency in femtosecond pump-probe experiments. Acknowledgments R. Dekker and A. Driessen would like to thank Freeband Impulse technology program of the Ministry of Economic Affairs of the Netherlands. All authors would like to acknowledge the European Network of Excellence on Photonic Integrated Components and Circuits (epixnet FAA5/WP11).
7 References 1. G. T. Reed, "Optical age of silicon", Nature, Vol 427, , V. Raghunathan, R. Claps, D. Dimitropoulos and B. Jalali, "Parametric Raman Wavelength Conversion in Scaled Silicon Waveguides", J.Lightwave.Technol, Vol 23 (6), pp , A. Liu, H. Rong, M. Paniccia, O. Cohen and D. Hak, "Net optical gain in a low loss silicon-on-insulator waveguide by stimulated Raman scattering", Opt.Express, Vol 12 (18), pp , Q. Xu, V. R. Almeida and M. Lipson, "Time-resolved study of Raman gain in highly confined silicon-on-insulator waveguides", Opt.Express, Vol 12 (19), pp , T. K. Liang, H. K. Tsang, I. E. Day, J. Drake, A. P. Knights and M. Asghari, "Silicon waveguide two-photon absorption detector at 1.5µm wavelength for autocorrelation measurements", Appl.Phys.Lett., Vol 84 (15), pp , O. Boyraz, T. Indukuri and B. Jalali, "Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides", Opt.Express, Vol 12 (5), pp , R. Dekker, E. J. Klein, J. Niehusmann, M. Först, F. Ondracek, J. Ctyroky, N. Usechak and A. Driessen, "Self Phase Modulation and Stimulated Raman Scattering due to High Power Femtosecond Pulse Propagation in Silicon-on- Insulator Waveguides." Symposium IEEE/LEOS Benelux Chapter, Mons, Belgium, pp , O. Boyraz, P. Koonath, V. Raghunathan and B. Jalali, "All optical switching and continuum generation in silicon waveguides", Opt.Express, Vol 12 (17), pp , H. Fukuda, K. Yamada, T. Shoji, M. Takahashi, T. Tsuchizawa, T. Watanabe, J. Takahashi and S. Itabashi, "Four-wave mixing in silicon wire waveguides", Opt.Express, Vol 13 (12), pp , M. Dinu, F. Quochi and H. Garcia, "Third-order nonlinearities in silicon at telecom wavelengths", Appl.Phys.Lett., Vol 82 (18), pp , R. A. Soref and B. R. Bennett, "Electrooptical Effects in Silicon", IEEE.J.Sel.Top.Quant.Electr., Vol QE-23 (1), pp , X. Chen, N. C. Panoiu and R.M.Jr.Osgood, "Theory of Raman-Mediated Pulsed Amplification in Silicon-Wire Waveguides", IEEE J. Quant. Electr., Vol 42 (2), pp , 2006.
Optical solitons in a silicon waveguide
 Optical solitons in a silicon waveguide Jidong Zhang 1, Qiang Lin 2, Giovanni Piredda 2, Robert W. Boyd 2, Govind P. Agrawal 2, and Philippe M. Fauchet 1,2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Optical solitons in a silicon waveguide Jidong Zhang 1, Qiang Lin 2, Giovanni Piredda 2, Robert W. Boyd 2, Govind P. Agrawal 2, and Philippe M. Fauchet 1,2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides
 Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides Ozdal Boyraz, Tejaswi Indukuri, and Bahram Jalali University of California, Los Angeles Department of Electrical Engineering, Los
Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides Ozdal Boyraz, Tejaswi Indukuri, and Bahram Jalali University of California, Los Angeles Department of Electrical Engineering, Los
Ultrafast pulse characterization using XPM in silicon
 Ultrafast pulse characterization using XPM in silicon Nuh S. Yuksek, Xinzhu Sang, En-Kuang Tien, Qi Song, Feng Qian, Ivan V. Tomov, Ozdal Boyraz Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science,
Ultrafast pulse characterization using XPM in silicon Nuh S. Yuksek, Xinzhu Sang, En-Kuang Tien, Qi Song, Feng Qian, Ivan V. Tomov, Ozdal Boyraz Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science,
Demonstration of directly modulated silicon Raman laser
 Demonstration of directly modulated silicon Raman laser Ozdal Boyraz and Bahram Jalali Optoelectronic Circuits and Systems Laboratory University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 995-1594 jalali@ucla.edu
Demonstration of directly modulated silicon Raman laser Ozdal Boyraz and Bahram Jalali Optoelectronic Circuits and Systems Laboratory University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 995-1594 jalali@ucla.edu
Inverse Raman Scattering in Silicon
 Inverse aman Scattering in Silicon Daniel. Solli, Prakash Koonath and Bahram Jalali Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90095-1594 Abstract: Stimulated
Inverse aman Scattering in Silicon Daniel. Solli, Prakash Koonath and Bahram Jalali Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90095-1594 Abstract: Stimulated
Four wave mixing and parametric amplification in Si-nano waveguides using reverse biased pnjunctions
 Four wave mixing and parametric amplification in Si-nano waveguides using reverse biased pnjunctions for carrier removal E-Mail: petermann@tu-berlin.de Acknowledgements A.Gajda 1, G.Winzer 1, L.Zimmermann
Four wave mixing and parametric amplification in Si-nano waveguides using reverse biased pnjunctions for carrier removal E-Mail: petermann@tu-berlin.de Acknowledgements A.Gajda 1, G.Winzer 1, L.Zimmermann
Low threshold continuous wave Raman silicon laser
 NATURE PHOTONICS, VOL. 1, APRIL, 2007 Low threshold continuous wave Raman silicon laser HAISHENG RONG 1 *, SHENGBO XU 1, YING-HAO KUO 1, VANESSA SIH 1, ODED COHEN 2, OMRI RADAY 2 AND MARIO PANICCIA 1 1:
NATURE PHOTONICS, VOL. 1, APRIL, 2007 Low threshold continuous wave Raman silicon laser HAISHENG RONG 1 *, SHENGBO XU 1, YING-HAO KUO 1, VANESSA SIH 1, ODED COHEN 2, OMRI RADAY 2 AND MARIO PANICCIA 1 1:
Tailored anomalous group-velocity dispersion in silicon channel waveguides
 Tailored anomalous group-velocity dispersion in silicon channel waveguides Amy C. Turner, Christina Manolatou, Bradley S. Schmidt, and Michal Lipson School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell
Tailored anomalous group-velocity dispersion in silicon channel waveguides Amy C. Turner, Christina Manolatou, Bradley S. Schmidt, and Michal Lipson School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell
Continuum White Light Generation. WhiteLase: High Power Ultrabroadband
 Continuum White Light Generation WhiteLase: High Power Ultrabroadband Light Sources Technology Ultrafast Pulses + Fiber Laser + Non-linear PCF = Spectral broadening from 400nm to 2500nm Ultrafast Fiber
Continuum White Light Generation WhiteLase: High Power Ultrabroadband Light Sources Technology Ultrafast Pulses + Fiber Laser + Non-linear PCF = Spectral broadening from 400nm to 2500nm Ultrafast Fiber
Chad A. Husko 1,, Sylvain Combrié 2, Pierre Colman 2, Jiangjun Zheng 1, Alfredo De Rossi 2, Chee Wei Wong 1,
 SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration
 1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers
 Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Silicon based optical pulse shaping and characterization
 Invited Paper Silicon based optical pulse shaping and characterization Ozdal Boyraz, Xinzhu Sang, En-Kuang Tien, Qi Song, Feng Qian and Metin Akdas Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science,
Invited Paper Silicon based optical pulse shaping and characterization Ozdal Boyraz, Xinzhu Sang, En-Kuang Tien, Qi Song, Feng Qian and Metin Akdas Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science,
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Figure1. To construct a light pulse, the electric component of the plane wave should be multiplied with a bell shaped function.
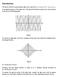 Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Title. Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori. CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type.
 Title Polarization-independent optical directional coupler Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): 56-58 Issue Date 2006 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/948 Rights
Title Polarization-independent optical directional coupler Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): 56-58 Issue Date 2006 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/948 Rights
Two-Photon Photovoltaic Effect in Silicon Sasan Fathpour, Member, IEEE, Kevin K. Tsia, Member, IEEE, and Bahram Jalali, Fellow, IEEE
 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 43, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2007 1211 Two-Photon Photovoltaic Effect in Silicon Sasan Fathpour, Member, IEEE, Kevin K. Tsia, Member, IEEE, and Bahram Jalali, Fellow,
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 43, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2007 1211 Two-Photon Photovoltaic Effect in Silicon Sasan Fathpour, Member, IEEE, Kevin K. Tsia, Member, IEEE, and Bahram Jalali, Fellow,
Impact of Fiber Non-Linearities in Performance of Optical Communication
 Impact of Fiber Non-Linearities in Performance of Optical Communication Narender Kumar Sihval 1, Vivek Kumar Malik 2 M. Tech Students in ECE Department, DCRUST-Murthal, Sonipat, India Abstract: Non-linearity
Impact of Fiber Non-Linearities in Performance of Optical Communication Narender Kumar Sihval 1, Vivek Kumar Malik 2 M. Tech Students in ECE Department, DCRUST-Murthal, Sonipat, India Abstract: Non-linearity
Ultrashort Pulse Measurement Using High Sensitivity Two Photon Absorption Waveguide Semiconductor
 Ultrashort Pulse Measurement Using High Sensitivity Two Photon Absorption Wguide Semiconductor MOHAMMAD MEHDI KARKHANEHCHI Department of Electronics, Faculty of Engineering Razi University Taghbostan,
Ultrashort Pulse Measurement Using High Sensitivity Two Photon Absorption Wguide Semiconductor MOHAMMAD MEHDI KARKHANEHCHI Department of Electronics, Faculty of Engineering Razi University Taghbostan,
LASER Transmitters 1 OBJECTIVE 2 PRE-LAB
 LASER Transmitters 1 OBJECTIVE Investigate the L-I curves and spectrum of a FP Laser and observe the effects of different cavity characteristics. Learn to perform parameter sweeps in OptiSystem. 2 PRE-LAB
LASER Transmitters 1 OBJECTIVE Investigate the L-I curves and spectrum of a FP Laser and observe the effects of different cavity characteristics. Learn to perform parameter sweeps in OptiSystem. 2 PRE-LAB
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3000 cm 1
 Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
Frequency conversion over two-thirds of an octave in silicon nanowaveguides
 Frequency conversion over two-thirds of an octave in silicon nanowaveguides Amy C. Turner-Foster 1, Mark A. Foster 2, Reza Salem 2, Alexander L. Gaeta 2, and Michal Lipson 1 * 1 School of Electrical and
Frequency conversion over two-thirds of an octave in silicon nanowaveguides Amy C. Turner-Foster 1, Mark A. Foster 2, Reza Salem 2, Alexander L. Gaeta 2, and Michal Lipson 1 * 1 School of Electrical and
Energy harvesting in silicon optical modulators
 Energy harvesting in silicon optical modulators Sasan Fathpour and Bahram Jalali Optoelectronic Circuits and Systems Laboratory Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles,
Energy harvesting in silicon optical modulators Sasan Fathpour and Bahram Jalali Optoelectronic Circuits and Systems Laboratory Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles,
Testing with Femtosecond Pulses
 Testing with Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.3 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
Testing with Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.3 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
Theoretical Approach. Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION:
 Theoretical Approach Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION: Generating ultrashort laser pulses that last a few femtoseconds is a highly active area of research that is finding applications
Theoretical Approach Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION: Generating ultrashort laser pulses that last a few femtoseconds is a highly active area of research that is finding applications
A continuous-wave Raman silicon laser
 A continuous-wave Raman silicon laser Haisheng Rong, Richard Jones,.. - Intel Corporation Ultrafast Terahertz nanoelectronics Lab Jae-seok Kim 1 Contents 1. Abstract 2. Background I. Raman scattering II.
A continuous-wave Raman silicon laser Haisheng Rong, Richard Jones,.. - Intel Corporation Ultrafast Terahertz nanoelectronics Lab Jae-seok Kim 1 Contents 1. Abstract 2. Background I. Raman scattering II.
All-optical logic based on silicon micro-ring resonators
 All-optical logic based on silicon micro-ring resonators Qianfan Xu and Michal Lipson School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University 411 Phillips Hall, Ithaca, NY 14853 lipson@ece.cornell.edu
All-optical logic based on silicon micro-ring resonators Qianfan Xu and Michal Lipson School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University 411 Phillips Hall, Ithaca, NY 14853 lipson@ece.cornell.edu
Study of cross-phase modulation and free-carrier dispersion in silicon photonic wires for Mamyshev signal regenerators
 Study of cross-phase modulation and free-carrier dispersion in silicon photonic wires for Mamyshev signal regenerators Hong-Sheng Hsieh, 1 Kai-Ming Feng, and Ming-Chang M. Lee 1 * 1 Institute of Photonics
Study of cross-phase modulation and free-carrier dispersion in silicon photonic wires for Mamyshev signal regenerators Hong-Sheng Hsieh, 1 Kai-Ming Feng, and Ming-Chang M. Lee 1 * 1 Institute of Photonics
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Active coupling control in densely packed subwavelength waveguides via dark mode interaction Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1- Effective coupling in three waveguides
Supplementary Information Active coupling control in densely packed subwavelength waveguides via dark mode interaction Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1- Effective coupling in three waveguides
STUDY OF CHIRPED PULSE COMPRESSION IN OPTICAL FIBER FOR ALL FIBER CPA SYSTEM
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJECE) ISSN(P): 78-991; ISSN(E): 78-991X Vol. 4, Issue 6, Oct - Nov 15, 9-16 IASE SUDY OF CHIRPED PULSE COMPRESSION IN OPICAL FIBER FOR
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJECE) ISSN(P): 78-991; ISSN(E): 78-991X Vol. 4, Issue 6, Oct - Nov 15, 9-16 IASE SUDY OF CHIRPED PULSE COMPRESSION IN OPICAL FIBER FOR
G. Norris* & G. McConnell
 Relaxed damage threshold intensity conditions and nonlinear increase in the conversion efficiency of an optical parametric oscillator using a bi-directional pump geometry G. Norris* & G. McConnell Centre
Relaxed damage threshold intensity conditions and nonlinear increase in the conversion efficiency of an optical parametric oscillator using a bi-directional pump geometry G. Norris* & G. McConnell Centre
How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser
 How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser Daniele Brida 17.02.2016 Konstanz Ultrafast laser Time domain : pulse train Frequency domain: comb 3 26.03.2016 Frequency comb laser Time domain : pulse train
How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser Daniele Brida 17.02.2016 Konstanz Ultrafast laser Time domain : pulse train Frequency domain: comb 3 26.03.2016 Frequency comb laser Time domain : pulse train
High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers
 High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average powers. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical
High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average powers. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical
2-R REGENERATION EXPLOITING SELF-PHASE MODULATION IN A SEMICONDUCTOR OPTICAL AMPLIFIER
 2-R REGENERATION EXPLOITING SELF-PHASE MODULATION IN A SEMICONDUCTOR OPTICAL AMPLIFIER Gianluca Meloni,^ Antonella Bogoni,^ and Luca Poti^ Scuola Superiore Sunt'Anna, P.zza dei Martin della Libertd 33,
2-R REGENERATION EXPLOITING SELF-PHASE MODULATION IN A SEMICONDUCTOR OPTICAL AMPLIFIER Gianluca Meloni,^ Antonella Bogoni,^ and Luca Poti^ Scuola Superiore Sunt'Anna, P.zza dei Martin della Libertd 33,
APE Autocorrelator Product Family
 APE Autocorrelator Product Family APE Autocorrelators The autocorrelator product family by APE includes a variety of impressive features and properties, designed to cater for a wide range of ultrafast
APE Autocorrelator Product Family APE Autocorrelators The autocorrelator product family by APE includes a variety of impressive features and properties, designed to cater for a wide range of ultrafast
Fabrication of low-loss SOI nano-waveguides including BEOL processes for nonlinear applications
 J. Europ. Opt. Soc. Rap. Public. 7, 12032 (2012) www.jeos.org Fabrication of low-loss SOI nano-waveguides including BEOL processes for nonlinear applications H. Tian tian@ihp-microelectronics.com IHP GmbH,
J. Europ. Opt. Soc. Rap. Public. 7, 12032 (2012) www.jeos.org Fabrication of low-loss SOI nano-waveguides including BEOL processes for nonlinear applications H. Tian tian@ihp-microelectronics.com IHP GmbH,
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication
 InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion
 36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania
 Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania Razvan Dabu, Daniel Ursescu INFLPR, Magurele, Romania Contents GiWALAS laser facility TEWALAS laser facility CETAL project
Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania Razvan Dabu, Daniel Ursescu INFLPR, Magurele, Romania Contents GiWALAS laser facility TEWALAS laser facility CETAL project
High Energy Non - Collinear OPA
 High Energy Non - Collinear OPA Basics of Operation FEATURES Pulse Duration less than 10 fs possible High Energy (> 80 microjoule) Visible Output Wavelength Tuning Computer Controlled Tuning Range 250-375,
High Energy Non - Collinear OPA Basics of Operation FEATURES Pulse Duration less than 10 fs possible High Energy (> 80 microjoule) Visible Output Wavelength Tuning Computer Controlled Tuning Range 250-375,
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression
 Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
Fundamental Optics ULTRAFAST THEORY ( ) = ( ) ( q) FUNDAMENTAL OPTICS. q q = ( A150 Ultrafast Theory
 ULTRAFAST THEORY The distinguishing aspect of femtosecond laser optics design is the need to control the phase characteristic of the optical system over the requisite wide pulse bandwidth. CVI Laser Optics
ULTRAFAST THEORY The distinguishing aspect of femtosecond laser optics design is the need to control the phase characteristic of the optical system over the requisite wide pulse bandwidth. CVI Laser Optics
Soliton Resonances in Dispersion Oscillating Optical Fibers
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 2009 416 Soliton Resonances in Dispersion Oscillating Optical Fibers Andrey Konyukhov 1, Leonid Melnikov 1, Vladimir Khopin 2, Vladimir Stasuyk 3, and Alexej Sysoliatin 4 1
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 2009 416 Soliton Resonances in Dispersion Oscillating Optical Fibers Andrey Konyukhov 1, Leonid Melnikov 1, Vladimir Khopin 2, Vladimir Stasuyk 3, and Alexej Sysoliatin 4 1
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion
 Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Optical Fiber Technology. Photonic Network By Dr. M H Zaidi
 Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method.
 PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
High-Power Femtosecond Lasers
 High-Power Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average power. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical design optimized
High-Power Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average power. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical design optimized
SILICON has many desirable physical and economical properties
 2094 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 6, JUNE 2005 Parametric Raman Wavelength Conversion in Scaled Silicon Waveguides Varun Raghunathan, Ricardo Claps, Dimitrios Dimitropoulos, and Bahram
2094 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 6, JUNE 2005 Parametric Raman Wavelength Conversion in Scaled Silicon Waveguides Varun Raghunathan, Ricardo Claps, Dimitrios Dimitropoulos, and Bahram
Fabrication of Photorefractive Grating With 800 nm Femtosecond Lasers in Fe: LiNbO 3 and Rh:BaTiO 3 Crystals
 Fabrication of Photorefractive Grating With 8 nm Femtosecond Lasers in Fe: LiNbO 3 and Rh:BaTiO 3 Crystals Md. Masudul Kabir (D3) Abstract Refractive index gratings have been successfully formed in Fe:LiNbO
Fabrication of Photorefractive Grating With 8 nm Femtosecond Lasers in Fe: LiNbO 3 and Rh:BaTiO 3 Crystals Md. Masudul Kabir (D3) Abstract Refractive index gratings have been successfully formed in Fe:LiNbO
All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating
 All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating Pavel Honzatko a, a Institute of Photonics and Electronics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, v.v.i.,
All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating Pavel Honzatko a, a Institute of Photonics and Electronics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, v.v.i.,
Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks.
 Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks. Hercules Simos * National and Kapodistrian University
Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks. Hercules Simos * National and Kapodistrian University
Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH. Competence Area: Fiber Devices
 Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH Competence Area: Fiber Devices Topics in this Area Fiber lasers, including exotic types Fiber amplifiers, including telecom-type devices and high power
Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH Competence Area: Fiber Devices Topics in this Area Fiber lasers, including exotic types Fiber amplifiers, including telecom-type devices and high power
Notes on Optical Amplifiers
 Notes on Optical Amplifiers Optical amplifiers typically use energy transitions such as those in atomic media or electron/hole recombination in semiconductors. In optical amplifiers that use semiconductor
Notes on Optical Amplifiers Optical amplifiers typically use energy transitions such as those in atomic media or electron/hole recombination in semiconductors. In optical amplifiers that use semiconductor
pulsecheck The Modular Autocorrelator
 pulsecheck The Modular Autocorrelator Pulse Measurement Perfection with the Multitalent from APE It is good to have plenty of options at hand. Suitable for the characterization of virtually any ultrafast
pulsecheck The Modular Autocorrelator Pulse Measurement Perfection with the Multitalent from APE It is good to have plenty of options at hand. Suitable for the characterization of virtually any ultrafast
Physics of Waveguide Photodetectors with Integrated Amplification
 Physics of Waveguide Photodetectors with Integrated Amplification J. Piprek, D. Lasaosa, D. Pasquariello, and J. E. Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa
Physics of Waveguide Photodetectors with Integrated Amplification J. Piprek, D. Lasaosa, D. Pasquariello, and J. E. Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa
Designing for Femtosecond Pulses
 Designing for Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-1100-00 Revision 1.1 July 2013 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
Designing for Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-1100-00 Revision 1.1 July 2013 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse
 Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse Nan Yang 1, Hai-Wei Du * 1 Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry of Education) and Department of Physics, Shanghai Jiaotong
Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse Nan Yang 1, Hai-Wei Du * 1 Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry of Education) and Department of Physics, Shanghai Jiaotong
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information Real-space imaging of transient carrier dynamics by nanoscale pump-probe microscopy Yasuhiko Terada, Shoji Yoshida, Osamu Takeuchi, and Hidemi Shigekawa*
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information Real-space imaging of transient carrier dynamics by nanoscale pump-probe microscopy Yasuhiko Terada, Shoji Yoshida, Osamu Takeuchi, and Hidemi Shigekawa*
Lecture 3 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1
 Lecture 3 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion Limitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Lecture 3 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion Limitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier
 Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.2 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Fiber lasers offer advantages in maintaining stable operation over
Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.2 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Fiber lasers offer advantages in maintaining stable operation over
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance
 Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
CHAPTER 5 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM
 61 CHAPTER 5 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM 5.1 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM Due to the ever-expanding Internet data traffic, telecommunication networks are witnessing a demand for high-speed data transfer.
61 CHAPTER 5 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM 5.1 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM Due to the ever-expanding Internet data traffic, telecommunication networks are witnessing a demand for high-speed data transfer.
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/2/e1700324/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Photocarrier generation from interlayer charge-transfer transitions in WS2-graphene heterostructures Long Yuan, Ting-Fung
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/2/e1700324/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Photocarrier generation from interlayer charge-transfer transitions in WS2-graphene heterostructures Long Yuan, Ting-Fung
Integrated disruptive components for 2µm fibre Lasers ISLA. 2 µm Sub-Picosecond Fiber Lasers
 Integrated disruptive components for 2µm fibre Lasers ISLA 2 µm Sub-Picosecond Fiber Lasers Advantages: 2 - microns wavelength offers eye-safety potentially higher pulse energy and average power in single
Integrated disruptive components for 2µm fibre Lasers ISLA 2 µm Sub-Picosecond Fiber Lasers Advantages: 2 - microns wavelength offers eye-safety potentially higher pulse energy and average power in single
Application Instruction 002. Superluminescent Light Emitting Diodes: Device Fundamentals and Reliability
 I. Introduction II. III. IV. SLED Fundamentals SLED Temperature Performance SLED and Optical Feedback V. Operation Stability, Reliability and Life VI. Summary InPhenix, Inc., 25 N. Mines Road, Livermore,
I. Introduction II. III. IV. SLED Fundamentals SLED Temperature Performance SLED and Optical Feedback V. Operation Stability, Reliability and Life VI. Summary InPhenix, Inc., 25 N. Mines Road, Livermore,
Variable splitting ratio 2 2 MMI couplers using multimode waveguide holograms
 Variable splitting ratio 2 2 MMI couplers using multimode waveguide holograms Shuo-Yen Tseng, Canek Fuentes-Hernandez, Daniel Owens, and Bernard Kippelen Center for Organic Photonics and Electronics, School
Variable splitting ratio 2 2 MMI couplers using multimode waveguide holograms Shuo-Yen Tseng, Canek Fuentes-Hernandez, Daniel Owens, and Bernard Kippelen Center for Organic Photonics and Electronics, School
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS
 UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
All-optical logic gates using a semiconductor optical amplifier assisted by an optical filter
 All-optical logic gates using a semiconductor optical amplifier assisted by an optical filter Z. Li, Y. Liu, S. Zhang, H. Ju, H. de Waardt, G.D. Khoe H.J.S. Dorren and D. Lenstra Abstract: A simple all-optical
All-optical logic gates using a semiconductor optical amplifier assisted by an optical filter Z. Li, Y. Liu, S. Zhang, H. Ju, H. de Waardt, G.D. Khoe H.J.S. Dorren and D. Lenstra Abstract: A simple all-optical
Improving the efficiency of an optical parametric oscillator by tailoring the pump pulse shape
 Improving the efficiency of an optical parametric oscillator by tailoring the pump pulse shape Zachary Sacks, 1,* Ofer Gayer, 2 Eran Tal, 1 and Ady Arie 2 1 Elbit Systems El Op, P.O. Box 1165, Rehovot
Improving the efficiency of an optical parametric oscillator by tailoring the pump pulse shape Zachary Sacks, 1,* Ofer Gayer, 2 Eran Tal, 1 and Ady Arie 2 1 Elbit Systems El Op, P.O. Box 1165, Rehovot
Single Mode Optical Fiber - Dispersion
 Single Mode Optical Fiber - Dispersion 1 OBJECTIVE Characterize analytically and through simulation the effects of dispersion on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB A single mode fiber, as the name implies, supports
Single Mode Optical Fiber - Dispersion 1 OBJECTIVE Characterize analytically and through simulation the effects of dispersion on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB A single mode fiber, as the name implies, supports
SILICON MICRORING WITHIN A FIBER LASER CAVITY FOR HIGH-REPETITION-RATE PULSE TRAIN GENERATION
 Romanian Reports in Physics 7, 45 (218) SILICON MICRORING WITHIN A FIBER LASER CAVITY FOR HIGH-REPETITION-RATE PULSE TRAIN GENERATION M. MEISTERHANS 1, A. COILLET 1,*, F. AMRANI 1,2, O. DEMICHEL 1, J.-B.
Romanian Reports in Physics 7, 45 (218) SILICON MICRORING WITHIN A FIBER LASER CAVITY FOR HIGH-REPETITION-RATE PULSE TRAIN GENERATION M. MEISTERHANS 1, A. COILLET 1,*, F. AMRANI 1,2, O. DEMICHEL 1, J.-B.
taccor Optional features Overview Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser
 taccor Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser Self-locking and maintaining Stable and robust True hands off turn-key system Wavelength tunable Integrated pump laser Overview The taccor is a unique turn-key femtosecond
taccor Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser Self-locking and maintaining Stable and robust True hands off turn-key system Wavelength tunable Integrated pump laser Overview The taccor is a unique turn-key femtosecond
Picosecond Pulses for Test & Measurement
 Picosecond Pulses for Test & Measurement White Paper PN 200-0100-00 Revision 1.1 September 2003 Calmar Optcom, Inc www.calamropt.com Overview Calmar s picosecond laser sources are actively mode-locked
Picosecond Pulses for Test & Measurement White Paper PN 200-0100-00 Revision 1.1 September 2003 Calmar Optcom, Inc www.calamropt.com Overview Calmar s picosecond laser sources are actively mode-locked
A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier
 Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2004 Vol.47 No.6 767 772 767 A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier ZHU Heyuan, XU Guang, WANG Tao, QIAN Liejia & FAN Dianyuan State
Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2004 Vol.47 No.6 767 772 767 A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier ZHU Heyuan, XU Guang, WANG Tao, QIAN Liejia & FAN Dianyuan State
Design and Simulation of Optical Power Splitter By using SOI Material
 J. Pure Appl. & Ind. Phys. Vol.3 (3), 193-197 (2013) Design and Simulation of Optical Power Splitter By using SOI Material NAGARAJU PENDAM * and C P VARDHANI 1 * Research Scholar, Department of Physics,
J. Pure Appl. & Ind. Phys. Vol.3 (3), 193-197 (2013) Design and Simulation of Optical Power Splitter By using SOI Material NAGARAJU PENDAM * and C P VARDHANI 1 * Research Scholar, Department of Physics,
Multimode Optical Fiber
 Multimode Optical Fiber 1 OBJECTIVE Determine the optical modes that exist for multimode step index fibers and investigate their performance on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB The backbone of optical systems
Multimode Optical Fiber 1 OBJECTIVE Determine the optical modes that exist for multimode step index fibers and investigate their performance on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB The backbone of optical systems
Two-pump four-wave mixing in silicon waveguides for broadband wavelength conversion
 Two-pump four-wave mixing in silicon waveguides for broadband wavelength conversion Shiming Gao *a,b, Lizhong Cao a, En-Kuang Tien b, Yuewang Huang b, Qiang Liu a, Qi Song b, Salih K. Kalyoncu b, Sailing
Two-pump four-wave mixing in silicon waveguides for broadband wavelength conversion Shiming Gao *a,b, Lizhong Cao a, En-Kuang Tien b, Yuewang Huang b, Qiang Liu a, Qi Song b, Salih K. Kalyoncu b, Sailing
Application Instruction 001. The Enhanced Functionalities of Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and their Role in Advanced Optical Networking
 The Enhanced Functionalities of Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and their Role in Advanced Optical Networking I. Introduction II. III. IV. SOA Fundamentals Wavelength Conversion based on SOAs The Role
The Enhanced Functionalities of Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and their Role in Advanced Optical Networking I. Introduction II. III. IV. SOA Fundamentals Wavelength Conversion based on SOAs The Role
Slow-light Enhanced Nonlinear Optics in Silicon Photonic Crystal Waveguides
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 6, NO. 3, 2010 273 Slow-light Enhanced Nonlinear Optics in Silicon Photonic Crystal Waveguides D. J. Moss 1, B. Corcoran 1, C. Monat 1, C. Grillet 1, T. P. White 2, L. O Faolain 2, T.
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 6, NO. 3, 2010 273 Slow-light Enhanced Nonlinear Optics in Silicon Photonic Crystal Waveguides D. J. Moss 1, B. Corcoran 1, C. Monat 1, C. Grillet 1, T. P. White 2, L. O Faolain 2, T.
Integrated Optical Waveguide Sensor for Lighting Impulse Electric Field Measurement
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 4, No. 3, 2014: 215 219 Integrated Optical Waveguide Sensor for Lighting Impulse Electric Field Measurement Jiahong ZHANG *, Fushen CHEN, Bao SUN, and Kaixin CHEN Key Laboratory
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 4, No. 3, 2014: 215 219 Integrated Optical Waveguide Sensor for Lighting Impulse Electric Field Measurement Jiahong ZHANG *, Fushen CHEN, Bao SUN, and Kaixin CHEN Key Laboratory
Phase Sensitive Amplifier Based on Ultrashort Pump Pulses
 Phase Sensitive Amplifier Based on Ultrashort Pump Pulses Alexander Gershikov and Gad Eisenstein Department of Electrical Engineering, Technion, Haifa, 32000, Israel. Corresponding author: alexger@campus.technion.ac.il
Phase Sensitive Amplifier Based on Ultrashort Pump Pulses Alexander Gershikov and Gad Eisenstein Department of Electrical Engineering, Technion, Haifa, 32000, Israel. Corresponding author: alexger@campus.technion.ac.il
Power adjustable visible supercontinuum generation using amplified nanosecond gainswitched
 Power adjustable visible supercontinuum generation using amplified nanosecond gainswitched laser diode Malay Kumar 1*, Chenan Xia 1, Xiuquan Ma 1, Vinay V. Alexander 1, Mohammed N. Islam 1, Fred L. Terry
Power adjustable visible supercontinuum generation using amplified nanosecond gainswitched laser diode Malay Kumar 1*, Chenan Xia 1, Xiuquan Ma 1, Vinay V. Alexander 1, Mohammed N. Islam 1, Fred L. Terry
HIGH-EFFICIENCY MQW ELECTROABSORPTION MODULATORS
 HIGH-EFFICIENCY MQW ELECTROABSORPTION MODULATORS J. Piprek, Y.-J. Chiu, S.-Z. Zhang (1), J. E. Bowers, C. Prott (2), and H. Hillmer (2) University of California, ECE Department, Santa Barbara, CA 93106
HIGH-EFFICIENCY MQW ELECTROABSORPTION MODULATORS J. Piprek, Y.-J. Chiu, S.-Z. Zhang (1), J. E. Bowers, C. Prott (2), and H. Hillmer (2) University of California, ECE Department, Santa Barbara, CA 93106
MULTI-STAGE YTTERBIUM FIBER-AMPLIFIER SEEDED BY A GAIN-SWITCHED LASER DIODE
 MULTI-STAGE YTTERBIUM FIBER-AMPLIFIER SEEDED BY A GAIN-SWITCHED LASER DIODE Authors: M. Ryser, S. Pilz, A. Burn, V. Romano DOI: 10.12684/alt.1.101 Corresponding author: e-mail: M. Ryser manuel.ryser@iap.unibe.ch
MULTI-STAGE YTTERBIUM FIBER-AMPLIFIER SEEDED BY A GAIN-SWITCHED LASER DIODE Authors: M. Ryser, S. Pilz, A. Burn, V. Romano DOI: 10.12684/alt.1.101 Corresponding author: e-mail: M. Ryser manuel.ryser@iap.unibe.ch
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication
 InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
Ultrafast instrumentation (No Alignment!)
 Ultrafast instrumentation (No Alignment!) We offer products specialized in ultrafast metrology with strong expertise in the production and characterization of high energy ultrashort pulses. We provide
Ultrafast instrumentation (No Alignment!) We offer products specialized in ultrafast metrology with strong expertise in the production and characterization of high energy ultrashort pulses. We provide
Optical systems have carrier frequencies of ~100 THz. This corresponds to wavelengths from µm.
 Introduction A communication system transmits information form one place to another. This could be from one building to another or across the ocean(s). Many systems use an EM carrier wave to transmit information.
Introduction A communication system transmits information form one place to another. This could be from one building to another or across the ocean(s). Many systems use an EM carrier wave to transmit information.
Optics Communications
 Optics Communications 283 (2010) 3678 3682 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Ultra-low-loss inverted taper coupler for silicon-on-insulator
Optics Communications 283 (2010) 3678 3682 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Ultra-low-loss inverted taper coupler for silicon-on-insulator
Flat Frequency Comb Generation Based on Efficiently Multiple Four-Wave Mixing Without Polarization Control
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 1, 216: 85 89 Flat Frequency Comb Generation Based on Efficiently Multiple Four-Wave Mixing Without Polarization Control Qimeng DONG, Bao SUN *, Fushen CHEN, and Jun JIANG
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 1, 216: 85 89 Flat Frequency Comb Generation Based on Efficiently Multiple Four-Wave Mixing Without Polarization Control Qimeng DONG, Bao SUN *, Fushen CHEN, and Jun JIANG
REU Student: Si (Athena) Pan Connecticut College Mentor: Dimitre Ouzounov Graduate Student Mentor: Heng Li Summer 2008
 REU Student: Si (Athena) Pan Connecticut College Mentor: Dimitre Ouzounov Graduate Student Mentor: Heng Li Summer 008 Ultrashort pulses, its measurement and motivation of my project Two-photon absorption
REU Student: Si (Athena) Pan Connecticut College Mentor: Dimitre Ouzounov Graduate Student Mentor: Heng Li Summer 008 Ultrashort pulses, its measurement and motivation of my project Two-photon absorption
Slow, Fast, and Backwards Light: Fundamental Aspects
 Slow, Fast, and Backwards Light: Fundamental Aspects Robert W. Boyd University of Rochester Paul Narum Norwegian Defence Research Establishment with George Gehring, Giovanni Piredda, Aaron Schweinsberg,
Slow, Fast, and Backwards Light: Fundamental Aspects Robert W. Boyd University of Rochester Paul Narum Norwegian Defence Research Establishment with George Gehring, Giovanni Piredda, Aaron Schweinsberg,
Fiber Lasers for EUV Lithography
 Fiber Lasers for EUV Lithography A. Galvanauskas, Kai Chung Hou*, Cheng Zhu CUOS, EECS Department, University of Michigan P. Amaya Arbor Photonics, Inc. * Currently with Cymer, Inc 2009 International Workshop
Fiber Lasers for EUV Lithography A. Galvanauskas, Kai Chung Hou*, Cheng Zhu CUOS, EECS Department, University of Michigan P. Amaya Arbor Photonics, Inc. * Currently with Cymer, Inc 2009 International Workshop
The Development of a High Quality and a High Peak Power Pulsed Fiber Laser With a Flexible Tunability of the Pulse Width
 The Development of a High Quality and a High Peak Power Pulsed Fiber Laser With a Flexible Tunability of the Pulse Width Ryo Kawahara *1, Hiroshi Hashimoto *1, Jeffrey W. Nicholson *2, Eisuke Otani *1,
The Development of a High Quality and a High Peak Power Pulsed Fiber Laser With a Flexible Tunability of the Pulse Width Ryo Kawahara *1, Hiroshi Hashimoto *1, Jeffrey W. Nicholson *2, Eisuke Otani *1,
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW INJECTION LOCKING RING LASER AMPLIFIER USING A COUNTER INJECTION: MULTIWAVELENGTH AMPLIFICATION
 DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW INJECTION LOCKING RING LASER AMPLIFIER USING A COUNTER INJECTION: MULTAVELENGTH AMPLIFICATION Rosen Vanyuhov Peev 1, Margarita Anguelova Deneva 1, Marin Nenchev Nenchev 1,2 1 Dept.
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW INJECTION LOCKING RING LASER AMPLIFIER USING A COUNTER INJECTION: MULTAVELENGTH AMPLIFICATION Rosen Vanyuhov Peev 1, Margarita Anguelova Deneva 1, Marin Nenchev Nenchev 1,2 1 Dept.
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015
 Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015 Chapter 9: Optical Parametric Amplifiers and Oscillators 9.8 Noncollinear optical parametric amplifier (NOPA) 9.9 Optical parametric chirped-pulse
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015 Chapter 9: Optical Parametric Amplifiers and Oscillators 9.8 Noncollinear optical parametric amplifier (NOPA) 9.9 Optical parametric chirped-pulse
Arbitrary Power Splitting Couplers Based on 3x3 Multimode Interference Structures for All-optical Computing
 Arbitrary Power Splitting Couplers Based on 3x3 Multimode Interference Structures for All-optical Computing Trung-Thanh Le Abstract--Chip level optical links based on VLSI photonic integrated circuits
Arbitrary Power Splitting Couplers Based on 3x3 Multimode Interference Structures for All-optical Computing Trung-Thanh Le Abstract--Chip level optical links based on VLSI photonic integrated circuits
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 35. Self-Phase-Modulation
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
Optical Transport Tutorial
 Optical Transport Tutorial 4 February 2015 2015 OpticalCloudInfra Proprietary 1 Content Optical Transport Basics Assessment of Optical Communication Quality Bit Error Rate and Q Factor Wavelength Division
Optical Transport Tutorial 4 February 2015 2015 OpticalCloudInfra Proprietary 1 Content Optical Transport Basics Assessment of Optical Communication Quality Bit Error Rate and Q Factor Wavelength Division
Simulation of semiconductor modelocked ring lasers with monolithically integrated pulse shaping elements
 Simulation of semiconductor modelocked ring lasers with monolithically integrated pulse shaping elements Martijn Heck, Yohan Barbarin, Erwin Bente Daan Lenstra Meint Smit Richard Nötzel, Xaveer Leijtens,
Simulation of semiconductor modelocked ring lasers with monolithically integrated pulse shaping elements Martijn Heck, Yohan Barbarin, Erwin Bente Daan Lenstra Meint Smit Richard Nötzel, Xaveer Leijtens,
Chapter 3 Signal Degradation in Optical Fibers
 What about the loss in optical fiber? Why and to what degree do optical signals gets distorted as they propagate along a fiber? Fiber links are limited by in path length by attenuation and pulse distortion.
What about the loss in optical fiber? Why and to what degree do optical signals gets distorted as they propagate along a fiber? Fiber links are limited by in path length by attenuation and pulse distortion.
