Test of pan and zoom tools in visual and non-visual audio haptic environments. Magnusson, Charlotte; Gutierrez, Teresa; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten
|
|
|
- Isabella McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Test of pan and zoom tools in visual and non-visual audio haptic environments Magnusson, Charlotte; Gutierrez, Teresa; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten Published in: ENACTIVE Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Magnusson, C., Gutierrez, T., & Rassmus-Gröhn, K. (2007). Test of pan and zoom tools in visual and non-visual audio haptic environments. In ENACTIVE 07 General rights Copyright and moral rights for the publications made accessible in the public portal are retained by the authors and/or other copyright owners and it is a condition of accessing publications that users recognise and abide by the legal requirements associated with these rights. Users may download and print one copy of any publication from the public portal for the purpose of private study or research. You may not further distribute the material or use it for any profit-making activity or commercial gain You may freely distribute the URL identifying the publication in the public portal Take down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. L UNDUNI VERS I TY PO Box L und Download date: 06. Mar. 2019
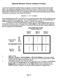
2 Test of pan and zoom tools in visual and non-visual audio haptic environments Charlotte Magnusson * Teresa Gutierrez * Kirsten Rassmus-Gröhn * (*)Lund University, Lund, Sweden (* )LABEIN, Bilbao, Spain charlotte.magnusson@certec.lth.se, tere@labein.es, kirre@certec.lth.se Abstract To enable visually impaired users to experience large virtual 3D models with a relatively small haptic device a test of a set of pan and zoom tools has been performed. The pan tools tested (keyboard, pressing the sides of the limiting box and click & drag using the PHANToM) were all seen to be useful. For the zoom tool the discrete keyboard press design was seen to work well, while the drag type zoom implemented worked poorly and will need to be redesigned. The test results show different preferences in visual and non-visual navigation, indicating the need for specially designed interaction utilities for the non-visual case. 1. Introduction In most haptic virtual environments for the blind, the working area of the haptic device (such as the PHANToM) limits the size and complexity of the virtual environment that can be displayed. Haptic non-visual pan and zooming using a PHANToM device has been studied to some limited extent. Within the ENORASI study described in [1], a simple pan function was tested by a subset of the test users. Zoom functions to gain access to greater detail in virtual haptic line graphs are also suggested by Roberts et al [2], a test of a set of pan and zoom functions has been reported in [3] and this type of functions were also included in the virtual audiohaptic traffic environment described in [4]. The studies described in this paper were designed to further investigate pan and zoom utilities in a more realistic environment. 2. Test environment The environment used was essentially the traffic model described in [4] (see figure 1), but with the model no longer divided into five parts, but instead joined into a single model. Three different pan or scroll functions were implemented. They were similar to the ones used in [3]: moving the world using the arrow keys, moving the world by pushing the sides of the limiting box with the PHANToM stylus and moving the world by clicking & dragging using the PHANToM stylus. Figure 1. Views from the traffic environment model used. When moved by pressing the arrow keys, the world moved in the direction of the key pressed. When the user pushed the limiting box, the world moved as if the box was actually pushed by the user over the model. For the click and drag pan function the world became attached to the PHANToM stylus, although to avoid unpredicted movements in the vertical direction the movement was restricted to the horizontal plane. The two discrete move functions (arrow keys and limiting box) allowed for different move lengths. The move length that should be used was selected by the user. For the zoom we used two basically different implementations: stepwise zoom by pressing a key on the keyboard and click & drag zoom using the PHANToM stylus. The click & drag zoom was implemented based on a rubber band metaphor i.e two points can be dragged with respect to each other to enlarge or reduce the size of the model (like you would to enlarge or reduce the size of a rubber band). Since the interaction device (the PHANToM) only has one interaction point, the position of the first point was indicated by a point and click action, and then the user pointed the stylus at the second point, held down the switch and used drag to resize the world. The stepwise zoom used fixed zoom factors of 0.8 for zooming out and 1.25 for zooming in. It was implemented so that the tip of the PHANToM stylus Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Enactive Interfaces Grenoble, France, November 19 th -22 nd,
3 was always in the same position relative to the world before & after the zoom. To test the importance of knowing the contact point with respect to the world, users were asked to do the stepwise zoom in two different ways: in contact with the model and lifting the stylus a distance above the world. 3. Test setup The test was performed by 12 sighted users (age 23-60). To speed up the learning process and also to compare sighted interaction with interaction using only touch and hearing the test users first performed the test with vision and after that without visual feedback. The order in which the tools within the pan and zoom groups were tested was permuted to avoid learning effects. The pan tools were tested before the zoom tools both in the visual and the non-visual case. All test persons started the test with visual feedback, and were initially allowed to familiarize themselves with the environment and with the different move lengths. The move lengths were not tested individually, but instead the users were instructed to use whatever lengths they wanted and the usage of different length settings was recorded. After the initial familiarization, the pan test task was performed for all three pan tools. The pan task was to locate the bus stop in the south part of the environment and then to move the PHANToM stylus to a rocket in the north part of the environment while making use of the specified pan tool when panning was needed. The initial position of the world was always the same (showing the middle part of the world). The zoom test task was to first locate the bus stop and then to zoom in and point to 3 objects at the bus stop: the waste paper basket, the sofa and the stairs. This task was done for all three zoom tools. As a final task the user was asked to do the pan and the zoom tasks once again but this time using his or her favorite tools the user could use any of the tested tools, and the tool use was recorded. After this, all these test tasks were performed again but without visual feedback. 4. Results All users were able to complete the test tasks both with and without visual feedback. The results were analyzed with analysis of variance (ANOVA) where the independent within-group variable was the navigational strategy used. Post hoc tests were done using the Tukey test and the significance level was set to 0.05 throughout the analyses. Pan method Mean (s) Sd (s) Arrow keys, vision Limiting box, vision PHANToM drag, vision Arrow keys, no vision Limiting box, no vision PHANToM drag, no vision Favorite pan, vision Favorite pan, no vision Table 1. Means and standard deviations (Sd) for the time to complete for the different pan tasks. For the pan tools, the ANOVA for the dependent variable time to complete (see table 1) revealed significant differences (F(7,77)=14,1, p<0.05). As expected, the post hoc test showed significant differences between all three pan methods with vision and all the three non-visual pan methods, while the difference between the favorite pan with and without vision, although showing a tendency in this direction, did not turn out to be significant (Q(8,77)=3,2). In the non-visual condition the use of the arrow keys and the PHANToM drag was significantly slower than the final test where the favorite tool(s) was(were) used (Q(8,77)=6.5, 4.5). A tendency (Q(8,77)=3,2) was seen also for the comparison with the limiting box. No such effect was seen for the visual case which indicates a stronger training effect for the non-visual interaction. As expected all the non-visual pan methods were all significantly slower than the favorite pan with vision. In the visual condition, the favorite tool selected for the final task by 8 users was the arrow keys while 5 users preferred the drag (one user used both). None of the users preferred pushing the limiting box for interaction in the visual case. For the non-visual condition, the tools preferred by the users in the final pan test task are different. For non-visual interaction 6 users preferred the PHANToM drag, 4 users preferred the arrow keys and 2 users preferred pushing the limiting box. For the discrete pan tools, the most often used move factors were 10, 20 and 60 in both conditions. The results in the non-visual condition were a bit more pronounced (probably due to the fact that the users now were more familiar with the environment) but the same move factors were most frequently used. The actual length of the move was calculated as m (the proxy radius) times the move factor. In the current environment a move factor of 60 corresponded to a page up/page down type of move: if the environment was moved in the north south direction, the move was done so that the points visible at a bottom south position would be visible at a top north position after the move. 166
4 Zoom method Mean (s) Sd (s) Keyboard no contact, vision Keyboard with contact, vision Zoom drag, vision Keyboard no contact, no vision Keyboard with vision, no contact Zoom drag, no vision Favorite zoom, vision Favorite zoom, no vision Table 2. Means and standard deviations (Sd) for the time to complete for the different zoom tasks. The results for the zoom are summarized in table 2. The zoom drag turned out to be hard to use, which also shows up in the post hoc test. While both keyboard zooms were significantly faster than all the zoom tools without vision, this was not the case for the zoom drag. The tendency for the favorite zoom with vision to be faster than the non visual favorite is more pronounced than for the pan tools (Q(8,77)=4.2) but it is not significant (the significance level is at 4.4). Comparing the zoom tools with the corresponding favorites did not show any significant differences (less of a training effect). This could be due to the fact that the zoom tools were tested after the pan tools but the task for the zoom operations also appeared to be less favored by the visual interaction (some of the objects the user should locate were usually hidden from view). In the non-visual condition, one very experienced PHANToM user liked the zoom drag tool (due both to the fact that this tool provided some feedback about the amount of zoom and to the fact that one only needed to zoom once). Finally, if we look only at the mean values, we see that after some training and with a choice of interaction techniques the completion times for the non-visual case are only 2-3 times longer than the times obtained with vision. 5. A related study A related study was performed at LABEIN, Bilbao, Spain. Figure 2. The types of graphs used in the LABEIN test. This test was done using the GRAB [5] two-point haptic device, and tested the way visually impaired users were able to interact with audio-haptic maps and graphs (figure 2). The applications used in this test include pan and zoom utilities, it provides an interesting complement to the results presented above Pan and zoom implementation The pan function in the LABEIN test was implemented so that the position of the control finger was fixed relative to the virtual graph scene. The movement of the control finger was then used for translating the scene. While the users were panning, they received a resistance force to indicate that the workspace was being moved. The user was unable to move outside the graph scene. This implementation was similar to the click & drag panning tested in the Lund test (although in Lund you could pan outside the model). The zoom function implemented for the LABEIN tests was designed in a similar way as the stepwise zoom function used in the Lund test. As the size was changed by pressing a keyboard key the control finger remained in the same position relative to the world, while the other finger would end up in a different position due to the size change Test results The LABEIN test was performed with visually impaired users the map application was tested by 4 congenitally blind persons and 5 persons with low vision, while the graphs application was tested by 4 congenitally blind persons and 6 persons with low vision. The users were allowed a training session before the actual test to familiarize themselves with the applications. For the graphs application 7 users thought the advanced utilities such as pan and zoom were easy to use while 3 thought they were not too easy but not too hard. For the maps application 8 users thought these utilities were easy to use and one user thought it was not too easy but not too hard. Looking at the user feedback received, two users with low vision stated that the panning was not intuitive. These users were used to work with magnifiers so they hoped to move the workspace (or the tool) and not the graph. Some users found it hard to realize that a graph did not fit in the workspace (indicating the usefulness of feedback on this point). It was also seen that it could be useful to be able to select the range of the zooming and scaling, or at least to provide the user with feedback about the range. 167
5 6. Discussion and conclusion The results of the Lund traffic environment pan and zoom test show that all the pan function designs are working quite well. In contrast with [3], it now turns out the PHANToM drag is the most popular pan tool for non-visual interaction. The usefulness of the drag function is further strengthened by the results obtained at LABEIN. Still, all three tool designs were shown to be useful (as in [3]). One problem with the arrow key panning is to know which way the world will move. In the present implementation it is the model that moves in the direction of the arrows. Some users initially had problems with this, which indicates the importance of providing the user with feedback of what has happened. In Lund no users had problems with the direction of the click and drag type of panning, while in the LABEIN test two users had problems with the panning direction for this type of panning. The test result shows the need of at least two (maybe three) different move lengths for the discrete pan operations. One really large, like a page down/page up and one shorter for the finer adjustments is needed. In the current test the proportions for the three most used lengths were 1:2:6. One problem was the fact that it was possible to move the model far away from the work space. This indicates that when the size of the world is known an environment like this should simply not allow the model to move completely out of the workspace (already implemented in the LABEIN applications). For the zooming operations it was clear that the design where the user is in contact with the same point of the model before and after the zoom works well. Despite this, several users complained about the lack of feedback on how much the world was zoomed, and more feedback on this point needs to be added. Both these results agree with the results from the LABEIN test. The design of the drag zoom function was not a success. Despite this the user responses indicate that some kind of direct manipulation type zoom could be quite useful. Further investigation is clearly needed on this point. The results obtained also support the earlier study by Jansson et al [6] which show the importance of training our results for the pan tools indicate a training effect particularly for the non-visual interaction. The Lund test highlights the fact that user preferences depend a lot on whether or not they have access to visual feedback. This is a reminder for anyone developing non-visual applications that the interaction needs to be specially designed for the non-visual case. Finally this test confirms that it is quite possible to understand and interact with large and complex haptic environment also in the non-visual case. 7. Acknowledgements The study was carried out with the financial assistance of the European Commission which cofunded the IP ENABLED, FP IST - 2, No and the NoE ENACTIVE - ENACTIVE Interfaces, FP IST-1, No IST The authors are grateful to the EU for the support given in carrying out these activities. References [1] C. Magnusson, K. Rassmus-Gröhn, C. Sjöström and H. Danielsson, Navigation and recog-nition in complex haptic virtual environments reports from an extensive study with blind users, Eurohaptics 2002, Edinburgh, UK [2] J.C. Roberts, K. Franklin, and J. Cullinane, Virtual Haptic Exploratory Visualization of Line Graphs and Charts, The Engineering Reality of Virtual Reality 2002, Mark T. Bolas, editor, volume 4660B of Electronic Imaging Conference, page 10. IS&T/SPIE, January 2002 [3] C. Magnusson, K. Rassmus-Gröhn, Non-visual Zoom and Scrolling Operations in a Virtual Haptic Environment, EuroHaptics 2003, Dublin, Ireland [4] C. Magnusson, K. Rassmus-Gröhn, A Virtual Traffic Environment for People with Visual Impairments, Visual Impairment Research, pp 1-12 Vol 7. No [5] R. Iglesias, S. Casado, T. Gutiérrez, J.I. Barbero, C.A. Avizzano, S. Marcheschi, M. Bergamasco, Computer graphics access for blind people through a haptic and audiovirtual environment, HAVE 2004 (Ottawa, Canada, 2-3 October 2004) [6] G.Jansson and A. Ivås, Can the efficiency of a haptic display be increased by short-time practice in exploration? Proceedings of Haptic Human-Computer Interaction
The ENABLED Editor and Viewer simple tools for more accessible on line 3D models. Magnusson, Charlotte; Gutierrez, Teresa; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten
 The ENABLED Editor and Viewer simple tools for more accessible on line 3D models Magnusson, Charlotte; Gutierrez, Teresa; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten Published in: 5th international conference on Enactive Interfaces
The ENABLED Editor and Viewer simple tools for more accessible on line 3D models Magnusson, Charlotte; Gutierrez, Teresa; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten Published in: 5th international conference on Enactive Interfaces
Magnusson, Charlotte; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Szymczak, Delphine
 Show me the direction how accurate does it have to be? Magnusson, Charlotte; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Szymczak, Delphine Published: 2010-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Magnusson,
Show me the direction how accurate does it have to be? Magnusson, Charlotte; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Szymczak, Delphine Published: 2010-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Magnusson,
An Audio-Haptic Mobile Guide for Non-Visual Navigation and Orientation
 An Audio-Haptic Mobile Guide for Non-Visual Navigation and Orientation Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Molina, Miguel; Magnusson, Charlotte; Szymczak, Delphine Published in: Poster Proceedings from 5th International
An Audio-Haptic Mobile Guide for Non-Visual Navigation and Orientation Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Molina, Miguel; Magnusson, Charlotte; Szymczak, Delphine Published in: Poster Proceedings from 5th International
Published in: HAVE IEEE International Workshop on Haptic Audio Visual Environments and their Applications
 AHEAD - Audio-haptic drawing editor and explorer for education Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Magnusson, Charlotte; Eftring, Håkan Published in: HAVE 2007 - IEEE International Workshop on Haptic Audio Visual
AHEAD - Audio-haptic drawing editor and explorer for education Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Magnusson, Charlotte; Eftring, Håkan Published in: HAVE 2007 - IEEE International Workshop on Haptic Audio Visual
Angle sizes for pointing gestures Magnusson, Charlotte; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Szymczak, Delphine
 Angle sizes for pointing gestures Magnusson, Charlotte; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Szymczak, Delphine Published in: Proceedings of Workshop on Multimodal Location Based Techniques for Extreme Navigation Published:
Angle sizes for pointing gestures Magnusson, Charlotte; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Szymczak, Delphine Published in: Proceedings of Workshop on Multimodal Location Based Techniques for Extreme Navigation Published:
Magnusson, Charlotte; Molina, Miguel; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Szymczak, Delphine
 Pointing for non-visual orientation and navigation Magnusson, Charlotte; Molina, Miguel; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Szymczak, Delphine Published in: Proceedings of the 6th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer
Pointing for non-visual orientation and navigation Magnusson, Charlotte; Molina, Miguel; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten; Szymczak, Delphine Published in: Proceedings of the 6th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer
Local Coloring and Regional Identity:
 Local Coloring and Regional Identity: Kjellström, Richard 2004 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Kjellström, R. (2004). Local Coloring and Regional Identity:. Paper presented at
Local Coloring and Regional Identity: Kjellström, Richard 2004 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Kjellström, R. (2004). Local Coloring and Regional Identity:. Paper presented at
Heterogeneity and homogeneity in library and information science research
 Heterogeneity and homogeneity in library and information science research Åström, Fredrik Published in: Information Research Published: 2007-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
Heterogeneity and homogeneity in library and information science research Åström, Fredrik Published in: Information Research Published: 2007-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
A 100MHz CMOS wideband IF amplifier
 A 100MHz CMOS wideband IF amplifier Sjöland, Henrik; Mattisson, Sven Published in: IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits DOI: 10.1109/4.663569 1998 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
A 100MHz CMOS wideband IF amplifier Sjöland, Henrik; Mattisson, Sven Published in: IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits DOI: 10.1109/4.663569 1998 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
Citation for published version (APA): Olausson, D., & Ekengren, F. (2014). Editorial. Lund Archaeological Review, 20, 5-5.
 Editorial Olausson, Deborah; Ekengren, Fredrik Published in: Lund Archaeological Review 2014 Document Version: Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link to publication Citation for published
Editorial Olausson, Deborah; Ekengren, Fredrik Published in: Lund Archaeological Review 2014 Document Version: Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link to publication Citation for published
Interactive Exploration of City Maps with Auditory Torches
 Interactive Exploration of City Maps with Auditory Torches Wilko Heuten OFFIS Escherweg 2 Oldenburg, Germany Wilko.Heuten@offis.de Niels Henze OFFIS Escherweg 2 Oldenburg, Germany Niels.Henze@offis.de
Interactive Exploration of City Maps with Auditory Torches Wilko Heuten OFFIS Escherweg 2 Oldenburg, Germany Wilko.Heuten@offis.de Niels Henze OFFIS Escherweg 2 Oldenburg, Germany Niels.Henze@offis.de
Impact of the size of the hearing aid on the mobile phone near fields Bonev, Ivan Bonev; Franek, Ondrej; Pedersen, Gert F.
 Aalborg Universitet Impact of the size of the hearing aid on the mobile phone near fields Bonev, Ivan Bonev; Franek, Ondrej; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium
Aalborg Universitet Impact of the size of the hearing aid on the mobile phone near fields Bonev, Ivan Bonev; Franek, Ondrej; Pedersen, Gert F. Published in: Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium
Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs
 Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs Gustafsson, Mats Published: 24-- Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gustafsson, M. (24). Broadband
Broadband array antennas using a self-complementary antenna array and dielectric slabs Gustafsson, Mats Published: 24-- Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gustafsson, M. (24). Broadband
Measured propagation characteristics for very-large MIMO at 2.6 GHz
 Measured propagation characteristics for very-large MIMO at 2.6 GHz Gao, Xiang; Tufvesson, Fredrik; Edfors, Ove; Rusek, Fredrik Published in: [Host publication title missing] Published: 2012-01-01 Link
Measured propagation characteristics for very-large MIMO at 2.6 GHz Gao, Xiang; Tufvesson, Fredrik; Edfors, Ove; Rusek, Fredrik Published in: [Host publication title missing] Published: 2012-01-01 Link
Aspemyr, Lars; Jacobsson, Harald; Bao, Mingquan; Sjöland, Henrik; Ferndal, Mattias; Carchon, G
 A 15 GHz and a 2 GHz low noise amplifier in 9 nm RF CMOS Aspemyr, Lars; Jacobsson, Harald; Bao, Mingquan; Sjöland, Henrik; Ferndal, Mattias; Carchon, G Published in: Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic
A 15 GHz and a 2 GHz low noise amplifier in 9 nm RF CMOS Aspemyr, Lars; Jacobsson, Harald; Bao, Mingquan; Sjöland, Henrik; Ferndal, Mattias; Carchon, G Published in: Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic
SUSPENSION CRITERIA FOR IMAGE MONITORS AND VIEWING BOXES.
 SUSPENSION CRITERIA FOR IMAGE MONITORS AND VIEWING BOXES. Tingberg, Anders Published in: Radiation Protection Dosimetry DOI: 10.1093/rpd/ncs302 Published: 2013-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published
SUSPENSION CRITERIA FOR IMAGE MONITORS AND VIEWING BOXES. Tingberg, Anders Published in: Radiation Protection Dosimetry DOI: 10.1093/rpd/ncs302 Published: 2013-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published
Open Access to music research in Sweden the pros and cons of publishing in university digital archives
 Open Access to music research in Sweden the pros and cons of publishing in university digital archives Berry, Peter Published in: [Host publication title missing] 2008 Link to publication Citation for
Open Access to music research in Sweden the pros and cons of publishing in university digital archives Berry, Peter Published in: [Host publication title missing] 2008 Link to publication Citation for
Evaluation of the Danish Safety by Design in Construction Framework (SDCF)
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 15, 2017 Evaluation of the Danish Safety by Design in Construction Framework (SDCF) Schultz, Casper Siebken; Jørgensen, Kirsten Publication date: 2015 Link back to
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 15, 2017 Evaluation of the Danish Safety by Design in Construction Framework (SDCF) Schultz, Casper Siebken; Jørgensen, Kirsten Publication date: 2015 Link back to
QS Spiral: Visualizing Periodic Quantified Self Data
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: May 12, 2018 QS Spiral: Visualizing Periodic Quantified Self Data Larsen, Jakob Eg; Cuttone, Andrea; Jørgensen, Sune Lehmann Published in: Proceedings of CHI 2013 Workshop
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: May 12, 2018 QS Spiral: Visualizing Periodic Quantified Self Data Larsen, Jakob Eg; Cuttone, Andrea; Jørgensen, Sune Lehmann Published in: Proceedings of CHI 2013 Workshop
The Archaeology of Time travel An introduction
 The Archaeology of Time travel An introduction Petersson, Bodil; Holtorf, Cornelius Published in: Lund Archaeological Review 2010 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Petersson, B.,
The Archaeology of Time travel An introduction Petersson, Bodil; Holtorf, Cornelius Published in: Lund Archaeological Review 2010 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Petersson, B.,
Microsoft Scrolling Strip Prototype: Technical Description
 Microsoft Scrolling Strip Prototype: Technical Description Primary features implemented in prototype Ken Hinckley 7/24/00 We have done at least some preliminary usability testing on all of the features
Microsoft Scrolling Strip Prototype: Technical Description Primary features implemented in prototype Ken Hinckley 7/24/00 We have done at least some preliminary usability testing on all of the features
Petersson, Mikael; Årzén, Karl-Erik; Sandberg, Henrik; de Maré, Lena
 Implementation of a Tool for Control Structure Assessment Petersson, Mikael; Årzén, Karl-Erik; Sandberg, Henrik; de Maré, Lena Published in: Proceedings of the 15th IFAC world congress Link to publication
Implementation of a Tool for Control Structure Assessment Petersson, Mikael; Årzén, Karl-Erik; Sandberg, Henrik; de Maré, Lena Published in: Proceedings of the 15th IFAC world congress Link to publication
Log-periodic dipole antenna with low cross-polarization
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Feb 13, 2018 Log-periodic dipole antenna with low cross-polarization Pivnenko, Sergey Published in: Proceedings of the European Conference on Antennas and Propagation Link
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Feb 13, 2018 Log-periodic dipole antenna with low cross-polarization Pivnenko, Sergey Published in: Proceedings of the European Conference on Antennas and Propagation Link
Haptic Camera Manipulation: Extending the Camera In Hand Metaphor
 Haptic Camera Manipulation: Extending the Camera In Hand Metaphor Joan De Boeck, Karin Coninx Expertise Center for Digital Media Limburgs Universitair Centrum Wetenschapspark 2, B-3590 Diepenbeek, Belgium
Haptic Camera Manipulation: Extending the Camera In Hand Metaphor Joan De Boeck, Karin Coninx Expertise Center for Digital Media Limburgs Universitair Centrum Wetenschapspark 2, B-3590 Diepenbeek, Belgium
Haptic presentation of 3D objects in virtual reality for the visually disabled
 Haptic presentation of 3D objects in virtual reality for the visually disabled M Moranski, A Materka Institute of Electronics, Technical University of Lodz, Wolczanska 211/215, Lodz, POLAND marcin.moranski@p.lodz.pl,
Haptic presentation of 3D objects in virtual reality for the visually disabled M Moranski, A Materka Institute of Electronics, Technical University of Lodz, Wolczanska 211/215, Lodz, POLAND marcin.moranski@p.lodz.pl,
Guiding Tourists through Haptic Interaction: Vibration Feedback in the Lund Time Machine
 Guiding Tourists through Haptic Interaction: Vibration Feedback in the Lund Time Machine Szymczak, Delphine; Magnusson, Charlotte; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten Published in: Lecture Notes in Computer Science
Guiding Tourists through Haptic Interaction: Vibration Feedback in the Lund Time Machine Szymczak, Delphine; Magnusson, Charlotte; Rassmus-Gröhn, Kirsten Published in: Lecture Notes in Computer Science
The Game Experience Questionnaire
 The Game Experience Questionnaire IJsselsteijn, W.A.; de Kort, Y.A.W.; Poels, K. Published: 01/01/2013 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as Version of Record (includes final page, issue and
The Game Experience Questionnaire IJsselsteijn, W.A.; de Kort, Y.A.W.; Poels, K. Published: 01/01/2013 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as Version of Record (includes final page, issue and
The Effect of Haptic Feedback on Basic Social Interaction within Shared Virtual Environments
 The Effect of Haptic Feedback on Basic Social Interaction within Shared Virtual Environments Elias Giannopoulos 1, Victor Eslava 2, María Oyarzabal 2, Teresa Hierro 2, Laura González 2, Manuel Ferre 2,
The Effect of Haptic Feedback on Basic Social Interaction within Shared Virtual Environments Elias Giannopoulos 1, Victor Eslava 2, María Oyarzabal 2, Teresa Hierro 2, Laura González 2, Manuel Ferre 2,
E90 Project Proposal. 6 December 2006 Paul Azunre Thomas Murray David Wright
 E90 Project Proposal 6 December 2006 Paul Azunre Thomas Murray David Wright Table of Contents Abstract 3 Introduction..4 Technical Discussion...4 Tracking Input..4 Haptic Feedack.6 Project Implementation....7
E90 Project Proposal 6 December 2006 Paul Azunre Thomas Murray David Wright Table of Contents Abstract 3 Introduction..4 Technical Discussion...4 Tracking Input..4 Haptic Feedack.6 Project Implementation....7
Leading the Agenda. Everyday technology: A focus group with children, young people and their carers
 Leading the Agenda Everyday technology: A focus group with children, young people and their carers March 2018 1 1.0 Introduction Assistive technology is an umbrella term that includes assistive, adaptive,
Leading the Agenda Everyday technology: A focus group with children, young people and their carers March 2018 1 1.0 Introduction Assistive technology is an umbrella term that includes assistive, adaptive,
Falsework & Formwork Visualisation Software
 User Guide Falsework & Formwork Visualisation Software The launch of cements our position as leaders in the use of visualisation technology to benefit our customers and clients. Our award winning, innovative
User Guide Falsework & Formwork Visualisation Software The launch of cements our position as leaders in the use of visualisation technology to benefit our customers and clients. Our award winning, innovative
Interacting within Virtual Worlds (based on talks by Greg Welch and Mark Mine)
 Interacting within Virtual Worlds (based on talks by Greg Welch and Mark Mine) Presentation Working in a virtual world Interaction principles Interaction examples Why VR in the First Place? Direct perception
Interacting within Virtual Worlds (based on talks by Greg Welch and Mark Mine) Presentation Working in a virtual world Interaction principles Interaction examples Why VR in the First Place? Direct perception
3D Modelling Is Not For WIMPs Part II: Stylus/Mouse Clicks
 3D Modelling Is Not For WIMPs Part II: Stylus/Mouse Clicks David Gauldie 1, Mark Wright 2, Ann Marie Shillito 3 1,3 Edinburgh College of Art 79 Grassmarket, Edinburgh EH1 2HJ d.gauldie@eca.ac.uk, a.m.shillito@eca.ac.uk
3D Modelling Is Not For WIMPs Part II: Stylus/Mouse Clicks David Gauldie 1, Mark Wright 2, Ann Marie Shillito 3 1,3 Edinburgh College of Art 79 Grassmarket, Edinburgh EH1 2HJ d.gauldie@eca.ac.uk, a.m.shillito@eca.ac.uk
Ubiquitous Computing Summer Episode 16: HCI. Hannes Frey and Peter Sturm University of Trier. Hannes Frey and Peter Sturm, University of Trier 1
 Episode 16: HCI Hannes Frey and Peter Sturm University of Trier University of Trier 1 Shrinking User Interface Small devices Narrow user interface Only few pixels graphical output No keyboard Mobility
Episode 16: HCI Hannes Frey and Peter Sturm University of Trier University of Trier 1 Shrinking User Interface Small devices Narrow user interface Only few pixels graphical output No keyboard Mobility
Design and Measurement of a 2.45 Ghz On-Body Antenna Optimized for Hearing Instrument Applications
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Design and of a 2.45 Ghz On-Body Antenna Optimized for Hearing Instrument Applications Kvist, Søren Helstrup; Jakobsen, Kaj Bjarne; Thaysen, Jesper Published
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Design and of a 2.45 Ghz On-Body Antenna Optimized for Hearing Instrument Applications Kvist, Søren Helstrup; Jakobsen, Kaj Bjarne; Thaysen, Jesper Published
Drumtastic: Haptic Guidance for Polyrhythmic Drumming Practice
 Drumtastic: Haptic Guidance for Polyrhythmic Drumming Practice ABSTRACT W e present Drumtastic, an application where the user interacts with two Novint Falcon haptic devices to play virtual drums. The
Drumtastic: Haptic Guidance for Polyrhythmic Drumming Practice ABSTRACT W e present Drumtastic, an application where the user interacts with two Novint Falcon haptic devices to play virtual drums. The
The Forensic Architecture Project : Virtual imagery as evidence in the contemporary context of the war on terror
 The Forensic Architecture Project : Virtual imagery as evidence in the contemporary context of the war on terror Lee-Morrison, Lila Unpublished: 2015-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version
The Forensic Architecture Project : Virtual imagery as evidence in the contemporary context of the war on terror Lee-Morrison, Lila Unpublished: 2015-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version
The workspace design concept: A new framework of participatory ergonomics
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 16, 2017 The workspace design concept: A new framework of participatory ergonomics Broberg, Ole Published in: Ergonomics for a future Publication date: 2007 Document
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 16, 2017 The workspace design concept: A new framework of participatory ergonomics Broberg, Ole Published in: Ergonomics for a future Publication date: 2007 Document
Lightning transient analysis in wind turbine blades
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 15, 2018 Lightning transient analysis in wind turbine blades Candela Garolera, Anna; Holbøll, Joachim; Madsen, Søren Find Published in: Proceedings of International
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 15, 2018 Lightning transient analysis in wind turbine blades Candela Garolera, Anna; Holbøll, Joachim; Madsen, Søren Find Published in: Proceedings of International
Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 1, 218 Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna Kim, Oleksiy S. Published in: iwat Link to article, DOI: 1.119/IWAT.21.546485 Publication date: 21
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 1, 218 Novel Electrically Small Spherical Electric Dipole Antenna Kim, Oleksiy S. Published in: iwat Link to article, DOI: 1.119/IWAT.21.546485 Publication date: 21
Human Factors. We take a closer look at the human factors that affect how people interact with computers and software:
 Human Factors We take a closer look at the human factors that affect how people interact with computers and software: Physiology physical make-up, capabilities Cognition thinking, reasoning, problem-solving,
Human Factors We take a closer look at the human factors that affect how people interact with computers and software: Physiology physical make-up, capabilities Cognition thinking, reasoning, problem-solving,
Educating Maritime Engineers for a Globalised Industry
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Educating Maritime Engineers for a Globalised Industry Nielsen, Ulrik Dam Publication date: 2013 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Educating Maritime Engineers for a Globalised Industry Nielsen, Ulrik Dam Publication date: 2013 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of
Aalborg Universitet. Linderum Electricity Quality - Measurements and Analysis Silva, Filipe Miguel Faria da; Bak, Claus Leth. Publication date: 2013
 Aalborg Universitet Linderum Electricity Quality - Measurements and Analysis Silva, Filipe Miguel Faria da; Bak, Claus Leth Publication date: 3 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of
Aalborg Universitet Linderum Electricity Quality - Measurements and Analysis Silva, Filipe Miguel Faria da; Bak, Claus Leth Publication date: 3 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of
Published in: Proceedings of NAM 98, Nordic Acoustical Meeting, September 6-9, 1998, Stockholm, Sweden
 Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: januar 27, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Sound pressure distribution in rooms at low frequencies Olesen, Søren Krarup; Møller, Henrik Published in: Proceedings of NAM 98, Nordic
Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: januar 27, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Sound pressure distribution in rooms at low frequencies Olesen, Søren Krarup; Møller, Henrik Published in: Proceedings of NAM 98, Nordic
Understanding OpenGL
 This document provides an overview of the OpenGL implementation in Boris Red. About OpenGL OpenGL is a cross-platform standard for 3D acceleration. GL stands for graphics library. Open refers to the ongoing,
This document provides an overview of the OpenGL implementation in Boris Red. About OpenGL OpenGL is a cross-platform standard for 3D acceleration. GL stands for graphics library. Open refers to the ongoing,
Direct Manipulation. and Instrumental Interaction. CS Direct Manipulation
 Direct Manipulation and Instrumental Interaction 1 Review: Interaction vs. Interface What s the difference between user interaction and user interface? Interface refers to what the system presents to the
Direct Manipulation and Instrumental Interaction 1 Review: Interaction vs. Interface What s the difference between user interaction and user interface? Interface refers to what the system presents to the
Citation for published version (APA): Parigi, D. (2013). Performance-Aided Design (PAD). A&D Skriftserie, 78,
 Aalborg Universitet Performance-Aided Design (PAD) Parigi, Dario Published in: A&D Skriftserie Publication date: 2013 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link to publication
Aalborg Universitet Performance-Aided Design (PAD) Parigi, Dario Published in: A&D Skriftserie Publication date: 2013 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link to publication
Photoshop Exercise 2 Developing X
 Photoshop Exercise 2 Developing X X-ray Vision: In this exercise, you will learn to take original photographs and combine them, using special effects. The objective is to create a portrait of someone holding
Photoshop Exercise 2 Developing X X-ray Vision: In this exercise, you will learn to take original photographs and combine them, using special effects. The objective is to create a portrait of someone holding
Characteristic mode based pattern reconfigurable antenna for mobile handset
 Characteristic mode based pattern reconfigurable antenna for mobile handset Li, Hui; Ma, Rui; Chountalas, John; Lau, Buon Kiong Published in: European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), 2015
Characteristic mode based pattern reconfigurable antenna for mobile handset Li, Hui; Ma, Rui; Chountalas, John; Lau, Buon Kiong Published in: European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), 2015
Effect of ohmic heating parameters on inactivation of enzymes and quality of not-fromconcentrate
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 25, 2018 Effect of ohmic heating parameters on inactivation of enzymes and quality of not-fromconcentrate mango juice Abedelmaksoud, Tarek; Mohsen, Sobhy Mohamed; Duedahl-Olesen,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 25, 2018 Effect of ohmic heating parameters on inactivation of enzymes and quality of not-fromconcentrate mango juice Abedelmaksoud, Tarek; Mohsen, Sobhy Mohamed; Duedahl-Olesen,
Methods for Haptic Feedback in Teleoperated Robotic Surgery
 Young Group 5 1 Methods for Haptic Feedback in Teleoperated Robotic Surgery Paper Review Jessie Young Group 5: Haptic Interface for Surgical Manipulator System March 12, 2012 Paper Selection: A. M. Okamura.
Young Group 5 1 Methods for Haptic Feedback in Teleoperated Robotic Surgery Paper Review Jessie Young Group 5: Haptic Interface for Surgical Manipulator System March 12, 2012 Paper Selection: A. M. Okamura.
Assessing the utility of dual finger haptic interaction with 3D virtual environments for blind people
 Assessing the utility of dual finger haptic interaction with 3D virtual environments for blind people K Gladstone 1, H Graupp 1 and C Avizzano 2 1 isys R&D, Royal National Institute of the Blind, 105 Judd
Assessing the utility of dual finger haptic interaction with 3D virtual environments for blind people K Gladstone 1, H Graupp 1 and C Avizzano 2 1 isys R&D, Royal National Institute of the Blind, 105 Judd
Calculation of antenna radiation center using angular momentum
 Calculation of antenna radiation center using angular momentum Fridén, Jonas; Kristensson, Gerhard Published in: 7th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), 2013 2013 Link to publication
Calculation of antenna radiation center using angular momentum Fridén, Jonas; Kristensson, Gerhard Published in: 7th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), 2013 2013 Link to publication
Consumer Behavior when Zooming and Cropping Personal Photographs and its Implications for Digital Image Resolution
 Consumer Behavior when Zooming and Cropping Personal Photographs and its Implications for Digital Image Michael E. Miller and Jerry Muszak Eastman Kodak Company Rochester, New York USA Abstract This paper
Consumer Behavior when Zooming and Cropping Personal Photographs and its Implications for Digital Image Michael E. Miller and Jerry Muszak Eastman Kodak Company Rochester, New York USA Abstract This paper
Evaluation of Visuo-haptic Feedback in a 3D Touch Panel Interface
 Evaluation of Visuo-haptic Feedback in a 3D Touch Panel Interface Xu Zhao Saitama University 255 Shimo-Okubo, Sakura-ku, Saitama City, Japan sheldonzhaox@is.ics.saitamau.ac.jp Takehiro Niikura The University
Evaluation of Visuo-haptic Feedback in a 3D Touch Panel Interface Xu Zhao Saitama University 255 Shimo-Okubo, Sakura-ku, Saitama City, Japan sheldonzhaox@is.ics.saitamau.ac.jp Takehiro Niikura The University
Characterization of additive manufacturing processes for polymer micro parts productions using direct light processing (DLP) method
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 30, 2018 Characterization of additive manufacturing processes for polymer micro parts productions using direct light processing (DLP) method Davoudinejad, Ali; Pedersen,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 30, 2018 Characterization of additive manufacturing processes for polymer micro parts productions using direct light processing (DLP) method Davoudinejad, Ali; Pedersen,
AutoCAD 2D. Table of Contents. Lesson 1 Getting Started
 AutoCAD 2D Lesson 1 Getting Started Pre-reqs/Technical Skills Basic computer use Expectations Read lesson material Implement steps in software while reading through lesson material Complete quiz on Blackboard
AutoCAD 2D Lesson 1 Getting Started Pre-reqs/Technical Skills Basic computer use Expectations Read lesson material Implement steps in software while reading through lesson material Complete quiz on Blackboard
Discrimination of Virtual Haptic Textures Rendered with Different Update Rates
 Discrimination of Virtual Haptic Textures Rendered with Different Update Rates Seungmoon Choi and Hong Z. Tan Haptic Interface Research Laboratory Purdue University 465 Northwestern Avenue West Lafayette,
Discrimination of Virtual Haptic Textures Rendered with Different Update Rates Seungmoon Choi and Hong Z. Tan Haptic Interface Research Laboratory Purdue University 465 Northwestern Avenue West Lafayette,
Distance Protection of Cross-Bonded Transmission Cable-Systems
 Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: April 19, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Distance Protection of Cross-Bonded Transmission Cable-Systems Bak, Claus Leth; F. Jensen, Christian Published in: Proceedings of the 12th
Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: April 19, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Distance Protection of Cross-Bonded Transmission Cable-Systems Bak, Claus Leth; F. Jensen, Christian Published in: Proceedings of the 12th
RKSLAM Android Demo 1.0
 RKSLAM Android Demo 1.0 USER MANUAL VISION GROUP, STATE KEY LAB OF CAD&CG, ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY HTTP://WWW.ZJUCVG.NET TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 1-3 1.1 Product Specification...1-3 1.2 Feature
RKSLAM Android Demo 1.0 USER MANUAL VISION GROUP, STATE KEY LAB OF CAD&CG, ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY HTTP://WWW.ZJUCVG.NET TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 1-3 1.1 Product Specification...1-3 1.2 Feature
Automatic Online Haptic Graph Construction
 Automatic Online Haptic Graph Construction Wai Yu, Kenneth Cheung, Stephen Brewster Glasgow Interactive Systems Group, Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK {rayu, stephen}@dcs.gla.ac.uk
Automatic Online Haptic Graph Construction Wai Yu, Kenneth Cheung, Stephen Brewster Glasgow Interactive Systems Group, Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK {rayu, stephen}@dcs.gla.ac.uk
Comparing Two Haptic Interfaces for Multimodal Graph Rendering
 Comparing Two Haptic Interfaces for Multimodal Graph Rendering Wai Yu, Stephen Brewster Glasgow Interactive Systems Group, Department of Computing Science, University of Glasgow, U. K. {rayu, stephen}@dcs.gla.ac.uk,
Comparing Two Haptic Interfaces for Multimodal Graph Rendering Wai Yu, Stephen Brewster Glasgow Interactive Systems Group, Department of Computing Science, University of Glasgow, U. K. {rayu, stephen}@dcs.gla.ac.uk,
Phantom-X. Unnur Gretarsdottir, Federico Barbagli and Kenneth Salisbury
 Phantom-X Unnur Gretarsdottir, Federico Barbagli and Kenneth Salisbury Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford CA 94305, USA, [ unnurg, barbagli, jks ] @stanford.edu Abstract. This paper
Phantom-X Unnur Gretarsdottir, Federico Barbagli and Kenneth Salisbury Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford CA 94305, USA, [ unnurg, barbagli, jks ] @stanford.edu Abstract. This paper
Exploring Geometric Shapes with Touch
 Exploring Geometric Shapes with Touch Thomas Pietrzak, Andrew Crossan, Stephen Brewster, Benoît Martin, Isabelle Pecci To cite this version: Thomas Pietrzak, Andrew Crossan, Stephen Brewster, Benoît Martin,
Exploring Geometric Shapes with Touch Thomas Pietrzak, Andrew Crossan, Stephen Brewster, Benoît Martin, Isabelle Pecci To cite this version: Thomas Pietrzak, Andrew Crossan, Stephen Brewster, Benoît Martin,
Repeated Measures Twoway Analysis of Variance
 Repeated Measures Twoway Analysis of Variance A researcher was interested in whether frequency of exposure to a picture of an ugly or attractive person would influence one's liking for the photograph.
Repeated Measures Twoway Analysis of Variance A researcher was interested in whether frequency of exposure to a picture of an ugly or attractive person would influence one's liking for the photograph.
ArcGIS Pro: Tips & Tricks
 ArcGIS Pro: Tips & Tricks James Sullivan Solution Engineer Agenda Project Structure/Set Up Data Visualization/Map Authoring Data/Map Exploration Geoprocessing Editing Layouts Sharing Working with the Ribbon
ArcGIS Pro: Tips & Tricks James Sullivan Solution Engineer Agenda Project Structure/Set Up Data Visualization/Map Authoring Data/Map Exploration Geoprocessing Editing Layouts Sharing Working with the Ribbon
Copyright Digital Film Tools, LLC All Rights Reserved
 2 About this Guide ABOUT THIS GUIDE This User Guide is a reference for the Rays plug-in made for Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Photoshop Lightroom, Adobe Photoshop Elements and Apple Aperture. You can read from
2 About this Guide ABOUT THIS GUIDE This User Guide is a reference for the Rays plug-in made for Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Photoshop Lightroom, Adobe Photoshop Elements and Apple Aperture. You can read from
Audio makes a difference in haptic collaborative virtual environments
 Audio makes a difference in haptic collaborative virtual environments JONAS MOLL, YING YING HUANG, EVA-LOTTA SALLNÄS HCI Dept., School of Computer Science and Communication, Royal Institute of Technology,
Audio makes a difference in haptic collaborative virtual environments JONAS MOLL, YING YING HUANG, EVA-LOTTA SALLNÄS HCI Dept., School of Computer Science and Communication, Royal Institute of Technology,
Directional dependence of loudness and binaural summation Sørensen, Michael Friis; Lydolf, Morten; Frandsen, Peder Christian; Møller, Henrik
 Aalborg Universitet Directional dependence of loudness and binaural summation Sørensen, Michael Friis; Lydolf, Morten; Frandsen, Peder Christian; Møller, Henrik Published in: Proceedings of 15th International
Aalborg Universitet Directional dependence of loudness and binaural summation Sørensen, Michael Friis; Lydolf, Morten; Frandsen, Peder Christian; Møller, Henrik Published in: Proceedings of 15th International
12. Creating a Product Mockup in Perspective
 12. Creating a Product Mockup in Perspective Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Understand perspective drawing. Use grid presets. Adjust the perspective grid. Draw and
12. Creating a Product Mockup in Perspective Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Understand perspective drawing. Use grid presets. Adjust the perspective grid. Draw and
Yu, W. and Brewster, S.A. (2003) Evaluation of multimodal graphs for blind people. Universal Access in the Information Society 2(2):pp
 Yu, W. and Brewster, S.A. (2003) Evaluation of multimodal graphs for blind people. Universal Access in the Information Society 2(2):pp. 105-124. http://eprints.gla.ac.uk/3273/ Glasgow eprints Service http://eprints.gla.ac.uk
Yu, W. and Brewster, S.A. (2003) Evaluation of multimodal graphs for blind people. Universal Access in the Information Society 2(2):pp. 105-124. http://eprints.gla.ac.uk/3273/ Glasgow eprints Service http://eprints.gla.ac.uk
An image-based method for objectively assessing injection moulded plastic quality
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 23, 2018 An image-based method for objectively assessing injection moulded plastic quality Hannemose, Morten; Nielsen, Jannik Boll; Zsíros, László; Aanæs, Henrik Published
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 23, 2018 An image-based method for objectively assessing injection moulded plastic quality Hannemose, Morten; Nielsen, Jannik Boll; Zsíros, László; Aanæs, Henrik Published
Can a haptic force feedback display provide visually impaired people with useful information about texture roughness and 3D form of virtual objects?
 Can a haptic force feedback display provide visually impaired people with useful information about texture roughness and 3D form of virtual objects? Gunnar Jansson Department of Psychology, Uppsala University
Can a haptic force feedback display provide visually impaired people with useful information about texture roughness and 3D form of virtual objects? Gunnar Jansson Department of Psychology, Uppsala University
First English edition for Ulead COOL 360 version 1.0, February 1999.
 First English edition for Ulead COOL 360 version 1.0, February 1999. 1992-1999 Ulead Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
First English edition for Ulead COOL 360 version 1.0, February 1999. 1992-1999 Ulead Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
Direct Manipulation. and Instrumental Interaction. Direct Manipulation 1
 Direct Manipulation and Instrumental Interaction Direct Manipulation 1 Direct Manipulation Direct manipulation is when a virtual representation of an object is manipulated in a similar way to a real world
Direct Manipulation and Instrumental Interaction Direct Manipulation 1 Direct Manipulation Direct manipulation is when a virtual representation of an object is manipulated in a similar way to a real world
The Visible Ear Simulator Dissection Manual.
 The Visible Ear Simulator Dissection Manual. Stereoscopic Tutorialized Version 3.1, August 2017 Peter Trier Mikkelsen, the Alexandra Institute A/S, Aarhus, Denmark Mads Sølvsten Sørensen & Steven Andersen,
The Visible Ear Simulator Dissection Manual. Stereoscopic Tutorialized Version 3.1, August 2017 Peter Trier Mikkelsen, the Alexandra Institute A/S, Aarhus, Denmark Mads Sølvsten Sørensen & Steven Andersen,
A Quick Spin on Autodesk Revit Building
 11/28/2005-3:00 pm - 4:30 pm Room:Americas Seminar [Lab] (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida A Quick Spin on Autodesk Revit Building Amy Fietkau - Autodesk and John Jansen;
11/28/2005-3:00 pm - 4:30 pm Room:Americas Seminar [Lab] (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida A Quick Spin on Autodesk Revit Building Amy Fietkau - Autodesk and John Jansen;
Adaptive Level of Detail in Dynamic, Refreshable Tactile Graphics
 Adaptive Level of Detail in Dynamic, Refreshable Tactile Graphics Vincent Lévesque University of British Columbia Grégory Petit, Aude Dufresne Université de Montréal Vincent Hayward UPMC Univ Paris 06
Adaptive Level of Detail in Dynamic, Refreshable Tactile Graphics Vincent Lévesque University of British Columbia Grégory Petit, Aude Dufresne Université de Montréal Vincent Hayward UPMC Univ Paris 06
A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 25, 2018 A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles Dich, Mikael; Rengarajan, S.R. Published in: Proc. of IEEE Antenna and Propagation Society
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 25, 2018 A Waveguide Transverse Broad Wall Slot Radiating Between Baffles Dich, Mikael; Rengarajan, S.R. Published in: Proc. of IEEE Antenna and Propagation Society
PRODIM CT 3.0 MANUAL the complete solution
 PRODIM CT 3.0 MANUAL the complete solution We measure it all! General information Copyright All rights reserved. Apart from the legally laid down exceptions, no part of this publication may be reproduced,
PRODIM CT 3.0 MANUAL the complete solution We measure it all! General information Copyright All rights reserved. Apart from the legally laid down exceptions, no part of this publication may be reproduced,
Direct Manipulation. and Instrumental Interaction. Direct Manipulation
 Direct Manipulation and Instrumental Interaction Direct Manipulation 1 Direct Manipulation Direct manipulation is when a virtual representation of an object is manipulated in a similar way to a real world
Direct Manipulation and Instrumental Interaction Direct Manipulation 1 Direct Manipulation Direct manipulation is when a virtual representation of an object is manipulated in a similar way to a real world
Investigation of a Hybrid Winding Concept for Toroidal Inductors using 3D Finite Element Modeling
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Investigation of a Hybrid Winding Concept for Toroidal Inductors using 3D Finite Element Modeling Schneider, Henrik; Andersen, Thomas; Mønster, Jakob Døllner;
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Investigation of a Hybrid Winding Concept for Toroidal Inductors using 3D Finite Element Modeling Schneider, Henrik; Andersen, Thomas; Mønster, Jakob Døllner;
Multisensory virtual environment for supporting blind persons acquisition of spatial cognitive mapping, orientation, and mobility skills
 Multisensory virtual environment for supporting blind persons acquisition of spatial cognitive mapping, orientation, and mobility skills O Lahav and D Mioduser School of Education, Tel Aviv University,
Multisensory virtual environment for supporting blind persons acquisition of spatial cognitive mapping, orientation, and mobility skills O Lahav and D Mioduser School of Education, Tel Aviv University,
RF Explorer. User Manual. RF Explorer User Manual v Page 1 of 13. Updated to firmware v1.05. Edition date: 2011/Mar/01.
 RF Explorer User Manual v1.05 - Page 1 of 13 RF Explorer User Manual Updated to firmware v1.05 Edition date: 2011/Mar/01 www.rf-explorer.com Please consider the environment before printing this manual.
RF Explorer User Manual v1.05 - Page 1 of 13 RF Explorer User Manual Updated to firmware v1.05 Edition date: 2011/Mar/01 www.rf-explorer.com Please consider the environment before printing this manual.
The current distribution on the feeding probe in an air filled rectangular microstrip antenna
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 28, 2019 The current distribution on the feeding probe in an air filled rectangular microstrip antenna Brown, K Published in: Antennas and Propagation Society International
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 28, 2019 The current distribution on the feeding probe in an air filled rectangular microstrip antenna Brown, K Published in: Antennas and Propagation Society International
Rodil, Kasper; Eskildsen, Søren; Morrison, Ann Judith; Rehm, Matthias; Winschiers- Theophilus, Heike
 Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: January 24, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Unlocking good design does not rely on designers alone Rodil, Kasper; Eskildsen, Søren; Morrison, Ann Judith; Rehm, Matthias; Winschiers-
Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: January 24, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Unlocking good design does not rely on designers alone Rodil, Kasper; Eskildsen, Søren; Morrison, Ann Judith; Rehm, Matthias; Winschiers-
Benefits of using haptic devices in textile architecture
 28 September 2 October 2009, Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Spain Alberto DOMINGO and Carlos LAZARO (eds.) Benefits of using haptic devices in textile architecture Javier SANCHEZ *, Joan SAVALL a
28 September 2 October 2009, Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Spain Alberto DOMINGO and Carlos LAZARO (eds.) Benefits of using haptic devices in textile architecture Javier SANCHEZ *, Joan SAVALL a
The Danish Test Facilities Megavind Offspring
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 24, 2018 The Danish Test Facilities Megavind Offspring Madsen, Peter Hauge; Jensen, Peter Hjuler Publication date: 2013 Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Madsen,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 24, 2018 The Danish Test Facilities Megavind Offspring Madsen, Peter Hauge; Jensen, Peter Hjuler Publication date: 2013 Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Madsen,
Bandwidth limitations in current mode and voltage mode integrated feedback amplifiers
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 13, 2018 Bandwidth limitations in current mode and voltage mode integrated feedback amplifiers Bruun, Erik Published in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 13, 2018 Bandwidth limitations in current mode and voltage mode integrated feedback amplifiers Bruun, Erik Published in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium
Cricut Design Space App for ipad User Manual
 Cricut Design Space App for ipad User Manual Cricut Explore design-and-cut system From inspiration to creation in just a few taps! Cricut Design Space App for ipad 1. ipad Setup A. Setting up the app B.
Cricut Design Space App for ipad User Manual Cricut Explore design-and-cut system From inspiration to creation in just a few taps! Cricut Design Space App for ipad 1. ipad Setup A. Setting up the app B.
Map Direct Lite. Contents. Quick Start Guide: Drawing 11/05/2015
 Map Direct Lite Quick Start Guide: Drawing 11/05/2015 Contents Quick Start Guide: Drawing... 1 Drawing, Measuring and Analyzing in Map Direct Lite.... 2 Measure Distance and Area.... 3 Place the Map Marker
Map Direct Lite Quick Start Guide: Drawing 11/05/2015 Contents Quick Start Guide: Drawing... 1 Drawing, Measuring and Analyzing in Map Direct Lite.... 2 Measure Distance and Area.... 3 Place the Map Marker
Detection of mechanical instability in DI-fluxgate sensors
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 18, 2018 Detection of mechanical instability in DI-fluxgate sensors Pedersen, Lars William; Matzka, Jürgen Published in: Proceedings of the XVth IAGA Workshop on Geomagnetic
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 18, 2018 Detection of mechanical instability in DI-fluxgate sensors Pedersen, Lars William; Matzka, Jürgen Published in: Proceedings of the XVth IAGA Workshop on Geomagnetic
Lettering Fabric Preparation deco 340 aurora 430E & 440QEE NAME artista 630E, 635LE & 640E
 Lettering Fabric Preparation Deco 340 Hoop a piece of firm woven fabric backed with tear-away stabilizer in the Large hoop. aurora, artista, and 8 Series Hoop a piece of firm woven fabric backed with tear-away
Lettering Fabric Preparation Deco 340 Hoop a piece of firm woven fabric backed with tear-away stabilizer in the Large hoop. aurora, artista, and 8 Series Hoop a piece of firm woven fabric backed with tear-away
Calibration of current-steering D/A Converters
 Calibration of current-steering D/A Converters Citation for published version (APA): Radulov,. I., Quinn, P. J., Hegt, J. A., & Roermund, van, A. H. M. (2009). Calibration of current-steering D/A Converters.
Calibration of current-steering D/A Converters Citation for published version (APA): Radulov,. I., Quinn, P. J., Hegt, J. A., & Roermund, van, A. H. M. (2009). Calibration of current-steering D/A Converters.
Photoshop Elements Hints by Steve Miller
 2015 Elements 13 A brief tutorial for basic photo file processing To begin, click on the Elements 13 icon, click on Photo Editor in the first box that appears. We will not be discussing the Organizer portion
2015 Elements 13 A brief tutorial for basic photo file processing To begin, click on the Elements 13 icon, click on Photo Editor in the first box that appears. We will not be discussing the Organizer portion
Presentations from The Bolund Experiment: Workshop 3-4th December 2009
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 26, 2018 Presentations from The Bolund Experiment: Workshop 3-4th December 2009 Bechmann, Andreas Publication date: 2010 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 26, 2018 Presentations from The Bolund Experiment: Workshop 3-4th December 2009 Bechmann, Andreas Publication date: 2010 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known
Glasgow eprints Service
 Yu, W. and Kangas, K. (2003) Web-based haptic applications for blind people to create virtual graphs. In, 11th Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, 22-23 March
Yu, W. and Kangas, K. (2003) Web-based haptic applications for blind people to create virtual graphs. In, 11th Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, 22-23 March
VIRTUAL MUSEUM BETA 1 INTRODUCTION MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS WHAT DOES BETA 1 MEAN? CASTLEFORD TIGERS HERITAGE PROJECT
 CASTLEFORD TIGERS HERITAGE PROJECT VIRTUAL MUSEUM BETA 1 INTRODUCTION The Castleford Tigers Virtual Museum is an interactive 3D environment containing a celebratory showcase of material gathered throughout
CASTLEFORD TIGERS HERITAGE PROJECT VIRTUAL MUSEUM BETA 1 INTRODUCTION The Castleford Tigers Virtual Museum is an interactive 3D environment containing a celebratory showcase of material gathered throughout
Photo Editing in Mac and ipad and iphone
 Page 1 Photo Editing in Mac and ipad and iphone Switching to Edit mode in Photos for Mac To edit a photo you ll first need to double-click its thumbnail to open it for viewing, and then click the Edit
Page 1 Photo Editing in Mac and ipad and iphone Switching to Edit mode in Photos for Mac To edit a photo you ll first need to double-click its thumbnail to open it for viewing, and then click the Edit
