Treatment of primary tailings and middlings from the hot water extraction process for recovering bitumen from tar sand
|
|
|
- Rodger Wilcox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 United States Patent: 4,545,892 ( 22 of 76 ) United States Patent 4,545,892 Cymbalisty, et al. October 8, 1985 Treatment of primary tailings and middlings from the hot water extraction process for recovering bitumen from tar sand Abstract The primary tailings and middlings are combined and fed to a vessel having the general form of a deep cone thickener. The feed is deflected outwardly and generally horizontally by a baffle, as it is delivered to the vessel. Simultaneously, the outwardly radiating layer of newly added feed is contacted from below by an upwelling stream of aerated middlings, which stream moves in parallel with the aforesaid layer. Bitumen froth is formed and recovered. The upwelling stream is provided by circulating middlings through eductor/aerator assemblies and a plenum chamber mounted centrally in the body of middlings in the vessel. A generally circular circulation of middlings is generated. In this manner, the newly added bitumen is quickly and efficiently recovered. Recirculation of middlings to the aeration zone yields an additional recovery of bitumen. Use of the deep cone ensures that the tailings from the vessel are relatively low in water and bitumen content. Inventors: Cymbalisty; Lubomyr M. O. (Edmonton, CA); Cymerman; George J. (Edmonton, CA) Assignee: Alberta Energy Company Ltd. (Calgary, CA); Canadian Occidental Petroleum Ltd. (Calgary, CA); Esso Resources Canada Limited (Calgary, CA); Gulf Canada Limited (Toronto, CA); Her Majesty the Queen in right of Canada, as represented by the Minister (Edmonton, CA); HBOG-Oil Sands Limited (Calgary, CA); Pan Canadian Petroleum Limited (Calgary, CA); Petro-Canada Inc. (Calgary, CA) Appl. No.: Filed: April 15, 1985 Current U.S. Class:208/391; 208/409; 208/425; 208/432; 209/164; 209/165; 209/170; 261/DIG75; 422/261; 422/269 Intern'l Class: C10G 001/00 Field of Search: 208/11 LE,8 LE 422/261,269 References Cited [Referenced By] U.S. Patent Documents
2 Jun., 1924Streppel208/ Apr., 1957Eyre208/ Jan., 1959Lowman, Jr. et al.208/ Sep., 1959Fischer et al.208/ Dec., 1960Price208/ Dec., 1964Bichard et al.208/ Sep., 1966Clark208/ Jun., 1973Terry et al.208/ Nov., 1974Cymbalisty208/ Jul., 1975Canevari208/ May., 1976Davitt208/ Oct., 1976Baillie et al.208/ Jun., 1978Porritt et al.208/ Aug., 1978McQuitty208/ Aug., 1978Lorenz208/ Feb., 1982Barger208/ Jul., 1983Roth et al.208/11. Foreign Patent Documents Feb., 1963CA208/ Oct., 1974CA208/11. Primary Examiner: Gantz; D. E. Assistant Examiner: Pal; A. Attorney, Agent or Firm: Johnson; Ernest Peter Claims The embodiments of the invention in which an exclusive property or privilege is claimed are defined as follows: 1. A method for continuously recovering bitumen from a feed stream comprising water, sand, fines, and bitumen in a vessel having a conical lower end and which defines a processing chamber, comprising: delivering said feed stream to be processed at the surface of the body of middlings already in the chamber; substantially simultaneously contacting the newly added feed with a current of outwardly and generally horizontally moving aerated middlings; whereby said newly added feed moves generally radially of the chamber in contact with the aerated middlings current, part of the bitumen contained in said newly added feed forms a froth layer at the surface of the body, bitumen-depleted feed forms a body of middlings in the chamber below the froth layer, and sand particles contained in said newly added feed settle downwardly; concentrating the settling sand particles in the conical lower end of the vessel into the form of a dense solids bed, thereby separating the greatest part of the liquid phase from the solids phase; recovering the greatest part of the froth from the vessel;
3 withdrawing an underflow tailings stream from the base of the vessel; and withdrawing a middlings stream from the vessel mid-section. 2. The method as set forth in claim 1, comprising: causing middlings in the chamber to circulate upwardly, centrally of the chamber, to generate an upwelling current; and injecting air into said upwelling middlings to permeate them with air bubbles. 3. The method as set forth in claim 2 comprising: removing some middlings from the chamber and pumping them back into the central portion of the chamber to induce a circulation of middlings which manifests itself as the upwelling central current. 4. The method as set forth in claim 1 comprising: providing a plenum assembly centrally of the chamber, said assembly having one or more eductor/aerator assemblies communicating therewith; removing some middlings from the chamber and pumping them through the eductor/aerator assemblies to induce a circulation which manifests itself as the upwelling central current; and injecting air into said eductor/aerator assemblies to permeate the middlings, passing therethrough, with air bubbles. 5. The method as set forth in claim 2 comprising: deflecting the feed stream outwardly into a generally horizontal plane as it is delivered at the surface of the body of middlings; and directing the upwelling current outwardly into a generally horizontal plane as it reaches the surface of the body of middlings; whereby said feed stream and upwelling current move outwardly adjacent said surface and mix. 6. The method as set forth in claim 4 comprising: deflecting the feed stream outwardly into a generally horizontal plane as it is delivered at the surface of the body of middlings; and directing the upwelling current outwardly into a generally horizontal plane as it reaches the surface of the body of middlings; whereby said feed stream and upwelling current move outwardly adjacent said surface and mix. 7. The method as set forth in claim 1 wherein: the sand particles are concentrated to form a bed having a density of at least 65% by weight. 8. The method as set forth in claim 3 wherein:
4 the sand particles are concentrated to form a bed having a density of at least 65% by weight. 9. The method as set forth in claim 4 wherein: the sand particles are concentrated to form a bed having a density of at least 65% by weight. 10. The method as set forth in claim 1 comprising: washing the froth with a spray of water at the periphery of the vessel before the froth is recovered. 11. The method as set forth in claim 3 comprising: washing the froth with a spray of water at the periphery of the vessel before the froth is recovered. 12. The method as set forth in claim 7 comprising: washing the froth with a spray of water at the periphery of the vessel before the froth is recovered. 13. The method as set forth in claim 1 comprising: fluidizing the base of the sand bed with an aqueous stream, to produce a flowable stream of tailings which may be withdrawn. 14. The method as set forth in claim 3 comprising: fluidizing the base of the sand bed with an aqueous stream, to produce a flowable stream of tailings which may be withdrawn. 15. The method as set forth in claim 4 comprising: fluidizing the base of the sand bed with an aqueous stream, to produce a flowable stream of tailings which may be withdrawn. 16. The method as set forth in claim 5 comprising: fluidizing the base of the sand bed with an aqueous stream, to produce a flowable stream of tailings which may be withdrawn. 17. The method as set forth in claim 7 comprising: fluidizing the base of the sand bed with an aqueous stream, to produce a flowable stream of tailings which may be withdrawn. 18. The method as set forth in claim 1 wherein: the feed stream comprises a mixture of hot water extraction process primary tailings and middlings. 19. The method as set forth in claim 2 wherein: the feed stream comprises a mixture of hot water extraction process primary
5 tailings and middlings. 20. The method as set forth in claim 3 wherein: the feed stream comprises a mixture of hot water extraction process primary tailings and middlings. 21. The method as set forth in claim 4 wherein: the feed stream comprises a mixture of hot water extraction process primary tailings and middlings. 22. The method as set forth in claim 5 wherein: the feed stream comprises a mixture of hot water extraction process primary tailings and middlings. 23. The method as set forth in claim 6 wherein: the feed stream comprises a mixture of hot water extraction process primary tailings and middlings. Description FIELD OF THE INVENTION This invention relates to a method and apparatus for recovering bitumen from a feed stream comprising solids, water and bitumen, preferaby one or both of the tailings and middlings streams from the primary separation vessel used in the extraction of bitumen from tar sand by the hot water process. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION Tar sand is currently being exploited for the recovery of bitumen therefrom by two large commercial plants in the Athabasca region of Alberta. In general, the tar sand is mined, the bitumen is extracted from it by means of the hot water process, and the bitumen is upgraded in a refinery-like operation to produce synthetic crude. The mined tar sand comprises coarse sand particles, individually sheathed in a thin film of connate water, with bitumen trapped in the interstices and clay-size mineral particles (termed `fines`) distributed in the sheaths. The tar sand is not constant in composition. There is a significant variation in its nature and processibility. In general, the bitumen content diminishes and the fines content increases as the grade of the tar sand deteriorates. A "rich" tar sand typically might comprise: Total solids 85.0% bitumen >12% fines 5% of total solids
6 A "poor" tar sand typically might comprise: Total solids >85% bitumen 8.0% fines up to 25% of total solids Typically, one might expect to recover greater than 90% of the contained bitumen from a "rich" tar sand and only about 60% from a "poor" tar sand, in the primary separation step of the hot water extraction process. The variation in the nature and quality of the tar sand feed depends on factors such as location, depth in the deposit, and the like. As a general statement, it is true that the ever-varying quality of the tar sand feed generates significant operating and recovery problems for the extraction plant. At this point, it is appropriate to describe the hot water process in a general sense. The details of the process are well documented in the literature. In the first step of the process, the as-mined tar sand is fed into a horizontal, rotating drum. Hot water, having a temperature of about 180.degree. F., is also fed into the drum and steam is sparged into the mixture, to maintain a slurry temperature of about 180.degree. F. The rotating drum cascades the porridge-like mixture, with the result that air bubbles become entrained therein. After a residence time of perhaps 10 minutes, the slurry is discharged onto a screen, to separate oversize material. This initial step is referred to as "conditioning". Pursuant to it, the bitumen is heated; the tar sand components are diluted with water and dispersed in a preliminary fashion; and air bubbles are entrained in the mixture. The screened, conditioned slurry is then diluted wirh additional hot water and introduced into a thickener-like flotation vessel. This vessel is referred to as the primary separation vessel ("PSV"). It is shown schematically in FIG. 1a. As illustrated, it is an open-topped vessel, having a cylindrical upper end and a shallow cone lower end. The angularity of the cone end is in the order of 23.degree.. The vessel has a launder at its upper end, so that froth formed at the surface of the vessel contents may overflow and be recovered. It further has an internal rake assembly in the cone, for moving sand collected and concentrated therein to a bottom outlet. The slurry feed is added to the vessel contents via a conduit and central well. An outlet is provided in the mid-section of the vessel, for the withdrawal of middlings. In the PSV, the bulk of the sand settles into the conical end, where it is concentrated, with a concomitant expulsion of liquid phase. The resultant sand layer typically has a liquid content of 65% by weight. This product, termed "primary tailings", is withdrawn through the bottom outlet. Most of the bitumen particles entering the PSV with the feed slurry are attached to or become attached to air bubbles and rise to form a froth layer at the surface of the vessel contents. This froth is recovered via the launder, as aforesaid, and is referred to as "primary froth". The bulk of the water in the feed, together with some bitumen and solids, collects in the mid-section of the vessel and is referred to as PSV "middlings". A dragstream of middlings is continuously withdrawn at a controlled rate through outlets in the vessel side wall. The desired level of the froth-middlings interface is maintained by control of the rate of PSV middlings withdrawal. The level of the middlings-sand interface is
7 controlled by varying the rate of tailings withdrawal. As stated, the PSV middlings is largely water, but it includes some bitumen and solids. The bitumen was insufficiently buoyant to reach the froth layer in the PSV. The solids is mostly fines. The middlings dragstream is processed in one or more induced air flotation cells. Each of these cells, termed "secondary recovery cells", is equipped with an up-throwing impellor positioned in its bottom end. Air is induced to flow downwardly through the hollow shaft of the impellor and is released at the impellor blade. So the cells incorporate turbulent agitation and copious aeration. As a result, some of the middlings bitumen forms a froth layer on the surface of the cell contents. This froth, called "secondary froth", is recovered. A bitumen-depleted, watery underflow, termed "secondary tailings" is withdrawn through an outlet in the base of the cell. The secondary froth is settled in a tank, to remove some water and solids from it, and then is combined with the primary froth. This latter stream is subjected to downstream cleaning and upgrading, to yield a saleable product. The primary and secondary tailings are combined and impounded in waste ponds. Now, two main objectives in managing the hot water process are to maximize the proportion of feed bitumen which reports as primary froth and to minimize the proportion lost with the two tailings streams. The losses with the tailings are substantial. In applicant's plant, which produces in the order of 130,000 barrels of synthetic crude per day, the combined tailings are produced at a typical rate of 7600 kg./sec. and the present bitumen losses with said tailings is in the order of 6 million barrels per year. In managing the process, the withdrawal of middlings and tailings from the PSV is adjusted as required: to try to maintain the froth-middlings interface at a generally constant elevation; and to try to maintain the solids content of the withdrawn tailings as close to about 65% by weight as possible, by controlling the depth of the sand bed in the cone. If the level of the froth-middlings interface rises, the PSV will overflow; if the level drops, then bitumen losses will rise. If too much liquid leaves with the tailings, then bitumen losses again rise, as the bitumen accompanies the water. Another complicating factor affecting the performance of the PSV is the nature or grade of the tar sand being processed. If the feed is "rich" tar sand, then the fines content in the slurry is relatively low and thus the slurry viscosity is relatively low. The bitumen particles in rich tar sand are relatively large in size and are more likely to have become aerated. Thus they can relatively easily rise through the middlings and primary froth recovery is relatively high. And all this can be realized with relatively modest water addition. But if the feed is "poor" tar sand, then fines content is high and the viscosity of the middlings rises. In addition, the bitumen particles are smaller with this type of feed and they do not aerate well. As a result, they do not rise well and the primary froth yield diminishes. So the operator must make process adjustments, to try to minimize the undesirable effects taking place.
8 If the operator is varying water addition, then it follows that the middlings withdrawal rates have to be varied, to maintain the froth-middlings interface level constant and to maintain the primary tailings dense. Varying the feed rate to the secondary recovery circuit can lead to overloading of that circuit. As a result, bitumen losses with the secondary tailings increase, in conjunction with an increase in other operating difficulties. With this background in mind, it will be appreciated that there is a need to improve the hot water process to achieve the following: reduction in bitumen losses with the tailings; and relief of the need to widely vary primary middlings widhdrawal rates, by loosening the required density control on the primary tailings. This would smooth out fluctuations in the feed rate to the secondary circuit and permit of better management of that circuit. In a general sense, this would involve treating the primary tailings. In considering how to obtain such as improvement, one is faced with certain problematical facts, namely: that the potential feedstock, PSV tailings, has a very large proportion of solids and a small proportion of bitumen (see Table I following below); that the volume of such a feedstock is very large and there is relatively little valuable product to be obtained from it, so the process used must be simple and inexpensive; and that the bitumen in the tailings is bitumen which was insufficiently buoyant to be recoverable from the medium of the dilute middlings in the PSV. TABLE I Composition of a Typical Primary Tailings Bitumen 0.4 weight % Water 34.6 weight % Solids 65.0 weight % SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION In accordance with the invention, a feed stream, comprising water, sand, bitumen and fines, preferably consisting of combined PSV tailings and PSV middlings, is fed to a tailings oil recovery vessel (TORV). This vessel preferably has the form of a deep cone thickener-that is, it has a cylindrical upper section and a sharp angled, conical lower section. No rake assembly is provided in the conical section. The fresh feed is delivered to the surface of the middlings in the TORV and is spread or deflected outwardly, preferably with a transversely extending baffle or the like, so that said newly added feed tends to assume a generally horizontal, outwardly radiating form as it joins the feed already in the TORV. At the same time, the newly added feed is contacted from below by an upwelling aerated middlings current. This current is generated in the middlings already in
9 the TORV. Preferably, the current is generated by withdrawing middlings from the TORV and pumping them through a conduit loop to discharge upwardly through a nozzle into an eductor positioned centrally in the TORV middlings. The middlings so pumped induce additional middlings to circulate upwardly through the eductor and an upwelling, central current is thus generated. This current is aerated, for example by a sparger associated with the nozzle, with a multitude of small air bubbles. By means of this preferred combination of mechanical and hydraulic deflection, the bitumen particles in the feed are to a considerable extent initially kept from plunging into the depths of the TORV middlings and are mixed with copious quantities of air bubbles. It is found that much of the bitumen in the newly added feed forms froth as a result and may be recovered. By using TORV middlings to provide the upwelling current, many of the bitumen particles which have settled into the middlings zone are recycled to the aerated zone and may be recovered. The water in the feed, and some associated bitumen and solids, accumulates as middlings in the mid-section of the TORV. Such middlings are withdrawn from the TORV mid-section and are preferably fed to the secondary recovery circuit. The sand in the feed is distributed across the cross-section of the TORV contents when first delivered. Most of its settles through the middlings and enters the deep cone section. Here the liquid associated with the sand is largely squeezed or displaced out, to rejoin the middlings. There is produced at the base of the conical section a high solids (in the order of >65% by wt. solids) sand bed which is very low in bitumen content. In most circumstances, it is necessary to dilute this stream with some water brought into the cone from an external source, to fluidize the sand-laden tailings so that it will flow out of the TORV through a bottom outlet. From the foregoing, it will be noted that the invention involves two features in combination, namely: maximizing quick and extensive conversion of bitumen to froth, so that there is a low concentration of bitumen in any water lost with the TORV underflow; and minimizing the loss of liquid with the TORV underflow tailings, by creating a dense sand bed in the deep cone section, to squeeze out a relatively high proportion of the liquid associated with the sand. The invention is characterized by a number of advantages, including: 1. All of the feed passes through the aeration zone and a significant recovery of bitumen is realized; 2. Aeration of the bitumen occurs at the surface of the TORV contents, thus minimizing the length of the travel that an aerated bubble of bitumen must traverse (in contradistinction to the situation in a secondary flotation cell, wherein the air is introduced at the base of the cell); 3. A TORV tailings underflow is obtained which is quite clean, with the result that the environmental impact of the pond into which the stream is discharged is improved; 4. The fluctuations in feed rate to the secondary recovery circuit are to a significant extent smoothed out;
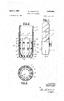
10 5. The need for close control of the bitumen content in the PSV underflow is diminished, as this bitumen can be recaptured in the TORV-this simplifies operating problems heretofore associated with the PSV; 6. The process mechanisms of aeration, flotation, mixing, settling, separation, and removal are all practised together in one vessel without internal moving parts; 7. The combination of the deep cone and fluidization permits of gravity of suction transport of the sand to the bottom outlet, without need for a rake system and the problems attendant therewith; and 8. The sensitivity of the hot water extraction process plant to variations in tar sand feed grade is diminished. Broadly stated, the invention is a method for continuously recovering bitumen from a feed stream comprising water, sand, bitumen and fines in a vessel having a conical lower end and which defines a processing chamber, comprising: delivering said feed stream to be processed at the surface of the body of middlings already in the chamber; substantially simultaneously contacting the newly added feed with a current of outwardly and generally horizontally moving aerated middlings; whereby said newly added feed moves generally radially of the chamber in contact with the aerated middlings current, part of the bitumen contained in said newly added feed forms a froth layer at the surface of the body, bitumen-depleted feed forms a body of middlings in the chamber below the froth layer, and sand particles contained in said newly added feed settle downwardly; concentrating the settling sand particles in the conical lower end of the vessel into the form of a dense solids bed, thereby separating the greatest part of the liquid phase from the solids phase; recovering the greatest part of the froth from the vessel; withdrawing an underflow tailings stream from the base of the vessel; and withdrawing a middlings stream from the vessel mid-section. DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1(a) is a schematic side section view showing a prior art PSV; FIG. 1(b) is a schematic side section view showing the TORV of the present invention; FIG. 2 is a schematic, partly sectional, side view of the TORV, with arrows indicating the current upwelling centrally and circulating downwardly in the outer reaches of the vessel chamber; FIG. 3 is a schematic, partly sectional, side view of the eductor/aerator assembly and plenum chamber positioned in the TORV, with the air bubbles, sand grains, froth and current suitably identified; FIG. 4 is a schematic showing the TORV incorporated into a hot water process plant; and FIG. 5 is a sectional side view of a single eductor/aerator assembly. DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT The tailings oil recovery vessel (TORV) 1 has the general configuration of a
11 deep cone thickener. It comprises a generally cylindrical upper section 2, a shallow angle (60.degree.) intermediate cone section 3, a steeper angle (68.degree.) lower cone section 4, and a cylindrical base section 5. A feed assembly 6 is centrally mounted on the TORV 1 at its upper end. The feed stream to be processed is delivered to the TORV via this assembly. More particularly, the assembly 6 comprises a vertically positioned, tubular feed well 7 supported by a cross-member 8 attached to the TORV sidewall. A vertical, tubular feed pipe 9 is mounted in the feed well 7 and extends donwardly through the floor of the latter. A feed conduit 10 connects tangentially with the side wall of the feed well 7 and communicates with the feed well chamber 11. The feed to be processed, preferably comprising a slurry of sand, bitumen, water, and fines, most preferably being a mixture of PSV tailings and middlings, is introduced to the feed well 7 through the conduit 10. The slurry rises in the well chamber 11 and overflows into the pipe 9, from whence it discharges downwardly into the TORV. A conical distributor baffle 12 is positioned directly below the outlet of the feed pipe 9 and extends transversely thereacross. The baffle 12 is suspended in spaced relation to the feed pipe outlet by members 13 secured to the cross-member 8. The distributor baffle 12 functions to deflect the slurry, discharging fromthe feed pipe 9, outwardly into a generally horizontal plane, so that it spreads radially along the surface 13a of the body 14 of middlings already present in the vessel chamber 15. A plenum assembly 16, forming a plenum chamber 17, is attached to the underside of the distribution baffle 12. The plenum assembly 16 is centrally positioned in the body 14 of middlings and is submerged therein. The upper and lower walls 18, 19 of the plenum assembly 16 combine to form a peripheral, slot-like outlet 20 extending around the upper edge of the plenum chamber 17. A plurality of open-ended eductor tubes 21 extend outwardly from the plenum assembly lower wall 19 and interconnect the plenum chamber 16 with the body 14 of the middlings. As shown in FIG. 5, a tubular nozzle member 22 is mounted in coaxial, outwardly spaced alignment on each such eductor tube 21 by a bracket 23. Each nozzle member 2 is circumscribed by a tubular sparger 23a mounted thereon. This sparger 23a is connected by a line 24 with a source (not shown) of pressurized air. At its end remote from the plenum assembly, the nozzle member 22 is connected by a line 25 with a pump 26, which supplies recirculated middlings under pressure from a storage tank 27. At its end adjacent the eductor tube 21, the nozzle member 22 forms an orifice 28 for the discharge of a jet of aerated middlings. The eductor tube 21, nozzle member 22, and sparger 23a together combine to form an eductor/aerator assembly 61. Each of these eductor/aerator assemblies 61 is operative to direct or inject a jet of copiously aerated, recirculated middlings into the inlet 29 of the eductor tube 21. These injected streams or jets function to induce additional middlings, from the main body 14, to flow into the plenum chamber 17 through the tubes 21. The aerated middlings are discharged outwardly, slightly upwardly, and
12 generally radially from the plenum chamber 17 through the slot-like outlet 20. As a result of such middlings injection, a generally circular pattern is established in the TORV, as indicated by the arrows in the drawing. This current pattern includes an upwelling leg through the plenum chamber, an outwardly, radially moving leg contiguous to the outwardly radiating, newly introduced slurry, and a downwardly descending leg in the outer reaches of the body 14 of middlings. The incoming slurry is spread as a thin layer on top of the fast-moving layer of aerated middlings discharged from the plenum assembly. As the two layers contact and mix, the fine air bubbles have an opportunity to contact the bitumen in the newly arrived slurry and recirculated middlings and form froth. The formed froth accumulates as a layer 29a at the periphery of the middlings surface 13a. A vertical, circular weir 30 is suspended in the vessel chamber 15 in spaced relation to the side wall 37 of the cylindrical upper section 2. The weir 30 is positioned so that its upper edge is just below the anticipated upper surface of the froth layer 29a. The weir 30 is submerged, but functions to retain most of the layer 29a of froth. A second vertical, circular weir 31 is positioned outwardly from the weir 30 in spaced relation. This second weir 31 extends downwardly a short distance below the top edge of the first weir 30. Between them, the weirs 30, 31 form a zone 32 referred to as the froth wash zone. A circular pipe 33 is mounted on the TORV immediately above the froth wash zone 32. The pipe 33 has spaced spray nozzles 34 extending downwardly from it and is connected to a source (not shown) of pressurized, clean water. The pipe 33 is thus operative to deliver a spray of water down onto the froth which has overflowed the inner weir 30. This water partly deaerates the froth and washes away some of the solids attached to it. The TORV froth thus accumulates as a layer 29a, overflows into the zone 32, and is washed by the water spray. The cleaned, partly deaerated froth can leave the wash zone 32 by moving beneath the outer weir 31. A froth launder 35, having a discharge pipe 36, is attached to the TORV sidewall on the outer side of the outer weir 31. The cleaned, partly deaerated froth overflows into this launder 35 and is recovered. The side wall 37 of the vessel's cylindrical upper section 2 has a vertically movable weir 38 attached thereto at its upper end. This weir 38 can be adjusted up or down to control the level of the upper surface 13a of the body 14 of middlings. A middlings launder 39 is secured to the side wall 37, whereby excess middlings may overflow the weir 38 and drop thereinto. The middlings launder 39 is connected by a line 40 with the storage tank 27. Means are provided in the lower end of the TORV 1 for withdrawing sand collected there. Such means comprise a suction spider 41, having a plurality of inlets 42, and a suction conduit 43 connected with the spider and extending out of the vessel. The conduit 43 is connected with a pump for applying suction. Flush nozzles 44, connected with a source of pressurized water, are provided at the spider inlets 42, to direct jets of water at the inlets to unplug them on start-up. The sand grains contained in the newly delivered slurry settle downwardly in the
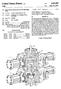
13 chamber 15 and collect in the form of a relatively high density (>65% by weight) sand bed 45. The density and height of this sand bed 45 are adjusted to desired levels by varying the rate of tailings withdrawal. The TORV is shown in FIG. 4 in the context of a flow circuit. The general operation of this circuit will now be described, with particular detail given as to the process mechanisms which take place within the TORV. Conditioned tar sand slurry from a drum or tumbler 50 is discharged into a flood box 51, wherein it is diluted with flood water. The dilute slurry is pumped through line 52 into a PSV 53. Primary froth from the PSV is produced through line 54. The PSV underflow tailings are pumped through feed conduit 10 to the TORV 1. The PSV middlings are pumped through line 55 to connect with feed conduit 10, wherein they combine with the PSV primary tailings to form the TORV feed. The froth produced by the TORV is removed through line 36. Overflow middlings are produced through line 40 into storage tank 27. Middlings are withdrawn from the tank 27 and pumped through line 25 to nozzle members 22. The tailings stream produced by the TORV is removed through line 43 for disposal in a pond or the like. All of the excess middlings in the storage tank 27 are pumped through line 56 to the secondary recovery flotation cells 57. Secondary froth from the flotation cells 57 is produced through line 58 and secondary tailings is produced through line 59. Some of the secondary tailings is diverted from line 59 through feed line 60, to supply fluidizing fluid to the spider nozzles 44. In the TORV, the incoming feed is delivered downwardly onto the distributor baffle 12, which deflects and distributes the slurry outwardly and generally horizontally as a relatively thin sheet, on top of the fast moving, underlying, upwelling layer of aerated middlings. At the same time, aerated middlings are being discharged from the circular slot-like outlet 20 of the plenum assembly 16 in a radial, outward, and gradually upwelling flow. As the outwardly-moving and slightly upwelling flow of aerated middlings comes into contact with the superimposed layer of bitumen-laden feed, the bubbles of air released from the middlings must pass upwardly through the layer of feed before escaping to atmosphere and all feed must pass downwardly through the layer of aerated middlings before entering the main body 14 of middlings. As the two streams contact and mix, both move outwardly towards the periphery of the TORV. As the outward flow velocity slackens, the aerated globules of bitumen remain on the surface in the form of light, loose froth, whereas the sand particles settle downwardly. The water and suspended fine solids, as well as suspended fine bitumen globules which did not form froth, join the body 14 of middlings. A portion of those middlings is induced to move through the plenum assembly 16 and the excess overflows the rim of the vessel over the adjustable weir 38 into the middlings launder 39 and is collected in the middlings storage tank 27. The sand particles settle downwardly in the cone sections 3,4 and concentrate into a dense bed 45 of sand, having a solids content typically in the order of at least 65% by weight. The bottom portion of this bed 45 is continually removed by the suction means. If necessary the density of the widthdrawn underflow stream can be reduced by injection of water through the flush nozzles 44. EXAMPLE I This example gives the results obtained from the operation of a 3m diameter field pilot vessel.
14 3m TORV Run TORV FEED PSV tails rate (kg/s) % bitumen % solids PSV middlings rate (kg/s) % bitumen % solids CONDITION Middlings recycle Rate (L/s) Air addition Rate (L/s) TORV PRODUCTS TORV Froth before cleaning Rate (kg/s) % bitumen % solids TORV Middlings to further flot.sup.n Rate (kg/s) % bitumen % solids TORV Tails Rate (kg/s) % bitumen % solids When converted into commercial process rates, these results could represent a saving of 2 million barrels of bitumen per year. EXAMPLE II 1m Diameter TORV The 1m diameter TORV was an investigatory research-scale pilot vessel having a vertical draft tube and eductor, instead of the eductor and plenum assembly of the 3m vessel. The distribution of bitumen in four separate runs is presented. Both the hot water extraction process and the tailings oil recovery were performed in continuous units. For this reason, there is some variation in the streams which were fed to the TORV. The data shows the different results obtained with the TORV, as one alters middlings recycle rate and air addition.
15 Also shown is the improvement obtained in TORV froth quality, which results from washing the froth. The table presents these results for a low bitumen and a higher bitumen TORV froth. Middlings recycle rate Air addition (kg/h) (scfm) Run a 0 0 Run b Run c 0 40 Run d Run a b c d Feed (i.e., PSV tails + PSV middlings) Rate (kg/h) Bitumen (wt. %) Froth (before settling in cleaner) Rate (kg/h) Bitumen (wt. %) Recovery (expressed as % of TORV feed bitumen) Sand bed density (kg/l) Froth (after settling) Rate (kg/h) Bitumen (wt. %) Middlings Rate (kg/h) Bitumen (wt. %) Tailings (after dilution) Rate (kg/h) Bitumen (wt. %) Density (kg/l) % Bitumen lost based on total bitumen entering TORV as feed Examples of improved froth quality as a result of froth washing Ratio of solids/ % Bitumen % Solids bitumen Raw froth from TORV
16 Froth after washing * * * * *
Warp length compensator for a triaxial weaving machine
 United States Patent: 4,170,249 2/15/03 8:18 AM ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 4,170,249 Trost October 9, 1979 Warp length compensator for a triaxial weaving machine Abstract A fixed cam located between
United States Patent: 4,170,249 2/15/03 8:18 AM ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 4,170,249 Trost October 9, 1979 Warp length compensator for a triaxial weaving machine Abstract A fixed cam located between
United States Patent: 4,486,294. ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 4,486,294 Miller, et al. * December 4, 1984
 United States Patent: 4,486,294 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 4,486,294 Miller, et al. * December 4, 1984 Process for separating high viscosity bitumen from tar sands Abstract A novel process for separating
United States Patent: 4,486,294 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 4,486,294 Miller, et al. * December 4, 1984 Process for separating high viscosity bitumen from tar sands Abstract A novel process for separating
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,616,442 B2
 USOO6616442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Venizelos et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2003 (54) LOW NO PREMIX BURNER APPARATUS 5,201,650 A 4/1993 Johnson... 431/9 AND METHODS 5,238,395
USOO6616442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Venizelos et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2003 (54) LOW NO PREMIX BURNER APPARATUS 5,201,650 A 4/1993 Johnson... 431/9 AND METHODS 5,238,395
March 6, 1962 W, E, MITCHELL 3,023,968 RECIRCULATING PAINT SPRAY SYSTEM INVENTOR. 2% 4.2% A. $227-2,724. as-1
 March 6, 1962 W, E, MITCHELL RECIRCULATING PAINT SPRAY SYSTEM Filed Sept. 22, 198 2 Sheets-Sheet in INVENTOR. 2% 4.2% A. $227-2,724. as-1 March 6, 1962 W. E. MITCHEL. RECIRCULATING PAINT SPRAY SYSTEM Filed
March 6, 1962 W, E, MITCHELL RECIRCULATING PAINT SPRAY SYSTEM Filed Sept. 22, 198 2 Sheets-Sheet in INVENTOR. 2% 4.2% A. $227-2,724. as-1 March 6, 1962 W. E. MITCHEL. RECIRCULATING PAINT SPRAY SYSTEM Filed
Jacquard -harness of a weaving machine
 Wednesday, December 26, 2001 United States Patent: 4,057,084 Page: 1 ( 251 of 266 ) United States Patent 4,057,084 Mueller November 8, 1977 Jacquard -harness of a weaving machine Abstract An improvement
Wednesday, December 26, 2001 United States Patent: 4,057,084 Page: 1 ( 251 of 266 ) United States Patent 4,057,084 Mueller November 8, 1977 Jacquard -harness of a weaving machine Abstract An improvement
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2
 USOO6663057B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2 Garelick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLE PEDESTAL FOR BOAT 5,297.849 A * 3/1994 Chancellor... 297/344.
USOO6663057B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2 Garelick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLE PEDESTAL FOR BOAT 5,297.849 A * 3/1994 Chancellor... 297/344.
Double-lift Jacquard mechanism
 United States Patent: 4,416,310 1/20/03 4:08 PM ( 102 of 131 ) United States Patent 4,416,310 Sage November 22, 1983 Double-lift Jacquard mechanism Abstract A double-lift Jacquard mechanism in which the
United States Patent: 4,416,310 1/20/03 4:08 PM ( 102 of 131 ) United States Patent 4,416,310 Sage November 22, 1983 Double-lift Jacquard mechanism Abstract A double-lift Jacquard mechanism in which the
75 Inventors: Onofre Costilla-Vela, Nuevo Leon; : R. SS II.
 USOO5924.47OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,924,470 Costilla-Vela et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 1999 54 METHOD FOR PREHEATING MOLDS FOR 1-91960 4/1989 Japan... 164/457 ALUMINUM CASTINGS
USOO5924.47OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,924,470 Costilla-Vela et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 1999 54 METHOD FOR PREHEATING MOLDS FOR 1-91960 4/1989 Japan... 164/457 ALUMINUM CASTINGS
United States Patent (19.
 United States Patent (19. Etcheverry (54) BUTTERFLY VALVE (75) Inventor: John P. Etcheverry, Sylmar, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Telephone and Telegraph Corporation, New York, N.Y. 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19. Etcheverry (54) BUTTERFLY VALVE (75) Inventor: John P. Etcheverry, Sylmar, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Telephone and Telegraph Corporation, New York, N.Y. 21 Appl. No.:
Universal mounting bracket for laser targeting and feedback system
 University of Northern Iowa UNI ScholarWorks Patents (University of Northern Iowa) 5-6-2003 Universal mounting bracket for laser targeting and feedback system Richard J. Kelin II Follow this and additional
University of Northern Iowa UNI ScholarWorks Patents (University of Northern Iowa) 5-6-2003 Universal mounting bracket for laser targeting and feedback system Richard J. Kelin II Follow this and additional
Method and weaving loom for producing a leno ground fabric
 Wednesday, December 26, 2001 United States Patent: 6,311,737 Page: 1 ( 9 of 319 ) United States Patent 6,311,737 Wahhoud, et al. November 6, 2001 Method and weaving loom for producing a leno ground fabric
Wednesday, December 26, 2001 United States Patent: 6,311,737 Page: 1 ( 9 of 319 ) United States Patent 6,311,737 Wahhoud, et al. November 6, 2001 Method and weaving loom for producing a leno ground fabric
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,920,822 B2
 USOO6920822B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Finan (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2005 (54) DIGITAL CAN DECORATING APPARATUS 5,186,100 A 2/1993 Turturro et al. 5,677.719 A * 10/1997 Granzow...
USOO6920822B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Finan (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2005 (54) DIGITAL CAN DECORATING APPARATUS 5,186,100 A 2/1993 Turturro et al. 5,677.719 A * 10/1997 Granzow...
Spring connection device and assembly in a jacquard harness
 Thursday, December 27, 2001 United States Patent: 6,302,154 Page: 1 ( 6 of 266 ) United States Patent 6,302,154 Bassi, et al. October 16, 2001 Spring connection device and assembly in a jacquard harness
Thursday, December 27, 2001 United States Patent: 6,302,154 Page: 1 ( 6 of 266 ) United States Patent 6,302,154 Bassi, et al. October 16, 2001 Spring connection device and assembly in a jacquard harness
United States Patent 19 Couture et al.
 United States Patent 19 Couture et al. 54 VEGETABLE PEELINGAPPARATUS 76 Inventors: Fernand Couture; René Allard, both of 2350 Edouard-Montpetit Blvd., Montreal, Quebec, Canada, H3T 1J4 21 Appl. No.: 805,985
United States Patent 19 Couture et al. 54 VEGETABLE PEELINGAPPARATUS 76 Inventors: Fernand Couture; René Allard, both of 2350 Edouard-Montpetit Blvd., Montreal, Quebec, Canada, H3T 1J4 21 Appl. No.: 805,985
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,083,443 B1. Circosta et al. 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011
 United States Patent USOO8083443B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,083,443 B1 Circosta et al. 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011 9 (54) POCKET HOLE PLUG CUTTER 5,800,099 A * 9/1998 Cooper... 408.1 R 5,807,036
United States Patent USOO8083443B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,083,443 B1 Circosta et al. 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011 9 (54) POCKET HOLE PLUG CUTTER 5,800,099 A * 9/1998 Cooper... 408.1 R 5,807,036
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2
 US0083 04995 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2 Ku et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) LAMP WITH SNOW REMOVING (56) References Cited STRUCTURE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
US0083 04995 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2 Ku et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) LAMP WITH SNOW REMOVING (56) References Cited STRUCTURE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al.
 United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al. 11 Patent Number: (4) Date of Patent: 4,21,042 Jun. 4, 198 4 THREADED CONNECTION 7) Inventors: Jan W. Blackburn, Kingwood; Burl E. Baron, Houston, both of Tex.
United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al. 11 Patent Number: (4) Date of Patent: 4,21,042 Jun. 4, 198 4 THREADED CONNECTION 7) Inventors: Jan W. Blackburn, Kingwood; Burl E. Baron, Houston, both of Tex.
Loom for carpets, tapestry, and the like and method of using
 United States Patent: 4,655,863 1/20/03 4:22 PM ( 54 of 105 ) United States Patent 4,655,863 Franco April 7, 1987 Loom for carpets, tapestry, and the like and method of using Abstract A power loom for
United States Patent: 4,655,863 1/20/03 4:22 PM ( 54 of 105 ) United States Patent 4,655,863 Franco April 7, 1987 Loom for carpets, tapestry, and the like and method of using Abstract A power loom for
Researched By: D. M. Frosaker Process Engineer, US Steel - MOO. Written By: D.M. Frosaker Process Engineer, US Steel - MOO. September 30, 2004
 Researched By: D. M. Frosaker Process Engineer, US Steel - MOO Written By: D.M. Frosaker Process Engineer, US Steel - MOO September 30, 2004 Prepared for: Minnesota Department of Natural Resources Taconite
Researched By: D. M. Frosaker Process Engineer, US Steel - MOO Written By: D.M. Frosaker Process Engineer, US Steel - MOO September 30, 2004 Prepared for: Minnesota Department of Natural Resources Taconite
Smith et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, (73 Assignee: Molex Incorporated, Lisle, Ill. 57) ABSTRACT
 United States Patent (19) 11 US005577318A Patent Number: Smith et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 1996 54 ELECTRICAL TERMINAL APPLICATOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS WEMPROVED TRACK ADJUSTMENT 2643514 8/1990
United States Patent (19) 11 US005577318A Patent Number: Smith et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 1996 54 ELECTRICAL TERMINAL APPLICATOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS WEMPROVED TRACK ADJUSTMENT 2643514 8/1990
Articles and Abstracts. Roger Graves, Director of Writing Across the Curriculum and Heather Graves Associate Professor, English and Film Studies
 Articles and Abstracts Roger Graves, Director of Writing Across the Curriculum and Heather Graves Associate Professor, English and Film Studies http://www.ualberta.ca/~graves1/index.html Roger Graves http://www.humanities.ualberta.ca/wac/
Articles and Abstracts Roger Graves, Director of Writing Across the Curriculum and Heather Graves Associate Professor, English and Film Studies http://www.ualberta.ca/~graves1/index.html Roger Graves http://www.humanities.ualberta.ca/wac/
Micro valve arrays for fluid flow control
 ( 1 of 14 ) United States Patent 6,705,345 Bifano March 16, 2004 Micro valve arrays for fluid flow control Abstract An array of micro valves, and the process for its formation, used for control of a fluid
( 1 of 14 ) United States Patent 6,705,345 Bifano March 16, 2004 Micro valve arrays for fluid flow control Abstract An array of micro valves, and the process for its formation, used for control of a fluid
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) US00564117OA 11 Patent Number: 5,641,170 Helm 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 1997 54 76) 21 22 51 52 58 PORTABLE TOOL CARRER AND DISPLAY BOX Inventor: Paul E. Helm, 2028 Ridge Rd.,
United States Patent (19) US00564117OA 11 Patent Number: 5,641,170 Helm 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 1997 54 76) 21 22 51 52 58 PORTABLE TOOL CARRER AND DISPLAY BOX Inventor: Paul E. Helm, 2028 Ridge Rd.,
United States Patent (19) 11) 3,711,874 Gajer (45) Jan. 23, 1973
 United States Patent (19) 11) 3,711,874 Gajer (45) Jan. 23, 1973 54 BASKETSINK STRAINER 3,007, 179 1/1961 Bertulli... 4/287 3,096,527 7/1963 Eynon......41287 (75) Inventor: Israel Gajer, Wyandanch, N.Y.
United States Patent (19) 11) 3,711,874 Gajer (45) Jan. 23, 1973 54 BASKETSINK STRAINER 3,007, 179 1/1961 Bertulli... 4/287 3,096,527 7/1963 Eynon......41287 (75) Inventor: Israel Gajer, Wyandanch, N.Y.
MHC Series Hydrocyclone
 MHC Series Hydrocyclone Exceptional efficiency for optimized performance MHC Hydrocyclone 1 Metso Beneficiation Solutions Metso Beneficiation Solutions for minerals processing aim for maximizing ore recovery
MHC Series Hydrocyclone Exceptional efficiency for optimized performance MHC Hydrocyclone 1 Metso Beneficiation Solutions Metso Beneficiation Solutions for minerals processing aim for maximizing ore recovery
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 US00593.4021A 11 Patent Number: 5,934,021 Conway (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 1999 54 PIVOTABLE SAFETY GATE 2,874,819 2/1959 Nutter... 49/68 3,421,260 1/1969 Dickinson... 49/122
United States Patent 19 US00593.4021A 11 Patent Number: 5,934,021 Conway (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 1999 54 PIVOTABLE SAFETY GATE 2,874,819 2/1959 Nutter... 49/68 3,421,260 1/1969 Dickinson... 49/122
11 Patent Number: 5,584,458 Rando 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 17, (56) References Cited (54) SEAERS FOR U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 United States Patent (19) III IIHIIII USOO5584458A 11 Patent Number: 5,584,458 Rando 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 17, 1996 (56) References Cited (54) SEAERS FOR U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,926,722 5/1990 Sorensen
United States Patent (19) III IIHIIII USOO5584458A 11 Patent Number: 5,584,458 Rando 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 17, 1996 (56) References Cited (54) SEAERS FOR U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,926,722 5/1990 Sorensen
58 Field of Search... 53/443, 448, 176, Spaced relation along the membrane and, portions of a
 USOO5918738A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Leistner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) TEE-NUT STRIP WITH EDGE MEMBRANES 4,955,476 9/1990 Nakata et al.... 206/346 5,762,190 6/1998 Leistner...
USOO5918738A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Leistner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) TEE-NUT STRIP WITH EDGE MEMBRANES 4,955,476 9/1990 Nakata et al.... 206/346 5,762,190 6/1998 Leistner...
Wednesday, February 20, 2002 United States Patent: 3,990,481 Page: 1. United States Patent 3,990,481 Graf November 9, 1976.
 Wednesday, February 20, 2002 United States Patent: 3,990,481 Page: 1 ( 241 of 247 ) United States Patent 3,990,481 Graf November 9, 1976 Leno heddles Abstract A wear resistant leno heddle is disclosed
Wednesday, February 20, 2002 United States Patent: 3,990,481 Page: 1 ( 241 of 247 ) United States Patent 3,990,481 Graf November 9, 1976 Leno heddles Abstract A wear resistant leno heddle is disclosed
United States Patent (19) Shahan
 United States Patent (19) Shahan 54, HEAVY DUTY SHACKLE 75 Inventor: James B. Shahan, Tulsa, Okla. (73) Assignee: American Hoist & Derrick Company, Tulsa, Okla. (21) Appl. No.: 739,056 22 Filed: Nov. 5,
United States Patent (19) Shahan 54, HEAVY DUTY SHACKLE 75 Inventor: James B. Shahan, Tulsa, Okla. (73) Assignee: American Hoist & Derrick Company, Tulsa, Okla. (21) Appl. No.: 739,056 22 Filed: Nov. 5,
Silk velvet textile and method of manufacturing the same
 ( 45 of 131 ) United States Patent 5,598,615 Takada February 4, 1997 Silk velvet textile and method of manufacturing the same Abstract The invention relates to a silk velvet textile and the method of manufacturing
( 45 of 131 ) United States Patent 5,598,615 Takada February 4, 1997 Silk velvet textile and method of manufacturing the same Abstract The invention relates to a silk velvet textile and the method of manufacturing
April 10, L. MALICAY 2,373,584 COCOANUT CUTTING MACHINE. HEDEar N--- acacases. \ Zeanaze A? a leay. 20%ive s?alafa.
 April 10, 1945. L. MALICAY 2,373,584 COCOANUT CUTTING MACHINE Filed Sept. 23, 1943 4 Sheets-Sheet l Y HEDEar N--- acacases \ Zeanaze A? a leay 20%ive s?alafa. April 10, 1945. L. MACAY 2,373,584 COCOANUT
April 10, 1945. L. MALICAY 2,373,584 COCOANUT CUTTING MACHINE Filed Sept. 23, 1943 4 Sheets-Sheet l Y HEDEar N--- acacases \ Zeanaze A? a leay 20%ive s?alafa. April 10, 1945. L. MACAY 2,373,584 COCOANUT
Ay:44, 444-, INven TOR HARVEY R. PLUMMER. Jan. 3, 1967 H. R. PLUMMER 3,295,187. ArTws, Filed March l, Sheets-Sheet
 Jan. 3, 1967 H. R. PLUMMER Filed March l, 1965 2 Sheets-Sheet INven TOR HARVEY R. PLUMMER Ay:44, 444-, 14-42--- ArTws, Jan. 3, 1967 H. R. PUMMER Filed March 1, 1965 2. Sheets-Sheet 2 INVENTOR HARVEY R.
Jan. 3, 1967 H. R. PLUMMER Filed March l, 1965 2 Sheets-Sheet INven TOR HARVEY R. PLUMMER Ay:44, 444-, 14-42--- ArTws, Jan. 3, 1967 H. R. PUMMER Filed March 1, 1965 2. Sheets-Sheet 2 INVENTOR HARVEY R.
III IIII. United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. application of welds thereto for attaching the hub member to
 United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. 54) EARTH SCREW ANCHOR ASSEMBLY HAVING ENHANCED PENETRATING CAPABILITY (75) Inventors: Daniel V. Hamilton; Robert M. Hoyt, both of Centralia; Patricia J. Halferty,
United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. 54) EARTH SCREW ANCHOR ASSEMBLY HAVING ENHANCED PENETRATING CAPABILITY (75) Inventors: Daniel V. Hamilton; Robert M. Hoyt, both of Centralia; Patricia J. Halferty,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1
 USOO6386952B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1 White (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) SINGLE STATION BLADE SHARPENING 2,692.457 A 10/1954 Bindszus METHOD AND APPARATUS 2,709,874
USOO6386952B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1 White (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) SINGLE STATION BLADE SHARPENING 2,692.457 A 10/1954 Bindszus METHOD AND APPARATUS 2,709,874
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,050,541 B2
 US007050541B (1) United States Patent () Patent No.: Bitt (45) Date of Patent: May 3, 006 (54) X-RAY TUBE WITH LIQUID-METAL FLUID (56) References Cited BEARNG U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Herbert
US007050541B (1) United States Patent () Patent No.: Bitt (45) Date of Patent: May 3, 006 (54) X-RAY TUBE WITH LIQUID-METAL FLUID (56) References Cited BEARNG U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Herbert
Leno selvedge device and method of forming a leno selvedge
 Friday, December 28, 2001 United States Patent: 3,945,406 Page: 1 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 3,945,406 Wueger March 23, 1976 Leno selvedge device and method of forming a leno selvedge Abstract A leno
Friday, December 28, 2001 United States Patent: 3,945,406 Page: 1 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 3,945,406 Wueger March 23, 1976 Leno selvedge device and method of forming a leno selvedge Abstract A leno
April 5, 1960 D. J. GRAOY 2,931,630 DRILL BIT INVENTOR. Daniel J. Grady. ...s.l., r ATTORNEYS
 April 5, 1960 D. J. GRAOY 2,931,630 DRILL BIT Filed Dec. 30, 1957 2 Sheets-Sheet INVENTOR Daniel J. Grady...s.l., r ATTORNEYS April 5, 1960 Filed Dec. 30, 1957 D. J. GRAOY DRILL BIT 2,931,630 2 Sheets-Sheet
April 5, 1960 D. J. GRAOY 2,931,630 DRILL BIT Filed Dec. 30, 1957 2 Sheets-Sheet INVENTOR Daniel J. Grady...s.l., r ATTORNEYS April 5, 1960 Filed Dec. 30, 1957 D. J. GRAOY DRILL BIT 2,931,630 2 Sheets-Sheet
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,931,325. Filipov (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999
 USOO593 1325A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,931,325 Filipov (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999 54 ADJUSTABLE MUDRING FOR Primary Examiner Steven Pollard CONVENTIONAL ELECTRICAL OUTLET BOX
USOO593 1325A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,931,325 Filipov (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999 54 ADJUSTABLE MUDRING FOR Primary Examiner Steven Pollard CONVENTIONAL ELECTRICAL OUTLET BOX
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Device Patent No 30: Last updated: 24th June 2007 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent shows a method of altering a standard electrical generator intended to be
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Device Patent No 30: Last updated: 24th June 2007 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent shows a method of altering a standard electrical generator intended to be
United States Patent (19) (11) 4,185,925
 United States Patent (19) (11) Gazzoni (45) Jan. 29, 1980 (54) SMALLSIZED TAPERED-END PLASTICS SILO, ESPECIALLY MATERAL FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 1208570 9/1959 France... 366/319 75 Inventor I tor:
United States Patent (19) (11) Gazzoni (45) Jan. 29, 1980 (54) SMALLSIZED TAPERED-END PLASTICS SILO, ESPECIALLY MATERAL FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 1208570 9/1959 France... 366/319 75 Inventor I tor:
United States Patent (19) Kwiatkowski
 United States Patent (19) Kwiatkowski 54 76) (21) 22 63) (51) (52) 58) 56 CANDLE BOX Inventor: Joseph Kwiatkowski, Rte. 1, Box 1040, Rainier, Wash. 98576 Appl. No.: 914,894 Filed: Jun. 12, 1978 Related
United States Patent (19) Kwiatkowski 54 76) (21) 22 63) (51) (52) 58) 56 CANDLE BOX Inventor: Joseph Kwiatkowski, Rte. 1, Box 1040, Rainier, Wash. 98576 Appl. No.: 914,894 Filed: Jun. 12, 1978 Related
I III. United States Patent (19) Samejima et al. Kyotani; Masaji Kure; Hideo Okura, extending toward the ground, and a covering wall surround
 United States Patent (19) Samejima et al. I III US005457947A 11 Patent Number: 5,457,947 (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 1995 54 MULCHING MOWER UNIT 75) Inventors: Kazuo Samejima; Junji Miyata; Mitsuhiro
United States Patent (19) Samejima et al. I III US005457947A 11 Patent Number: 5,457,947 (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 1995 54 MULCHING MOWER UNIT 75) Inventors: Kazuo Samejima; Junji Miyata; Mitsuhiro
Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner. Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green
 III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
April 1, 1969 W. JONAs ET AL 3,435,988. PAPER Cup DISPENSER. Filed March 20, 1968 Sheet / of 2 N S. INVENTORs WALTER JONAS. ADOLF PFUND. ATTORNEY.
 April 1, 1969 W. JONAs ET AL. PAPER Cup DISPENSER Filed March 20, 1968 Sheet / of 2 N S. N ) INVENTORs WALTER JONAS. ADOLF PFUND. ATTORNEY. April 1, 1969 filed March 20, 1968 Sºzzzzzzzz!,, ~~~~ FIG 5.
April 1, 1969 W. JONAs ET AL. PAPER Cup DISPENSER Filed March 20, 1968 Sheet / of 2 N S. N ) INVENTORs WALTER JONAS. ADOLF PFUND. ATTORNEY. April 1, 1969 filed March 20, 1968 Sºzzzzzzzz!,, ~~~~ FIG 5.
75) Inventor: Charles L. Truman, Hendersonville, N.C. 57 ABSTRACT
 United States Patent 19 Truman Oct. 5, 1976 54) TAMPON-INSERTER STCK COMBINATION WITH A MODIFIED STCK-RECEIVING SOCKET Primary Examiner-Aldrich F. Medbery Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Daniel J. Hanlon, Jr.;
United States Patent 19 Truman Oct. 5, 1976 54) TAMPON-INSERTER STCK COMBINATION WITH A MODIFIED STCK-RECEIVING SOCKET Primary Examiner-Aldrich F. Medbery Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Daniel J. Hanlon, Jr.;
United States Patent (19) Lacombe
 United States Patent (19) Lacombe (54) SPACER FOR GLASS SEALED UNT AND INTERLOCK MEMBER THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Gaetan Y. Lacombe, Duvernay, Canada 73 Assignee: D. C. Glass Limited, Anjou, Canada 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Lacombe (54) SPACER FOR GLASS SEALED UNT AND INTERLOCK MEMBER THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Gaetan Y. Lacombe, Duvernay, Canada 73 Assignee: D. C. Glass Limited, Anjou, Canada 21 Appl.
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/90/101999790.jpg) United States Patent [19] Landeis 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005904033A [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: May 18, 1999 [54] VINE CUTTER [76] Inventor:
United States Patent [19] Landeis 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005904033A [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: May 18, 1999 [54] VINE CUTTER [76] Inventor:
United States Patent 6,359,257 Clauer, et al. March 19, Abstract
 United States Patent 6,359,257 Clauer, et al. March 19, 2002 Beam path clearing for laser peening Abstract An apparatus and method for providing a substantially debris-free laser beam path for use during
United States Patent 6,359,257 Clauer, et al. March 19, 2002 Beam path clearing for laser peening Abstract An apparatus and method for providing a substantially debris-free laser beam path for use during
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,612,223 B2. Leonard et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003
 USOO6612223B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,612,223 B2 Leonard et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003 (54) PNEUMATIC ACTUATOR 5,178,367 A * 1/1993 Vaughen... 254/93 HP 5,461.207 A 10/1995
USOO6612223B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,612,223 B2 Leonard et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003 (54) PNEUMATIC ACTUATOR 5,178,367 A * 1/1993 Vaughen... 254/93 HP 5,461.207 A 10/1995
United States Patent (19) Bowman
 United States Patent (19) Bowman 54) 76) 22 21 (52) 51 (58 (56) FIRE HYDRANT LOCKING DEVICE Inventor: Harold M. Bowman, 29355 Ranney Parkway, Cleveland, Ohio 44145 Filed: June 16, 1976 Appl. No.: 696,757
United States Patent (19) Bowman 54) 76) 22 21 (52) 51 (58 (56) FIRE HYDRANT LOCKING DEVICE Inventor: Harold M. Bowman, 29355 Ranney Parkway, Cleveland, Ohio 44145 Filed: June 16, 1976 Appl. No.: 696,757
ejector solutions Produced Water & Sand Management
 ejector solutions Produced Water & Sand Management How Ejectors Work Sand Slurry Ejectors (also referred to as Jet Pumps or Eductors) provide a simple, robust and reliable method of pumping and pressure
ejector solutions Produced Water & Sand Management How Ejectors Work Sand Slurry Ejectors (also referred to as Jet Pumps or Eductors) provide a simple, robust and reliable method of pumping and pressure
United States Patent (19) Cobb
 United States Patent (19) Cobb 54 RAM-SHEAR AND SLIP DEVICE FOR WELL PIPE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: A. Tom Cobb, Seabrook, Tex. Continental Oil Company, Ponca City, Okla. 21 Appl. No.: 671,464 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Cobb 54 RAM-SHEAR AND SLIP DEVICE FOR WELL PIPE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: A. Tom Cobb, Seabrook, Tex. Continental Oil Company, Ponca City, Okla. 21 Appl. No.: 671,464 22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004.0060551A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0060551A1 Gallops, JR. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING (21) Appl. No.: 10/255.287
US 2004.0060551A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0060551A1 Gallops, JR. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING (21) Appl. No.: 10/255.287
United States Patent 19 Clifton
 United States Patent 19 Clifton (54) TAPE MEASURING SQUARE AND ADJUSTABLE TOOL GUIDE 76 Inventor: Norman L. Clifton, 49 S. 875 West, Orem, Utah 84058-5267 21 Appl. No.: 594,082 22 Filed: Jan. 30, 1996
United States Patent 19 Clifton (54) TAPE MEASURING SQUARE AND ADJUSTABLE TOOL GUIDE 76 Inventor: Norman L. Clifton, 49 S. 875 West, Orem, Utah 84058-5267 21 Appl. No.: 594,082 22 Filed: Jan. 30, 1996
Optical spray painting practice and training system
 University of Northern Iowa UNI ScholarWorks Patents (University of Northern Iowa) 9-14-1999 Optical spray painting practice and training system Richard J. Klein II Follow this and additional works at:
University of Northern Iowa UNI ScholarWorks Patents (University of Northern Iowa) 9-14-1999 Optical spray painting practice and training system Richard J. Klein II Follow this and additional works at:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,283,971 B1
 USOO6283971B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,283,971 B1 Temeles (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 4, 2001 (54) EXPANDABLE ACETABULAR REAMING Primary Examiner Paul J. Hirsch SYSTEM Assistant Examiner
USOO6283971B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,283,971 B1 Temeles (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 4, 2001 (54) EXPANDABLE ACETABULAR REAMING Primary Examiner Paul J. Hirsch SYSTEM Assistant Examiner
IIH. United States Patent (19) Chen. (11) Patent Number: 5,318,090 (45. Date of Patent: Jun. 7, 1994
 United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
SAGITTAL SAW BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
 SAGITTAL SAW BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION Sagittal bone saws function through angular oscillation of the saw cutting blade, and are used primarily in applications that require plunge cutting of bone. However,
SAGITTAL SAW BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION Sagittal bone saws function through angular oscillation of the saw cutting blade, and are used primarily in applications that require plunge cutting of bone. However,
III. United States Patent (19) Ruzskai et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,580,295 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996
 United States Patent (19) Ruzskai et al. III USOO5580295A 11 Patent Number: 5,580,295 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996 54 ARMS FOR A TOY FIGURE (75 Inventors: Frank Ruzskai, Copenhagen; Bent Landling,
United States Patent (19) Ruzskai et al. III USOO5580295A 11 Patent Number: 5,580,295 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996 54 ARMS FOR A TOY FIGURE (75 Inventors: Frank Ruzskai, Copenhagen; Bent Landling,
UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE
 Patented Jan., 1937 2,066,61 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE 2,066,61 METALLOSCOPE Gerhard R. Fisher, Palo Alto, Calif. Application January 16, 1933, Serial No. 61,974 Renewed August 6, 1936 3 Claims. (Cl.
Patented Jan., 1937 2,066,61 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE 2,066,61 METALLOSCOPE Gerhard R. Fisher, Palo Alto, Calif. Application January 16, 1933, Serial No. 61,974 Renewed August 6, 1936 3 Claims. (Cl.
Schaeff, LLP. 22 Filed: Nov. 2, 1998 (51) Int. Cl."... B21D 51/ U.S. Cl... 72/329; 72/ Field of Search... 72/327, 328, 329, 72/348
 United States Patent Turner et al. 19 USOO607.9249A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 27, 2000 54 METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING A BEADED CAN END 75 Inventors: Stephen B. Turner, Kettering;
United States Patent Turner et al. 19 USOO607.9249A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 27, 2000 54 METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING A BEADED CAN END 75 Inventors: Stephen B. Turner, Kettering;
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Strandberg 54 SUCKER ROD FITTING 75 Inventor: Donald G. Strandberg, Park Forest, Ill. 73) Assignee: Park-Ohio Industries, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio (21) Appl. No.: 482,800 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Strandberg 54 SUCKER ROD FITTING 75 Inventor: Donald G. Strandberg, Park Forest, Ill. 73) Assignee: Park-Ohio Industries, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio (21) Appl. No.: 482,800 22 Filed:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 172314B2 () Patent No.: Currie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) SOLID STATE ELECTRIC LIGHT BULB (58) Field of Classification Search... 362/2, 362/7, 800, 243,
(12) United States Patent US007 172314B2 () Patent No.: Currie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) SOLID STATE ELECTRIC LIGHT BULB (58) Field of Classification Search... 362/2, 362/7, 800, 243,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Crompton 54 AMUSEMENT MACHINE 75 Inventor: Gordon Crompton, Kent, United Kingdom 73 Assignee: Cromptons Leisure Machines Limited, Kent, United Kingdom 21 Appl. No.: 08/827,053
United States Patent (19) Crompton 54 AMUSEMENT MACHINE 75 Inventor: Gordon Crompton, Kent, United Kingdom 73 Assignee: Cromptons Leisure Machines Limited, Kent, United Kingdom 21 Appl. No.: 08/827,053
4/ /hoe 2eceolónzee-zee-ee. E 6 Ée, S. 2&772zz, z/7%zz. J422/s, Feb. 22, s. MANDL 2,108,866. Avezzr. Filed April 17, Sheets-Sheet l. 2.
 Feb. 22, 1938. s. MANDL SOCKET WRENCH Filed April 17, 1936 2 Sheets-Sheet l. Se E 6 Ée, S. 2.72 N NS s Na w Avezzr. 2&772zz, z/7%zz 4/ /hoe 2eceolónzee-zee-ee J422/s, Feb. 22, 1938. S. MAND SOCKET WRENCH
Feb. 22, 1938. s. MANDL SOCKET WRENCH Filed April 17, 1936 2 Sheets-Sheet l. Se E 6 Ée, S. 2.72 N NS s Na w Avezzr. 2&772zz, z/7%zz 4/ /hoe 2eceolónzee-zee-ee J422/s, Feb. 22, 1938. S. MAND SOCKET WRENCH
Feb. 7, R. DOPYERA 1896,484
 Feb. 7, 1933. R. DPYERA 1896,484 MUSICAL ISTRUMET Filed Feb. 1, 1932 2 Sheets-Sheet l Z2ZZZZZZZZZz7 SAVera S as - SSA; S S. S s IVETR. Rudolph Dopyera. 5 ATTREY. Feb. 7, 1933. R. DPYERA MUSICAL ISTRUMET
Feb. 7, 1933. R. DPYERA 1896,484 MUSICAL ISTRUMET Filed Feb. 1, 1932 2 Sheets-Sheet l Z2ZZZZZZZZZz7 SAVera S as - SSA; S S. S s IVETR. Rudolph Dopyera. 5 ATTREY. Feb. 7, 1933. R. DPYERA MUSICAL ISTRUMET
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110081842A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0081842 A1 SEP et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) DISTRIBUTOR FOR CONTINUOUSLY FEEDINGABRASIVE MATERAL
(19) United States US 20110081842A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0081842 A1 SEP et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) DISTRIBUTOR FOR CONTINUOUSLY FEEDINGABRASIVE MATERAL
DS-CD-01 Rev 3
 Coalescers OVERVIEW There are numerous industrial applications requiring effective physical separation of two process liquids. HAT has developed a number of AlphaSEP Coalescers to handle a wide range of
Coalescers OVERVIEW There are numerous industrial applications requiring effective physical separation of two process liquids. HAT has developed a number of AlphaSEP Coalescers to handle a wide range of
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,711,560 Gilbertson 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 27, 1998
 USOO571 1560A d United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,711,560 Gilbertson 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 27, 1998 54) DOOR SECURITY WEDGE 5,056,836 10/1991 Wells... 292/288 5,217.269 6/1993 Wiltberger......
USOO571 1560A d United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,711,560 Gilbertson 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 27, 1998 54) DOOR SECURITY WEDGE 5,056,836 10/1991 Wells... 292/288 5,217.269 6/1993 Wiltberger......
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Markle 54 CARTRIDGE SHELL FLASH HLE UNFRMER 76) Inventor: Kenneth E. Markle, 2525 Primrose La, York, Pa. 17404 (21) Appl. No.: 163,747 22 Filed: Mar. 3, 1988 51) Int. Cl."...
United States Patent (19) Markle 54 CARTRIDGE SHELL FLASH HLE UNFRMER 76) Inventor: Kenneth E. Markle, 2525 Primrose La, York, Pa. 17404 (21) Appl. No.: 163,747 22 Filed: Mar. 3, 1988 51) Int. Cl."...
United States Patent (19) Breslow
 United States Patent (19) Breslow (54. SHELVING ASSEMBLY 75 Inventor: David S. Breslow, Chicago, Ill. 73 Assignee: RTC Industries, Inc., Chicago, Ill. (21) Appl. No.: 325,395 22 Filed: Mar. 20, 1989 5ll
United States Patent (19) Breslow (54. SHELVING ASSEMBLY 75 Inventor: David S. Breslow, Chicago, Ill. 73 Assignee: RTC Industries, Inc., Chicago, Ill. (21) Appl. No.: 325,395 22 Filed: Mar. 20, 1989 5ll
Double-embroidered lace
 Thursday, August 22, 2002 United States Patent: 5,111,760 Page: 1 ( 66 of 113 ) United States Patent 5,111,760 Garzone, Jr. May 12, 1992 Double-embroidered lace Abstract A multi-embroidered lace comprising
Thursday, August 22, 2002 United States Patent: 5,111,760 Page: 1 ( 66 of 113 ) United States Patent 5,111,760 Garzone, Jr. May 12, 1992 Double-embroidered lace Abstract A multi-embroidered lace comprising
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2
 USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
"4-(2- Feb. 15, 1966 H. F. YOUNG 3,235,290 GLASS LINED FITTING AND PROCESS FOR. Filed Dec. 7, Sheets-Sheet 1 GLASS LINING OF PIPE FITTING
 Feb. 15, 1966 H. F. YOUNG GLASS LINED FITTING AND PROCESS FOR GLASS LINING OF PIPE FITTING Filed Dec. 7, 1960 2. Sheets-Sheet 1 INVENTOR. HERBERT F YOUWG "4-(2- A T TO RAVE YS Feb. 15, 1966 H. F. YOUNG
Feb. 15, 1966 H. F. YOUNG GLASS LINED FITTING AND PROCESS FOR GLASS LINING OF PIPE FITTING Filed Dec. 7, 1960 2. Sheets-Sheet 1 INVENTOR. HERBERT F YOUWG "4-(2- A T TO RAVE YS Feb. 15, 1966 H. F. YOUNG
OIL AND WATER SEPARATION AT ITS BEST
 OIL AND WATER SEPARATION AT ITS BEST Looking for faster and more efficient separation of produced water from crude oil as well as increased production? Vessel Internal Electrostatic Coalescers (VIEC) have
OIL AND WATER SEPARATION AT ITS BEST Looking for faster and more efficient separation of produced water from crude oil as well as increased production? Vessel Internal Electrostatic Coalescers (VIEC) have
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004000017OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0000170 A1 Matsumura et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2004 (54) OPTICAL ELEMENT MOLDING APPARATUS (30) Foreign
US 2004000017OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0000170 A1 Matsumura et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2004 (54) OPTICAL ELEMENT MOLDING APPARATUS (30) Foreign
United States Patent (19) Morita et al.
 United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
(10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ Al (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (57)
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Coleman et al. 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 us 20040151491Al (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0151491
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Coleman et al. 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 us 20040151491Al (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0151491
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,805,823 B2. Sembritzky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 2010
 US007805823B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,805,823 B2 Sembritzky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 2010 (54) AXIAL SWAGE ALIGNMENT TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: David
US007805823B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,805,823 B2 Sembritzky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 2010 (54) AXIAL SWAGE ALIGNMENT TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: David
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Dekerle 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 1991 54 NIPPLE ADAPTER FOR A BOTTLE COMPRISING ASCREW RING 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Benoit Dekerle, Evian, France Societe
United States Patent (19) Dekerle 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 1991 54 NIPPLE ADAPTER FOR A BOTTLE COMPRISING ASCREW RING 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Benoit Dekerle, Evian, France Societe
United States Patent
 United States Patent This PDF file contains a digital copy of a United States patent that relates to the Native American Flute. It is part of a collection of Native American Flute resources available at
United States Patent This PDF file contains a digital copy of a United States patent that relates to the Native American Flute. It is part of a collection of Native American Flute resources available at
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Spatz 54 (75) 73) (21) 22) 51) (52) (58) (56) DESPENSING DEVICE FOR COSMETIC STICKS AND THE LIKE Inventor: Assignee: Walter Spatz, Pacific Palisades, Calif. Spatz Laboratories,
United States Patent (19) Spatz 54 (75) 73) (21) 22) 51) (52) (58) (56) DESPENSING DEVICE FOR COSMETIC STICKS AND THE LIKE Inventor: Assignee: Walter Spatz, Pacific Palisades, Calif. Spatz Laboratories,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,708,159 B2. Darr et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2010
 USOO7708159B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Darr et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2010 (54) PLASTIC CONTAINER 4,830,251 A 5/1989 Conrad 6,085,924 A 7/2000 Henderson (75) Inventors: Richard
USOO7708159B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Darr et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2010 (54) PLASTIC CONTAINER 4,830,251 A 5/1989 Conrad 6,085,924 A 7/2000 Henderson (75) Inventors: Richard
ORGANISATION AFRICAINE DE LA PROPRIETE INTELLECTUELLE
 19 ORGANISATION AFRICAINE DE LA PROPRIETE INTELLECTUELLE 11 N 8 51 Inter. CI. C10G 1/04; C10C 3/00 FASCICULE DE BREVET D INVENTION 21 22 Numéro de dépôt : 1201400181 (PCT/IB12/055849) Date de dépôt : 24/10/2012
19 ORGANISATION AFRICAINE DE LA PROPRIETE INTELLECTUELLE 11 N 8 51 Inter. CI. C10G 1/04; C10C 3/00 FASCICULE DE BREVET D INVENTION 21 22 Numéro de dépôt : 1201400181 (PCT/IB12/055849) Date de dépôt : 24/10/2012
Attorney Docket No Date: 9 July 2007
 DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIDMSION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: (401) 832-3653 FAX: (401) 832-4432 NEWPORT DSN: 432-3653 Date: 9 July 2007 The below identified patent application
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIDMSION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: (401) 832-3653 FAX: (401) 832-4432 NEWPORT DSN: 432-3653 Date: 9 July 2007 The below identified patent application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,068,465 B2
 USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kurz USOO6287057B1 (10) Patent o.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 11, 2001 (54) DEVICE FOR MACHIIG BORES I A WORKPIECE AD A METHOD FOR MACHIIG BORES BY EMPLOYIG SUCH DEVICE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Kurz USOO6287057B1 (10) Patent o.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 11, 2001 (54) DEVICE FOR MACHIIG BORES I A WORKPIECE AD A METHOD FOR MACHIIG BORES BY EMPLOYIG SUCH DEVICE (75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) Greenland
 United States Patent (19) Greenland 54) COMPACT MOTORIZED TABLE SAW 76 Inventor: Darrell Greenland, 1650 Tenth St., Santa Monica, Calif. 90404 21 Appl. No.: 08/906,356 22 Filed: Aug. 5, 1997 Related U.S.
United States Patent (19) Greenland 54) COMPACT MOTORIZED TABLE SAW 76 Inventor: Darrell Greenland, 1650 Tenth St., Santa Monica, Calif. 90404 21 Appl. No.: 08/906,356 22 Filed: Aug. 5, 1997 Related U.S.
United States Patent (15) 3,652,141 Histen et al. (45) Mar. 28, ) COMBINED THREE-SECTIONAL 56) References Cited
 United States Patent (15) 3,652,141 Histen et al. (45) Mar. 28, 1972 54) COMBINED THREE-SECTIONAL 56) References Cited...As ROLLERTURNING FOREIGN PATENTS ORAPPLICATIONS (72) Inventors: Werner Histen, Hellinghausen;
United States Patent (15) 3,652,141 Histen et al. (45) Mar. 28, 1972 54) COMBINED THREE-SECTIONAL 56) References Cited...As ROLLERTURNING FOREIGN PATENTS ORAPPLICATIONS (72) Inventors: Werner Histen, Hellinghausen;
Feb. 12, 1952 E. ALTMAN 2,585,073 PEACH PITTING MACHINE INVENTOR. BY 6%au-v62. ATTORNEYS.
 Feb. 12, 1952 E. ALTMAN 2,585,073 Filed Feb. 9, 1949 5 Sheets-Sheet INVENTOR BY 6%au-v62. ATTORNEYS. Feb. 12, 1952 E. ALTMAN 2,585,073 Filed Feb. 9, 1949 5 Sheets-Sheet 2 /6- /2 72.2. Zsz27Z ZZZZZZZZ,
Feb. 12, 1952 E. ALTMAN 2,585,073 Filed Feb. 9, 1949 5 Sheets-Sheet INVENTOR BY 6%au-v62. ATTORNEYS. Feb. 12, 1952 E. ALTMAN 2,585,073 Filed Feb. 9, 1949 5 Sheets-Sheet 2 /6- /2 72.2. Zsz27Z ZZZZZZZZ,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1
 US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) USOO54O907A 11) Patent Number: 5,140,907 Svatek (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 25, 1992 (54) METHOD FOR SURFACE MINING WITH 4,966,077 10/1990 Halliday et al.... 1O2/313 X DRAGLINE
United States Patent (19) USOO54O907A 11) Patent Number: 5,140,907 Svatek (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 25, 1992 (54) METHOD FOR SURFACE MINING WITH 4,966,077 10/1990 Halliday et al.... 1O2/313 X DRAGLINE
United States Patent (19) Swartwout
 United States Patent (19) Swartwout 54 BOTTLE CAP WITH INTEGRAL MEASURING CUP AND BOTTLE CLOSURE 76 Inventor: Everett W. Swartwout, 5816A S, Wolf Rd., Western Springs, Ill. 60558 (21) Appl. No.: 325,295
United States Patent (19) Swartwout 54 BOTTLE CAP WITH INTEGRAL MEASURING CUP AND BOTTLE CLOSURE 76 Inventor: Everett W. Swartwout, 5816A S, Wolf Rd., Western Springs, Ill. 60558 (21) Appl. No.: 325,295
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,959,246 Gretz (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 28, 1999
 USOO5959246A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,959,246 Gretz (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 28, 1999 54 ELECTRIC BOX EXTENDER AND 3,770,873 11/1973 Brown... 174/58 SUPPLEMENTAL PART 4,044,908 8/1977
USOO5959246A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,959,246 Gretz (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 28, 1999 54 ELECTRIC BOX EXTENDER AND 3,770,873 11/1973 Brown... 174/58 SUPPLEMENTAL PART 4,044,908 8/1977
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Jirgens et al. 54 on ETRIP WINDOW. CUTTING TOOL METHOD AND APPARATUS (75) Inventors: Rainer Jirgens; Dietmar Krehl, both of Celle, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Baker Hughes
United States Patent (19) Jirgens et al. 54 on ETRIP WINDOW. CUTTING TOOL METHOD AND APPARATUS (75) Inventors: Rainer Jirgens; Dietmar Krehl, both of Celle, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Baker Hughes
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
Drawing. Fig. 1 Drawing
 Drawing Drawing is a metalworking process which uses tensile forces to stretch metal. It is broken up into two types: sheet metal drawing and wire, bar, and tube drawing. The specific definition for sheet
Drawing Drawing is a metalworking process which uses tensile forces to stretch metal. It is broken up into two types: sheet metal drawing and wire, bar, and tube drawing. The specific definition for sheet
Advanced Machining Processes Professor Vijay K. Jain Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 06
 Advanced Machining Processes Professor Vijay K. Jain Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 06 (Refer Slide Time: 00:17) Today we are going to discuss about
Advanced Machining Processes Professor Vijay K. Jain Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 06 (Refer Slide Time: 00:17) Today we are going to discuss about
