The shape of luminance increments at the intersection alters the magnitude of the scintillating grid illusion
|
|
|
- Arleen Rich
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The shape of luminance increments at the intersection alters the magnitude of the scintillating grid illusion Kun Qian a, Yuki Yamada a, Takahiro Kawabe b, Kayo Miura b a Graduate School of Human-Environment Studies, Kyushu University, Japan b Faculty of Human-Environment Studies, Kyushu University, Japan Abstract The scintillating grid illusion refers to an illusory perception of black spots on the luminance increments at the intersections of gray grids on a black background. In this study, we examined how the shape of luminance increments modulated the strength of the illusion. In Experiment 1, we concurrently controlled the size and shape of luminance increments, and found significant reduction of the illusory strength on the square, compared with circle and diamond, in the largest size condition. In Experiment 2, we controlled overall orientation of squared luminance increments, and confirmed the significant reduction of the illusion when the relative edge orientation of luminance increments and the grids was larger than 30 deg. This indicates that not the categorical difference of the shape, but the orientation difference between the grids and the luminance increments determines the strength of the illusion. We discussed about the contribution of orientation processing to scintillating grid illusion. Illusory gray spots are observed on the intersections of white grids against a black background (Fig. 1). The well-known phenomenon is referred to as Hermann Grid Illusion (Brewster, 1844; Hermann, 1870). Previous studies designed several variations of the illusion and showed that the illusion existed even when the grids were sloped (Spillmann, 1994). Lateral inhibition is known as a convincing mechanism for the illusion (Baumgartner, 1960). Figure 1. Hermann Grid Illusion By adding circular luminance increments to the intersections of Figure 1 and reducing the
2 luminance level of the intersections, illusory black spots are observed on the luminance increments (Fig. 2). This illusion is so called, scintillating grid illusion (Schrauf, Lingelbach, & Wist, 1997). Figure 2. Scintillating Grid Illusion The scintillating grid illusion is critically different from the Hermann grid illusion in that the illusory black spots are not constantly perceived, but momently scintillated. Why does the percept of scintillation occur? Schrauf and his colleagues conducted experiments on 3 different conditions, pursuit eye movement on stationary grids, smooth displacement of the grids with steady gaze, and brief exposure of the stationary grids, and found that not the eye movement itself but a transient stimulation caused by the eye movements or brief exposures is essential for generating scintillating grid illusion (Schrauf, Wist & Ehrenstein, 2000). They also showed that high stimulus speed or brief exposure less than 210 ms either reduced the strength of the illusion. This indicates that the spatial and temporal integration of the activity of visual neurons is important for generating the illusion. Recently, VanRullen & Dong (2003) reported that the distance between an attended location and intersections determined the strength of illusory spots at the intersections, and implied that the spatial distribution of covert attention affects the illusion. Perhaps, the slow temporal course of scintillating grid illusion may be related with attention shifts that seem to be required for the scintillation of illusory spots. Furthermore, scintillating grid illusion likely stems from the different mechanism for Hermann grid illusion. As described above, Hermann grid illusion is explained with lateral inhibition (Baumgartner, 1960). However, because of the complexity of the intersections due to the luminance increments, the explanation with Hermann grid illusion cannot perfectly stand for scintillating grid illusion. Moreover, scintillating grid illusion is evidently affected by the diameters of luminance increments that do not exist in Hermann grid illusion. In this study, we explored the underlying mechanism for the scintillating grid illusion by concurrently controlling the shapes and sizes of the luminance increments. Previous studies examined the effects of sizes and luminance on the illusion (Schrauf, Lingelbach, & Wist, 1997). However, the shape of the luminance increments was not examined: Only circle shape was introduced into luminance increments at the intersections. Thus, it was unclear whether the effect of sizes of luminance increments was common among variable shapes. We planned
3 to test diamond and square shapes beside the original circle shape. Although the two new shapes have the same side length and interior angles, they are different in terms of their overall orientation. By using three kinds of shape, we tried to confirm the role of edge orientation of luminance increments in the illusion. By comparing the strength of the illusion among three shapes, we discuss the underlying mechanism for the illusion in terms of orientation processing. Subjects Methods Five observers (2 males, 3 females; mean age: 26.4 years) served as subjects in Experiment 1 while other five observers (2 males, 3 females; mean age: 26.8 years) participated in Experiment 2. All of them had normal or corrected-to-normal visual acuity. They were naive as to the purpose of the experiments. Apparatus and stimuli Stimuli were generated by a computer (VAIO, SONY, Japan) and displayed on the screen of a 19 inch. CRT monitor (FlexScan T761, EIZO, Japan). The subject s head was fixated by a chin rest located 60 cm away from the monitor. The test stimulus was a 8 6 scintillating grid with deg of visual angle. A bar of a grid had a luminance of 9.72 cd/m 2 and a width of 0.33 deg. The gap between bars was 1.7 deg. Luminance increments had a luminance of 99.5 cd/m 2 and variable sizes. They were presented against a background with a luminance of 2.21 cd/m 2 ). In Experiment 1, we employed luminance increments with three shapes (circle, square, and diamond) and with five sizes (0.20, 0.26, 0.33, 0.46, and 0.59 deg). The sizes denote the side length for square and diamond while that of radius of circle. Fifteen stimuli (3 shapes 5 sizes) were used in total. In Experiment 2, we used squares of luminance increments with the size of 0.59 deg and 6 different orientations (0, 15, 30, 45, 60, and 75 ). Each of them appeared twice in a randomized order for each observer (Fig, 3). (Diamond, 0.46 deg) (Square, 0.46 deg) Fig. 3. Stimuli used in Experiment 1
4 Procedure For both the experiments, the subjects were asked to rate the strength of the illusion in 7 rating grades without time limits. They were asked for a pilot observation of all the stimuli before rating, to set the criterion for the rating. Before the presentation of each stimulus, the stimulus number was presented for 1 sec. The order of the stimuli for rating was identical to the pilot observation. Results and Discussion Experiment 1: the effects of shape and size of the luminance increments Fig. 4 illustrates the mean rated strength in Experiment 1. A two-way ANOVA revealed the significant main effects of the shape [F (2, 8) = 8.604, p <.05] and the size [F (4, 16) = 3.931, p <.05]. The interaction between them was also significant [F (8, 32) = 3.508, p <.01]. A simple main effect of the shape was significant when the sizes were 0.46 deg (p <.05) and 0.59deg (p <.001), while that of size was significant in the circle (p <.005) and square (p <.005) conditions. Post hoc comparison showed that, in the 0.46 deg condition, the rated strength of circle was significantly greater than that of square (p<.05). In the 0.59 deg condition, the rated strengths of circle and diamond were significantly larger than that of square. Fig. 4. Strength of illusory black spots in Experiment 1 (N = 5, Error Bar: SEM) The results of Experiment 1 suggested that the scintillating grid illusion was weakened or
5 disappeared when the luminance increments had square shape. In particular, the rated values drastically decreased in the 0.46 deg and 0.59 deg conditions only when the square condition, even though square and diamond had the same area, side length, and internal angles. This indicates that the mechanism of the scintillating grid illusion involves edge orientation of the luminance increments. We further examined this factor in experiment 2. Experiment 2: Orientations of the quadrangles Fig. 5 showed the results of Experiment 2. An ANOVA with orientation as factor revealed the significant main effect of the orientation [F (5, 20) = , p <.0001]. Multiple comparison tests showed that a pairs of quadrangles which differs more than 30 from 45 were significantly different. The illusion is most prominent when the orientation of quadrangle was 45, and correspondingly decreased as the orientation changed towards 0. The results of Experiment 2 also implied that the edge orientation of the luminance increments is concerned in the mechanism of scintillating grid illusion. Fig. 5. Strength of illusory black spots in Experiment 2 (N = 5, Error Bar: SEM) General Discussion In this study, we examined whether the edge orientation of the luminance increments affected the strength of scintillating grid illusion. In previous researches, only circle shape was introduced into luminance increments in order to investigate the illusion. Meanwhile, the present study used circle, diamond, and square and demonstrated the scintillating effect. However, the strength of the illusion varied with the shapes as well as size. Overall, the variations of size and strength of the illusion in the circle and diamond conditions appeared similar but significantly differed from those of the square condition (Experiment 1). Although the diamond which rotated by 45 consisted with the square, the rated strength in the former
6 shape was significantly greater than the latter shape (Experiment 2). These results indicate that edge orientation of luminance increments affected the illusion. We consider that the mechanism of the scintillating grid illusion has an orientation tuning. The large population of neurons in the primary visual cortex has an orientation tuning with a bandwidth ranging from 20 to 40 (DeValois & DeValois, 1990). In the present study, the rated strength of the illusion was strongest with 45 deg condition, and was significantly reduced with less than 15 deg and more than 75 deg conditions, in other words, with the overall orientation differences more than 30 from 45 deg conditions. The results are consistent with the orientation tuning found in V1. Therefore, we suggest that orientation processing for luminance increments is one of underlying factors of the scintillating grid illusion. Reference Baumgartner, G., (1960). Indirekte Größenbestimmung der rezeptiven Felder der Retina beim Menschen mittels der Hermannschen Gittertäuschung. Pflügers Archiv für die gesamte Physiologie, 272, Brewster, Sir. D., (1844). A notice explaining the cause of an optical phenomenon observed by the Rev. W. Selwyn. Report of the Fourteenth Meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science (London: John Murray) p.8. De Valois, R. L., & De Valois, K. K. (1990). Spatial vision. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Hermann, L., (1870). Eine Erscheinung des simultanen Contrastes. Pflügers Archiv für die gesamte Physiologie, 3, Spillmann, L. (1994). The Hermann grid illusion: a tool for studying human perceptive field organization. Perception, 23, Schrauf, M., Lingelbach, B., & Wist, E. R. (1997). The scintillating grid illusion. Vision Research, 37, Schrauf, M., Wist, E.R., & Ehrenstein, W. H. (2000). The scintillating grid illusion during smooth pursuit, stimulus motion, and brief exposure in humans. Neuroscience Letters, 284, VanRullen, R., & Dong, T. (2003). Attention and scintillation. Vision Research, 43,
The role of orientation processing in the scintillating grid illusion
 Atten Percept Psychophys () 7: DOI.758/s--95-y The role of orientation processing in the scintillating grid illusion Kun Qian & Takahiro Kawabe & Yuki Yamada & Kayo Miura Published online: 9 April # Psychonomic
Atten Percept Psychophys () 7: DOI.758/s--95-y The role of orientation processing in the scintillating grid illusion Kun Qian & Takahiro Kawabe & Yuki Yamada & Kayo Miura Published online: 9 April # Psychonomic
Effects of orientation and contrast upon targets in straight and curved arrays MS 7237_AG. Michael W. Levine 1,2. Jennifer E.
 Effects of orientation and contrast upon targets in straight and curved arrays MS 7237_AG Michael W. Levine 1,2 Jennifer E. Anderson 1 J. Jason McAnany 1,3 University of Illinois at Chicago 1 Department
Effects of orientation and contrast upon targets in straight and curved arrays MS 7237_AG Michael W. Levine 1,2 Jennifer E. Anderson 1 J. Jason McAnany 1,3 University of Illinois at Chicago 1 Department
The effects of curvature on the grid illusions
 Perception ms. 5691 TT The effects of curvature on the grid illusions Michael W. Levine J. Jason McAnany Department of Psychology and Laboratory for Integrative Neuroscience University of Illinois at Chicago,
Perception ms. 5691 TT The effects of curvature on the grid illusions Michael W. Levine J. Jason McAnany Department of Psychology and Laboratory for Integrative Neuroscience University of Illinois at Chicago,
Modulating motion-induced blindness with depth ordering and surface completion
 Vision Research 42 (2002) 2731 2735 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Modulating motion-induced blindness with depth ordering and surface completion Erich W. Graf *, Wendy J. Adams, Martin Lages Department
Vision Research 42 (2002) 2731 2735 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Modulating motion-induced blindness with depth ordering and surface completion Erich W. Graf *, Wendy J. Adams, Martin Lages Department
Takeharu Seno 1,3,4, Akiyoshi Kitaoka 2, Stephen Palmisano 5 1
 Perception, 13, volume 42, pages 11 1 doi:1.168/p711 SHORT AND SWEET Vection induced by illusory motion in a stationary image Takeharu Seno 1,3,4, Akiyoshi Kitaoka 2, Stephen Palmisano 1 Institute for
Perception, 13, volume 42, pages 11 1 doi:1.168/p711 SHORT AND SWEET Vection induced by illusory motion in a stationary image Takeharu Seno 1,3,4, Akiyoshi Kitaoka 2, Stephen Palmisano 1 Institute for
7Motion Perception. 7 Motion Perception. 7 Computation of Visual Motion. Chapter 7
 7Motion Perception Chapter 7 7 Motion Perception Computation of Visual Motion Eye Movements Using Motion Information The Man Who Couldn t See Motion 7 Computation of Visual Motion How would you build a
7Motion Perception Chapter 7 7 Motion Perception Computation of Visual Motion Eye Movements Using Motion Information The Man Who Couldn t See Motion 7 Computation of Visual Motion How would you build a
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction. Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc.
 Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
The Scintillating Grid Illusion
 Pergamon PH: S0042-6989(96)00255-6 Vision lk~,, Vol. 37, No. 8, pp. 1033-1038, 1997 01997 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain 0042-6989/97 $17.00 + 0.()() The Scintillating
Pergamon PH: S0042-6989(96)00255-6 Vision lk~,, Vol. 37, No. 8, pp. 1033-1038, 1997 01997 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain 0042-6989/97 $17.00 + 0.()() The Scintillating
Limitations of the Oriented Difference of Gaussian Filter in Special Cases of Brightness Perception Illusions
 Short Report Limitations of the Oriented Difference of Gaussian Filter in Special Cases of Brightness Perception Illusions Perception 2016, Vol. 45(3) 328 336! The Author(s) 2015 Reprints and permissions:
Short Report Limitations of the Oriented Difference of Gaussian Filter in Special Cases of Brightness Perception Illusions Perception 2016, Vol. 45(3) 328 336! The Author(s) 2015 Reprints and permissions:
The Honeycomb illusion: Uniform textures not perceived as such
 Article The Honeycomb illusion: Uniform textures not perceived as such i-perception July-August 2016, 1 15! The Author(s) 2016 DOI: 10.1177/2041669516660727 ipe.sagepub.com Marco Bertamini University of
Article The Honeycomb illusion: Uniform textures not perceived as such i-perception July-August 2016, 1 15! The Author(s) 2016 DOI: 10.1177/2041669516660727 ipe.sagepub.com Marco Bertamini University of
The Influence of Visual Illusion on Visually Perceived System and Visually Guided Action System
 The Influence of Visual Illusion on Visually Perceived System and Visually Guided Action System Yu-Hung CHIEN*, Chien-Hsiung CHEN** * Graduate School of Design, National Taiwan University of Science and
The Influence of Visual Illusion on Visually Perceived System and Visually Guided Action System Yu-Hung CHIEN*, Chien-Hsiung CHEN** * Graduate School of Design, National Taiwan University of Science and
Directional Bias in the Perception of Cast Shadows
 Article Directional Bias in the Perception of Cast Shadows i-perception January-February 2017: 1 17! The Author(s) 2017 DOI: 10.1177/2041669516682267 journals.sagepub.com/home/ipe Tomomi Koizumi Graduate
Article Directional Bias in the Perception of Cast Shadows i-perception January-February 2017: 1 17! The Author(s) 2017 DOI: 10.1177/2041669516682267 journals.sagepub.com/home/ipe Tomomi Koizumi Graduate
Chapter 73. Two-Stroke Apparent Motion. George Mather
 Chapter 73 Two-Stroke Apparent Motion George Mather The Effect One hundred years ago, the Gestalt psychologist Max Wertheimer published the first detailed study of the apparent visual movement seen when
Chapter 73 Two-Stroke Apparent Motion George Mather The Effect One hundred years ago, the Gestalt psychologist Max Wertheimer published the first detailed study of the apparent visual movement seen when
IOC, Vector sum, and squaring: three different motion effects or one?
 Vision Research 41 (2001) 965 972 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres IOC, Vector sum, and squaring: three different motion effects or one? L. Bowns * School of Psychology, Uni ersity of Nottingham, Uni ersity
Vision Research 41 (2001) 965 972 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres IOC, Vector sum, and squaring: three different motion effects or one? L. Bowns * School of Psychology, Uni ersity of Nottingham, Uni ersity
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION. Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh
 B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
vertical horizonta fovea Figure by MIT OCW.
 Visual Prosthetics 90 5 4 3 Lunate Sulcus Central Sulcus 2 1 180 0 vertical 270 horizonta 8 7 6 5 fovea 4 3 2 1 V1 Figure by MIT OCW. Present two visual targets Present one visual target and stimulate
Visual Prosthetics 90 5 4 3 Lunate Sulcus Central Sulcus 2 1 180 0 vertical 270 horizonta 8 7 6 5 fovea 4 3 2 1 V1 Figure by MIT OCW. Present two visual targets Present one visual target and stimulate
The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery
 Perception, 1999, volume 28, pages 617-621 The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery Jocelyn Faubert, Andrew M Herbert Ecole d'optometrie, Universite de Montreal, CP 6128,
Perception, 1999, volume 28, pages 617-621 The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery Jocelyn Faubert, Andrew M Herbert Ecole d'optometrie, Universite de Montreal, CP 6128,
Background stripes affect apparent speed of rotation
 Perception, 2006, volume 35, pages 959 ^ 964 DOI:10.1068/p5557 Background stripes affect apparent speed of rotation Stuart Anstis Department of Psychology, University of California at San Diego, 9500 Gilman
Perception, 2006, volume 35, pages 959 ^ 964 DOI:10.1068/p5557 Background stripes affect apparent speed of rotation Stuart Anstis Department of Psychology, University of California at San Diego, 9500 Gilman
Apparent depth with motion aftereffect and head movement
 Perception, 1994, volume 23, pages 1241-1248 Apparent depth with motion aftereffect and head movement Hiroshi Ono, Hiroyasu Ujike Centre for Vision Research and Department of Psychology, York University,
Perception, 1994, volume 23, pages 1241-1248 Apparent depth with motion aftereffect and head movement Hiroshi Ono, Hiroyasu Ujike Centre for Vision Research and Department of Psychology, York University,
Experiments on the locus of induced motion
 Perception & Psychophysics 1977, Vol. 21 (2). 157 161 Experiments on the locus of induced motion JOHN N. BASSILI Scarborough College, University of Toronto, West Hill, Ontario MIC la4, Canada and JAMES
Perception & Psychophysics 1977, Vol. 21 (2). 157 161 Experiments on the locus of induced motion JOHN N. BASSILI Scarborough College, University of Toronto, West Hill, Ontario MIC la4, Canada and JAMES
Copyright 2002 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. Solid State Lighting II: Proceedings of SPIE
 Copyright 2002 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Solid State Lighting II: Proceedings of SPIE and is made available as an electronic reprint with permission
Copyright 2002 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Solid State Lighting II: Proceedings of SPIE and is made available as an electronic reprint with permission
GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY
 Journal of Experimental Psychology 1964, Vol. 67, No. 6, 531-538 GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY IRVIN ROCK AND LEONARD BROSGOLE l Yeshiva University The question was raised whether the Gestalt
Journal of Experimental Psychology 1964, Vol. 67, No. 6, 531-538 GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY IRVIN ROCK AND LEONARD BROSGOLE l Yeshiva University The question was raised whether the Gestalt
Understanding Optical Illusions. Mohit Gupta
 Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
Vision Research 48 (2008) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Vision Research. journal homepage:
 Vision Research 48 (2008) 2403 2414 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Vision Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/visres The Drifting Edge Illusion: A stationary edge abutting an
Vision Research 48 (2008) 2403 2414 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Vision Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/visres The Drifting Edge Illusion: A stationary edge abutting an
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015
 Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015 EXTENDED SUMMARY Lesson #10: Dec. 01 st 2014 Lecture plan: VISUAL ILLUSIONS THE STUDY OF VISUAL
Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015 EXTENDED SUMMARY Lesson #10: Dec. 01 st 2014 Lecture plan: VISUAL ILLUSIONS THE STUDY OF VISUAL
THE POGGENDORFF ILLUSION WITH ANOMALOUS SURFACES: MANAGING PAC-MANS, PARALLELS LENGTH AND TYPE OF TRANSVERSAL.
 THE POGGENDORFF ILLUSION WITH ANOMALOUS SURFACES: MANAGING PAC-MANS, PARALLELS LENGTH AND TYPE OF TRANSVERSAL. Spoto, A. 1, Massidda, D. 1, Bastianelli, A. 1, Actis-Grosso, R. 2 and Vidotto, G. 1 1 Department
THE POGGENDORFF ILLUSION WITH ANOMALOUS SURFACES: MANAGING PAC-MANS, PARALLELS LENGTH AND TYPE OF TRANSVERSAL. Spoto, A. 1, Massidda, D. 1, Bastianelli, A. 1, Actis-Grosso, R. 2 and Vidotto, G. 1 1 Department
The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays
 The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays Damian Gordon * and David Vernon Department of Computer Science Maynooth College Ireland ABSTRACT
The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays Damian Gordon * and David Vernon Department of Computer Science Maynooth College Ireland ABSTRACT
Magnification rate of objects in a perspective image to fit to our perception
 Japanese Psychological Research 2008, Volume 50, No. 3, 117 127 doi: 10.1111./j.1468-5884.2008.00368.x Blackwell ORIGINAL Publishing ARTICLES rate to Asia fit to perception Magnification rate of objects
Japanese Psychological Research 2008, Volume 50, No. 3, 117 127 doi: 10.1111./j.1468-5884.2008.00368.x Blackwell ORIGINAL Publishing ARTICLES rate to Asia fit to perception Magnification rate of objects
Self-motion perception from expanding and contracting optical flows overlapped with binocular disparity
 Vision Research 45 (25) 397 42 Rapid Communication Self-motion perception from expanding and contracting optical flows overlapped with binocular disparity Hiroyuki Ito *, Ikuko Shibata Department of Visual
Vision Research 45 (25) 397 42 Rapid Communication Self-motion perception from expanding and contracting optical flows overlapped with binocular disparity Hiroyuki Ito *, Ikuko Shibata Department of Visual
70 The Fraser-Wilcox illusion and its extension
 70 The Fraser-Wilcox illusion and its extension Akiyoshi Kitaoka (Department of Psychology, Ritsumeikan University, Kyoto, Japan) Alex Fraser (1923-2002), a geneticist and a painter, reported a motion
70 The Fraser-Wilcox illusion and its extension Akiyoshi Kitaoka (Department of Psychology, Ritsumeikan University, Kyoto, Japan) Alex Fraser (1923-2002), a geneticist and a painter, reported a motion
Psychophysical study of LCD motion-blur perception
 Psychophysical study of LD motion-blur perception Sylvain Tourancheau a, Patrick Le allet a, Kjell Brunnström b, and Börje Andrén b a IRyN, University of Nantes b Video and Display Quality, Photonics Dep.
Psychophysical study of LD motion-blur perception Sylvain Tourancheau a, Patrick Le allet a, Kjell Brunnström b, and Börje Andrén b a IRyN, University of Nantes b Video and Display Quality, Photonics Dep.
Munker ^ White-like illusions without T-junctions
 Perception, 2002, volume 31, pages 711 ^ 715 DOI:10.1068/p3348 Munker ^ White-like illusions without T-junctions Arash Yazdanbakhsh, Ehsan Arabzadeh, Baktash Babadi, Arash Fazl School of Intelligent Systems
Perception, 2002, volume 31, pages 711 ^ 715 DOI:10.1068/p3348 Munker ^ White-like illusions without T-junctions Arash Yazdanbakhsh, Ehsan Arabzadeh, Baktash Babadi, Arash Fazl School of Intelligent Systems
A Three-Dimensional Evaluation of Body Representation Change of Human Upper Limb Focused on Sense of Ownership and Sense of Agency
 A Three-Dimensional Evaluation of Body Representation Change of Human Upper Limb Focused on Sense of Ownership and Sense of Agency Shunsuke Hamasaki, Atsushi Yamashita and Hajime Asama Department of Precision
A Three-Dimensional Evaluation of Body Representation Change of Human Upper Limb Focused on Sense of Ownership and Sense of Agency Shunsuke Hamasaki, Atsushi Yamashita and Hajime Asama Department of Precision
Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion
 Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion Motion perception occurs (a) when a stationary observer perceives moving stimuli, such as this couple crossing the street; and (b) when a moving observer, like this basketball
Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion Motion perception occurs (a) when a stationary observer perceives moving stimuli, such as this couple crossing the street; and (b) when a moving observer, like this basketball
THE POGGENDORFF ILLUSION: THE PRESENCE OF ANOMALOUS FIGURE IN GENERATING THE EFFECT. Department of General Psychology, University of Padua, Italy
 THE POGGENDORFF ILLUSION: THE PRESENCE OF ANOMALOUS FIGURE IN GENERATING THE EFFECT Massidda, D. 1, Spoto, A. 1, Bastianelli, A. 1, Actis-Grosso, R. 2, and Vidotto, G. 1 1 Department of General Psychology,
THE POGGENDORFF ILLUSION: THE PRESENCE OF ANOMALOUS FIGURE IN GENERATING THE EFFECT Massidda, D. 1, Spoto, A. 1, Bastianelli, A. 1, Actis-Grosso, R. 2, and Vidotto, G. 1 1 Department of General Psychology,
Poles for Increasing the Sensibility of Vertical Gradient. in a Downhill Road
 Poles for Increasing the Sensibility of Vertical Gradient 1 Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Yamaguchi University 2-16-1 Tokiwadai,Ube 755-8611, Japan r007vm@yamaguchiu.ac.jp in a Downhill Road
Poles for Increasing the Sensibility of Vertical Gradient 1 Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Yamaguchi University 2-16-1 Tokiwadai,Ube 755-8611, Japan r007vm@yamaguchiu.ac.jp in a Downhill Road
Low-Frequency Transient Visual Oscillations in the Fly
 Kate Denning Biophysics Laboratory, UCSD Spring 2004 Low-Frequency Transient Visual Oscillations in the Fly ABSTRACT Low-frequency oscillations were observed near the H1 cell in the fly. Using coherence
Kate Denning Biophysics Laboratory, UCSD Spring 2004 Low-Frequency Transient Visual Oscillations in the Fly ABSTRACT Low-frequency oscillations were observed near the H1 cell in the fly. Using coherence
T-junctions in inhomogeneous surrounds
 Vision Research 40 (2000) 3735 3741 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres T-junctions in inhomogeneous surrounds Thomas O. Melfi *, James A. Schirillo Department of Psychology, Wake Forest Uni ersity, Winston
Vision Research 40 (2000) 3735 3741 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres T-junctions in inhomogeneous surrounds Thomas O. Melfi *, James A. Schirillo Department of Psychology, Wake Forest Uni ersity, Winston
Vection in depth during consistent and inconsistent multisensory stimulation
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Health and Behavioural Sciences - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2011 Vection in depth during consistent and inconsistent multisensory
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Health and Behavioural Sciences - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2011 Vection in depth during consistent and inconsistent multisensory
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
How Many Pixels Do We Need to See Things?
 How Many Pixels Do We Need to See Things? Yang Cai Human-Computer Interaction Institute, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, 5000 Forbes Avenue, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA ycai@cmu.edu
How Many Pixels Do We Need to See Things? Yang Cai Human-Computer Interaction Institute, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, 5000 Forbes Avenue, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA ycai@cmu.edu
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception
 COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 9: Motion perception Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 9: Motion perception Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
Footsteps and inchworms: Illusions show that contrast affects apparent speed
 Perception, 2001, volume 30, pages 785 ^ 794 DOI:10.1068/p3211 Footsteps and inchworms: Illusions show that contrast affects apparent speed Stuart Anstis Department of Psychology, University of California,
Perception, 2001, volume 30, pages 785 ^ 794 DOI:10.1068/p3211 Footsteps and inchworms: Illusions show that contrast affects apparent speed Stuart Anstis Department of Psychology, University of California,
Three elemental illusions determine the Zöllner illusion
 Perception & Psychophysics 2000, 62 (3), 569-575 Three elemental illusions determine the Zöllner illusion AKIYOSHI KITAOKA Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience, Fuchu, Tokyo, Japan and MASAMI
Perception & Psychophysics 2000, 62 (3), 569-575 Three elemental illusions determine the Zöllner illusion AKIYOSHI KITAOKA Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience, Fuchu, Tokyo, Japan and MASAMI
Three stimuli for visual motion perception compared
 Perception & Psychophysics 1982,32 (1),1-6 Three stimuli for visual motion perception compared HANS WALLACH Swarthmore Col/ege, Swarthmore, Pennsylvania ANN O'LEARY Stanford University, Stanford, California
Perception & Psychophysics 1982,32 (1),1-6 Three stimuli for visual motion perception compared HANS WALLACH Swarthmore Col/ege, Swarthmore, Pennsylvania ANN O'LEARY Stanford University, Stanford, California
Analysis of retinal images for retinal projection type super multiview 3D head-mounted display
 https://doi.org/10.2352/issn.2470-1173.2017.5.sd&a-376 2017, Society for Imaging Science and Technology Analysis of retinal images for retinal projection type super multiview 3D head-mounted display Takashi
https://doi.org/10.2352/issn.2470-1173.2017.5.sd&a-376 2017, Society for Imaging Science and Technology Analysis of retinal images for retinal projection type super multiview 3D head-mounted display Takashi
Vision V Perceiving Movement
 Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference
 1 Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference Alan L. Gilchrist 1 & Ana Radonjic 2 1 Rutgers University, Newark, USA 2 University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
1 Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference Alan L. Gilchrist 1 & Ana Radonjic 2 1 Rutgers University, Newark, USA 2 University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
Classifying Illusory Contours: Edges Defined by Pacman and Monocular Tokens
 Classifying Illusory Contours: Edges Defined by Pacman and Monocular Tokens GERALD WESTHEIMER AND WU LI Division of Neurobiology, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720-3200 Westheimer, Gerald
Classifying Illusory Contours: Edges Defined by Pacman and Monocular Tokens GERALD WESTHEIMER AND WU LI Division of Neurobiology, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720-3200 Westheimer, Gerald
Vision V Perceiving Movement
 Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
COLOR, TILT, AND THE HERMANN GRID ILLUSION
 COLOR, TILT, AND THE HERMANN GRID ILLUSION A thesis presented to the graduate faculty of The New England College of Optometry in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
COLOR, TILT, AND THE HERMANN GRID ILLUSION A thesis presented to the graduate faculty of The New England College of Optometry in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
Moon Illusion. (McCready, ; 1. What is Moon Illusion and what it is not
 Moon Illusion (McCready, 1997-2007; http://facstaff.uww.edu/mccreadd/index.html) 1. What is Moon Illusion and what it is not 2. Aparent distance theory (SD only) 3. Visual angle contrast theory (VSD) 4.
Moon Illusion (McCready, 1997-2007; http://facstaff.uww.edu/mccreadd/index.html) 1. What is Moon Illusion and what it is not 2. Aparent distance theory (SD only) 3. Visual angle contrast theory (VSD) 4.
Low Vision Assessment Components Job Aid 1
 Low Vision Assessment Components Job Aid 1 Eye Dominance Often called eye dominance, eyedness, or seeing through the eye, is the tendency to prefer visual input a particular eye. It is similar to the laterality
Low Vision Assessment Components Job Aid 1 Eye Dominance Often called eye dominance, eyedness, or seeing through the eye, is the tendency to prefer visual input a particular eye. It is similar to the laterality
The cyclopean (stereoscopic) barber pole illusion
 Vision Research 38 (1998) 2119 2125 The cyclopean (stereoscopic) barber pole illusion Robert Patterson *, Christopher Bowd, Michael Donnelly Department of Psychology, Washington State Uni ersity, Pullman,
Vision Research 38 (1998) 2119 2125 The cyclopean (stereoscopic) barber pole illusion Robert Patterson *, Christopher Bowd, Michael Donnelly Department of Psychology, Washington State Uni ersity, Pullman,
Optical Illusions and Human Visual System: Can we reveal more? Imaging Science Innovative Student Micro-Grant Proposal 2011
 Optical Illusions and Human Visual System: Can we reveal more? Imaging Science Innovative Student Micro-Grant Proposal 2011 Prepared By: Principal Investigator: Siddharth Khullar 1,4, Ph.D. Candidate (sxk4792@rit.edu)
Optical Illusions and Human Visual System: Can we reveal more? Imaging Science Innovative Student Micro-Grant Proposal 2011 Prepared By: Principal Investigator: Siddharth Khullar 1,4, Ph.D. Candidate (sxk4792@rit.edu)
Illusory displacement of equiluminous kinetic edges
 Perception, 1990, volume 19, pages 611-616 Illusory displacement of equiluminous kinetic edges Vilayanur S Ramachandran, Stuart M Anstis Department of Psychology, C-009, University of California at San
Perception, 1990, volume 19, pages 611-616 Illusory displacement of equiluminous kinetic edges Vilayanur S Ramachandran, Stuart M Anstis Department of Psychology, C-009, University of California at San
A NEURODYNAMICAL RETINAL NETWORK BASED ON REACTION-DIFFUSION SYSTEMS
 A NEURODYNAMICAL RETINAL NETWORK BASED ON REACTION-DIFFUSION SYSTEMS Matthias S. Keil and Gabriel Cristóbal Instituto de Óptica (CSIC) Image and Vision Department Serrano 121, 28006 Madrid (Spain) Heiko
A NEURODYNAMICAL RETINAL NETWORK BASED ON REACTION-DIFFUSION SYSTEMS Matthias S. Keil and Gabriel Cristóbal Instituto de Óptica (CSIC) Image and Vision Department Serrano 121, 28006 Madrid (Spain) Heiko
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Size Illusion on an Asymmetrically Divided Circle
 Size Illusion on an Asymmetrically Divided Circle W.A. Kreiner Faculty of Natural Sciences University of Ulm 2 1. Introduction In the Poggendorff (18) illusion a line, inclined by about 45 0 to the horizontal,
Size Illusion on an Asymmetrically Divided Circle W.A. Kreiner Faculty of Natural Sciences University of Ulm 2 1. Introduction In the Poggendorff (18) illusion a line, inclined by about 45 0 to the horizontal,
Factors affecting curved versus straight path heading perception
 Perception & Psychophysics 2006, 68 (2), 184-193 Factors affecting curved versus straight path heading perception CONSTANCE S. ROYDEN, JAMES M. CAHILL, and DANIEL M. CONTI College of the Holy Cross, Worcester,
Perception & Psychophysics 2006, 68 (2), 184-193 Factors affecting curved versus straight path heading perception CONSTANCE S. ROYDEN, JAMES M. CAHILL, and DANIEL M. CONTI College of the Holy Cross, Worcester,
TRAFFIC SIGN DETECTION AND IDENTIFICATION.
 TRAFFIC SIGN DETECTION AND IDENTIFICATION Vaughan W. Inman 1 & Brian H. Philips 2 1 SAIC, McLean, Virginia, USA 2 Federal Highway Administration, McLean, Virginia, USA Email: vaughan.inman.ctr@dot.gov
TRAFFIC SIGN DETECTION AND IDENTIFICATION Vaughan W. Inman 1 & Brian H. Philips 2 1 SAIC, McLean, Virginia, USA 2 Federal Highway Administration, McLean, Virginia, USA Email: vaughan.inman.ctr@dot.gov
Depth-dependent contrast gain-control
 Vision Research 44 (24) 685 693 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Depth-dependent contrast gain-control Richard N. Aslin *, Peter W. Battaglia, Robert A. Jacobs Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences,
Vision Research 44 (24) 685 693 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Depth-dependent contrast gain-control Richard N. Aslin *, Peter W. Battaglia, Robert A. Jacobs Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences,
better make it a triple (3 x)
 Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Limulus eye: a filter cascade. Limulus 9/23/2011. Dynamic Response to Step Increase in Light Intensity
 Crab cam (Barlow et al., 2001) self inhibition recurrent inhibition lateral inhibition - L17. Neural processing in Linear Systems 2: Spatial Filtering C. D. Hopkins Sept. 23, 2011 Limulus Limulus eye:
Crab cam (Barlow et al., 2001) self inhibition recurrent inhibition lateral inhibition - L17. Neural processing in Linear Systems 2: Spatial Filtering C. D. Hopkins Sept. 23, 2011 Limulus Limulus eye:
Chapter 3. Adaptation to disparity but not to perceived depth
 Chapter 3 Adaptation to disparity but not to perceived depth The purpose of the present study was to investigate whether adaptation can occur to disparity per se. The adapting stimuli were large random-dot
Chapter 3 Adaptation to disparity but not to perceived depth The purpose of the present study was to investigate whether adaptation can occur to disparity per se. The adapting stimuli were large random-dot
PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8
 Motion 1 Perception (PSY 4204) Christine L. Ruva, Ph.D. PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8 Overview of Questions Why do some animals freeze in place when they sense danger? How do films create movement from still
Motion 1 Perception (PSY 4204) Christine L. Ruva, Ph.D. PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8 Overview of Questions Why do some animals freeze in place when they sense danger? How do films create movement from still
UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works
 UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works Title Depth from subjective color and apparent motion Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8fn78237 Journal Vision Research, 42(18) ISSN 0042-6989 Authors
UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works Title Depth from subjective color and apparent motion Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8fn78237 Journal Vision Research, 42(18) ISSN 0042-6989 Authors
AD-A lji llllllllllii l
 Perception, 1992, volume 21, pages 359-363 AD-A259 238 lji llllllllllii1111111111111l lll~ lit DEC The effect of defocussing the image on the perception of the temporal order of flashing lights Saul M
Perception, 1992, volume 21, pages 359-363 AD-A259 238 lji llllllllllii1111111111111l lll~ lit DEC The effect of defocussing the image on the perception of the temporal order of flashing lights Saul M
Articulation: brightness, apparent illumination, and contrast ratios
 Perception, 2, volume 31, pages 161 ^ 169 DOI:.68/p9sp Articulation: brightness, apparent illumination, and contrast ratios James A Schirillo Department of Psychology, Wake Forest University, PO Box 7778
Perception, 2, volume 31, pages 161 ^ 169 DOI:.68/p9sp Articulation: brightness, apparent illumination, and contrast ratios James A Schirillo Department of Psychology, Wake Forest University, PO Box 7778
Spatial Judgments from Different Vantage Points: A Different Perspective
 Spatial Judgments from Different Vantage Points: A Different Perspective Erik Prytz, Mark Scerbo and Kennedy Rebecca The self-archived postprint version of this journal article is available at Linköping
Spatial Judgments from Different Vantage Points: A Different Perspective Erik Prytz, Mark Scerbo and Kennedy Rebecca The self-archived postprint version of this journal article is available at Linköping
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
CYCLOPEAN MOTION AFTEREFFECTS USING SPIRAL PATTERNS: DISSOCIATION BETWEEN LOCAL AND GLOBAL PROCESSING JASON ALAN ROGERS
 CYCLOPEAN MOTION AFTEREFFECTS USING SPIRAL PATTERNS: DISSOCIATION BETWEEN LOCAL AND GLOBAL PROCESSING By JASON ALAN ROGERS A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
CYCLOPEAN MOTION AFTEREFFECTS USING SPIRAL PATTERNS: DISSOCIATION BETWEEN LOCAL AND GLOBAL PROCESSING By JASON ALAN ROGERS A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
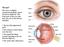 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
STREAK DETECTION ALGORITHM FOR SPACE DEBRIS DETECTION ON OPTICAL IMAGES
 STREAK DETECTION ALGORITHM FOR SPACE DEBRIS DETECTION ON OPTICAL IMAGES Alessandro Vananti, Klaus Schild, Thomas Schildknecht Astronomical Institute, University of Bern, Sidlerstrasse 5, CH-3012 Bern,
STREAK DETECTION ALGORITHM FOR SPACE DEBRIS DETECTION ON OPTICAL IMAGES Alessandro Vananti, Klaus Schild, Thomas Schildknecht Astronomical Institute, University of Bern, Sidlerstrasse 5, CH-3012 Bern,
A Fraser illusion without local cues?
 Vision Research 40 (2000) 873 878 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Rapid communication A Fraser illusion without local cues? Ariella V. Popple *, Dov Sagi Neurobiology, The Weizmann Institute of Science,
Vision Research 40 (2000) 873 878 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Rapid communication A Fraser illusion without local cues? Ariella V. Popple *, Dov Sagi Neurobiology, The Weizmann Institute of Science,
The effect of rotation on configural encoding in a face-matching task
 Perception, 2007, volume 36, pages 446 ^ 460 DOI:10.1068/p5530 The effect of rotation on configural encoding in a face-matching task Andrew J Edmondsô, Michael B Lewis School of Psychology, Cardiff University,
Perception, 2007, volume 36, pages 446 ^ 460 DOI:10.1068/p5530 The effect of rotation on configural encoding in a face-matching task Andrew J Edmondsô, Michael B Lewis School of Psychology, Cardiff University,
First-order structure induces the 3-D curvature contrast effect
 Vision Research 41 (2001) 3829 3835 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres First-order structure induces the 3-D curvature contrast effect Susan F. te Pas a, *, Astrid M.L. Kappers b a Psychonomics, Helmholtz
Vision Research 41 (2001) 3829 3835 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres First-order structure induces the 3-D curvature contrast effect Susan F. te Pas a, *, Astrid M.L. Kappers b a Psychonomics, Helmholtz
Discriminating direction of motion trajectories from angular speed and background information
 Atten Percept Psychophys (2013) 75:1570 1582 DOI 10.3758/s13414-013-0488-z Discriminating direction of motion trajectories from angular speed and background information Zheng Bian & Myron L. Braunstein
Atten Percept Psychophys (2013) 75:1570 1582 DOI 10.3758/s13414-013-0488-z Discriminating direction of motion trajectories from angular speed and background information Zheng Bian & Myron L. Braunstein
A Pilot Study: Introduction of Time-domain Segment to Intensity-based Perception Model of High-frequency Vibration
 A Pilot Study: Introduction of Time-domain Segment to Intensity-based Perception Model of High-frequency Vibration Nan Cao, Hikaru Nagano, Masashi Konyo, Shogo Okamoto 2 and Satoshi Tadokoro Graduate School
A Pilot Study: Introduction of Time-domain Segment to Intensity-based Perception Model of High-frequency Vibration Nan Cao, Hikaru Nagano, Masashi Konyo, Shogo Okamoto 2 and Satoshi Tadokoro Graduate School
Analysis of Gaze on Optical Illusions
 Analysis of Gaze on Optical Illusions Thomas Rapp School of Computing Clemson University Clemson, South Carolina 29634 tsrapp@g.clemson.edu Abstract A comparison of human gaze patterns on illusions before
Analysis of Gaze on Optical Illusions Thomas Rapp School of Computing Clemson University Clemson, South Carolina 29634 tsrapp@g.clemson.edu Abstract A comparison of human gaze patterns on illusions before
The horizon line, linear perspective, interposition, and background brightness as determinants of the magnitude of the pictorial moon illusion
 Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics 2009, 71 (1), 131-142 doi:10.3758/app.71.1.131 The horizon line, linear perspective, interposition, and background brightness as determinants of the magnitude of
Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics 2009, 71 (1), 131-142 doi:10.3758/app.71.1.131 The horizon line, linear perspective, interposition, and background brightness as determinants of the magnitude of
Effect of Stimulus Duration on the Perception of Red-Green and Yellow-Blue Mixtures*
 Reprinted from JOURNAL OF THE OPTICAL SOCIETY OF AMERICA, Vol. 55, No. 9, 1068-1072, September 1965 / -.' Printed in U. S. A. Effect of Stimulus Duration on the Perception of Red-Green and Yellow-Blue
Reprinted from JOURNAL OF THE OPTICAL SOCIETY OF AMERICA, Vol. 55, No. 9, 1068-1072, September 1965 / -.' Printed in U. S. A. Effect of Stimulus Duration on the Perception of Red-Green and Yellow-Blue
The human visual system
 The human visual system Vision and hearing are the two most important means by which humans perceive the outside world. 1 Low-level vision Light is the electromagnetic radiation that stimulates our visual
The human visual system Vision and hearing are the two most important means by which humans perceive the outside world. 1 Low-level vision Light is the electromagnetic radiation that stimulates our visual
Motion Perception II Chapter 8
 Motion Perception II Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2019 Eye movements: also give rise to retinal motion. important to distinguish motion due to
Motion Perception II Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2019 Eye movements: also give rise to retinal motion. important to distinguish motion due to
PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE. Research Report
 Research Report STEREOSCOPIC SURFACE INTERPOLATION SUPPORTS LIGHTNESS CONSTANCY Laurie M. Wilcox and Philip A. Duke Centre for Vision Research, York University, Toronto, Ontario, Canada Abstract The human
Research Report STEREOSCOPIC SURFACE INTERPOLATION SUPPORTS LIGHTNESS CONSTANCY Laurie M. Wilcox and Philip A. Duke Centre for Vision Research, York University, Toronto, Ontario, Canada Abstract The human
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See
 Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Häkkinen, Jukka; Gröhn, Lauri Turning water into rock
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Häkkinen, Jukka; Gröhn, Lauri Turning
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Häkkinen, Jukka; Gröhn, Lauri Turning
Human Visual System. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Left aspl Right aspl Detailed description of the fmri activation during allocentric action observation in the aspl. Averaged activation (N=13) during observation of the allocentric
Supplementary Figure 1 Left aspl Right aspl Detailed description of the fmri activation during allocentric action observation in the aspl. Averaged activation (N=13) during observation of the allocentric
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
The influence of exploration mode, orientation, and configuration on the haptic Mu«ller-Lyer illusion
 Perception, 2005, volume 34, pages 1475 ^ 1500 DOI:10.1068/p5269 The influence of exploration mode, orientation, and configuration on the haptic Mu«ller-Lyer illusion Morton A Heller, Melissa McCarthy,
Perception, 2005, volume 34, pages 1475 ^ 1500 DOI:10.1068/p5269 The influence of exploration mode, orientation, and configuration on the haptic Mu«ller-Lyer illusion Morton A Heller, Melissa McCarthy,
SMALL VOLUNTARY MOVEMENTS OF THE EYE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 746. SMALL VOLUNTARY MOVEMENTS OF THE EYE* BY B. L. GINSBORG Physics Department, University of Reading IT is well known that the transfer of the gaze from one point to another,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 746. SMALL VOLUNTARY MOVEMENTS OF THE EYE* BY B. L. GINSBORG Physics Department, University of Reading IT is well known that the transfer of the gaze from one point to another,
Modulation frequency and orientation tuning of second-order texture mechanisms
 Arsenault et al. Vol. 16, No. 3/March 1999/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 427 Modulation frequency and orientation tuning of second-order texture mechanisms A. Serge Arsenault and Frances Wilkinson Department of Psychology,
Arsenault et al. Vol. 16, No. 3/March 1999/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 427 Modulation frequency and orientation tuning of second-order texture mechanisms A. Serge Arsenault and Frances Wilkinson Department of Psychology,
A new illusion of height and width: taller people are perceived as thinner
 Psychon Bull Rev (2013) 20:1154 1160 DOI 10.3758/s13423-013-0454-8 BRIEF REPORT A new illusion of height and width: taller people are perceived as thinner Diane M. Beck & Barbara Emanuele & Silvia Savazzi
Psychon Bull Rev (2013) 20:1154 1160 DOI 10.3758/s13423-013-0454-8 BRIEF REPORT A new illusion of height and width: taller people are perceived as thinner Diane M. Beck & Barbara Emanuele & Silvia Savazzi
Colour: Design & Creativity
 http://www.colour-journal.org/2010/5/3/ A Brief Classification of Colour Illusions Akiyoshi Kitaoka Department of Psychology, Ritsumeikan University, Toji-in Kitamachi, Kita-ku, Kyoto 603-8577, Japan Email:
http://www.colour-journal.org/2010/5/3/ A Brief Classification of Colour Illusions Akiyoshi Kitaoka Department of Psychology, Ritsumeikan University, Toji-in Kitamachi, Kita-ku, Kyoto 603-8577, Japan Email:
Learning Targets. Module 19
 Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
A Three-Channel Model for Generating the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex in Each Eye
 A Three-Channel Model for Generating the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex in Each Eye LAURENCE R. HARRIS, a KARL A. BEYKIRCH, b AND MICHAEL FETTER c a Department of Psychology, York University, Toronto, Canada
A Three-Channel Model for Generating the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex in Each Eye LAURENCE R. HARRIS, a KARL A. BEYKIRCH, b AND MICHAEL FETTER c a Department of Psychology, York University, Toronto, Canada
