H30: Specification of Colour, Munsell and NCS
|
|
|
- Mary Carter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 page 1 of 7 H30: Specification of Colour, Munsell and NCS James H Nobbs Colour4Free.org You may be wondering why methods of colour specification are needed when we have such a complex and sensitive system of colour appreciation built into our heads. On the other hand, if you have ever tried to buy an item to match something else, which you don t have with you at the time, you will know why colour specification is important. Our colour memory is quite poor, and verbal colour communication is no better (how many shades of navy blue can you imagine?). Add to these the problem of the relatively high frequency of colour vision deficiency and the case for standardised methods of colour specification is clear. A formal specification of colour is important in the protection of intellectual property such as design copyright or the colours used in a trademark. We are all familiar with Coca Cola Red and Kodak Yellow. In the UK: the company Cadbury s have successfully registered the colour purple (Pantone 2685C) for use in packaging for chocolate; the AA has the exclusive right to use recovery and repair vehicles painted yellow (Pantone 109C); the company Orange has registered Pantone 151C in the UK for telecoms services, telephones and pagers. Disputes can arise, for example the company Orange is in dispute with the airline company EasyGroup who have applied to register Pantone 021C, a similar shade of orange to Pantone 151C, in respect of a host of services. It is unfortunate that the accepted method of colour specification in these examples is the Pantone system, since Pantone is neither a national nor an international standard method of specifying colour. An example of good practice is shown in Figure 1 where the London Underground specifications of acceptable colours for the corporate roundel are given in a number of systems, including an international standard method (NCS). Pantone CYMK RGB NCS Blue: Blue: Blue: Blue: 485C C 100, M 79 45G, 115B S 3560-R80B 072C M 100, Y R, 0G, 44B S 1085-Y80R Figure 1: Corporate specification of the London Underground roundel There are many ways of specifying the colour appearance of an object or a surface. The most useful methods are those that do not lead to confusion and where the method has a clear interpretation. In this section we will be looking at the way that colours can be specified by selecting samples from a colour atlas which forms part of a colour order system. Colour order systems A colour order system is a rational method or a plan of ordering and specifying object colours. The associated colour atlas provides a set of material standards selected from the order system to represent the whole gamut of object colours. Advantages: An easy concept to understand. It is possible for a person to colour match with a standard and a trial side by side, without the need for complex instruction or complex instrumentation. Colour4Free.org H30ColourAtlasV02~Arial.tmd page 1 of 7
2 page 2 of 7 Drawbacks: There are only a limited number of samples in an atlas. This leads to large differences between the colours of neighbouring samples. The colour of the samples may change with time and with use. The accuracy of colour specification depends on the level of agreement between the colours of the samples in the atlas's. The colour gamut available to the designer or to the colour mixer may not be fully represented in the atlas. Most colour order systems are based on the arrangement devised by Sigrid Aron Forsius, a Swedish monk and astronomer who, in 1611, suggested a central vertical axis displaying neutral shades from white to black. The central axis is surround by the hues arranged in a circle. Munsell Color Notation In 1905 the north-american artist Albert H. Munsell suggested a form of colour notation as an aid to artists in the selection and use of colour. The associated colour atlas was produced in The system has been accepted as an international standard method for the specification of colour. Ordering system The rules of the system are: a. Hue, chroma and lightness are ordered according to the Forsius arrangement, Figure 2. b. Hue circle is arranged so that mixing together two paints with hues on opposite sides of the hue circle can form a neutral grey. c. There are equal distances represent equal visual steps of colour within the lightness scale, within the chroma scale and around an arc of the hue circle. Figure 2: Munsell hue, value and chroma The colour of the panel associated with each code in the atlas was determined by visual assessment by a large number of observers. Typical notation A typical notation for a colour is 7.5YR 7/12 and this code represents the colour shown in Figure 3. The notation 7.5YR 7/12 has the sequence; Hue then Value then Chroma Figure 3: 7.5YR 7/12 Hue (7.5YR): Value (7): The hues arranged in a circle in clockwise order: red, yellow, green, blue, purple and red. To represent lightness: "the quality by which we distinguish a light color from a dark one". Colour4Free.org H30ColourAtlasV02~Arial.tmd page 2 of 7
3 page 3 of 7 Chroma(12): To represent the intensity of the colour: the quality that distinguishes the difference from a pure hue to a gray shade. Munsell Hue In order to satisfy rule b, Munsell used five principle colours Red, Yellow, Green, Blue, Purple Principle hues The principle hues are arranged in clockwise sequence around a circle as shown in Figure 4. Pure red has the hue code 5R Pure yellow has the hue code (5Y) Pure green has the hue code (5G) Pure blue has the hue code (5B) Pure purple has the hue code (5P) Figure 4: The Munsell hue circle Intermediate hues Opposite each principal hue on the circle is an intermediate hue. The intermediate hues are yellow-red (5YR), green-yellow (5GY), blue-green (5BG), purple-blue (5PB) and The sequence is shown in Figure 4. Hue steps red-purple (5RP). There are 10 hue steps associated with the each primary hue. For example, 5R representing pure red, 2.5R representing a purple shade red and 7.5 R representing a yellow shade red, as shown in Figure 5. There are 10 hue steps associated with each intermediate hue with 5YR representing the intermediate hue that has an equal Figure 5: Part of the hue circle balance between the yellowness and the redness characteristics of the shade. Munsell Value (lightness) The Value axis is normal to the hue plane, as shown in Figure 6. There are 10 steps in the Value scale, starting with pure black at 0 N, through a series of greys to pure white at 10 N. Representative panels from the Munsell grey scale, are 9N white, 7N light grey, 5N mid grey, 3N dark grey and 1N black. Figure 6: Munsell hue, Value and Chroma Colour4Free.org H30ColourAtlasV02~Arial.tmd page 3 of 7
4 page 4 of 7 Munsell Chroma (intensity of colour) The Chroma is a measure of the intensity of the colour sensation. Neutral grey panels have zero chroma and colour intensity increases as the panel move further away from the neutral axis, as shown in Figure 6. There is not a fixed upper limit to Chroma, the maximum value that can be achieved for a hue depends on the optical properties of the colorants used in the panel. For example, in the current atlas the fullest colour for 5RP has a chroma of 26, yet the fullest colour for 10 YR has a chroma of 10 (Figure 7). Figure 7: Pages from the Munsell atlas, LHS hue 5RP, max chroma 26. RHS hue 10YR, max chroma 10 Visual scaling Value The positions of the steps of the Value scale were intended to be perceptually uniform and were decided by observer judgements. The results of measurement of the panels representing the Value scale formed the basis of the relationship between L* and Y used by the CIE L* a* b* (1976) colour space. Chroma The scaling of unit step in Chroma is not visually the same as the scaling of unit step in Value. The system is defined to have: 1 unit of Value» 2 units of Chroma Hue The relative size of the hue step depends on the Chroma of the panel. At a Chroma of 5: 1 unit of value» 3 units of Hue Munsell colour solid The different levels of colour intensity that can be achieved at each hue produce a very asymmetrical shape to the samples in the colour atlas. The shape is illustrated in Figure 8. Figure 8: Munsell colour solid Colour4Free.org H30ColourAtlasV02~Arial.tmd page 4 of 7
5 page 5 of 7 Natural Colour System NCS The Swedish Colour Foundation established the Natural Colour System in The representation of the NCS notation in CIE co-ordinates was defined in 1983 by a Swedish national standard. Ordering system The rules of the NCS ordering the system are: a. Lightness, intensity of colour and hue ordered according to the Forsius arrangement. b. The primary hues are arranged according to the opponent theory of colour vision. c. The spacing of the codes is determined by visual assessment by a large number of observers. The notation describes how close a shade resembles the characteristics of six elemental appearance properties. NCS elemental appearance properties Four Two elemental hues Yellow (Y), Red (R), Blue (B) and Green (G) The hues are equally spaced around the hue circle. Yellow is diametrically opposite to blue, and red is diametrically opposite to green, in agreement with the opponent theory of colour vision. elemental colours of White (W) and Black (S) represent the lightness quality on an axis normal to the hue. Basic rules of ordering The six elemental colour attributes are imagined to be arranged in space to form a double cone, as shown in Figure 9. All surface colours can be placed in this three-dimensional model and thus be given an exact NCS notation. Typical notation A typical notation is 2030 Y90R. In order to understand the NCS notation, the double cone is divided into two parts. The notation 2030 locates the blackness and chromaticness of the sample within Figure 9: Arrangement of the six elemental colours the NCS colour triangle, a radial plane that is normal to the hue circle and contains colours with the same hue, as shown in Figure 10. The notation Y90R identifies the hue of the sample within the NCS hue circle, a horizontal plane showing samples with the same whiteness (or blackness), as shown in Figure 11. The notation has the sequence; blackness then chromaticness then hue. For example 2030 Y90R Blackness (20): Chromaticness (30): Hue (Y90R): The degree of difference from the lightest shade that has the same hue and chromaticness The intensity of the colour sensation The hues arranged in a circle in clockwise order: yellow, red, blue green. Colour4Free.org H30ColourAtlasV02~Arial.tmd page 5 of 7
6 page 6 of 7 NCS colour triangle, e.g The first part the NCS notation describes the independent attributes of blackness(s) and chromaticness(c) of the shade. The scales of chromaticness (C) and of blackness (S) have the range of 0 to 100. The codes form an equilateral triangle with the corners being pure white (W) at the top, pure black (S) at the bottom and the perfect chromatic colour at the side, as shown in Figure 10. The triangle shape arises as a consequence of the rule that the combined attributes of chromaticness, whiteness and blackness add up to exactly 100. C + S + W = 100 Since the sum of the attributes adds to 100, it is only necessary to quote two of the attributes. The two attributes chosen were blackness and chromaticness. The third attribute, whiteness, is easily obtained by the difference of the sum of the other 2 from 100, W = (C + S). NCS Blackness (20) The concept of blackness has already been established, what can be confusing is the way in which blackness is represented on the NCS triangle. Shades with equal blackness form a series of straight lines parallel to the line joining the pure white point W and the pure chromatic point C. The lines are indicated by the markers on the left-hand edge of the triangle shown in Figure 10. NCS Chromaticness (30) The chromaticness is used to indicate the intensity of the colour. The most visually intense shade of a surface colour is defined to have a chromaticness of 100 and a blackness of 0 (and a whiteness of 0). A slightly less intense shade of the same hue may have a chromaticness of 80, for example. The lightest possible shade with that intensity of colour has a whiteness value of 20 and a blackness value of 0. The darkest possible shade with that intensity of colour has a whiteness value of 0 and a blackness value of 20. Don't forget that the sum of the three attributes always adds to 100. Shades with equal chromaticness form a series of vertical columns in the NCS colour triangle. The equal chromaticness lines are indicated by the markers on the bottom, right hand edge of the triangle in Figure Y90R Figure 10: NCS Colour Triangle, hue page Y90R NCS hue circle e.g. Y90R The four primary colours are arranged clockwise in the sequence yellow, red, blue and green. The NCS atlas contains pages at 40 hue divisions, around the hue circle. Each quadrant between the primary hues being represented by 10 pages in the atlas, as shown in Figure 11. The hue of a shade is characterised by the relative amounts of the two primaries hues that make up the colour. Thus in the red to blue quadrant, the hue code R7OB refers to a hue with a 30% resemblance to pure red, and a 70% resemblance to pure blue, as shown in Figure 11. Colour4Free.org H30ColourAtlasV02~Arial.tmd page 6 of 7
7 page 7 of 7 Note that the hues in the notation are quoted in the clockwise order as shown in Figure 11. The sequence of hues is similar to the CIE L* a* b* arrangement. Y is before R, R is before B, B is before G and G is before Y It follows that Y50R is an NCS hue code, but R50Y is not. Figure 11: NCS Colour (Hue) Circle H30: Specification of Colour, Munsell and NCS James H Nobbs Colour4Free.org Colour4Free.org H30ColourAtlasV02~Arial.tmd page 7 of 7
COLOR and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
CIE tri-stimulus experiment. Color Value Functions. CIE 1931 Standard. Color. Diagram. Color light intensity for visual color match
 CIE tri-stimulus experiment diffuse reflecting screen diffuse reflecting screen 770 769 768 test light 382 381 380 observer test light 445 535 630 445 535 630 observer light intensity for visual color
CIE tri-stimulus experiment diffuse reflecting screen diffuse reflecting screen 770 769 768 test light 382 381 380 observer test light 445 535 630 445 535 630 observer light intensity for visual color
H10: Description of Colour
 page 1 of 7 H10: Description of Colour Appearance of objects and materials Appearance attributes can be split into primary and secondary parts, as shown in Table 1. Table 1: The attributes of the appearance
page 1 of 7 H10: Description of Colour Appearance of objects and materials Appearance attributes can be split into primary and secondary parts, as shown in Table 1. Table 1: The attributes of the appearance
COLOR. and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
Color Theory: Defining Brown
 Color Theory: Defining Brown Defining Colors Colors can be defined in many different ways. Computer users are often familiar with colors defined as percentages or amounts of red, green, and blue (RGB).
Color Theory: Defining Brown Defining Colors Colors can be defined in many different ways. Computer users are often familiar with colors defined as percentages or amounts of red, green, and blue (RGB).
Brillux Scala - Development of an Application-Orientated Colour System
 Brillux Scala - Development of an Application-Orientated Colour System Rahe, Ulrike 1 1. Department of Product- and Production Development, Division of Design Chalmers University of Technology, SE-412
Brillux Scala - Development of an Application-Orientated Colour System Rahe, Ulrike 1 1. Department of Product- and Production Development, Division of Design Chalmers University of Technology, SE-412
Geography 360 Principles of Cartography. April 24, 2006
 Geography 360 Principles of Cartography April 24, 2006 Outlines 1. Principles of color Color as physical phenomenon Color as physiological phenomenon 2. How is color specified? (color model) Hardware-oriented
Geography 360 Principles of Cartography April 24, 2006 Outlines 1. Principles of color Color as physical phenomenon Color as physiological phenomenon 2. How is color specified? (color model) Hardware-oriented
Color Appearance, Color Order, & Other Color Systems
 Color Appearance, Color Order, & Other Color Systems Mark Fairchild Rochester Institute of Technology Integrated Sciences Academy Program of Color Science / Munsell Color Science Laboratory ISCC/AIC Munsell
Color Appearance, Color Order, & Other Color Systems Mark Fairchild Rochester Institute of Technology Integrated Sciences Academy Program of Color Science / Munsell Color Science Laboratory ISCC/AIC Munsell
LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO
 MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR LIGHT AND SPECTRA Visible light is an electromagnetic wave in the 400nm 700 nm range. The eye is basically similar
MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR LIGHT AND SPECTRA Visible light is an electromagnetic wave in the 400nm 700 nm range. The eye is basically similar
Figure 1: Energy Distributions for light
 Lecture 4: Colour The physical description of colour Colour vision is a very complicated biological and psychological phenomenon. It can be described in many different ways, including by physics, by subjective
Lecture 4: Colour The physical description of colour Colour vision is a very complicated biological and psychological phenomenon. It can be described in many different ways, including by physics, by subjective
Color Science. What light is. Measuring light. CS 4620 Lecture 15. Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD)
 Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 1 2 What light is Measuring light Light is electromagnetic radiation Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD) [Lawrence Berkeley Lab / MicroWorlds] exists
Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 1 2 What light is Measuring light Light is electromagnetic radiation Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD) [Lawrence Berkeley Lab / MicroWorlds] exists
Colors in Images & Video
 LECTURE 8 Colors in Images & Video CS 5513 Multimedia Systems Spring 2009 Imran Ihsan Principal Design Consultant OPUSVII www.opuseven.com Faculty of Engineering & Applied Sciences 1. Light and Spectra
LECTURE 8 Colors in Images & Video CS 5513 Multimedia Systems Spring 2009 Imran Ihsan Principal Design Consultant OPUSVII www.opuseven.com Faculty of Engineering & Applied Sciences 1. Light and Spectra
Introduction. The Spectral Basis for Color
 Introduction Color is an extremely important part of most visualizations. Choosing good colors for your visualizations involves understanding their properties and the perceptual characteristics of human
Introduction Color is an extremely important part of most visualizations. Choosing good colors for your visualizations involves understanding their properties and the perceptual characteristics of human
Lindab Colour Chart. Lindab Colour Chart. For every colour under the rainbow
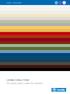 Lindab Colour Chart For every colour under the rainbow Assortment chart Rainline and Seamline Number Name Nearest NCS Nearest RAL Rainline Standing seam roofing 001 Antique white S 1002-G50Y 9002 015 Black
Lindab Colour Chart For every colour under the rainbow Assortment chart Rainline and Seamline Number Name Nearest NCS Nearest RAL Rainline Standing seam roofing 001 Antique white S 1002-G50Y 9002 015 Black
Chapter Objectives. Color Management. Color Management. Chapter Objectives 1/27/12. Beyond Design
 1/27/12 Copyright 2009 Fairchild Books All rights reserved. No part of this presentation covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means graphic, electronic, or mechanical,
1/27/12 Copyright 2009 Fairchild Books All rights reserved. No part of this presentation covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means graphic, electronic, or mechanical,
Elements of Art. Define: Line. Shape. Value. Texture. Color. Form. Space
 Elements of Art Line Shape Value Texture Color Form Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements. In the space below, draw a picture
Elements of Art Line Shape Value Texture Color Form Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements. In the space below, draw a picture
Chapter 3¾Examination and Description of Soils SOIL SURVEY MANUAL 73. Soil Color
 Chapter 3¾Examination and Description of Soils SOIL SURVEY MANUAL 73 Soil Color Elements of soil color descriptions are the color name, the Munsell notation, the water state, and the physical state: "brown
Chapter 3¾Examination and Description of Soils SOIL SURVEY MANUAL 73 Soil Color Elements of soil color descriptions are the color name, the Munsell notation, the water state, and the physical state: "brown
Optical properties. Quality Characteristics of Agricultural Materials
 Optical properties Quality Characteristics of Agricultural Materials Color Analysis Three major aspects of food acceptance : Color Flavor Texture Color is the most important The product does not look right,
Optical properties Quality Characteristics of Agricultural Materials Color Analysis Three major aspects of food acceptance : Color Flavor Texture Color is the most important The product does not look right,
Interactive Computer Graphics
 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 4: Colour Graphics Lecture 4: Slide 1 Ways of looking at colour 1. Physics 2. Human visual receptors 3. Subjective assessment Graphics Lecture 4: Slide 2 The physics
Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 4: Colour Graphics Lecture 4: Slide 1 Ways of looking at colour 1. Physics 2. Human visual receptors 3. Subjective assessment Graphics Lecture 4: Slide 2 The physics
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso. Color Image Processing
 For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
Colour Analysis of Unison Pastels
 Colour Analysis of Unison Pastels Paul Centore c February 15, 2014 Abstract Munsell specifications, calculated from spectrophotometric measurements, are presented for Unison Colour s complete line of 422
Colour Analysis of Unison Pastels Paul Centore c February 15, 2014 Abstract Munsell specifications, calculated from spectrophotometric measurements, are presented for Unison Colour s complete line of 422
Advanced Colour Similarity: 6.1 Hue
 olour imilarity: 6.1 Hue Hue hue. In each group the colours should have the same hue - i.e. the relation between the two chromatic elementary attributes should be constant (in this case redness-blueness-greeness).
olour imilarity: 6.1 Hue Hue hue. In each group the colours should have the same hue - i.e. the relation between the two chromatic elementary attributes should be constant (in this case redness-blueness-greeness).
Color Appearance Models
 Color Appearance Models Arjun Satish Mitsunobu Sugimoto 1 Today's topic Color Appearance Models CIELAB The Nayatani et al. Model The Hunt Model The RLAB Model 2 1 Terminology recap Color Hue Brightness/Lightness
Color Appearance Models Arjun Satish Mitsunobu Sugimoto 1 Today's topic Color Appearance Models CIELAB The Nayatani et al. Model The Hunt Model The RLAB Model 2 1 Terminology recap Color Hue Brightness/Lightness
Color vision and representation
 Color vision and representation S M L 0.0 0.44 0.52 Mark Rzchowski Physics Department 1 Eye perceives different wavelengths as different colors. Sensitive only to 400nm - 700 nm range Narrow piece of the
Color vision and representation S M L 0.0 0.44 0.52 Mark Rzchowski Physics Department 1 Eye perceives different wavelengths as different colors. Sensitive only to 400nm - 700 nm range Narrow piece of the
What is Color. Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception.
 Color What is Color Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception. By fundamental we mean that it is so unique that its meaning cannot be fully appreciated without direct experience. How
Color What is Color Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception. By fundamental we mean that it is so unique that its meaning cannot be fully appreciated without direct experience. How
Development of 3D Color Space to Improve Learning of Color Theory Ng Woon Lam, Xiao Yikai
 2nd International Conference on Modern Management, Education Technology, and Social Science (MMETSS 2017) Development of 3D Color Space to Improve Learning of Color Theory Ng Woon Lam, Xiao Yikai School
2nd International Conference on Modern Management, Education Technology, and Social Science (MMETSS 2017) Development of 3D Color Space to Improve Learning of Color Theory Ng Woon Lam, Xiao Yikai School
Color and Color Model. Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin
 Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color
 Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color 1 ACHROMATIC LIGHT (Grayscale) Quantity of light physics sense of energy
Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color 1 ACHROMATIC LIGHT (Grayscale) Quantity of light physics sense of energy
Color Image Processing
 Color Image Processing Jesus J. Caban Outline Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Color Perception & Analysis 1 Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Due next Monday, Oct 4th Project proposal Submit
Color Image Processing Jesus J. Caban Outline Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Color Perception & Analysis 1 Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Due next Monday, Oct 4th Project proposal Submit
Optical Illusion Sketchbook Project Art 1201
 Optical Illusion Sketchbook Project Art 1201 Before beginning our final optical illusion project, we need to practice drawing optical illusions so we will have a better understanding of how to construct
Optical Illusion Sketchbook Project Art 1201 Before beginning our final optical illusion project, we need to practice drawing optical illusions so we will have a better understanding of how to construct
LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS
 LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS COLORS LIGHTING Interior Design Department Third grade/ Fall semester Siba nazem Kady COLORS THEORIES OF COLOR DESIGN Review The Hue REVIEW HUE,VALUE, AND SATURATION - Gradation of
LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS COLORS LIGHTING Interior Design Department Third grade/ Fall semester Siba nazem Kady COLORS THEORIES OF COLOR DESIGN Review The Hue REVIEW HUE,VALUE, AND SATURATION - Gradation of
Digital Image Processing. Lecture # 8 Color Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 8 Color Processing 1 COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING Color Importance Color is an excellent descriptor Suitable for object Identification and Extraction
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 8 Color Processing 1 COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING Color Importance Color is an excellent descriptor Suitable for object Identification and Extraction
Image and video processing (EBU723U) Colour Images. Dr. Yi-Zhe Song
 Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements
 Vocabulary The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements 1. The Practice: Concept + Composition are ingredients that a designer uses to communicate
Vocabulary The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements 1. The Practice: Concept + Composition are ingredients that a designer uses to communicate
The Principles of Chromatics
 The Principles of Chromatics 03/20/07 2 Light Electromagnetic radiation, that produces a sight perception when being hit directly in the eye The wavelength of visible light is 400-700 nm 1 03/20/07 3 Visible
The Principles of Chromatics 03/20/07 2 Light Electromagnetic radiation, that produces a sight perception when being hit directly in the eye The wavelength of visible light is 400-700 nm 1 03/20/07 3 Visible
Inductive Reasoning Practice Test. Solution Booklet. 1
 Inductive Reasoning Practice Test Solution Booklet 1 www.assessmentday.co.uk Question 1 Solution: B In this question, there are two rules to follow. The first rule is that the curved and straight-edged
Inductive Reasoning Practice Test Solution Booklet 1 www.assessmentday.co.uk Question 1 Solution: B In this question, there are two rules to follow. The first rule is that the curved and straight-edged
NEWTONIAN COLOR THEORY
 THEORY 2D Design Color Crash Course NEWTONIAN THEORY Color in a picture is like enthusiasm in life. -incent an Gogh In 1666 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) passed a beam of light through a prism and proved
THEORY 2D Design Color Crash Course NEWTONIAN THEORY Color in a picture is like enthusiasm in life. -incent an Gogh In 1666 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) passed a beam of light through a prism and proved
Elements of Art and Fashion
 Elements of Art and Fashion Ø Line Ø Shape Ø Value Ø Texture Ø Color Ø Volume/Form Ø Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements.
Elements of Art and Fashion Ø Line Ø Shape Ø Value Ø Texture Ø Color Ø Volume/Form Ø Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements.
6 Color Image Processing
 6 Color Image Processing Angela Chih-Wei Tang ( 唐之瑋 ) Department of Communication Engineering National Central University JhongLi, Taiwan 2009 Fall Outline Color fundamentals Color models Pseudocolor image
6 Color Image Processing Angela Chih-Wei Tang ( 唐之瑋 ) Department of Communication Engineering National Central University JhongLi, Taiwan 2009 Fall Outline Color fundamentals Color models Pseudocolor image
Introduction to computer vision. Image Color Conversion. CIE Chromaticity Diagram and Color Gamut. Color Models
 Introduction to computer vision In general, computer vision covers very wide area of issues concerning understanding of images by computers. It may be considered as a part of artificial intelligence and
Introduction to computer vision In general, computer vision covers very wide area of issues concerning understanding of images by computers. It may be considered as a part of artificial intelligence and
Digital Image Processing. Lecture # 6 Corner Detection & Color Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 6 Corner Detection & Color Processing 1 Corners Corners (interest points) Unlike edges, corners (patches of pixels surrounding the corner) do not necessarily correspond
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 6 Corner Detection & Color Processing 1 Corners Corners (interest points) Unlike edges, corners (patches of pixels surrounding the corner) do not necessarily correspond
The Performance of CIECAM02
 The Performance of CIECAM02 Changjun Li 1, M. Ronnier Luo 1, Robert W. G. Hunt 1, Nathan Moroney 2, Mark D. Fairchild 3, and Todd Newman 4 1 Color & Imaging Institute, University of Derby, Derby, United
The Performance of CIECAM02 Changjun Li 1, M. Ronnier Luo 1, Robert W. G. Hunt 1, Nathan Moroney 2, Mark D. Fairchild 3, and Todd Newman 4 1 Color & Imaging Institute, University of Derby, Derby, United
Perception to visualization I
 Perception to visualization I C. Andrews 2014-02-25 Visualization Pipeline Raw Data data tables visual structures visualization data transformations visual mappings view transformations user interaction
Perception to visualization I C. Andrews 2014-02-25 Visualization Pipeline Raw Data data tables visual structures visualization data transformations visual mappings view transformations user interaction
H34: Putting Numbers to Colour: srgb
 page 1 of 5 H34: Putting Numbers to Colour: srgb James H Nobbs Colour4Free.org Introduction The challenge of publishing multicoloured images is to capture a scene and then to display or to print the image
page 1 of 5 H34: Putting Numbers to Colour: srgb James H Nobbs Colour4Free.org Introduction The challenge of publishing multicoloured images is to capture a scene and then to display or to print the image
Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red.
 Hue Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red. Hues are determined (and can be measured) by a color's wavelength. There are millions of hues
Hue Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red. Hues are determined (and can be measured) by a color's wavelength. There are millions of hues
LEVEL: 2 CREDITS: 5.00 GRADE: PREREQUISITE: None
 DESIGN #588 LEVEL: 2 CREDITS: 5.00 GRADE: 10-11 PREREQUISITE: None This course will familiarize the beginning art student with the elements and principles of design. Students will learn how to construct
DESIGN #588 LEVEL: 2 CREDITS: 5.00 GRADE: 10-11 PREREQUISITE: None This course will familiarize the beginning art student with the elements and principles of design. Students will learn how to construct
CSE 332/564: Visualization. Fundamentals of Color. Perception of Light Intensity. Computer Science Department Stony Brook University
 Perception of Light Intensity CSE 332/564: Visualization Fundamentals of Color Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University How Many Intensity Levels Do We Need? Dynamic Intensity Range
Perception of Light Intensity CSE 332/564: Visualization Fundamentals of Color Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University How Many Intensity Levels Do We Need? Dynamic Intensity Range
Hello, welcome to the video lecture series on Digital image processing. (Refer Slide Time: 00:30)
 Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module 11 Lecture Number 52 Conversion of one Color
Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module 11 Lecture Number 52 Conversion of one Color
Color Theory. Color Mixing Intro (ch. 7 pp. 77ff) Liquitex Color Map. Value Staff Intrinsic Value Staff
 Color Mixing Intro (ch. 7 pp. 77ff) Liquitex Color Map Color Theory Value Staff Intrinsic Value Staff Munsell color notation (HVC) HC color mapping HV color mapping Strait Line Mixing (2clr/3clr Y ) 1st
Color Mixing Intro (ch. 7 pp. 77ff) Liquitex Color Map Color Theory Value Staff Intrinsic Value Staff Munsell color notation (HVC) HC color mapping HV color mapping Strait Line Mixing (2clr/3clr Y ) 1st
Comp/Phys/Apsc 715. Example Videos. Administrative 1/23/2014. Lecture 5: Trichromacy, Color Spaces, Properties of Color
 Comp/Phys/Apsc 715 Lecture 5: Trichromacy, Color Spaces, Properties of Color 1 Example Videos Segmentation and visualization of neurons Astro Visualization (the Millennium Run) Dragonfly Flight Analysis
Comp/Phys/Apsc 715 Lecture 5: Trichromacy, Color Spaces, Properties of Color 1 Example Videos Segmentation and visualization of neurons Astro Visualization (the Millennium Run) Dragonfly Flight Analysis
The Principles and Elements of Design. These are the building blocks of all good floral design
 The Principles and Elements of Design These are the building blocks of all good floral design ELEMENTS OF DESIGN The Elements of Design are those you can see and touch LINE FORM COLOUR TEXTURE SPACE LINE
The Principles and Elements of Design These are the building blocks of all good floral design ELEMENTS OF DESIGN The Elements of Design are those you can see and touch LINE FORM COLOUR TEXTURE SPACE LINE
Abstract shape: a shape that is derived from a visual source, but is so transformed that it bears little visual resemblance to that source.
 Glossary of Terms Abstract shape: a shape that is derived from a visual source, but is so transformed that it bears little visual resemblance to that source. Accent: 1)The least prominent shape or object
Glossary of Terms Abstract shape: a shape that is derived from a visual source, but is so transformed that it bears little visual resemblance to that source. Accent: 1)The least prominent shape or object
The art of colour Date: Venerdì, febbraio 12:17:49 CET Topic: Educational Lighting Site
 The art of colour Date: Venerdì, febbraio 15 @ 12:17:49 CET Topic: Educational Lighting Site Primary colours Newton's disc Complementary colours Secondary colours Tertiary colours Warm and cold colours
The art of colour Date: Venerdì, febbraio 15 @ 12:17:49 CET Topic: Educational Lighting Site Primary colours Newton's disc Complementary colours Secondary colours Tertiary colours Warm and cold colours
Elements and Principles
 Elements and Principles of Art The building blocks and how we use them Your recipe for creating art! Lets learn the ingredients! ART INGREDIENTS! Elements of Art: The basic building blocks/ foundation
Elements and Principles of Art The building blocks and how we use them Your recipe for creating art! Lets learn the ingredients! ART INGREDIENTS! Elements of Art: The basic building blocks/ foundation
Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology
 Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology Physics of Color Light Light or visible light is the portion of electromagnetic radiation that
Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology Physics of Color Light Light or visible light is the portion of electromagnetic radiation that
Master digital black and white conversion with our Photoshop plug-in. Black & White Studio plug-in - Tutorial
 Master digital black and white conversion with our Photoshop plug-in This Photoshop plug-in turns Photoshop into a digital darkroom for black and white. Use the light sensitivity of films (Tri-X, etc)
Master digital black and white conversion with our Photoshop plug-in This Photoshop plug-in turns Photoshop into a digital darkroom for black and white. Use the light sensitivity of films (Tri-X, etc)
Color Science. CS 4620 Lecture 15
 Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 2013 Steve Marschner 1 [source unknown] 2013 Steve Marschner 2 What light is Light is electromagnetic radiation exists as oscillations of different frequency (or, wavelength)
Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 2013 Steve Marschner 1 [source unknown] 2013 Steve Marschner 2 What light is Light is electromagnetic radiation exists as oscillations of different frequency (or, wavelength)
Colour for Presentation Graphics
 DSC 2003 Working Papers (Draft Versions) http://www.ci.tuwien.ac.at/conferences/dsc-2003/ Colour for Presentation Graphics Ross Ihaka Department of Statistics University of Auckland Abstract Choosing a
DSC 2003 Working Papers (Draft Versions) http://www.ci.tuwien.ac.at/conferences/dsc-2003/ Colour for Presentation Graphics Ross Ihaka Department of Statistics University of Auckland Abstract Choosing a
excite the cones in the same way.
 Humans have 3 kinds of cones Color vision Edward H. Adelson 9.35 Trichromacy To specify a light s spectrum requires an infinite set of numbers. Each cone gives a single number (univariance) when stimulated
Humans have 3 kinds of cones Color vision Edward H. Adelson 9.35 Trichromacy To specify a light s spectrum requires an infinite set of numbers. Each cone gives a single number (univariance) when stimulated
Master digital black and white conversion with our Photoshop plug-in. Black & White Studio plug-in - Tutorial
 Master digital black and white conversion with our Photoshop plug-in This Photoshop plug-in turns Photoshop into a digital darkroom for black and white. Use the light sensitivity of films (Tri-X, etc)
Master digital black and white conversion with our Photoshop plug-in This Photoshop plug-in turns Photoshop into a digital darkroom for black and white. Use the light sensitivity of films (Tri-X, etc)
VC 16/17 TP4 Colour and Noise
 VC 16/17 TP4 Colour and Noise Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Hélder Filipe Pinto de Oliveira Outline Colour spaces Colour processing
VC 16/17 TP4 Colour and Noise Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Hélder Filipe Pinto de Oliveira Outline Colour spaces Colour processing
Color and Perception. CS535 Fall Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Color and Perception CS535 Fall 2014 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Elements of Color Perception 2 Elements of Color Physics: Illumination Electromagnetic spectra; approx.
Color and Perception CS535 Fall 2014 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Elements of Color Perception 2 Elements of Color Physics: Illumination Electromagnetic spectra; approx.
Fig Color spectrum seen by passing white light through a prism.
 1. Explain about color fundamentals. Color of an object is determined by the nature of the light reflected from it. When a beam of sunlight passes through a glass prism, the emerging beam of light is not
1. Explain about color fundamentals. Color of an object is determined by the nature of the light reflected from it. When a beam of sunlight passes through a glass prism, the emerging beam of light is not
Color Computer Vision Spring 2018, Lecture 15
 Color http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/ 16-385 Computer Vision Spring 2018, Lecture 15 Course announcements Homework 4 has been posted. - Due Friday March 23 rd (one-week homework!) - Any questions about the
Color http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/ 16-385 Computer Vision Spring 2018, Lecture 15 Course announcements Homework 4 has been posted. - Due Friday March 23 rd (one-week homework!) - Any questions about the
THE MEANING OF COLOR VISUAL COMMUNICATION III 3D DESIGN PRINCIPLES
 COLOR THE MEANING OF COLOR Color in design is very subjective. What evokes one reaction in one person may evoke a very different reaction in someone else. Sometimes this is due to personal preference,
COLOR THE MEANING OF COLOR Color in design is very subjective. What evokes one reaction in one person may evoke a very different reaction in someone else. Sometimes this is due to personal preference,
Colour + Perception. CMPT 467/767 Visualization Torsten Möller. Pfister/Möller
 Colour + Perception CMPT 467/767 Visualization Torsten Möller Recommended Reading http://www.stonesc.com/ 2 Where / What 3 Based on slide from Mazur Contours & Texture C. Ware, Visual Thinking for Design
Colour + Perception CMPT 467/767 Visualization Torsten Möller Recommended Reading http://www.stonesc.com/ 2 Where / What 3 Based on slide from Mazur Contours & Texture C. Ware, Visual Thinking for Design
The Advantages of the New HP Nine-Ink Color Printing System
 The Advantages of the New HP Nine-Ink Color Printing System HP Nine-ink printing The new HP Photosmart 8750 Professional Photo Printer (introduced in Spring 2005) uses nine HP Vivera Inks in three cartridges,
The Advantages of the New HP Nine-Ink Color Printing System HP Nine-ink printing The new HP Photosmart 8750 Professional Photo Printer (introduced in Spring 2005) uses nine HP Vivera Inks in three cartridges,
EECS490: Digital Image Processing. Lecture #12
 Lecture #12 Image Correlation (example) Color basics (Chapter 6) The Chromaticity Diagram Color Images RGB Color Cube Color spaces Pseudocolor Multispectral Imaging White Light A prism splits white light
Lecture #12 Image Correlation (example) Color basics (Chapter 6) The Chromaticity Diagram Color Images RGB Color Cube Color spaces Pseudocolor Multispectral Imaging White Light A prism splits white light
Elements & Principles of Art
 Elements & Principles of Art in a recipe Elements of Art The elements are components or parts which can be isolated and defined in any visual design or work of art. They are the structure of the work,
Elements & Principles of Art in a recipe Elements of Art The elements are components or parts which can be isolated and defined in any visual design or work of art. They are the structure of the work,
Using Curves and Histograms
 Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-2003 Digital Light & Color Introduction Although many of the operations, tools, and terms used in digital image manipulation have direct equivalents in conventional
Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-2003 Digital Light & Color Introduction Although many of the operations, tools, and terms used in digital image manipulation have direct equivalents in conventional
A World of Color. Session 4 Color Spaces. OLLI at Illinois Spring D. H. Tracy
 A World of Color Session 4 Color Spaces OLLI at Illinois Spring 2018 D. H. Tracy Course Outline 1. Overview, History and Spectra 2. Nature and Sources of Light 3. Eyes and Color Vision 4. Color Spaces
A World of Color Session 4 Color Spaces OLLI at Illinois Spring 2018 D. H. Tracy Course Outline 1. Overview, History and Spectra 2. Nature and Sources of Light 3. Eyes and Color Vision 4. Color Spaces
CH 21 2-SPACE. Ch 21 2-Space. y-axis (vertical) x-axis. Introduction
 197 CH 21 2-SPACE Introduction S omeone once said A picture is worth a thousand words. This is especially true in math, where many ideas are very abstract. The French mathematician-philosopher René Descartes
197 CH 21 2-SPACE Introduction S omeone once said A picture is worth a thousand words. This is especially true in math, where many ideas are very abstract. The French mathematician-philosopher René Descartes
Wright Field Scale Modelers. Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong.
 Wright Field Scale Modelers Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong. Sources http://www.huevaluechroma.com/ Written by a color scientist, Dr. Briggs. It is a bit technical. Principles
Wright Field Scale Modelers Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong. Sources http://www.huevaluechroma.com/ Written by a color scientist, Dr. Briggs. It is a bit technical. Principles
CSE512 :: 6 Feb Color. Jeffrey Heer University of Washington
 CSE512 :: 6 Feb 2014 Color Jeffrey Heer University of Washington 1 Color in Visualization Identify, Group, Layer, Highlight Colin Ware 2 Purpose of Color To label To measure To represent and imitate To
CSE512 :: 6 Feb 2014 Color Jeffrey Heer University of Washington 1 Color in Visualization Identify, Group, Layer, Highlight Colin Ware 2 Purpose of Color To label To measure To represent and imitate To
IMAGE INTENSIFICATION TECHNIQUE USING HORIZONTAL SITUATION INDICATOR
 IMAGE INTENSIFICATION TECHNIQUE USING HORIZONTAL SITUATION INDICATOR Naveen Kumar Mandadi 1, B.Praveen Kumar 2, M.Nagaraju 3, 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, SRTIST, Nalgonda (India) ABSTRACT
IMAGE INTENSIFICATION TECHNIQUE USING HORIZONTAL SITUATION INDICATOR Naveen Kumar Mandadi 1, B.Praveen Kumar 2, M.Nagaraju 3, 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, SRTIST, Nalgonda (India) ABSTRACT
Name: Period: THE ELEMENTS OF ART
 Name: Period: THE ELEMENTS OF ART Name: Period: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with
Name: Period: THE ELEMENTS OF ART Name: Period: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with
Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory
 Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory Colour Systems Available colour systems are dependent on the medium with which a designer is working. When painting, an artist has a variety
Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory Colour Systems Available colour systems are dependent on the medium with which a designer is working. When painting, an artist has a variety
Color. Maneesh Agrawala Jessica Hullman. CS : Visualization Fall Assignment 3: Visualization Software
 Color Maneesh Agrawala Jessica Hullman CS 294-10: Visualization Fall 2014 Assignment 3: Visualization Software Create a small interactive visualization application you choose data domain and visualization
Color Maneesh Agrawala Jessica Hullman CS 294-10: Visualization Fall 2014 Assignment 3: Visualization Software Create a small interactive visualization application you choose data domain and visualization
Chapter 3 Part 2 Color image processing
 Chapter 3 Part 2 Color image processing Motivation Color fundamentals Color models Pseudocolor image processing Full-color image processing: Component-wise Vector-based Recent and current work Spring 2002
Chapter 3 Part 2 Color image processing Motivation Color fundamentals Color models Pseudocolor image processing Full-color image processing: Component-wise Vector-based Recent and current work Spring 2002
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
Digital Image Processing (DIP)
 University of Kurdistan Digital Image Processing (DIP) Lecture 6: Color Image Processing Instructor: Kaveh Mollazade, Ph.D. Department of Biosystems Engineering, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Kurdistan,
University of Kurdistan Digital Image Processing (DIP) Lecture 6: Color Image Processing Instructor: Kaveh Mollazade, Ph.D. Department of Biosystems Engineering, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Kurdistan,
Colour. Electromagnetic Spectrum (1: visible is very small part 2: not all colours are present in the rainbow!) Colour Lecture!
 Colour Lecture! ITNP80: Multimedia 1 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Richardson,
Colour Lecture! ITNP80: Multimedia 1 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Richardson,
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals
 color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
Color Theory and Mixing
 MODULE 4 Color Theory and Mixing? What is explored in this module? In this module, we ll look at basic color theory and mixing colors. You ll find that color theory and mixing is not a perfect science.
MODULE 4 Color Theory and Mixing? What is explored in this module? In this module, we ll look at basic color theory and mixing colors. You ll find that color theory and mixing is not a perfect science.
Formal Elements of Art Principles of Design
 Formal Elements of Art Principles of Design Formal Elements = Line, Space, Color, Light, Texture, Pattern, Time, Motion Principles of Design = Balance, Proportion/Scale, Rhythm, Emphasis, Unity Formal
Formal Elements of Art Principles of Design Formal Elements = Line, Space, Color, Light, Texture, Pattern, Time, Motion Principles of Design = Balance, Proportion/Scale, Rhythm, Emphasis, Unity Formal
Dragnet Abstract Test 4 Solution Booklet
 Dragnet Abstract Test 4 Solution Booklet Instructions This Abstract reasoning test comprises 16 questions. You will have 16 minutes in which to correctly answer as many as you can. In each question you
Dragnet Abstract Test 4 Solution Booklet Instructions This Abstract reasoning test comprises 16 questions. You will have 16 minutes in which to correctly answer as many as you can. In each question you
Our Color Vision is Limited
 CHAPTER Our Color Vision is Limited 5 Human color perception has both strengths and limitations. Many of those strengths and limitations are relevant to user interface design: l Our vision is optimized
CHAPTER Our Color Vision is Limited 5 Human color perception has both strengths and limitations. Many of those strengths and limitations are relevant to user interface design: l Our vision is optimized
Missing Sequence. You have 10 minutes to complete this test. Select the square that comes next in the sequence.
 Missing Sequence Select the square that comes next in the sequence. 1. 2. 3. Similarities 4. 5. 6. Analogies 7. 8. ` 9. Odd one out 10. 11. 12. Complete the grid 13. 14. 15. Answers 1. A- The pattern along
Missing Sequence Select the square that comes next in the sequence. 1. 2. 3. Similarities 4. 5. 6. Analogies 7. 8. ` 9. Odd one out 10. 11. 12. Complete the grid 13. 14. 15. Answers 1. A- The pattern along
Unit 8: Color Image Processing
 Unit 8: Color Image Processing Colour Fundamentals In 666 Sir Isaac Newton discovered that when a beam of sunlight passes through a glass prism, the emerging beam is split into a spectrum of colours The
Unit 8: Color Image Processing Colour Fundamentals In 666 Sir Isaac Newton discovered that when a beam of sunlight passes through a glass prism, the emerging beam is split into a spectrum of colours The
Comparing Sound and Light. Light and Color. More complicated light. Seeing colors. Rods and cones
 Light and Color Eye perceives EM radiation of different wavelengths as different colors. Sensitive only to the range 4nm - 7 nm This is a narrow piece of the entire electromagnetic spectrum. Comparing
Light and Color Eye perceives EM radiation of different wavelengths as different colors. Sensitive only to the range 4nm - 7 nm This is a narrow piece of the entire electromagnetic spectrum. Comparing
The Elements and Principles of Design. The Building Blocks of Art
 The Elements and Principles of Design The Building Blocks of Art 1 Line An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark
The Elements and Principles of Design The Building Blocks of Art 1 Line An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark
Color Mixing. Color Systems and Additive and Subtractive Colors. MODIFIED FROM Dr. Patricia Hill, Millersville University
 Color Mixing Color Systems and Additive and Subtractive Colors MODIFIED FROM Dr. Patricia Hill, Millersville University Describing Color Color Attributes Hue (color) Brightness Saturation or Purity corresponds
Color Mixing Color Systems and Additive and Subtractive Colors MODIFIED FROM Dr. Patricia Hill, Millersville University Describing Color Color Attributes Hue (color) Brightness Saturation or Purity corresponds
Colour. Why/How do we perceive colours? Electromagnetic Spectrum (1: visible is very small part 2: not all colours are present in the rainbow!
 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Colour Lecture (2 lectures)! Richardson, Chapter
Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Colour Lecture (2 lectures)! Richardson, Chapter
.VP CREATING AN INVENTED ONE POINT PERSPECTIVE SPACE
 PAGE ONE Organize an invented 1 point perspective drawing in the following order: 1 Establish an eye level 2 Establish a Center Line Vision eye level vision Remember that the vanishing point () in one
PAGE ONE Organize an invented 1 point perspective drawing in the following order: 1 Establish an eye level 2 Establish a Center Line Vision eye level vision Remember that the vanishing point () in one
Multi-View Drawing Review
 Multi-View Drawing Review Sacramento City College EDT 300/ENGR 306 EDT 300 / ENGR 306 - Chapter 5 1 Objectives Identify and select the various views of an object. Determine the number of views needed to
Multi-View Drawing Review Sacramento City College EDT 300/ENGR 306 EDT 300 / ENGR 306 - Chapter 5 1 Objectives Identify and select the various views of an object. Determine the number of views needed to
Mahdi Amiri. March Sharif University of Technology
 Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2014 Sharif University of Technology The wavelength λ of a sinusoidal waveform traveling at constant speed ν is given by Physics of
Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2014 Sharif University of Technology The wavelength λ of a sinusoidal waveform traveling at constant speed ν is given by Physics of
Color , , Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 7
 Color http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 7 Course announcements Homework 2 is out. - Due September 28 th. - Requires camera and
Color http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 7 Course announcements Homework 2 is out. - Due September 28 th. - Requires camera and
THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR
 THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR Colour can be described as a light wavelength coming from a light source striking the surface of an object which in turns reflects the incoming light from were it is received by the
THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR Colour can be described as a light wavelength coming from a light source striking the surface of an object which in turns reflects the incoming light from were it is received by the
APPLICATION OF COMPUTER VISION FOR DETERMINATION OF SYMMETRICAL OBJECT POSITION IN THREE DIMENSIONAL SPACE
 APPLICATION OF COMPUTER VISION FOR DETERMINATION OF SYMMETRICAL OBJECT POSITION IN THREE DIMENSIONAL SPACE Najirah Umar 1 1 Jurusan Teknik Informatika, STMIK Handayani Makassar Email : najirah_stmikh@yahoo.com
APPLICATION OF COMPUTER VISION FOR DETERMINATION OF SYMMETRICAL OBJECT POSITION IN THREE DIMENSIONAL SPACE Najirah Umar 1 1 Jurusan Teknik Informatika, STMIK Handayani Makassar Email : najirah_stmikh@yahoo.com
