Fundamentals of Interferometry
|
|
|
- Octavia Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fundamentals of Interferometry ERIS, Rimini, Sept
2 Outline What is an interferometer? Basic theory Interlude: Fourier transforms for birdwatchers Review of assumptions and complications Interferometers and arrays: a few technical issues
3 Why Interferometry? Diffraction limit for a single-dish radio telescope ~λ/d radians Maximum aperture D ~ 300m (Arecibo) λ/d ~ 40 arcsec at 5 GHz For steerable telescopes D ~100m (Effelsberg) Solution: interferometry. Used at optical wavelengths in the early 20th century by Michelson and at radio wavelengths since Resolution is now ~λ/d radians, where d is the separation of the interferometer elements potentially d > Earth diameter. But how does this really work?
4 Young's slit experiment Angular spacing of fringes = λ/d Familiar from optics Essentially the way that astronomical interferometers operate in the optical and infrared ( direct detection )
5 Build up an image from many slits Number of apertures increases from frame to frame: 2, 4, 8,
6 But this is not how radio interferometers work in practice... The two techniques are closely related, and thinking of an image as built up of sinusoidal fringes from many pairs of apertures is intuitively very useful. But radio interferometers collect radiation (antenna), turn it into a digital signal (receiver) and generate the interference pattern in a special-purpose computer (correlator). How does this work? In order to understand the process and its assumptions, I find it simplest to start with the concept of the mutual coherence of a radio signal received from the same object at two different places. Many current developments involve the simplifying assumptions, so I will try to state these clearly (and return to them later).
7 The ideal interferometer (1) An astrophysical source at location R causes a time-variable electric field E(R,t). An electromagnetic wave propagates to us at point r. Express the field as a Fourier series in which the only time-varying functions are complex exponentials. We are interested only in the (complex) coefficients of this series, Eν(R). E(R,t) = Eν(R)exp(2πiνt)dν Simplification 1: monochromatic radiation Eν(r) = Pν(R,r) Eν(R) dx dy dz where Pν(R,r) is the propagator Simplification 2: scalar field (ignore polarization) Simplification 3: sources are all far away Therefore, equivalent to having all sources at a fixed distance R - no depth information.
8 The ideal interferometer (2) Simplification 4: space between us and the sources is empty In this case, the propagator is quite simple (Huygens' Principle): Eν(r) = Eν(R){exp[2πi R-r /c]/ R-r } ds (ds is the element of area at distance R ) What we can measure is the correlation of the field at two different observing locations. This is Cν(r1,r2) = <Eν(r1)E*ν(r2)> where <> denotes an expectation value and * means complex conjugation. Simplification 5: radiation from astronomical objects is not spatially coherent ('random noise'). <Eν(R1)E*ν(R2)> = 0 unless R1 = R2
9 The ideal interferometer (3) Now write s = R/ R and Iν(s) = R 2< Eν(s) 2> (the observed intensity). Using the approximation of large distance to the source again: Cν(r1,r2) = Iν(s) exp [-2πiνs.(r1-r2)/c] dω Cν(r1,r2), the spatial coherence function, depends only on separation r1-r2, so we can keep one point fixed and move the other around. It is a complex function, with real and imaginary parts, or an amplitude and phase. An interferometer is a device for measuring the spatial coherence function
10 u,v,w and direction cosines
11 Basic Fourier Relation Simplification 6: receiving elements have no direction dependence Simplification 7A: all measurements are in the same plane, w=0. C(r1,r2) = Vν(u,v,0) = Iν(l,m) {exp[-2πi(ul+vm)]/(1-l2-m2)1/2} dl dm This is a Fourier transform relation between the complex visibility Vν (the spatial coherence function with separations expressed in wavelengths) and a modified intensity Iν(l,m) /(1-l2-m2)1/2. Simplification 7B: all sources are in a small region of sky Pick a special coordinate system such that the phase tracking centre has s0 = (0,0,1) C(r1,r2) = exp(-2πiw)v'ν(u,v), where V'ν(u,v) = Iν(l,m) exp[-2πi(ul+vm)] dl dm
12 Fourier Inversion In either simplified case, we can invert the Fourier transform to derive the intensity, e.g.: Iν(l,m) = V'ν(u,v) exp[2πi(ul+vm)] du dv This is the fundamental equation of synthesis imaging. Interferometrists like to refer to the (u,v) plane. Remember that u, v (and w) are measured in wavelengths. Simplification 8: We have so far implicitly assumed that we can measure the visibility everywhere.
13 Interlude: Fourier transforms for birdwatchers Some useful properties of Fourier transforms to keep in mind. Fourier transform pairs in one dimension Convolution
14 Simple 1D Fourier transform pairs
15 More 1D Fourier transform pairs N.B.: Sharp edges in the intensity distribution lead to ripples in visibility, and vice versa.
16 Fourier Transforms of Gaussians The Fourier transform of a Gaussian function is another Gaussian FWHM on sky is inversely proportional to FWHM in spatial frequency: fat objects have thin Fourier transforms and vice versa.
17 Guess the image competition This is the amplitude of the Fourier transform of an image of a well-known object. Can you: - Say something about its size, shape and orientation? - Deduce anything about its fine-scale structure?
18 The answer
19 You need phase and amplitude Phase only Amplitude only
20 Simplification 1 Radiation is monochromatic We are interested in observing wide bands, both for spectroscopy (e.g. HI, molecular lines) and for extra sensitivity for continuum imaging, so we have to get round this restriction. In fact, we can easily divide the band into multiple spectral channels (details later) There are imaging restrictions only if the individual channels are too wide for the field size (often the case for older VLA continuum data) see imaging lectures. This effect, bandwidth smearing, restricts the usable field of view. The angular extent is roughly (Δν/ν0)(l2+m2)1/2 Much less of an issue for modern correlators, which have many more frequency channels per unit frequency.
21 Simplifications 2 and 3 Treat the radiation field as a scalar quantity. The field is a vector, and we are interested in both components (i.e. its polarization). In fact this makes no difference to the analysis as long as we measure two states of polarization (e.g. right and left circular or crossed linear) and account for coupling between the states. Come back to this later. Sources are all a long way away Strictly speaking, this means in the far field of the interferometer, so that the distance is > D2/λ, where D is the interferometer baseline. This is true except in the extreme case of very long baseline observations of solar-system objects.
22 Simplification 4 Radiation is not spatially coherent Generally true, even if the radiation mechanism is itself coherent (masers, pulsars) May become detectable in observations with extremely high spatial and spectral resolution. Coherence can be produced by scattering (since signals from the same location in a source are spatially coherent, but travel by different paths through the interstellar or interplanetary medium)
23 Simplifications 5 and 6 Space between us and the source is empty The receiving elements have no direction dependence Closely related and not true in general. Examples: Antennas are usually designed to be highly directional Ionospheric and tropospheric fluctuations (which lead to path/phase and amplitude errors, sometimes seriously direction-dependent) Ionospheric Faraday rotation, which changes the plane of polarization. Interstellar or interplanetary scattering Standard calibration deals with the case that there is no direction dependence (i.e. each antenna has an associated amplitude and phase which may be time-variable) Direction dependence is harder to deal with, but is becoming more important as field sizes increase.
24 Primary Beam If the response of the antenna + atmosphere is direction-dependent, then we are measuring Iν(l,m) D1ν(l,m)D*2ν(l,m) instead of Iν(l,m) (ignore polarization for now) An easier case is when the direction dependence is just due to the antennas, and they all have the same response Aν(l,m) = Dν(l,m) 2 In this case, V'ν(u,v) = Aν(l,m)Iν(l,m) exp[-2πi(ul+vm)] dl dm We just make the standard Fourier inversion and then divide by the primary beam Aν(l,m) Doesn't work for the atmosphere, or if antennas are different
25 Simplification 7 (A) Antennas are in a single plane or (B) the field is small Not true for wide-field imaging (except for snapshots) Particularly relevant at low frequencies Basic imaging equation becomes: Vν(u,v,w) = Iν(l,m) {exp[-2πi(ul+vm+(1-l2-m2)1/2w)]/(1-l2-m2)1/2} dl dm No longer a 2D Fourier transform, so analysis becomes much more complicated (the w term ) Map individual small fields ( facets ) and combine later w-projection See lectures on low-frequency imaging and LOFAR
26 Simplification 8 We have implicitly assumed that we can measure the visibility function everywhere. In fact: We have a number of antennas at fixed locations on the Earth The Earth rotates We make measurements over finite (usually short) time intervals This means that we actually measure only at discrete u, v (and w) positions.
27 Sampling In 2D, this process can be described by a sampling function S(u,v) which is a delta function where we have taken data and zero elsewhere. IDν(l,m) = Vν(u,v) S(u,v) exp[2πi(ul+vm)] du dv is the dirty image, which is the Fourier transform of the sampled visibility data. Using the convolution theorem: IDν(l,m) = Iν(l,m) B(l,m) where the denotes convolution and B(l,m) = S(u,v) exp[2πi(ul+vm)] du dv is the synthesised beam. The dirty image is the convolution of the true image of the sky with the dirty beam. Working out the true image of the sky from this is deconvolution.
28 Sampling and imaging Model Dirty beam Coverage Dirty image This is a snapshot observation.
29 Deconvolution The next stage in the imaging process is to estimate the convolution of the sky with a well-behaved restoring beam (usually a Gaussian function) rather than the dirty beam. This is deconvolution. Methods for this include CLEAN and maximum entropy see lecture on imaging. Model Convolved model Dirty image CLEAN image (noise added)
30 Resolution, maximum scale and field size Some useful parameters: Resolution /rad: λ/dmax Maximum observable scale /rad: λ/dmin Primary beam/rad: λ/d Good coverage of the u-v plane (many antennas, Earth rotation) allows high-quality imaging. Some brightness distributions are in principle undetectable: Uniform Sinusoid with Fourier transform in an unsampled part of the u-v plane. Sources with all brightness on scales >λ/dmin are resolved out. Sources with all brightess on scales < λ/dmax look like points,
31 Multiconfiguration imaging
32 Noise RMS noise level Srms Tsys is the system temperature, Aeff is the effective area of the antennas, NA is the number of antennas, Δν is the bandwidth, tint is the integration time and k is Boltzmann's constant For good sensitivity, you need low Tsys (receivers), large Aeff (big, accurate antennas), large NA (many antennas) and, for continuum, large bandwidth Δν.
33 Interferometry in practice Antennas collect RF signal Receivers amplify, mix with a phase-stable local oscillator signal to convert to lower frequencies and digitize Correlator corrects for geometrical delays and calculates complex visibilities for multiple spectral channels Pipeline/off-line software applies calibrations and makes images from visibilities.
34 Antennas Antennas for high frequencies are usually paraboloidal dishes, used in a Cassegrain configuration and highly directional. Surface rms should be <λ/10. Low-frequency antennas can be dipoles, yagis etc. and are often electronically steered.
35 Receivers Cryogenically cooled for low noise (except at low frequencies) Normally detect two polarization states (Amplify RF signal), mix with phase-stable local oscillator signal to make intermediate frequency (IF) Two sidebands (one or both used) Possibly additional stages of frequency conversion and/or filtering Digitize in coarse frequency blocks variously known as IF's, basebands, sub-bands, etc. Send to correlator (e.g. over optical fibre) or store (VLBI).
36 Polarization The receiver usually measures two (nominally) orthogonal polarization states, e.g. right and left circular or crossed linear. Then the polarization is described by a 2 x 2 matrix of correlations between components, which we can correlate and image separately. Measurement equation formalism used to describe calibration (see lecture on polarization). For right and left circular polarizations (e.g. VLA, emerlin): RR* RL* RL* LR* LL* LL* = RR* RL* I+V Q+iU LR* LL* Q iu I V
37 Example: ALMA signal flow
38 Geometrical delay A delay just corresponds to a change in arrival time of the wavefront. It is equivalent to a frequency-dependent phase change 2πτν. Geometrical delay is known for a given source and antenna position and can be removed by the correlator.
39 Complex correlator Signals from antennas Real Imaginary
40 Multiple spectral channels We make multiple channels by correlating with different values of lag, τ. This is a delay introduced into the signal from one antenna with respect to another as in the previous slide. For each quasimonochromatic frequency channel, a lag is equivalent to a phase shift 2πiτν, i.e. V(u,v,τ) = V(u,v,ν)exp(2πiτν) dν This is another Fourier transform relation with complementary variables ν and τ, and can be inverted to extract the desired visibility as a function of frequency. In practice, we do this digitally, in finite frequency channels: V(u,v,jΔν) = Σk V(u,v, kδτ) exp(-2πijkδνδτ) Each spectral channel is then imaged (and deconvolved) individually. The final product is a data cube, regularly gridded in two spatial and one spectral coordinate.
41 Basic steps in data processing Start with complex visibilities Correct for instrumental signature - CALIBRATION Fourier transform, deconvolve correct for antenna response IMAGING Iterate to improve calibration, especially for atmospheric effects SELF-CALIBRATION Derive quantities of astronomical interest IMAGE ANALYSIS
42 References and thanks Synthesis Imaging in Radio Astronomy II (ASP Conference Series 180, eds Taylor, Carilli & Perley, 1999), especially lecture 1 by B. Clark. On-line lectures of recent NRAO Summer School (2010) Born & Wolf, Principles of Optics (1980) [for coherence functions] Thomson, Moran & Swenson (2000), Interferometry and Synthesis in Radio Astronomy [for a more hardware-orientated point of view] Thanks for illustrations to: Rick Perley, Anita Richards, Katherine Blundell, Cornelia Lang
Fundamentals of Interferometry
 Fundamentals of Interferometry ERIS, Dwingeloo, Sept 8-13 2013 Outline What is an interferometer? Basic theory Interlude: Fourier transforms for birdwatchers Review of assumptions and complications Interferometers
Fundamentals of Interferometry ERIS, Dwingeloo, Sept 8-13 2013 Outline What is an interferometer? Basic theory Interlude: Fourier transforms for birdwatchers Review of assumptions and complications Interferometers
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry. Robert Laing (ESO)
 Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Robert Laing (ESO) 1 ERIS 2015 Objectives A more formal approach to radio interferometry using coherence functions A complementary way of looking at the technique Simplifying
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Robert Laing (ESO) 1 ERIS 2015 Objectives A more formal approach to radio interferometry using coherence functions A complementary way of looking at the technique Simplifying
Introduction to Interferometry. Michelson Interferometer. Fourier Transforms. Optics: holes in a mask. Two ways of understanding interferometry
 Introduction to Interferometry P.J.Diamond MERLIN/VLBI National Facility Jodrell Bank Observatory University of Manchester ERIS: 5 Sept 005 Aim to lay the groundwork for following talks Discuss: General
Introduction to Interferometry P.J.Diamond MERLIN/VLBI National Facility Jodrell Bank Observatory University of Manchester ERIS: 5 Sept 005 Aim to lay the groundwork for following talks Discuss: General
INTERFEROMETRY: II Nissim Kanekar (NCRA TIFR)
 INTERFEROMETRY: II Nissim Kanekar (NCRA TIFR) WSRT GMRT VLA ATCA ALMA SKA MID PLAN Introduction. The van Cittert Zernike theorem. A 2 element interferometer. The fringe pattern. 2 D and 3 D interferometers.
INTERFEROMETRY: II Nissim Kanekar (NCRA TIFR) WSRT GMRT VLA ATCA ALMA SKA MID PLAN Introduction. The van Cittert Zernike theorem. A 2 element interferometer. The fringe pattern. 2 D and 3 D interferometers.
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry
 Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro Fourteenth NRAO Synthesis Imaging Summer School Socorro, NM Topics Why Interferometry? The Single Dish as an interferometer The Basic Interferometer
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro Fourteenth NRAO Synthesis Imaging Summer School Socorro, NM Topics Why Interferometry? The Single Dish as an interferometer The Basic Interferometer
Introduction to Imaging in CASA
 Introduction to Imaging in CASA Mark Rawlings, Juergen Ott (NRAO) Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long Baseline Array Overview
Introduction to Imaging in CASA Mark Rawlings, Juergen Ott (NRAO) Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long Baseline Array Overview
Cross Correlators. Jayce Dowell/Greg Taylor. University of New Mexico Spring Astronomy 423 at UNM Radio Astronomy
 Cross Correlators Jayce Dowell/Greg Taylor University of New Mexico Spring 2017 Astronomy 423 at UNM Radio Astronomy Outline 2 Re-cap of interferometry What is a correlator? The correlation function Simple
Cross Correlators Jayce Dowell/Greg Taylor University of New Mexico Spring 2017 Astronomy 423 at UNM Radio Astronomy Outline 2 Re-cap of interferometry What is a correlator? The correlation function Simple
Basic Mapping Simon Garrington JBO/Manchester
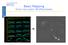 Basic Mapping Simon Garrington JBO/Manchester Introduction Output from radio arrays (VLA, VLBI, MERLIN etc) is just a table of the correlation (amp. & phase) measured on each baseline every few seconds.
Basic Mapping Simon Garrington JBO/Manchester Introduction Output from radio arrays (VLA, VLBI, MERLIN etc) is just a table of the correlation (amp. & phase) measured on each baseline every few seconds.
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry
 Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro ATNF Radio Astronomy School Narrabri, NSW 29 Sept. 03 Oct. 2014 Topics Introduction: Sensors, Antennas, Brightness, Power Quasi-Monochromatic
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro ATNF Radio Astronomy School Narrabri, NSW 29 Sept. 03 Oct. 2014 Topics Introduction: Sensors, Antennas, Brightness, Power Quasi-Monochromatic
Introduction to Radio Astronomy. Richard Porcas Max-Planck-Institut fuer Radioastronomie, Bonn
 Introduction to Radio Astronomy Richard Porcas Max-Planck-Institut fuer Radioastronomie, Bonn 1 Contents Radio Waves Radio Emission Processes Radio Noise Radio source names and catalogues Radio telescopes
Introduction to Radio Astronomy Richard Porcas Max-Planck-Institut fuer Radioastronomie, Bonn 1 Contents Radio Waves Radio Emission Processes Radio Noise Radio source names and catalogues Radio telescopes
Imaging Simulations with CARMA-23
 BIMA memo 101 - July 2004 Imaging Simulations with CARMA-23 M. C. H. Wright Radio Astronomy laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 94720 ABSTRACT We simulated imaging for the 23-antenna CARMA
BIMA memo 101 - July 2004 Imaging Simulations with CARMA-23 M. C. H. Wright Radio Astronomy laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 94720 ABSTRACT We simulated imaging for the 23-antenna CARMA
Interferometry I Parkes Radio School Jamie Stevens ATCA Senior Systems Scientist
 Interferometry I Parkes Radio School 2011 Jamie Stevens ATCA Senior Systems Scientist 2011-09-28 References This talk will reuse material from many previous Radio School talks, and from the excellent textbook
Interferometry I Parkes Radio School 2011 Jamie Stevens ATCA Senior Systems Scientist 2011-09-28 References This talk will reuse material from many previous Radio School talks, and from the excellent textbook
Practicalities of Radio Interferometry
 Practicalities of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro Fourth INPE Course in Astrophysics: Radio Astronomy in the 21 st Century Topics Practical Extensions to the Theory: Finite bandwidth Rotating
Practicalities of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro Fourth INPE Course in Astrophysics: Radio Astronomy in the 21 st Century Topics Practical Extensions to the Theory: Finite bandwidth Rotating
Radio Interferometry. Xuening Bai. AST 542 Observational Seminar May 4, 2011
 Radio Interferometry Xuening Bai AST 542 Observational Seminar May 4, 2011 Outline Single-dish radio telescope Two-element interferometer Interferometer arrays and aperture synthesis Very-long base line
Radio Interferometry Xuening Bai AST 542 Observational Seminar May 4, 2011 Outline Single-dish radio telescope Two-element interferometer Interferometer arrays and aperture synthesis Very-long base line
Practicalities of Radio Interferometry
 Practicalities of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro 13 th Synthesis Imaging Summer School 29 May 5 June, 2012 Socorro, NM Topics Practical Extensions to the Theory: Finite bandwidth Rotating
Practicalities of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro 13 th Synthesis Imaging Summer School 29 May 5 June, 2012 Socorro, NM Topics Practical Extensions to the Theory: Finite bandwidth Rotating
Antennas. Greg Taylor. University of New Mexico Spring Astronomy 423 at UNM Radio Astronomy
 Antennas Greg Taylor University of New Mexico Spring 2017 Astronomy 423 at UNM Radio Astronomy Outline 2 Fourier Transforms Interferometer block diagram Antenna fundamentals Types of antennas Antenna performance
Antennas Greg Taylor University of New Mexico Spring 2017 Astronomy 423 at UNM Radio Astronomy Outline 2 Fourier Transforms Interferometer block diagram Antenna fundamentals Types of antennas Antenna performance
The Basics of Radio Interferometry. Frédéric Boone LERMA, Observatoire de Paris
 The Basics of Radio Interferometry LERMA, Observatoire de Paris The Basics of Radio Interferometry The role of interferometry in astronomy = role of venetian blinds in Film Noir 2 The Basics of Radio Interferometry
The Basics of Radio Interferometry LERMA, Observatoire de Paris The Basics of Radio Interferometry The role of interferometry in astronomy = role of venetian blinds in Film Noir 2 The Basics of Radio Interferometry
Introduction to Radio Interferometry Anand Crossley Alison Peck, Jim Braatz, Ashley Bemis (NRAO)
 Introduction to Radio Interferometry Anand Crossley Alison Peck, Jim Braatz, Ashley Bemis (NRAO) Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope
Introduction to Radio Interferometry Anand Crossley Alison Peck, Jim Braatz, Ashley Bemis (NRAO) Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope
Introduction to Radio Astronomy!
 Introduction to Radio Astronomy! Sources of radio emission! Radio telescopes - collecting the radiation! Processing the radio signal! Radio telescope characteristics! Observing radio sources Sources of
Introduction to Radio Astronomy! Sources of radio emission! Radio telescopes - collecting the radiation! Processing the radio signal! Radio telescope characteristics! Observing radio sources Sources of
Introduction to Radio Interferometry Sabrina Stierwalt Alison Peck, Jim Braatz, Ashley Bemis
 Introduction to Radio Interferometry Sabrina Stierwalt Alison Peck, Jim Braatz, Ashley Bemis Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very
Introduction to Radio Interferometry Sabrina Stierwalt Alison Peck, Jim Braatz, Ashley Bemis Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very
Why Single Dish? Darrel Emerson NRAO Tucson. NAIC-NRAO School on Single-Dish Radio Astronomy. Green Bank, August 2003.
 Why Single Dish? Darrel Emerson NRAO Tucson NAIC-NRAO School on Single-Dish Radio Astronomy. Green Bank, August 2003. Why Single Dish? What's the Alternative? Comparisons between Single-Dish, Phased Array
Why Single Dish? Darrel Emerson NRAO Tucson NAIC-NRAO School on Single-Dish Radio Astronomy. Green Bank, August 2003. Why Single Dish? What's the Alternative? Comparisons between Single-Dish, Phased Array
Why Single Dish? Darrel Emerson NRAO Tucson. NAIC-NRAO School on Single-Dish Radio Astronomy. Green Bank, August 2003.
 Why Single Dish? Darrel Emerson NRAO Tucson NAIC-NRAO School on Single-Dish Radio Astronomy. Green Bank, August 2003. Why Single Dish? What's the Alternative? Comparisons between Single-Dish, Phased Array
Why Single Dish? Darrel Emerson NRAO Tucson NAIC-NRAO School on Single-Dish Radio Astronomy. Green Bank, August 2003. Why Single Dish? What's the Alternative? Comparisons between Single-Dish, Phased Array
Radio Interferometry -- II
 Radio Interferometry -- II Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro ATNF School on Radio Astronomy Narrabri, NSW 29 Sept 3 Oct, 2014 Topics Practical Extensions to the Theory: Finite bandwidth Rotating reference frames
Radio Interferometry -- II Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro ATNF School on Radio Astronomy Narrabri, NSW 29 Sept 3 Oct, 2014 Topics Practical Extensions to the Theory: Finite bandwidth Rotating reference frames
Radio Interferometry -- II
 Radio Interferometry -- II Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro 15 th Synthesis Imaging Summer School June 1 9, 2016 Socorro, NM Topics Practical Extensions to the Theory: Real Sensors Finite bandwidth Rotating reference
Radio Interferometry -- II Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro 15 th Synthesis Imaging Summer School June 1 9, 2016 Socorro, NM Topics Practical Extensions to the Theory: Real Sensors Finite bandwidth Rotating reference
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry
 Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro Green Bank Interferometry School NRAO/GB 12 14 July, 2015 Topics The Need for Interferometry Some Basics: Antennas as E-field Converters Conceptual
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro Green Bank Interferometry School NRAO/GB 12 14 July, 2015 Topics The Need for Interferometry Some Basics: Antennas as E-field Converters Conceptual
Volume 82 VERY LONG BASELINE INTERFEROMETRY AND THE VLBA. J. A. Zensus, P. J. Diamond, and P. J. Napier
 ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC CONFERENCE SERIES Volume 82 VERY LONG BASELINE INTERFEROMETRY AND THE VLBA Proceedings of a Summer School held in Socorro, New Mexico 23-30 June 1993 NRAO Workshop No.
ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC CONFERENCE SERIES Volume 82 VERY LONG BASELINE INTERFEROMETRY AND THE VLBA Proceedings of a Summer School held in Socorro, New Mexico 23-30 June 1993 NRAO Workshop No.
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry
 Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro 15 th Synthesis Imaging School Socorro, NM 01 09 June, 2016 Topics The Need for Interferometry Some Basics: Antennas as E-field Converters
Fundamentals of Radio Interferometry Rick Perley, NRAO/Socorro 15 th Synthesis Imaging School Socorro, NM 01 09 June, 2016 Topics The Need for Interferometry Some Basics: Antennas as E-field Converters
Radio Astronomy: SKA-Era Interferometry and Other Challenges. Dr Jasper Horrell, SKA SA (and Dr Oleg Smirnov, Rhodes and SKA SA)
 Radio Astronomy: SKA-Era Interferometry and Other Challenges Dr Jasper Horrell, SKA SA (and Dr Oleg Smirnov, Rhodes and SKA SA) ASSA Symposium, Cape Town, Oct 2012 Scope SKA antenna types Single dishes
Radio Astronomy: SKA-Era Interferometry and Other Challenges Dr Jasper Horrell, SKA SA (and Dr Oleg Smirnov, Rhodes and SKA SA) ASSA Symposium, Cape Town, Oct 2012 Scope SKA antenna types Single dishes
Large-field imaging. Frédéric Gueth, IRAM Grenoble. 7th IRAM Millimeter Interferometry School 4 8 October 2010
 Large-field imaging Frédéric Gueth, IRAM Grenoble 7th IRAM Millimeter Interferometry School 4 8 October 2010 Large-field imaging The problems The field of view is limited by the antenna primary beam width
Large-field imaging Frédéric Gueth, IRAM Grenoble 7th IRAM Millimeter Interferometry School 4 8 October 2010 Large-field imaging The problems The field of view is limited by the antenna primary beam width
Antennas. Greg Taylor. University of New Mexico Spring Astronomy 423 at UNM Radio Astronomy
 Antennas Greg Taylor University of New Mexico Spring 2011 Astronomy 423 at UNM Radio Astronomy Radio Window 2 spans a wide range of λ and ν from λ ~ 0.33 mm to ~ 20 m! (ν = 1300 GHz to 15 MHz ) Outline
Antennas Greg Taylor University of New Mexico Spring 2011 Astronomy 423 at UNM Radio Astronomy Radio Window 2 spans a wide range of λ and ν from λ ~ 0.33 mm to ~ 20 m! (ν = 1300 GHz to 15 MHz ) Outline
Why Single Dish? Why Single Dish? Darrel Emerson NRAO Tucson
 Why Single Dish? Darrel Emerson NRAO Tucson Why Single Dish? What's the Alternative? Comparisons between Single-Dish, Phased Array & Interferometers Advantages and Disadvantages of Correlation Interferometer
Why Single Dish? Darrel Emerson NRAO Tucson Why Single Dish? What's the Alternative? Comparisons between Single-Dish, Phased Array & Interferometers Advantages and Disadvantages of Correlation Interferometer
Sideband Smear: Sideband Separation with the ALMA 2SB and DSB Total Power Receivers
 and DSB Total Power Receivers SCI-00.00.00.00-001-A-PLA Version: A 2007-06-11 Prepared By: Organization Date Anthony J. Remijan NRAO A. Wootten T. Hunter J.M. Payne D.T. Emerson P.R. Jewell R.N. Martin
and DSB Total Power Receivers SCI-00.00.00.00-001-A-PLA Version: A 2007-06-11 Prepared By: Organization Date Anthony J. Remijan NRAO A. Wootten T. Hunter J.M. Payne D.T. Emerson P.R. Jewell R.N. Martin
Principles of Radio Interferometry. Ast735: Submillimeter Astronomy IfA, University of Hawaii
 Principles of Radio Interferometry Ast735: Submillimeter Astronomy IfA, University of Hawaii 1 Resources IRAM millimeter interferometry school hdp://www.iram- inshtute.org/en/content- page- 248-7- 67-248-
Principles of Radio Interferometry Ast735: Submillimeter Astronomy IfA, University of Hawaii 1 Resources IRAM millimeter interferometry school hdp://www.iram- inshtute.org/en/content- page- 248-7- 67-248-
Observational Astronomy
 Observational Astronomy Instruments The telescope- instruments combination forms a tightly coupled system: Telescope = collecting photons and forming an image Instruments = registering and analyzing the
Observational Astronomy Instruments The telescope- instruments combination forms a tightly coupled system: Telescope = collecting photons and forming an image Instruments = registering and analyzing the
EVLA and LWA Imaging Challenges
 EVLA and LWA Imaging Challenges Steven T. Myers IGPP, Los Alamos National Laboratory and National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, NM 1 EVLA key issues 2 Key algorithmic issues ambitious goals / hard
EVLA and LWA Imaging Challenges Steven T. Myers IGPP, Los Alamos National Laboratory and National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, NM 1 EVLA key issues 2 Key algorithmic issues ambitious goals / hard
Correlator Development at Haystack. Roger Cappallo Haystack-NRAO Technical Mtg
 Correlator Development at Haystack Roger Cappallo Haystack-NRAO Technical Mtg. 2006.10.26 History of Correlator Development at Haystack ~1973 Mk I 360 Kb/s x 2 stns. 1981 Mk III 112 Mb/s x 4 stns. 1986
Correlator Development at Haystack Roger Cappallo Haystack-NRAO Technical Mtg. 2006.10.26 History of Correlator Development at Haystack ~1973 Mk I 360 Kb/s x 2 stns. 1981 Mk III 112 Mb/s x 4 stns. 1986
Wide-Band Imaging. Outline : CASS Radio Astronomy School Sept 2012 Narrabri, NSW, Australia. - What is wideband imaging?
 Wide-Band Imaging 24-28 Sept 2012 Narrabri, NSW, Australia Outline : - What is wideband imaging? - Two Algorithms Urvashi Rau - Many Examples National Radio Astronomy Observatory Socorro, NM, USA 1/32
Wide-Band Imaging 24-28 Sept 2012 Narrabri, NSW, Australia Outline : - What is wideband imaging? - Two Algorithms Urvashi Rau - Many Examples National Radio Astronomy Observatory Socorro, NM, USA 1/32
VLBI Post-Correlation Analysis and Fringe-Fitting
 VLBI Post-Correlation Analysis and Fringe-Fitting Michael Bietenholz With (many) Slides from George Moellenbroek and Craig Walker NRAO Calibration is important! What Is Delivered by a Synthesis Array?
VLBI Post-Correlation Analysis and Fringe-Fitting Michael Bietenholz With (many) Slides from George Moellenbroek and Craig Walker NRAO Calibration is important! What Is Delivered by a Synthesis Array?
Laboratorio di Astrofisica (laboratorio radio)
 Daniele Dallacasa Laboratorio di Astrofisica (laboratorio radio) Basic Theory: 1. Fraunhofer diffraction & Fourier Transforms why radio telescopes are diffraction limited. Antenna concepts (as specific
Daniele Dallacasa Laboratorio di Astrofisica (laboratorio radio) Basic Theory: 1. Fraunhofer diffraction & Fourier Transforms why radio telescopes are diffraction limited. Antenna concepts (as specific
Introduction to Radioastronomy: Interferometers and Aperture Synthesis
 Introduction to Radioastronomy: Interferometers and Aperture Synthesis J.Köppen joachim.koppen@astro.unistra.fr http://astro.u-strasbg.fr/~koppen/jkhome.html Problem No.2: Angular resolution Diffraction
Introduction to Radioastronomy: Interferometers and Aperture Synthesis J.Köppen joachim.koppen@astro.unistra.fr http://astro.u-strasbg.fr/~koppen/jkhome.html Problem No.2: Angular resolution Diffraction
LOFAR: Special Issues
 Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy LOFAR: Special Issues John McKean (ASTRON) ASTRON is part of the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) 1 Preamble http://www.astron.nl/~mckean/eris-2011-2.pdf
Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy LOFAR: Special Issues John McKean (ASTRON) ASTRON is part of the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) 1 Preamble http://www.astron.nl/~mckean/eris-2011-2.pdf
Fourier Transforms in Radio Astronomy
 Fourier Transforms in Radio Astronomy Kavilan Moodley, UKZN Slides taken from N Gupta s lectures: SKA School 2013 van-cittert Zernike theorem Extended, quasi-monochromatic, incoherent source X (l,m) Y
Fourier Transforms in Radio Astronomy Kavilan Moodley, UKZN Slides taken from N Gupta s lectures: SKA School 2013 van-cittert Zernike theorem Extended, quasi-monochromatic, incoherent source X (l,m) Y
Propagation effects (tropospheric and ionospheric phase calibration)
 Propagation effects (tropospheric and ionospheric phase calibration) Prof. Steven Tingay Curtin University of Technology Perth, Australia With thanks to Alan Roy (MPIfR), James Anderson (JIVE), Tasso Tzioumis
Propagation effects (tropospheric and ionospheric phase calibration) Prof. Steven Tingay Curtin University of Technology Perth, Australia With thanks to Alan Roy (MPIfR), James Anderson (JIVE), Tasso Tzioumis
Antennas & Receivers in Radio Astronomy
 Antennas & Receivers in Radio Astronomy Mark McKinnon Fifteenth Synthesis Imaging Workshop 1-8 June 2016 Purpose & Outline Purpose: describe how antenna elements can affect the quality of images produced
Antennas & Receivers in Radio Astronomy Mark McKinnon Fifteenth Synthesis Imaging Workshop 1-8 June 2016 Purpose & Outline Purpose: describe how antenna elements can affect the quality of images produced
Phased Array Feeds A new technology for wide-field radio astronomy
 Phased Array Feeds A new technology for wide-field radio astronomy Aidan Hotan ASKAP Project Scientist 29 th September 2017 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE Outline Review of radio astronomy concepts
Phased Array Feeds A new technology for wide-field radio astronomy Aidan Hotan ASKAP Project Scientist 29 th September 2017 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE Outline Review of radio astronomy concepts
REDUCTION OF ALMA DATA USING CASA SOFTWARE
 REDUCTION OF ALMA DATA USING CASA SOFTWARE Student: Nguyen Tran Hoang Supervisor: Pham Tuan Anh Hanoi, September - 2016 1 CONTENS Introduction Interferometry Scientific Target M100 Calibration Imaging
REDUCTION OF ALMA DATA USING CASA SOFTWARE Student: Nguyen Tran Hoang Supervisor: Pham Tuan Anh Hanoi, September - 2016 1 CONTENS Introduction Interferometry Scientific Target M100 Calibration Imaging
Introduction to interferometry with bolometers: Bob Watson and Lucio Piccirillo
 Introduction to interferometry with bolometers: Bob Watson and Lucio Piccirillo Paris, 19 June 2008 Interferometry (heterodyne) In general we have i=1,...,n single dishes (with a single or dual receiver)
Introduction to interferometry with bolometers: Bob Watson and Lucio Piccirillo Paris, 19 June 2008 Interferometry (heterodyne) In general we have i=1,...,n single dishes (with a single or dual receiver)
Heterogeneous Array Imaging with the CARMA Telescope
 Heterogeneous Array Imaging with the CARMA Telescope M. C. H. Wright Radio Astronomy laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 94720 February 1, 2011 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Many people have made the
Heterogeneous Array Imaging with the CARMA Telescope M. C. H. Wright Radio Astronomy laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 94720 February 1, 2011 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Many people have made the
Richard Dodson 1/28/2014 NARIT-KASI Winter School
 Goals: Technical introduction very short So what to cover? Things which are essential: How radio power is received - I How an interferometer works -II Antenna Fundamentals Black Body Radiation Brightness
Goals: Technical introduction very short So what to cover? Things which are essential: How radio power is received - I How an interferometer works -II Antenna Fundamentals Black Body Radiation Brightness
A Crash Course in Radio Astronomy and Interferometry: 1. Basic Radio/mm Astronomy
 A Crash Course in Radio Astronomy and Interferometry: 1. Basic Radio/mm Astronomy James Di Francesco National Research Council of Canada North American ALMA Regional Center Victoria (thanks to S. Dougherty,
A Crash Course in Radio Astronomy and Interferometry: 1. Basic Radio/mm Astronomy James Di Francesco National Research Council of Canada North American ALMA Regional Center Victoria (thanks to S. Dougherty,
Phased Array Feeds A new technology for multi-beam radio astronomy
 Phased Array Feeds A new technology for multi-beam radio astronomy Aidan Hotan ASKAP Deputy Project Scientist 2 nd October 2015 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE Outline Review of radio astronomy concepts.
Phased Array Feeds A new technology for multi-beam radio astronomy Aidan Hotan ASKAP Deputy Project Scientist 2 nd October 2015 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE Outline Review of radio astronomy concepts.
Spectral Line Observing
 Spectral Line Observing Ylva Pihlström, UNM Eleventh Synthesis Imaging Workshop Socorro, June 10-17, 2008 Introduction 2 Spectral line observers use many channels of width δν, over a total bandwidth Δν.
Spectral Line Observing Ylva Pihlström, UNM Eleventh Synthesis Imaging Workshop Socorro, June 10-17, 2008 Introduction 2 Spectral line observers use many channels of width δν, over a total bandwidth Δν.
How small can you get? reducing data volume, retaining good imaging
 How small can you get? reducing data volume, retaining good imaging Anita Richards UK ALMA Regional Centre Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics University of Manchester thanks to Crystal Brogan and all
How small can you get? reducing data volume, retaining good imaging Anita Richards UK ALMA Regional Centre Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics University of Manchester thanks to Crystal Brogan and all
EVLA System Commissioning Results
 EVLA System Commissioning Results EVLA Advisory Committee Meeting, March 19-20, 2009 Rick Perley EVLA Project Scientist t 1 Project Requirements EVLA Project Book, Chapter 2, contains the EVLA Project
EVLA System Commissioning Results EVLA Advisory Committee Meeting, March 19-20, 2009 Rick Perley EVLA Project Scientist t 1 Project Requirements EVLA Project Book, Chapter 2, contains the EVLA Project
High Fidelity Imaging of Extended Sources. Rick Perley NRAO Socorro, NM
 High Fidelity Imaging of Extended Sources Rick Perley NRAO Socorro, NM A Brief History of Calibration (VLA) An Amazing Fact: The VLA was proposed, and funded, without any real concept of how to calibrate
High Fidelity Imaging of Extended Sources Rick Perley NRAO Socorro, NM A Brief History of Calibration (VLA) An Amazing Fact: The VLA was proposed, and funded, without any real concept of how to calibrate
Radio Interferometer Array Point Spread Functions I. Theory and Statistics
 ALMA MEMO 389 Radio Interferometer Array Point Spread Functions I. Theory and Statistics David Woody Abstract This paper relates the optical definition of the PSF to radio interferometer arrays. The statistical
ALMA MEMO 389 Radio Interferometer Array Point Spread Functions I. Theory and Statistics David Woody Abstract This paper relates the optical definition of the PSF to radio interferometer arrays. The statistical
Antennas and Receivers in Radio Astronomy
 Antennas and Receivers in Radio Astronomy Mark McKinnon Eleventh Synthesis Imaging Workshop Socorro, June 10-17, 2008 Outline 2 Context Types of antennas Antenna fundamentals Reflector antennas Mounts
Antennas and Receivers in Radio Astronomy Mark McKinnon Eleventh Synthesis Imaging Workshop Socorro, June 10-17, 2008 Outline 2 Context Types of antennas Antenna fundamentals Reflector antennas Mounts
Sources classification
 Sources classification Radiometry relates to the measurement of the energy radiated by one or more sources in any region of the electromagnetic spectrum. As an antenna, a source, whose largest dimension
Sources classification Radiometry relates to the measurement of the energy radiated by one or more sources in any region of the electromagnetic spectrum. As an antenna, a source, whose largest dimension
Very Long Baseline Interferometry
 Very Long Baseline Interferometry Cormac Reynolds, JIVE European Radio Interferometry School, Bonn 12 Sept. 2007 VLBI Arrays EVN (Europe, China, South Africa, Arecibo) VLBA (USA) EVN + VLBA coordinate
Very Long Baseline Interferometry Cormac Reynolds, JIVE European Radio Interferometry School, Bonn 12 Sept. 2007 VLBI Arrays EVN (Europe, China, South Africa, Arecibo) VLBA (USA) EVN + VLBA coordinate
Very Long Baseline Interferometry. Richard Porcas Max-Planck-Institut fuer Radioastronomie, Bonn
 Very Long Baseline Interferometry Richard Porcas Max-Planck-Institut fuer Radioastronomie, Bonn 1 Contents Introduction Principles and Practice of VLBI High angular resolution of long baselines The geophysics
Very Long Baseline Interferometry Richard Porcas Max-Planck-Institut fuer Radioastronomie, Bonn 1 Contents Introduction Principles and Practice of VLBI High angular resolution of long baselines The geophysics
To print higher-resolution math symbols, click the Hi-Res Fonts for Printing button on the jsmath control panel.
 To print higher-resolution math symbols, click the Hi-Res Fonts for Printing button on the jsmath control panel. Radiometers Natural radio emission from the cosmic microwave background, discrete astronomical
To print higher-resolution math symbols, click the Hi-Res Fonts for Printing button on the jsmath control panel. Radiometers Natural radio emission from the cosmic microwave background, discrete astronomical
Deconvolution. Amy Mioduszewski National Radio Astronomy Observatory. Synthesis Imaging g in Radio Astronomy
 Deconvolution Amy Mioduszewski National Radio Astronomy Observatory Synthesis Imaging g in Radio Astronomy (based on a talk given by David Wilner (CfA) at the NRAO s 2010 Synthesis Imaging Workshop) 1
Deconvolution Amy Mioduszewski National Radio Astronomy Observatory Synthesis Imaging g in Radio Astronomy (based on a talk given by David Wilner (CfA) at the NRAO s 2010 Synthesis Imaging Workshop) 1
Guide to observation planning with GREAT
 Guide to observation planning with GREAT G. Sandell GREAT is a heterodyne receiver designed to observe spectral lines in the THz region with high spectral resolution and sensitivity. Heterodyne receivers
Guide to observation planning with GREAT G. Sandell GREAT is a heterodyne receiver designed to observe spectral lines in the THz region with high spectral resolution and sensitivity. Heterodyne receivers
1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter
 8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
THEORY OF MEASUREMENTS
 THEORY OF MEASUREMENTS Brian Mason Fifth NAIC-NRAO School on Single-Dish Radio Astronomy Arecibo, PR July 2009 OUTLINE Antenna-Sky Coupling Noise the Radiometer Equation Minimum Tsys Performance measures
THEORY OF MEASUREMENTS Brian Mason Fifth NAIC-NRAO School on Single-Dish Radio Astronomy Arecibo, PR July 2009 OUTLINE Antenna-Sky Coupling Noise the Radiometer Equation Minimum Tsys Performance measures
James M Anderson. in collaboration with Jan Noordam and Oleg Smirnov. MPIfR, Bonn, 2006 Dec 07
 Ionospheric Calibration for Long-Baseline, Low-Frequency Interferometry in collaboration with Jan Noordam and Oleg Smirnov Page 1/36 Outline The challenge for radioastronomy Introduction to the ionosphere
Ionospheric Calibration for Long-Baseline, Low-Frequency Interferometry in collaboration with Jan Noordam and Oleg Smirnov Page 1/36 Outline The challenge for radioastronomy Introduction to the ionosphere
More Radio Astronomy
 More Radio Astronomy Radio Telescopes - Basic Design A radio telescope is composed of: - a radio reflector (the dish) - an antenna referred to as the feed on to which the radiation is focused - a radio
More Radio Astronomy Radio Telescopes - Basic Design A radio telescope is composed of: - a radio reflector (the dish) - an antenna referred to as the feed on to which the radiation is focused - a radio
Towards SKA Multi-beam concepts and technology
 Towards SKA Multi-beam concepts and technology SKA meeting Meudon Observatory, 16 June 2009 Philippe Picard Station de Radioastronomie de Nançay philippe.picard@obs-nancay.fr 1 Square Kilometre Array:
Towards SKA Multi-beam concepts and technology SKA meeting Meudon Observatory, 16 June 2009 Philippe Picard Station de Radioastronomie de Nançay philippe.picard@obs-nancay.fr 1 Square Kilometre Array:
Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long Baseline Array
 Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long Baseline Array Basics of Interferometry Data Reduction Scott Schnee (NRAO) ALMA Data
Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long Baseline Array Basics of Interferometry Data Reduction Scott Schnee (NRAO) ALMA Data
Phased Array Feeds & Primary Beams
 Phased Array Feeds & Primary Beams Aidan Hotan ASKAP Deputy Project Scientist 3 rd October 2014 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE Outline Review of parabolic (dish) antennas. Focal plane response to a
Phased Array Feeds & Primary Beams Aidan Hotan ASKAP Deputy Project Scientist 3 rd October 2014 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE Outline Review of parabolic (dish) antennas. Focal plane response to a
Components of Imaging at Low Frequencies: Status & Challenges
 Components of Imaging at Low Frequencies: Status & Challenges Dec. 12th 2013 S. Bhatnagar NRAO Collaborators: T.J. Cornwell, R. Nityananda, K. Golap, U. Rau J. Uson, R. Perley, F. Owen Telescope sensitivity
Components of Imaging at Low Frequencies: Status & Challenges Dec. 12th 2013 S. Bhatnagar NRAO Collaborators: T.J. Cornwell, R. Nityananda, K. Golap, U. Rau J. Uson, R. Perley, F. Owen Telescope sensitivity
Heterodyne Interferometry with a Supercontinuum Local Oscillator. Pavel Gabor Vatican Observatory, 933 N Cherry Ave., Tucson AZ 85721, USA
 **Volume Title** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **Volume Number** **Author** c **Copyright Year** Astronomical Society of the Pacific Heterodyne Interferometry with a Supercontinuum Local Oscillator Pavel
**Volume Title** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **Volume Number** **Author** c **Copyright Year** Astronomical Society of the Pacific Heterodyne Interferometry with a Supercontinuum Local Oscillator Pavel
RADIOMETRIC TRACKING. Space Navigation
 RADIOMETRIC TRACKING Space Navigation October 24, 2016 D. Kanipe Space Navigation Elements SC orbit determination Knowledge and prediction of SC position & velocity SC flight path control Firing the attitude
RADIOMETRIC TRACKING Space Navigation October 24, 2016 D. Kanipe Space Navigation Elements SC orbit determination Knowledge and prediction of SC position & velocity SC flight path control Firing the attitude
DESIGN NOTE: DIFFRACTION EFFECTS
 NASA IRTF / UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII Document #: TMP-1.3.4.2-00-X.doc Template created on: 15 March 2009 Last Modified on: 5 April 2010 DESIGN NOTE: DIFFRACTION EFFECTS Original Author: John Rayner NASA Infrared
NASA IRTF / UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII Document #: TMP-1.3.4.2-00-X.doc Template created on: 15 March 2009 Last Modified on: 5 April 2010 DESIGN NOTE: DIFFRACTION EFFECTS Original Author: John Rayner NASA Infrared
Adaptive selective sidelobe canceller beamformer with applications in radio astronomy
 Adaptive selective sidelobe canceller beamformer with applications in radio astronomy Ronny Levanda and Amir Leshem 1 Abstract arxiv:1008.5066v1 [astro-ph.im] 30 Aug 2010 We propose a new algorithm, for
Adaptive selective sidelobe canceller beamformer with applications in radio astronomy Ronny Levanda and Amir Leshem 1 Abstract arxiv:1008.5066v1 [astro-ph.im] 30 Aug 2010 We propose a new algorithm, for
EC ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION
 EC6602 - ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION FUNDAMENTALS PART-B QUESTION BANK UNIT 1 1. Define the following parameters w.r.t antenna: i. Radiation resistance. ii. Beam area. iii. Radiation intensity. iv. Directivity.
EC6602 - ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION FUNDAMENTALS PART-B QUESTION BANK UNIT 1 1. Define the following parameters w.r.t antenna: i. Radiation resistance. ii. Beam area. iii. Radiation intensity. iv. Directivity.
Technical Considerations: Nuts and Bolts Project Planning and Technical Justification
 Technical Considerations: Nuts and Bolts Project Planning and Technical Justification Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long
Technical Considerations: Nuts and Bolts Project Planning and Technical Justification Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long
Image Simulator for One Dimensional Synthetic Aperture Microwave Radiometer
 524 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 25, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 Image Simulator for One Dimensional Synthetic Aperture Microwave Radiometer Qiong Wu, Hao Liu, and Ji Wu Center for
524 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 25, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 Image Simulator for One Dimensional Synthetic Aperture Microwave Radiometer Qiong Wu, Hao Liu, and Ji Wu Center for
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 6b: Path Models Rayleigh, Rician Fading, MIMO
 Antennas and Propagation b: Path Models Rayleigh, Rician Fading, MIMO Introduction From last lecture How do we model H p? Discrete path model (physical, plane waves) Random matrix models (forget H p and
Antennas and Propagation b: Path Models Rayleigh, Rician Fading, MIMO Introduction From last lecture How do we model H p? Discrete path model (physical, plane waves) Random matrix models (forget H p and
Fringe Parameter Estimation and Fringe Tracking. Mark Colavita 7/8/2003
 Fringe Parameter Estimation and Fringe Tracking Mark Colavita 7/8/2003 Outline Visibility Fringe parameter estimation via fringe scanning Phase estimation & SNR Visibility estimation & SNR Incoherent and
Fringe Parameter Estimation and Fringe Tracking Mark Colavita 7/8/2003 Outline Visibility Fringe parameter estimation via fringe scanning Phase estimation & SNR Visibility estimation & SNR Incoherent and
EVLA Memo 146 RFI Mitigation in AIPS. The New Task UVRFI
 EVLA Memo 1 RFI Mitigation in AIPS. The New Task UVRFI L. Kogan, F. Owen 1 (1) - National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, New Mexico, USA June, 1 Abstract Recently Ramana Athrea published a new algorithm
EVLA Memo 1 RFI Mitigation in AIPS. The New Task UVRFI L. Kogan, F. Owen 1 (1) - National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, New Mexico, USA June, 1 Abstract Recently Ramana Athrea published a new algorithm
Antenna 2: τ=0: 7 8 τ=0.5: τ=1: 9 10 τ=1.5: τ=2: 11 12
 Cross Correlators What is a Correlator? In an optical telescope a lens or a mirror collects the light & brings it to a focus Michael P. Rupen NRAO/Socorro a spectrograph separates the different frequencies
Cross Correlators What is a Correlator? In an optical telescope a lens or a mirror collects the light & brings it to a focus Michael P. Rupen NRAO/Socorro a spectrograph separates the different frequencies
Physics 1C Lecture 27B
 Physics 1C Lecture 27B Single Slit Interference! Example! Light of wavelength 750nm passes through a slit 1.00μm wide. How wide is the central maximum in centimeters, in a Fraunhofer diffraction pattern
Physics 1C Lecture 27B Single Slit Interference! Example! Light of wavelength 750nm passes through a slit 1.00μm wide. How wide is the central maximum in centimeters, in a Fraunhofer diffraction pattern
RADIOMETRIC TRACKING. Space Navigation
 RADIOMETRIC TRACKING Space Navigation Space Navigation Elements SC orbit determination Knowledge and prediction of SC position & velocity SC flight path control Firing the attitude control thrusters to
RADIOMETRIC TRACKING Space Navigation Space Navigation Elements SC orbit determination Knowledge and prediction of SC position & velocity SC flight path control Firing the attitude control thrusters to
Wide Bandwidth Imaging
 Wide Bandwidth Imaging 14th NRAO Synthesis Imaging Workshop 13 20 May, 2014, Socorro, NM Urvashi Rau National Radio Astronomy Observatory 1 Why do we need wide bandwidths? Broad-band receivers => Increased
Wide Bandwidth Imaging 14th NRAO Synthesis Imaging Workshop 13 20 May, 2014, Socorro, NM Urvashi Rau National Radio Astronomy Observatory 1 Why do we need wide bandwidths? Broad-band receivers => Increased
IF/LO Systems for Single Dish Radio Astronomy Centimeter Wave Receivers
 IF/LO Systems for Single Dish Radio Astronomy Centimeter Wave Receivers Lisa Wray NAIC, Arecibo Observatory Abstract. Radio astronomy receivers designed to detect electromagnetic waves from faint celestial
IF/LO Systems for Single Dish Radio Astronomy Centimeter Wave Receivers Lisa Wray NAIC, Arecibo Observatory Abstract. Radio astronomy receivers designed to detect electromagnetic waves from faint celestial
9. Microwaves. 9.1 Introduction. Safety consideration
 MW 9. Microwaves 9.1 Introduction Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths of the order of 1 mm to 1 m, or equivalently, with frequencies from 0.3 GHz to 0.3 THz, are commonly known as microwaves, sometimes
MW 9. Microwaves 9.1 Introduction Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths of the order of 1 mm to 1 m, or equivalently, with frequencies from 0.3 GHz to 0.3 THz, are commonly known as microwaves, sometimes
(The basics of) VLBI Basics. Pedro Elosegui MIT Haystack Observatory. With big thanks to many of you, here and out there
 (The basics of) VLBI Basics Pedro Elosegui MIT Haystack Observatory With big thanks to many of you, here and out there Some of the Points Will Cover Today Geodetic radio telescopes VLBI vs GPS concept
(The basics of) VLBI Basics Pedro Elosegui MIT Haystack Observatory With big thanks to many of you, here and out there Some of the Points Will Cover Today Geodetic radio telescopes VLBI vs GPS concept
What does reciprocity mean
 Antennas Definition of antenna: A device for converting electromagnetic radiation in space into electrical currents in conductors or vice-versa. Radio telescopes are antennas Reciprocity says we can treat
Antennas Definition of antenna: A device for converting electromagnetic radiation in space into electrical currents in conductors or vice-versa. Radio telescopes are antennas Reciprocity says we can treat
Signal Flow & Radiometer Equation. Aletha de Witt AVN-Newton Fund/DARA 2018 Observational & Technical Training HartRAO
 Signal Flow & Radiometer Equation Aletha de Witt AVN-Newton Fund/DARA 2018 Observational & Technical Training HartRAO Understanding Radio Waves The meaning of radio waves How radio waves are created -
Signal Flow & Radiometer Equation Aletha de Witt AVN-Newton Fund/DARA 2018 Observational & Technical Training HartRAO Understanding Radio Waves The meaning of radio waves How radio waves are created -
Fundamentals of Radio Astronomy. Lyle Hoffman, Lafayette College ALFALFA Undergraduate Workshop Arecibo Observatory, 2008 Jan. 13
 Fundamentals of Radio Astronomy Lyle Hoffman, Lafayette College ALFALFA Undergraduate Workshop Arecibo Observatory, 2008 Jan. 13 Outline Sources in brief Radiotelescope components Radiotelescope characteristics
Fundamentals of Radio Astronomy Lyle Hoffman, Lafayette College ALFALFA Undergraduate Workshop Arecibo Observatory, 2008 Jan. 13 Outline Sources in brief Radiotelescope components Radiotelescope characteristics
High resolution/high frequency radio interferometry
 High resolution/high frequency radio interferometry Anita Richards UK ALMA Regional Centre Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics University of Manchester thanks to fellow tutors, ALMA and JBCA colleagues
High resolution/high frequency radio interferometry Anita Richards UK ALMA Regional Centre Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics University of Manchester thanks to fellow tutors, ALMA and JBCA colleagues
EVLA Memo 105. Phase coherence of the EVLA radio telescope
 EVLA Memo 105 Phase coherence of the EVLA radio telescope Steven Durand, James Jackson, and Keith Morris National Radio Astronomy Observatory, 1003 Lopezville Road, Socorro, NM, USA 87801 ABSTRACT The
EVLA Memo 105 Phase coherence of the EVLA radio telescope Steven Durand, James Jackson, and Keith Morris National Radio Astronomy Observatory, 1003 Lopezville Road, Socorro, NM, USA 87801 ABSTRACT The
ANT5: Space and Line Current Radiation
 In this lecture, we study the general case of radiation from z-directed spatial currents. The far-field radiation equations that result from this treatment form some of the foundational principles of all
In this lecture, we study the general case of radiation from z-directed spatial currents. The far-field radiation equations that result from this treatment form some of the foundational principles of all
DECEMBER 1964 NUMBER OF COPIES: 75
 NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY Green Bank, West Virginia E ectronics Division Internal Report No. 42 A DIGITAL CROSS-CORRELATION INTERFEROMETER Nigel J. Keen DECEMBER 964 NUMBER OF COPIES: 75 A DIGITAL
NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY Green Bank, West Virginia E ectronics Division Internal Report No. 42 A DIGITAL CROSS-CORRELATION INTERFEROMETER Nigel J. Keen DECEMBER 964 NUMBER OF COPIES: 75 A DIGITAL
An Introduction to Antennas
 May 11, 010 An Introduction to Antennas 1 Outline Antenna definition Main parameters of an antenna Types of antennas Antenna radiation (oynting vector) Radiation pattern Far-field distance, directivity,
May 11, 010 An Introduction to Antennas 1 Outline Antenna definition Main parameters of an antenna Types of antennas Antenna radiation (oynting vector) Radiation pattern Far-field distance, directivity,
Detrimental Interference Levels at Individual LWA Sites LWA Engineering Memo RFS0012
 Detrimental Interference Levels at Individual LWA Sites LWA Engineering Memo RFS0012 Y. Pihlström, University of New Mexico August 4, 2008 1 Introduction The Long Wavelength Array (LWA) will optimally
Detrimental Interference Levels at Individual LWA Sites LWA Engineering Memo RFS0012 Y. Pihlström, University of New Mexico August 4, 2008 1 Introduction The Long Wavelength Array (LWA) will optimally
A model for the SKA. Melvyn Wright. Radio Astronomy laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA, ABSTRACT
 SKA memo 16. 21 March 2002 A model for the SKA Melvyn Wright Radio Astronomy laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 94720 ABSTRACT This memo reviews the strawman design for the SKA telescope.
SKA memo 16. 21 March 2002 A model for the SKA Melvyn Wright Radio Astronomy laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 94720 ABSTRACT This memo reviews the strawman design for the SKA telescope.
Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long Baseline Array
 Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long Baseline Array Self-Calibration Ed Fomalont (NRAO) ALMA Data workshop Dec. 2, 2011 Atacama
Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope Very Long Baseline Array Self-Calibration Ed Fomalont (NRAO) ALMA Data workshop Dec. 2, 2011 Atacama
