Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion
|
|
|
- Patrick Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion Motion perception occurs (a) when a stationary observer perceives moving stimuli, such as this couple crossing the street; and (b) when a moving observer, like this basketball player, perceives moving stimuli, such as the other players on the court. Figure 8-1 p176 Functions of Movement Perception Motion provides information about what is going on and where we are moving. Survival in the environment Predators use movement of prey as a primary means of location in hunting Attentional capture - motion attracts attention to the moving object. While trying to find your friend in a crowd, you have no idea where to look. But you suddenly see a person waving and recognize that it is your friend. As you are having a conversation, your attention may suddenly be captured by something moving in your peripheral vision. Thus if prey remains motionless, it is less likely to be noticed. Heider and Simmel (1944) showed a 2 and a halfminute animated film to subjects and asked them to describe what was happening in the movie. The movie consisted of a house and three characters The objects moved in various ways, going in and out of the house and sometimes interacting with each other. The nature of the movements led subjects to make up stories that often described the objects as having feelings, motivations, and personalities. Figure 8-2 p176 1
2 3/23/16 Functions of Movement Perception continued Functions of Movement Perception Akinetopsia blindness to motion. Perceiving objects and events Lesions in the posterior side of visual cortex ( v=b47js1mtt4w) Made it difficult for a person to pour tea or coffee into a cup because the liquid appeared frozen, so she couldn t perceive the fluid rising in the cup and had trouble knowing when to stop pouring. People suddenly appeared or disappeared, because she couldn t see them approaching. Crossing the street presented serious problems because at first a car might seem far away, but then suddenly, without warning, it would appear very near. Movement of objects or the observer s movement through objects assists in organization of stimuli Motion of an object can reveal characteristics of the object that might not be obvious from a single, stationary view. An example of how movement enhances the perception of form. See the VL. Moving around this horse reveals its true shape. The bird becomes camouflaged when the random lines are superimposed on it. When the bird is moved relative to the lines, it becomes visible. Figure 8-3 p177 Figure 8-4 p178 2
3 Studying Motion Perception Apparent motion (a) between two dots when they are flashed one after the other. When do we perceive motion? Obvious answer: Real motion - an object is physically moving. There are also a number of ways to produce the perception of motion that involve stimuli that are not moving! Illusory motion (there is no actual/real motion) Apparent movement - stationary stimuli are presented in slightly different locations. simply dots flashing on and off. Figure 8-5 p179 Studying Motion Perception The other illusory motion is Induced motion - movement of one object results in the perception of movement in another object. E.g. the moon usually appears stationary in the sky. However, if clouds are moving past the moon on a windy night, the moon may appear to be racing through the clouds. induced/ Studying Motion Perception - continued Motion aftereffect Observer looks at movement of object for 30 to 60 seconds. Then observer looks at a stationary object. Movement appears to occur in the opposite direction from the original movement. The waterfall illusion is an example of this. 3
4 (a) Observation of motion in one direction, such as occurs when viewing a waterfall, can cause (b) the perception of motion in the opposite direction, indicated by the arrows, when viewing stationary objects in the environment. Comparison of Real and Apparent Motion Experiment by Larsen et al. (2006). Participant is scanned by an fmri while viewing three displays Control condition - two dots in different positions are flashed simultaneously. Real motion - a small dot is moved back and forth. Apparent motion - dots are flashed one after another so they appear to move. Figure 8-6 p179 See at VL. The activation associated with apparent motion is similar to the activation for the real motion display. Comparison of Real and Apparent Motion - continued Results showed that Control condition - each dot activated a separate area of visual cortex Apparent and real motion - activation of visual cortex from both sets of stimuli was similar Thus the perception of motion in both cases is related to the same brain mechanism. In (c), the brain is activated in the space that represents the area between the two dots, where movement was perceived but no stimuli were present. Figure 8-7 p180 4
5 What We Want to Explain An object moves, and the observer is stationary. Movement creates an image that moves on the observer s retina. An object moves, and the observer follows the object with his or her eyes. Movement is tracked so that the image is stationary on the retina. What We Want to Explain - continued An observer moves through a stationary environment. Image of environment moves across retina but environment is perceived as stationary. There is motion across the retina but no perception that objects are moving What mechanism explains all three situations? Motion Perception: Information in the Environment Motion perception can t be explained by considering just what is happening on the retina. One solution comes from Ecological approach (by Gibson) The info is located not on the retina, rather information is directly available in the environment for perception. Optic array - structure created by surfaces, textures, and contours, which change as the observer moves through the environment. Figure 8-8 p181 5
6 Motion Perception: Information in the Environment - continued Local disturbance in the optic array Portions of the optic array become covered as he walks and then are uncovered as he moves on. The man covering and uncovering the stationary background (8.8.a). This provides information that the man is moving relative to the environment. The fact that everything moves at once in response to movement of the observer s eyes or body is called global optic flow; this signals that the environment is stationary. Indicates that observer is moving and not the environment. (8.8.c) Motion Perception: Retina/Eye Information Corollary discharge theory takes eye movements into account. movement perception depends on three signals Image displacement signal (IDS) - movement of image stimulating receptors across the retina Motor signal (MS) - signal sent to eyes to move eye muscles Corollary discharge signal (CDS) - When a motor signal (MS) to move the eyes is sent to the eye muscles, so the eye can follow a moving object, there is a corollary discharge signal (CDS). Motion Perception: Retina/Eye Information When Maria keeps her eyes stationary and Jeremy s image moves across her retina, only an IDS occurs. Corollary discharge theory The visual system takes into account both information about stimulation of the receptors and information about movement of the eyes. Maria moves her eyes to follow Jeremy so Jeremy s image doesn t move across her retina, only a CDS occurs. Figure 8-10 p183 6
7 Motion Perception: Retina/Eye Information - continued Movement is perceived when comparator receives input from: corollary discharge signal. image displacement signal. Movement is not perceived when comparator (brain contains a structure or mechanism) receives input from: both corollary discharge and image displacement signals at the same time. When only one type of signal, either the IDS or the CDS, is sent to the brain, motion is perceived. if both a CDS and an IDS reach the comparator simultaneously, they cancel each other, so no signals are sent to the brain and no motion is perceived. Figure 8-11 p184 Behavioral Evidence for Corollary Discharge Theory Creating a perception of motion even though there is no motion across the retina. Pick a point in the environment and keep looking at it while very gently pushing back and forth on the side of your eyelid. Physiological Evidence for Corollary Discharge Theory Damage to the medial superior temporal area in humans leads to perception of movement of stationary environment with movement of eyes. As the person moved his eyes, the stationary environment appeared to move with a velocity that matched the velocity with which he was moving his eyes. Real-movement neurons found in monkeys that respond only when a stimulus moves and do not respond when eyes move. 7
8 the extrastriate cortex of a monkey. Motion Perception in the Brain MT (medial temporal) cortex is specialized for processing information about motion. Coherence: the degree to which the dots move in the same direction. (a) The neuron fires when the bar moves to the left across the receptive field. (b) The neuron doesn t fire when the eye moves to the right even though this also causes the bar to move across the receptive field. Figure 8-15 p185 Motion Perception in the Brain Newsome and coworkers used these moving dot stimuli to determine the relationship between (1) a monkey s ability to judge the direction in which dots were moving and (2) the response of a neuron in the monkey s MT cortex. Measuring the relationship between physiological responding and perception. Presenting a stimulus and determining whether motion is perceived. Coherence of movement of dot patterns was varied. Monkeys were taught to judge direction of dot movement and measurements were taken from MT neurons. Results: As the dots coherence increased; (1) the monkey judged the direction of motion more accurately, and (2) the MT neuron fired more rapidly. Presenting a movement stimulus and measuring neural responding Figure 8-17 p187 8
9 Effect of Lesioning and Microstimulation That experiments showed that MT cortex is important for motion perception. On the other hand, it is important to show how the perception of motion is affected by (1) lesioning (destroying or deactivating) some or all of the MT cortex or (2) electrically stimulating neurons in the MT cortex. Motion Perception in the Brain - continued - continued Lesioning experiment by Newsome and Paré Normal monkeys can detect motion with coherence of 1 or 2%. Monkeys with lesions in MT cortex cannot detect motion until the coherence is 10 to 20%. Effect of Lesioning and Microstimulation Microstimulation experiment by Movshon and Newsome (1992) Monkey trained to indicate direction of fields of moving dots. Neurons in MT cortex that respond to specific direction were activated. Remember: Neurons are organized in columns in the cortex, with neurons in the same column responding best to one orientation. Experimenter used microstimulation to activate different direction sensitive neurons. Monkey shifted judgment to the artificially stimulated direction. (a) A monkey judges the motion of dots moving horizontally to the right. (b) When a column of neurons that prefer downward motion is stimulated, the monkey judges the same motion as being downward and to the right. Figure 8-18 p188 9
10 Effect of Lesioning and Microstimulation In addition to the MT cortex, medial superior temporal (MST) area is the other one involved in motion perception. Motion for a single Neuron s Point of View Complex cortical cells respond preferentially to an oriented bar moving in a specific direction. Aperture problem - observation of small portion of larger stimulus leads to misleading information about direction of movement Activity of a single complex cell does not provide accurate information about direction of movement. The pole s overall motion is horizontally to the right (blue arrows). The ellipse represents the area in an observer s field of view that corresponds to the receptive field of a cortical neuron on the observer s retina. The pole s motion across the receptive field is also horizontal to the right (red arrows). Figure 8-19 p188 What happens if the woman climbs some steps? As she walks up the steps, she and the pole are now moving up and to the right (blue arrow). But the neuron, which only sees movement through the narrow view of its receptive field, only receives information about the rightward movement. (red arrows) Figure 8-20 p189 10
11 Moving a pencil behind an aperture Make a small aperture, about 1 inch in diameter, by creating a circle with the fingers of your left hand. Then orient a pencil vertically, and move the pencil from left to right behind the circle. As you do this, focus on the direction that the front edge of the pencil appears to be moving across the aperture. Now, again holding the pencil vertically, position the pencil below the circle, and move it up behind the aperture at a 45-degree angle. Again, notice the direction in which the front edge of the pencil appears to be moving across the aperture. Figure 8-21 p189 When you moved the pencil so that you could see its tip moving through the aperture, you could tell that the pencil was moving up. Thus, When the pencil is moved up and to the right, movement of the tip of the pencil provides information indicating that the pencil is moving up and to the right. See VL. Motion binding Figure 8-22 p190 Motion and the Human Body Motion and the Human Body Apparent Motion of the Body The pictures were alternated either rapidly or more slowly. See the VL. (b) When alternated rapidly, observers perceived the hand as moving through the head. (c) When alternated more slowly, the hand was seen as moving around the head. 2 conclusions: The visual system needs time to process information in order to perceive the movement of complex meaningful stimuli; and They suggest that there may be something special about the meaning of the stimulus in this case, the human body that influences the way movement is perceived. 11
12 Motion and the Human Body To find out, Jennifer Stevens and coworkers (2000) measured brain activation using the PET scan technique. They found that both movement through the head and movement around the head activated areas in the parietal cortex associated with movement. However, when the observers saw movement as occurring around the head, the motor cortex was activated as well. Thus, the motor cortex is activated when the perceived movements are humanly possible but isn t activated when the perceived movements are not possible. Motion and the Human Body Point-light walker stimulus - biological motion made by placing lights in specific places on a person. walks in the dark so only the lights can be seen. This self- produced motion of a person or other living organism is called biological motion. (see VL.) Motion and the Human Body Neurological studies show biological motion is processed by superior temporal sulcus (STS) and fusiform face area (FFA). They measured observers brain activity as they viewed the moving dots created by a point-light walker (Figure 8.25a) and as they viewed dots that moved similarly to the pointlight walker dots, but were scrambled so they did not result in the impression of a person walking (Figure 8.25b). They found STS and FFA activation. Figure 8-25 p192 12
13 Motion and the Human Body - continued Grossman et al. Participants viewed point-light stimuli for activities. Task was to determine whether motion was biological or scrambled. Noise was added to dots so they could only achieve 71% accuracy. Transcranial magnetic stimulation applied to STS caused a decrease in ability to detect biological motion. The disrupting operation of the STS in humans decreases the ability to perceive biological motion Figure 8-26 p192 Motion and the Human Body - continued (a) Biological motion stimulus. (b) Scrambled stimulus. (c) Biological motion stimulus with noise added. The dots corresponding to the walker are indicated by lines (which were not seen by the observer). (d) How the stimulus appears to the observer. Magnetic stimulation of other motion-sensitive areas, such as the MT cortex, had no effect on the perception of biological motion. From this result, Grossman concluded that normal functioning of the biological motion area, STS, is necessary for perceiving biological motion. This conclusion is also supported by studies showing that people who have suffered damage to this area have trouble perceiving biological motion Biological motion is more than just motion Figure 8-27 p193 13
PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8
 Motion 1 Perception (PSY 4204) Christine L. Ruva, Ph.D. PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8 Overview of Questions Why do some animals freeze in place when they sense danger? How do films create movement from still
Motion 1 Perception (PSY 4204) Christine L. Ruva, Ph.D. PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8 Overview of Questions Why do some animals freeze in place when they sense danger? How do films create movement from still
Vision V Perceiving Movement
 Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement
 Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
PERCEIVING MOVEMENT. Ways to create movement
 PERCEIVING MOVEMENT Ways to create movement Perception More than one ways to create the sense of movement Real movement is only one of them Slide 2 Important for survival Animals become still when they
PERCEIVING MOVEMENT Ways to create movement Perception More than one ways to create the sense of movement Real movement is only one of them Slide 2 Important for survival Animals become still when they
7Motion Perception. 7 Motion Perception. 7 Computation of Visual Motion. Chapter 7
 7Motion Perception Chapter 7 7 Motion Perception Computation of Visual Motion Eye Movements Using Motion Information The Man Who Couldn t See Motion 7 Computation of Visual Motion How would you build a
7Motion Perception Chapter 7 7 Motion Perception Computation of Visual Motion Eye Movements Using Motion Information The Man Who Couldn t See Motion 7 Computation of Visual Motion How would you build a
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception
 COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 9: Motion perception Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 9: Motion perception Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
Vision: Motion perception
 Vision: Motion perception Velocity detection thresholds Without background: 10-20 minutes of angular velocity per second (a minute is 1/60 th of a degree) (the motion in this display is much faster than
Vision: Motion perception Velocity detection thresholds Without background: 10-20 minutes of angular velocity per second (a minute is 1/60 th of a degree) (the motion in this display is much faster than
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION. Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh
 B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
What you see is not what you get. Grade Level: 3-12 Presentation time: minutes, depending on which activities are chosen
 Optical Illusions What you see is not what you get The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to basic principles of visual processing. Much of the lesson revolves around the use of visual illusions
Optical Illusions What you see is not what you get The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to basic principles of visual processing. Much of the lesson revolves around the use of visual illusions
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2)
 Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
Object Perception. 23 August PSY Object & Scene 1
 Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Motion perception PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 24. Aperture problem
 Motion perception PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 24 How do you see motion here? Aperture problem A detector that only sees part of a scene cannot precisely identify the motion direction or speed of an edge
Motion perception PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 24 How do you see motion here? Aperture problem A detector that only sees part of a scene cannot precisely identify the motion direction or speed of an edge
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 3: Visual Perception of Objects
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 3: Visual Perception of Objects www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 What is after V1?... 2 Assembling Simple Features into Objects... 4 Illusory Contours...
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 3: Visual Perception of Objects www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 What is after V1?... 2 Assembling Simple Features into Objects... 4 Illusory Contours...
Lecture 14. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017
 Motion Perception Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 (chap 6 leftovers) Defects in Stereopsis Strabismus eyes not aligned, so diff images fall on
Motion Perception Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 (chap 6 leftovers) Defects in Stereopsis Strabismus eyes not aligned, so diff images fall on
Prof. Greg Francis 5/27/08
 Visual Perception : Motion IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Dr. Francis Lecture 11 Motion Motion is of tremendous importance for survival (Demo) Try to find the hidden bird in the figure below (http://illusionworks.com/hidden.htm)
Visual Perception : Motion IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Dr. Francis Lecture 11 Motion Motion is of tremendous importance for survival (Demo) Try to find the hidden bird in the figure below (http://illusionworks.com/hidden.htm)
Chapter 73. Two-Stroke Apparent Motion. George Mather
 Chapter 73 Two-Stroke Apparent Motion George Mather The Effect One hundred years ago, the Gestalt psychologist Max Wertheimer published the first detailed study of the apparent visual movement seen when
Chapter 73 Two-Stroke Apparent Motion George Mather The Effect One hundred years ago, the Gestalt psychologist Max Wertheimer published the first detailed study of the apparent visual movement seen when
Embodiment illusions via multisensory integration
 Embodiment illusions via multisensory integration COGS160: sensory systems and neural coding presenter: Pradeep Shenoy 1 The illusory hand Botvinnik, Science 2004 2 2 This hand is my hand An illusion of
Embodiment illusions via multisensory integration COGS160: sensory systems and neural coding presenter: Pradeep Shenoy 1 The illusory hand Botvinnik, Science 2004 2 2 This hand is my hand An illusion of
Sensation & Perception
 Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview
 Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight at is the one extent
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight at is the one extent
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
Perceiving Motion and Events
 Perceiving Motion and Events Chienchih Chen Yutian Chen The computational problem of motion space-time diagrams: image structure as it changes over time 1 The computational problem of motion space-time
Perceiving Motion and Events Chienchih Chen Yutian Chen The computational problem of motion space-time diagrams: image structure as it changes over time 1 The computational problem of motion space-time
IN VISION, AS IN OTHER mental operations, we experience
 Chapter 28 Perception of Motion, Depth, and Form 549 28 A Stripes in area 8 Perception of Motion, Depth, and Form lnterblob Blob V2 V The Parvocellular and Magnocellular Pathways Feed nto Two Processing
Chapter 28 Perception of Motion, Depth, and Form 549 28 A Stripes in area 8 Perception of Motion, Depth, and Form lnterblob Blob V2 V The Parvocellular and Magnocellular Pathways Feed nto Two Processing
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
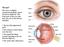 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version
 Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight is one at of the extent five senses of peripheral that
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight is one at of the extent five senses of peripheral that
The visual and oculomotor systems. Peter H. Schiller, year The visual cortex
 The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2006 The visual cortex V1 Anatomical Layout Monkey brain central sulcus Central Sulcus V1 Principalis principalis Arcuate Lunate lunate Figure
The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2006 The visual cortex V1 Anatomical Layout Monkey brain central sulcus Central Sulcus V1 Principalis principalis Arcuate Lunate lunate Figure
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Prof. Greg Francis and the eye PSY 310 Greg Francis The perceptual process Perception Recognition Processing Action Transduction Lecture 03 Why does my daughter look like a demon? Stimulus on receptors
Prof. Greg Francis and the eye PSY 310 Greg Francis The perceptual process Perception Recognition Processing Action Transduction Lecture 03 Why does my daughter look like a demon? Stimulus on receptors
Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 10 Perception Role of Culture in Perception Till now we have
Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 10 Perception Role of Culture in Perception Till now we have
Contents 1 Motion and Depth
 Contents 1 Motion and Depth 5 1.1 Computing Motion.............................. 8 1.2 Experimental Observations of Motion................... 26 1.3 Binocular Depth................................ 36 1.4
Contents 1 Motion and Depth 5 1.1 Computing Motion.............................. 8 1.2 Experimental Observations of Motion................... 26 1.3 Binocular Depth................................ 36 1.4
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction. Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc.
 Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Lecture 5. The Visual Cortex. Cortical Visual Processing
 Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
P rcep e t p i t on n a s a s u n u c n ons n c s ious u s i nf n e f renc n e L ctur u e 4 : Recogni n t i io i n
 Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Vision Basics Measured in:
 Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Perception. How we interpret the information our senses receive. Overview Perception
 Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
the dimensionality of the world Travelling through Space and Time Learning Outcomes Johannes M. Zanker
 Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
Discussion and Application of 3D and 2D Aperture Problems
 Discussion and Application of 3D and 2D Aperture Problems Guang-Dah Chen, National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, Taiwan Yi-Yin Wang, National Yunlin University of Science and Technology,
Discussion and Application of 3D and 2D Aperture Problems Guang-Dah Chen, National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, Taiwan Yi-Yin Wang, National Yunlin University of Science and Technology,
better make it a triple (3 x)
 Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Moon Illusion. (McCready, ; 1. What is Moon Illusion and what it is not
 Moon Illusion (McCready, 1997-2007; http://facstaff.uww.edu/mccreadd/index.html) 1. What is Moon Illusion and what it is not 2. Aparent distance theory (SD only) 3. Visual angle contrast theory (VSD) 4.
Moon Illusion (McCready, 1997-2007; http://facstaff.uww.edu/mccreadd/index.html) 1. What is Moon Illusion and what it is not 2. Aparent distance theory (SD only) 3. Visual angle contrast theory (VSD) 4.
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling
 Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain
 Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning
 Perceived Depth is Enhanced with Parallax Scanning March 1, 1999 Dennis Proffitt & Tom Banton Department of Psychology University of Virginia Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning Background
Perceived Depth is Enhanced with Parallax Scanning March 1, 1999 Dennis Proffitt & Tom Banton Department of Psychology University of Virginia Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning Background
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Learning Targets. Module 19
 Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
The Ecological View of Perception. Lecture 14
 The Ecological View of Perception Lecture 14 1 Ecological View of Perception James J. Gibson (1950, 1966, 1979) Eleanor J. Gibson (1967) Stimulus provides information Perception involves extracting this
The Ecological View of Perception Lecture 14 1 Ecological View of Perception James J. Gibson (1950, 1966, 1979) Eleanor J. Gibson (1967) Stimulus provides information Perception involves extracting this
Refraction of Light. Refraction of Light
 1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
Sensory and Perception. Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague
 Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
The Visual System. Computing and the Brain. Visual Illusions. Give us clues as to how the visual system works
 The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
The Grand Illusion and Petit Illusions
 Bruce Bridgeman The Grand Illusion and Petit Illusions Interactions of Perception and Sensory Coding The Grand Illusion, the experience of a rich phenomenal visual world supported by a poor internal representation
Bruce Bridgeman The Grand Illusion and Petit Illusions Interactions of Perception and Sensory Coding The Grand Illusion, the experience of a rich phenomenal visual world supported by a poor internal representation
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
PSY 214 Lecture # (09/14/2011) (Introduction to Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 4 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 44-54
 Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
Sensation and Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Sensation
 Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays
 The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays Damian Gordon * and David Vernon Department of Computer Science Maynooth College Ireland ABSTRACT
The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays Damian Gordon * and David Vernon Department of Computer Science Maynooth College Ireland ABSTRACT
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
CS510: Image Computation. Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018
 CS510: Image Computation Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018 Class Goals Prepare you to do research in computer vision Provide big picture (comparison to humans) Give you experience reading papers Familiarize
CS510: Image Computation Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018 Class Goals Prepare you to do research in computer vision Provide big picture (comparison to humans) Give you experience reading papers Familiarize
Illusory displacement of equiluminous kinetic edges
 Perception, 1990, volume 19, pages 611-616 Illusory displacement of equiluminous kinetic edges Vilayanur S Ramachandran, Stuart M Anstis Department of Psychology, C-009, University of California at San
Perception, 1990, volume 19, pages 611-616 Illusory displacement of equiluminous kinetic edges Vilayanur S Ramachandran, Stuart M Anstis Department of Psychology, C-009, University of California at San
Sensation and perception
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14
 Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015
 Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015 EXTENDED SUMMARY Lesson #10: Dec. 01 st 2014 Lecture plan: VISUAL ILLUSIONS THE STUDY OF VISUAL
Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015 EXTENDED SUMMARY Lesson #10: Dec. 01 st 2014 Lecture plan: VISUAL ILLUSIONS THE STUDY OF VISUAL
The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery
 Perception, 1999, volume 28, pages 617-621 The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery Jocelyn Faubert, Andrew M Herbert Ecole d'optometrie, Universite de Montreal, CP 6128,
Perception, 1999, volume 28, pages 617-621 The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery Jocelyn Faubert, Andrew M Herbert Ecole d'optometrie, Universite de Montreal, CP 6128,
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Moving in a Fog: Stimulus contrast affects the perceived speed and direction of motion
 Moving in a Fog: Stimulus contrast affects the perceived speed and direction of motion Stuart Anstis Dept of Psychology UCSD 9500 Gilman Drive La Jolla CA 92093-0109 sanstis @ucsd.edu Abstract - Moving
Moving in a Fog: Stimulus contrast affects the perceived speed and direction of motion Stuart Anstis Dept of Psychology UCSD 9500 Gilman Drive La Jolla CA 92093-0109 sanstis @ucsd.edu Abstract - Moving
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Experiments on the locus of induced motion
 Perception & Psychophysics 1977, Vol. 21 (2). 157 161 Experiments on the locus of induced motion JOHN N. BASSILI Scarborough College, University of Toronto, West Hill, Ontario MIC la4, Canada and JAMES
Perception & Psychophysics 1977, Vol. 21 (2). 157 161 Experiments on the locus of induced motion JOHN N. BASSILI Scarborough College, University of Toronto, West Hill, Ontario MIC la4, Canada and JAMES
Optical Illusions and Human Visual System: Can we reveal more? Imaging Science Innovative Student Micro-Grant Proposal 2011
 Optical Illusions and Human Visual System: Can we reveal more? Imaging Science Innovative Student Micro-Grant Proposal 2011 Prepared By: Principal Investigator: Siddharth Khullar 1,4, Ph.D. Candidate (sxk4792@rit.edu)
Optical Illusions and Human Visual System: Can we reveal more? Imaging Science Innovative Student Micro-Grant Proposal 2011 Prepared By: Principal Investigator: Siddharth Khullar 1,4, Ph.D. Candidate (sxk4792@rit.edu)
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
Face Perception. The Thatcher Illusion. The Thatcher Illusion. Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Face Inversion Effect
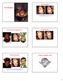 The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang
 A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang Vestibular Responses in Dorsal Visual Stream and Their Role in Heading Perception Recent experiments
A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang Vestibular Responses in Dorsal Visual Stream and Their Role in Heading Perception Recent experiments
Sensation and Perception. Sensation. Sensory Receptors. Sensation. General Properties of Sensory Systems
 Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Vision. Sensation & Perception. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye
 Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Self-motion perception from expanding and contracting optical flows overlapped with binocular disparity
 Vision Research 45 (25) 397 42 Rapid Communication Self-motion perception from expanding and contracting optical flows overlapped with binocular disparity Hiroyuki Ito *, Ikuko Shibata Department of Visual
Vision Research 45 (25) 397 42 Rapid Communication Self-motion perception from expanding and contracting optical flows overlapped with binocular disparity Hiroyuki Ito *, Ikuko Shibata Department of Visual
Touch. Touch & the somatic senses. Josh McDermott May 13,
 The different sensory modalities register different kinds of energy from the environment. Touch Josh McDermott May 13, 2004 9.35 The sense of touch registers mechanical energy. Basic idea: we bump into
The different sensory modalities register different kinds of energy from the environment. Touch Josh McDermott May 13, 2004 9.35 The sense of touch registers mechanical energy. Basic idea: we bump into
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
Maps in the Brain Introduction
 Maps in the Brain Introduction 1 Overview A few words about Maps Cortical Maps: Development and (Re-)Structuring Auditory Maps Visual Maps Place Fields 2 What are Maps I Intuitive Definition: Maps are
Maps in the Brain Introduction 1 Overview A few words about Maps Cortical Maps: Development and (Re-)Structuring Auditory Maps Visual Maps Place Fields 2 What are Maps I Intuitive Definition: Maps are
vertical horizonta fovea Figure by MIT OCW.
 Visual Prosthetics 90 5 4 3 Lunate Sulcus Central Sulcus 2 1 180 0 vertical 270 horizonta 8 7 6 5 fovea 4 3 2 1 V1 Figure by MIT OCW. Present two visual targets Present one visual target and stimulate
Visual Prosthetics 90 5 4 3 Lunate Sulcus Central Sulcus 2 1 180 0 vertical 270 horizonta 8 7 6 5 fovea 4 3 2 1 V1 Figure by MIT OCW. Present two visual targets Present one visual target and stimulate
Putting The Hole Thing Together
 Opt: An Illusionary Tale (GPN # 76) Author: Arline and Joseph Baum Publisher: Viking Children s Books Program Description: How are illusions created? Le- Var helps demystify illusions as he shows how a
Opt: An Illusionary Tale (GPN # 76) Author: Arline and Joseph Baum Publisher: Viking Children s Books Program Description: How are illusions created? Le- Var helps demystify illusions as he shows how a
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I
 DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I 4 Topics to Cover Light and EM Spectrum Visual Perception Structure Of Human Eyes Image Formation on the Eye Brightness Adaptation and
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I 4 Topics to Cover Light and EM Spectrum Visual Perception Structure Of Human Eyes Image Formation on the Eye Brightness Adaptation and
CHAPTER 4. Sensation & Perception. Lecture Overview. Introduction to Sensation & Perception PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY. Understanding Sensation
 CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
CHAPTER. Line and Shape
 CHAPTER 4 Line and Shape Lines are everywhere in the real world. For example, doorways have two vertical lines, and a volleyball has one curved line. The real world is also full of shapes. A door is a
CHAPTER 4 Line and Shape Lines are everywhere in the real world. For example, doorways have two vertical lines, and a volleyball has one curved line. The real world is also full of shapes. A door is a
IOC, Vector sum, and squaring: three different motion effects or one?
 Vision Research 41 (2001) 965 972 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres IOC, Vector sum, and squaring: three different motion effects or one? L. Bowns * School of Psychology, Uni ersity of Nottingham, Uni ersity
Vision Research 41 (2001) 965 972 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres IOC, Vector sum, and squaring: three different motion effects or one? L. Bowns * School of Psychology, Uni ersity of Nottingham, Uni ersity
Color, Vision, & Perception. Outline
 Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1
 The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
Somatosensory Reception. Somatosensory Reception
 Somatosensory Reception Professor Martha Flanders fland001 @ umn.edu 3-125 Jackson Hall Proprioception, Tactile sensation, (pain and temperature) All mechanoreceptors respond to stretch Classified by adaptation
Somatosensory Reception Professor Martha Flanders fland001 @ umn.edu 3-125 Jackson Hall Proprioception, Tactile sensation, (pain and temperature) All mechanoreceptors respond to stretch Classified by adaptation
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Chapter 4 PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
