Int n r t o r d o u d c u ti t on o n to t o Remote Sensing
|
|
|
- Gervais McDowell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Remote Sensing
2
3 Definition of Remote Sensing Remote sensing refers to the activities of recording/observing/perceiving(sensing)objects or events at far away (remote) places. In remote sensing, the sensors are not in direct contact with the objects or events being observed. The information needs a physical carrier to travel from the objects/events to the sensors through an intervening medium. The electromagnetic radiation is normally used as an information carrierinremotesensing.
4 Definition of Remote Sensing The output of a remote sensing system is usually an image representing the scene being observed. A further step of image analysis and interpretation is required in order to extract usefulinformationfromtheimage. The human visual system is an example of a remotesensingsysteminthisgeneralsense.
5 Definition of Remote Sensing In a more restricted sense, remote sensing usually refers to the technology of acquiring information about the earth s surface (land and ocean) and atmosphere using sensors onboard airborne (aircraft, balloons) or space borne (satellites,spaceshuttles)platforms.
6
7 Application of Remote Sensing
8 Satellite Image of Entire Globe: Global Landcover
9 Satellite Image of a Region(Australia)
10 10
11
12
13
14 Main Goal of Remote Sensing The main goal of Remote Sensing (RS)istheproductionof: Thematicmap Topographicmap
15 Definitions: Topographic Map A topographic map is a type of map characterized by large-scale detail and quantitative representation of relief or terrain, usually using contour lines.
16 Definitions: Thematic Map A thematic map is a type of map or chart especially designed to show a particular theme connected with a specific geographic area. These maps can portray physical, social, political, cultural, economic, sociological, agricultural, or any other aspects of a city, state, region, nation, or continent
17 Definitions: Contour Map In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height) above a given level, such as mean sea level. A contour map is a map illustrated with contour lines. The contour interval of a contour map is the difference in elevation between successive contour lines.
18 Example of Topographic Map
19 A Park: Map Representation
20 Satellite Image of the Park
21 Terrain Information of the Park
22 Example of Thematic Map
23 Thematic Map of Bangladesh: Landuse Map
24 Thematic Map of Bangladesh: Road Network
25 Thematic Map of Bangladesh: Flood Prone Area
26 Basics of Remote Sensing
27 Remote Sensing Basics: EM Spectrum Electromagnetic (EM) spectrum is monodimensional continuous, consisting of a set of radiations ordered according to wavelength, frequency or photonic energy; it includes waves of any wavelength, ranging from fractions of Angstrom (one tenth of a millimicron Å = m) to many kilometers.
28 Remote Sensing Basics: EM Spectrum
29 Remote Sensing Processes Information acquisition with techniques of remote sensing is developed in three phases Collection of data from the ground, aerial and/or satellite acquisition stations; Processing of the collected data; Data interpretation, followed by map production
30 Remote Sensing Processes
31 Instrument Types The instruments are divided into: passive sensors active sensors
32 Passive Sensors Records the intensity of the reflected electromagnetic energy coming from the Sun or emitted by the Earth. Sensors types: photo cameras, scanners, thermal cameras and video cameras Sensors operate in wavelength intervals from ultraviolet to thermal infrared
33 Passive Remote Sensing: Energy from Sun
34 Active Sensors The acquisition systems emit radiation themselves, collecting the back signal (radar); the radiation is backscattered to the sensor with intensity depending on the structural characteristics of the examined surface and on the wavelength (λ) of the incident radiation. Active sensors operate in microwave intervals
35 Active Remote Sensing: Energy Emitted fromsatelliteitself
36 Types of Remote Sensing optical: spectral range in the interval µm, (typical of passive remote sensing) panchromatic: one band including the visible range and in some cases part of the near infrared; multispectral: 2 9 spectral bands; super-spectral: spectral bands; hyperspectral: more than 16 spectral bands; radar: microwaves ranging from 1 mm to 1 m
37 Optical Passive Remote Sensing
38 Source of Energy for Optical Passive RS Main Source: The Sun and Earth The electromagnetic radiation emitted by the Sun ranges from cosmic rays to radio waves. Visible spectral range is about 50% The Earth, with an average surface temperature of about 15 o C, mostly radiates in the thermal infrared band, ranging from 8 to 14 µm EM radiation is affected by: Earth Sun distance; Absorption and scattering processes characterizing the atmosphere. about 1/200,000 of the energy emitted by Sun reaches the external limit of the atmosphere
39 Reflected Energy Recorded by Sensorsin Satellite
40 Physical Principles for Optical Passive RS Remote sensing is based on electromagnetic energy properties. The fundamental laws of radiation defining its quantitative aspects are Kirchhoff s radiation law: regulates the relationship among the coefficients of reflection, transmission, absorption and emission; Planck s radiation law Stefan Boltzmann s radiation law Wien s displacement law
41 Physical Principles for Optical Passive RS Kirchhoff s radiation law Every radiation incident on a real surface reacts following three phenomena: reflection, absorption and transmission. From the principle of the conservation of energy: Ei = Er + Ea + Et Where Ei : incident radiation Er : reflected radiation Ea : absorbed radiation Et : transmitted radiation
42 Terrestrial Albedo The albedo is defined as the ratio of the electromagnetic energy reflected or diffused by a surface to the total incident energy. This relationship is usually expressed as a percentage. The values of albedo vary with the Sun s angle.
43 Terrestrial Albedo The following table provides albedo value for different surfaces: Surface Albedo (%) Coniferous Broadleaf Cultivated field Light soil (sand) Dark soil (organic soil) 5 10 Desert Recent snow Water (incidence angle < 45 ) 5 10 Water (incidence angle > 45 ) 5 99
44 Radiometry Radiometry is concerned with defining and measuring radiometric units, variable in function of the wavelength. Therefore when radiometric units are used, the interval of wavelengths to which they refer must be specified.
45 Radiometric Terminology Radiant Energy: energy of the electromagnetic waves Radiant Power: radiant energy transferred from a point or from a surface to another in the time Radiant Exitance: radiation that is leaving an object or a surface Irradiance: radiation that is incident on an object or a surface
46 Radiometric Terminology Radiance: The radiance (L) is the most important radiometric unit, as it describes what in the real world is measured by the sensors used in remote sensing. The optical-passive sensors are sensitive only to the radiance. The radiance refers to the radiation according to a certain angle of observation, indicating the radiant outgoing flux per surface unit and per solid angle unit, measured on a perpendicular plane to the considered direction.
47 Spectral Response The visualization of satellite digital images is the result of the conversion of the signal recorded by the sensor into discrete value or Digital Number (DN) associated to each pixel. Since this signal is a function of the physical structural characteristics of the detected object, it is possible to establish a correspondence between the quantity and the quality of the reflected energy and the nature of the objects, in relation to the different wavelengths.
48 Spectral Response The signal recorded by the sensor can be represented in graphical terms as reflection capability in function of the wavelength known as the spectral response, which is a key instrument for satellite image quantitative analysis. Spectral responses of some natural terrestrial elements are shown in the following figure:
49
50 Spectral Response The energy reflected in the visible contains spectral information also concerning the color of the reflecting surface. The reflectance is determined by the: geometric structure of the surfaces bodies nature, vegetation pigmentation, etc. For example, chlorophyll strongly absorbs the radiant energy in wavelength intervals near 0.45 µm (blue) and 0.65 µm (red), while reflecting the green radiation, near 0.55 µm wavelength, visually perceived as the leaves color and reflects more in the region of near infrared from 0.8 to 1.3µm.
51 Spectral Response The spectral behaviors of objects belonging to the same class can generate different spectral responses. The factors that produce variations in the spectral reflectance curves can be: Static: such as slope and ground exposition; Dynamic: inducing differences in spectral behavior of the same elementary cell over time. Among them are vegetation phenological phase, phytosanitary conditions and fractional cover, soil surface humidity, atmospheric transparency, Sun position, etc.
52 Interaction of EM Radiation with Atmosphere Absorption Reflection Transmission
53 Atmospheric Effect in the Visible
54 Atmospheric Effect in the Visible: Absorption Absorption is very selective: each atmospheric component(aerosols and chemical species in general) absorbs the radiation in function of its wavelength. The chemical compounds responsible for the absorption of X-ray and ultraviolet(uv)radiationsareo,o 2 ando 3,whileH 2 O.and O 3 absorb in the visible range, and H 2 O and CO 2 in the infrared. As a consequence, atmosphere transmissivity (or transparency) of radiation is variable, limiting the possibility to collect signals in the EM intervals. Atmospheric windows define wavelength rangesinwhichtheatmosphereisparticularly transmissiveofenergy
55 Atmospheric Window Figure: Atmospheric windows of electromagnetic radiation transmission referred to the gas absorption. The white area represents the atmospheric windows, where the radiation passes through
56 Remote Sensing Platform and Sensors
57 Orbits and Swath Orbit:Thepathfollowedbyasatelliteisreferredtoas its orbit. Swath Width: It is defined as the width of the strip, parallel to satellite s track, from which radiation is received Geostationary Orbits: Satellites which view the same portion of the earth s surface at all times have geostationary orbit. Geostationary satellites orbit in the equatorial plane of the earth at a speed equivalent to the earth s rotation. Weather and Communication Satellites commonly have these types of orbits.
58 Many satellites are designed to follow a north south orbit which, in conjunction with the earth s rotation(west-east), allows them to cover most of the earth s surface over a period of time. These are Near-polar orbits. Near polar orbits also mean that the satellite travels northward on one side of the earth and the southward on thesecondhalfofitsorbit.thesearecalledascendingand Descending passes. Many of these satellites orbits are also Sun-synchronous such that they cover each area of the world at a constant localtimeofday. The surface directly below the satellite is called the Nadir Point.
59 Orbits and Swath
60 Satellite Sensor Characteristics The basic functions of most satellite sensors are to collect information about the reflected radiation along a pathway, also known as the field of view (FOV), as the satellite orbits the Earth. The smallest area of ground that is sampled is called the instantaneous field of view (IFOV). The IFOV is also described as the pixel size of the sensor. This sampling or measurement occurs in one or many spectral bands of the EM spectrum. The data collected by each satellite sensor can be described in terms of spatial, spectral and temporal resolution.
61 Spatial Resolution Spatial resolution refers to the size of the smallest object that can be resolved on the ground. In a digital image, the resolution is limited by thepixelsize,i.e.thesmallestresolvableobject cannotbesmallerthanthepixelsize. Spatial resolution can be degraded by factors whichintroduceblurringoftheimage,suchas improper focusing, atmospheric scattering andtargetmotion.
62 Spatial Resolution The pixel size is determined by the samplingdistance. "High Resolution" image refers to one with a small pixel size. Fine details can beseeninahighresolutionimage. "Low Resolution" image is one with a large pixel size, i.e. only coarse features canbeobservedintheimage.
63 Low Resolution MODIS Image Image Resolution: 1Km
64 Medium Resolution SPOT Image Image Resolution: 20m
65 High Resolution IKONOS Image Image Resolution: 4m
66 Super High Resolution QuickbirdImage Image Resolution: 0.6m
67 Super High Resolution Geoeye1 Image Image Resolution: 0.4m
68 Radiometric Resolution Referstothesmallestchangeinintensity levelthatcanbedetectedbythesensing system. It is the capability to differentiate the spectral reflectance between various targets.
69 Radiometric Resolution This depends on the number of quantizationlevelswithinthespectralband In other words, the number of bits of digital data in the spectral band or number of grey level value will decide sensorsensitivity Itiscommonlyexpressedasthenumberof binarydigitsrequiredtostorethemaximum levelvalue.thusthenumberofbitsrequired for 2, 4, 8, 16, 256 levels is 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 respectively
70 Panchromatic Image
71 Spectral Resolution The spectral resolution of a sensor system is the number and width of spectral bands in the sensing device. The simplest form of spectral resolution is a sensor with one band only, which senses visible light. An image from this sensor would be similar in appearance to a black and white photograph from an aircraft. A sensor with three spectral bands in the visible region of the EM spectrum would collect similar information to that of the human vision system.
72 Spectral Resolution Panchromatic image: Consistsofonlyoneband. It is usually displayed as a grey scale image or black-and-white (i.e. the displayed brightness of a particular pixel is proportional to the pixel digital number which is related to the intensity of solar radiation reflected by the targets in the pixel and detected by the detector)
73 Spectral Resolution Multispectral and hyperspectral images consist of several bands of data. For visual display, each band of the image may be displayedonebandatatimeasagreyscaleimage Or in combination of three bands at a time as a color composite image. Interpretation of a multispectral color composite image will require the knowledge of the spectral reflectance signature of the targets in the scene.
74 Temporal Resolution Temporal resolution is a measure of the repeat cycle or frequency with which a sensor revisits the same part of the Earth s surface. The frequency will vary from several times per day, for a typical weather satellite, to 8-20 times a year for a moderate ground resolution satellite, such as Landsat TM. The frequency characteristics will be determined by the design of the satellite sensor and its orbit pattern.
75 Different Types of Satellites Satellites Camera Mode Spatial Resolution GeoEye1 Simultaneous Panchromatic and Multispectral, Panchromatic Multispectral WorldView-2 Panchromatic 8 Multispectral 0.41m(P) m(P) 1.8m Repeat Cycle day Swath Width Km Single Point Scene Altitude Km Application x Earth Observation Satellite (Environmental Monitoring, Meteorology, Map making) Land use Planning Disaster Relief Defense & Intelligence WorldView-1 Panchromatic 0.55m(P) x geo-location capabilities Rapid targeting, Stereo Collection. QuickBird Panchromatic Multispectral 0.61m(P) 2.4m x Land use Change Agriculture, Forest Climate Oil & Gas Exploration IKONOS Panchromatic Multispectral 0.82m(P) 3.2m x Natural Resource Mapping Forestry Agriculture Landsat TM 7 spectral bands 30m Thematic Mapping MODIS Multispectral x10 Surface Temperature
76 Infrared Image
Introduction to Remote Sensing
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Spatial, spectral, temporal resolutions Image display alternatives Vegetation Indices Image classifications Image change detections Accuracy assessment Satellites & Air-Photos
Introduction to Remote Sensing Spatial, spectral, temporal resolutions Image display alternatives Vegetation Indices Image classifications Image change detections Accuracy assessment Satellites & Air-Photos
An Introduction to Geomatics. Prepared by: Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq خاص بطلبة مساق مقدمة في علم. Associate Professor of Surveying IUG
 An Introduction to Geomatics خاص بطلبة مساق مقدمة في علم الجيوماتكس Prepared by: Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq Associate Professor of Surveying IUG 1 Airborne Imagery Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq Associate Professor
An Introduction to Geomatics خاص بطلبة مساق مقدمة في علم الجيوماتكس Prepared by: Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq Associate Professor of Surveying IUG 1 Airborne Imagery Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq Associate Professor
NON-PHOTOGRAPHIC SYSTEMS: Multispectral Scanners Medium and coarse resolution sensor comparisons: Landsat, SPOT, AVHRR and MODIS
 NON-PHOTOGRAPHIC SYSTEMS: Multispectral Scanners Medium and coarse resolution sensor comparisons: Landsat, SPOT, AVHRR and MODIS CLASSIFICATION OF NONPHOTOGRAPHIC REMOTE SENSORS PASSIVE ACTIVE DIGITAL
NON-PHOTOGRAPHIC SYSTEMS: Multispectral Scanners Medium and coarse resolution sensor comparisons: Landsat, SPOT, AVHRR and MODIS CLASSIFICATION OF NONPHOTOGRAPHIC REMOTE SENSORS PASSIVE ACTIVE DIGITAL
Geo/SAT 2 INTRODUCTION TO REMOTE SENSING
 Geo/SAT 2 INTRODUCTION TO REMOTE SENSING Paul R. Baumann, Professor Emeritus State University of New York College at Oneonta Oneonta, New York 13820 USA COPYRIGHT 2008 Paul R. Baumann Introduction Remote
Geo/SAT 2 INTRODUCTION TO REMOTE SENSING Paul R. Baumann, Professor Emeritus State University of New York College at Oneonta Oneonta, New York 13820 USA COPYRIGHT 2008 Paul R. Baumann Introduction Remote
Introduction to Remote Sensing Fundamentals of Satellite Remote Sensing. Mads Olander Rasmussen
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Fundamentals of Satellite Remote Sensing Mads Olander Rasmussen (mora@dhi-gras.com) 01. Introduction to Remote Sensing DHI What is remote sensing? the art, science, and technology
Introduction to Remote Sensing Fundamentals of Satellite Remote Sensing Mads Olander Rasmussen (mora@dhi-gras.com) 01. Introduction to Remote Sensing DHI What is remote sensing? the art, science, and technology
746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS
 746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 1 Concepts of remote sensing and Basic principle of Photogrammetry Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University What
746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 1 Concepts of remote sensing and Basic principle of Photogrammetry Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University What
remote sensing? What are the remote sensing principles behind these Definition
 Introduction to remote sensing: Content (1/2) Definition: photogrammetry and remote sensing (PRS) Radiation sources: solar radiation (passive optical RS) earth emission (passive microwave or thermal infrared
Introduction to remote sensing: Content (1/2) Definition: photogrammetry and remote sensing (PRS) Radiation sources: solar radiation (passive optical RS) earth emission (passive microwave or thermal infrared
An Introduction to Remote Sensing & GIS. Introduction
 An Introduction to Remote Sensing & GIS Introduction Remote sensing is the measurement of object properties on Earth s surface using data acquired from aircraft and satellites. It attempts to measure something
An Introduction to Remote Sensing & GIS Introduction Remote sensing is the measurement of object properties on Earth s surface using data acquired from aircraft and satellites. It attempts to measure something
REMOTE SENSING. Topic 10 Fundamentals of Digital Multispectral Remote Sensing MULTISPECTRAL SCANNERS MULTISPECTRAL SCANNERS
 REMOTE SENSING Topic 10 Fundamentals of Digital Multispectral Remote Sensing Chapter 5: Lillesand and Keifer Chapter 6: Avery and Berlin MULTISPECTRAL SCANNERS Record EMR in a number of discrete portions
REMOTE SENSING Topic 10 Fundamentals of Digital Multispectral Remote Sensing Chapter 5: Lillesand and Keifer Chapter 6: Avery and Berlin MULTISPECTRAL SCANNERS Record EMR in a number of discrete portions
Govt. Engineering College Jhalawar Model Question Paper Subject- Remote Sensing & GIS
 Govt. Engineering College Jhalawar Model Question Paper Subject- Remote Sensing & GIS Time: Max. Marks: Q1. What is remote Sensing? Explain the basic components of a Remote Sensing system. Q2. What is
Govt. Engineering College Jhalawar Model Question Paper Subject- Remote Sensing & GIS Time: Max. Marks: Q1. What is remote Sensing? Explain the basic components of a Remote Sensing system. Q2. What is
REMOTE SENSING INTERPRETATION
 REMOTE SENSING INTERPRETATION Jan Clevers Centre for Geo-Information - WU Remote Sensing --> RS Sensor at a distance EARTH OBSERVATION EM energy Earth RS is a tool; one of the sources of information! 1
REMOTE SENSING INTERPRETATION Jan Clevers Centre for Geo-Information - WU Remote Sensing --> RS Sensor at a distance EARTH OBSERVATION EM energy Earth RS is a tool; one of the sources of information! 1
Blacksburg, VA July 24 th 30 th, 2010 Remote Sensing Page 1. A condensed overview. For our purposes
 A condensed overview George McLeod Prepared by: With support from: NSF DUE-0903270 in partnership with: Geospatial Technician Education Through Virginia s Community Colleges (GTEVCC) The art and science
A condensed overview George McLeod Prepared by: With support from: NSF DUE-0903270 in partnership with: Geospatial Technician Education Through Virginia s Community Colleges (GTEVCC) The art and science
Final Examination Introduction to Remote Sensing. Time: 1.5 hrs Max. Marks: 50. Section-I (50 x 1 = 50 Marks)
 Final Examination Introduction to Remote Sensing Time: 1.5 hrs Max. Marks: 50 Note: Attempt all questions. Section-I (50 x 1 = 50 Marks) 1... is the technology of acquiring information about the Earth's
Final Examination Introduction to Remote Sensing Time: 1.5 hrs Max. Marks: 50 Note: Attempt all questions. Section-I (50 x 1 = 50 Marks) 1... is the technology of acquiring information about the Earth's
Outline. Introduction. Introduction: Film Emulsions. Sensor Systems. Types of Remote Sensing. A/Prof Linlin Ge. Photographic systems (cf(
 GMAT x600 Remote Sensing / Earth Observation Types of Sensor Systems (1) Outline Image Sensor Systems (i) Line Scanning Sensor Systems (passive) (ii) Array Sensor Systems (passive) (iii) Antenna Radar
GMAT x600 Remote Sensing / Earth Observation Types of Sensor Systems (1) Outline Image Sensor Systems (i) Line Scanning Sensor Systems (passive) (ii) Array Sensor Systems (passive) (iii) Antenna Radar
Introduction to Remote Sensing. Electromagnetic Energy. Data From Wave Phenomena. Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) Electromagnetic Energy
 A Basic Introduction to Remote Sensing (RS) ~~~~~~~~~~ Rev. Ronald J. Wasowski, C.S.C. Associate Professor of Environmental Science University of Portland Portland, Oregon 1 September 2015 Introduction
A Basic Introduction to Remote Sensing (RS) ~~~~~~~~~~ Rev. Ronald J. Wasowski, C.S.C. Associate Professor of Environmental Science University of Portland Portland, Oregon 1 September 2015 Introduction
GIS Data Collection. Remote Sensing
 GIS Data Collection Remote Sensing Data Collection Remote sensing Introduction Concepts Spectral signatures Resolutions: spectral, spatial, temporal Digital image processing (classification) Other systems
GIS Data Collection Remote Sensing Data Collection Remote sensing Introduction Concepts Spectral signatures Resolutions: spectral, spatial, temporal Digital image processing (classification) Other systems
The studies began when the Tiros satellites (1960) provided man s first synoptic view of the Earth s weather systems.
 Remote sensing of the Earth from orbital altitudes was recognized in the mid-1960 s as a potential technique for obtaining information important for the effective use and conservation of natural resources.
Remote sensing of the Earth from orbital altitudes was recognized in the mid-1960 s as a potential technique for obtaining information important for the effective use and conservation of natural resources.
Some Basic Concepts of Remote Sensing. Lecture 2 August 31, 2005
 Some Basic Concepts of Remote Sensing Lecture 2 August 31, 2005 What is remote sensing Remote Sensing: remote sensing is science of acquiring, processing, and interpreting images and related data that
Some Basic Concepts of Remote Sensing Lecture 2 August 31, 2005 What is remote sensing Remote Sensing: remote sensing is science of acquiring, processing, and interpreting images and related data that
746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS. Multi spectral, thermal and hyper spectral sensing and usage
 746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 3 Multi spectral, thermal and hyper spectral sensing and usage Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University Multi
746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 3 Multi spectral, thermal and hyper spectral sensing and usage Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University Multi
Ground Truth for Calibrating Optical Imagery to Reflectance
 Visual Information Solutions Ground Truth for Calibrating Optical Imagery to Reflectance The by: Thomas Harris Whitepaper Introduction: Atmospheric Effects on Optical Imagery Remote sensing of the Earth
Visual Information Solutions Ground Truth for Calibrating Optical Imagery to Reflectance The by: Thomas Harris Whitepaper Introduction: Atmospheric Effects on Optical Imagery Remote sensing of the Earth
Important Missions. weather forecasting and monitoring communication navigation military earth resource observation LANDSAT SEASAT SPOT IRS
 Fundamentals of Remote Sensing Pranjit Kr. Sarma, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Geography Mangaldai College Email: prangis@gmail.com Ph. No +91 94357 04398 Remote Sensing Remote sensing is defined
Fundamentals of Remote Sensing Pranjit Kr. Sarma, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Geography Mangaldai College Email: prangis@gmail.com Ph. No +91 94357 04398 Remote Sensing Remote sensing is defined
Lecture Notes Prepared by Prof. J. Francis Spring Remote Sensing Instruments
 Lecture Notes Prepared by Prof. J. Francis Spring 2005 Remote Sensing Instruments Material from Remote Sensing Instrumentation in Weather Satellites: Systems, Data, and Environmental Applications by Rao,
Lecture Notes Prepared by Prof. J. Francis Spring 2005 Remote Sensing Instruments Material from Remote Sensing Instrumentation in Weather Satellites: Systems, Data, and Environmental Applications by Rao,
Spectral Signatures. Vegetation. 40 Soil. Water WAVELENGTH (microns)
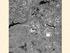 Spectral Signatures % REFLECTANCE VISIBLE NEAR INFRARED Vegetation Soil Water.5. WAVELENGTH (microns). Spectral Reflectance of Urban Materials 5 Parking Lot 5 (5=5%) Reflectance 5 5 5 5 5 Wavelength (nm)
Spectral Signatures % REFLECTANCE VISIBLE NEAR INFRARED Vegetation Soil Water.5. WAVELENGTH (microns). Spectral Reflectance of Urban Materials 5 Parking Lot 5 (5=5%) Reflectance 5 5 5 5 5 Wavelength (nm)
Lecture 2. Electromagnetic radiation principles. Units, image resolutions.
 NRMT 2270, Photogrammetry/Remote Sensing Lecture 2 Electromagnetic radiation principles. Units, image resolutions. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
NRMT 2270, Photogrammetry/Remote Sensing Lecture 2 Electromagnetic radiation principles. Units, image resolutions. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
Atmospheric interactions; Aerial Photography; Imaging systems; Intro to Spectroscopy Week #3: September 12, 2018
 GEOL 1460/2461 Ramsey Introduction/Advanced Remote Sensing Fall, 2018 Atmospheric interactions; Aerial Photography; Imaging systems; Intro to Spectroscopy Week #3: September 12, 2018 I. Quick Review from
GEOL 1460/2461 Ramsey Introduction/Advanced Remote Sensing Fall, 2018 Atmospheric interactions; Aerial Photography; Imaging systems; Intro to Spectroscopy Week #3: September 12, 2018 I. Quick Review from
John P. Stevens HS: Remote Sensing Test
 Name(s): Date: Team name: John P. Stevens HS: Remote Sensing Test 1 Scoring: Part I - /18 Part II - /40 Part III - /16 Part IV - /14 Part V - /93 Total: /181 2 I. History (3 pts. each) 1. What is the name
Name(s): Date: Team name: John P. Stevens HS: Remote Sensing Test 1 Scoring: Part I - /18 Part II - /40 Part III - /16 Part IV - /14 Part V - /93 Total: /181 2 I. History (3 pts. each) 1. What is the name
Lecture 6: Multispectral Earth Resource Satellites. The University at Albany Fall 2018 Geography and Planning
 Lecture 6: Multispectral Earth Resource Satellites The University at Albany Fall 2018 Geography and Planning Outline SPOT program and other moderate resolution systems High resolution satellite systems
Lecture 6: Multispectral Earth Resource Satellites The University at Albany Fall 2018 Geography and Planning Outline SPOT program and other moderate resolution systems High resolution satellite systems
Introduction of Satellite Remote Sensing
 Introduction of Satellite Remote Sensing Spatial Resolution (Pixel size) Spectral Resolution (Bands) Resolutions of Remote Sensing 1. Spatial (what area and how detailed) 2. Spectral (what colors bands)
Introduction of Satellite Remote Sensing Spatial Resolution (Pixel size) Spectral Resolution (Bands) Resolutions of Remote Sensing 1. Spatial (what area and how detailed) 2. Spectral (what colors bands)
Remote Sensing 1 Principles of visible and radar remote sensing & sensors
 Remote Sensing 1 Principles of visible and radar remote sensing & sensors Nick Barrand School of Geography, Earth & Environmental Sciences University of Birmingham, UK Field glaciologist collecting data
Remote Sensing 1 Principles of visible and radar remote sensing & sensors Nick Barrand School of Geography, Earth & Environmental Sciences University of Birmingham, UK Field glaciologist collecting data
IKONOS High Resolution Multispectral Scanner Sensor Characteristics
 High Spatial Resolution and Hyperspectral Scanners IKONOS High Resolution Multispectral Scanner Sensor Characteristics Launch Date View Angle Orbit 24 September 1999 Vandenberg Air Force Base, California,
High Spatial Resolution and Hyperspectral Scanners IKONOS High Resolution Multispectral Scanner Sensor Characteristics Launch Date View Angle Orbit 24 September 1999 Vandenberg Air Force Base, California,
Remote Sensing Platforms
 Types of Platforms Lighter-than-air Remote Sensing Platforms Free floating balloons Restricted by atmospheric conditions Used to acquire meteorological/atmospheric data Blimps/dirigibles Major role - news
Types of Platforms Lighter-than-air Remote Sensing Platforms Free floating balloons Restricted by atmospheric conditions Used to acquire meteorological/atmospheric data Blimps/dirigibles Major role - news
Ghazanfar A. Khattak National Centre of Excellence in Geology University of Peshawar
 INTRODUCTION TO REMOTE SENSING Ghazanfar A. Khattak National Centre of Excellence in Geology University of Peshawar WHAT IS REMOTE SENSING? Remote sensing is the science of acquiring information about
INTRODUCTION TO REMOTE SENSING Ghazanfar A. Khattak National Centre of Excellence in Geology University of Peshawar WHAT IS REMOTE SENSING? Remote sensing is the science of acquiring information about
Course overview; Remote sensing introduction; Basics of image processing & Color theory
 GEOL 1460 /2461 Ramsey Introduction to Remote Sensing Fall, 2018 Course overview; Remote sensing introduction; Basics of image processing & Color theory Week #1: 29 August 2018 I. Syllabus Review we will
GEOL 1460 /2461 Ramsey Introduction to Remote Sensing Fall, 2018 Course overview; Remote sensing introduction; Basics of image processing & Color theory Week #1: 29 August 2018 I. Syllabus Review we will
Remote Sensing and GIS
 Remote Sensing and GIS Atmosphere Reflected radiation, e.g. Visible Emitted radiation, e.g. Infrared Backscattered radiation, e.g. Radar (λ) Visible TIR Radar & Microwave 11/9/2017 Geo327G/386G, U Texas,
Remote Sensing and GIS Atmosphere Reflected radiation, e.g. Visible Emitted radiation, e.g. Infrared Backscattered radiation, e.g. Radar (λ) Visible TIR Radar & Microwave 11/9/2017 Geo327G/386G, U Texas,
Chapter 8. Remote sensing
 1. Remote sensing 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Remote sensing 8.3 Resolution 8.4 Landsat 8.5 Geostationary satellites GOES 8.1 Introduction What is remote sensing? One can describe remote sensing in different
1. Remote sensing 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Remote sensing 8.3 Resolution 8.4 Landsat 8.5 Geostationary satellites GOES 8.1 Introduction What is remote sensing? One can describe remote sensing in different
Introduction to Remote Sensing
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Outline Remote Sensing Defined Resolution Electromagnetic Energy (EMR) Types Interpretation Applications Remote Sensing Defined Remote Sensing is: The art and science of
Introduction to Remote Sensing Outline Remote Sensing Defined Resolution Electromagnetic Energy (EMR) Types Interpretation Applications Remote Sensing Defined Remote Sensing is: The art and science of
Lecture 13: Remotely Sensed Geospatial Data
 Lecture 13: Remotely Sensed Geospatial Data A. The Electromagnetic Spectrum: The electromagnetic spectrum (Figure 1) indicates the different forms of radiation (or simply stated light) emitted by nature.
Lecture 13: Remotely Sensed Geospatial Data A. The Electromagnetic Spectrum: The electromagnetic spectrum (Figure 1) indicates the different forms of radiation (or simply stated light) emitted by nature.
INF-GEO Introduction to remote sensing. Anne Solberg
 INF-GEO 4310 Introduction to remote sensing Anne Solberg (anne@ifi.uio.no) Satellites, orbits and repeat cycles Optical remote sensing Useful links: Glossary for remote sensing terms: http://www.ccrs.nracn.gc.ca/glossary/index_e.php
INF-GEO 4310 Introduction to remote sensing Anne Solberg (anne@ifi.uio.no) Satellites, orbits and repeat cycles Optical remote sensing Useful links: Glossary for remote sensing terms: http://www.ccrs.nracn.gc.ca/glossary/index_e.php
Remote Sensing in Daily Life. What Is Remote Sensing?
 Remote Sensing in Daily Life What Is Remote Sensing? First time term Remote Sensing was used by Ms Evelyn L Pruitt, a geographer of US in mid 1950s. Minimal definition (not very useful): remote sensing
Remote Sensing in Daily Life What Is Remote Sensing? First time term Remote Sensing was used by Ms Evelyn L Pruitt, a geographer of US in mid 1950s. Minimal definition (not very useful): remote sensing
Monitoring agricultural plantations with remote sensing imagery
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Monitoring agricultural plantations with remote sensing imagery Camelia Slave and Anca Rotman University of Agronomic Sciences and Veterinary Medicine - Bucharest Romania,
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Monitoring agricultural plantations with remote sensing imagery Camelia Slave and Anca Rotman University of Agronomic Sciences and Veterinary Medicine - Bucharest Romania,
Sommersemester Prof. Dr. Christoph Kleinn Institut für Waldinventur und Waldwachstum Arbeitsbereich Fernerkundung und Waldinventur.
 Basics of Remote Sensing Some literature references Franklin, SE 2001 Remote Sensing for Sustainable Forest Management Lewis Publishers 407p Lillesand, Kiefer 2000 Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation
Basics of Remote Sensing Some literature references Franklin, SE 2001 Remote Sensing for Sustainable Forest Management Lewis Publishers 407p Lillesand, Kiefer 2000 Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation
EE 529 Remote Sensing Techniques. Introduction
 EE 529 Remote Sensing Techniques Introduction Course Contents Radar Imaging Sensors Imaging Sensors Imaging Algorithms Imaging Algorithms Course Contents (Cont( Cont d) Simulated Raw Data y r Processing
EE 529 Remote Sensing Techniques Introduction Course Contents Radar Imaging Sensors Imaging Sensors Imaging Algorithms Imaging Algorithms Course Contents (Cont( Cont d) Simulated Raw Data y r Processing
Part I. The Importance of Image Registration for Remote Sensing
 Part I The Importance of Image Registration for Remote Sensing 1 Introduction jacqueline le moigne, nathan s. netanyahu, and roger d. eastman Despite the importance of image registration to data integration
Part I The Importance of Image Registration for Remote Sensing 1 Introduction jacqueline le moigne, nathan s. netanyahu, and roger d. eastman Despite the importance of image registration to data integration
INF-GEO Introduction to remote sensing
 INF-GEO 4310 Introduction to remote sensing Anne Solberg (anne@ifi.uio.no) Satellites, orbits and repeat cycles Optical remote sensings Based on a tutorial adapted from Canadian Center for Remote Sensing,
INF-GEO 4310 Introduction to remote sensing Anne Solberg (anne@ifi.uio.no) Satellites, orbits and repeat cycles Optical remote sensings Based on a tutorial adapted from Canadian Center for Remote Sensing,
Remote Sensing for Rangeland Applications
 Remote Sensing for Rangeland Applications Jay Angerer Ecological Training June 16, 2012 Remote Sensing The term "remote sensing," first used in the United States in the 1950s by Ms. Evelyn Pruitt of the
Remote Sensing for Rangeland Applications Jay Angerer Ecological Training June 16, 2012 Remote Sensing The term "remote sensing," first used in the United States in the 1950s by Ms. Evelyn Pruitt of the
A (very) brief introduction to Remote Sensing: From satellites to maps!
 Spatial Data Analysis and Modeling for Agricultural Development, with R - Workshop A (very) brief introduction to Remote Sensing: From satellites to maps! Earthlights DMSP 1994-1995 https://wikimedia.org/
Spatial Data Analysis and Modeling for Agricultural Development, with R - Workshop A (very) brief introduction to Remote Sensing: From satellites to maps! Earthlights DMSP 1994-1995 https://wikimedia.org/
RADIOMETRIC CALIBRATION
 1 RADIOMETRIC CALIBRATION Lecture 10 Digital Image Data 2 Digital data are matrices of digital numbers (DNs) There is one layer (or matrix) for each satellite band Each DN corresponds to one pixel 3 Digital
1 RADIOMETRIC CALIBRATION Lecture 10 Digital Image Data 2 Digital data are matrices of digital numbers (DNs) There is one layer (or matrix) for each satellite band Each DN corresponds to one pixel 3 Digital
FOR 353: Air Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry. Lecture 2. Electromagnetic Energy/Camera and Film characteristics
 FOR 353: Air Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Energy/Camera and Film characteristics Lecture Outline Electromagnetic Radiation Theory Digital vs. Analog (i.e. film ) Systems
FOR 353: Air Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Energy/Camera and Film characteristics Lecture Outline Electromagnetic Radiation Theory Digital vs. Analog (i.e. film ) Systems
9/12/2011. Training Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods September 2011
 Training Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Remote Sensing Platforms Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl 1 Overview Platforms & missions aerial surveys
Training Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Remote Sensing Platforms Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl 1 Overview Platforms & missions aerial surveys
Fundamentals of Remote Sensing
 Climate Variability, Hydrology, and Flooding Fundamentals of Remote Sensing May 19-22, 2015 GEO-Latin American & Caribbean Water Cycle Capacity Building Workshop Cartagena, Colombia 1 Objective To provide
Climate Variability, Hydrology, and Flooding Fundamentals of Remote Sensing May 19-22, 2015 GEO-Latin American & Caribbean Water Cycle Capacity Building Workshop Cartagena, Colombia 1 Objective To provide
Remote Sensing. Measuring an object from a distance. For GIS, that means using photographic or satellite images to gather spatial data
 Remote Sensing Measuring an object from a distance For GIS, that means using photographic or satellite images to gather spatial data Remote Sensing measures electromagnetic energy reflected or emitted
Remote Sensing Measuring an object from a distance For GIS, that means using photographic or satellite images to gather spatial data Remote Sensing measures electromagnetic energy reflected or emitted
Microwave Remote Sensing (1)
 Microwave Remote Sensing (1) Microwave sensing encompasses both active and passive forms of remote sensing. The microwave portion of the spectrum covers the range from approximately 1cm to 1m in wavelength.
Microwave Remote Sensing (1) Microwave sensing encompasses both active and passive forms of remote sensing. The microwave portion of the spectrum covers the range from approximately 1cm to 1m in wavelength.
Remote Sensing Platforms
 Remote Sensing Platforms Remote Sensing Platforms - Introduction Allow observer and/or sensor to be above the target/phenomena of interest Two primary categories Aircraft Spacecraft Each type offers different
Remote Sensing Platforms Remote Sensing Platforms - Introduction Allow observer and/or sensor to be above the target/phenomena of interest Two primary categories Aircraft Spacecraft Each type offers different
Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing. DeeDee Whitaker SW Guilford High EES & Chemistry
 Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing DeeDee Whitaker SW Guilford High EES & Chemistry whitakd@gcsnc.com Outline What is remote sensing? How does remote sensing work? What role does the electromagnetic
Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing DeeDee Whitaker SW Guilford High EES & Chemistry whitakd@gcsnc.com Outline What is remote sensing? How does remote sensing work? What role does the electromagnetic
Module 3 Introduction to GIS. Lecture 8 GIS data acquisition
 Module 3 Introduction to GIS Lecture 8 GIS data acquisition GIS workflow Data acquisition (geospatial data input) GPS Remote sensing (satellites, UAV s) LiDAR Digitized maps Attribute Data Management Data
Module 3 Introduction to GIS Lecture 8 GIS data acquisition GIS workflow Data acquisition (geospatial data input) GPS Remote sensing (satellites, UAV s) LiDAR Digitized maps Attribute Data Management Data
Outline for today. Geography 411/611 Remote sensing: Principles and Applications. Remote sensing: RS for biogeochemical cycles
 Geography 411/611 Remote sensing: Principles and Applications Thomas Albright, Associate Professor Laboratory for Conservation Biogeography, Department of Geography & Program in Ecology, Evolution, & Conservation
Geography 411/611 Remote sensing: Principles and Applications Thomas Albright, Associate Professor Laboratory for Conservation Biogeography, Department of Geography & Program in Ecology, Evolution, & Conservation
Introduction to Remote Sensing
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Daniel McInerney Urban Institute Ireland, University College Dublin, Richview Campus, Clonskeagh Drive, Dublin 14. 16th June 2009 Presentation Outline 1 2 Spaceborne Sensors
Introduction to Remote Sensing Daniel McInerney Urban Institute Ireland, University College Dublin, Richview Campus, Clonskeagh Drive, Dublin 14. 16th June 2009 Presentation Outline 1 2 Spaceborne Sensors
JP Stevens High School: Remote Sensing
 1 Name(s): ANSWER KEY Date: Team name: JP Stevens High School: Remote Sensing Scoring: Part I - /18 Part II - /40 Part III - /16 Part IV - /14 Part V - /93 Total: /181 2 I. History (3 pts each) 1. What
1 Name(s): ANSWER KEY Date: Team name: JP Stevens High School: Remote Sensing Scoring: Part I - /18 Part II - /40 Part III - /16 Part IV - /14 Part V - /93 Total: /181 2 I. History (3 pts each) 1. What
Microwave Remote Sensing
 Provide copy on a CD of the UCAR multi-media tutorial to all in class. Assign Ch-7 and Ch-9 (for two weeks) as reading material for this class. HW#4 (Due in two weeks) Problems 1,2,3 and 4 (Chapter 7)
Provide copy on a CD of the UCAR multi-media tutorial to all in class. Assign Ch-7 and Ch-9 (for two weeks) as reading material for this class. HW#4 (Due in two weeks) Problems 1,2,3 and 4 (Chapter 7)
9/12/2011. Training Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods September 2011
 Training Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Introduction to Remote Sensing Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl 1 Overview Some definitions Remote
Training Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Introduction to Remote Sensing Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl 1 Overview Some definitions Remote
Remote Sensing of the Environment An Earth Resource Perspective John R. Jensen Second Edition
 Remote Sensing of the Environment An Earth Resource Perspective John R. Jensen Second Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout
Remote Sensing of the Environment An Earth Resource Perspective John R. Jensen Second Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout
Remote Sensing. Ch. 3 Microwaves (Part 1 of 2)
 Remote Sensing Ch. 3 Microwaves (Part 1 of 2) 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Radar Basics 3.3 Viewing Geometry and Spatial Resolution 3.4 Radar Image Distortions 3.1 Introduction Microwave (1cm to 1m in wavelength)
Remote Sensing Ch. 3 Microwaves (Part 1 of 2) 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Radar Basics 3.3 Viewing Geometry and Spatial Resolution 3.4 Radar Image Distortions 3.1 Introduction Microwave (1cm to 1m in wavelength)
Data Sources. The computer is used to assist the role of photointerpretation.
 Data Sources Digital Image Data - Remote Sensing case: data of the earth's surface acquired from either aircraft or spacecraft platforms available in digital format; spatially the data is composed of discrete
Data Sources Digital Image Data - Remote Sensing case: data of the earth's surface acquired from either aircraft or spacecraft platforms available in digital format; spatially the data is composed of discrete
earthobservation.wordpress.com
 Dirty REMOTE SENSING earthobservation.wordpress.com Stuart Green Teagasc Stuart.Green@Teagasc.ie 1 Purpose Give you a very basic skill set and software training so you can: find free satellite image data.
Dirty REMOTE SENSING earthobservation.wordpress.com Stuart Green Teagasc Stuart.Green@Teagasc.ie 1 Purpose Give you a very basic skill set and software training so you can: find free satellite image data.
INF-GEO Introduction to remote sensing
 INF-GEO 4310 Introduction to remote sensing Anne Solberg (anne@ifi.uio.no) Satellites, orbits and repeat cycles Optical remote sensing Based on a tutorialt adapted d from Canadian Center for Remote Sensing,
INF-GEO 4310 Introduction to remote sensing Anne Solberg (anne@ifi.uio.no) Satellites, orbits and repeat cycles Optical remote sensing Based on a tutorialt adapted d from Canadian Center for Remote Sensing,
Remote Sensing. in Agriculture. Dr. Baqer Ramadhan CRP 514 Geographic Information System. Adel M. Al-Rebh G Term Paper.
 Remote Sensing in Agriculture Term Paper to Dr. Baqer Ramadhan CRP 514 Geographic Information System By Adel M. Al-Rebh G199325390 May 2012 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Objective... 4 3.0
Remote Sensing in Agriculture Term Paper to Dr. Baqer Ramadhan CRP 514 Geographic Information System By Adel M. Al-Rebh G199325390 May 2012 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Objective... 4 3.0
Philpot & Philipson: Remote Sensing Fundamentals Scanners 8.1 W.D. Philpot, Cornell University, Fall 2015
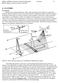 Philpot & Philipson: Remote Sensing Fundamentals Scanners 8.1 8. SCANNERS 8.1 General Scanners are scanning radiometers which, when operated from an airborne or spaceborne platform, image the terrain in
Philpot & Philipson: Remote Sensing Fundamentals Scanners 8.1 8. SCANNERS 8.1 General Scanners are scanning radiometers which, when operated from an airborne or spaceborne platform, image the terrain in
The studies began when the Tiros satellites (1960) provided man s first synoptic view of the Earth s weather systems.
 Remote sensing of the Earth from orbital altitudes was recognized in the mid-1960 s as a potential technique for obtaining information important for the effective use and conservation of natural resources.
Remote sensing of the Earth from orbital altitudes was recognized in the mid-1960 s as a potential technique for obtaining information important for the effective use and conservation of natural resources.
SATELLITE OCEANOGRAPHY
 SATELLITE OCEANOGRAPHY An Introduction for Oceanographers and Remote-sensing Scientists I. S. Robinson Lecturer in Physical Oceanography Department of Oceanography University of Southampton JOHN WILEY
SATELLITE OCEANOGRAPHY An Introduction for Oceanographers and Remote-sensing Scientists I. S. Robinson Lecturer in Physical Oceanography Department of Oceanography University of Southampton JOHN WILEY
Remote sensing in archaeology from optical to lidar. Krištof Oštir ModeLTER Scientific Research Centre of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts
 Remote sensing in archaeology from optical to lidar Krištof Oštir ModeLTER Scientific Research Centre of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts Introduction Optical remote sensing Systems Search for
Remote sensing in archaeology from optical to lidar Krištof Oštir ModeLTER Scientific Research Centre of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts Introduction Optical remote sensing Systems Search for
Remote Sensing. Division C. Written Exam
 Remote Sensing Division C Written Exam Team Name: Team #: Team Members: _ Score: /132 A. Matching (10 points) 1. Nadir 2. Albedo 3. Diffraction 4. Refraction 5. Spatial Resolution 6. Temporal Resolution
Remote Sensing Division C Written Exam Team Name: Team #: Team Members: _ Score: /132 A. Matching (10 points) 1. Nadir 2. Albedo 3. Diffraction 4. Refraction 5. Spatial Resolution 6. Temporal Resolution
Interpreting land surface features. SWAC module 3
 Interpreting land surface features SWAC module 3 Interpreting land surface features SWAC module 3 Different kinds of image Panchromatic image True-color image False-color image EMR : NASA Echo the bat
Interpreting land surface features SWAC module 3 Interpreting land surface features SWAC module 3 Different kinds of image Panchromatic image True-color image False-color image EMR : NASA Echo the bat
Introduction Active microwave Radar
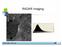 RADAR Imaging Introduction 2 Introduction Active microwave Radar Passive remote sensing systems record electromagnetic energy that was reflected or emitted from the surface of the Earth. There are also
RADAR Imaging Introduction 2 Introduction Active microwave Radar Passive remote sensing systems record electromagnetic energy that was reflected or emitted from the surface of the Earth. There are also
Remote Sensing. Odyssey 7 Jun 2012 Benjamin Post
 Remote Sensing Odyssey 7 Jun 2012 Benjamin Post Definitions Applications Physics Image Processing Classifiers Ancillary Data Data Sources Related Concepts Outline Big Picture Definitions Remote Sensing
Remote Sensing Odyssey 7 Jun 2012 Benjamin Post Definitions Applications Physics Image Processing Classifiers Ancillary Data Data Sources Related Concepts Outline Big Picture Definitions Remote Sensing
ACTIVE SENSORS RADAR
 ACTIVE SENSORS RADAR RADAR LiDAR: Light Detection And Ranging RADAR: RAdio Detection And Ranging SONAR: SOund Navigation And Ranging Used to image the ocean floor (produce bathymetic maps) and detect objects
ACTIVE SENSORS RADAR RADAR LiDAR: Light Detection And Ranging RADAR: RAdio Detection And Ranging SONAR: SOund Navigation And Ranging Used to image the ocean floor (produce bathymetic maps) and detect objects
A map says to you, 'Read me carefully, follow me closely, doubt me not.' It says, 'I am the Earth in the palm of your hand. Without me, you are alone
 A map says to you, 'Read me carefully, follow me closely, doubt me not.' It says, 'I am the Earth in the palm of your hand. Without me, you are alone and lost. Beryl Markham (West With the Night, 1946
A map says to you, 'Read me carefully, follow me closely, doubt me not.' It says, 'I am the Earth in the palm of your hand. Without me, you are alone and lost. Beryl Markham (West With the Night, 1946
Passive Microwave Sensors LIDAR Remote Sensing Laser Altimetry. 28 April 2003
 Passive Microwave Sensors LIDAR Remote Sensing Laser Altimetry 28 April 2003 Outline Passive Microwave Radiometry Rayleigh-Jeans approximation Brightness temperature Emissivity and dielectric constant
Passive Microwave Sensors LIDAR Remote Sensing Laser Altimetry 28 April 2003 Outline Passive Microwave Radiometry Rayleigh-Jeans approximation Brightness temperature Emissivity and dielectric constant
typical spectral signatures of photosynthetically active and non-photosynthetically active vegetation (Beeri et al., 2007)
 typical spectral signatures of photosynthetically active and non-photosynthetically active vegetation (Beeri et al., 2007) Xie, Y. et al. J Plant Ecol 2008 1:9-23; doi:10.1093/jpe/rtm005 Copyright restrictions
typical spectral signatures of photosynthetically active and non-photosynthetically active vegetation (Beeri et al., 2007) Xie, Y. et al. J Plant Ecol 2008 1:9-23; doi:10.1093/jpe/rtm005 Copyright restrictions
AR M. Sc. (Rural Technology) II Semester Fundamental of Remote Sensing Model Paper
 1. Multiple choice question ; AR- 7251 M. Sc. (Rural Technology) II Semester Fundamental of Remote Sensing Model Paper 1. Chlorophyll strongly absorbs radition of : (b) Red and Blue wavelength (ii) Which
1. Multiple choice question ; AR- 7251 M. Sc. (Rural Technology) II Semester Fundamental of Remote Sensing Model Paper 1. Chlorophyll strongly absorbs radition of : (b) Red and Blue wavelength (ii) Which
9/12/2011. Training Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods September 2011
 Training Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Popular Remote Sensing Sensors & their Selection Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl 1 Overview Low resolution
Training Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Popular Remote Sensing Sensors & their Selection Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl 1 Overview Low resolution
Environmental and Natural Resources Issues in Minnesota. A Remote Sensing Overview: Principles and Fundamentals. Outline. Challenges.
 A Remote Sensing Overview: Principles and Fundamentals Marvin Bauer Remote Sensing and Geospatial Analysis Laboratory College of Natural Resources University of Minnesota Remote Sensing for GIS Users Workshop,
A Remote Sensing Overview: Principles and Fundamentals Marvin Bauer Remote Sensing and Geospatial Analysis Laboratory College of Natural Resources University of Minnesota Remote Sensing for GIS Users Workshop,
Satellite Remote Sensing: Earth System Observations
 Satellite Remote Sensing: Earth System Observations Land surface Water Atmosphere Climate Ecosystems 1 EOS (Earth Observing System) Develop an understanding of the total Earth system, and the effects of
Satellite Remote Sensing: Earth System Observations Land surface Water Atmosphere Climate Ecosystems 1 EOS (Earth Observing System) Develop an understanding of the total Earth system, and the effects of
CHARACTERISTICS OF REMOTELY SENSED IMAGERY. Spatial Resolution
 CHARACTERISTICS OF REMOTELY SENSED IMAGERY Spatial Resolution There are a number of ways in which images can differ. One set of important differences relate to the various resolutions that images express.
CHARACTERISTICS OF REMOTELY SENSED IMAGERY Spatial Resolution There are a number of ways in which images can differ. One set of important differences relate to the various resolutions that images express.
Copernicus Introduction Lisbon, Portugal 13 th & 14 th February 2014
 Copernicus Introduction Lisbon, Portugal 13 th & 14 th February 2014 Contents Introduction GMES Copernicus Six thematic areas Infrastructure Space data An introduction to Remote Sensing In-situ data Applications
Copernicus Introduction Lisbon, Portugal 13 th & 14 th February 2014 Contents Introduction GMES Copernicus Six thematic areas Infrastructure Space data An introduction to Remote Sensing In-situ data Applications
Remote Sensing is the observation of the Earth from satellites or aircrafts.
 Remote Sensing? Remote Sensing is the observation of the Earth from satellites or aircrafts. Sensors mounted on these platforms capture images of the Earth that reveal features may or may not apparent
Remote Sensing? Remote Sensing is the observation of the Earth from satellites or aircrafts. Sensors mounted on these platforms capture images of the Earth that reveal features may or may not apparent
Introduction to Remote Sensing Part 1
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Part 1 A Primer on Electromagnetic Radiation Digital, Multi-Spectral Imagery The 4 Resolutions Displaying Images Corrections and Enhancements Passive vs. Active Sensors Radar
Introduction to Remote Sensing Part 1 A Primer on Electromagnetic Radiation Digital, Multi-Spectral Imagery The 4 Resolutions Displaying Images Corrections and Enhancements Passive vs. Active Sensors Radar
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction One of the major achievements of mankind is to record the data of what we observe in the form of photography which is dated to 1826. Man has always tried to reach greater heights
Chapter 1 Introduction One of the major achievements of mankind is to record the data of what we observe in the form of photography which is dated to 1826. Man has always tried to reach greater heights
RADAR REMOTE SENSING
 RADAR REMOTE SENSING Jan G.P.W. Clevers & Steven M. de Jong Chapter 8 of L&K 1 Wave theory for the EMS: Section 1.2 of L&K E = electrical field M = magnetic field c = speed of light : propagation direction
RADAR REMOTE SENSING Jan G.P.W. Clevers & Steven M. de Jong Chapter 8 of L&K 1 Wave theory for the EMS: Section 1.2 of L&K E = electrical field M = magnetic field c = speed of light : propagation direction
AVHRR/3 Operational Calibration
 AVHRR/3 Operational Calibration Jörg Ackermann, Remote Sensing and Products Division 1 Workshop`Radiometric Calibration for European Missions, 30/31 Aug. 2017`,Frascati (EUM/RSP/VWG/17/936014) AVHRR/3
AVHRR/3 Operational Calibration Jörg Ackermann, Remote Sensing and Products Division 1 Workshop`Radiometric Calibration for European Missions, 30/31 Aug. 2017`,Frascati (EUM/RSP/VWG/17/936014) AVHRR/3
Digital Image Processing - A Remote Sensing Perspective
 ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) Digital Image Processing - A Remote Sensing Perspective D.Sarala Department of Physics & Electronics St. Ann s College for Women, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad, India Sunita Jacob Head,
ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) Digital Image Processing - A Remote Sensing Perspective D.Sarala Department of Physics & Electronics St. Ann s College for Women, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad, India Sunita Jacob Head,
Remote Sensing of Environment (RSE)
 I N T R O Introduction to Introduction to Remote Sensing T O R S E Remote Sensing of Environment (RSE) with TNTmips page 1 TNTview Before Getting Started Imagery acquired by airborne or satellite sensors
I N T R O Introduction to Introduction to Remote Sensing T O R S E Remote Sensing of Environment (RSE) with TNTmips page 1 TNTview Before Getting Started Imagery acquired by airborne or satellite sensors
Introduction. Introduction. Introduction. Introduction. Introduction
 Identifying habitat change and conservation threats with satellite imagery Extinction crisis Volker Radeloff Department of Forest Ecology and Management Extinction crisis Extinction crisis Conservationists
Identifying habitat change and conservation threats with satellite imagery Extinction crisis Volker Radeloff Department of Forest Ecology and Management Extinction crisis Extinction crisis Conservationists
A broad survey of remote sensing applications for many environmental disciplines
 1 2 3 4 A broad survey of remote sensing applications for many environmental disciplines 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. First definition is very general and applies to many types of remote sensing. You use your eyes
1 2 3 4 A broad survey of remote sensing applications for many environmental disciplines 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. First definition is very general and applies to many types of remote sensing. You use your eyes
Introduction to Remote Sensors and Image Processing and its Applications
 Introduction to Remote Sensors and Image Processing and its Applications A. A. Daptardar, Senior Lecturer Department of Computer Science and Engineering Hirasugar Institute Of Technology, Nidasoshi, Karnataka,
Introduction to Remote Sensors and Image Processing and its Applications A. A. Daptardar, Senior Lecturer Department of Computer Science and Engineering Hirasugar Institute Of Technology, Nidasoshi, Karnataka,
Lecture 1 Introduction to Remote Sensing
 Lecture 1 Introduction to Remote Sensing Dr Ian Leiper School of Environmental and Life Sciences Bldg Purple 12.2.27 1 2 Lecture Outline Introductions Unit admin Learning outcomes Unit outline Practicals
Lecture 1 Introduction to Remote Sensing Dr Ian Leiper School of Environmental and Life Sciences Bldg Purple 12.2.27 1 2 Lecture Outline Introductions Unit admin Learning outcomes Unit outline Practicals
On the use of water color missions for lakes in 2021
 Lakes and Climate: The Role of Remote Sensing June 01-02, 2017 On the use of water color missions for lakes in 2021 Cédric G. Fichot Department of Earth and Environment 1 Overview 1. Past and still-ongoing
Lakes and Climate: The Role of Remote Sensing June 01-02, 2017 On the use of water color missions for lakes in 2021 Cédric G. Fichot Department of Earth and Environment 1 Overview 1. Past and still-ongoing
3/31/03. ESM 266: Introduction 1. Observations from space. Remote Sensing: The Major Source for Large-Scale Environmental Information
 Remote Sensing: The Major Source for Large-Scale Environmental Information Jeff Dozier Observations from space Sun-synchronous polar orbits Global coverage, fixed crossing, repeat sampling Typical altitude
Remote Sensing: The Major Source for Large-Scale Environmental Information Jeff Dozier Observations from space Sun-synchronous polar orbits Global coverage, fixed crossing, repeat sampling Typical altitude
NRS 415 Remote Sensing of Environment
 NRS 415 Remote Sensing of Environment 1 High Oblique Perspective (Side) Low Oblique Perspective (Relief) 2 Aerial Perspective (See What s Hidden) An example of high spatial resolution true color remote
NRS 415 Remote Sensing of Environment 1 High Oblique Perspective (Side) Low Oblique Perspective (Relief) 2 Aerial Perspective (See What s Hidden) An example of high spatial resolution true color remote
Introduction to Radar
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration ARSET Applied Remote Sensing Training http://arset.gsfc.nasa.gov @NASAARSET Introduction to Radar Jul. 16, 2016 www.nasa.gov Objective The objective of this
National Aeronautics and Space Administration ARSET Applied Remote Sensing Training http://arset.gsfc.nasa.gov @NASAARSET Introduction to Radar Jul. 16, 2016 www.nasa.gov Objective The objective of this
CHARACTERISTICS OF REMOTELY SENSED IMAGERY. Radiometric Resolution
 CHARACTERISTICS OF REMOTELY SENSED IMAGERY Radiometric Resolution There are a number of ways in which images can differ. One set of important differences relate to the various resolutions that images express.
CHARACTERISTICS OF REMOTELY SENSED IMAGERY Radiometric Resolution There are a number of ways in which images can differ. One set of important differences relate to the various resolutions that images express.
