Feasibility and Design for the Simplex Electronic Telescope. Brian Dodson
|
|
|
- Silvia Bruce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Feasibility and Design for the Simplex Electronic Telescope Brian Dodson Charge: A feasibility check and design hints are wanted for the proposed Simplex Electronic Telescope (SET). The telescope is based on a conventional reflector telescope, with a concave mirror at the end of a tube focusing a distant image. The mirror might be of parabolic or spherical cross-section. Instead of a secondary mirror, the SET has an electronic image sensor (EIS, typically a CCD or CMOS device) as used in digital cameras or video cameras. Input from the EIS is fed directly to form the image on a screen (such as an LCD). For most applications, the image will be displayed upright. The screen may be behind the telescope tube or may be separate, according to the application. The telescope could be usable for astronomical viewing and/or closer viewing, as for a security system. For a convenient hand instrument, the screen may be of similar size to the telescope tube end, and the device could be held by a handle as on a megaphone. Focusing can be achieved by sliding the EIS up or down in the ray path. Magnification can be by 'digital zoom', just presenting an enlarged version of part of the image. To combat excessive pixilation with digital zoom, it may be possible to use EIS devices with higher resolution of detector sites towards the centre.
2 Discussion: The SET described is a simple version of a modern observatory telescope, in which no one observes directly, but rather manipulates data generated by an electronic image sensor at the focal position of the telescope. These professional sensors are of sophisticated design and enormous (now measured in Gigapixels), but in essence are identical to the CCD image sensor in your cell phone or webcam. It is commonplace for amateur astronomers to use what is essentially a 1 MPixel webcam mounted in their telescope instead of an eyepiece. Such a camera cannot be set for time exposures, and hence is only useful for observing the moon and planets, as well as earthly scenes. This sort of camera, if mass produced, would cost less than $10 to manufacture. The approach used to image astronomical objects with this class of camera is generally to take a large number of exposures (these cameras usually work at frames per second), and then add the frames together using software. It is possible to obtain reasonably good planetary images on a steady night by simply adding the images together continuously in a computer, using an algorithm that eventually forgets the earlier images, but the best performance comes from carefully aligning details on successive frames (or on selected high-quality frames) to build up an image. This process can t be done in real time with amateur capabilities.
3 Just to give an idea of scale, most webcam CCD chips have an active area about 4 mm across. If you fit one with a standard 3 f/15 refractor, pointing it accurately is a tricky business. Aimed at the Moon, the image would show about 1/3 of the moon s width. On a 32 screen, Jupiter would appear to be about 2.5 inches across. The theoretical limit of resolution would be just about equal to the distance between pixels. What is the next step what do you do better? The answer is time exposures and cooled CCDs, if you want a SET that can view any deep-sky objects. Unfortunately, using time exposures removes some of the immediacy of pointing the scope and seeing, say, the Ring Nebula M27. On the other hand, the view can be quite exciting, and the anticipation builds as an image slowly emerges out of apparently random noise on a monitor. The best compromise here for an astronomical SET is an uncooled CCD camera capable of time exposures. Such sensors appear in those digital cameras which are capable of taking time exposures. As they are uncooled, exposures in excess of about a minute are not very useful (high thermal noise), but they will allow just about anything you can see by eye to show up on a screen within seconds. A problem is that the SET has to remain still during the exposure. This increases the mechanical complexity, weight, and portability. The cost of such a camera for this application could be a lot less than a good digital camera maybe less than $50 to manufacture. Another approach to visual observation involves direct observation through the telescope using an eyepiece integrated with an image intensifier. These devices are not common, as they
4 are expensive ($2K and up), and have definite limitations. They will not display on a screen unless you install a camera instead of the eyepiece. Used with one s eye, these devices extend the sensitivity of the telescope by about 2 magnitudes while at the same time slightly reducing the contrast of the observed image (which is usually from a greenish phosphor). Although from an astronomical point of view this is probably offers the user experience closest to that which you want, the cost and somewhat unnatural appearance of the image suggest that image intensifiers are not best for the SET. Handheld SET For a handheld device, I think you are essentially describing a modified digital camera. It doesn t much matter if the optical system is reflecting or refracting, save that you might want more optical zoom capability than would be easy to build into a reflector using a ccd camera as a secondary mirror. As to the structure and optical design of the SET, I don t see that anything particularly tricky has to be done. The easiest implementation would be very much like a compact digital camera. Make a camera body just the size of the desired display (probably an OLED display say 4-8 inches diagonal, once those are reasonably priced), mount a time exposure capable CCD sensor inside, mount a wide-range zoom lens (perhaps even with macro capability, so you also get a low-power microscope), and have fun. Let s look at a specific example. Take a 1/2.5 standard CCD sensor, as are commonly used in compact digital cameras. This has an imaging area of 5.76mmx4.29mm about 1/6 the size of
5 old fashioned 35mm film and may have 5-8 Mpixels, each of which is about 2-3 microns in size. Then put on a wide range zoom lens. The Kodak Z has a 30x zoom lens 5-150mm focal length, and the camera sells for $200 street price. Although the camera took a beating in reviews, its lens system did quite well. At the widest zoom, the diagonal field of view would be about 80 o wide, while at 150mm focal length the diagonal field of view would be about 2.5 o wide. The effective diameter of the lens at the longest setting is about 30mm, the size of a small pair of binoculars. The moon would be 1/5 the size of the screen diagonal say around an inch on the viewer screen. Jupiter would be about a millimeter probably too small to see a disk. One could give up wide angle capability for more magnification if astronomy was the main goal of the SET system. (At some point, it would become too high in optical power to hold by hand, although this problem would be reduced by conventional antishake technology.) In macro mode the effective magnification on the screen would be somewhere around 30-50X, I believe. Mounted SET For a larger device, mounted temporarily or permanently on a secure and vibration-free support, we are now talking about a special device that mounts on a special telescope. It doesn t really matter if the telescope is reflecting or refracting, save that for a given size the reflecting optics will usually cost much less.
6 The device will be a ccd imager with a zoom lens that acts as a variable power eyepiece for the ccd chip (the technique is called eyepiece projection). If the SET is intended for amateur or professional astronomy, the ccd will be able to take time exposures, and might be cooled in a high-end package to reduce thermal noise. Devices similar to this part of the SET currently run $500-1K for introductory amateur systems (a few Mpixels). The easiest approach from an optical point of view is to mount the imager device as if it were a Cassegrain secondary mirror on the optical axis of a parabolic mirror, save that it would be positioned at the focus of the mirror. A small motorized rack or screw device could adjust the focus over a wide range, so that the SET could be used on close-up terrestrial targets. The obscuration of the mirror by the ccd device would be minimal, as the complete imager could easily be built within a 1 diameter device, even with cooling. Imperfect SET optics It is in the area of optically flawed optics where interesting possibilities enter. You suggested a spherical primary, or a Herschlean (tilted Newtonian) telescope. These give relatively poor images, and short of using special and difficult to construct correction lenses with the ccd imager, would not work well at all. However, there is an interesting possibility. Imagine you use a short focus spherical primary, so that you are dealing with strong spherical aberration, or even a short focus paraboloid, giving a lot of off-axis coma. In the absence of corrective optics, it is still possible to obtain a good image, although not quite in real time as
7 yet. If you send light from a point source through an optical system, it is distorted to some extent by the optics. This is not like atmospheric distortion, which can be corrected using active optics, but is static in nature the same point of light in the same direction always forms the same distorted image. The distorted light image is called the convolution of the original pristine point of light with the optical transfer function of the optical system. In nearly all cases the result is a blurry or smeared image, in which information about the incoming light has been lost. The trick is, the loss of information, while real, isn t as great as you think on observing the image. If the image source is a single point of light, you can observe that the image is just that you expect from a point of light, and can mathematically perform a transformation that replaces the faulty image with that of a nearly perfect point of light. This transformation is called deconvolution a procedure in which the known flaws of an optical system are removed from an image it produced, to the extent allowed by information entropy. Deconvolution works amazingly well, depending on the magnitude and character of the errors in the optical system. Generally, errors that take points to more or less centered distributions of light will be better corrected than those which are smeared. This suggests that spherical aberration may be more correctable than coma. Also, one of the easiest targets for deconvolution is an image that you know is largely made up of points of light, such as star fields.
8 However, the process of deconvolution is computationally intense. I am not currently aware of a non-professional image processing system that can deconvolute a megapixel size image in real-time. Despite this, it may be another approach toward the construction of cheaper large telescopes.
The New. Astronomy. 2 Practical Focusing
 The New 2 Practical Focusing Astronomy CCD cameras represent some pretty fancy technology, but in some ways they are just like ordinary cameras. As with a traditional film camera, the difference between
The New 2 Practical Focusing Astronomy CCD cameras represent some pretty fancy technology, but in some ways they are just like ordinary cameras. As with a traditional film camera, the difference between
Lecture PowerPoint. Chapter 25 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoint Chapter 25 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture PowerPoint Chapter 25 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Getting started with Digital Astrophotography - Part I Rodger King - May 2016
 Getting started with Digital Astrophotography - Part I Rodger King - May 2016 Flame Nebula orsehead Nebula. Question Astronomy Which type of Telescope is better - A Lens or Mirror? 500-900 More compact
Getting started with Digital Astrophotography - Part I Rodger King - May 2016 Flame Nebula orsehead Nebula. Question Astronomy Which type of Telescope is better - A Lens or Mirror? 500-900 More compact
Applications of Optics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Types of lenses. Shown below are various types of lenses, both converging and diverging.
 Types of lenses Shown below are various types of lenses, both converging and diverging. Any lens that is thicker at its center than at its edges is a converging lens with positive f; and any lens that
Types of lenses Shown below are various types of lenses, both converging and diverging. Any lens that is thicker at its center than at its edges is a converging lens with positive f; and any lens that
PHYSICS. Chapter 35 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 35 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 35 Optical Instruments IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about some common optical instruments and
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 35 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 35 Optical Instruments IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about some common optical instruments and
Puntino. Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor for optimizing telescopes. The software people for optics
 Puntino Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor for optimizing telescopes 1 1. Optimize telescope performance with a powerful set of tools A finely tuned telescope is the key to obtaining deep, high-quality astronomical
Puntino Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor for optimizing telescopes 1 1. Optimize telescope performance with a powerful set of tools A finely tuned telescope is the key to obtaining deep, high-quality astronomical
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments
 Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 25 Cameras, Film, and Digital The Human Eye; Corrective Lenses Magnifying Glass Telescopes Compound Microscope Aberrations of Lenses and Mirrors Limits of
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 25 Cameras, Film, and Digital The Human Eye; Corrective Lenses Magnifying Glass Telescopes Compound Microscope Aberrations of Lenses and Mirrors Limits of
The Imaging Chain in Optical Astronomy
 The Imaging Chain in Optical Astronomy Review and Overview Imaging Chain includes these elements: 1. energy source 2. object 3. collector 4. detector (or sensor) 5. processor 6. display 7. analysis 8.
The Imaging Chain in Optical Astronomy Review and Overview Imaging Chain includes these elements: 1. energy source 2. object 3. collector 4. detector (or sensor) 5. processor 6. display 7. analysis 8.
The Imaging Chain in Optical Astronomy
 The Imaging Chain in Optical Astronomy 1 Review and Overview Imaging Chain includes these elements: 1. energy source 2. object 3. collector 4. detector (or sensor) 5. processor 6. display 7. analysis 8.
The Imaging Chain in Optical Astronomy 1 Review and Overview Imaging Chain includes these elements: 1. energy source 2. object 3. collector 4. detector (or sensor) 5. processor 6. display 7. analysis 8.
Chapter 23. Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Mirrors and Lenses The development of mirrors and lenses aided the progress of science. It led to the microscopes and telescopes. Allowed the study of objects from microbes
Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Mirrors and Lenses The development of mirrors and lenses aided the progress of science. It led to the microscopes and telescopes. Allowed the study of objects from microbes
Optics and Telescopes
 Optics and Telescopes Properties of Light Law of Reflection - reflection Angle of Incidence = Angle of Law of Refraction - Light beam is bent towards the normal when passing into a medium of higher Index
Optics and Telescopes Properties of Light Law of Reflection - reflection Angle of Incidence = Angle of Law of Refraction - Light beam is bent towards the normal when passing into a medium of higher Index
Secrets of Telescope Resolution
 amateur telescope making Secrets of Telescope Resolution Computer modeling and mathematical analysis shed light on instrumental limits to angular resolution. By Daniel W. Rickey even on a good night, the
amateur telescope making Secrets of Telescope Resolution Computer modeling and mathematical analysis shed light on instrumental limits to angular resolution. By Daniel W. Rickey even on a good night, the
There is a range of distances over which objects will be in focus; this is called the depth of field of the lens. Objects closer or farther are
 Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Some Topics in Chapter 25 Cameras The Human Eye; Corrective Lenses Magnifying Glass Telescopes Compound Microscope Aberrations of Lenses and Mirrors Limits of Resolution
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Some Topics in Chapter 25 Cameras The Human Eye; Corrective Lenses Magnifying Glass Telescopes Compound Microscope Aberrations of Lenses and Mirrors Limits of Resolution
Useful Optics Information
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences 12.409 Observing Stars and Planets, Spring 2002 Handout 7 week of February 25, 2002 Copyright 1999 Created
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences 12.409 Observing Stars and Planets, Spring 2002 Handout 7 week of February 25, 2002 Copyright 1999 Created
Astrophotography for the Amateur
 Astrophotography for the Amateur Second edition MICHAEL A. COVINGTON CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Notes to the reader Symbols used in formulae xi xiii xiv 3.7 Zodiacal light, Gegenschein, and 3.8
Astrophotography for the Amateur Second edition MICHAEL A. COVINGTON CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Notes to the reader Symbols used in formulae xi xiii xiv 3.7 Zodiacal light, Gegenschein, and 3.8
Chapter 3 Optical Systems
 Chapter 3 Optical Systems The Human Eye [Reading Assignment, Hecht 5.7.1-5.7.3; see also Smith Chapter 5] retina aqueous vitreous fovea-macula cornea lens blind spot optic nerve iris cornea f b aqueous
Chapter 3 Optical Systems The Human Eye [Reading Assignment, Hecht 5.7.1-5.7.3; see also Smith Chapter 5] retina aqueous vitreous fovea-macula cornea lens blind spot optic nerve iris cornea f b aqueous
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB
 ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
Geometrical Optics Optical systems
 Phys 322 Lecture 16 Chapter 5 Geometrical Optics Optical systems Magnifying glass Purpose: enlarge a nearby object by increasing its image size on retina Requirements: Image should not be inverted Image
Phys 322 Lecture 16 Chapter 5 Geometrical Optics Optical systems Magnifying glass Purpose: enlarge a nearby object by increasing its image size on retina Requirements: Image should not be inverted Image
Reflectors vs. Refractors
 1 Telescope Types - Telescopes collect and concentrate light (which can then be magnified, dispersed as a spectrum, etc). - In the end it is the collecting area that counts. - There are two primary telescope
1 Telescope Types - Telescopes collect and concentrate light (which can then be magnified, dispersed as a spectrum, etc). - In the end it is the collecting area that counts. - There are two primary telescope
Lecture Outline Chapter 27. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 27 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 27 The Human Eye and the Camera Lenses in Combination and Corrective Optics The Magnifying
Lecture Outline Chapter 27 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 27 The Human Eye and the Camera Lenses in Combination and Corrective Optics The Magnifying
UNCOMPLICATED ASTROPHOTOGRAPHY. Bill Weaver
 UNCOMPLICATED ASTROPHOTOGRAPHY Bill Weaver WHAT CAN YOU REALLY SEE & CAPTURE? Star Party Marvel OVERVIEW OF PHOTOGRAPHIC DEVICES Discuss and display fundamental equipment, techniques & factors for simple
UNCOMPLICATED ASTROPHOTOGRAPHY Bill Weaver WHAT CAN YOU REALLY SEE & CAPTURE? Star Party Marvel OVERVIEW OF PHOTOGRAPHIC DEVICES Discuss and display fundamental equipment, techniques & factors for simple
Some Notes on Video Camera Astronomy and use of the Phil Dyer Colour Camera
 Some Notes on Video Camera Astronomy and use of the Phil Dyer Colour Camera Introduction I always wanted to look through a telescope and see those wonderful images of planets, spiral galaxies, nebulae
Some Notes on Video Camera Astronomy and use of the Phil Dyer Colour Camera Introduction I always wanted to look through a telescope and see those wonderful images of planets, spiral galaxies, nebulae
General Physics II. Optical Instruments
 General Physics II Optical Instruments 1 The Thin-Lens Equation 2 The Thin-Lens Equation Using geometry, one can show that 1 1 1 s+ =. s' f The magnification of the lens is defined by For a thin lens,
General Physics II Optical Instruments 1 The Thin-Lens Equation 2 The Thin-Lens Equation Using geometry, one can show that 1 1 1 s+ =. s' f The magnification of the lens is defined by For a thin lens,
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A plane mirror is placed on the level bottom of a swimming pool that holds water (n =
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A plane mirror is placed on the level bottom of a swimming pool that holds water (n =
The techniques covered so far -- visual focusing, and
 Section 4: Aids to Focusing The techniques covered so far -- visual focusing, and focusing using numeric data from the software -- can work and work well. But a variety of variables, including everything
Section 4: Aids to Focusing The techniques covered so far -- visual focusing, and focusing using numeric data from the software -- can work and work well. But a variety of variables, including everything
Make a Refractor Telescope
 Make a Refractor Telescope In this activity students will build, and observe with, simple refractory telescope providing an interactive introduction to light, lenses and refraction. LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Make a Refractor Telescope In this activity students will build, and observe with, simple refractory telescope providing an interactive introduction to light, lenses and refraction. LEARNING OBJECTIVES
OPTICS LENSES AND TELESCOPES
 ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 97 Optics - Lenses & Telescopes OPTICS LENSES AND TELESCOPES SYNOPSIS: In this lab you will explore the fundamental properties of a lens and investigate refracting and reflecting
ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 97 Optics - Lenses & Telescopes OPTICS LENSES AND TELESCOPES SYNOPSIS: In this lab you will explore the fundamental properties of a lens and investigate refracting and reflecting
COURSE NAME: PHOTOGRAPHY AND AUDIO VISUAL PRODUCTION (VOCATIONAL) FOR UNDER GRADUATE (FIRST YEAR)
 COURSE NAME: PHOTOGRAPHY AND AUDIO VISUAL PRODUCTION (VOCATIONAL) FOR UNDER GRADUATE (FIRST YEAR) PAPER TITLE: BASIC PHOTOGRAPHIC UNIT - 3 : SIMPLE LENS TOPIC: LENS PROPERTIES AND DEFECTS OBJECTIVES By
COURSE NAME: PHOTOGRAPHY AND AUDIO VISUAL PRODUCTION (VOCATIONAL) FOR UNDER GRADUATE (FIRST YEAR) PAPER TITLE: BASIC PHOTOGRAPHIC UNIT - 3 : SIMPLE LENS TOPIC: LENS PROPERTIES AND DEFECTS OBJECTIVES By
Option G 2: Lenses. The diagram below shows the image of a square grid as produced by a lens that does not cause spherical aberration.
 Name: Date: Option G 2: Lenses 1. This question is about spherical aberration. The diagram below shows the image of a square grid as produced by a lens that does not cause spherical aberration. In the
Name: Date: Option G 2: Lenses 1. This question is about spherical aberration. The diagram below shows the image of a square grid as produced by a lens that does not cause spherical aberration. In the
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Chapter 23. Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to
Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to
Activity 6.1 Image Formation from Spherical Mirrors
 PHY385H1F Introductory Optics Practicals Day 6 Telescopes and Microscopes October 31, 2011 Group Number (number on Intro Optics Kit):. Facilitator Name:. Record-Keeper Name: Time-keeper:. Computer/Wiki-master:..
PHY385H1F Introductory Optics Practicals Day 6 Telescopes and Microscopes October 31, 2011 Group Number (number on Intro Optics Kit):. Facilitator Name:. Record-Keeper Name: Time-keeper:. Computer/Wiki-master:..
INTRODUCTION THIN LENSES. Introduction. given by the paraxial refraction equation derived last lecture: Thin lenses (19.1) = 1. Double-lens systems
 Chapter 9 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Introduction Thin lenses Double-lens systems Aberrations Camera Human eye Compound microscope Summary INTRODUCTION Knowledge of geometrical optics, diffraction and interference,
Chapter 9 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Introduction Thin lenses Double-lens systems Aberrations Camera Human eye Compound microscope Summary INTRODUCTION Knowledge of geometrical optics, diffraction and interference,
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
IMAGE SENSOR SOLUTIONS. KAC-96-1/5" Lens Kit. KODAK KAC-96-1/5" Lens Kit. for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors. November 2004 Revision 2
 KODAK for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors November 2004 Revision 2 1.1 Introduction Choosing the right lens is a critical aspect of designing an imaging system. Typically the trade off between image
KODAK for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors November 2004 Revision 2 1.1 Introduction Choosing the right lens is a critical aspect of designing an imaging system. Typically the trade off between image
Problems with filters can have the strangest causes
 Problems with filters can have the strangest causes If you switch from simple astrophotography to more difficult fields of activity and start working with different filters, correctors and systems, you
Problems with filters can have the strangest causes If you switch from simple astrophotography to more difficult fields of activity and start working with different filters, correctors and systems, you
SIPS instructions for installation and use
 SIPS instructions for installation and use Introduction Thank you for purchasing the Starlight Integrated Paracorr System (referred to as SIPS hereafter), which incorporates the best focuser on the market
SIPS instructions for installation and use Introduction Thank you for purchasing the Starlight Integrated Paracorr System (referred to as SIPS hereafter), which incorporates the best focuser on the market
Introducing Celestron s EdgeHD Optical System
 Introducing Celestron s EdgeHD Optical System See the Universe in HD EdgeHD is an Aplanatic Schmidt telescope designed to produce aberration free images across a wide visual and photographic field of view.
Introducing Celestron s EdgeHD Optical System See the Universe in HD EdgeHD is an Aplanatic Schmidt telescope designed to produce aberration free images across a wide visual and photographic field of view.
GRADE 11-LESSON 2 PHENOMENA RELATED TO OPTICS
 REFLECTION OF LIGHT GRADE 11-LESSON 2 PHENOMENA RELATED TO OPTICS 1.i. What is reflection of light?.. ii. What are the laws of reflection? a...... b.... iii. Consider the diagram at the right. Which one
REFLECTION OF LIGHT GRADE 11-LESSON 2 PHENOMENA RELATED TO OPTICS 1.i. What is reflection of light?.. ii. What are the laws of reflection? a...... b.... iii. Consider the diagram at the right. Which one
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging
 Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Image Formation. Light from distant things. Geometrical optics. Pinhole camera. Chapter 36
 Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
Geometric Optics. Find the focal lengths of lenses and mirrors; Draw and understand ray diagrams; and Build a simple telescope
 Geometric Optics I. OBJECTIVES Galileo is known for his many wondrous astronomical discoveries. Many of these discoveries shook the foundations of Astronomy and forced scientists and philosophers alike
Geometric Optics I. OBJECTIVES Galileo is known for his many wondrous astronomical discoveries. Many of these discoveries shook the foundations of Astronomy and forced scientists and philosophers alike
Consumer digital CCD cameras
 CAMERAS Consumer digital CCD cameras Leica RC-30 Aerial Cameras Zeiss RMK Zeiss RMK in aircraft Vexcel UltraCam Digital (note multiple apertures Lenses for Leica RC-30. Many elements needed to minimize
CAMERAS Consumer digital CCD cameras Leica RC-30 Aerial Cameras Zeiss RMK Zeiss RMK in aircraft Vexcel UltraCam Digital (note multiple apertures Lenses for Leica RC-30. Many elements needed to minimize
Telescope Basics by Keith Beadman
 Telescope Basics 2009 by Keith Beadman Table of Contents Introduction...1 The Basics...2 What a telescope is...2 Aperture size...3 Focal length...4 Focal ratio...5 Magnification...6 Introduction In the
Telescope Basics 2009 by Keith Beadman Table of Contents Introduction...1 The Basics...2 What a telescope is...2 Aperture size...3 Focal length...4 Focal ratio...5 Magnification...6 Introduction In the
30 Lenses. Lenses change the paths of light.
 Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
Life Science Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
INSIDE LAB 6: The Properties of Lenses and Telescopes
 INSIDE LAB 6: The Properties of Lenses and Telescopes OBJECTIVE: To construct a simple refracting telescope and to measure some of its properties. DISCUSSION: In tonight s lab we will build a simple telescope
INSIDE LAB 6: The Properties of Lenses and Telescopes OBJECTIVE: To construct a simple refracting telescope and to measure some of its properties. DISCUSSION: In tonight s lab we will build a simple telescope
O5: Lenses and the refractor telescope
 O5. 1 O5: Lenses and the refractor telescope Introduction In this experiment, you will study converging lenses and the lens equation. You will make several measurements of the focal length of lenses and
O5. 1 O5: Lenses and the refractor telescope Introduction In this experiment, you will study converging lenses and the lens equation. You will make several measurements of the focal length of lenses and
Evaluating Commercial Scanners for Astronomical Images. The underlying technology of the scanners: Pixel sizes:
 Evaluating Commercial Scanners for Astronomical Images Robert J. Simcoe Associate Harvard College Observatory rjsimcoe@cfa.harvard.edu Introduction: Many organizations have expressed interest in using
Evaluating Commercial Scanners for Astronomical Images Robert J. Simcoe Associate Harvard College Observatory rjsimcoe@cfa.harvard.edu Introduction: Many organizations have expressed interest in using
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics (Part 2)
 Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics (Part 2) Brief review Optical instruments Camera Human eye Magnifying glass Telescope Microscope Optical Aberrations Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 31, Pg 1 The Lens Equation
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics (Part 2) Brief review Optical instruments Camera Human eye Magnifying glass Telescope Microscope Optical Aberrations Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 31, Pg 1 The Lens Equation
Optical basics for machine vision systems. Lars Fermum Chief instructor STEMMER IMAGING GmbH
 Optical basics for machine vision systems Lars Fermum Chief instructor STEMMER IMAGING GmbH www.stemmer-imaging.de AN INTERNATIONAL CONCEPT STEMMER IMAGING customers in UK Germany France Switzerland Sweden
Optical basics for machine vision systems Lars Fermum Chief instructor STEMMER IMAGING GmbH www.stemmer-imaging.de AN INTERNATIONAL CONCEPT STEMMER IMAGING customers in UK Germany France Switzerland Sweden
Telescope Thermal Effects. LDAS talk MLewis 1
 Telescope Thermal Effects LDAS talk 30-6-10 MLewis 1 Telescope Thermal Effects The purpose of a telescope is to gather more light than the eye on its own can, and to resolve features finer than the eye
Telescope Thermal Effects LDAS talk 30-6-10 MLewis 1 Telescope Thermal Effects The purpose of a telescope is to gather more light than the eye on its own can, and to resolve features finer than the eye
CH. 23 Mirrors and Lenses HW# 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 21, 25, 31, 33, 35
 CH. 23 Mirrors and Lenses HW# 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 21, 25, 31, 33, 35 Mirrors Rays of light reflect off of mirrors, and where the reflected rays either intersect or appear to originate from, will be the location
CH. 23 Mirrors and Lenses HW# 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 21, 25, 31, 33, 35 Mirrors Rays of light reflect off of mirrors, and where the reflected rays either intersect or appear to originate from, will be the location
Chapter 29/30. Wave Fronts and Rays. Refraction of Sound. Dispersion in a Prism. Index of Refraction. Refraction and Lenses
 Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Chapter 25. Optical Instruments
 Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Chapter 23. Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments
 Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments HITT 1 You stand two feet away from a plane mirror. How far is it from you to your image? a. 2.0 ft b. 3.0 ft c. 4.0 ft d. 5.0 ft
Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments HITT 1 You stand two feet away from a plane mirror. How far is it from you to your image? a. 2.0 ft b. 3.0 ft c. 4.0 ft d. 5.0 ft
Optical Systems: Pinhole Camera Pinhole camera: simple hole in a box: Called Camera Obscura Aristotle discussed, Al-Hazen analyzed in Book of Optics
 Optical Systems: Pinhole Camera Pinhole camera: simple hole in a box: Called Camera Obscura Aristotle discussed, Al-Hazen analyzed in Book of Optics 1011CE Restricts rays: acts as a single lens: inverts
Optical Systems: Pinhole Camera Pinhole camera: simple hole in a box: Called Camera Obscura Aristotle discussed, Al-Hazen analyzed in Book of Optics 1011CE Restricts rays: acts as a single lens: inverts
Physics 1C. Lecture 25B
 Physics 1C Lecture 25B "More than 50 years ago, Austrian researcher Ivo Kohler gave people goggles thats severely distorted their vision: The lenses turned the world upside down. After several weeks, subjects
Physics 1C Lecture 25B "More than 50 years ago, Austrian researcher Ivo Kohler gave people goggles thats severely distorted their vision: The lenses turned the world upside down. After several weeks, subjects
Physics 1230 Homework 8 Due Friday June 24, 2016
 At this point, you know lots about mirrors and lenses and can predict how they interact with light from objects to form images for observers. In the next part of the course, we consider applications of
At this point, you know lots about mirrors and lenses and can predict how they interact with light from objects to form images for observers. In the next part of the course, we consider applications of
Chapter 2 - Geometric Optics
 David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image on the retina. The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image on the retina. The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image
1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter
 8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
10/25/2017. Light and Telescope. Reflector - Mirror. Refractor - Lens. PHYS 1411 Introduction to Astronomy. Topics for Today s class
 PHYS 1411 Introduction to Astronomy Light and Telescope Chapter 6 Reminders Homework on Chapter 4, 5 and 6 due November 1 st. No extensions. Lab 8 handout is on class web page. Due Week of November 27
PHYS 1411 Introduction to Astronomy Light and Telescope Chapter 6 Reminders Homework on Chapter 4, 5 and 6 due November 1 st. No extensions. Lab 8 handout is on class web page. Due Week of November 27
The Design and Construction of an Inexpensive CCD Camera for Astronomical Imaging
 The Design and Construction of an Inexpensive CCD Camera for Astronomical Imaging Mr. Ben Teasdel III South Carolina State University Abstract The design, construction and testing results of an inexpensive
The Design and Construction of an Inexpensive CCD Camera for Astronomical Imaging Mr. Ben Teasdel III South Carolina State University Abstract The design, construction and testing results of an inexpensive
UltraGraph Optics Design
 UltraGraph Optics Design 5/10/99 Jim Hagerman Introduction This paper presents the current design status of the UltraGraph optics. Compromises in performance were made to reach certain product goals. Cost,
UltraGraph Optics Design 5/10/99 Jim Hagerman Introduction This paper presents the current design status of the UltraGraph optics. Compromises in performance were made to reach certain product goals. Cost,
Two Fundamental Properties of a Telescope
 Two Fundamental Properties of a Telescope 1. Angular Resolution smallest angle which can be seen = 1.22 / D 2. Light-Collecting Area The telescope is a photon bucket A = (D/2)2 D A Parts of the Human Eye
Two Fundamental Properties of a Telescope 1. Angular Resolution smallest angle which can be seen = 1.22 / D 2. Light-Collecting Area The telescope is a photon bucket A = (D/2)2 D A Parts of the Human Eye
Prac%ce Quiz 7. These are Q s from old quizzes. I do not guarantee that the Q s on this year s quiz will be the same, or even similar.
 Prac%ce Quiz 7 These are Q s from old quizzes. I do not guarantee that the Q s on this year s quiz will be the same, or even similar. D B cameras zoom lens covers the focal length range from 38mm to 110
Prac%ce Quiz 7 These are Q s from old quizzes. I do not guarantee that the Q s on this year s quiz will be the same, or even similar. D B cameras zoom lens covers the focal length range from 38mm to 110
Section 3. Imaging With A Thin Lens
 3-1 Section 3 Imaging With A Thin Lens Object at Infinity An object at infinity produces a set of collimated set of rays entering the optical system. Consider the rays from a finite object located on the
3-1 Section 3 Imaging With A Thin Lens Object at Infinity An object at infinity produces a set of collimated set of rays entering the optical system. Consider the rays from a finite object located on the
Readings: Hecht, Chapter 24
 5. GEOMETRIC OPTICS Readings: Hecht, Chapter 24 Introduction In this lab you will measure the index of refraction of glass using Snell s Law, study the application of the laws of geometric optics to systems
5. GEOMETRIC OPTICS Readings: Hecht, Chapter 24 Introduction In this lab you will measure the index of refraction of glass using Snell s Law, study the application of the laws of geometric optics to systems
Unit 3: Energy On the Move
 14 14 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 14: Mirrors and Lenses 14.1: Mirrors 14.2: Lenses 14.3: Optical Instruments 14.1 Mirrors How do you use light to see? When light travels from
14 14 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 14: Mirrors and Lenses 14.1: Mirrors 14.2: Lenses 14.3: Optical Instruments 14.1 Mirrors How do you use light to see? When light travels from
Binocular and Scope Performance 57. Diffraction Effects
 Binocular and Scope Performance 57 Diffraction Effects The resolving power of a perfect optical system is determined by diffraction that results from the wave nature of light. An infinitely distant point
Binocular and Scope Performance 57 Diffraction Effects The resolving power of a perfect optical system is determined by diffraction that results from the wave nature of light. An infinitely distant point
Optics: An Introduction
 It is easy to overlook the contribution that optics make to a system; beyond basic lens parameters such as focal distance, the details can seem confusing. This Tech Tip presents a basic guide to optics
It is easy to overlook the contribution that optics make to a system; beyond basic lens parameters such as focal distance, the details can seem confusing. This Tech Tip presents a basic guide to optics
A. Focal Length. 3. Lens Maker Equation. 2. Diverging Systems. f = 2 R. A. Focal Length B. Lens Law, object & image C. Optical Instruments
 Physics 700 Geometric Optics Geometric Optics (rough drat) A. Focal Length B. Lens Law, object & image C. Optical Instruments W. Pezzaglia Updated: 0Aug A. Focal Length 3. Converging Systems 4. Converging
Physics 700 Geometric Optics Geometric Optics (rough drat) A. Focal Length B. Lens Law, object & image C. Optical Instruments W. Pezzaglia Updated: 0Aug A. Focal Length 3. Converging Systems 4. Converging
Notation for Mirrors and Lenses. Chapter 23. Types of Images for Mirrors and Lenses. More About Images
 Notation for Mirrors and Lenses Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Sections: 4, 6 Problems:, 8, 2, 25, 27, 32 The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image
Notation for Mirrors and Lenses Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Sections: 4, 6 Problems:, 8, 2, 25, 27, 32 The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image
Chapter 34: Geometric Optics
 Chapter 34: Geometric Optics It is all about images How we can make different kinds of images using optical devices Optical device example: mirror, a piece of glass, telescope, microscope, kaleidoscope,
Chapter 34: Geometric Optics It is all about images How we can make different kinds of images using optical devices Optical device example: mirror, a piece of glass, telescope, microscope, kaleidoscope,
Chapter 18 Optical Elements
 Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Sharpness, Resolution and Interpolation
 Sharpness, Resolution and Interpolation Introduction There are a lot of misconceptions about resolution, camera pixel count, interpolation and their effect on astronomical images. Some of the confusion
Sharpness, Resolution and Interpolation Introduction There are a lot of misconceptions about resolution, camera pixel count, interpolation and their effect on astronomical images. Some of the confusion
Physics 6C. Cameras and the Human Eye. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Physics 6C Cameras and the Human Eye CAMERAS A typical camera uses a converging lens to focus a real (inverted) image onto photographic film (or in a digital camera the image is on a CCD chip). Light goes
Physics 6C Cameras and the Human Eye CAMERAS A typical camera uses a converging lens to focus a real (inverted) image onto photographic film (or in a digital camera the image is on a CCD chip). Light goes
Chapter 23. Light Geometric Optics
 Chapter 23. Light Geometric Optics There are 3 basic ways to gather light and focus it to make an image. Pinhole - Simple geometry Mirror - Reflection Lens - Refraction Pinhole Camera Image Formation (the
Chapter 23. Light Geometric Optics There are 3 basic ways to gather light and focus it to make an image. Pinhole - Simple geometry Mirror - Reflection Lens - Refraction Pinhole Camera Image Formation (the
AN INTRODUCTION TO CHROMATIC ABERRATION IN REFRACTORS
 AN INTRODUCTION TO CHROMATIC ABERRATION IN REFRACTORS The popularity of high-quality refractors draws attention to color correction in such instruments. There are several point of confusion and misconceptions.
AN INTRODUCTION TO CHROMATIC ABERRATION IN REFRACTORS The popularity of high-quality refractors draws attention to color correction in such instruments. There are several point of confusion and misconceptions.
Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Lenses convex (converging) concave (diverging) Mirrors Ray Tracing for Mirrors We use three principal rays in finding the image produced by a curved mirror. The parallel ray
Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Lenses convex (converging) concave (diverging) Mirrors Ray Tracing for Mirrors We use three principal rays in finding the image produced by a curved mirror. The parallel ray
Potential benefits of freeform optics for the ELT instruments. J. Kosmalski
 Potential benefits of freeform optics for the ELT instruments J. Kosmalski Freeform Days, 12-13 th October 2017 Summary Introduction to E-ELT intruments Freeform design for MAORY LGS Free form design for
Potential benefits of freeform optics for the ELT instruments J. Kosmalski Freeform Days, 12-13 th October 2017 Summary Introduction to E-ELT intruments Freeform design for MAORY LGS Free form design for
Classical Optical Solutions
 Petzval Lens Enter Petzval, a Hungarian mathematician. To pursue a prize being offered for the development of a wide-field fast lens system he enlisted Hungarian army members seeing a distraction from
Petzval Lens Enter Petzval, a Hungarian mathematician. To pursue a prize being offered for the development of a wide-field fast lens system he enlisted Hungarian army members seeing a distraction from
TESTING VISUAL TELESCOPIC DEVICES
 TESTING VISUAL TELESCOPIC DEVICES About Wells Research Joined TRIOPTICS mid 2012. Currently 8 employees Product line compliments TRIOPTICS, with little overlap Entry level products, generally less expensive
TESTING VISUAL TELESCOPIC DEVICES About Wells Research Joined TRIOPTICS mid 2012. Currently 8 employees Product line compliments TRIOPTICS, with little overlap Entry level products, generally less expensive
Converging Lenses. Parallel rays are brought to a focus by a converging lens (one that is thicker in the center than it is at the edge).
 Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
In our discussion of the behavior of light in the two previous Chapters, we
 Of the many optical devices we discuss in this Chapter, the magnifying glass is the simplest. Here it is magnifying part of page 722 of this Chapter, which describes how the magnifying glass works according
Of the many optical devices we discuss in this Chapter, the magnifying glass is the simplest. Here it is magnifying part of page 722 of this Chapter, which describes how the magnifying glass works according
Physics 11. Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2
 Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2 (c) Refraction (i) Introduction: Snell s law Like water waves, when light is traveling from one medium to another, not only does its wavelength, and in turn the
Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2 (c) Refraction (i) Introduction: Snell s law Like water waves, when light is traveling from one medium to another, not only does its wavelength, and in turn the
Lab 10: Lenses & Telescopes
 Physics 2020, Fall 2010 Lab 8 page 1 of 6 Circle your lab day and time. Your name: Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri TA name: 8-10 10-12 12-2 2-4 4-6 INTRODUCTION Lab 10: Lenses & Telescopes In this experiment, you
Physics 2020, Fall 2010 Lab 8 page 1 of 6 Circle your lab day and time. Your name: Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri TA name: 8-10 10-12 12-2 2-4 4-6 INTRODUCTION Lab 10: Lenses & Telescopes In this experiment, you
Physics 1202: Lecture 19 Today s Agenda
 Physics 1202: Lecture 19 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems today Team 12: Kervell Baird, Matthew George, Derek Schultz Team 13: Paxton Stowik, Stacey Ann Burke Team 14: Gregory Desautels, Benjamin
Physics 1202: Lecture 19 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems today Team 12: Kervell Baird, Matthew George, Derek Schultz Team 13: Paxton Stowik, Stacey Ann Burke Team 14: Gregory Desautels, Benjamin
A Schiefspiegler toolkit
 A Schiefspiegler toolkit Arjan te Marvelde, initial version Feb 2013, this version Nov 2018 In a 1958 publication of Sky Publishing (Bulletin A: Gleanings for ATMs), Anton Kutter presented a set of design
A Schiefspiegler toolkit Arjan te Marvelde, initial version Feb 2013, this version Nov 2018 In a 1958 publication of Sky Publishing (Bulletin A: Gleanings for ATMs), Anton Kutter presented a set of design
Geometric optics & aberrations
 Geometric optics & aberrations Department of Astrophysical Sciences University AST 542 http://www.northerneye.co.uk/ Outline Introduction: Optics in astronomy Basics of geometric optics Paraxial approximation
Geometric optics & aberrations Department of Astrophysical Sciences University AST 542 http://www.northerneye.co.uk/ Outline Introduction: Optics in astronomy Basics of geometric optics Paraxial approximation
Phys 2310 Mon. Oct. 16, 2017 Today s Topics. Finish Chapter 34: Geometric Optics Homework this Week
 Phys 2310 Mon. Oct. 16, 2017 Today s Topics Finish Chapter 34: Geometric Optics Homework this Week 1 Homework this Week (HW #10) Homework this week due Mon., Oct. 23: Chapter 34: #47, 57, 59, 60, 61, 62,
Phys 2310 Mon. Oct. 16, 2017 Today s Topics Finish Chapter 34: Geometric Optics Homework this Week 1 Homework this Week (HW #10) Homework this week due Mon., Oct. 23: Chapter 34: #47, 57, 59, 60, 61, 62,
Astronomical Cameras
 Astronomical Cameras I. The Pinhole Camera Pinhole Camera (or Camera Obscura) Whenever light passes through a small hole or aperture it creates an image opposite the hole This is an effect wherever apertures
Astronomical Cameras I. The Pinhole Camera Pinhole Camera (or Camera Obscura) Whenever light passes through a small hole or aperture it creates an image opposite the hole This is an effect wherever apertures
Lecture 15 Chap. 6 Optical Instruments. Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass. Two lens Telescope & binoculars Microscope
 Lecture 15 Chap. 6 Optical Instruments Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens Telescope & binoculars Microscope The projector Projection lens Field lens October 12, 2010 all these
Lecture 15 Chap. 6 Optical Instruments Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens Telescope & binoculars Microscope The projector Projection lens Field lens October 12, 2010 all these
Chapter 34. Images. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 34 Images Copyright 34-1 Images and Plane Mirrors Learning Objectives 34.01 Distinguish virtual images from real images. 34.02 Explain the common roadway mirage. 34.03 Sketch a ray diagram for
Chapter 34 Images Copyright 34-1 Images and Plane Mirrors Learning Objectives 34.01 Distinguish virtual images from real images. 34.02 Explain the common roadway mirage. 34.03 Sketch a ray diagram for
PHYSICS FOR THE IB DIPLOMA CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Option C Imaging C Introduction to imaging Learning objectives In this section we discuss the formation of images by lenses and mirrors. We will learn how to construct images graphically as well as algebraically.
Option C Imaging C Introduction to imaging Learning objectives In this section we discuss the formation of images by lenses and mirrors. We will learn how to construct images graphically as well as algebraically.
Getting started with Digital Astrophotography - Part II Rodger King - Dec 2016
 Getting started with Digital Astrophotography - Part II Rodger King - Dec 2016 RECAP Getting started with Digital Astrophotography - Part I Rodger King - May 2016 Visual Astronomy Equipment Telescope Tripod
Getting started with Digital Astrophotography - Part II Rodger King - Dec 2016 RECAP Getting started with Digital Astrophotography - Part I Rodger King - May 2016 Visual Astronomy Equipment Telescope Tripod
12:40-2:40 3:00-4:00 PM
 Physics 294H l Professor: Joey Huston l email:huston@msu.edu l office: BPS3230 l Homework will be with Mastering Physics (and an average of 1 hand-written problem per week) Help-room hours: 12:40-2:40
Physics 294H l Professor: Joey Huston l email:huston@msu.edu l office: BPS3230 l Homework will be with Mastering Physics (and an average of 1 hand-written problem per week) Help-room hours: 12:40-2:40
Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II. + 1 s i. = 1 f
 Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II Last time, developed idea of ray optics approximation to wave theory Introduced paraxial approximation: rays with θ 1 Will continue to use Started disussing
Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II Last time, developed idea of ray optics approximation to wave theory Introduced paraxial approximation: rays with θ 1 Will continue to use Started disussing
The Wonderful World of Amateur Digital Microscopy. "How To Get Your Astrophotography Fix During Times of Poor Weather"
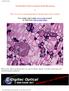 The Wonderful World of Amateur Digital Microscopy or "How To Get Your Astrophotography Fix During Times of Poor Weather" Ever wonder what is inside your average coconut? by Mark Estes Click to email author
The Wonderful World of Amateur Digital Microscopy or "How To Get Your Astrophotography Fix During Times of Poor Weather" Ever wonder what is inside your average coconut? by Mark Estes Click to email author
