Color Perception and Applications. Penny Rheingans University of Maryland Baltimore County. Overview
|
|
|
- Vivien Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Color Perception and Applications SIGGRAPH 99 Course: Fundamental Issues of Visual Perception for Effective Image Generation Penny Rheingans University of Maryland Baltimore County Overview Characteristics of Color Perception Mechanisms of Color Perception Color Specification Using Color to Represent Information
2 Characteristics of Color Perception Fundamental, independent visual process after-images color deficient vision Relative, not absolute Interactions between color and other visual properties Physiology: Receptors Rods active at low light levels (scotopic vision) only one wavelength sensitivity function Cones active at normal light levels three types: sensitivity functions with different peaks
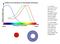
3 Cone Sensitivity Functions Glassner 95, p. 16. Physiology: Ganglia Transform incoming SML into opponent color responses Long (R) G - R - R - G Y - B (Y = R+G) W R+G) Medium (G) Short (B) Characteristics concentric receptive fields logarithmic response of receptors adaption + Yellow - Achrom atic Y-B
4 Physiology: Brain Lateral geniculate nuclei assemble data for single side of visual field 2 monochromatic layers => magnocellular path 4 chromatic layers => parvocellular path Visual cortex visual area 1: blobs visual area 2: thick stripes visual area 4 Visual Pathway Murch, 87.
5 Parvocellular Division Role in vision discrimination of fine detail color Characteristics color: sensitive to wavelength variations acuity: small RF centers speed: relatively slow response Color Models Device-derived convenient for describing display device levels RGB, CMY Intuitive based in familiar color description terms HSV, HSB, HLS Perceptually uniform device independent, perceptually uniform CIELUV, CIELAB, Munsell
6 Color Models Device-derived convenient for describing display device levels RGB, CMY Intuitive based in familiar color description terms HSV, HSB, HLS Perceptually uniform device independent, perceptually uniform CIELUV, CIELAB, Munsell
7 Color Models Device-derived convenient for describing display device levels RGB, CMY Intuitive based in familiar color description terms HSV, HSB, HLS Perceptually uniform device independent, perceptually uniform CIELUV, CIELAB, Munsell
8 Hill et al. 97, pg. 136 Uses of Color Show classification Mimic reality Show value Draw attention Show grouping
9 Uses of Color Show classification Mimic reality Show value Draw attention Show grouping
10 Uses of Color Show classification Mimic reality Show value Draw attention Show grouping
11 Uses of Color Show classification Mimic reality Show value Draw attention Show grouping
12 Uses of Color Show classification Mimic reality Show value Draw attention Show grouping
13 Ware and Beatty 85, p. 22 Perceptual Distortions Color-deficiency Interactions between color components saturation - brightness (Helmholtz-Kohlraush effect) brightness - hue (Bezold-Brucke Phenomenon) Simultaneous contrast brightness hue Small field achrominance Effects of color on perceived size
14 Bezold-Brucke Phenomenon Hurvich 81, pg. 73. Perceptual Distortions Color-deficiency Interactions between color components saturation - brightness (Helmholtz-Kohlraush effect) brightness - hue (Bezold-Brucke Phenomenon) Simultaneous contrast brightness hue Small field achrominance Effects of color on perceived size
15 Simultaneous Contrast Simultaneous Contrast
16 Perceptual Distortions Color-deficiency Interactions between color components saturation - brightness (Helmholtz-Kohlraush effect) brightness - hue (Bezold-Brucke Phenomenon) Simultaneous contrast brightness hue Small field achrominance Effects of color on perceived size Small Field Achrominance Wandell 95, cp. 3.
17 Perceptual Distortions Color-deficiency Interactions between color components saturation - brightness (Helmholtz-Kohlraush effect) brightness - hue (Bezold-Brucke Phenomenon) Simultaneous contrast brightness hue Small field achrominance Effects of color on perceived size Color-size Illusion Cleveland and McGill 83.
18 Some Color Scales Univariate color model component optimal scales double-ended Multivariate color model components Census Bureau TVCM complementary display parameters
19
20 Some Color Scales Univariate color model component optimal scales double-ended Multivariate color model components Census Bureau TVCM complementary display parameters
21 Some Color Scales Univariate color model component optimal scales double-ended Multivariate color model components Census Bureau TVCM complementary display parameters Olson 97, fig
22 Some Color Scales Univariate color model component optimal scales double-ended Multivariate color model components Census Bureau TVCM complementary display parameters
23 Some Color Scales Univariate color model component optimal scales double-ended Multivariate color model components Census Bureau TVCM complementary display parameters Tufte 83, pg. 153.
24 Some Color Scales Univariate color model component optimal scales double-ended Multivariate color model components Census Bureau TVCM complementary display parameters
25 Evaluating Color Scales Trumbo s Principles Order: ordered values should be represented by ordered colors Separation: significantly different levels should be represented by distinguishable colors Rows and columns: to preserve univariate information, display parameters should not obscure one another Diagonal: to show positive association, displayed colors should group into three perceptual classes: diagonal, above, below
26
27 Evaluating Color Scales Trumbo s Principles Order: ordered values should be represented by ordered colors Separation: significantly different levels should be represented by distinguishable colors Rows and columns: to preserve univariate information, display parameters should not obscure one another Diagonal: to show positive association, displayed colors should group into three perceptual classes: diagonal, above, below
28 Evaluating Color Scales Trumbo s Principles Order: ordered values should be represented by ordered colors Separation: significantly different levels should be represented by distinguishable colors Rows and columns: to preserve univariate information, display parameters should not obscure one another Diagonal: to show positive association, displayed colors should group into three perceptual classes: diagonal, above, below
29 Tufte 83, pg. 153.
30 Evaluating Color Scales Trumbo s Principles Order: ordered values should be represented by ordered colors Separation: significantly different levels should be represented by distinguishable colors Rows and columns: to preserve univariate information, display parameters should not obscure one another Diagonal: to show positive association, displayed colors should group into three perceptual classes: diagonal, above, below
31 Evaluating Color Scales (cont.) Ware s experiments metric (quantitative) judgements surface (qualititative) judgements redundant color scales
32 Tufte 97, pg. 77. Tufte 97, pg. 76.
33 Ware s Color Scales Ware 88.
34
35 Considerations Consider goals Consider data Consider audience Consider color connotations
36 Does this work? Final Consideration
37 Principles of Color Representation Avoid distortions Exploit the familiar Emphasize the interesting Say it again (redundant mappings) Select appropriate level of detail
38 Color Models: Device-derived Blue Cyan Magenta White Black Green Red Yellow Red-Green-Blue
39 Color Models: Intuitive L = 1 White Green Yellow Cyan Blue S = 1 S = 0 V = 1 White Magenta Red Cyan Green S = 0 Yellow S = 1 Red Blue Magenta V = 0 Black Hue Hue = 0 L = 0 Black Hue Hue = 0 Hue-Saturation-Value Hue-Lightness-Saturation Color Models: Perceptually Uniform v' Yellowish green Yellow green Green Bluish green Greenish blue Blue White Greenish Yellow Orange Yellow Yellow Orange Reddish orange Yellowish pink Purple Pink Purplish pink Red Reddish purple Purplish red Purplish blue u' CIELUV
40 Opponent Channel Recoding Long (R) - R - G Medium (G) Short (B) + Yellow - Achromatic Y-B
Color Perception. This lecture is (mostly) thanks to Penny Rheingans at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County
 Color Perception This lecture is (mostly) thanks to Penny Rheingans at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County Characteristics of Color Perception Fundamental, independent visual process after-images
Color Perception This lecture is (mostly) thanks to Penny Rheingans at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County Characteristics of Color Perception Fundamental, independent visual process after-images
Comp/Phys/Apsc 715. Example Videos. Administrative 1/23/2014. Lecture 5: Trichromacy, Color Spaces, Properties of Color
 Comp/Phys/Apsc 715 Lecture 5: Trichromacy, Color Spaces, Properties of Color 1 Example Videos Segmentation and visualization of neurons Astro Visualization (the Millennium Run) Dragonfly Flight Analysis
Comp/Phys/Apsc 715 Lecture 5: Trichromacy, Color Spaces, Properties of Color 1 Example Videos Segmentation and visualization of neurons Astro Visualization (the Millennium Run) Dragonfly Flight Analysis
Image and video processing (EBU723U) Colour Images. Dr. Yi-Zhe Song
 Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
Color. Maneesh Agrawala Jessica Hullman. CS : Visualization Fall Assignment 3: Visualization Software
 Color Maneesh Agrawala Jessica Hullman CS 294-10: Visualization Fall 2014 Assignment 3: Visualization Software Create a small interactive visualization application you choose data domain and visualization
Color Maneesh Agrawala Jessica Hullman CS 294-10: Visualization Fall 2014 Assignment 3: Visualization Software Create a small interactive visualization application you choose data domain and visualization
Color, Vision, & Perception. Outline
 Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Additive. Subtractive
 Physics 106 Additive Subtractive Subtractive Mixing Rules: Mixing Cyan + Magenta, one gets Blue Mixing Cyan + Yellow, one gets Green Mixing Magenta + Yellow, one gets Red Mixing any two of the Blue, Red,
Physics 106 Additive Subtractive Subtractive Mixing Rules: Mixing Cyan + Magenta, one gets Blue Mixing Cyan + Yellow, one gets Green Mixing Magenta + Yellow, one gets Red Mixing any two of the Blue, Red,
Reading. Foley, Computer graphics, Chapter 13. Optional. Color. Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA 1995.
 Reading Foley, Computer graphics, Chapter 13. Color Optional Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA 1995. Gerald S. Wasserman. Color Vision: An Historical ntroduction.
Reading Foley, Computer graphics, Chapter 13. Color Optional Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA 1995. Gerald S. Wasserman. Color Vision: An Historical ntroduction.
COLOR and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
Colour + Perception. CMPT 467/767 Visualization Torsten Möller. Pfister/Möller
 Colour + Perception CMPT 467/767 Visualization Torsten Möller Recommended Reading http://www.stonesc.com/ 2 Where / What 3 Based on slide from Mazur Contours & Texture C. Ware, Visual Thinking for Design
Colour + Perception CMPT 467/767 Visualization Torsten Möller Recommended Reading http://www.stonesc.com/ 2 Where / What 3 Based on slide from Mazur Contours & Texture C. Ware, Visual Thinking for Design
EECS490: Digital Image Processing. Lecture #12
 Lecture #12 Image Correlation (example) Color basics (Chapter 6) The Chromaticity Diagram Color Images RGB Color Cube Color spaces Pseudocolor Multispectral Imaging White Light A prism splits white light
Lecture #12 Image Correlation (example) Color basics (Chapter 6) The Chromaticity Diagram Color Images RGB Color Cube Color spaces Pseudocolor Multispectral Imaging White Light A prism splits white light
CIE tri-stimulus experiment. Color Value Functions. CIE 1931 Standard. Color. Diagram. Color light intensity for visual color match
 CIE tri-stimulus experiment diffuse reflecting screen diffuse reflecting screen 770 769 768 test light 382 381 380 observer test light 445 535 630 445 535 630 observer light intensity for visual color
CIE tri-stimulus experiment diffuse reflecting screen diffuse reflecting screen 770 769 768 test light 382 381 380 observer test light 445 535 630 445 535 630 observer light intensity for visual color
Geography 360 Principles of Cartography. April 24, 2006
 Geography 360 Principles of Cartography April 24, 2006 Outlines 1. Principles of color Color as physical phenomenon Color as physiological phenomenon 2. How is color specified? (color model) Hardware-oriented
Geography 360 Principles of Cartography April 24, 2006 Outlines 1. Principles of color Color as physical phenomenon Color as physiological phenomenon 2. How is color specified? (color model) Hardware-oriented
Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal. Victor Ostromoukhov - Université de Montréal
 IFT3355 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
IFT3355 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
excite the cones in the same way.
 Humans have 3 kinds of cones Color vision Edward H. Adelson 9.35 Trichromacy To specify a light s spectrum requires an infinite set of numbers. Each cone gives a single number (univariance) when stimulated
Humans have 3 kinds of cones Color vision Edward H. Adelson 9.35 Trichromacy To specify a light s spectrum requires an infinite set of numbers. Each cone gives a single number (univariance) when stimulated
Color & Graphics. Color & Vision. The complete display system is: We'll talk about: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain
 Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
Color images C1 C2 C3
 Color imaging Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..) Digital
Color imaging Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..) Digital
Question From Last Class
 Question From Last Class What is it about matter that determines its color? e.g., what's the difference between a surface that reflects only long wavelengths (reds) and a surfaces the reflects only medium
Question From Last Class What is it about matter that determines its color? e.g., what's the difference between a surface that reflects only long wavelengths (reds) and a surfaces the reflects only medium
COLOR. and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
Chapter 3 Part 2 Color image processing
 Chapter 3 Part 2 Color image processing Motivation Color fundamentals Color models Pseudocolor image processing Full-color image processing: Component-wise Vector-based Recent and current work Spring 2002
Chapter 3 Part 2 Color image processing Motivation Color fundamentals Color models Pseudocolor image processing Full-color image processing: Component-wise Vector-based Recent and current work Spring 2002
Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology
 Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology Physics of Color Light Light or visible light is the portion of electromagnetic radiation that
Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology Physics of Color Light Light or visible light is the portion of electromagnetic radiation that
CS 565 Computer Vision. Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour
 CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
What is Color. Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception.
 Color What is Color Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception. By fundamental we mean that it is so unique that its meaning cannot be fully appreciated without direct experience. How
Color What is Color Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception. By fundamental we mean that it is so unique that its meaning cannot be fully appreciated without direct experience. How
Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4
 Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 20, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 From last time T. M. D'Zmura 2 Rod Transduction
Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 20, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 From last time T. M. D'Zmura 2 Rod Transduction
Vision IV. Overview of Topics. Overview of Topics. Colour Vision
 Vision IV Colour Vision Chapter 11 in Chaudhuri 1 1 Overview of Topics Overview of Topics "Avoid vertebrates because they are too complicated, avoid colour vision because it is much too complicated, and
Vision IV Colour Vision Chapter 11 in Chaudhuri 1 1 Overview of Topics Overview of Topics "Avoid vertebrates because they are too complicated, avoid colour vision because it is much too complicated, and
Visual Perception. Overview. The Eye. Information Processing by Human Observer
 Visual Perception Spring 06 Instructor: K. J. Ray Liu ECE Department, Univ. of Maryland, College Park Overview Last Class Introduction to DIP/DVP applications and examples Image as a function Concepts
Visual Perception Spring 06 Instructor: K. J. Ray Liu ECE Department, Univ. of Maryland, College Park Overview Last Class Introduction to DIP/DVP applications and examples Image as a function Concepts
Using Color in Scientific Visualization
 Using Color in Scientific Visualization Mike Bailey The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place is a complex matter. Indeed, so difficult
Using Color in Scientific Visualization Mike Bailey The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place is a complex matter. Indeed, so difficult
Colors in Images & Video
 LECTURE 8 Colors in Images & Video CS 5513 Multimedia Systems Spring 2009 Imran Ihsan Principal Design Consultant OPUSVII www.opuseven.com Faculty of Engineering & Applied Sciences 1. Light and Spectra
LECTURE 8 Colors in Images & Video CS 5513 Multimedia Systems Spring 2009 Imran Ihsan Principal Design Consultant OPUSVII www.opuseven.com Faculty of Engineering & Applied Sciences 1. Light and Spectra
Color. Color. Colorfull world IFT3350. Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal. Victor Ostromoukhov - Université de Montréal
 IFT3350 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
IFT3350 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
Vision IV. Overview of Topics. Evolution of Vision. Overview of Topics. Colour Vision
 Overview of Topics Vision IV Colour Vision Chapter 11 in Chaudhuri "Avoid vertebrates because they are too complicated, avoid colour vision because it is much too complicated, and avoid the combination
Overview of Topics Vision IV Colour Vision Chapter 11 in Chaudhuri "Avoid vertebrates because they are too complicated, avoid colour vision because it is much too complicated, and avoid the combination
any kind, you have two receptive fields, one the small center region, the other the surround region.
 In a centersurround cell of any kind, you have two receptive fields, one the small center region, the other the surround region. + _ In a chromatic center-surround field, each in innervated by one class
In a centersurround cell of any kind, you have two receptive fields, one the small center region, the other the surround region. + _ In a chromatic center-surround field, each in innervated by one class
Digital Image Processing. Lecture # 8 Color Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 8 Color Processing 1 COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING Color Importance Color is an excellent descriptor Suitable for object Identification and Extraction
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 8 Color Processing 1 COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING Color Importance Color is an excellent descriptor Suitable for object Identification and Extraction
Color Image Processing
 Color Image Processing Jesus J. Caban Outline Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Color Perception & Analysis 1 Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Due next Monday, Oct 4th Project proposal Submit
Color Image Processing Jesus J. Caban Outline Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Color Perception & Analysis 1 Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Due next Monday, Oct 4th Project proposal Submit
Bettina Selig. Centre for Image Analysis. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University
 2011-10-26 Bettina Selig Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Illumination - Reflection - Detection The Human Eye Digital
2011-10-26 Bettina Selig Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Illumination - Reflection - Detection The Human Eye Digital
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones.
 Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Adapted from the Slides by Dr. Mike Bailey at Oregon State University
 Colors in Visualization Adapted from the Slides by Dr. Mike Bailey at Oregon State University The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place
Colors in Visualization Adapted from the Slides by Dr. Mike Bailey at Oregon State University The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place
The Principles of Chromatics
 The Principles of Chromatics 03/20/07 2 Light Electromagnetic radiation, that produces a sight perception when being hit directly in the eye The wavelength of visible light is 400-700 nm 1 03/20/07 3 Visible
The Principles of Chromatics 03/20/07 2 Light Electromagnetic radiation, that produces a sight perception when being hit directly in the eye The wavelength of visible light is 400-700 nm 1 03/20/07 3 Visible
Color Image Processing. Gonzales & Woods: Chapter 6
 Color Image Processing Gonzales & Woods: Chapter 6 Objectives What are the most important concepts and terms related to color perception? What are the main color models used to represent and quantify color?
Color Image Processing Gonzales & Woods: Chapter 6 Objectives What are the most important concepts and terms related to color perception? What are the main color models used to represent and quantify color?
Introduction to Color Science (Cont)
 Lecture 24: Introduction to Color Science (Cont) Computer Graphics and Imaging UC Berkeley Empirical Color Matching Experiment Additive Color Matching Experiment Show test light spectrum on left Mix primaries
Lecture 24: Introduction to Color Science (Cont) Computer Graphics and Imaging UC Berkeley Empirical Color Matching Experiment Additive Color Matching Experiment Show test light spectrum on left Mix primaries
LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO
 MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR LIGHT AND SPECTRA Visible light is an electromagnetic wave in the 400nm 700 nm range. The eye is basically similar
MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR LIGHT AND SPECTRA Visible light is an electromagnetic wave in the 400nm 700 nm range. The eye is basically similar
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
CS 544 Human Abilities
 CS 544 Human Abilities Color Perception and Guidelines for Design Preattentive Processing Acknowledgement: Some of the material in these lectures is based on material prepared for similar courses by Saul
CS 544 Human Abilities Color Perception and Guidelines for Design Preattentive Processing Acknowledgement: Some of the material in these lectures is based on material prepared for similar courses by Saul
Mahdi Amiri. March Sharif University of Technology
 Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2014 Sharif University of Technology The wavelength λ of a sinusoidal waveform traveling at constant speed ν is given by Physics of
Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2014 Sharif University of Technology The wavelength λ of a sinusoidal waveform traveling at constant speed ν is given by Physics of
Color. Bilkent University. CS554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu
 1 Color CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University 2 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power (watts) λ is wavelength
1 Color CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University 2 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power (watts) λ is wavelength
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Light and Colour. Sir Isaac Newton The Founder of Colour Science
 Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Color and Color Model. Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin
 Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
Colors in images. Color spaces, perception, mixing, printing, manipulating...
 Colors in images Color spaces, perception, mixing, printing, manipulating... Tomáš Svoboda Czech Technical University, Faculty of Electrical Engineering Center for Machine Perception, Prague, Czech Republic
Colors in images Color spaces, perception, mixing, printing, manipulating... Tomáš Svoboda Czech Technical University, Faculty of Electrical Engineering Center for Machine Perception, Prague, Czech Republic
Color image processing
 Color image processing Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..)
Color image processing Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..)
12 Color Models and Color Applications. Chapter 12. Color Models and Color Applications. Department of Computer Science and Engineering 12-1
 Chapter 12 Color Models and Color Applications 12-1 12.1 Overview Color plays a significant role in achieving realistic computer graphic renderings. This chapter describes the quantitative aspects of color,
Chapter 12 Color Models and Color Applications 12-1 12.1 Overview Color plays a significant role in achieving realistic computer graphic renderings. This chapter describes the quantitative aspects of color,
Color Image Processing
 Color Image Processing Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Color Used heavily in human vision. Visible spectrum for humans is 400 nm (blue) to 700
Color Image Processing Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Color Used heavily in human vision. Visible spectrum for humans is 400 nm (blue) to 700
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I
 OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
Perception to visualization I
 Perception to visualization I C. Andrews 2014-02-25 Visualization Pipeline Raw Data data tables visual structures visualization data transformations visual mappings view transformations user interaction
Perception to visualization I C. Andrews 2014-02-25 Visualization Pipeline Raw Data data tables visual structures visualization data transformations visual mappings view transformations user interaction
Color in Scientific Visualization
 Color in Scientific Visualization Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu colorinvis.pptx The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place is a complex
Color in Scientific Visualization Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu colorinvis.pptx The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place is a complex
CSE512 :: 6 Feb Color. Jeffrey Heer University of Washington
 CSE512 :: 6 Feb 2014 Color Jeffrey Heer University of Washington 1 Color in Visualization Identify, Group, Layer, Highlight Colin Ware 2 Purpose of Color To label To measure To represent and imitate To
CSE512 :: 6 Feb 2014 Color Jeffrey Heer University of Washington 1 Color in Visualization Identify, Group, Layer, Highlight Colin Ware 2 Purpose of Color To label To measure To represent and imitate To
Image Perception & 2D Images
 Image Perception & 2D Images Vision is a matter of perception. Perception is a matter of vision. ES Overview Introduction to ES 2D Graphics in Entertainment Systems Sound, Speech & Music 3D Graphics in
Image Perception & 2D Images Vision is a matter of perception. Perception is a matter of vision. ES Overview Introduction to ES 2D Graphics in Entertainment Systems Sound, Speech & Music 3D Graphics in
Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing
 I22: Digital Image processing Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing Prof. YingLi Tian Sept. 13, 217 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University of New York
I22: Digital Image processing Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing Prof. YingLi Tian Sept. 13, 217 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University of New York
Christoph Wagner Colour Theory
 Colour Theory Hue, Saturation and Lightness (HSL) This model is one of the most intuitive ones in describing colour and I find it most useful for our purposes. There are other models, but we'll focus on
Colour Theory Hue, Saturation and Lightness (HSL) This model is one of the most intuitive ones in describing colour and I find it most useful for our purposes. There are other models, but we'll focus on
Color Theory: Defining Brown
 Color Theory: Defining Brown Defining Colors Colors can be defined in many different ways. Computer users are often familiar with colors defined as percentages or amounts of red, green, and blue (RGB).
Color Theory: Defining Brown Defining Colors Colors can be defined in many different ways. Computer users are often familiar with colors defined as percentages or amounts of red, green, and blue (RGB).
Interactive Computer Graphics
 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 4: Colour Graphics Lecture 4: Slide 1 Ways of looking at colour 1. Physics 2. Human visual receptors 3. Subjective assessment Graphics Lecture 4: Slide 2 The physics
Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 4: Colour Graphics Lecture 4: Slide 1 Ways of looking at colour 1. Physics 2. Human visual receptors 3. Subjective assessment Graphics Lecture 4: Slide 2 The physics
Contrast, Luminance and Colour
 Contrast, Luminance and Colour Week 3 Lecture 1 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Some of these slides have been borrowed and adapted from Maureen Stone and Colin Ware What is gray? Colour space is 3 dimensions 1 achromatic
Contrast, Luminance and Colour Week 3 Lecture 1 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Some of these slides have been borrowed and adapted from Maureen Stone and Colin Ware What is gray? Colour space is 3 dimensions 1 achromatic
Marks + Channels. Large Data Visualization Torsten Möller. Munzner/Möller
 Marks + Channels Large Data Visualization Torsten Möller Overview Marks + channels Channel effectiveness Accuracy Discriminability Separability Popout Channel characteristics Spatial position Colour Size
Marks + Channels Large Data Visualization Torsten Möller Overview Marks + channels Channel effectiveness Accuracy Discriminability Separability Popout Channel characteristics Spatial position Colour Size
II-1. Color in Scientific Visualization. Let s start with the most important component in a visualization system You!
 Color in Scientific Visualization The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place is a complex matter. Indeed, so difficult and subtle that avoiding
Color in Scientific Visualization The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place is a complex matter. Indeed, so difficult and subtle that avoiding
Color and Color Models
 Einführung in Visual Computing 186.822 Color and Color Models Werner Purgathofer Color problem specification light and perception colorimetry device color systems color ordering systems color symbolism
Einführung in Visual Computing 186.822 Color and Color Models Werner Purgathofer Color problem specification light and perception colorimetry device color systems color ordering systems color symbolism
Color images C1 C2 C3
 Color imaging Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..) Digital
Color imaging Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..) Digital
COLOR. Elements of color. Visible spectrum. The Human Visual System. The Fovea. There are three types of cones, S, M and L. r( λ)
 COLOR Elements of color Angel, 4th ed. 1, 2.5, 7.13 excerpt from Joakim Lindblad Color = The eye s and the brain s impression of electromagnetic radiation in the visual spectra How is color perceived?
COLOR Elements of color Angel, 4th ed. 1, 2.5, 7.13 excerpt from Joakim Lindblad Color = The eye s and the brain s impression of electromagnetic radiation in the visual spectra How is color perceived?
COLOR. Elements of color. Visible spectrum. The Fovea. Lecture 3 October 30, Ingela Nyström 1. There are three types of cones, S, M and L
 COLOR Elements of color Angel 1.4, 2.4, 7.12 J. Lindblad 2001-11-01 Color = The eye s and the brain s impression of electromagnetic radiation in the visual spectra. How is color perceived? Visible spectrum
COLOR Elements of color Angel 1.4, 2.4, 7.12 J. Lindblad 2001-11-01 Color = The eye s and the brain s impression of electromagnetic radiation in the visual spectra. How is color perceived? Visible spectrum
Color in Scientific Visualization
 Color in Scientific Visualization Mike Bailey, PhD San Diego Supercomputer Center and University of California at San Diego mjb@sdsc sdsc.edu 858-534-5142 The often scant benefits derived from coloring
Color in Scientific Visualization Mike Bailey, PhD San Diego Supercomputer Center and University of California at San Diego mjb@sdsc sdsc.edu 858-534-5142 The often scant benefits derived from coloring
Problems. How do cameras measure light and color? How do humans perceive light and color?
 Light and Color Problems How do cameras measure light and color? Radiometry How do humans perceive light and color? Photometry How do computers represent light and color? How do monitors display light
Light and Color Problems How do cameras measure light and color? Radiometry How do humans perceive light and color? Photometry How do computers represent light and color? How do monitors display light
To discuss. Color Science Color Models in image. Computer Graphics 2
 Color To discuss Color Science Color Models in image Computer Graphics 2 Color Science Light & Spectra Light is an electromagnetic wave It s color is characterized by its wavelength Laser consists of single
Color To discuss Color Science Color Models in image Computer Graphics 2 Color Science Light & Spectra Light is an electromagnetic wave It s color is characterized by its wavelength Laser consists of single
CSE1710. Big Picture. Reminder
 CSE1710 Click to edit Master Week text 10, styles Lecture 19 Second level Third level Fourth level Fifth level Fall 2013 Thursday, Nov 14, 2013 1 Big Picture For the next three class meetings, we will
CSE1710 Click to edit Master Week text 10, styles Lecture 19 Second level Third level Fourth level Fifth level Fall 2013 Thursday, Nov 14, 2013 1 Big Picture For the next three class meetings, we will
White light can be split into constituent wavelengths (or colors) using a prism or a grating.
 Colors and the perception of colors Visible light is only a small member of the family of electromagnetic (EM) waves. The wavelengths of EM waves that we can observe using many different devices span from
Colors and the perception of colors Visible light is only a small member of the family of electromagnetic (EM) waves. The wavelengths of EM waves that we can observe using many different devices span from
Werner Purgathofer
 Einführung in Visual Computing 186.822 Color and Color Models Werner Purgathofer Color problem specification light and perceptionp colorimetry device color systems color ordering systems color symbolism
Einführung in Visual Computing 186.822 Color and Color Models Werner Purgathofer Color problem specification light and perceptionp colorimetry device color systems color ordering systems color symbolism
Chapter 9: Color. What is Color? Wavelength is a property of an electromagnetic wave in the frequency range we call light
 Chapter 9: Color What is color? Color mixtures Intensity-distribution curves Additive Mixing Partitive Mixing Specifying colors RGB Color Chromaticity What is Color? Wavelength is a property of an electromagnetic
Chapter 9: Color What is color? Color mixtures Intensity-distribution curves Additive Mixing Partitive Mixing Specifying colors RGB Color Chromaticity What is Color? Wavelength is a property of an electromagnetic
Introduction to Color Theory
 Systems & Biomedical Engineering Department SBE 306B: Computer Systems III (Computer Graphics) Dr. Ayman Eldeib Spring 2018 Introduction to With colors you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a
Systems & Biomedical Engineering Department SBE 306B: Computer Systems III (Computer Graphics) Dr. Ayman Eldeib Spring 2018 Introduction to With colors you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a
What Is Color? How Brains Make Color Sensations Contents
 What Is Color? How Brains Make Color Sensations Contents Abstract... 4 Keywords... 4 1. Anatomy... 5 1.1. Eye... 5 1.1.1. Eyeball layers... 5 1.1.2. Eyeball front... 5 1.1.3. Fluids... 5 1.1.4. Eye muscles...
What Is Color? How Brains Make Color Sensations Contents Abstract... 4 Keywords... 4 1. Anatomy... 5 1.1. Eye... 5 1.1.1. Eyeball layers... 5 1.1.2. Eyeball front... 5 1.1.3. Fluids... 5 1.1.4. Eye muscles...
Raster Graphics. Overview קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' What is an image? What is an image? Image Acquisition. Image display 5/19/2008.
 Overview Images What is an image? How are images displayed? Color models How do we perceive colors? How can we describe and represent colors? קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' Raster Graphics 1 חלק מהשקפים
Overview Images What is an image? How are images displayed? Color models How do we perceive colors? How can we describe and represent colors? קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' Raster Graphics 1 חלק מהשקפים
קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' Raster Graphics 1 חלק מהשקפים מעובדים משקפים של פרדו דוראנד, טומס פנקהאוסר ודניאל כהן-אור
 קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' Raster Graphics 1 חלק מהשקפים מעובדים משקפים של פרדו דוראנד, טומס פנקהאוסר ודניאל כהן-אור Images What is an image? How are images displayed? Color models Overview How
קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' Raster Graphics 1 חלק מהשקפים מעובדים משקפים של פרדו דוראנד, טומס פנקהאוסר ודניאל כהן-אור Images What is an image? How are images displayed? Color models Overview How
University of British Columbia CPSC 414 Computer Graphics
 University of British Columbia CPSC 414 Computer Graphics Color 2 Week 10, Fri 7 Nov 2003 Tamara Munzner 1 Readings Chapter 1.4: color plus supplemental reading: A Survey of Color for Computer Graphics,
University of British Columbia CPSC 414 Computer Graphics Color 2 Week 10, Fri 7 Nov 2003 Tamara Munzner 1 Readings Chapter 1.4: color plus supplemental reading: A Survey of Color for Computer Graphics,
Color and Perception. CS535 Fall Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Color and Perception CS535 Fall 2014 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Elements of Color Perception 2 Elements of Color Physics: Illumination Electromagnetic spectra; approx.
Color and Perception CS535 Fall 2014 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Elements of Color Perception 2 Elements of Color Physics: Illumination Electromagnetic spectra; approx.
Vision and Color. Reading. Optics, cont d. Lenses. d d f. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015
 Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Introduction & Colour
 Introduction & Colour Eric C. McCreath School of Computer Science The Australian National University ACT 0200 Australia ericm@cs.anu.edu.au Overview 2 Computer Graphics Uses (Chapter 1) Basic Hardware
Introduction & Colour Eric C. McCreath School of Computer Science The Australian National University ACT 0200 Australia ericm@cs.anu.edu.au Overview 2 Computer Graphics Uses (Chapter 1) Basic Hardware
VC 16/17 TP4 Colour and Noise
 VC 16/17 TP4 Colour and Noise Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Hélder Filipe Pinto de Oliveira Outline Colour spaces Colour processing
VC 16/17 TP4 Colour and Noise Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Hélder Filipe Pinto de Oliveira Outline Colour spaces Colour processing
IFT3355: Infographie Couleur. Victor Ostromoukhov, Pierre Poulin Dép. I.R.O. Université de Montréal
 IFT3355: Infographie Couleur Victor Ostromoukhov, Pierre Poulin Dép. I.R.O. Université de Montréal Color Appearance Visual Range Electromagnetic waves (in nanometres) γ rays X rays ultraviolet violet
IFT3355: Infographie Couleur Victor Ostromoukhov, Pierre Poulin Dép. I.R.O. Université de Montréal Color Appearance Visual Range Electromagnetic waves (in nanometres) γ rays X rays ultraviolet violet
Figure 1: Energy Distributions for light
 Lecture 4: Colour The physical description of colour Colour vision is a very complicated biological and psychological phenomenon. It can be described in many different ways, including by physics, by subjective
Lecture 4: Colour The physical description of colour Colour vision is a very complicated biological and psychological phenomenon. It can be described in many different ways, including by physics, by subjective
Colour spaces. Project for the Digital signal processing course
 Colour spaces Project for the Digital signal processing course Marko Tkalčič, author prof. Jurij F. Tasič, mentor Faculty of electrical engineering University of Ljubljana Tržaška 25, 1001 Ljubljana, Slovenia
Colour spaces Project for the Digital signal processing course Marko Tkalčič, author prof. Jurij F. Tasič, mentor Faculty of electrical engineering University of Ljubljana Tržaška 25, 1001 Ljubljana, Slovenia
INSTITUTIONEN FÖR SYSTEMTEKNIK LULEÅ TEKNISKA UNIVERSITET
 INSTITUTIONEN FÖR SYSTEMTEKNIK LULEÅ TEKNISKA UNIVERSITET Some color images on this slide Last Lecture 2D filtering frequency domain The magnitude of the 2D DFT gives the amplitudes of the sinusoids and
INSTITUTIONEN FÖR SYSTEMTEKNIK LULEÅ TEKNISKA UNIVERSITET Some color images on this slide Last Lecture 2D filtering frequency domain The magnitude of the 2D DFT gives the amplitudes of the sinusoids and
Lecture 4. Opponent Colors. Hue Cancellation Experiment HUV Color Space
 Lecture 4 Opponent Colors Hue Cancellation Experiment HUV Color Space 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100
Lecture 4 Opponent Colors Hue Cancellation Experiment HUV Color Space 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100
Computers and Imaging
 Computers and Imaging Telecommunications 1 P. Mathys Two Different Methods Vector or object-oriented graphics. Images are generated by mathematical descriptions of line (vector) segments. Bitmap or raster
Computers and Imaging Telecommunications 1 P. Mathys Two Different Methods Vector or object-oriented graphics. Images are generated by mathematical descriptions of line (vector) segments. Bitmap or raster
Multimedia Systems and Technologies
 Multimedia Systems and Technologies Faculty of Engineering Master s s degree in Computer Engineering Marco Porta Computer Vision & Multimedia Lab Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione
Multimedia Systems and Technologies Faculty of Engineering Master s s degree in Computer Engineering Marco Porta Computer Vision & Multimedia Lab Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione
The human visual system
 The human visual system Vision and hearing are the two most important means by which humans perceive the outside world. 1 Low-level vision Light is the electromagnetic radiation that stimulates our visual
The human visual system Vision and hearing are the two most important means by which humans perceive the outside world. 1 Low-level vision Light is the electromagnetic radiation that stimulates our visual
Revised Edition: 2016 ISBN All rights reserved.
 Revised Edition: 2016 ISBN 978-1-283-50430-0 All rights reserved. Published by: White Word Publications 48 West 48 Street, Suite 1116, New York, NY 10036, United States Email: info@wtbooks.com Table of
Revised Edition: 2016 ISBN 978-1-283-50430-0 All rights reserved. Published by: White Word Publications 48 West 48 Street, Suite 1116, New York, NY 10036, United States Email: info@wtbooks.com Table of
THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR
 THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR Colour can be described as a light wavelength coming from a light source striking the surface of an object which in turns reflects the incoming light from were it is received by the
THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR Colour can be described as a light wavelength coming from a light source striking the surface of an object which in turns reflects the incoming light from were it is received by the
check it out online at
 check it out online at www.belyea.com/svc/all_about_color.pdf Who am I? I got the blues Experience and Emotions through color PASSION JOY Depression HARMONY CREATIVITY PEACE MOURNING It s a bird, it s
check it out online at www.belyea.com/svc/all_about_color.pdf Who am I? I got the blues Experience and Emotions through color PASSION JOY Depression HARMONY CREATIVITY PEACE MOURNING It s a bird, it s
Colors in Visualization. By Mike Bailey Oregon State University
 Colors in Visualization By Mike Bailey Oregon State University The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place is a complex matter. Indeed, so
Colors in Visualization By Mike Bailey Oregon State University The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place is a complex matter. Indeed, so
A Brief Plug. Color in Information Display. Color includes Gray. Information Display. Color In Information Display, SIAT 1/24/2006
 A Brief Plug Color in Information Display Maureen Stone StoneSoup Consulting Woodinville, WA Information Display Color includes Gray Graphical presentation of information Charts, graphs, diagrams, maps,
A Brief Plug Color in Information Display Maureen Stone StoneSoup Consulting Woodinville, WA Information Display Color includes Gray Graphical presentation of information Charts, graphs, diagrams, maps,
CIE R1-57 Border between Blackish and Luminous Colours
 CIE R1-57 Border between Blackish and Luminous Colours Author: Thorstein Seim Norway Advisors: Klaus Richter Arne Valberg Germany Norway 1 CONTENTS CIE task:... 4 Introduction... 4 Description of concepts...
CIE R1-57 Border between Blackish and Luminous Colours Author: Thorstein Seim Norway Advisors: Klaus Richter Arne Valberg Germany Norway 1 CONTENTS CIE task:... 4 Introduction... 4 Description of concepts...
Introduction to Computer Vision and image processing
 Introduction to Computer Vision and image processing 1.1 Overview: Computer Imaging 1.2 Computer Vision 1.3 Image Processing 1.4 Computer Imaging System 1.6 Human Visual Perception 1.7 Image Representation
Introduction to Computer Vision and image processing 1.1 Overview: Computer Imaging 1.2 Computer Vision 1.3 Image Processing 1.4 Computer Imaging System 1.6 Human Visual Perception 1.7 Image Representation
Colors in Scientific Visualization. Mike Bailey Oregon State University
 Colors in Scientific Visualization Mike Bailey Oregon State University The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place is a complex matter. Indeed,
Colors in Scientific Visualization Mike Bailey Oregon State University The often scant benefits derived from coloring data indicate that even putting a good color in a good place is a complex matter. Indeed,
IMAGE PROCESSING >COLOR SPACES UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE
 IMAGE PROCESSING >COLOR SPACES UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE OUTLINE Human visual system Color images Color quantization Colorimetric color spaces HUMAN VISUAL SYSTEM HUMAN VISUAL SYSTEM HUMAN VISUAL
IMAGE PROCESSING >COLOR SPACES UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE OUTLINE Human visual system Color images Color quantization Colorimetric color spaces HUMAN VISUAL SYSTEM HUMAN VISUAL SYSTEM HUMAN VISUAL
Spectral colors. What is colour? 11/23/17. Colour Vision 1 - receptoral. Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision
 Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
