Silica-waveguide thermooptic phase shifter with low power consumption and low lateral heat diffusion
|
|
|
- Samuel Bridges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 24, 2018 Silica-waveguide thermooptic phase shifter with low power consumption and low lateral heat diffusion Andersen, Bo Asp Møller; Jensen, Lars; Laurent-Lund, Christian; Thirstrup, Carsten Published in: I E E E Photonics Technology Letters Link to article, DOI: / Publication date: 1993 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Andersen, B. A. M., Jensen, L., Laurent-Lund, C., & Thirstrup, C. (1993). Silica-waveguide thermooptic phase shifter with low power consumption and low lateral heat diffusion. I E E E Photonics Technology Letters, 5(12), DOI: / General rights Copyright and moral rights for the publications made accessible in the public portal are retained by the authors and/or other copyright owners and it is a condition of accessing publications that users recognise and abide by the legal requirements associated with these rights. Users may download and print one copy of any publication from the public portal for the purpose of private study or research. You may not further distribute the material or use it for any profit-making activity or commercial gain You may freely distribute the URL identifying the publication in the public portal If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim.
2 IEEE PHOTONICS TECHNOLOGY LETTERS, VOL. 5, NO. 12, DECEMBER Silica-Waveguide Thermooptic Phase Shifter with Low Power Consumption and Low Lateral Heat Diffusion Bo Asp Mdler, Lars Jensen, Member, ZEEE, Christian Laurent-Lund, and Carsten Thirstrup Abstract-A thermooptic (TO) phase shifter consisting of a thin film heater on the top of a loaded stripline silica waveguide on a silicon substrate is shown to exhibit faster time response than reported for phase shifters based on a buried silica waveguide configuration. The rise time was measured to be 0.24 ms, which is in good agreement with calculated thermal distributions in the structures. The lateral heat diffusion distance in the loaded stripline structure is shown to be smaller than in buried waveguide structures. This implies small thermal crosstalk and suggests a high-level integration of adjacent waveguides. I. INTRODUCTION N general, glass has a temperature-dependent refrac- I tive index which is known as the thermooptic (TO) effect. Active optical glass waveguides utilizing the (TO) effect such as modulators and switches have been demonstrated [1]-[4]. In particular, a TO phase shifter is an important component for making silica-based integrated optical circuits on silicon substrates, where it is used in Mach-Zehnder optical multiplexers/demultiplexers and switches [5]. Conventional TO phase shifters consist of a thin film heater deposited on top of the cladding of a buried channel waveguide which provides a refractive index change [4]. Since the thermal conductivity is larger in glass than in air, the heat will be conducted to the silicon substrate which acts as a heatsink in this configuration. One of the problems with these TO phase shifters, however, is the relatively large power consumption and lateral heat diffusion in the glass, leading to a temperature rise of the sample and thermal crosstalk between two adjacent waveguides [4]. This paper describes a TO phase shifter implemented as a silica-based single-mode loaded stripline waveguide on a silicon substrate. In loaded stripline waveguides, a narrow thin film heater can be employed which ensures lower power consumption and less lateral heat diffusion than in buried waveguides. For the TO waveguide phase shifter reported here, the time response and the frequency response have been determined and the electrical power required for a 7~ phase shift of the light guided in Manuscript received July 28, 1993; revised September 30, The authors are with Microelectronik Centret, Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800, Lyngby, Denmark. IEEE Log Number the waveguide has been measured by means of an external Mach-Zehnder interferometer. The lateral heat diffusion from the core region under the heater has been calculated and it is shown to be less than in a buried configuration. 11. STRUCTURE AND EXPERIMENTS The TO phase shifter is fabricated as a single-mode silica-based loaded stripline waveguide with a chrome heater element on the top. The silica structure, supplied by Photonic Integration Research Inc., USA, consists of three layers deposited on a silicon wafer by Flame Hydrolysis Deposition. A cross section of the phase shifter is shown in Fig. 1. The load is 7 pm thick and 14 pm wide, the thicknesses of the core layer and the cladding layer are 6 pm and 20 pm, respectively. The loads of the waveguides were made using reactive ion etching and a 0.44 pm thin chrome film was used as an etch mask. Thus, the thin film heater was formed as a self-aligned structure on top of the waveguide load. The heaters were 5 mm long and 14 pm wide, corresponding to the width of the waveguide load, and the electrical resistance of the heater was measured to be 1.56 klr. The losses in the waveguides were measured to be 6.9 db/cm for TE polarization, and larger than 30 db/cm for TM polarization. For TE polarization, the high losses are due to a rough surface at the interface between the glass and the air caused by the etch process. By optimizing the etch process to eliminate the surface textures the losses can be reduced substantially [61. For TM polarization, the additional losses are caused by the metal on top of the load. In order to measure the thermally-induced phase shift, the TO waveguide phase shifter was placed in one arm of an external Mach-Zehnder interferometer. A GaInAsP laser with a wavelength of 1.55 pm was used as the light source and the output light of the waveguides was detected by a GaInAs photodiode. Two types of experiments were carried out. In the first experiment, the frequency response of the TO phase shifter was determined by applying a triangular-wave voltage to the heater, and the phase shift was measured as a function of the applied electrical power. By tuning the frequency of the applied electrical power, the frequency characteristics were determined. The peak-to-peak voltage was set to 30 V and the /93$ IEEE - -~ - - ~ Authorized licensed use limited to: Danmarks Tekniske Informationscenter. Downloaded on November 27, 2009 at 06:42 from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.
3 Authorized licensed use limited to: Danmarks Tekniske Informationscenter. Downloaded on November 27, 2009 at 06:42 from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply IEEE PI HOTONICS TECHNOLOGY LETIERS, VOL. 5, NO. 12, DECEMBER Thinfilmheater (14 pm wide) 1 TABLE I CALCULATED RISE TIMES FOR THE FOUR TYPES (A-D) OF WAVEGUIDE STRUCTURES, SHOWN TOGETHER WITH MEASURED RISE TIMES Core (6 pm thick) Cladding (20 pm thick) Si substrate Fig. 1. Cross section of a TO phase shifter consisting of a single-mode loaded stripline silica waveguide on a silicon substrate with a chrome thin film heater on the top of the load. frequency range was from 100 Hz to 2 khz. In the second experiment, the time response of the TO phase shifter was determined by applying a voltage pulse to the heater. The pulse was a square pulse with a 7.5 V or 10 V amplitude, a frequency of 25 Hz, and a duty cycle of 7.5%, giving a pulse width of 3 ms THERMAL ANALYSIS AND MEASUREMENTS A simple model can explain the dynamic behavior of the heat flow in the TO waveguide phase shifter. The heat from the chrome film diffuses into the silica glass, the air, and the silicon substrate. Because of the large thermal conductivity of silicon compared to silica and air, the substrate can be considered a perfect heat sink [4]. The air above and surrounding the phase shifter has a low thermal conductivity compared to chrome and glass, and the heat flow into the air can therefore be neglected. The thickness of the heater is much smaller than the thickness of the glass and the heat capacity of the film heater can therefore also be neglected. Using these assumptions, the temperature can be calculated using a finite difference method [7]. In the calculations, the applied electrical power was set equal to 0.5 W, which is a typical value to obtain a rr phase shift of the light, and the temperature of the silicon substrate was kept constant at 300 K. The power consumption required for a rr phase shift in the loaded stripline configuration was measured to be 0.4 W, which is similar or better than reported in [4]. Material constants are the thermal conductivity of glass K = 1.40 W/mK [81, the specific heat of glass cp = J/kg. K [9], and the mass density of glass p = 2.21 x lo3 kg/m3 [8]. Four different configurations have been evaluated. Type A is a TO phase shifter based on a buried waveguide configuration with the vertical dimensions 21 pm for the upper cladding, 8 pm for the core, and 21 pm for the lower cladding. The film heater width is 50 pm [4]. Type B has the same dimensions as type A, except for the film heater width which is set equal to 14 pm. Type C is like type B, but with thinner upper cladding and core. The vertical dimensions of this structure are 7 pm for the upper Heater width (Fm) Upper clad/ load (i core (m) Lower clad (um) Calculated time conslant (ms) Measured 1.0 time constant (ms) Measured P, 0.44 (w) cladding, 6 pm for the core, 20 pm for the lower cladding, and the structure comprises a 14 pm wide film heater. Type D is like type C, but with a loaded stripline configuration, i.e., the upper cladding is etched except under the film heater (see Fig. 1). For the four different configurations, the temperature at the center of the waveguide has been calculated as a function of time when a square pulse is applied to the heater. The resulting responses have the form of integrated error functions due to the diffusion nature of the problem. To a very good approximation, the integrated error function can be fitted by an exponential function and a time constant (rise time or fall time) can be defined. The rise times and fall times are measured to be equal within the uncertainty range, which is also expected from the linear model that describes the heat flow in the system. Table I shows the calculated rise times for the four different configurations (types A-D), and the measured rise times for the loaded stripline waveguide (type D from this work) and for the buried waveguide (type A from [4]). Fig. 2 shows the measured frequency response of the phase shifter, and the calculated frequency response for the four configurations as found from the calculated rise times. The normalized modulation with standard deviation for measured data is plotted as a function of frequency. From Table I and Fig. 2, it is observed that the model agrees well with the measured data (type A and type D). The large change in switching time between type B and type C indicates that there are mainly two parameters which affect the switching speed and the power P, necessary to provide a rr phase shift. Most significantly, a smaller total volume of the glass will increase the switching speed because of the smaller heat capacitance. Secondly, a core closer to the heater will decrease the power needed for obtaining the same temperature in the core. 0.4
4 MOLLER et al.: SILICA WAVEGUIDE THERMOOPTIC PHASE SHIFTER 1417 I I 0 \b. \\ I --structure type A "\ -.-Structure type B \it:, --Structure type C -Structure type D \\ 1 1 \ Frequency (Hz) Fig. 2. Measured frequency response of the TO phase shifter (the error bars indicate the standard deviations of the measurements), and the calculated frequency response of (a) a buried waveguide structure with a total thickness of 50 pm and a heater width of 50 pm (type A), (b) As (a), but with a heater width of 14 pm (type B), (c) a buried waveguide structure with a total thickness of 33 pm and a heater width of 14 pm (type C), and (d) a loaded stripline waveguide structure with a 7 pm upper cladding, a 6 pm core, a 20 pm lower cladding and a heater with a width of 14 pm (type D). There is an additional increase of the switching speed from type C to type D since the load structure provides a stronger confinement of the heatflow than the buried waveguide structure. The difference between the switching times for type A and type B is small indicating that the phase shifter is not very sensitive to the width of the film heater. As a consequence of the effect of these parameters, the switching time for a loaded stripline waveguide structure is about four times smaller than for the buried waveguide structure reported by Sugita et al. [4] (see Table I). However, the increase in switching speed is obtained with penalty in optical losses. The smaller distance from the core to the heater leads to absorption of the TM polarized light [lo]. Fig. 3 shows contour plots of the temperature in (a) a type A structure and (b) a type D structure. The thermal spreading, defined here as the lateral distance where the temperature rise is one-tenth of the temperature rise at the center of the waveguide core, is found to be 84 pm for the type A structure and 39 pm for the type D structure. This indicates the possibility of having waveguides more closely spaced and thereby minimizing the required space for, e.g., A Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Fig. 3 also shows the difference in core temperature for the two structures. IV. CONCLUSIONS We have presented a thermooptic phase shifter fabricated as a single-mode loaded stripline silica waveguide on a silicon substrate with a thin film heater on the top of the load. A rise time of 0.24 ms was measured, which is faster than what has been achieved in TO phase shifters based on buried waveguides. The temperature distribution in the glass was calculated and the model showed good E 3. v -20 G 8 a -40 n E 3. v c Glass 1 Substrate -60 I.... I...., Width (pm) (a) Width (pm) Fig. 3. Calculated temperature distribution in (a) a buried waveguide structure (type A), and (b) a loaded stripline waveguide structure (type D). The glass/substrate interface has a temperature of 300 K, the applied electrical power is 0.5 W, and the contour plots are shown in steps of 5 K. The core regions of the waveguides are marked on the figures. Note that the x axis and the y axis have different scales. agreement with the measured time response. The increased switching time is contributed to the smaller total glass volume and the shorter distance from the core to the heater. From the model, the lateral heat diffusion in the glass structure was calculated and it was found to be less than in a buried waveguide based TO phase shifter by a factor of two or more. The low lateral heat diffusion enables a higher integration-density of the waveguides. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors thank 0. Hansen for his constructive comments and advice during our discussions, and G. Holm Larsen from Briiel & Kjaer A/S for providing help with the measurements. Authorized licensed use limited to: Danmarks Tekniske Informationscenter. Downloaded on November 27, 2009 at 06:42 from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.
5 Authorized licensed use limited to: Danmarks Tekniske Informationscenter. Downloaded on November 27, 2009 at 06:42 from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply IEEE PHOTONICS TECHNOLOGY LETERS, VOL. 5, NO. 12, DECEMBER 1993 REFERENCES [l] M. Haruna and J. Koyama, Thermooptic deflection and switching in glass, Appl. Opt., vol. 21, pp , [2] N. Takato, K. Jinguji, M. Yaso, H. Toba, and M. Kawachi, Silicabased single-mode waveguides on silicon and their application to guided-wave optical interferometers, J. Lightwave Technol., vol. 6, pp , [3] Y. Inoue, K. Katoh, and M. Kawachi, Polarization sensitivity of a silica waveguide thermooptic phase shifter for planar lightwave circuits, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., vol. 4, pp , [4] A. Sugita, K. Jinguji, N. Takato, K. Katoh, and M. Kawachi, Bridge-suspended silica-waveguide thermooptic phase shifter and its application to Mach-Zehnder type optical switch, Trans. IEICE, vol. E73, no. 1, pp , Jan [5] M. Kawachi, Silica waveguides on silicon and their application to integrated-optic components, Opt. Quantum Electron., vol. 22, pp , [6] L. Jensen and B. Asp Moller, Glass waveguides on a silicon substrate, Master of Science Thesis, Mikroelektronik Centret, Tech. Univ. Denmark, Jan (in Danish). [7] W. E. Milne, Numerical Solution of Differential Equations. New York Dover, A. S. Grove, Physics and Technology of Semiconductor Deuices. New York Wiley, [9] Kaye & Laby, Tables of Physical and Chemical Constants. New York Longman, [lo] H. Nishihara, M. Haruna, and T. Suhara, Optical Integrated Circuits. New York: McGraw-Hill, ARROW-Type Polarizer Utilizing Form Birefringence in Multilayer First Cladding Y. Kokubun and S. Asakawa Abstract-We proposed a novel waveguide polarizer using an ARROW structure, of which the first cladding consists of three thin layers. Theoretical calculation shows that this polarizer can achieve a high isolation over 30 db/cm with small insertion loss of 0.01 db / cm at the wavelength of 1.3 pm. The isolation of 83 db / cm with the insertion loss of 4.3 db / cm was experimentally obtained at the wavelength of Fm. This structure is suitable for the integration of a polarization splitter and photodetector. I. INTRODUCTION HOTONIC circuits based on multilayer waveguides P are suitable for various functional devices, and for a dense integration of photonic circuits with stacked configuration. In particular, ARROW (antiresonant reflecting optical waveguide) [ll, [21 has many advantages for such integrated photonics on a semiconductor substrate. We have reported some applications of ARROWs, such as a wavelength filter [3], an integrated structure of a waveguide and photodetector [4], and a stacked configuration of ARROWs [5], [61. One of the advantage of an AR- ROW is the strong polarization dependence of propagation loss, i.e., only the TE, mode can be guided with low loss, while the TM, mode is radiated to the substrate. However, when the core thickness is as thick as that of optical fibers, the TM, mode loss is not large enough for a compact waveguide polarizer. This is because the ratio Manuscript received June 29, 1993; revised August 31, The authors are with Yokohama National University, Division of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Hodogayaku, Yokohama, 240 Japan. IEEE Log Number of radiation losses of the TE, and TM, modes in db is almost constant for any combination of materials, i.e., the core and first cladding materials. On the other hand, when the core thickness decreases, the isolation is high enough for a compact device. However, a spot-size transformer is needed in the circuit. On the other hand, several waveguide polarizers have been developed by using a selective attenuation in a metal cladding [7] or a semiconductor cladding 81, and a selective cutoff in a birefringent cladding consisting of a single crystal [9]. However, these polarizers have some drawbacks such as the insufficient low-insertion loss of transmitted light and the difficulty in fabrication. In this letter, we introduce a novel ARROW-type polarizer of which the first cladding consists of alternate high-index and low-index layers to produce so-called Form birefringence. This polarizer can achieve a high-isolation and low-insertion loss for any core thickness. The design and fabrication of the ARROW-type polarizer will be presented. 11. STRUCTURE AND DESIGN In the fundamental structure of ARROW, an interference cladding which is sandwiched between the core and the substrate consists of a high-index layer designated the first cladding and a low-index layer designated the second cladding as shown on the left of Fig. 1. The radiation loss characteristics of TE, and TM, modes plotted against the thickness of the first cladding (single layer) are shown by dash-dotted and dash-double-dotted lines, respectively, in Fig. 2. The radiation losses of TE, and TM, modes /93$ IEEE
High precision planar waveguide propagation loss measurement technique using a Fabry-Perot cavity
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jan 07, 2018 High precision planar waveguide propagation loss measurement technique using a Fabry-Perot cavity Feuchter, Thomas; Thirstrup, Carsten Published in: I E E
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jan 07, 2018 High precision planar waveguide propagation loss measurement technique using a Fabry-Perot cavity Feuchter, Thomas; Thirstrup, Carsten Published in: I E E
Title. Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori. CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type.
 Title Polarization-independent optical directional coupler Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): 56-58 Issue Date 2006 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/948 Rights
Title Polarization-independent optical directional coupler Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): 56-58 Issue Date 2006 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/948 Rights
Compensation of gain saturation in SOA-gates by interferometric Mach-Zehnder wavelength converters
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 29, 2018 Compensation of gain saturation in SOA-gates by interferometric Mach-Zehnder wavelength converters Danielsen, Søren Lykke; Jørgensen, Carsten; Hansen, Peter
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 29, 2018 Compensation of gain saturation in SOA-gates by interferometric Mach-Zehnder wavelength converters Danielsen, Søren Lykke; Jørgensen, Carsten; Hansen, Peter
Self-Resonant Electrically Small Loop Antennas for Hearing-Aids Application
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 5, 218 Self-Resonant Electrically Small Loop Antennas for Hearing-Aids Application Zhang, Jiaying; Breinbjerg, Olav Published in: EuCAP 21 Publication date: 21 Link
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 5, 218 Self-Resonant Electrically Small Loop Antennas for Hearing-Aids Application Zhang, Jiaying; Breinbjerg, Olav Published in: EuCAP 21 Publication date: 21 Link
AMACH Zehnder interferometer (MZI) based on the
 1284 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 Optimal Design of Planar Wavelength Circuits Based on Mach Zehnder Interferometers and Their Cascaded Forms Qian Wang and Sailing He, Senior
1284 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 Optimal Design of Planar Wavelength Circuits Based on Mach Zehnder Interferometers and Their Cascaded Forms Qian Wang and Sailing He, Senior
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER
 CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
New Waveguide Fabrication Techniques for Next-generation PLCs
 New Waveguide Fabrication Techniques for Next-generation PLCs Masaki Kohtoku, Toshimi Kominato, Yusuke Nasu, and Tomohiro Shibata Abstract New waveguide fabrication techniques will be needed to make highly
New Waveguide Fabrication Techniques for Next-generation PLCs Masaki Kohtoku, Toshimi Kominato, Yusuke Nasu, and Tomohiro Shibata Abstract New waveguide fabrication techniques will be needed to make highly
DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M.
 DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M. Published in: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium of the IEEE Photonics
DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M. Published in: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium of the IEEE Photonics
Log-periodic dipole antenna with low cross-polarization
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Feb 13, 2018 Log-periodic dipole antenna with low cross-polarization Pivnenko, Sergey Published in: Proceedings of the European Conference on Antennas and Propagation Link
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Feb 13, 2018 Log-periodic dipole antenna with low cross-polarization Pivnenko, Sergey Published in: Proceedings of the European Conference on Antennas and Propagation Link
Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices
 644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
Published in: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium of the IEEE Photonics Benelux Chapter, November 2015, Brussels, Belgium
 A Si3N4 optical ring resonator true time delay for optically-assisted satellite radio beamforming Tessema, N.M.; Cao, Z.; van Zantvoort, J.H.C.; Tangdiongga, E.; Koonen, A.M.J. Published in: Proceedings
A Si3N4 optical ring resonator true time delay for optically-assisted satellite radio beamforming Tessema, N.M.; Cao, Z.; van Zantvoort, J.H.C.; Tangdiongga, E.; Koonen, A.M.J. Published in: Proceedings
Fiber-Optic Polarizer Using Resonant Tunneling through a Multilayer Overlay
 Fiber-Optic Polarizer Using Resonant Tunneling through a Multilayer Overlay Arun Kumar, Rajeev Jindal, and R. K. Varshney Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi 110 016 India
Fiber-Optic Polarizer Using Resonant Tunneling through a Multilayer Overlay Arun Kumar, Rajeev Jindal, and R. K. Varshney Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi 110 016 India
Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 1, 218 Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna Kim, Oleksiy S. Published in: iwat Link to article, DOI: 1.119/IWAT.21.546485 Publication date: 21
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 1, 218 Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna Kim, Oleksiy S. Published in: iwat Link to article, DOI: 1.119/IWAT.21.546485 Publication date: 21
The current distribution on the feeding probe in an air filled rectangular microstrip antenna
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 28, 2019 The current distribution on the feeding probe in an air filled rectangular microstrip antenna Brown, K Published in: Antennas and Propagation Society International
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 28, 2019 The current distribution on the feeding probe in an air filled rectangular microstrip antenna Brown, K Published in: Antennas and Propagation Society International
Index. Cambridge University Press Silicon Photonics Design Lukas Chrostowski and Michael Hochberg. Index.
 absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 25, 2018 A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles Dich, Mikael; Rengarajan, S.R. Published in: Proc. of IEEE Antenna and Propagation Society
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 25, 2018 A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles Dich, Mikael; Rengarajan, S.R. Published in: Proc. of IEEE Antenna and Propagation Society
E LECTROOPTICAL(EO)modulatorsarekeydevicesinoptical
 286 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 26, NO. 2, JANUARY 15, 2008 Design and Fabrication of Sidewalls-Extended Electrode Configuration for Ridged Lithium Niobate Electrooptical Modulator Yi-Kuei Wu,
286 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 26, NO. 2, JANUARY 15, 2008 Design and Fabrication of Sidewalls-Extended Electrode Configuration for Ridged Lithium Niobate Electrooptical Modulator Yi-Kuei Wu,
Optics Communications
 Optics Communications 283 (2010) 3678 3682 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Ultra-low-loss inverted taper coupler for silicon-on-insulator
Optics Communications 283 (2010) 3678 3682 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Ultra-low-loss inverted taper coupler for silicon-on-insulator
Development of Vertical Spot Size Converter (SSC) with Low Coupling Loss Using 2.5%Δ Silica-Based Planar Lightwave Circuit
 Development of Vertical Spot Size Converter (SSC) with Low Coupling Loss Using 2.5%Δ Silica-Based Planar Lightwave Circuit Yasuyoshi Uchida *, Hiroshi Kawashima *, and Kazutaka Nara * Recently, new planar
Development of Vertical Spot Size Converter (SSC) with Low Coupling Loss Using 2.5%Δ Silica-Based Planar Lightwave Circuit Yasuyoshi Uchida *, Hiroshi Kawashima *, and Kazutaka Nara * Recently, new planar
On-chip Si-based Bragg cladding waveguide with high index contrast bilayers
 On-chip Si-based Bragg cladding waveguide with high index contrast bilayers Yasha Yi, Shoji Akiyama, Peter Bermel, Xiaoman Duan, and L. C. Kimerling Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts
On-chip Si-based Bragg cladding waveguide with high index contrast bilayers Yasha Yi, Shoji Akiyama, Peter Bermel, Xiaoman Duan, and L. C. Kimerling Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts
Analysis and design of lumped element Marchand baluns
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.d on: Mar 14, 218 Analysis and design of lumped element Marchand baluns Johansen, Tom Keinice; Krozer, Vitor Published in: 17th International Conference on Microwaves, Radar and
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.d on: Mar 14, 218 Analysis and design of lumped element Marchand baluns Johansen, Tom Keinice; Krozer, Vitor Published in: 17th International Conference on Microwaves, Radar and
Compact microstrip bandpass filter with tunable notch
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Feb 16, 2018 Compact microstrip bandpass filter with tunable notch Christensen, Silas; Zhurbenko, Vitaliy; Johansen, Tom Keinicke Published in: Proceedings of 2014 20th
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Feb 16, 2018 Compact microstrip bandpass filter with tunable notch Christensen, Silas; Zhurbenko, Vitaliy; Johansen, Tom Keinicke Published in: Proceedings of 2014 20th
Decreasing the commutation failure frequency in HVDC transmission systems
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 06, 2017 Decreasing the commutation failure frequency in HVDC transmission systems Hansen (retired June, 2000), Arne; Havemann (retired June, 2000), Henrik Published
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 06, 2017 Decreasing the commutation failure frequency in HVDC transmission systems Hansen (retired June, 2000), Arne; Havemann (retired June, 2000), Henrik Published
Circular Piezoelectric Accelerometer for High Band Width Application
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 27, 2018 Circular Piezoelectric Accelerometer for High Band Width Application Hindrichsen, Christian Carstensen; Larsen, Jack; Lou-Møller, Rasmus; Hansen, K.; Thomsen,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 27, 2018 Circular Piezoelectric Accelerometer for High Band Width Application Hindrichsen, Christian Carstensen; Larsen, Jack; Lou-Møller, Rasmus; Hansen, K.; Thomsen,
Microwave Radiometer Linearity Measured by Simple Means
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 27, 2018 Microwave Radiometer Linearity Measured by Simple Means Skou, Niels Published in: Proceedings of IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 27, 2018 Microwave Radiometer Linearity Measured by Simple Means Skou, Niels Published in: Proceedings of IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium
Ultra-Low-Loss Athermal AWG Module with a Large Number of Channels
 Ultra-Low-Loss Athermal AWG Module with a Large Number of Channels by Junichi Hasegawa * and Kazutaka Nara * There is an urgent need for an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG), the device ABSTRACT that handles
Ultra-Low-Loss Athermal AWG Module with a Large Number of Channels by Junichi Hasegawa * and Kazutaka Nara * There is an urgent need for an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG), the device ABSTRACT that handles
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide
 Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
Novel Optical Waveguide Design Based on Wavefront Matching Method
 Novel Optical Waveguide Design Based on Wavefront Matching Method Hiroshi Takahashi, Takashi Saida, Yohei Sakamaki, and Toshikazu Hashimoto Abstract The wavefront matching method provides a new way to
Novel Optical Waveguide Design Based on Wavefront Matching Method Hiroshi Takahashi, Takashi Saida, Yohei Sakamaki, and Toshikazu Hashimoto Abstract The wavefront matching method provides a new way to
Multi-mode to single-mode conversion in a 61 port photonic lantern
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 13, 2018 Multi-mode to single-mode conversion in a 61 port photonic lantern Noordegraaf, Danny; Skovgaard, Peter M.W.; Maack, Martin D.; Bland-Hawthorn, Joss; Lægsgaard,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 13, 2018 Multi-mode to single-mode conversion in a 61 port photonic lantern Noordegraaf, Danny; Skovgaard, Peter M.W.; Maack, Martin D.; Bland-Hawthorn, Joss; Lægsgaard,
On-chip two-mode division multiplexing using tapered directional coupler-based mode multiplexer and demultiplexer
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Feb 01, 2018 On-chip two-mode division multiplexing using tapered directional coupler-based mode multiplexer and demultiplexer Ding, Yunhong; Xu, Jing; Da Ros, Francesco;
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Feb 01, 2018 On-chip two-mode division multiplexing using tapered directional coupler-based mode multiplexer and demultiplexer Ding, Yunhong; Xu, Jing; Da Ros, Francesco;
Applications of Cladding Stress Induced Effects for Advanced Polarization Control in Silicon Photonics
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 3, NO. 3, 27 329 Applications of Cladding Stress Induced Effects for Advanced Polarization Control in licon Photonics D.-X. Xu, P. Cheben, A. Delâge, S. Janz, B. Lamontagne, M.-J. Picard
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 3, NO. 3, 27 329 Applications of Cladding Stress Induced Effects for Advanced Polarization Control in licon Photonics D.-X. Xu, P. Cheben, A. Delâge, S. Janz, B. Lamontagne, M.-J. Picard
Optical Interconnection in Silicon LSI
 The Fifth Workshop on Nanoelectronics for Tera-bit Information Processing, 1 st Century COE, Hiroshima University Optical Interconnection in Silicon LSI Shin Yokoyama, Yuichiro Tanushi, and Masato Suzuki
The Fifth Workshop on Nanoelectronics for Tera-bit Information Processing, 1 st Century COE, Hiroshima University Optical Interconnection in Silicon LSI Shin Yokoyama, Yuichiro Tanushi, and Masato Suzuki
UC Santa Barbara UC Santa Barbara Previously Published Works
 UC Santa Barbara UC Santa Barbara Previously Published Works Title Compact broadband polarizer based on shallowly-etched silicon-on-insulator ridge optical waveguides Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/959523wq
UC Santa Barbara UC Santa Barbara Previously Published Works Title Compact broadband polarizer based on shallowly-etched silicon-on-insulator ridge optical waveguides Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/959523wq
Title. Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori. CitationOptics Express, 18(5): Issue Date Doc URL.
 Title A design method of a fiber-based mode multi/demultip Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 18(5): 4709-4716 Issue Date 2010-03-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/46825
Title A design method of a fiber-based mode multi/demultip Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 18(5): 4709-4716 Issue Date 2010-03-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/46825
Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.15, No.2, 1 6 Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna Hiroshi Hashiguchi a), Toshihiko Baba, and Hiroyuki Arai Graduate School of
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.15, No.2, 1 6 Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna Hiroshi Hashiguchi a), Toshihiko Baba, and Hiroyuki Arai Graduate School of
Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers with Low Noise Figure
 Hideaki Hasegawa *, Masaki Funabashi *, Kazuomi Maruyama *, Kazuaki Kiyota *, and Noriyuki Yokouchi * In the multilevel phase modulation which is expected to provide the nextgeneration modulation format
Hideaki Hasegawa *, Masaki Funabashi *, Kazuomi Maruyama *, Kazuaki Kiyota *, and Noriyuki Yokouchi * In the multilevel phase modulation which is expected to provide the nextgeneration modulation format
HIGH-EFFICIENCY MQW ELECTROABSORPTION MODULATORS
 HIGH-EFFICIENCY MQW ELECTROABSORPTION MODULATORS J. Piprek, Y.-J. Chiu, S.-Z. Zhang (1), J. E. Bowers, C. Prott (2), and H. Hillmer (2) University of California, ECE Department, Santa Barbara, CA 93106
HIGH-EFFICIENCY MQW ELECTROABSORPTION MODULATORS J. Piprek, Y.-J. Chiu, S.-Z. Zhang (1), J. E. Bowers, C. Prott (2), and H. Hillmer (2) University of California, ECE Department, Santa Barbara, CA 93106
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #3 is due today No class Monday, Feb 26 Pre-record
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #3 is due today No class Monday, Feb 26 Pre-record
Fiber-wireless links supporting high-capacity W-band channels
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 05, 2019 Fiber-wireless links supporting high-capacity W-band channels Vegas Olmos, Juan José; Tafur Monroy, Idelfonso Published in: Proceedings of PIERS 2013 Publication
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 05, 2019 Fiber-wireless links supporting high-capacity W-band channels Vegas Olmos, Juan José; Tafur Monroy, Idelfonso Published in: Proceedings of PIERS 2013 Publication
A high-speed CMOS current op amp for very low supply voltage operation
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 31, 2018 A high-speed CMOS current op amp for very low supply voltage operation Bruun, Erik Published in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 31, 2018 A high-speed CMOS current op amp for very low supply voltage operation Bruun, Erik Published in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits
CoSMOS: Performance of Kurtosis Algorithm for Radio Frequency Interference Detection and Mitigation
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 4, 18 CoSMOS: Performance of Kurtosis Algorithm for Radio Frequency Interference Detection and Mitigation Misra, Sidharth; Kristensen, Steen Savstrup; Skou, Niels;
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 4, 18 CoSMOS: Performance of Kurtosis Algorithm for Radio Frequency Interference Detection and Mitigation Misra, Sidharth; Kristensen, Steen Savstrup; Skou, Niels;
High-Resolution AWG-based fiber bragg grating interrogator Pustakhod, D.; Kleijn, E.; Williams, K.A.; Leijtens, X.J.M.
 High-Resolution AWG-based fiber bragg grating interrogator Pustakhod, D.; Kleijn, E.; Williams, K.A.; Leijtens, X.J.M. Published in: IEEE Photonics Technology Letters DOI: 10.1109/LPT.2016.2587812 Published:
High-Resolution AWG-based fiber bragg grating interrogator Pustakhod, D.; Kleijn, E.; Williams, K.A.; Leijtens, X.J.M. Published in: IEEE Photonics Technology Letters DOI: 10.1109/LPT.2016.2587812 Published:
Influence of dielectric substrate on the responsivity of microstrip dipole-antenna-coupled infrared microbolometers
 Influence of dielectric substrate on the responsivity of microstrip dipole-antenna-coupled infrared microbolometers Iulian Codreanu and Glenn D. Boreman We report on the influence of the dielectric substrate
Influence of dielectric substrate on the responsivity of microstrip dipole-antenna-coupled infrared microbolometers Iulian Codreanu and Glenn D. Boreman We report on the influence of the dielectric substrate
Evaluation of the Danish Safety by Design in Construction Framework (SDCF)
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 15, 2017 Evaluation of the Danish Safety by Design in Construction Framework (SDCF) Schultz, Casper Siebken; Jørgensen, Kirsten Publication date: 2015 Link back to
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 15, 2017 Evaluation of the Danish Safety by Design in Construction Framework (SDCF) Schultz, Casper Siebken; Jørgensen, Kirsten Publication date: 2015 Link back to
Aspemyr, Lars; Jacobsson, Harald; Bao, Mingquan; Sjöland, Henrik; Ferndal, Mattias; Carchon, G
 A 15 GHz and a 2 GHz low noise amplifier in 9 nm RF CMOS Aspemyr, Lars; Jacobsson, Harald; Bao, Mingquan; Sjöland, Henrik; Ferndal, Mattias; Carchon, G Published in: Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic
A 15 GHz and a 2 GHz low noise amplifier in 9 nm RF CMOS Aspemyr, Lars; Jacobsson, Harald; Bao, Mingquan; Sjöland, Henrik; Ferndal, Mattias; Carchon, G Published in: Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic
A 240W Monolithic Class-D Audio Amplifier Output Stage
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jun 30, 208 A 240W Monolithic Class-D Audio Amplifier Output Stage Nyboe, Flemming; Kaya, Cetin; Risbo, Lars; Andreani, Pietro Published in: IEEE International Solid-State
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jun 30, 208 A 240W Monolithic Class-D Audio Amplifier Output Stage Nyboe, Flemming; Kaya, Cetin; Risbo, Lars; Andreani, Pietro Published in: IEEE International Solid-State
Hybrid Integration Technology of Silicon Optical Waveguide and Electronic Circuit
 Hybrid Integration Technology of Silicon Optical Waveguide and Electronic Circuit Daisuke Shimura Kyoko Kotani Hiroyuki Takahashi Hideaki Okayama Hiroki Yaegashi Due to the proliferation of broadband services
Hybrid Integration Technology of Silicon Optical Waveguide and Electronic Circuit Daisuke Shimura Kyoko Kotani Hiroyuki Takahashi Hideaki Okayama Hiroki Yaegashi Due to the proliferation of broadband services
A Novel technique to measure propagation loss of optical waveguides. Abstract. I. Introduction
 A Novel technique to measure propagation loss of optical waveguides Samit Barai, ASelvarajan, T.Srinivas,T.Madhan and R. Fazludeen' Applied Photonics Lab, ECE Dept. Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore,
A Novel technique to measure propagation loss of optical waveguides Samit Barai, ASelvarajan, T.Srinivas,T.Madhan and R. Fazludeen' Applied Photonics Lab, ECE Dept. Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore,
Property improvement of flat-top 50 GHz-88 ch arrayed waveguide grating using phase correction waveguides
 Property improvement of flat-top 50 GHz-88 ch arrayed waveguide grating using phase correction waveguides Kazutaka Nara 1a) and Noritaka Matsubara 2 1 FITEL Photonics Laboratory, Furukawa Electric Co.,
Property improvement of flat-top 50 GHz-88 ch arrayed waveguide grating using phase correction waveguides Kazutaka Nara 1a) and Noritaka Matsubara 2 1 FITEL Photonics Laboratory, Furukawa Electric Co.,
Cross-polarization and sidelobe suppression in dual linear polarization antenna arrays
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jun 06, 2018 Cross-polarization and sidelobe suppression in dual linear polarization antenna arrays Woelders, Kim; Granholm, Johan Published in: I E E E Transactions on
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jun 06, 2018 Cross-polarization and sidelobe suppression in dual linear polarization antenna arrays Woelders, Kim; Granholm, Johan Published in: I E E E Transactions on
A Novel SFG Structure for C-T Highpass Filters
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 17, 2017 A Novel SFG Structure for C-T Highpass Filters Nielsen, Ivan Riis Published in: Proceedings of the Eighteenth European Solid-State Circuits Conference Publication
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 17, 2017 A Novel SFG Structure for C-T Highpass Filters Nielsen, Ivan Riis Published in: Proceedings of the Eighteenth European Solid-State Circuits Conference Publication
Optimizing Inductor Winding Geometry for Lowest DC-Resistance using LiveLink between COMSOL and MATLAB
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 14, 2018 Optimizing Inductor Winding Geometry for Lowest DC-Resistance using LiveLink between COMSOL and MATLAB Schneider, Henrik; Andersen, Thomas; Mønster, Jakob
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 14, 2018 Optimizing Inductor Winding Geometry for Lowest DC-Resistance using LiveLink between COMSOL and MATLAB Schneider, Henrik; Andersen, Thomas; Mønster, Jakob
An area efficient low noise 100 Hz low-pass filter
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 13, 2018 An area efficient low noise 100 Hz low-pass filter Ølgaard, Christian; Sassene, Haoues; Perch-Nielsen, Ivan R. Published in: Proceedings of the IEEE International
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 13, 2018 An area efficient low noise 100 Hz low-pass filter Ølgaard, Christian; Sassene, Haoues; Perch-Nielsen, Ivan R. Published in: Proceedings of the IEEE International
Electro-optic Electric Field Sensor Utilizing Ti:LiNbO 3 Symmetric Mach-Zehnder Interferometers
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 16, No. 1, March 2012, pp. 47-52 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2012.16.1.047 Electro-optic Electric Field Sensor Utilizing Ti:LiNbO 3 Symmetric Mach-Zehnder
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 16, No. 1, March 2012, pp. 47-52 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2012.16.1.047 Electro-optic Electric Field Sensor Utilizing Ti:LiNbO 3 Symmetric Mach-Zehnder
Power enhancement of piezoelectric transformers for power supplies.
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 08, 2017 Power enhancement of piezoelectric transformers for power supplies. Ekhtiari, Marzieh; Steenstrup, Anders Resen ; Zhang, Zhe; Andersen, Michael A. E. Published
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 08, 2017 Power enhancement of piezoelectric transformers for power supplies. Ekhtiari, Marzieh; Steenstrup, Anders Resen ; Zhang, Zhe; Andersen, Michael A. E. Published
Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs
 Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs Gustafsson, Mats Published: 24-- Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gustafsson, M. (24). Broadband
Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs Gustafsson, Mats Published: 24-- Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gustafsson, M. (24). Broadband
ECE 6323 Ridge Waveguide Laser homework
 ECE 633 Ridge Waveguide Laser homework Introduction This is a slide from a lecture we will study later on. It is about diode lasers. Although we haven t studied diode lasers, there is one aspect about
ECE 633 Ridge Waveguide Laser homework Introduction This is a slide from a lecture we will study later on. It is about diode lasers. Although we haven t studied diode lasers, there is one aspect about
Long-Wavelength Waveguide Photodiodes for Optical Subscriber Networks
 Long-Wavelength Waveguide Photodiodes for Optical Subscriber Networks by Masaki Funabashi *, Koji Hiraiwa *, Kazuaki Nishikata * 2, Nobumitsu Yamanaka *, Norihiro Iwai * and Akihiko Kasukawa * Waveguide
Long-Wavelength Waveguide Photodiodes for Optical Subscriber Networks by Masaki Funabashi *, Koji Hiraiwa *, Kazuaki Nishikata * 2, Nobumitsu Yamanaka *, Norihiro Iwai * and Akihiko Kasukawa * Waveguide
Photonics and Optical Communication
 Photonics and Optical Communication (Course Number 300352) Spring 2007 Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/dknipp/ 1 Photonics and Optical Communication
Photonics and Optical Communication (Course Number 300352) Spring 2007 Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/dknipp/ 1 Photonics and Optical Communication
Microphotonics Readiness for Commercial CMOS Manufacturing. Marco Romagnoli
 Microphotonics Readiness for Commercial CMOS Manufacturing Marco Romagnoli MicroPhotonics Consortium meeting MIT, Cambridge October 15 th, 2012 Passive optical structures based on SOI technology Building
Microphotonics Readiness for Commercial CMOS Manufacturing Marco Romagnoli MicroPhotonics Consortium meeting MIT, Cambridge October 15 th, 2012 Passive optical structures based on SOI technology Building
Design and Fabrication of an Efficient Extreme Ultraviolet Beam Splitter
 EUV Beam Splitter 1 Design and Fabrication of an Efficient Extreme Ultraviolet Beam Splitter First Semester Report Full Report By: Andrew Wiley Maram Alfaraj Prepared to partially fulfill the requirements
EUV Beam Splitter 1 Design and Fabrication of an Efficient Extreme Ultraviolet Beam Splitter First Semester Report Full Report By: Andrew Wiley Maram Alfaraj Prepared to partially fulfill the requirements
High-speed Ge photodetector monolithically integrated with large cross silicon-on-insulator waveguide
 [ APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS ] High-speed Ge photodetector monolithically integrated with large cross silicon-on-insulator waveguide Dazeng Feng, Shirong Liao, Roshanak Shafiiha. etc Contents 1. Introduction
[ APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS ] High-speed Ge photodetector monolithically integrated with large cross silicon-on-insulator waveguide Dazeng Feng, Shirong Liao, Roshanak Shafiiha. etc Contents 1. Introduction
Performance of silicon micro ring modulator with an interleaved p-n junction for optical interconnects
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 55, May 2017, pp. 363-367 Performance of silicon micro ring modulator with an interleaved p-n junction for optical interconnects Priyanka Goyal* & Gurjit Kaur
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 55, May 2017, pp. 363-367 Performance of silicon micro ring modulator with an interleaved p-n junction for optical interconnects Priyanka Goyal* & Gurjit Kaur
System grounding of wind farm medium voltage cable grids
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 23, 2018 System grounding of wind farm medium voltage cable grids Hansen, Peter; Østergaard, Jacob; Christiansen, Jan S. Published in: NWPC 2007 Publication date: 2007
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 23, 2018 System grounding of wind farm medium voltage cable grids Hansen, Peter; Østergaard, Jacob; Christiansen, Jan S. Published in: NWPC 2007 Publication date: 2007
Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications by Stuart M. Wentworth Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
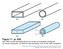 Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Limitations in distance and frequency due to chromatic dispersion in fibre-optic microwave and millimeter-wave links
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 30, 2018 Limitations in distance and frequency due to chromatic dispersion in fibre-optic microwave and millimeter-wave links Gliese, Ulrik Bo; Nielsen, Søren Nørskov;
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 30, 2018 Limitations in distance and frequency due to chromatic dispersion in fibre-optic microwave and millimeter-wave links Gliese, Ulrik Bo; Nielsen, Søren Nørskov;
Simulation of advanced ultrasound systems using Field II
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 16, 218 Simulation of advanced ultrasound systems using Field II Jensen, Jørgen Arendt Published in: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Engineering 24 Link
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 16, 218 Simulation of advanced ultrasound systems using Field II Jensen, Jørgen Arendt Published in: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Engineering 24 Link
A Novel Method for HBT Intrinsic Collector Resistance Extraction from S-parameters
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 1, 218 A Novel Method for HBT Intrinsic Collector Resistance Extraction from S-parameters Johansen, Tom Keinicke; Krozer, Viktor; Hadziabdic, Dzenan; Jiang, Chenhui;
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 1, 218 A Novel Method for HBT Intrinsic Collector Resistance Extraction from S-parameters Johansen, Tom Keinicke; Krozer, Viktor; Hadziabdic, Dzenan; Jiang, Chenhui;
Technical Brief #5. Power Monitors
 Technical Brief #5 Power Monitors What is a power monitor?...2 Evanescent field power monitor...2 Responsivity...2 Insertion loss...3 Polarization Dependent Responsivity (PDR)...4 Polarization Dependent
Technical Brief #5 Power Monitors What is a power monitor?...2 Evanescent field power monitor...2 Responsivity...2 Insertion loss...3 Polarization Dependent Responsivity (PDR)...4 Polarization Dependent
Module 16 : Integrated Optics I
 Module 16 : Integrated Optics I Lecture : Integrated Optics I Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Electro-Optic Effect Optical Phase Modulator Optical Amplitude Modulator
Module 16 : Integrated Optics I Lecture : Integrated Optics I Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Electro-Optic Effect Optical Phase Modulator Optical Amplitude Modulator
Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors
 846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
On-chip antenna integration for single-chip millimeterwave FMCW radars Adela, B.B.; Pual, P.T.M; Smolders, A.B.
 On-chip antenna integration for single-chip millimeterwave FMCW radars Adela, B.B.; Pual, P.T.M; Smolders, A.B. Published in: Proceedings of the 2015 9th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation
On-chip antenna integration for single-chip millimeterwave FMCW radars Adela, B.B.; Pual, P.T.M; Smolders, A.B. Published in: Proceedings of the 2015 9th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation
Scanning laser Doppler vibrometry
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 17, 2018 Scanning laser Doppler vibrometry Brøns, Marie; Thomsen, Jon Juel Publication date: 2016 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 17, 2018 Scanning laser Doppler vibrometry Brøns, Marie; Thomsen, Jon Juel Publication date: 2016 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record
Silicon nitride based TriPleX Photonic Integrated Circuits for sensing applications
 Silicon nitride based TriPleX Photonic Integrated Circuits for sensing applications Arne Leinse a.leinse@lionix-int.com 2 Our chips drive your business 2 What are Photonic ICs (PICs)? Photonic Integrated
Silicon nitride based TriPleX Photonic Integrated Circuits for sensing applications Arne Leinse a.leinse@lionix-int.com 2 Our chips drive your business 2 What are Photonic ICs (PICs)? Photonic Integrated
Long-range surface plasmon polariton nanowire waveguides for device applications
 Long-range surface plasmon polariton nanowire waveguides for device applications K. Leosson, 1 T. Nikolajsen, 2 A. Boltasseva 3 and S. I. Bozhevolnyi 4 1 Science Institute, University of Iceland, Dunhagi
Long-range surface plasmon polariton nanowire waveguides for device applications K. Leosson, 1 T. Nikolajsen, 2 A. Boltasseva 3 and S. I. Bozhevolnyi 4 1 Science Institute, University of Iceland, Dunhagi
Design and Simulation of Optical Power Splitter By using SOI Material
 J. Pure Appl. & Ind. Phys. Vol.3 (3), 193-197 (2013) Design and Simulation of Optical Power Splitter By using SOI Material NAGARAJU PENDAM * and C P VARDHANI 1 * Research Scholar, Department of Physics,
J. Pure Appl. & Ind. Phys. Vol.3 (3), 193-197 (2013) Design and Simulation of Optical Power Splitter By using SOI Material NAGARAJU PENDAM * and C P VARDHANI 1 * Research Scholar, Department of Physics,
Comparison of AWGs and Echelle Gratings for Wavelength Division Multiplexing on Silicon-on-Insulator
 Comparison of AWGs and Echelle Gratings for Wavelength Division Multiplexing on Silicon-on-Insulator Volume 6, Number 5, October 2014 S. Pathak, Member, IEEE P. Dumon, Member, IEEE D. Van Thourhout, Senior
Comparison of AWGs and Echelle Gratings for Wavelength Division Multiplexing on Silicon-on-Insulator Volume 6, Number 5, October 2014 S. Pathak, Member, IEEE P. Dumon, Member, IEEE D. Van Thourhout, Senior
Dynamic range of low-voltage cascode current mirrors
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 04, 2018 Dynamic range of low-voltage cascode current mirrors Bruun, Erik; Shah, Peter Jivan Published in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 04, 2018 Dynamic range of low-voltage cascode current mirrors Bruun, Erik; Shah, Peter Jivan Published in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits
Figure 1 Basic waveguide structure
 Recent Progress in SOI Nanophotonic Waveguides D. Van Thourhout, P. Dumon, W. Bogaerts, G. Roelkens, D. Taillaert, G. Priem, R. Baets IMEC-Ghent University, Department of Information Technology, St. Pietersnieuwstraat
Recent Progress in SOI Nanophotonic Waveguides D. Van Thourhout, P. Dumon, W. Bogaerts, G. Roelkens, D. Taillaert, G. Priem, R. Baets IMEC-Ghent University, Department of Information Technology, St. Pietersnieuwstraat
Oxidation of hydrogen-passivated silicon surfaces by scanning near-field optical lithography using uncoated and aluminum-coated fiber probes
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 07, 2018 Oxidation of hydrogen-passivated silicon surfaces by scanning near-field optical lithography using uncoated and aluminum-coated fiber probes Madsen, Steen;
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 07, 2018 Oxidation of hydrogen-passivated silicon surfaces by scanning near-field optical lithography using uncoated and aluminum-coated fiber probes Madsen, Steen;
Encoding of inductively measured k-space trajectories in MR raw data
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 10, 2018 Encoding of inductively measured k-space trajectories in MR raw data Pedersen, Jan Ole; Hanson, Christian G.; Xue, Rong; Hanson, Lars G. Publication date:
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 10, 2018 Encoding of inductively measured k-space trajectories in MR raw data Pedersen, Jan Ole; Hanson, Christian G.; Xue, Rong; Hanson, Lars G. Publication date:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION J. C. F. Matthews, A. Politi, A. Stefanov, and J. L. O Brien We provide here supplementary materials for our Article which details the experimental setup used for the reported
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION J. C. F. Matthews, A. Politi, A. Stefanov, and J. L. O Brien We provide here supplementary materials for our Article which details the experimental setup used for the reported
Propagation loss study of very compact GaAs/AlGaAs substrate removed waveguides
 Propagation loss study of very compact GaAs/AlGaAs substrate removed waveguides JaeHyuk Shin, Yu-Chia Chang and Nadir Dagli * Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, University of California at
Propagation loss study of very compact GaAs/AlGaAs substrate removed waveguides JaeHyuk Shin, Yu-Chia Chang and Nadir Dagli * Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, University of California at
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication
 InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS 2010 Silicon Photonic Circuits: On-CMOS Integration, Fiber Optical Coupling, and Packaging
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS 2010 Silicon Photonic Circuits: On-CMOS Integration, Fiber Optical Coupling, and Packaging Christophe Kopp, St ephane Bernab e, Badhise Ben Bakir,
IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS 2010 Silicon Photonic Circuits: On-CMOS Integration, Fiber Optical Coupling, and Packaging Christophe Kopp, St ephane Bernab e, Badhise Ben Bakir,
I poses (for instance Cable-TV) there is a need for l-by-
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 13, NO. 1, OCTOBER 1995 269 Design and Performance Evaluation of 1 -by-64 Multimode Interference Power Splitter for Optical Communications Thomas Rasmussen, Jesper
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 13, NO. 1, OCTOBER 1995 269 Design and Performance Evaluation of 1 -by-64 Multimode Interference Power Splitter for Optical Communications Thomas Rasmussen, Jesper
Effect of ohmic heating parameters on inactivation of enzymes and quality of not-fromconcentrate
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 25, 2018 Effect of ohmic heating parameters on inactivation of enzymes and quality of not-fromconcentrate mango juice Abedelmaksoud, Tarek; Mohsen, Sobhy Mohamed; Duedahl-Olesen,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 25, 2018 Effect of ohmic heating parameters on inactivation of enzymes and quality of not-fromconcentrate mango juice Abedelmaksoud, Tarek; Mohsen, Sobhy Mohamed; Duedahl-Olesen,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Room-temperature continuous-wave electrically injected InGaN-based laser directly grown on Si Authors: Yi Sun 1,2, Kun Zhou 1, Qian Sun 1 *, Jianping Liu 1, Meixin Feng 1, Zengcheng Li 1, Yu Zhou 1, Liqun
Room-temperature continuous-wave electrically injected InGaN-based laser directly grown on Si Authors: Yi Sun 1,2, Kun Zhou 1, Qian Sun 1 *, Jianping Liu 1, Meixin Feng 1, Zengcheng Li 1, Yu Zhou 1, Liqun
INTEGRATED ACOUSTO-OPTICAL HETERODYNE INTERFEROMETER FOR DISPLACEMENT AND VIBRATION MEASUREMENT
 INTEGRATED ACOUSTO-OPTICAL HETERODYNE INTERFEROMETER FOR DISPLACEMENT AND VIBRATION MEASUREMENT AGUS RUBIYANTO Abstract A complex, fully packaged heterodyne interferometer has been developed for displacement
INTEGRATED ACOUSTO-OPTICAL HETERODYNE INTERFEROMETER FOR DISPLACEMENT AND VIBRATION MEASUREMENT AGUS RUBIYANTO Abstract A complex, fully packaged heterodyne interferometer has been developed for displacement
Si Nano-Photonics Innovate Next Generation Network Systems and LSI Technologies
 Si Nano-Photonics Innovate Next Generation Network Systems and LSI Technologies NISHI Kenichi, URINO Yutaka, OHASHI Keishi Abstract Si nanophotonics controls light by employing a nano-scale structural
Si Nano-Photonics Innovate Next Generation Network Systems and LSI Technologies NISHI Kenichi, URINO Yutaka, OHASHI Keishi Abstract Si nanophotonics controls light by employing a nano-scale structural
Electronically tunable fabry-perot interferometers with double liquid crystal layers
 Electronically tunable fabry-perot interferometers with double liquid crystal layers Kuen-Cherng Lin *a, Kun-Yi Lee b, Cheng-Chih Lai c, Chin-Yu Chang c, and Sheng-Hsien Wong c a Dept. of Computer and
Electronically tunable fabry-perot interferometers with double liquid crystal layers Kuen-Cherng Lin *a, Kun-Yi Lee b, Cheng-Chih Lai c, Chin-Yu Chang c, and Sheng-Hsien Wong c a Dept. of Computer and
Silicon Photonics Technology Platform To Advance The Development Of Optical Interconnects
 Silicon Photonics Technology Platform To Advance The Development Of Optical Interconnects By Mieke Van Bavel, science editor, imec, Belgium; Joris Van Campenhout, imec, Belgium; Wim Bogaerts, imec s associated
Silicon Photonics Technology Platform To Advance The Development Of Optical Interconnects By Mieke Van Bavel, science editor, imec, Belgium; Joris Van Campenhout, imec, Belgium; Wim Bogaerts, imec s associated
Integrated photonic circuit in silicon on insulator for Fourier domain optical coherence tomography
 Integrated photonic circuit in silicon on insulator for Fourier domain optical coherence tomography Günay Yurtsever *,a, Pieter Dumon a, Wim Bogaerts a, Roel Baets a a Ghent University IMEC, Photonics
Integrated photonic circuit in silicon on insulator for Fourier domain optical coherence tomography Günay Yurtsever *,a, Pieter Dumon a, Wim Bogaerts a, Roel Baets a a Ghent University IMEC, Photonics
Horizontal single and multiple slot waveguides: optical transmission at λ = 1550 nm
 Horizontal single and multiple slot waveguides: optical transmission at λ = 1550 nm Rong Sun 1 *, Po Dong 2 *, Ning-ning Feng 1, Ching-yin Hong 1, Jurgen Michel 1, Michal Lipson 2, Lionel Kimerling 1 1Department
Horizontal single and multiple slot waveguides: optical transmission at λ = 1550 nm Rong Sun 1 *, Po Dong 2 *, Ning-ning Feng 1, Ching-yin Hong 1, Jurgen Michel 1, Michal Lipson 2, Lionel Kimerling 1 1Department
Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings
 Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu Optical Engineering 52(9), 091708 (September 2013) Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu
Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu Optical Engineering 52(9), 091708 (September 2013) Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), th European Conference on
 Aalborg Universitet Beam-Steerable Microstrip-Fed Bow-Tie Antenna Array for Fifth Generation Cellular Communications Parchin, Naser Ojaroudi; Shen, Ming; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: Antennas and Propagation
Aalborg Universitet Beam-Steerable Microstrip-Fed Bow-Tie Antenna Array for Fifth Generation Cellular Communications Parchin, Naser Ojaroudi; Shen, Ming; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: Antennas and Propagation
INTELLIGENT OPTICAL CROSS-CONNECT SUBSYSTEM ON A CHIP
 INTELLIGENT OPTICAL CROSS-CONNECT SUBSYSTEM ON A CHIP wwwenablencecom September, 200 Introduction Abstract: We report on an intelligent -channel subsystem on a chip that integrates switching functionality
INTELLIGENT OPTICAL CROSS-CONNECT SUBSYSTEM ON A CHIP wwwenablencecom September, 200 Introduction Abstract: We report on an intelligent -channel subsystem on a chip that integrates switching functionality
Compact Distributed Phase Shifters at X-Band Using BST
 Integrated Ferroelectrics, 56: 1087 1095, 2003 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1058-4587 print/ 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580390259623 Compact Distributed Phase Shifters at X-Band Using
Integrated Ferroelectrics, 56: 1087 1095, 2003 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1058-4587 print/ 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580390259623 Compact Distributed Phase Shifters at X-Band Using
Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides
 Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides Yaming Li, Chong Li, Chuanbo Li, Buwen Cheng, * and Chunlai Xue State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics,
Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides Yaming Li, Chong Li, Chuanbo Li, Buwen Cheng, * and Chunlai Xue State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics,
A Multifrequency Radiometer System
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 17, 2017 A Multifrequency Radiometer System Skou, Niels Published in: Microwave Conference, 1977. 7th European Link to article, DOI: 10.1109/EUMA.1977.332460 Publication
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 17, 2017 A Multifrequency Radiometer System Skou, Niels Published in: Microwave Conference, 1977. 7th European Link to article, DOI: 10.1109/EUMA.1977.332460 Publication
