Perceiving Motion and Events
|
|
|
- Hortense Page
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Perceiving Motion and Events Chienchih Chen Yutian Chen The computational problem of motion space-time diagrams: image structure as it changes over time 1
2 The computational problem of motion space-time diagrams for some simple motion of a single dot p Stationary dot 2. Constant velocity motion 3. Harmonic motion 4. Apparent motion(stroboscopic motion) Continuous Motion An environmental object is considered to be moving if its position changes over time. p469 Motion perception threshold ex. The blades of a window fan The moon The movement of clock hands 2
3 Adaptation and Aftereffects Adaptation Motion Aftereffects o Waterfall illusion o Paradoxical motion o Spiral aftereffect Where are they occurred in the visual system? There are both monocular and binocular components to the motion perception system. Simultaneous Motion Contrast If a stationary path of random dots is surrounded by a field of dots moving steadily downward, the central patch will appear to drift upward. 3
4 Apparent Motion Human visual system can be fooled into perceiving continuous motion from a sequence of "snapshots" or "frames" presented at the proper rate. Early Gestalt Investigations Two lights across a fixed distance turn on and off alternatively from very fast to very slow: p Simultaneous flickering 2. Phi motion 3. Beta motion 4. Sequential alternation 4
5 Korte's laws Korte examined the quality of apparent motion as a function of the relations among three parameters: the alternation rate, the separation between the two points of light, and the intensity of the two lights. Separation vs. intensity: Larger separations require higher intensityes Rate vs. intensity: Slower rates require higher intensities Separation vs. rate: Larger separations require slower rates Motion picture technology 24 frames per second lies squarely within the range that produces beta motion, the most convincing perception of smooth continuous movement A flicker rate of at least 60 times per second is needed for flicker fusion--in which a flickering light appears to be on continuously. Thus, 72 flashes and 24 frames per second to produce good perception of apparent motion. As for TV and videotape, each video frame is effectively presented twice by interlacing the odd- and even- numbered lines of the video image. 30 frames per second. 5
6 The Correspondence Problem of Apparent Motion Motion is perceived between corresponding objects, but which objects are the "corresponding" ones? Wagon wheel illusion 6
7 Do other factors affect correspondence problem? Short-range VS. Long-range Apparent Motion Random-dot Kinematogram Classical phenomena of apparent motion 7
8 Short-range VS. Long-range Apparent Motion Short-range motion system is responsible for performance on Random-dot Kinematogram. And it is thought to occur fairly early in visual processing, before information from the two eyes has been integrated and before shape and color have been extensively analyzed. Long-range motion system is responsible for classical phenomena of apparent motion with large-scale, individual figures. It is thought to occur much later in visual processing, after information from the two eyes has been integrated. The Aperture Problem 8
9 The Barberpole illusion Plaid grating 9
10 Physiological Mechanisms The Magno and Parvo System Cortical Analysis of Motion Neuropsychology of Motion Perception The Magno and Parvo System In comparison to P cells, M cells respond rapidly to changes in stimulation, are highly sensitive to luminance contrast, have large receptive fields, and are low in spatial resolution. M cells are the first step in the visual system's analysis of image motion. 10
11 Cortical Analysis of Motion Selective response to different directions o component cells o pattern cells Neuropsychology of Motion Perception A patient was admitted to the hospital complaining of severe headaches, vertigo, nausea, and the inability to perceive motion. She reported that the world appeared to her as a series of frozen snapshots. Brain image tests indicated that the lesion in her brain was located in the border region between occipital and temporal cortex, clearly outside of primary visual cortex. 11
12 Computational Theories Directionally selective cells play a crucial role in our ability to perceive motion. But, how? Delay-and-Compare Networks 12
13 Edge-Based Models Analyze the change in illumination over time in conjunction with an edge detector Spatial-Frequency-Based Models 13
14 Integrating Local Motion Integrating Local Motion 14
15 next... Object Motion Depth and Motion Long-Range Apparent Motion Dynamic Perceptual Organization Self-Motion and Optic Flow 15
16 Image Motion Vs. Object Motion Image motion must be interpreted to provide information about the motion in environmental objects Image motion + movement of eye, head, body... => motion constancy Velocity Constancy Object speed, rather than image speed Good depth information is needed Adjust speed of moving objects at different depth (Rock, Hill, & Fineman, 1968) 16
17 Depth and Motion When only motion information is present, does the visual system interpret differential motion in terms of depth? Rigid Motion in Depth (Gunnar Johansson 1950) Rigidity heuristic The Kinetic Depth Effect (KDE) Experiment by Wallach and O Connell (1953) Using a shadow-casting technique to present 2-D images of angular 3-D wire objects to observers 17
18 Rigidity Heuristic All else being equal, if there is an interpretation in which rigid motion can be perceived, it will be. Correspondence Problem Unique points, such as vertices and endpoints (but not cross-points), appear to play an important role in the conditions required for veridical perception of rigid motion What if the correspondence problem is solved incorrectly? 18
19 The Stereo-Kinetic Effect Perception of Nonrigid Motion 19
20 Long-Range Apparent Motion Long-range apparent motion is fundamentally a 3-D, object-based perception Experiment by Shepard and Judd (1976) Two sets of displays for picture-plane rotation (A) and 3-D rotation in depth (B) Determine the fastest alternation rate for smooth rigid motion The process underlying apparent rotation is a continuous process that requires time to go through intermediate orientations, just as real objects do. The linear increase was virtually identical for the pairs related by picture-plane rotations and depth rotations. 20
21 Geometrical Model Map object motions to geometrical paths in a high-dimensional space Motion hyperspace Any continuous motion can be represented as a continuous path within the higher-dimensional space. Path impletion The visual system interprets apparent motion by traversing (impleting) one of many possible paths between corresponded points of the two displays. Maximum speed Rigid apparent motion will be perceived if and only if the alternation rate is sufficiently slow that the shortest path along the rigid-rotation surface can be traversed at or below a maximum speed in the time between two displays. Curved Apparent Motion 1. A translation along a straightline path from left to right with a concomitant clockwise rotation about the center of the line minimize the work required to move the object 2. A global rotation about a point below the two lines in which the points on the line follow curved paths minimize motion in kinematical geometry 21
22 Path-guided apparent motion The visual system has internalized the structure of motions in the real world to a remarkable degree Allowing it to fill in the most likely motion in apparent motion displays Dynamic Perceptual Organization What regions are perceived to be part of the same object or group of objects? How do we organize the motions of different objects? How they move with respect to each other? 22
23 Grouping by Movement Common fate: the tendency to group together units that move with the same velocity (direction and speed) Put back two or more parts of a single moving object separated by occluding objects 23
24 Common fate can destroy even the best natural camouflage Configural Motion 24
25 The visual system performs a vector analysis of the motion of objects moving synchronously. Motion vectors are decomposed in to two components: common motion and relative motion Induced Motion The moon is moving through the cloud rather than the cloud passes in front of the moon Karl Duncker (1929/1937) Two assumptions: 1. Sensitivity to relative motion 2. Stationarity of the surrounding object 25
26 Induced self-motion Self-Motion and Optic Flow Two differences between induced self-motion and induced motion 1. The motion of the environment is well above the threshold of absolute motion 2. There is an initial period of veridical perception: You first perceive the drum as rotating and yourself as stationary Perceiving Self-Motion Optic flow: the global patterns of retinal motion Direction 26
27 Speed of Self-Motion Information about absolute speed is not available solely from optic flow absolute distance is not available A A a b B B Time to contact: the length of time it will take the observer to reach the surface toward which he or she is heading under present motion conditions t=distance/speed 27
28 Understanding Events How balls move when one collides with another? How objects behave under gravitational free-fall when dropped from a moving object? Biological Motion Meaningless points when seated motionlessly Perceived as a person immediately and unmistakably when began to move Even walking versus jogging were easly discriminated 28
29 Biological Motion Biological Motion 29
30 Perceiving Causation Launching effect Triggering effect Entraining effect Perceiving Mass Relations Ricochet heuristic: When the incoming ball ricochets at a higher velocity than the forward motion of the initially stationary ball, the stationary ball is heavier than the incoming one Clobbering heuristic: When the stationary ball moves off with high velocity, the incoming ball is heavier than the stationary one The two heuristic conflict when the ricocheting ball moved more slowly than the ball it struck. Thus people appear to be recovering information about mass from visual information, but not with the quantitative precision and sophistication his analysis implied 30
31 Perceiving Mass Relations Intuitive Physics 31
32 Intuitive Physics Intuitive Physics One possibility is that the high-level cognitive system that is responsible for generating solutions to statically stated problems simply does not have access to the perceptual system's expertise in these domains reason: many of the same people who favored the curved trajectory when presented with the static version of the C-tube problem chose the correct, straight trajectory in the dynamic version 32
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION. Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh
 B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
the dimensionality of the world Travelling through Space and Time Learning Outcomes Johannes M. Zanker
 Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
PERCEIVING MOVEMENT. Ways to create movement
 PERCEIVING MOVEMENT Ways to create movement Perception More than one ways to create the sense of movement Real movement is only one of them Slide 2 Important for survival Animals become still when they
PERCEIVING MOVEMENT Ways to create movement Perception More than one ways to create the sense of movement Real movement is only one of them Slide 2 Important for survival Animals become still when they
7Motion Perception. 7 Motion Perception. 7 Computation of Visual Motion. Chapter 7
 7Motion Perception Chapter 7 7 Motion Perception Computation of Visual Motion Eye Movements Using Motion Information The Man Who Couldn t See Motion 7 Computation of Visual Motion How would you build a
7Motion Perception Chapter 7 7 Motion Perception Computation of Visual Motion Eye Movements Using Motion Information The Man Who Couldn t See Motion 7 Computation of Visual Motion How would you build a
Vision V Perceiving Movement
 Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement
 Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision: Motion perception
 Vision: Motion perception Velocity detection thresholds Without background: 10-20 minutes of angular velocity per second (a minute is 1/60 th of a degree) (the motion in this display is much faster than
Vision: Motion perception Velocity detection thresholds Without background: 10-20 minutes of angular velocity per second (a minute is 1/60 th of a degree) (the motion in this display is much faster than
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion
 Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion Motion perception occurs (a) when a stationary observer perceives moving stimuli, such as this couple crossing the street; and (b) when a moving observer, like this basketball
Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion Motion perception occurs (a) when a stationary observer perceives moving stimuli, such as this couple crossing the street; and (b) when a moving observer, like this basketball
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception
 COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 9: Motion perception Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 9: Motion perception Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
Object Perception. 23 August PSY Object & Scene 1
 Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction. Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc.
 Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Lecture 14. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017
 Motion Perception Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 (chap 6 leftovers) Defects in Stereopsis Strabismus eyes not aligned, so diff images fall on
Motion Perception Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 (chap 6 leftovers) Defects in Stereopsis Strabismus eyes not aligned, so diff images fall on
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Perception. How we interpret the information our senses receive. Overview Perception
 Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Understanding Optical Illusions. Mohit Gupta
 Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8
 Motion 1 Perception (PSY 4204) Christine L. Ruva, Ph.D. PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8 Overview of Questions Why do some animals freeze in place when they sense danger? How do films create movement from still
Motion 1 Perception (PSY 4204) Christine L. Ruva, Ph.D. PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8 Overview of Questions Why do some animals freeze in place when they sense danger? How do films create movement from still
Motion perception PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 24. Aperture problem
 Motion perception PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 24 How do you see motion here? Aperture problem A detector that only sees part of a scene cannot precisely identify the motion direction or speed of an edge
Motion perception PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 24 How do you see motion here? Aperture problem A detector that only sees part of a scene cannot precisely identify the motion direction or speed of an edge
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
3D Space Perception. (aka Depth Perception)
 3D Space Perception (aka Depth Perception) 3D Space Perception The flat retinal image problem: How do we reconstruct 3D-space from 2D image? What information is available to support this process? Interaction
3D Space Perception (aka Depth Perception) 3D Space Perception The flat retinal image problem: How do we reconstruct 3D-space from 2D image? What information is available to support this process? Interaction
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception. Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation
 Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
P rcep e t p i t on n a s a s u n u c n ons n c s ious u s i nf n e f renc n e L ctur u e 4 : Recogni n t i io i n
 Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY
 Journal of Experimental Psychology 1964, Vol. 67, No. 6, 531-538 GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY IRVIN ROCK AND LEONARD BROSGOLE l Yeshiva University The question was raised whether the Gestalt
Journal of Experimental Psychology 1964, Vol. 67, No. 6, 531-538 GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY IRVIN ROCK AND LEONARD BROSGOLE l Yeshiva University The question was raised whether the Gestalt
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Perceptual Organization
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Perceptual Organization Module 16 2 Perceptual Organization Perceptual
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Perceptual Organization Module 16 2 Perceptual Organization Perceptual
Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by
 Perceptual Rules Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by inferring a third dimension. We can
Perceptual Rules Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by inferring a third dimension. We can
Chapter 73. Two-Stroke Apparent Motion. George Mather
 Chapter 73 Two-Stroke Apparent Motion George Mather The Effect One hundred years ago, the Gestalt psychologist Max Wertheimer published the first detailed study of the apparent visual movement seen when
Chapter 73 Two-Stroke Apparent Motion George Mather The Effect One hundred years ago, the Gestalt psychologist Max Wertheimer published the first detailed study of the apparent visual movement seen when
Perception: From Biology to Psychology
 Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
IOC, Vector sum, and squaring: three different motion effects or one?
 Vision Research 41 (2001) 965 972 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres IOC, Vector sum, and squaring: three different motion effects or one? L. Bowns * School of Psychology, Uni ersity of Nottingham, Uni ersity
Vision Research 41 (2001) 965 972 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres IOC, Vector sum, and squaring: three different motion effects or one? L. Bowns * School of Psychology, Uni ersity of Nottingham, Uni ersity
Perceptual Organization. Unit 3 RG 4e
 Perceptual Organization Unit 3 RG 4e Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Perceptual Illusions To understand how perception is organized, illusions
Perceptual Organization Unit 3 RG 4e Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Perceptual Illusions To understand how perception is organized, illusions
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Physics 131 Lab 1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION
 1 Name Date Partner(s) Physics 131 Lab 1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES To familiarize yourself with motion detector hardware. To explore how simple motions are represented on a displacement-time graph.
1 Name Date Partner(s) Physics 131 Lab 1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES To familiarize yourself with motion detector hardware. To explore how simple motions are represented on a displacement-time graph.
Discussion and Application of 3D and 2D Aperture Problems
 Discussion and Application of 3D and 2D Aperture Problems Guang-Dah Chen, National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, Taiwan Yi-Yin Wang, National Yunlin University of Science and Technology,
Discussion and Application of 3D and 2D Aperture Problems Guang-Dah Chen, National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, Taiwan Yi-Yin Wang, National Yunlin University of Science and Technology,
The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery
 Perception, 1999, volume 28, pages 617-621 The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery Jocelyn Faubert, Andrew M Herbert Ecole d'optometrie, Universite de Montreal, CP 6128,
Perception, 1999, volume 28, pages 617-621 The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery Jocelyn Faubert, Andrew M Herbert Ecole d'optometrie, Universite de Montreal, CP 6128,
Contents 1 Motion and Depth
 Contents 1 Motion and Depth 5 1.1 Computing Motion.............................. 8 1.2 Experimental Observations of Motion................... 26 1.3 Binocular Depth................................ 36 1.4
Contents 1 Motion and Depth 5 1.1 Computing Motion.............................. 8 1.2 Experimental Observations of Motion................... 26 1.3 Binocular Depth................................ 36 1.4
Prof. Greg Francis 5/27/08
 Visual Perception : Motion IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Dr. Francis Lecture 11 Motion Motion is of tremendous importance for survival (Demo) Try to find the hidden bird in the figure below (http://illusionworks.com/hidden.htm)
Visual Perception : Motion IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Dr. Francis Lecture 11 Motion Motion is of tremendous importance for survival (Demo) Try to find the hidden bird in the figure below (http://illusionworks.com/hidden.htm)
Learned Stimulation in Space and Motion Perception
 Learned Stimulation in Space and Motion Perception Hans Wallach Swarthmore College ABSTRACT: In the perception of distance, depth, and visual motion, a single property is often represented by two or more
Learned Stimulation in Space and Motion Perception Hans Wallach Swarthmore College ABSTRACT: In the perception of distance, depth, and visual motion, a single property is often represented by two or more
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Overview
 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL OVERVIEW 1
 OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang
 A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang Vestibular Responses in Dorsal Visual Stream and Their Role in Heading Perception Recent experiments
A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang Vestibular Responses in Dorsal Visual Stream and Their Role in Heading Perception Recent experiments
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Fun with visual illusions. Professor William Ayliffe Gresham Professor of Physic
 Gresham Lecture, Wednesday 13 October 2010 Fun with visual illusions Professor William Ayliffe Gresham Professor of Physic There are many definitions of what constitutes a visual illusion. We commonly
Gresham Lecture, Wednesday 13 October 2010 Fun with visual illusions Professor William Ayliffe Gresham Professor of Physic There are many definitions of what constitutes a visual illusion. We commonly
Sensation and Perception. Sensation. Sensory Receptors. Sensation. General Properties of Sensory Systems
 Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning
 Perceived Depth is Enhanced with Parallax Scanning March 1, 1999 Dennis Proffitt & Tom Banton Department of Psychology University of Virginia Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning Background
Perceived Depth is Enhanced with Parallax Scanning March 1, 1999 Dennis Proffitt & Tom Banton Department of Psychology University of Virginia Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning Background
Modulating motion-induced blindness with depth ordering and surface completion
 Vision Research 42 (2002) 2731 2735 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Modulating motion-induced blindness with depth ordering and surface completion Erich W. Graf *, Wendy J. Adams, Martin Lages Department
Vision Research 42 (2002) 2731 2735 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Modulating motion-induced blindness with depth ordering and surface completion Erich W. Graf *, Wendy J. Adams, Martin Lages Department
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Moving Man LAB #2 PRINT THESE PAGES AND TURN THEM IN BEFORE OR ON THE DUE DATE GIVEN IN YOUR .
 Moving Man LAB #2 Total : Start : Finish : Name: Date: Period: PRINT THESE PAGES AND TURN THEM IN BEFORE OR ON THE DUE DATE GIVEN IN YOUR EMAIL. POSITION Background Graphs are not just an evil thing your
Moving Man LAB #2 Total : Start : Finish : Name: Date: Period: PRINT THESE PAGES AND TURN THEM IN BEFORE OR ON THE DUE DATE GIVEN IN YOUR EMAIL. POSITION Background Graphs are not just an evil thing your
Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception
 Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception Physical characteristics of stimulus drive perception Realism Top-down perception Knowledge, expectations, or thoughts influence perception Constructivism:
Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception Physical characteristics of stimulus drive perception Realism Top-down perception Knowledge, expectations, or thoughts influence perception Constructivism:
Don t twinkle, little star!
 Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling
 Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
Limitations of the Oriented Difference of Gaussian Filter in Special Cases of Brightness Perception Illusions
 Short Report Limitations of the Oriented Difference of Gaussian Filter in Special Cases of Brightness Perception Illusions Perception 2016, Vol. 45(3) 328 336! The Author(s) 2015 Reprints and permissions:
Short Report Limitations of the Oriented Difference of Gaussian Filter in Special Cases of Brightness Perception Illusions Perception 2016, Vol. 45(3) 328 336! The Author(s) 2015 Reprints and permissions:
Lecture 5. The Visual Cortex. Cortical Visual Processing
 Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2)
 Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
Chapter 4 PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Motion Perception II Chapter 8
 Motion Perception II Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2019 Eye movements: also give rise to retinal motion. important to distinguish motion due to
Motion Perception II Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2019 Eye movements: also give rise to retinal motion. important to distinguish motion due to
Face Perception. The Thatcher Illusion. The Thatcher Illusion. Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Face Inversion Effect
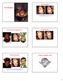 The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
Vision: Distance & Size Perception
 Vision: Distance & Size Perception Useful terms: Egocentric distance: distance from you to an object. Relative distance: distance between two objects in the environment. 3-d structure: Objects appear three-dimensional,
Vision: Distance & Size Perception Useful terms: Egocentric distance: distance from you to an object. Relative distance: distance between two objects in the environment. 3-d structure: Objects appear three-dimensional,
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception
 Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Today. Pattern Recognition. Introduction. Perceptual processing. Feature Integration Theory, cont d. Feature Integration Theory (FIT)
 Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Sensation & Perception
 Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation and Perception
 Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Non-Provisional Patent Application #
 Non-Provisional Patent Application # 14868045 VISUAL FUNCTIONS ASSESSMENT USING CONTRASTING STROBIC AREAS Inventor: Allan Hytowitz, Alpharetta, GA (US) 5 ABSTRACT OF THE DISCLOSURE: A test to assess visual
Non-Provisional Patent Application # 14868045 VISUAL FUNCTIONS ASSESSMENT USING CONTRASTING STROBIC AREAS Inventor: Allan Hytowitz, Alpharetta, GA (US) 5 ABSTRACT OF THE DISCLOSURE: A test to assess visual
Discriminating direction of motion trajectories from angular speed and background information
 Atten Percept Psychophys (2013) 75:1570 1582 DOI 10.3758/s13414-013-0488-z Discriminating direction of motion trajectories from angular speed and background information Zheng Bian & Myron L. Braunstein
Atten Percept Psychophys (2013) 75:1570 1582 DOI 10.3758/s13414-013-0488-z Discriminating direction of motion trajectories from angular speed and background information Zheng Bian & Myron L. Braunstein
Visual Rules. Why are they necessary?
 Visual Rules Why are they necessary? Because the image on the retina has just two dimensions, a retinal image allows countless interpretations of a visual object in three dimensions. Underspecified Poverty
Visual Rules Why are they necessary? Because the image on the retina has just two dimensions, a retinal image allows countless interpretations of a visual object in three dimensions. Underspecified Poverty
SPATIAL VISION. ICS 280: Visual Perception. ICS 280: Visual Perception. Spatial Frequency Theory. Spatial Frequency Theory
 SPATIAL VISION Spatial Frequency Theory So far, we have considered, feature detection theory Recent development Spatial Frequency Theory The fundamental elements are spatial frequency elements Does not
SPATIAL VISION Spatial Frequency Theory So far, we have considered, feature detection theory Recent development Spatial Frequency Theory The fundamental elements are spatial frequency elements Does not
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
TSBB15 Computer Vision
 TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See
 Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Static and Moving Patterns (part 2) Lyn Bartram IAT 814 week
 Static and Moving Patterns (part 2) Lyn Bartram IAT 814 week 9 5.11.2009 Administrivia Assignment 3 Final projects Static and Moving Patterns IAT814 5.11.2009 Transparency and layering Transparency affords
Static and Moving Patterns (part 2) Lyn Bartram IAT 814 week 9 5.11.2009 Administrivia Assignment 3 Final projects Static and Moving Patterns IAT814 5.11.2009 Transparency and layering Transparency affords
Learning Targets. Module 19
 Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 10 Perception Role of Culture in Perception Till now we have
Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 10 Perception Role of Culture in Perception Till now we have
LEARN * DREAM * AWAKEN* DISCOVER * ENLIGHTEN * INVESTIGATE * QUESTION * EXPLORE
 S C I E N C E ZOETROPE This Enrichment4You e-guide provides a brief overview of s. In this e-guide you will: Physical Science (Physics) O P T I C S *Learn Basic Information About the Development & Use
S C I E N C E ZOETROPE This Enrichment4You e-guide provides a brief overview of s. In this e-guide you will: Physical Science (Physics) O P T I C S *Learn Basic Information About the Development & Use
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Sensation and perception
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 10. Neurophysiology
 Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 10 A continuous surface infolded on itself. Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural
Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 10 A continuous surface infolded on itself. Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural
What you see is not what you get. Grade Level: 3-12 Presentation time: minutes, depending on which activities are chosen
 Optical Illusions What you see is not what you get The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to basic principles of visual processing. Much of the lesson revolves around the use of visual illusions
Optical Illusions What you see is not what you get The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to basic principles of visual processing. Much of the lesson revolves around the use of visual illusions
Understanding Spatial Disorientation and Vertigo. Dan Masys, MD EAA Chapter 162
 Understanding Spatial Disorientation and Vertigo Dan Masys, MD EAA Chapter 162 Topics Why this is important A little aviation history How the human body maintains balance and positional awareness Types
Understanding Spatial Disorientation and Vertigo Dan Masys, MD EAA Chapter 162 Topics Why this is important A little aviation history How the human body maintains balance and positional awareness Types
asgn2t -- PERCEPTION: Cognitive Models
 asgn2t -- PERCEPTION: Cognitive Models Cognitive psychologists who study perception try to infer ("figure out") the automatic, unconscious mental processes that let people perceive objects and events so
asgn2t -- PERCEPTION: Cognitive Models Cognitive psychologists who study perception try to infer ("figure out") the automatic, unconscious mental processes that let people perceive objects and events so
Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture
 59 JSL, Volume 2 (2006), 59 69 Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture Kazuo OHYA Following previous paper the purpose of this paper is to collect and publish some useful simple stimuli
59 JSL, Volume 2 (2006), 59 69 Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture Kazuo OHYA Following previous paper the purpose of this paper is to collect and publish some useful simple stimuli
Static and Moving Patterns
 Static and Moving Patterns Lyn Bartram IAT 814 week 7 18.10.2007 Pattern learning People who work with visualizations must learn the skill of seeing patterns in data. In terms of making visualizations
Static and Moving Patterns Lyn Bartram IAT 814 week 7 18.10.2007 Pattern learning People who work with visualizations must learn the skill of seeing patterns in data. In terms of making visualizations
This is due to Purkinje shift. At scotopic conditions, we are more sensitive to blue than to red.
 1. We know that the color of a light/object we see depends on the selective transmission or reflections of some wavelengths more than others. Based on this fact, explain why the sky on earth looks blue,
1. We know that the color of a light/object we see depends on the selective transmission or reflections of some wavelengths more than others. Based on this fact, explain why the sky on earth looks blue,
Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015
 Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015 EXTENDED SUMMARY Lesson #10: Dec. 01 st 2014 Lecture plan: VISUAL ILLUSIONS THE STUDY OF VISUAL
Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015 EXTENDED SUMMARY Lesson #10: Dec. 01 st 2014 Lecture plan: VISUAL ILLUSIONS THE STUDY OF VISUAL
D) visual capture. E) perceptual adaptation.
 1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays
 The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays Damian Gordon * and David Vernon Department of Computer Science Maynooth College Ireland ABSTRACT
The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays Damian Gordon * and David Vernon Department of Computer Science Maynooth College Ireland ABSTRACT
Simulating Biological Motion Perception Using a Recurrent Neural Network
 Simulating Biological Motion Perception Using a Recurrent Neural Network Roxanne L. Canosa Department of Computer Science Rochester Institute of Technology Rochester, NY 14623 rlc@cs.rit.edu Abstract People
Simulating Biological Motion Perception Using a Recurrent Neural Network Roxanne L. Canosa Department of Computer Science Rochester Institute of Technology Rochester, NY 14623 rlc@cs.rit.edu Abstract People
AD-A lji llllllllllii l
 Perception, 1992, volume 21, pages 359-363 AD-A259 238 lji llllllllllii1111111111111l lll~ lit DEC The effect of defocussing the image on the perception of the temporal order of flashing lights Saul M
Perception, 1992, volume 21, pages 359-363 AD-A259 238 lji llllllllllii1111111111111l lll~ lit DEC The effect of defocussing the image on the perception of the temporal order of flashing lights Saul M
Sensation and Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Sensation
 Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Visual Effects of. Light. Warmth. Light is life. Sun as a deity (god) If sun would turn off the life on earth would extinct
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Vision Research 48 (2008) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Vision Research. journal homepage:
 Vision Research 48 (2008) 2403 2414 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Vision Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/visres The Drifting Edge Illusion: A stationary edge abutting an
Vision Research 48 (2008) 2403 2414 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Vision Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/visres The Drifting Edge Illusion: A stationary edge abutting an
Takeharu Seno 1,3,4, Akiyoshi Kitaoka 2, Stephen Palmisano 5 1
 Perception, 13, volume 42, pages 11 1 doi:1.168/p711 SHORT AND SWEET Vection induced by illusory motion in a stationary image Takeharu Seno 1,3,4, Akiyoshi Kitaoka 2, Stephen Palmisano 1 Institute for
Perception, 13, volume 42, pages 11 1 doi:1.168/p711 SHORT AND SWEET Vection induced by illusory motion in a stationary image Takeharu Seno 1,3,4, Akiyoshi Kitaoka 2, Stephen Palmisano 1 Institute for
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
Apparent depth with motion aftereffect and head movement
 Perception, 1994, volume 23, pages 1241-1248 Apparent depth with motion aftereffect and head movement Hiroshi Ono, Hiroyasu Ujike Centre for Vision Research and Department of Psychology, York University,
Perception, 1994, volume 23, pages 1241-1248 Apparent depth with motion aftereffect and head movement Hiroshi Ono, Hiroyasu Ujike Centre for Vision Research and Department of Psychology, York University,
Perception of scene layout from optical contact, shadows, and motion
 Perception, 2004, volume 33, pages 1305 ^ 1318 DOI:10.1068/p5288 Perception of scene layout from optical contact, shadows, and motion Rui Ni, Myron L Braunstein Department of Cognitive Sciences, University
Perception, 2004, volume 33, pages 1305 ^ 1318 DOI:10.1068/p5288 Perception of scene layout from optical contact, shadows, and motion Rui Ni, Myron L Braunstein Department of Cognitive Sciences, University
HUMAN FACTORS FOR TECHNICAL COMMUNICATORS By Marlana Coe (Wiley Technical Communication Library) Lecture 6
 HUMAN FACTORS FOR TECHNICAL COMMUNICATORS By Marlana Coe (Wiley Technical Communication Library) Lecture 6 Human Factors Optimally designing for people takes into account not only the ergonomics of design,
HUMAN FACTORS FOR TECHNICAL COMMUNICATORS By Marlana Coe (Wiley Technical Communication Library) Lecture 6 Human Factors Optimally designing for people takes into account not only the ergonomics of design,
Three stimuli for visual motion perception compared
 Perception & Psychophysics 1982,32 (1),1-6 Three stimuli for visual motion perception compared HANS WALLACH Swarthmore Col/ege, Swarthmore, Pennsylvania ANN O'LEARY Stanford University, Stanford, California
Perception & Psychophysics 1982,32 (1),1-6 Three stimuli for visual motion perception compared HANS WALLACH Swarthmore Col/ege, Swarthmore, Pennsylvania ANN O'LEARY Stanford University, Stanford, California
Sensory and Perception. Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague
 Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Light and Colour. Sir Isaac Newton The Founder of Colour Science
 Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
