225 Lock-in Amplifier
|
|
|
- Juniper French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 225 Lock-in Amplifier Bentham Instruments Ltd 1
2 2 Bentham Instruments Ltd
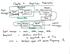
3 1. WHAT IS A LOCK-IN? There are a number of ways of visualising the operation and significance of a lock-in amplifier. As an introduction to the subject there follows a simple intuitive account biased towards light measurement applications. All lock-in amplifiers, whether analogue or digital, rely on the concept of phase sensitive detection for their operation. Stated simply, phase sensitive detection refers to the demodulation or rectification of an ac signal by a circuit which is controlled by a reference waveform derived from the device which caused the signal to be modulated. The phase sensitive detector effectively responds to signals which are coherent (same frequency and phase) with the reference waveform and rejects all others. In a light measurement system the device which causes the signal to be modulated is usually a chopper, the reference waveform is an output coherent with the chopping action provided by the chopper and the ac signal is the signal from the photodetector. As the lock-in is a solution to a measurement problem we can usefully describe its action and composition by looking at the sort of problems that occur when light measurements are pushed to the limit. Consider a simple light measurement system being used to measure transmission. Light from a stable light source is passed through a sample and reaches a detector. The resulting electrical signal from the detector is amplified and displayed on a meter. The meter reading gives an indication of the amount of light transmitted by the sample. Fig 1 Schematic of Lock-in Device Bentham Instruments Ltd 3
4 With medium to high transmission samples this system would be expected to give precise and reproducible results. Samples of increasing optical density could be accommodated by increasing the gain of the amplifier. What is always noticeable in such systems, however, is that as the signal level falls and the amplifier gain is increased so the precision with which the results can be recorded also falls. This is due to noise. Noise in this sense is anything which contributes to the meter reading but which is not due to the parameter being measured. It is generated in all parts of the electrical circuitry but in light measurement systems it is dominated by noise from the detector or noise associated with the optical signal. The following diagram shows the distribution of noise and signal power from the optical detector in terms of power per unit bandwidth as a function of frequency. This can be used for a situation where the density of the sample is so high that the signal is smaller than the noise with the result is that the instrument becomes unusable. Fig. 2 The most noticeable feature of this curve is the steady increase in noise power which occurs as zero Hz is approached. In our transmission measuring instrument this low frequency noise has several sources including flicker noise associated with semiconductor devices, variations in dark current (especially in photomultipliers) and variations in ambient light leaking into the instrument and reaching the detector. At higher frequencies the spectrum flattens out to give a reasonably constant shot noise background which is associated with the quantum nature of light. The small peaks of 50Hz and 150Hz are due to electrical interference from the power system. The larger peak at 100Hz is due to light from room lighting leaking into the instrument and reaching the detector. 4 Bentham Instruments Ltd
5 It is important to note that the y axis in this diagram is in units of power per unit bandwidth so the total noise and signal powers are represented by the area under the corresponding curves. Clearly therefor we can immediately improve the signal to noise ratio in this system by using an electronic filter to reject the higher frequency components which do not contain any signal information. Unfortunately the information relating to the transmission of the sample is also near zero hertz, so using a low pass filter to reject all noise components above say 30Hz will give only a small improvement in signal to noise ratio. Fig 3 Effect of Low Pass Filter What we really need to do if we want to measure high optical density with this system is to move the signal information away from the high noise zero hertz region. Fig 4 Effect of Bandpass Filter at 175 Hz Bentham Instruments Ltd 5
6 We can do this by placing an optical chopper, which will periodically interrupt the light, between the light source and the detector. The diagram below shows the detector output spectrum in this new situation with the chopper running at 175Hz. From the diagram this looks like a good move. We have moved the signal away from a region where the background noise is high to a region where it is low. We can now pass the signal through an electronic bandpass filter which will reject both the noise at higher and lower frequencies (including zero hertz) and hence significantly improve the signal to noise ratio. The problem now is that the signal is ac, i.e. its average value is zero so to record a value from it we must first rectify it. We might end up with an arrangement as shown in Fig 5 which includes an amplifier, a tuned filter whose centre frequency is at 175Hz, a rectifying circuit and a display. Fig 5 Tuned amplifiers, as these devices are called, are used in some simple systems but they suffer from 3 major disadvantages. The first concerns Q. Q is defined as the centre frequency of a filter divided by its bandwidth. In this application the narrower the bandwidth of the filter, the greater is the noise rejection. The maximum Q typically achievable for a tuned amplifier is in the region of 100, but in a demanding measurement situation we might need a Q of 1000 to achieve acceptable signal to noise ratio. Secondly, if such a filter could be produced any small shift in chopping frequency would result in large changes in output due to misalignment between signal frequency and filter centre frequency. The third problem lies in the rectifying device and the way it responds to noise which passes through the filter. Using a normal rectifying device such as a semiconductor diode the noise itself will be rectified and will thus give rise to a dc level at the meter which will be indistinguishable from that derived from the signal. 6 Bentham Instruments Ltd
7 All these problems are overcome by the phase sensitive detector. As first glance this device looks very simple. Fig 6 Synchronous Filter As before there is circuitry to amplify low level signals, but now there is no tuned filter or rectifying diode. Instead the amplifier is followed by a switch which is operated by a waveform derived from the chopper. When the level from the chopper is high the switch is closed and the output of the amplifier is connected directly to a low pass filter consisting of a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C). When the output of the chopper is low the switch is open and no connection is made. Rectification of the signal occurs when the waveform controlling the switch is exactly in phase with the ac signal at the input to the switch, hence the sometimes used description, synchronous rectifier. More importantly when the switch is closed the noise associated with the signal passes through un-rectified to the low pass RC filter beyond where it is smoothed or averaged to its mean value of zero. The device behaves as a bandpass filter and performs the same function as a tuned amplifier followed by a rectifier but with the following advantages. 1) The effective bandwidth and hence noise rejecting capability of the device is determined only by the values of the components used in the low pass filter. In fact the bandwidth is given by 1/4T where T is the time constant 1 of the RC filter. A time constant of 2.5 seconds will thus give a bandwidth of 0.1Hz which at centre frequency of 175Hz corresponds to a Q of ) The centre frequency of the filter is locked (hence lock-in) onto the chopper s frequency. The signal can never drift outside the pass band of the filter Bentham Instruments Ltd 7
8 3) Any noise which is present at the output is equally distributed about the mean value resulting from demodulation of the signal. It does not give rise to a dc level as with the diode rectifier and increasing the time constant will reduce its magnitude. An alternative approach is to visualising the phase sensitive detector is to consider the switch as a multiplier. Fig 7 Assuming that both the signal and reference waveforms are sinusoidal then the output of the multiplier will contain components at frequencies of f s +f r and f s -f r where f s and f r are the frequencies of the signal and reference waveforms respectively. If f s =f r as is the case where the reference waveform is derived from the device which is modulating the signal then there will be an output at 0Hz i.e. dc. Any other component in the signal e.g. a noise component at a frequency of f n will give rise to an ac output at frequencies of f n -f r and f n +f r which will be smoothed or averaged to the mean value of zero by the low pass filter. As the time constant (RC) of the filter is increased so the attenuation of the higher frequency components from the multiplier will increase thus effectively reducing the bandwidth of the overall device. Some Practical Points So far we have considered the phase sensitive demodulator as a single pole switch which is capable of synchronous rectification of only half of the signal. For a signal recovery device such a waste of signal information would be unacceptable. Commercial lock-in amplifiers therefore include a full wave synchronous demodulator which usually works by using inverting and non-inverting amplifiers to produce anti-phase versions of the signal (i.e. 180 out of phase). 8 Bentham Instruments Ltd
9 Fig 8 In all the diagrams shown so far the reference waveform available at the phase sensitive demodulator has conveniently been in phase with the signal - the condition for maximum output and hence best signal to noise ratio. In any real experimental set-up we can not always be sure that the relationship between the signal from the detector and the reference waveform from the chopper will be in phase. The phase relationship will be dependant on the position of the chopped light beam relative to the reference pick-up on the chopper and also on any phase modification of the signal introduced by the detector. To allow perfect phase matching at the demodulator, lock-in amplifiers include comprehensive and flexible phase shifting circuitry which allows a phase shift of over 360 degrees to be introduced. The phase controls on the lock-in usually take the form of a continuously variable of 0-95 degrees and 3 fixed increments of 90 degrees giving 365 degrees in total. The following diagrams show how the output of the psd varies with the reference to signal phase relationship. In figs 9a, 9b and 9c the reference waveform has been shifted by 90, 180 and 270 respectively from that in Fig Bentham Instruments Ltd 9
10 Fig 9a Fig 9b 10 Bentham Instruments Ltd
11 Fig 9c Harmonic Response In the multiplier model of our psd we made the assumption that the two waveforms were sinusoidal, but in practice, when using a simple switch we are effectively multiplying the signal not by a sine wave but by a square wave (the switch is either closed or open). Now a square wave is equivalent to a sine wave of the fundamental frequency plus all the odd harmonics of the fundamental 2. A psd using a simple switch therefore behaves as a filter centred at the fundamental but with windows at each odd harmonic. Fig Bentham Instruments Ltd 1 1
12 At first glance this looks to be a problem in that the noise present in these harmonic windows will be passed through to the low pass filter and degrade the signal to noise ratio at the output of the lock-in. However, this problem is not as bad as it looks, especially if the modulating device is a chopper. First of all the harmonic windows do not have the same sensitivity as the fundamental but reduce as 1/harmonic reflecting the Fourier composition of the square wave switching the demodulator 2. Secondly, if the modulating device is a chopper, then the signal itself will not be sinusoidal but more typically triangular or trapezoidal both of which have significant odd harmonic content so the harmonic windows will also transfer additional signal information to the output of the lock-in. The most dangerous situation is one in which a harmonic window coincides with a point in the spectrum where a large discrete interference is present but this should never occur in a properly designed light measurement system with the correct choice of chopping frequency. It is unfortunately the case that lock-ins are sometimes used to compensate for incorrect optical design. The most commonly encountered misconception regarding the use of lock-in amplifiers in light measurement concerns their ability to disregard a constant dc light level most commonly caused by ambient light leaking into the system and reaching the detector. This after all is the reason for including the chopper so that the signal information is shifted away from the dc region. The next intuitive step taken by many is to assume that there is no longer any need to make the system light tight - as long as ambient light reaching the detector does not cause saturation everything will be OK. This is not correct. Referring back to the earlier paragraphs we pointed out that the shot noise background is caused by the light itself and is associated with its quantum nature. Ambient light leaking into chopped light systems will always degrade signal to noise performance even though it does not give rise to a dc output from the lock-in. You can often improve signal to noise ratio just by making things light tight - if you cut down light leaks you may be able to reduce the time constant and make your measurements faster. 1 The time constant of the RC circuit in seconds is given by the product of the resistance in ohms and the capacitance in farrads. BENTHAM INSTRUMENTS LTD 2 Boulton Road, Reading, Berkshire, RG2 0NH Tel: +44 (0) Fax: +44 (0) sales@bentham.co.uk 12 Bentham Instruments Ltd
THE BENEFITS OF DSP LOCK-IN AMPLIFIERS
 THE BENEFITS OF DSP LOCK-IN AMPLIFIERS If you never heard of or don t understand the term lock-in amplifier, you re in good company. With the exception of the optics industry where virtually every major
THE BENEFITS OF DSP LOCK-IN AMPLIFIERS If you never heard of or don t understand the term lock-in amplifier, you re in good company. With the exception of the optics industry where virtually every major
Application Note (A12)
 Application Note (A2) The Benefits of DSP Lock-in Amplifiers Revision: A September 996 Gooch & Housego 4632 36 th Street, Orlando, FL 328 Tel: 47 422 37 Fax: 47 648 542 Email: sales@goochandhousego.com
Application Note (A2) The Benefits of DSP Lock-in Amplifiers Revision: A September 996 Gooch & Housego 4632 36 th Street, Orlando, FL 328 Tel: 47 422 37 Fax: 47 648 542 Email: sales@goochandhousego.com
Physics 262. Lab #1: Lock-In Amplifier. John Yamrick
 Physics 262 Lab #1: Lock-In Amplifier John Yamrick Abstract This lab studied the workings of a photodiode and lock-in amplifier. The linearity and frequency response of the photodiode were examined. Introduction
Physics 262 Lab #1: Lock-In Amplifier John Yamrick Abstract This lab studied the workings of a photodiode and lock-in amplifier. The linearity and frequency response of the photodiode were examined. Introduction
Detecting the Ratio of I ac. /I ave. photoelastic modulators
 Measurement of the Average Intensity of a Modulated Light Beam In any experiment using (PEMs it is necessary to compare the time average intensity of the light at the detector with the amplitude of a single
Measurement of the Average Intensity of a Modulated Light Beam In any experiment using (PEMs it is necessary to compare the time average intensity of the light at the detector with the amplitude of a single
Table of Contents...2. About the Tutorial...6. Audience...6. Prerequisites...6. Copyright & Disclaimer EMI INTRODUCTION Voltmeter...
 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
Operating Manual Ver 1.1
 Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Trainer ST2203 Operating Manual Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100
Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Trainer ST2203 Operating Manual Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Lock-Ins for electrical measurements
 Lock-Ins for electrical measurements At low temperatures small electrical signals, small signal changes interesting physics Problems: Noise Groundloops SNR FAM-Talk October 17 th 2014 1 Types of noise
Lock-Ins for electrical measurements At low temperatures small electrical signals, small signal changes interesting physics Problems: Noise Groundloops SNR FAM-Talk October 17 th 2014 1 Types of noise
DETECTING THE RATIO OF I AC
 T E C H N O L O G Y F O R P O L A R I Z A T I O N M E A S U R E M E N T DETECTING THE RATIO OF I AC MEASUREMENT OF THE RAGE INTENSITY OF A MODULATED LIGHT BEAM In any experiment using photoelastic modulators
T E C H N O L O G Y F O R P O L A R I Z A T I O N M E A S U R E M E N T DETECTING THE RATIO OF I AC MEASUREMENT OF THE RAGE INTENSITY OF A MODULATED LIGHT BEAM In any experiment using photoelastic modulators
multiplier input Env. Det. LPF Y (Vertical) VCO X (Horizontal)
 Spectrum Analyzer Objective: The aim of this project is to realize a spectrum analyzer using analog circuits and a CRT oscilloscope. This interface circuit will enable to use oscilloscopes as spectrum
Spectrum Analyzer Objective: The aim of this project is to realize a spectrum analyzer using analog circuits and a CRT oscilloscope. This interface circuit will enable to use oscilloscopes as spectrum
Testing Power Factor Correction Circuits For Stability
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, switching power supply, PFC, boost converter, flyback converter,
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, switching power supply, PFC, boost converter, flyback converter,
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory Amplitude Modulation (AM)
 ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
Measure the roll-off frequency of an acousto-optic modulator
 Slide 1 Goals of the Lab: Get to know some of the properties of pin photodiodes Measure the roll-off frequency of an acousto-optic modulator Measure the cut-off frequency of a pin photodiode as a function
Slide 1 Goals of the Lab: Get to know some of the properties of pin photodiodes Measure the roll-off frequency of an acousto-optic modulator Measure the cut-off frequency of a pin photodiode as a function
Comparison of Signal Attenuation of Multiple Frequencies Between Passive and Active High-Pass Filters
 Comparison of Signal Attenuation of Multiple Frequencies Between Passive and Active High-Pass Filters Aaron Batker Pritzker Harvey Mudd College 23 November 203 Abstract Differences in behavior at different
Comparison of Signal Attenuation of Multiple Frequencies Between Passive and Active High-Pass Filters Aaron Batker Pritzker Harvey Mudd College 23 November 203 Abstract Differences in behavior at different
Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation
 Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation PURPOSE In this assignment, you will explore the use of digital computers for the analysis, design, synthesis, and simulation of an amplitude modulation (AM)
Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation PURPOSE In this assignment, you will explore the use of digital computers for the analysis, design, synthesis, and simulation of an amplitude modulation (AM)
8.5 Modulation of Signals
 8.5 Modulation of Signals basic idea and goals measuring atomic absorption without modulation measuring atomic absorption with modulation the tuned amplifier, diode rectifier and low pass the lock-in amplifier
8.5 Modulation of Signals basic idea and goals measuring atomic absorption without modulation measuring atomic absorption with modulation the tuned amplifier, diode rectifier and low pass the lock-in amplifier
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 20
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 20 Photo-Detectors and Detector Noise Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept.
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 20 Photo-Detectors and Detector Noise Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept.
LM565/LM565C Phase Locked Loop
 LM565/LM565C Phase Locked Loop General Description The LM565 and LM565C are general purpose phase locked loops containing a stable, highly linear voltage controlled oscillator for low distortion FM demodulation,
LM565/LM565C Phase Locked Loop General Description The LM565 and LM565C are general purpose phase locked loops containing a stable, highly linear voltage controlled oscillator for low distortion FM demodulation,
About the Tutorial. Audience. Prerequisites. Copyright & Disclaimer. Linear Integrated Circuits Applications
 About the Tutorial Linear Integrated Circuits are solid state analog devices that can operate over a continuous range of input signals. Theoretically, they are characterized by an infinite number of operating
About the Tutorial Linear Integrated Circuits are solid state analog devices that can operate over a continuous range of input signals. Theoretically, they are characterized by an infinite number of operating
Electronics for Analog Signal Processing - I Prof. K. Radhakrishna Rao Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Madras
 Electronics for Analog Signal Processing - I Prof. K. Radhakrishna Rao Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Madras Lecture - 4 Rectifier We have had a discussion about
Electronics for Analog Signal Processing - I Prof. K. Radhakrishna Rao Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Madras Lecture - 4 Rectifier We have had a discussion about
Preliminary simulation study of the front-end electronics for the central detector PMTs
 Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 1-27 (Draft) Preliminary simulation study of the front-end electronics for the central detector PMTs A. F. Barbosa Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Fsicas - CBPF, e-mail:
Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 1-27 (Draft) Preliminary simulation study of the front-end electronics for the central detector PMTs A. F. Barbosa Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Fsicas - CBPF, e-mail:
AC Theory and Electronics
 AC Theory and Electronics An Alternating Current (AC) or Voltage is one whose amplitude is not constant, but varies with time about some mean position (value). Some examples of AC variation are shown below:
AC Theory and Electronics An Alternating Current (AC) or Voltage is one whose amplitude is not constant, but varies with time about some mean position (value). Some examples of AC variation are shown below:
EXPERIMENT 4 - Part I: DSB Amplitude Modulation
 OBJECTIVE To generate DSB amplitude modulated signal. EXPERIMENT 4 - Part I: DSB Amplitude Modulation PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In an amplitude modulation (AM) communications system, the message signal is
OBJECTIVE To generate DSB amplitude modulated signal. EXPERIMENT 4 - Part I: DSB Amplitude Modulation PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In an amplitude modulation (AM) communications system, the message signal is
ECEN5817 Lecture 4. Transfer function H(s) ) (t) i R. (t) v R
 ECEN5817 Lecture 4 A resonant dc-dc converter: Transfer function H(s) ) dc source v g i s L C s i R i v s v R v R N S N T N R N F Switch network Resonant tank network Rectifier network Low-pass dc filter
ECEN5817 Lecture 4 A resonant dc-dc converter: Transfer function H(s) ) dc source v g i s L C s i R i v s v R v R N S N T N R N F Switch network Resonant tank network Rectifier network Low-pass dc filter
LM565 LM565C Phase Locked Loop
 LM565 LM565C Phase Locked Loop General Description The LM565 and LM565C are general purpose phase locked loops containing a stable highly linear voltage controlled oscillator for low distortion FM demodulation
LM565 LM565C Phase Locked Loop General Description The LM565 and LM565C are general purpose phase locked loops containing a stable highly linear voltage controlled oscillator for low distortion FM demodulation
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
A Simple Notch Type Harmonic Distortion Analyzer
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Nov. 28, 2009, rev. Nov. 29, 2009 Introduction This note describes a simple notch type harmonic distortion analyzer that can be constructed with basic parts. It is intended for use in
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Nov. 28, 2009, rev. Nov. 29, 2009 Introduction This note describes a simple notch type harmonic distortion analyzer that can be constructed with basic parts. It is intended for use in
Notes on Noise Reduction
 Notes on Noise Reduction When setting out to make a measurement one often finds that the signal, the quantity we want to see, is masked by noise, which is anything that interferes with seeing the signal.
Notes on Noise Reduction When setting out to make a measurement one often finds that the signal, the quantity we want to see, is masked by noise, which is anything that interferes with seeing the signal.
Summer 2015 Examination
 Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
Practical Testing Techniques For Modern Control Loops
 VENABLE TECHNICAL PAPER # 16 Practical Testing Techniques For Modern Control Loops Abstract: New power supply designs are becoming harder to measure for gain margin and phase margin. This measurement is
VENABLE TECHNICAL PAPER # 16 Practical Testing Techniques For Modern Control Loops Abstract: New power supply designs are becoming harder to measure for gain margin and phase margin. This measurement is
Introduction. sig. ref. sig
 Introduction A lock-in amplifier, in common with most AC indicating instruments, provides a DC output proportional to the AC signal under investigation. The special rectifier, called a phase-sensitive
Introduction A lock-in amplifier, in common with most AC indicating instruments, provides a DC output proportional to the AC signal under investigation. The special rectifier, called a phase-sensitive
note application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise by David Owen
 application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise note by David Owen The stability of an RF source is often a critical parameter for many applications. Performance varies considerably with
application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise note by David Owen The stability of an RF source is often a critical parameter for many applications. Performance varies considerably with
UNIT-3. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
LBI-30398N. MAINTENANCE MANUAL MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 DESCRIPTION TABLE OF CONTENTS. Page. DESCRIPTION...
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 LBI-30398N TABLE OF CONTENTS DESCRIPTION...Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS... 1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS... 4 PARTS LIST AND PRODUCTION
MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 LBI-30398N TABLE OF CONTENTS DESCRIPTION...Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS... 1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS... 4 PARTS LIST AND PRODUCTION
UNIT 2. Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator. Ans. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
LABORATORY EXPERIMENT. Infrared Transmitter/Receiver
 LABORATORY EXPERIMENT Infrared Transmitter/Receiver (Note to Teaching Assistant: The week before this experiment is performed, place students into groups of two and assign each group a specific frequency
LABORATORY EXPERIMENT Infrared Transmitter/Receiver (Note to Teaching Assistant: The week before this experiment is performed, place students into groups of two and assign each group a specific frequency
Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers
 Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers Introduction Isolated converters are required to provide electrical isolation between two interrelated systems. Isolation between the power source and
Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers Introduction Isolated converters are required to provide electrical isolation between two interrelated systems. Isolation between the power source and
Optical Modulation and Frequency of Operation
 Optical Modulation and Frequency of Operation Developers AB Overby Objectives Preparation Background The objectives of this experiment are to describe and illustrate the differences between frequency of
Optical Modulation and Frequency of Operation Developers AB Overby Objectives Preparation Background The objectives of this experiment are to describe and illustrate the differences between frequency of
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
Visible & IR Femtowatt Photoreceivers Models 2151 & 2153
 USER S GUIDE Visible & IR Femtowatt Photoreceivers Models 2151 & 2153 5215 Hellyer Ave. San Jose, CA 95138-1001 USA phone: (408) 284 6808 fax: (408) 284 4824 e-mail: contact@newfocus.com www.newfocus.com
USER S GUIDE Visible & IR Femtowatt Photoreceivers Models 2151 & 2153 5215 Hellyer Ave. San Jose, CA 95138-1001 USA phone: (408) 284 6808 fax: (408) 284 4824 e-mail: contact@newfocus.com www.newfocus.com
ERICSSONZ LBI-30398P. MAINTENANCE MANUAL MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 DESCRIPTION TABLE OF CONTENTS
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION... Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS...1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS...4 PARTS LIST...5 PRODUCTION
MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION... Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS...1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS...4 PARTS LIST...5 PRODUCTION
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. AN120 An overview of switched-mode power supplies Dec
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS An overview of switched-mode power supplies 1988 Dec Conceptually, three basic approaches exist for obtaining regulated DC voltage from an AC power source. These are: Shunt regulation
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS An overview of switched-mode power supplies 1988 Dec Conceptually, three basic approaches exist for obtaining regulated DC voltage from an AC power source. These are: Shunt regulation
LIMITATIONS IN MAKING AUDIO BANDWIDTH MEASUREMENTS IN THE PRESENCE OF SIGNIFICANT OUT-OF-BAND NOISE
 LIMITATIONS IN MAKING AUDIO BANDWIDTH MEASUREMENTS IN THE PRESENCE OF SIGNIFICANT OUT-OF-BAND NOISE Bruce E. Hofer AUDIO PRECISION, INC. August 2005 Introduction There once was a time (before the 1980s)
LIMITATIONS IN MAKING AUDIO BANDWIDTH MEASUREMENTS IN THE PRESENCE OF SIGNIFICANT OUT-OF-BAND NOISE Bruce E. Hofer AUDIO PRECISION, INC. August 2005 Introduction There once was a time (before the 1980s)
CHAPTER 1 DIODE CIRCUITS. Semiconductor act differently to DC and AC currents
 CHAPTER 1 DIODE CIRCUITS Resistance levels Semiconductor act differently to DC and AC currents There are three types of resistances 1. DC or static resistance The application of DC voltage to a circuit
CHAPTER 1 DIODE CIRCUITS Resistance levels Semiconductor act differently to DC and AC currents There are three types of resistances 1. DC or static resistance The application of DC voltage to a circuit
1. An engineer measures the (step response) rise time of an amplifier as. Estimate the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier. (2 points)
 Exam 1 Name: Score /60 Question 1 Short Takes 1 point each unless noted otherwise. 1. An engineer measures the (step response) rise time of an amplifier as. Estimate the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier.
Exam 1 Name: Score /60 Question 1 Short Takes 1 point each unless noted otherwise. 1. An engineer measures the (step response) rise time of an amplifier as. Estimate the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB WORK EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB WORK EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT : 1 TITLE : Half-Wave Rectifier & Filter OUTCOME : Upon completion of this unit, the student should be able to: i. Construct
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB WORK EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT : 1 TITLE : Half-Wave Rectifier & Filter OUTCOME : Upon completion of this unit, the student should be able to: i. Construct
METHODS TO IMPROVE DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF POWER FACTOR PREREGULATORS: AN OVERVIEW
 METHODS TO IMPROE DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF POWER FACTOR PREREGULATORS: AN OERIEW G. Spiazzi*, P. Mattavelli**, L. Rossetto** *Dept. of Electronics and Informatics, **Dept. of Electrical Engineering University
METHODS TO IMPROE DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF POWER FACTOR PREREGULATORS: AN OERIEW G. Spiazzi*, P. Mattavelli**, L. Rossetto** *Dept. of Electronics and Informatics, **Dept. of Electrical Engineering University
Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers
 Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers INTRODUCTION Isolated converters are required to provide electrical isolation between two interrelated systems. Isolation between the power source and
Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers INTRODUCTION Isolated converters are required to provide electrical isolation between two interrelated systems. Isolation between the power source and
Topic Advanced Radio Receivers. Explain that an RF amplifier can be used to improve sensitivity;
 Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; Explain that an RF amplifier can be used to improve sensitivity; Explain that a superheterodyne receiver offers improved selectivity and
Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; Explain that an RF amplifier can be used to improve sensitivity; Explain that a superheterodyne receiver offers improved selectivity and
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
A Prototype Wire Position Monitoring System
 LCLS-TN-05-27 A Prototype Wire Position Monitoring System Wei Wang and Zachary Wolf Metrology Department, SLAC 1. INTRODUCTION ¹ The Wire Position Monitoring System (WPM) will track changes in the transverse
LCLS-TN-05-27 A Prototype Wire Position Monitoring System Wei Wang and Zachary Wolf Metrology Department, SLAC 1. INTRODUCTION ¹ The Wire Position Monitoring System (WPM) will track changes in the transverse
Harmonics White Paper
 Harmonics White Paper New Breakthrough In PWM Drives Technology Reduces Input Line Harmonics Without the Use of Filtering Devices Harmonic Distortion Damages Equipment and Creates a Host of Other Problems
Harmonics White Paper New Breakthrough In PWM Drives Technology Reduces Input Line Harmonics Without the Use of Filtering Devices Harmonic Distortion Damages Equipment and Creates a Host of Other Problems
LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers
 LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13700 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers, each with
LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13700 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers, each with
Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance
 Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
EE 400L Communications. Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation
 EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
Single Switch Forward Converter
 Single Switch Forward Converter This application note discusses the capabilities of PSpice A/D using an example of 48V/300W, 150 KHz offline forward converter voltage regulator module (VRM), design and
Single Switch Forward Converter This application note discusses the capabilities of PSpice A/D using an example of 48V/300W, 150 KHz offline forward converter voltage regulator module (VRM), design and
A Simplified Test Set for Op Amp Characterization
 A Simplified Test Set for Op Amp Characterization INTRODUCTION The test set described in this paper allows complete quantitative characterization of all dc operational amplifier parameters quickly and
A Simplified Test Set for Op Amp Characterization INTRODUCTION The test set described in this paper allows complete quantitative characterization of all dc operational amplifier parameters quickly and
Keywords: ISM, RF, transmitter, short-range, RFIC, switching power amplifier, ETSI
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP 4929 Keywords: ISM, RF, transmitter, short-range, RFIC, switching power amplifier, ETSI APPLICATION NOTE 4929 Adapting
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP 4929 Keywords: ISM, RF, transmitter, short-range, RFIC, switching power amplifier, ETSI APPLICATION NOTE 4929 Adapting
On The Causes And Cures Of Audio Distortion Of Received AM Signals Due To Fading
 On The Causes And Cures Of Audio Distortion Of Received AM Signals Due To Fading Dallas Lankford, 2/6/06, rev. 9/25/08 The purpose of this article is to investigate some of the causes and cures of audio
On The Causes And Cures Of Audio Distortion Of Received AM Signals Due To Fading Dallas Lankford, 2/6/06, rev. 9/25/08 The purpose of this article is to investigate some of the causes and cures of audio
11. Chapter: Amplitude stabilization of the harmonic oscillator
 Punčochář, Mohylová: TELO, Chapter 10 1 11. Chapter: Amplitude stabilization of the harmonic oscillator Time of study: 3 hours Goals: the student should be able to define basic principles of oscillator
Punčochář, Mohylová: TELO, Chapter 10 1 11. Chapter: Amplitude stabilization of the harmonic oscillator Time of study: 3 hours Goals: the student should be able to define basic principles of oscillator
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019 Spring Term 00.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019 Spring Term 00.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No.
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits
 EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture V James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Last Lecture: Review 1 Finished the diode conduction
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture V James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Last Lecture: Review 1 Finished the diode conduction
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS
 CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer. An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer
 1 An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer 2 Chapter 1. Introduction As a result of rapidly advancement in communication technology, all the mobile technology of applications has significantly and profoundly
1 An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer 2 Chapter 1. Introduction As a result of rapidly advancement in communication technology, all the mobile technology of applications has significantly and profoundly
Specifying A D and D A Converters
 Specifying A D and D A Converters The specification or selection of analog-to-digital (A D) or digital-to-analog (D A) converters can be a chancey thing unless the specifications are understood by the
Specifying A D and D A Converters The specification or selection of analog-to-digital (A D) or digital-to-analog (D A) converters can be a chancey thing unless the specifications are understood by the
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
6.776 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 14 Voltage Controlled Oscillators
 6.776 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 14 Voltage Controlled Oscillators Massachusetts Institute of Technology March 29, 2005 Copyright 2005 by Michael H. Perrott VCO Design for Narrowband
6.776 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 14 Voltage Controlled Oscillators Massachusetts Institute of Technology March 29, 2005 Copyright 2005 by Michael H. Perrott VCO Design for Narrowband
High Performance ZVS Buck Regulator Removes Barriers To Increased Power Throughput In Wide Input Range Point-Of-Load Applications
 WHITE PAPER High Performance ZVS Buck Regulator Removes Barriers To Increased Power Throughput In Wide Input Range Point-Of-Load Applications Written by: C. R. Swartz Principal Engineer, Picor Semiconductor
WHITE PAPER High Performance ZVS Buck Regulator Removes Barriers To Increased Power Throughput In Wide Input Range Point-Of-Load Applications Written by: C. R. Swartz Principal Engineer, Picor Semiconductor
Gechstudentszone.wordpress.com
 8.1 Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) UNIT 8: Operational Amplifier An operational amplifier ("op-amp") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended
8.1 Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) UNIT 8: Operational Amplifier An operational amplifier ("op-amp") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended
Chapter 2 Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion
 09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
Chapter 5 Window Functions. periodic with a period of N (number of samples). This is observed in table (3.1).
 Chapter 5 Window Functions 5.1 Introduction As discussed in section (3.7.5), the DTFS assumes that the input waveform is periodic with a period of N (number of samples). This is observed in table (3.1).
Chapter 5 Window Functions 5.1 Introduction As discussed in section (3.7.5), the DTFS assumes that the input waveform is periodic with a period of N (number of samples). This is observed in table (3.1).
How It Works The PPM Radio Control System: Part 1
 Technical M.E.C. Technical Note Note How It Works The PPM Radio Control System: Part 1 Foreword This Technical Note is divided into 3 parts to reduce the file size when downloading each section from the
Technical M.E.C. Technical Note Note How It Works The PPM Radio Control System: Part 1 Foreword This Technical Note is divided into 3 parts to reduce the file size when downloading each section from the
TDA Power Factor Controller. IC for High Power Factor and Active Harmonic Filtering
 Power Factor Controller IC for High Power Factor and Active Harmonic Filtering TDA 4817 Advance Information Bipolar IC Features IC for sinusoidal line-current consumption Power factor approaching 1 Controls
Power Factor Controller IC for High Power Factor and Active Harmonic Filtering TDA 4817 Advance Information Bipolar IC Features IC for sinusoidal line-current consumption Power factor approaching 1 Controls
RCTrms Technical Notes
 RCTrms Technical Notes All measuring instruments are subject to limitations. The purpose of these technical notes is to explain some of those limitations and to help the engineer maximise the many advantages
RCTrms Technical Notes All measuring instruments are subject to limitations. The purpose of these technical notes is to explain some of those limitations and to help the engineer maximise the many advantages
Definitions. Spectrum Analyzer
 SIGNAL ANALYZERS Spectrum Analyzer Definitions A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure
SIGNAL ANALYZERS Spectrum Analyzer Definitions A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure
An Introduction to Rectifier Circuits
 TRADEMARK OF INNOVATION An Introduction to Rectifier Circuits An important application of the diode is one that takes place in the design of the rectifier circuit. Simply put, this circuit converts alternating
TRADEMARK OF INNOVATION An Introduction to Rectifier Circuits An important application of the diode is one that takes place in the design of the rectifier circuit. Simply put, this circuit converts alternating
Introduction: Presence or absence of inherent error detection properties.
 Introduction: Binary data can be transmitted using a number of different types of pulses. The choice of a particular pair of pulses to represent the symbols 1 and 0 is called Line Coding and the choice
Introduction: Binary data can be transmitted using a number of different types of pulses. The choice of a particular pair of pulses to represent the symbols 1 and 0 is called Line Coding and the choice
Photometer System Mar 8, 2009
 John Menke 22500 Old Hundred Rd Barnesville, MD 20838 301-407-2224 john@menkescientific.com Photometer System Mar 8, 2009 Description This paper describes construction and testing of a photometer for fast
John Menke 22500 Old Hundred Rd Barnesville, MD 20838 301-407-2224 john@menkescientific.com Photometer System Mar 8, 2009 Description This paper describes construction and testing of a photometer for fast
UNIT - 5 OPTICAL RECEIVER
 UNIT - 5 LECTURE-1 OPTICAL RECEIVER Introduction, Optical Receiver Operation, receiver sensitivity, quantum limit, eye diagrams, coherent detection, burst mode receiver operation, Analog receivers. RECOMMENDED
UNIT - 5 LECTURE-1 OPTICAL RECEIVER Introduction, Optical Receiver Operation, receiver sensitivity, quantum limit, eye diagrams, coherent detection, burst mode receiver operation, Analog receivers. RECOMMENDED
 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Lecture 2 Analog circuits. Seeing the light..
 Lecture 2 Analog circuits Seeing the light.. I t IR light V1 9V +V IR detection Noise sources: Electrical (60Hz, 120Hz, 180Hz.) Other electrical IR from lights IR from cameras (autofocus) Visible light
Lecture 2 Analog circuits Seeing the light.. I t IR light V1 9V +V IR detection Noise sources: Electrical (60Hz, 120Hz, 180Hz.) Other electrical IR from lights IR from cameras (autofocus) Visible light
6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang. General Outline
 6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang General Outline We will build a superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver circuit that will have a bandwidth of the entire AM spectrum, and whose
6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang General Outline We will build a superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver circuit that will have a bandwidth of the entire AM spectrum, and whose
Laboratory 4. Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes
 Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
1) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz
 ) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz Solution: a) Input is of constant amplitude of 2 V from 0 to 0. ms and 2 V from 0. ms to 0.2 ms. The output
) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz Solution: a) Input is of constant amplitude of 2 V from 0 to 0. ms and 2 V from 0. ms to 0.2 ms. The output
CHAPTER 2 A SERIES PARALLEL RESONANT CONVERTER WITH OPEN LOOP CONTROL
 14 CHAPTER 2 A SERIES PARALLEL RESONANT CONVERTER WITH OPEN LOOP CONTROL 2.1 INTRODUCTION Power electronics devices have many advantages over the traditional power devices in many aspects such as converting
14 CHAPTER 2 A SERIES PARALLEL RESONANT CONVERTER WITH OPEN LOOP CONTROL 2.1 INTRODUCTION Power electronics devices have many advantages over the traditional power devices in many aspects such as converting
The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium. Some type of transmission medium is required for transmission:
 Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors: The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium is
Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors: The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium is
Experiment (1) Principles of Switching
 Experiment (1) Principles of Switching Introduction When you use microcontrollers, sometimes you need to control devices that requires more electrical current than a microcontroller can supply; for this,
Experiment (1) Principles of Switching Introduction When you use microcontrollers, sometimes you need to control devices that requires more electrical current than a microcontroller can supply; for this,
TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: Coil Losses:
 TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: To amplify the selective range of frequencies, the resistive load R C is replaced by a tuned circuit. The tuned circuit is capable of amplifying a signal over a narrow
TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: To amplify the selective range of frequencies, the resistive load R C is replaced by a tuned circuit. The tuned circuit is capable of amplifying a signal over a narrow
Applied Electronics II
 Applied Electronics II Chapter 3: Operational Amplifier Part 1- Op Amp Basics School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Addis Ababa Institute of Technology Addis Ababa University Daniel D./Getachew
Applied Electronics II Chapter 3: Operational Amplifier Part 1- Op Amp Basics School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Addis Ababa Institute of Technology Addis Ababa University Daniel D./Getachew
Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab. Facebook: Twitter:
 Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab www.vidyathiplus.in Facebook: www.facebook.com/vidyarthiplus Twitter: www.twitter.com/vidyarthiplus Copyright 2011-2015 Vidyarthiplus.in (VP Group) Page 1 CIRCUIT
Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab www.vidyathiplus.in Facebook: www.facebook.com/vidyarthiplus Twitter: www.twitter.com/vidyarthiplus Copyright 2011-2015 Vidyarthiplus.in (VP Group) Page 1 CIRCUIT
Advances in Averaged Switch Modeling
 Advances in Averaged Switch Modeling Robert W. Erickson Power Electronics Group University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado USA 80309-0425 rwe@boulder.colorado.edu http://ece-www.colorado.edu/~pwrelect 1
Advances in Averaged Switch Modeling Robert W. Erickson Power Electronics Group University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado USA 80309-0425 rwe@boulder.colorado.edu http://ece-www.colorado.edu/~pwrelect 1
CHAPTER 3. Instrumentation Amplifier (IA) Background. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Instrumentation Amplifier Architecture and Configurations
 CHAPTER 3 Instrumentation Amplifier (IA) Background 3.1 Introduction The IAs are key circuits in many sensor readout systems where, there is a need to amplify small differential signals in the presence
CHAPTER 3 Instrumentation Amplifier (IA) Background 3.1 Introduction The IAs are key circuits in many sensor readout systems where, there is a need to amplify small differential signals in the presence
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
EE 442 Homework #3 Solutions (Spring 2016 Due February 13, 2017 ) Print out homework and do work on the printed pages.
 NAME Solutions EE 44 Homework #3 Solutions (Spring 06 Due February 3, 07 ) Print out homework and do work on the printed pages. Textbook: B. P. Lathi & Zhi Ding, Modern Digital and Analog Communication
NAME Solutions EE 44 Homework #3 Solutions (Spring 06 Due February 3, 07 ) Print out homework and do work on the printed pages. Textbook: B. P. Lathi & Zhi Ding, Modern Digital and Analog Communication
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers
 Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
Physics 123: Homework 4: Op Amps II
 P123 HW 4: op amps II 1 Physics 123: Homework 4: Op Amps II Total points: 23.5; DUE Monday, Mar. 2, 2015 Contents 1 Review?: Capacitive coupling (5 pts) 2 1.1 Idealized next stage: R INX =, C INX =0.........
P123 HW 4: op amps II 1 Physics 123: Homework 4: Op Amps II Total points: 23.5; DUE Monday, Mar. 2, 2015 Contents 1 Review?: Capacitive coupling (5 pts) 2 1.1 Idealized next stage: R INX =, C INX =0.........
IC Preamplifier Challenges Choppers on Drift
 IC Preamplifier Challenges Choppers on Drift Since the introduction of monolithic IC amplifiers there has been a continual improvement in DC accuracy. Bias currents have been decreased by 5 orders of magnitude
IC Preamplifier Challenges Choppers on Drift Since the introduction of monolithic IC amplifiers there has been a continual improvement in DC accuracy. Bias currents have been decreased by 5 orders of magnitude
FREQUENCY AGILE FM MODULATOR INSTRUCTION BOOK IB
 FMT615C FREQUENCY AGILE FM MODULATOR INSTRUCTION BOOK IB1215-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION SUBJECT 1.0 Introduction 2.0 Installation & Operating Instructions 3.0 Specification 4.0 Functional Description
FMT615C FREQUENCY AGILE FM MODULATOR INSTRUCTION BOOK IB1215-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION SUBJECT 1.0 Introduction 2.0 Installation & Operating Instructions 3.0 Specification 4.0 Functional Description
