Low frequency sound reproduction in irregular rooms using CABS (Control Acoustic Bass System) Celestinos, Adrian; Nielsen, Sofus Birkedal
|
|
|
- Gilbert Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Aalborg Universitet Low frequency sound reproduction in irregular rooms using CABS (Control Acoustic Bass System) Celestinos, Adrian; Nielsen, Sofus Birkedal Published in: Acustica United with Acta Acustica Publication date: 2011 Document Version Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication from Aalborg University Citation for published version (APA): Celestinos, A., & Nielsen, S. B. (2011). Low frequency sound reproduction in irregular rooms using CABS (Control Acoustic Bass System). Acustica United with Acta Acustica, 97(Supplement 1), S 35. General rights Copyright and moral rights for the publications made accessible in the public portal are retained by the authors and/or other copyright owners and it is a condition of accessing publications that users recognise and abide by the legal requirements associated with these rights.? Users may download and print one copy of any publication from the public portal for the purpose of private study or research.? You may not further distribute the material or use it for any profit-making activity or commercial gain? You may freely distribute the URL identifying the publication in the public portal? Take down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us at vbn@aub.aau.dk providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: oktober 17, 2018
2 Low Sound Reproduction In Irregular Rooms using CABS (Control Acoustic Bass System) Adrian Celestinos Oticon A/S, DK-2765 Smørum, Denmark Sofus Birkedal Nielsen Acoustics, Department of Electronic Systems, Aalborg University, DK-9220 Aalborg East, Denmark Summary Early investigations on low frequency sound reproduction in rectangular rooms using CABS (Controlled Acoustic Bass System) have shown good results on simulations and measurements in real rooms. CABS takes the advantage of having a rectangular room with parallel walls. By using two low frequency loudspeakers well positioned at the end of the room a virtual array is formed propagating plane waves along the length of the room in one direction. This will correct the sound field distribution in the room. When plane wave arrives to the end wall two more loudspeakers have to be placed connected with the same signal in counter phase and with a delay corresponding to approximately the length of the room. This is to cancel the reflection and maintain the plane wave propagating along the room. Real life rooms are not necessary rectangular and can be of different shapes. In this paper simulations of an irregular room model using the FDTD (Finite Difference Time Domain) method has been presented. CABS has been simulated in the irregular room model. Measurements of CABS in a real irregular room haven been performed. The performance of CABS was affected by the irregular shape of the room due to the corner diffracting the plane wave. Nevertheless CABS improved spatial and magnitude deviations. PACS no Jz, Ka 1. Introduction Full range loudspeakers are typically used for high fidelity sound reproduction. These systems are typically placed in small or medium size listening spaces e.g. listening rooms, control rooms for studios, home theater rooms, cars etc. At the listener position the spectral response of the loudspeaker is extremely modified over the full frequency range. This is due to the combination of the direct sound and the multiple reflection, diffraction and scattering of sound at the walls and different objects in the sound path. Especially at low frequencies the sound level distribution over the room will experience differences of more than 20. Mid and high frequencies can be controlled by acoustic treatment of the room, but when the loudspeaker radiates longer wavelengths e.g. from 10 m to 3 m (34 Hz 114 Hz) the acoustic solutions become unpractical. To tackle these problems several approaches have been investigated by a number of (c) European Acoustics Association authors. Some efforts have been conducted towards the analysis and optimization of the placement of the loudspeakers in the room [1, 2]. Other approaches have been directed to control the acoustic radiation power of the loudspeaker [3], by means of digital signal processing but most of the investigations have been conducted on the correction of the loudspeaker room response by digital filters [4, 5]. Another approach also making use of digital filters presented in [6] has been implemented in a low frequency sound reproduction chamber at Aalborg University. This approach is based on the simulation of a plane wave in a small room by the use of 2 x 20 loudspeakers build into two opposite walls. Every loudspeaker is controlled by an independent amplification channel and a Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter. Differently from the solution proposed in Santillan s work the system presented in this paper utilizes less loudspeakers and can be implemented in larger rooms with a much simpler setup. The idea of the Controlled Acoustic Bass System (CABS) is to built a plane wave traveling towards the opposite wall with the front loudspeakers by optimizing their placement. This will produce uniform (c) European Acoustics Association, ISBN: , ISSN:
3 Celestinos, Low Sound in Rooms using CABS Table I. Absorption coefficient used in the simulation model. Wall A B C D E F G Floor Ceiling α sound field distribution only if the reflection is then cancelled out by similar loudspeakers at the rear wall with a delayed version of the signal but in anti phase maintaining the plane wave along the room [7, 8, 9]. The main goal of this paper is to evaluate CABS in a real irregular room by simulations and measurements Room simulation model By utilizing the Finite Differences in the Time Domain method (FDTD) the room simulation model is constructed in MATLAB [8, 10, 11]. This model solves the linear lossless wave equation applying the relation between the particle velocity (lossless wave equation) and the acoustic pressure (force equation). In this fashion these two equations are combined to compute the acoustic pressure produced by a number of sound sources in the entire enclosure. The boundary conditions are defined by calculating the wall impedance from estimated absorption coefficients α and the normal component of the particle velocity to the wall. The sound field produced by multiple loudspeakers in a rectangular room can be calculated. Moreover irregular room shapes can also be modeled [8]. In this method the calculations are performed directly in the time domain, and therefore the pressure amplitude and the particle velocity are always available for analysis and visualization purposes. In addition the impulse response of the transfer function from a number of sound sources to desired positions in the room can be obtained. The virtual room model can be seen in Figure 1 indicating the different walls with letters from A to G. To discretize the room a 12 cm cell size and a sampling frequency f s = 00 Hz has been used in the simulation model. The loudspeakers are modeled as vented box type ocupying 3 x 3 x 3 cells for each loudspeaker. Two pressure points in front of the box corresponding to the driver and vent are defined by two impulse responses. These impluse responses are calculated from a measurement of the particle velocity of a vented box type loudspeaker with a laser vibrometer. The absorption coefficient for each wall is shown in Table I. The impulse response in 5x5 = 25virtual microphone positions of a listening area of approx. 2 x2min the room is recorded. Aditionally a pure tone can be produced by the loudspeaker and the sound pressure level disribution can be calculated in the horizontal plane at a desired height in the room Loudspeaker room response simulations The response of the loudspeaker is highly influenced by the multiple reflections of sound on the walls of the Height G D C F E A B Length Width Figure 1. Irregular virtual room model. Length = m. Width = 7.32 m. Height = 2.64 m. Figure 2. response of the transfer function at 25 virtual microphone positions throughout the listening area. Loudspeaker placement: 1. m from wall A and 1.02 m from wall B, 1.26 m height. room. In some sections of the room there can be differences of more than 20 in amplitude. In Figures 2, 3 and 4 variation in sound pressure level distribution can be observed on three different loudspeaker positions in the room Room width sound field correction In a rectangular room the sound field distribution along the width of the room can be even up to 100 Hz by using two front loudspeakers placed at one end of the room each at 1/4 of the width from side walls, and at 1/2 height of the room [7]. In this way an infinite horizontal array is formed constructing plane waves traveling along the room in one direction. This effect 294 (c) European Acoustics Association, ISBN: , ISSN:
4 Celestinos, Low Sound in Rooms using CABS Figure 3. response of the transfer function at 25 virtual microphone positions throughout the listening area. Loudspeaker placement: 1.26 m from wall C and 3.18 m from wall B, 1.26 m height. Figure 4. response of the transfer function at 25 virtual microphone positions throughout the listening area. Loudspeaker placement: 0. m from wall A and 1. m from wall G, 1.26 m height. will cause even sound pressure distribution along the width of the room at a single frequency. But still great spectral (magnitude) variation will occur at single positions in the room Controlled Acoustic Bass System (CABS) Once the plane wave is formed then the reflection of the back wall has to be acoustically cancelled. This is done by adding two extra loudspeakers with proper gain at the rear wall with the same signal as the front loudspeakers but in counter phase and with a delay related to approximately the length of the room, see Figure. 5. This can be achieved e.g. with two subwoofers at the front wall and two sub woofers at the rear wall. Alternatively two full range loudspeakers can be used at the front wall and two full range loud- Figure 5. Block diagram of CABS.2.2 system to minimize the reflection of the rear wall, G its a factor according to the damping characteristics of the room and the attenuation of sound by the air. speakers at the rear wall. In the later case a low pass filter has to be connected before CABS to filter out the mid and high frequency content CABS notation A notation for CABS is introduced to easily indicate the number of loudspeakers used and their rough positions: CABS Fr.F.B (1) where Fr = number of front wall full range loudspeakers F = number of front wall low frequency loudspeakers B = number of back wall low frequency loudspeakers To indicate e.g. a stereo setup of two full range loudspeakers the notation is used. The notation indicates a configuration with two low frequency loudspeakers at the front wall of the room and two low frequency loudspeakers on the back wall CABS in irregular rooms It has been shown that CABS works fine in small and middle size rectangular rooms obtaining good results below 100 Hz depending on the size of the room. But in a irregular room the effect of CABS might be deteriorated by diffraction of sound at the corner of the room and addition of reflected sound to the sound field constructed by CABS. Another problem is that the reflection at the rear wall may not be completely removed. Since CABS is only able to cancel out one reflection e.g. at the rear wall. Therefore diffracted sound would propagate and reflect along the width+length of the room destroying the sound field formed by CABS The fundamental questions here are: 1. How much this room shape would deteriorate the effect of CABS? 2. What setup of CABS is optimal in an irregular room? To answer these questions simulations of CABS in an irregular room model have been calculated. (c) European Acoustics Association, ISBN: , ISSN:
5 Celestinos, Low Sound in Rooms using CABS 1.6. Simulations of CABS Three scenarios have been simulated in the irregular virtual room model. In each setup CABS and CABS is simulated. In Setup I the front loudspeakers are located as close as possible to wall A facing wall C, one at 1.02 m from wall B and one at 3.18 m from wall B. The rear loudspeakers are at wall C facing wall A at the same distances from wall B. Since the baffle is also included in the simulation the acoustic centre of the loudspeakers are 54 cm from the wall. In Setup II the loudspeakers are at the same position as in Setup I but the front loudspeakers are then at wall C and the rear ones are now at wall A instead. In Setup III the front loudspeakers are at wall G each at 0. m from walls A and F respectively. The rear loudspeakers are at the same positions as front loudspeakers but at the opposite wall B. In all setups Figure 8. Simulation of CABS in irregular virtual room Setup III. responses of transfer function at 25 virtual microphone positions throughout listening area; Grey curves, CABS Black curves, CABS Figure 6. Simulation of CABS in irregular virtual room Setup I. responses of transfer function at 25 virtual microphone positions throughout listening area; Grey curves, CABS Black curves, CABS Figure 7. Simulation of CABS in irregular virtual room Setup II. responses of transfer function at 25 virtual microphone positions throughout listening area; Grey curves, CABS Black curves, CABS the loudspeakers are at 1.26 m height. In Figures 6, 7 and 8 result of simulation of CABS in the three setups are shown. In Figure 9 the sound pressure level distribution resulted from simulation of CABS and CABS in the three setups is shown Measurements of CABS A laboratory room has been utilized to set up and evaluate CABS The laboratory has a rectangular room chamber inside dedicated to electro magnetic measurements. This chamber gives the irregular shape needed. The room dimensions are approx. the same as the simulation being: Length = m. Width = 7.37 m. Height = 2. m. The damping of the chamber walls is lower than the rest of the other walls. The ceiling is a false ceiling and the floor is concrete much harder than the rest of the walls. Different equipment and furniture as lab tables, chairs etc was in the room when measurements were performed. The internal corner (wall E) is actually a metal door for the chamber. The placement of the loudspeakers was compromised by some of the furniture and equipment in the room. In Setup I and II the loudspeakers at wall C and A were not place as optimal as in the simulations having a misplacement of about 30- cm from the optimal position. The loudspeakers were placed facing the room and the acoustic centre of the loudspeakers was located approx. cm from front wall and rear wall respectively. In Setup I and II the loudspeakers were set at a height of 1.26 m and in Setup III at a height of 1.38 m. The loudspeakers utilized are compact full-range vented type with a 16.5 cm woofer and 16 liters cabinet volume. The frequency response of the loudspeaker is 46 Hz - 25 khz, ± 3. The sensitivity is 89 at 2.83 V/m. The delay and gain was implemented in a professional audio DSP unit for loudpeaker management. A 4th order low pass filter was 296 (c) European Acoustics Association, ISBN: , ISSN:
6 Celestinos, Low Sound in Rooms using CABS Figure 9. Sound pressure level distribution resulting from the simulation of the irregular virtual room calculated on a plane at a height of 1.26 m. Left column, Setup I 46 Hz (modal frequency). Middle column, Setup II 46 Hz (modal frequency). Right column, Setup III 48 Hz (modal frequency). Upper row using only the front loudspeakers CABS Lower row using CABS used at 109 Hz (in Setup I and II) and at 200 Hz (in Setup III) to filter out the mid and high frequencies. Due to the present furniture and lab equipment only 8 to 10 microphone positions scattered around the listening area about 1.5 to 4 meters from the front loudspeakers were measured in every setup. In Setup III ten microphone positions were set in pairs with a separation of 1.25 m from each other along the width of the room and 1 m separation from each pair along the length of the room starting at 2.6 m from front loudspeakers. The parameters of the system (delay and gain of the rear loudspeakers) were fine-tuned empirically to achieve the best performance. A selective frequency sweep with a resolution of 0.49 Hz was utilized to measure the frequency response of the loudspeakers and the room with CABS. In Figures 10, 11 and 12. the frequency response measurements at the microphone positions with CABS compared to CABS are shown for each Setup. Figure 10. Measurements in irregular room Setup I. responses of transfer function at 8 microphone positions throughout listening area; Grey curves, CABS Black curves, CABS Figure 11. Measurements in irregular room Setup II. responses of transfer function at 8 microphone positions throughout listening area; Grey curves, CABS Black curves, CABS (c) European Acoustics Association, ISBN: , ISSN:
7 Celestinos, Low Sound in Rooms using CABS Figure 12. Measurements in irregular room Setup III. responses of transfer function at 10 microphone positions throughout listening area; Grey curves, CABS Black curves, CABS DISCUSSION From the three configurations in the irregular room CABS in Setup III presents the best results. Setup II presented satisfactory results. In Setup I CABS presented poor results though the simulation result is not as bad as the result in the real room. Although it is evident that the reflection at the rear wall C was reduced the spatial distribution could not be evened. This is because wall G is too far from the front loudspeakers and the horizontal array is not constructed properly. For Setup I the reflection of the metal door (wall E) is quite strong and destroys the sound field produced by CABS It was observed that the sound pressure level at some frequencies is higher close to wall B. In Setup I and II the cancelation of the rear wall reflection is achived but then the influence of the room resonances corresponding to the length and lenght+width of the room are still evident. In Setup III the plane waves are well formed and traveling in one direction until they arrive to the corner inside the room then waves start to diffract towards not only rear wall B but also wall C. These reflections will return an disturb the sound field. In Setup III apparently the rear wall reflection can be reduced but only good results can be seen below Hz. 3. CONCLUSIONS Three setups in the irregular room have been simulated and measured. CABS presented best results in Setup III and satisfactory results in Setup II. In Setup I CABS presented poor results. Simulations and measurements suggest that extra loudspeakers may be utilized e.g. in case of Setup II at wall G in counter phase with front loudspeakers with a delay correspondent to the traveling distance from wall C to G or width + length and proper gain. The same might be done for Setup III with an extra loudspeaker at wall C and/or extra loudspeakers along wall B. When CABS is set up in a irregular room in configurations with front loudspeakers at 1/4 of the width and at one end of the room the sound field at low frequencies can be improved. These configurations would form plane waves with the side walls having variations of about ± 6. This is a significant improvement compared to the resulting sound field from a single loudspeaker in a irregular room that would give about ± 20 deviations or the typical stereo setup that would give deviations of ± 15. References [1] R. F. Allison, The Sound Field in Home Listening Rooms II, J. Audio Eng. Soc., vol. 24, pp (January/February 1976). [2] T. Welti, How Many Subwoofers are Enough, presented at the 112th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, J. Audio Eng. Soc. (Abstracts), vol., p. 523 (June 2002), convention preprint 52. [3] J. A. Pedersen, Adjusting a Loudspeaker to Its Acoustic Environment The ABC System, presented at the 115th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, J. Audio Eng. Soc. (Abstracts), vol. 51, p (December 2003), convention preprint 58. [4] A. Mäkivirta and P. Antsalo, Modal Equalization of Loudspeaker Room Responses at Low Frequencies, J. Audio Eng. Soc., vol. 51, pp (May 2003). [5] R. Walker, Equalization of Room Acoustics and Adaptive Systems in the Equalization of Small Room Acoustics, presented at the 15th Int. Conf., Audio, Acoustics & Small Spaces, J. Audio Eng. Soc. (Abstracts), vol. 46, p. 789 (September 1998). [6] A. O. Santillán, C. S. Pedersen and M. Lydolf, Experimental implementation of a low-frequency global sound equalization method based on free field propagation, Applied Acoustics, vol. 68, pp (October 2007). [7] A. Celestinos and S. B. Nielsen, Controlled Acoustic Bass System (CABS) A Method to Achieve Uniform Sound Field Distribution at Low Frequencies in Rectangular Rooms, J. Audio Eng. Soc., vol. 56, pp (November 2008). [8] A. Celestinos, Low Sound Field Enhancement System for Rectangular Rooms, Using Multiple Loudspeakers, Ph.D. dissertation, Aalborg University (2007). [9] S. B. Nielsen and A. Celestinos Time Based Room Correction System for Low Frequencies Using Multiple Loudspeakers, presented at the 32nd Int. Conf., DSP for Loudspeakers, J. Audio Eng. Soc. (Abstracts), vol. 55, pp (June 2007). [10] A. Celestinos and S. B. Nielsen, Low- Loudspeaker-Room Simulation Using Finite Differences in Time Domain-Part 1: Analysis, J. Audio Eng. Soc., vol. 56, pp (October 2008). [11] D. Botteldooren. Finite-Difference Time-Domain Simulation of Low- Room Acoustic Problems, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., vol. 98, pp (December 1995). 298 (c) European Acoustics Association, ISBN: , ISSN:
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Acustica United with Acta Acustica. Publication date: Document Version Early version, also known as pre-print
 Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: april 08, 2018 Aalborg Universitet Low frequency sound field control in rectangular listening rooms using CABS (Controlled Acoustic Bass System) will also reduce sound transmission
Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: april 08, 2018 Aalborg Universitet Low frequency sound field control in rectangular listening rooms using CABS (Controlled Acoustic Bass System) will also reduce sound transmission
Improving room acoustics at low frequencies with multiple loudspeakers and time based room correction
 Improving room acoustics at low frequencies with multiple loudspeakers and time based room correction S.B. Nielsen a and A. Celestinos b a Aalborg University, Fredrik Bajers Vej 7 B, 9220 Aalborg Ø, Denmark
Improving room acoustics at low frequencies with multiple loudspeakers and time based room correction S.B. Nielsen a and A. Celestinos b a Aalborg University, Fredrik Bajers Vej 7 B, 9220 Aalborg Ø, Denmark
Directional dependence of loudness and binaural summation Sørensen, Michael Friis; Lydolf, Morten; Frandsen, Peder Christian; Møller, Henrik
 Aalborg Universitet Directional dependence of loudness and binaural summation Sørensen, Michael Friis; Lydolf, Morten; Frandsen, Peder Christian; Møller, Henrik Published in: Proceedings of 15th International
Aalborg Universitet Directional dependence of loudness and binaural summation Sørensen, Michael Friis; Lydolf, Morten; Frandsen, Peder Christian; Møller, Henrik Published in: Proceedings of 15th International
From time to time it is useful even for an expert to give a thought to the basics of sound reproduction. For instance, what the stereo is all about?
 HIFI FUNDAMENTALS, WHAT THE STEREO IS ALL ABOUT Gradient ltd.1984-2000 From the beginning of Gradient Ltd. some fundamental aspects of loudspeaker design has frequently been questioned by our R&D Director
HIFI FUNDAMENTALS, WHAT THE STEREO IS ALL ABOUT Gradient ltd.1984-2000 From the beginning of Gradient Ltd. some fundamental aspects of loudspeaker design has frequently been questioned by our R&D Director
ONLINE TUTORIALS. Log on using your username & password. (same as your ) Choose a category from menu. (ie: audio)
 ONLINE TUTORIALS Go to http://uacbt.arizona.edu Log on using your username & password. (same as your email) Choose a category from menu. (ie: audio) Choose what application. Choose which tutorial movie.
ONLINE TUTORIALS Go to http://uacbt.arizona.edu Log on using your username & password. (same as your email) Choose a category from menu. (ie: audio) Choose what application. Choose which tutorial movie.
DESIGN OF ROOMS FOR MULTICHANNEL AUDIO MONITORING
 DESIGN OF ROOMS FOR MULTICHANNEL AUDIO MONITORING A.VARLA, A. MÄKIVIRTA, I. MARTIKAINEN, M. PILCHNER 1, R. SCHOUSTAL 1, C. ANET Genelec OY, Finland genelec@genelec.com 1 Pilchner Schoustal Inc, Canada
DESIGN OF ROOMS FOR MULTICHANNEL AUDIO MONITORING A.VARLA, A. MÄKIVIRTA, I. MARTIKAINEN, M. PILCHNER 1, R. SCHOUSTAL 1, C. ANET Genelec OY, Finland genelec@genelec.com 1 Pilchner Schoustal Inc, Canada
INFLUENCE OF THE PERFOMANCE PARAMETERS IN TRANSMISSION LINE LOUDSPEAKER SYSTEM
 INFLUENCE OF THE PERFOMANCE PARAMETERS IN TRANSMISSION LINE LOUDSPEAKER SYSTEM PACS number: 43.38.Ja Basilio Pueo, José Escolano, and Miguel Romá Department of Physics, System Engineering and Signal Theory,
INFLUENCE OF THE PERFOMANCE PARAMETERS IN TRANSMISSION LINE LOUDSPEAKER SYSTEM PACS number: 43.38.Ja Basilio Pueo, José Escolano, and Miguel Romá Department of Physics, System Engineering and Signal Theory,
Published in: Proceedings of NAM 98, Nordic Acoustical Meeting, September 6-9, 1998, Stockholm, Sweden
 Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: januar 27, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Sound pressure distribution in rooms at low frequencies Olesen, Søren Krarup; Møller, Henrik Published in: Proceedings of NAM 98, Nordic
Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: januar 27, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Sound pressure distribution in rooms at low frequencies Olesen, Søren Krarup; Møller, Henrik Published in: Proceedings of NAM 98, Nordic
Active Control of Energy Density in a Mock Cabin
 Cleveland, Ohio NOISE-CON 2003 2003 June 23-25 Active Control of Energy Density in a Mock Cabin Benjamin M. Faber and Scott D. Sommerfeldt Department of Physics and Astronomy Brigham Young University N283
Cleveland, Ohio NOISE-CON 2003 2003 June 23-25 Active Control of Energy Density in a Mock Cabin Benjamin M. Faber and Scott D. Sommerfeldt Department of Physics and Astronomy Brigham Young University N283
Antenna Diversity on a UMTS HandHeld Phone Pedersen, Gert F.; Nielsen, Jesper Ødum; Olesen, Kim; Kovacs, Istvan
 Aalborg Universitet Antenna Diversity on a UMTS HandHeld Phone Pedersen, Gert F.; Nielsen, Jesper Ødum; Olesen, Kim; Kovacs, Istvan Published in: Proceedings of the 1th IEEE International Symposium on
Aalborg Universitet Antenna Diversity on a UMTS HandHeld Phone Pedersen, Gert F.; Nielsen, Jesper Ødum; Olesen, Kim; Kovacs, Istvan Published in: Proceedings of the 1th IEEE International Symposium on
Impact of the size of the hearing aid on the mobile phone near fields Bonev, Ivan Bonev; Franek, Ondrej; Pedersen, Gert F.
 Aalborg Universitet Impact of the size of the hearing aid on the mobile phone near fields Bonev, Ivan Bonev; Franek, Ondrej; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium
Aalborg Universitet Impact of the size of the hearing aid on the mobile phone near fields Bonev, Ivan Bonev; Franek, Ondrej; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium
Indoor measurements of low-frequency noise for annoyance assessment Pedersen, Steffen; Møller, Henrik; Waye, Kerstin Persson
 Aalborg Universitet Indoor measurements of low-frequency noise for annoyance assessment Pedersen, Steffen; Møller, Henrik; Waye, Kerstin Persson Published in: Proceedings of 19th International Congress
Aalborg Universitet Indoor measurements of low-frequency noise for annoyance assessment Pedersen, Steffen; Møller, Henrik; Waye, Kerstin Persson Published in: Proceedings of 19th International Congress
Monitor Setup Guide The right monitors. The correct setup. Proper sound.
 Monitor Setup Guide 2017 The right monitors. The correct setup. Proper sound. Table of contents Genelec Key Technologies 3 What is a monitor? 4 What is a reference monitor? 4 Selecting the correct monitors
Monitor Setup Guide 2017 The right monitors. The correct setup. Proper sound. Table of contents Genelec Key Technologies 3 What is a monitor? 4 What is a reference monitor? 4 Selecting the correct monitors
A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 25, 2018 A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles Dich, Mikael; Rengarajan, S.R. Published in: Proc. of IEEE Antenna and Propagation Society
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 25, 2018 A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles Dich, Mikael; Rengarajan, S.R. Published in: Proc. of IEEE Antenna and Propagation Society
Low-Profile Fabry-Pérot Cavity Antenna with Metamaterial SRR Cells for Fifth Generation Systems
 Aalborg Universitet Low-Profile Fabry-Pérot Cavity Antenna with Metamaterial SRR Cells for Fifth Generation Systems Ojaroudiparchin, Naser; Shen, Ming; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: Microwave, Radar
Aalborg Universitet Low-Profile Fabry-Pérot Cavity Antenna with Metamaterial SRR Cells for Fifth Generation Systems Ojaroudiparchin, Naser; Shen, Ming; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: Microwave, Radar
BIG 3 WAY SPEAKER: INTEGRATION OF BASS AND MIDRANGER DRIVERS. 3D Acoustics Research, January
 BIG 3 WAY SPEAKER: INTEGRATION OF BASS AND MIDRANGER DRIVERS 1. Introduction 3D Acoustics Research, January 2010 www.3dar.ru In this article we show how 3D Response simulator can be used in low mid frequency
BIG 3 WAY SPEAKER: INTEGRATION OF BASS AND MIDRANGER DRIVERS 1. Introduction 3D Acoustics Research, January 2010 www.3dar.ru In this article we show how 3D Response simulator can be used in low mid frequency
Investigating Electromagnetic and Acoustic Properties of Loudspeakers Using Phase Sensitive Equipment
 Investigating Electromagnetic and Acoustic Properties of Loudspeakers Using Phase Sensitive Equipment Katherine Butler Department of Physics, DePaul University ABSTRACT The goal of this project was to
Investigating Electromagnetic and Acoustic Properties of Loudspeakers Using Phase Sensitive Equipment Katherine Butler Department of Physics, DePaul University ABSTRACT The goal of this project was to
Electro-Voice S40. Full Range Compact Speaker System 160 Watts Power Handling Available is Black or White
 Electro-Voice S40 Full Range Compact Speaker System 160 Watts Power Handling Available is Black or White NOTE: This data sheet refers to several graphs. In order to keep the size of this document reasonable
Electro-Voice S40 Full Range Compact Speaker System 160 Watts Power Handling Available is Black or White NOTE: This data sheet refers to several graphs. In order to keep the size of this document reasonable
Holographic Measurement of the Acoustical 3D Output by Near Field Scanning by Dave Logan, Wolfgang Klippel, Christian Bellmann, Daniel Knobloch
 Holographic Measurement of the Acoustical 3D Output by Near Field Scanning 2015 by Dave Logan, Wolfgang Klippel, Christian Bellmann, Daniel Knobloch LOGAN,NEAR FIELD SCANNING, 1 Introductions LOGAN,NEAR
Holographic Measurement of the Acoustical 3D Output by Near Field Scanning 2015 by Dave Logan, Wolfgang Klippel, Christian Bellmann, Daniel Knobloch LOGAN,NEAR FIELD SCANNING, 1 Introductions LOGAN,NEAR
IT Series Woofers and Compression Drivers
 IT Series Woofers and Compression Drivers Enclosure and Crossover Applications The HC Design IT Series low frequency woofers and high frequency drivers are very high performance transducers designed for
IT Series Woofers and Compression Drivers Enclosure and Crossover Applications The HC Design IT Series low frequency woofers and high frequency drivers are very high performance transducers designed for
Scanning laser Doppler vibrometry
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 17, 2018 Scanning laser Doppler vibrometry Brøns, Marie; Thomsen, Jon Juel Publication date: 2016 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 17, 2018 Scanning laser Doppler vibrometry Brøns, Marie; Thomsen, Jon Juel Publication date: 2016 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record
University of Southampton Research Repository eprints Soton
 University of Southampton Research Repository eprints Soton Copyright and Moral Rights for this thesis are retained by the author and/or other copyright owners. A copy can be downloaded for personal non-commercial
University of Southampton Research Repository eprints Soton Copyright and Moral Rights for this thesis are retained by the author and/or other copyright owners. A copy can be downloaded for personal non-commercial
Small Room and Loudspeaker Interaction
 The common questions Several common questions are often asked related to loudspeaker s sound reproduction, such as: 1. Why does a loudspeaker sound different when moved to another room? 2. Why does my
The common questions Several common questions are often asked related to loudspeaker s sound reproduction, such as: 1. Why does a loudspeaker sound different when moved to another room? 2. Why does my
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), th European Conference on
 Aalborg Universitet On the Currents Magnitude of a Tunable Planar-Inverted-F Antenna for Low-Band Frequencies Barrio, Samantha Caporal Del; Pelosi, Mauro; Franek, Ondrej; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in:
Aalborg Universitet On the Currents Magnitude of a Tunable Planar-Inverted-F Antenna for Low-Band Frequencies Barrio, Samantha Caporal Del; Pelosi, Mauro; Franek, Ondrej; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in:
A Practical FPGA-Based LUT-Predistortion Technology For Switch-Mode Power Amplifier Linearization Cerasani, Umberto; Le Moullec, Yannick; Tong, Tian
 Aalborg Universitet A Practical FPGA-Based LUT-Predistortion Technology For Switch-Mode Power Amplifier Linearization Cerasani, Umberto; Le Moullec, Yannick; Tong, Tian Published in: NORCHIP, 2009 DOI
Aalborg Universitet A Practical FPGA-Based LUT-Predistortion Technology For Switch-Mode Power Amplifier Linearization Cerasani, Umberto; Le Moullec, Yannick; Tong, Tian Published in: NORCHIP, 2009 DOI
Aalborg Universitet. MEMS Tunable Antennas to Address LTE 600 MHz-bands Barrio, Samantha Caporal Del; Morris, Art; Pedersen, Gert F.
 Aalborg Universitet MEMS Tunable Antennas to Address LTE 6 MHz-bands Barrio, Samantha Caporal Del; Morris, Art; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: 9th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP),
Aalborg Universitet MEMS Tunable Antennas to Address LTE 6 MHz-bands Barrio, Samantha Caporal Del; Morris, Art; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: 9th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP),
RD75, RD50, RD40, RD28.1 Planar magnetic transducers with true line source characteristics
 RD75, RD50, RD40, RD28.1 Planar magnetic transducers true line source characteristics The RD line of planar-magnetic ribbon drivers represents the ultimate thin film diaphragm technology. The RD drivers
RD75, RD50, RD40, RD28.1 Planar magnetic transducers true line source characteristics The RD line of planar-magnetic ribbon drivers represents the ultimate thin film diaphragm technology. The RD drivers
A White Paper on Danley Sound Labs Tapped Horn and Synergy Horn Technologies
 Tapped Horn (patent pending) Horns have been used for decades in sound reinforcement to increase the loading on the loudspeaker driver. This is done to increase the power transfer from the driver to the
Tapped Horn (patent pending) Horns have been used for decades in sound reinforcement to increase the loading on the loudspeaker driver. This is done to increase the power transfer from the driver to the
From concert halls to noise barriers : attenuation from interference gratings
 From concert halls to noise barriers : attenuation from interference gratings Davies, WJ Title Authors Type URL Published Date 22 From concert halls to noise barriers : attenuation from interference gratings
From concert halls to noise barriers : attenuation from interference gratings Davies, WJ Title Authors Type URL Published Date 22 From concert halls to noise barriers : attenuation from interference gratings
DESIGN AND APPLICATION OF DDS-CONTROLLED, CARDIOID LOUDSPEAKER ARRAYS
 DESIGN AND APPLICATION OF DDS-CONTROLLED, CARDIOID LOUDSPEAKER ARRAYS Evert Start Duran Audio BV, Zaltbommel, The Netherlands Gerald van Beuningen Duran Audio BV, Zaltbommel, The Netherlands 1 INTRODUCTION
DESIGN AND APPLICATION OF DDS-CONTROLLED, CARDIOID LOUDSPEAKER ARRAYS Evert Start Duran Audio BV, Zaltbommel, The Netherlands Gerald van Beuningen Duran Audio BV, Zaltbommel, The Netherlands 1 INTRODUCTION
19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 VIRTUAL AUDIO REPRODUCED IN A HEADREST
 19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 VIRTUAL AUDIO REPRODUCED IN A HEADREST PACS: 43.25.Lj M.Jones, S.J.Elliott, T.Takeuchi, J.Beer Institute of Sound and Vibration Research;
19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 VIRTUAL AUDIO REPRODUCED IN A HEADREST PACS: 43.25.Lj M.Jones, S.J.Elliott, T.Takeuchi, J.Beer Institute of Sound and Vibration Research;
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), th European Conference on
 Aalborg Universitet Beam-Steerable Microstrip-Fed Bow-Tie Antenna Array for Fifth Generation Cellular Communications Parchin, Naser Ojaroudi; Shen, Ming; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: Antennas and Propagation
Aalborg Universitet Beam-Steerable Microstrip-Fed Bow-Tie Antenna Array for Fifth Generation Cellular Communications Parchin, Naser Ojaroudi; Shen, Ming; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: Antennas and Propagation
Sound engineering course
 Sound engineering course 1.Acustics 2.Transducers Fundamentals of acoustics: nature of sound, physical quantities, propagation, point and line sources. Psychoacoustics: sound levels in db, sound perception,
Sound engineering course 1.Acustics 2.Transducers Fundamentals of acoustics: nature of sound, physical quantities, propagation, point and line sources. Psychoacoustics: sound levels in db, sound perception,
Review Title. Secondary Title
 YG Acoustics Review Title Anat Reference Main Module 2,300,000 (per pair) Secondary Title Extremely Pleasant, Natural, Super-Energetic Sounds with Zero Irritation By Hiromi Wada Main Text My overall impression
YG Acoustics Review Title Anat Reference Main Module 2,300,000 (per pair) Secondary Title Extremely Pleasant, Natural, Super-Energetic Sounds with Zero Irritation By Hiromi Wada Main Text My overall impression
LOW FREQUENCY SOUND IN ROOMS
 Room boundaries reflect sound waves. LOW FREQUENCY SOUND IN ROOMS For low frequencies (typically where the room dimensions are comparable with half wavelengths of the reproduced frequency) waves reflected
Room boundaries reflect sound waves. LOW FREQUENCY SOUND IN ROOMS For low frequencies (typically where the room dimensions are comparable with half wavelengths of the reproduced frequency) waves reflected
ON THE APPLICABILITY OF DISTRIBUTED MODE LOUDSPEAKER PANELS FOR WAVE FIELD SYNTHESIS BASED SOUND REPRODUCTION
 ON THE APPLICABILITY OF DISTRIBUTED MODE LOUDSPEAKER PANELS FOR WAVE FIELD SYNTHESIS BASED SOUND REPRODUCTION Marinus M. Boone and Werner P.J. de Bruijn Delft University of Technology, Laboratory of Acoustical
ON THE APPLICABILITY OF DISTRIBUTED MODE LOUDSPEAKER PANELS FOR WAVE FIELD SYNTHESIS BASED SOUND REPRODUCTION Marinus M. Boone and Werner P.J. de Bruijn Delft University of Technology, Laboratory of Acoustical
Room Impulse Response Modeling in the Sub-2kHz Band using 3-D Rectangular Digital Waveguide Mesh
 Room Impulse Response Modeling in the Sub-2kHz Band using 3-D Rectangular Digital Waveguide Mesh Zhixin Chen ILX Lightwave Corporation Bozeman, Montana, USA Abstract Digital waveguide mesh has emerged
Room Impulse Response Modeling in the Sub-2kHz Band using 3-D Rectangular Digital Waveguide Mesh Zhixin Chen ILX Lightwave Corporation Bozeman, Montana, USA Abstract Digital waveguide mesh has emerged
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), th European Conference on
 Aalborg Universitet User Effect on the MIMO Performance of a Dual Antenna LTE Handset Buskgaard, Emil Feldborg; Tatomirescu, Alexandru; Barrio, Samantha Caporal Del; Franek, Ondrej; Pedersen, Gert F. Published
Aalborg Universitet User Effect on the MIMO Performance of a Dual Antenna LTE Handset Buskgaard, Emil Feldborg; Tatomirescu, Alexandru; Barrio, Samantha Caporal Del; Franek, Ondrej; Pedersen, Gert F. Published
describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves;
 1 Sound-Detailed Study Study Design 2009 2012 Unit 4 Detailed Study: Sound describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves; analyse sound using wavelength, frequency and speed
1 Sound-Detailed Study Study Design 2009 2012 Unit 4 Detailed Study: Sound describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves; analyse sound using wavelength, frequency and speed
Operational modal analysis applied to a horizontal washing machine: A comparative approach Sichani, Mahdi Teimouri; Mahjoob, Mohammad J.
 Aalborg Universitet Operational modal analysis applied to a horizontal washing machine: A comparative approach Sichani, Mahdi Teimouri; Mahjoob, Mohammad J. Publication date: 27 Document Version Publisher's
Aalborg Universitet Operational modal analysis applied to a horizontal washing machine: A comparative approach Sichani, Mahdi Teimouri; Mahjoob, Mohammad J. Publication date: 27 Document Version Publisher's
A Tutorial on Acoustical Transducers: Microphones and Loudspeakers
 A Tutorial on Acoustical Transducers: Microphones and Loudspeakers Robert C. Maher Montana State University EELE 217 Science of Sound Spring 2012 Test Sound Outline Introduction: What is sound? Microphones
A Tutorial on Acoustical Transducers: Microphones and Loudspeakers Robert C. Maher Montana State University EELE 217 Science of Sound Spring 2012 Test Sound Outline Introduction: What is sound? Microphones
What applications is a cardioid subwoofer configuration appropriate for?
 SETTING UP A CARDIOID SUBWOOFER SYSTEM Joan La Roda DAS Audio, Engineering Department. Introduction In general, we say that a speaker, or a group of speakers, radiates with a cardioid pattern when it radiates
SETTING UP A CARDIOID SUBWOOFER SYSTEM Joan La Roda DAS Audio, Engineering Department. Introduction In general, we say that a speaker, or a group of speakers, radiates with a cardioid pattern when it radiates
A Switchable 3D-Coverage Phased Array Antenna Package for 5G Mobile Terminals Parchin, Naser Ojaroudi; Shen, Ming; Zhang, Shuai; Pedersen, Gert F.
 Aalborg Universitet A Switchable 3D-Coverage Phased Array Antenna Package for 5G Mobile Terminals Parchin, Naser Ojaroudi; Shen, Ming; Zhang, Shuai; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: I E E E Antennas and
Aalborg Universitet A Switchable 3D-Coverage Phased Array Antenna Package for 5G Mobile Terminals Parchin, Naser Ojaroudi; Shen, Ming; Zhang, Shuai; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: I E E E Antennas and
Published in: IECON 2016: The 42nd Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics Society
 Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: marts 11, 219 Aalborg Universitet Harmonic Damping in DG-Penetrated Distribution Network Lu, Jinghang; Savaghebi, Mehdi; Guerrero, Josep M. Published in: IECON 216: The 42nd
Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: marts 11, 219 Aalborg Universitet Harmonic Damping in DG-Penetrated Distribution Network Lu, Jinghang; Savaghebi, Mehdi; Guerrero, Josep M. Published in: IECON 216: The 42nd
Self-Resonant Electrically Small Loop Antennas for Hearing-Aids Application
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 5, 218 Self-Resonant Electrically Small Loop Antennas for Hearing-Aids Application Zhang, Jiaying; Breinbjerg, Olav Published in: EuCAP 21 Publication date: 21 Link
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 5, 218 Self-Resonant Electrically Small Loop Antennas for Hearing-Aids Application Zhang, Jiaying; Breinbjerg, Olav Published in: EuCAP 21 Publication date: 21 Link
PanPhonics Panels in Active Control of Sound
 PanPhonics White Paper PanPhonics Panels in Active Control of Sound Seppo Uosukainen VTT Building and Transport Contents Introduction... 1 Active control of sound... 1 Interference... 2 Control system...
PanPhonics White Paper PanPhonics Panels in Active Control of Sound Seppo Uosukainen VTT Building and Transport Contents Introduction... 1 Active control of sound... 1 Interference... 2 Control system...
ViRAY. with DDP Dual Diaphragm Planar-wave-driver Technology. Compact 3-way symmetrical line array system. DDP Technology
 1 1 with DDP Dual Diaphragm Planar-wave-driver Technology Whether it s for live touring applications or high-end fixed installations, has been created to surpass and excite the needs of both user and listener
1 1 with DDP Dual Diaphragm Planar-wave-driver Technology Whether it s for live touring applications or high-end fixed installations, has been created to surpass and excite the needs of both user and listener
Technique for the Derivation of Wide Band Room Impulse Response
 Technique for the Derivation of Wide Band Room Impulse Response PACS Reference: 43.55 Behler, Gottfried K.; Müller, Swen Institute on Technical Acoustics, RWTH, Technical University of Aachen Templergraben
Technique for the Derivation of Wide Band Room Impulse Response PACS Reference: 43.55 Behler, Gottfried K.; Müller, Swen Institute on Technical Acoustics, RWTH, Technical University of Aachen Templergraben
Modeling Diffraction of an Edge Between Surfaces with Different Materials
 Modeling Diffraction of an Edge Between Surfaces with Different Materials Tapio Lokki, Ville Pulkki Helsinki University of Technology Telecommunications Software and Multimedia Laboratory P.O.Box 5400,
Modeling Diffraction of an Edge Between Surfaces with Different Materials Tapio Lokki, Ville Pulkki Helsinki University of Technology Telecommunications Software and Multimedia Laboratory P.O.Box 5400,
Case study for voice amplification in a highly absorptive conference room using negative absorption tuning by the YAMAHA Active Field Control system
 Case study for voice amplification in a highly absorptive conference room using negative absorption tuning by the YAMAHA Active Field Control system Takayuki Watanabe Yamaha Commercial Audio Systems, Inc.
Case study for voice amplification in a highly absorptive conference room using negative absorption tuning by the YAMAHA Active Field Control system Takayuki Watanabe Yamaha Commercial Audio Systems, Inc.
SOUND FIELD MEASUREMENTS INSIDE A REVERBERANT ROOM BY MEANS OF A NEW 3D METHOD AND COMPARISON WITH FEM MODEL
 SOUND FIELD MEASUREMENTS INSIDE A REVERBERANT ROOM BY MEANS OF A NEW 3D METHOD AND COMPARISON WITH FEM MODEL P. Guidorzi a, F. Pompoli b, P. Bonfiglio b, M. Garai a a Department of Industrial Engineering
SOUND FIELD MEASUREMENTS INSIDE A REVERBERANT ROOM BY MEANS OF A NEW 3D METHOD AND COMPARISON WITH FEM MODEL P. Guidorzi a, F. Pompoli b, P. Bonfiglio b, M. Garai a a Department of Industrial Engineering
DESIGN OF VOICE ALARM SYSTEMS FOR TRAFFIC TUNNELS: OPTIMISATION OF SPEECH INTELLIGIBILITY
 DESIGN OF VOICE ALARM SYSTEMS FOR TRAFFIC TUNNELS: OPTIMISATION OF SPEECH INTELLIGIBILITY Dr.ir. Evert Start Duran Audio BV, Zaltbommel, The Netherlands The design and optimisation of voice alarm (VA)
DESIGN OF VOICE ALARM SYSTEMS FOR TRAFFIC TUNNELS: OPTIMISATION OF SPEECH INTELLIGIBILITY Dr.ir. Evert Start Duran Audio BV, Zaltbommel, The Netherlands The design and optimisation of voice alarm (VA)
Gamut launch M inent Series in the UK
 PRESS RELEASE for immediate attention April 2012 Press contact: David Denyer 07976 646 404 david@ddpr.co.uk Gamut launch M inent Series in the UK The newest addition to the Gamut portfolio is the M inent
PRESS RELEASE for immediate attention April 2012 Press contact: David Denyer 07976 646 404 david@ddpr.co.uk Gamut launch M inent Series in the UK The newest addition to the Gamut portfolio is the M inent
SIA Software Company, Inc.
 SIA Software Company, Inc. One Main Street Whitinsville, MA 01588 USA SIA-Smaart Pro Real Time and Analysis Module Case Study #2: Critical Listening Room Home Theater by Sam Berkow, SIA Acoustics / SIA
SIA Software Company, Inc. One Main Street Whitinsville, MA 01588 USA SIA-Smaart Pro Real Time and Analysis Module Case Study #2: Critical Listening Room Home Theater by Sam Berkow, SIA Acoustics / SIA
Finger Ring Phased Antenna Array for 5G IoT and Sensor Networks at 28 GHz Syrytsin, Igor A.; Zhang, Shuai; Pedersen, Gert F.
 Aalborg Universitet Finger Ring Phased Antenna Array for 5G IoT and Sensor Networks at 28 GHz Syrytsin, Igor A.; Zhang, Shuai; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: 12th European Conference on Antenna and Propagation
Aalborg Universitet Finger Ring Phased Antenna Array for 5G IoT and Sensor Networks at 28 GHz Syrytsin, Igor A.; Zhang, Shuai; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: 12th European Conference on Antenna and Propagation
Low-Cost Planar MM-Wave Phased Array Antenna for Use in Mobile Satellite (MSAT) Platforms Parchin, Naser Ojaroudi; Shen, Ming; Pedersen, Gert F.
 Aalborg Universitet Low-Cost Planar MM-Wave Phased Array Antenna for Use in Mobile Satellite (MSAT) Platforms Parchin, Naser Ojaroudi; Shen, Ming; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: 23rd Telecommunications
Aalborg Universitet Low-Cost Planar MM-Wave Phased Array Antenna for Use in Mobile Satellite (MSAT) Platforms Parchin, Naser Ojaroudi; Shen, Ming; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: 23rd Telecommunications
Name: Lab Partner: Section:
 Chapter 11 Wave Phenomena Name: Lab Partner: Section: 11.1 Purpose Wave phenomena using sound waves will be explored in this experiment. Standing waves and beats will be examined. The speed of sound will
Chapter 11 Wave Phenomena Name: Lab Partner: Section: 11.1 Purpose Wave phenomena using sound waves will be explored in this experiment. Standing waves and beats will be examined. The speed of sound will
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Physical Acoustics Session 4aPA: Nonlinear Acoustics I 4aPA8. Radiation
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Physical Acoustics Session 4aPA: Nonlinear Acoustics I 4aPA8. Radiation
Simple Feedback Structure of Active Noise Control in a Duct
 Strojniški vestnik - Journal of Mechanical Engineering 54(28)1, 649-654 Paper received: 6.9.27 UDC 534.83 Paper accepted: 7.7.28 Simple Feedback Structure of Active Noise Control in a Duct Jan Černetič
Strojniški vestnik - Journal of Mechanical Engineering 54(28)1, 649-654 Paper received: 6.9.27 UDC 534.83 Paper accepted: 7.7.28 Simple Feedback Structure of Active Noise Control in a Duct Jan Černetič
New ON/OFF Absorption Technology That Includes Low Frequencies
 Toronto, Canada International Symposium on Room Acoustics 2013 June 9-11 ISRA 2013 New ON/OFF Absorption Technology That Includes Low Frequencies Niels W. Adelman-Larsen (nwl@flexac.com) Flex Acoustics
Toronto, Canada International Symposium on Room Acoustics 2013 June 9-11 ISRA 2013 New ON/OFF Absorption Technology That Includes Low Frequencies Niels W. Adelman-Larsen (nwl@flexac.com) Flex Acoustics
Non resonant slots for wide band 1D scanning arrays
 Non resonant slots for wide band 1D scanning arrays Bruni, S.; Neto, A.; Maci, S.; Gerini, G. Published in: Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, 3-8 July 2005,
Non resonant slots for wide band 1D scanning arrays Bruni, S.; Neto, A.; Maci, S.; Gerini, G. Published in: Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, 3-8 July 2005,
Three-dimensional sound field simulation using the immersive auditory display system Sound Cask for stage acoustics
 Stage acoustics: Paper ISMRA2016-34 Three-dimensional sound field simulation using the immersive auditory display system Sound Cask for stage acoustics Kanako Ueno (a), Maori Kobayashi (b), Haruhito Aso
Stage acoustics: Paper ISMRA2016-34 Three-dimensional sound field simulation using the immersive auditory display system Sound Cask for stage acoustics Kanako Ueno (a), Maori Kobayashi (b), Haruhito Aso
High Gain K-Band Patch Antenna for Low Earth Orbit Interlink Between Nanosatellites Squadrito, Paolo; Zhang, Shuai; Pedersen, Gert F.
 Aalborg Universitet High Gain K-Band Patch Antenna for Low Earth Orbit Interlink Between Nanosatellites Squadrito, Paolo; Zhang, Shuai; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: 12th European Conference on Antenna
Aalborg Universitet High Gain K-Band Patch Antenna for Low Earth Orbit Interlink Between Nanosatellites Squadrito, Paolo; Zhang, Shuai; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: 12th European Conference on Antenna
Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 1, 218 Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna Kim, Oleksiy S. Published in: iwat Link to article, DOI: 1.119/IWAT.21.546485 Publication date: 21
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 1, 218 Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna Kim, Oleksiy S. Published in: iwat Link to article, DOI: 1.119/IWAT.21.546485 Publication date: 21
Holographic Measurement of the 3D Sound Field using Near-Field Scanning by Dave Logan, Wolfgang Klippel, Christian Bellmann, Daniel Knobloch
 Holographic Measurement of the 3D Sound Field using Near-Field Scanning 2015 by Dave Logan, Wolfgang Klippel, Christian Bellmann, Daniel Knobloch KLIPPEL, WARKWYN: Near field scanning, 1 AGENDA 1. Pros
Holographic Measurement of the 3D Sound Field using Near-Field Scanning 2015 by Dave Logan, Wolfgang Klippel, Christian Bellmann, Daniel Knobloch KLIPPEL, WARKWYN: Near field scanning, 1 AGENDA 1. Pros
LINE ARRAY Q&A ABOUT LINE ARRAYS. Question: Why Line Arrays?
 Question: Why Line Arrays? First, what s the goal with any quality sound system? To provide well-defined, full-frequency coverage as consistently as possible from seat to seat. However, traditional speaker
Question: Why Line Arrays? First, what s the goal with any quality sound system? To provide well-defined, full-frequency coverage as consistently as possible from seat to seat. However, traditional speaker
An Optimized Version of a New Absolute Linear Encoder Dedicated to Intelligent Transportation Systems
 Aalborg Universitet An Optimized Version of a New Absolute Linear Encoder Dedicated to Intelligent Transportation Systems Argeseanu, Alin; Ritchie, Andrew Ewen; Leban, Krisztina Monika Published in: Proceedings
Aalborg Universitet An Optimized Version of a New Absolute Linear Encoder Dedicated to Intelligent Transportation Systems Argeseanu, Alin; Ritchie, Andrew Ewen; Leban, Krisztina Monika Published in: Proceedings
The Naim Balanced Mode Radiator The Naim Ovator Bass Driver
 1 The Naim Balanced Mode Radiator The Naim Ovator Bass Driver Lampos Ferekidis & Karl-Heinz Fink Fink Audio Consulting on behalf of Naim Audio Southampton Road, Salisbury SP1 2LN, ENGLAND The Balanced
1 The Naim Balanced Mode Radiator The Naim Ovator Bass Driver Lampos Ferekidis & Karl-Heinz Fink Fink Audio Consulting on behalf of Naim Audio Southampton Road, Salisbury SP1 2LN, ENGLAND The Balanced
Subwoofers UNDSTREAM. i. - I. \ INSTALLATION GUIDE. T E C H Iv 0 L,O G I E S
 Subwoofers UNDSTREAM T E C H N 0 L 0 G i E S SOUNDSTREAM TECHNOLOGIES 120 Blue Ravine Road Folsom California 95630 USA tel 916.351.I 288 fax 916.351.0414 (REV A, 7/22/97) ) OWNER S I t. 1 i. - I. \ b MANUAL
Subwoofers UNDSTREAM T E C H N 0 L 0 G i E S SOUNDSTREAM TECHNOLOGIES 120 Blue Ravine Road Folsom California 95630 USA tel 916.351.I 288 fax 916.351.0414 (REV A, 7/22/97) ) OWNER S I t. 1 i. - I. \ b MANUAL
PROFESSIONAL. EdgeMax EM90 and EM180 In-Ceiling Loudspeakers. Design Guide
 PROFESSIONAL EdgeMax and In-Ceiling Loudspeakers Design Guide Contents EdgeMax Loudspeaker Overview. 3 Comparison of In-Ceiling and Surface Mounted Loudspeaker Performance. 3 EdgeMax Loudspeaker Performance.
PROFESSIONAL EdgeMax and In-Ceiling Loudspeakers Design Guide Contents EdgeMax Loudspeaker Overview. 3 Comparison of In-Ceiling and Surface Mounted Loudspeaker Performance. 3 EdgeMax Loudspeaker Performance.
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Architectural Acoustics Session 2pAAa: Adapting, Enhancing, and Fictionalizing
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Architectural Acoustics Session 2pAAa: Adapting, Enhancing, and Fictionalizing
New transducer technology A.R.T. = Accelerated Ribbon Technology - evolution of the air motion transformer principle
 106. AES Convention Munich 1999 Klaus Heinz Berlin New transducer technology A.R.T. = Accelerated Ribbon Technology - evolution of the air motion transformer principle Abstract The paper describes new
106. AES Convention Munich 1999 Klaus Heinz Berlin New transducer technology A.R.T. = Accelerated Ribbon Technology - evolution of the air motion transformer principle Abstract The paper describes new
JBL Professional Application Note. Loudspeaker Array Low-Frequency Pattern Control using Filtered Array Technology
 JBL Professional Application Note Loudspeaker Array Low-Frequency Pattern Control using Filtered Array Technology 1: Overview Array directivity control theory is not new. Olson s Acoustical Engineering
JBL Professional Application Note Loudspeaker Array Low-Frequency Pattern Control using Filtered Array Technology 1: Overview Array directivity control theory is not new. Olson s Acoustical Engineering
Lecture Summary Chapter 2 Summation
 Lecture Summary Chapter 2 Summation stable summation criteria o matched origin o may have unlimited multiple inputs o may arrive from different directions o must have significant overlap duration adding
Lecture Summary Chapter 2 Summation stable summation criteria o matched origin o may have unlimited multiple inputs o may arrive from different directions o must have significant overlap duration adding
Assessment of active electroacoustic absorbers as low-frequency modal dampers in rooms
 Assessment of active electroacoustic absorbers as low-frequency modal dampers in rooms Hervé Lissek a) Romain Boulandet b) Etienne Rivet c) Iris Rigas d) Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, EPFL
Assessment of active electroacoustic absorbers as low-frequency modal dampers in rooms Hervé Lissek a) Romain Boulandet b) Etienne Rivet c) Iris Rigas d) Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, EPFL
Active control for adaptive sound zones in passenger train compartments
 Active control for adaptive sound zones in passenger train compartments Claes Rutger Kastby Master of Science Thesis Stockholm, Sweden 2013 Active control for adaptive sound zones in passenger train compartments
Active control for adaptive sound zones in passenger train compartments Claes Rutger Kastby Master of Science Thesis Stockholm, Sweden 2013 Active control for adaptive sound zones in passenger train compartments
Resonances in Collection Grids of Offshore Wind Farms
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Resonances in Collection Grids of Offshore Wind Farms Holdyk, Andrzej Publication date: 2013 Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Holdyk, A. (2013). Resonances
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Resonances in Collection Grids of Offshore Wind Farms Holdyk, Andrzej Publication date: 2013 Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Holdyk, A. (2013). Resonances
Aalborg Universitet. Linderum Electricity Quality - Measurements and Analysis Silva, Filipe Miguel Faria da; Bak, Claus Leth. Publication date: 2013
 Aalborg Universitet Linderum Electricity Quality - Measurements and Analysis Silva, Filipe Miguel Faria da; Bak, Claus Leth Publication date: 3 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of
Aalborg Universitet Linderum Electricity Quality - Measurements and Analysis Silva, Filipe Miguel Faria da; Bak, Claus Leth Publication date: 3 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of
The study on the woofer speaker characteristics due to design parameters
 The study on the woofer speaker characteristics due to design parameters Byoung-sam Kim 1 ; Jin-young Park 2 ; Xu Yang 3 ; Tae-keun Lee 4 ; Hongtu Sun 5 1 Wonkwang University, South Korea 2 Wonkwang University,
The study on the woofer speaker characteristics due to design parameters Byoung-sam Kim 1 ; Jin-young Park 2 ; Xu Yang 3 ; Tae-keun Lee 4 ; Hongtu Sun 5 1 Wonkwang University, South Korea 2 Wonkwang University,
Constant Power Point Source Array VHD5.0
 Constant Power Point Source Array VHD5.0 Constant Power Point Source Array VHD5.0 Product Overview video VHD5.0 Introduction VHD5.0 - Mid High Module VHD8.10 - Low Mid Module SL412 - Downfill VHD5.0 Amplifiers
Constant Power Point Source Array VHD5.0 Constant Power Point Source Array VHD5.0 Product Overview video VHD5.0 Introduction VHD5.0 - Mid High Module VHD8.10 - Low Mid Module SL412 - Downfill VHD5.0 Amplifiers
XLS Subwoofer Application note for Peerless XLS 10" subwoofer drive units
 XLS Subwoofer Application note for Peerless XLS 10" subwoofer drive units Introduction: The following is an application note of how to use the Peerless XLS family of subwoofer drive units. The application
XLS Subwoofer Application note for Peerless XLS 10" subwoofer drive units Introduction: The following is an application note of how to use the Peerless XLS family of subwoofer drive units. The application
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP) Publication date: 2017
 Aalborg Universitet Combining and Ground Plane Tuning to Efficiently Cover Tv White Spaces on Handsets Barrio, Samantha Caporal Del; Hejselbæk, Johannes; Morris, Art; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: 2017
Aalborg Universitet Combining and Ground Plane Tuning to Efficiently Cover Tv White Spaces on Handsets Barrio, Samantha Caporal Del; Hejselbæk, Johannes; Morris, Art; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: 2017
Technical Note Vol. 1, No. 10 Use Of The 46120K, 4671 OK, And 4660 Systems in Fixed instaiiation Sound Reinforcement
 Technical Note Vol. 1, No. 10 Use Of The 46120K, 4671 OK, And 4660 Systems in Fixed instaiiation Sound Reinforcement Introduction: For many small and medium scale sound reinforcement applications, preassembled
Technical Note Vol. 1, No. 10 Use Of The 46120K, 4671 OK, And 4660 Systems in Fixed instaiiation Sound Reinforcement Introduction: For many small and medium scale sound reinforcement applications, preassembled
ArrayCalc simulation software V8 ArrayProcessing feature, technical white paper
 ArrayProcessing feature, technical white paper Contents 1. Introduction.... 3 2. ArrayCalc simulation software... 3 3. ArrayProcessing... 3 3.1 Motivation and benefits... 4 Spectral differences in audience
ArrayProcessing feature, technical white paper Contents 1. Introduction.... 3 2. ArrayCalc simulation software... 3 3. ArrayProcessing... 3 3.1 Motivation and benefits... 4 Spectral differences in audience
Acoustic Doppler Effect
 Acoustic Doppler Effect TEP Related Topics Wave propagation, Doppler shift of frequency Principle If an emitter of sound or a detector is set into motion relative to the medium of propagation, the frequency
Acoustic Doppler Effect TEP Related Topics Wave propagation, Doppler shift of frequency Principle If an emitter of sound or a detector is set into motion relative to the medium of propagation, the frequency
Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs
 Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs Gustafsson, Mats Published: 24-- Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gustafsson, M. (24). Broadband
Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs Gustafsson, Mats Published: 24-- Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gustafsson, M. (24). Broadband
a Full Range System Excelsior Audio Design & Services State of the Art Loudspeaker Design for Live Sound Subwoofer Alignment with a Full Range System
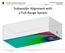 Subwoofer Alignment with a Full Range System 1 Target Response Perfect impulse at time t=0 Impulse Response Magnitude Response (Frequency) ETCResponse (Envelope Time Curve) Phase Response 2 Target Response
Subwoofer Alignment with a Full Range System 1 Target Response Perfect impulse at time t=0 Impulse Response Magnitude Response (Frequency) ETCResponse (Envelope Time Curve) Phase Response 2 Target Response
FIR Filter For Audio Practitioners
 Introduction Electronic correction in the form of Equalization (EQ) is one of the most useful audio tools for loudspeaker compensation/correction, whether it compensates from non linearities in the loudspeaker
Introduction Electronic correction in the form of Equalization (EQ) is one of the most useful audio tools for loudspeaker compensation/correction, whether it compensates from non linearities in the loudspeaker
Tower Mains. A new breed of Main Monitors
 Tower Mains A new breed of Main Monitors / TMS 36 In the search for precision it was decided to apply closed box designs only as they principally allow the best approximation to ideal transient behaviour.
Tower Mains A new breed of Main Monitors / TMS 36 In the search for precision it was decided to apply closed box designs only as they principally allow the best approximation to ideal transient behaviour.
Absorbers & Diffusers
 1 of 8 2/20/2008 12:18 AM Welcome to www.mhsoft.nl, a resource for DIY loudspeaker design and construction. Home Loudspeakers My System Acoustics Links Downloads Ads by Google Foam Absorber Microwave Absorber
1 of 8 2/20/2008 12:18 AM Welcome to www.mhsoft.nl, a resource for DIY loudspeaker design and construction. Home Loudspeakers My System Acoustics Links Downloads Ads by Google Foam Absorber Microwave Absorber
An Enclosure Design for TEBM35C10-4 BMR Loudspeaker Driver
 An Enclosure Design for TEBM35C10-4 BMR Loudspeaker Driver Introduction BMR is a patented loudspeaker technology that delivers true full range audio and wide directivity from a single drive unit. This
An Enclosure Design for TEBM35C10-4 BMR Loudspeaker Driver Introduction BMR is a patented loudspeaker technology that delivers true full range audio and wide directivity from a single drive unit. This
19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 ACOUSTICAL ASPECTS OF THE SAGRADA FAMILIA CHURCH
 19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 ACOUSTICAL ASPECTS OF THE SAGRADA FAMILIA CHURCH PACS: 43.55.Gx Yoshikawa, Shigeru; Narita, Takafumi 1 ; Nishimoto, Yasuko 2 Dept. of
19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 ACOUSTICAL ASPECTS OF THE SAGRADA FAMILIA CHURCH PACS: 43.55.Gx Yoshikawa, Shigeru; Narita, Takafumi 1 ; Nishimoto, Yasuko 2 Dept. of
REVERBERATION CHAMBER FOR EMI TESTING
 1 REVERBERATION CHAMBER FOR EMI TESTING INTRODUCTION EMI Testing 1. Whether a product is intended for military, industrial, commercial or residential use, while it must perform its intended function in
1 REVERBERATION CHAMBER FOR EMI TESTING INTRODUCTION EMI Testing 1. Whether a product is intended for military, industrial, commercial or residential use, while it must perform its intended function in
Sound Waves Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1. (D) It cannot be determined with the given information.
 Sound Waves Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1 Name Multiple Choice 1. Two sound sources S 1 and S 2 produce waves with frequencies 500 Hz and 250 Hz. When we compare the speed of wave 1 to the speed of
Sound Waves Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1 Name Multiple Choice 1. Two sound sources S 1 and S 2 produce waves with frequencies 500 Hz and 250 Hz. When we compare the speed of wave 1 to the speed of
The Mimir. Enclosure and stuffing. Drive units
 The Mimir Named after Mimir, a primal god of Norse mythology who was renowned for his knowledge and wisdom, we present a new high-end two-way speaker kit. The Mimir consist of an 18 cm long throw woofer
The Mimir Named after Mimir, a primal god of Norse mythology who was renowned for his knowledge and wisdom, we present a new high-end two-way speaker kit. The Mimir consist of an 18 cm long throw woofer
 15-8 1/31/2014 PRELAB PROBLEMS 1. Why is the boundary condition of the cavity such that the component of the air displacement χ perpendicular to a wall must vanish at the wall? 2. Show that equation (5)
15-8 1/31/2014 PRELAB PROBLEMS 1. Why is the boundary condition of the cavity such that the component of the air displacement χ perpendicular to a wall must vanish at the wall? 2. Show that equation (5)
Direction-Dependent Physical Modeling of Musical Instruments
 15th International Congress on Acoustics (ICA 95), Trondheim, Norway, June 26-3, 1995 Title of the paper: Direction-Dependent Physical ing of Musical Instruments Authors: Matti Karjalainen 1,3, Jyri Huopaniemi
15th International Congress on Acoustics (ICA 95), Trondheim, Norway, June 26-3, 1995 Title of the paper: Direction-Dependent Physical ing of Musical Instruments Authors: Matti Karjalainen 1,3, Jyri Huopaniemi
Published in: Proceedings of the 29th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, APEC 2014.
 Aalborg Universitet Method for introducing bias magnetization in ungaped cores Aguilar, Andres Revilla; Munk-Nielsen, Stig Published in: Proceedings of the 29th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference
Aalborg Universitet Method for introducing bias magnetization in ungaped cores Aguilar, Andres Revilla; Munk-Nielsen, Stig Published in: Proceedings of the 29th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference
Finding the Prototype for Stereo Loudspeakers
 Finding the Prototype for Stereo Loudspeakers The following presentation slides from the AES 51st Conference on Loudspeakers and Headphones summarize my activities and observations for the design of loudspeakers
Finding the Prototype for Stereo Loudspeakers The following presentation slides from the AES 51st Conference on Loudspeakers and Headphones summarize my activities and observations for the design of loudspeakers
Localization of underwater moving sound source based on time delay estimation using hydrophone array
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Localization of underwater moving sound source based on time delay estimation using hydrophone array To cite this article: S. A. Rahman et al 2016
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Localization of underwater moving sound source based on time delay estimation using hydrophone array To cite this article: S. A. Rahman et al 2016
