Parallels and Euclidean Geometry
|
|
|
- Leon Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Parallels and Euclidean Geometry Lines l and m which are coplanar but do not meet are said to be parallel; we denote this by writing l m. Likewise, segments or rays are parallel if they are subsets of parallel lines. Given any two lines m and n, any third line l that meets both m and n in distinct points is called a transversal. This configuration makes a total of 8 angles with l, four with m and another four with n. Let l and m meet at A and let l and n meet at B. Any one of the angles at A is said to be alternate with respect to any angle at B that lies on the opposite side of l. Either of the two angles at A whose sides include B are called interior angles, as are either of the two angles at B whose sides contain A; the other four angles are exterior angles of the configuration. Finally, any two of these angles not at the same vertex and on the same side of l which are not both interior angles or both exterior angles are said to be corresponding angles. A central story in the history of geometry is the reaction to the manner in which Euclid developed the concept of parallelism in his Elements. A study of Book I shows that the first 28 Propositions were developed in absolute geometry; this was Proposition 28:
2 Theorem If two coplanar lines are cut by a transversal so that some pair of alternate interior angles are congruent, then the two lines are parallel. // Proposition i.29 is the converse of this theorem, but it is not a theorem of absolute geometry: to prove it, Euclid made use of a new axiom, his last and Fifth Postulate: If two coplanar lines are cut by a transversal so that some pair of interior angles on the same side of the transversal have total measure less than 180, then the two lines meet on that side of the transversal. This postulate is effectively equivalent to Proposition i.29: If two coplanar parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then both pairs of alternate interior angles are congruent. Following Euclid, we will also add a new axiom to absolute geometry which is logically equivalent to, but simpler than, the Fifth Postulate. It was formulated by the Greek geometer Proclus in the 5th century CE, but is more often attributed to John Playfair (the Scottish geometry professor who in 1795 published a classroom edition of the Elements with this variant replacing the Fifth Postulate). [P-1] For any line l and point P not on l, there exists in the same plane as l and P a unique line passing through P and parallel to l.
3 Theorem If two coplanar parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then both pairs of interior angles on the same side of the transversal have total measure equal to 180. // From this we deduce a number of useful transversal properties. (See Figure 4.7, p. 215, for an explanation of why they have these names.) Corollary [The C Property] If two coplanar lines and only if some pair of interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary. // Corollary [The F Property] If two coplanar lines and only if some pair of corresponding angles are congruent. // Corollary [The Z Property] If two coplanar lines and only if some pair of alternate interior angles are congruent. // Theorem Parallelism is an equivalence relation on the set of all lines. //
4 Theorem [The Exterior Angle Theorem] The measure of any exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of the measures of the two opposite interior angles. // Corollary [Euclidean Triangle Angle Sums] The angle sum of any triangle is 180. // Theorem [The Midpoint Connector Theorem] The segment joining the midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and has half the length. // A convex quadrilateral is called a parallelogram if both pairs of opposite sides are parallel, a rhombus if, in addition, some pair of adjacent sides are congruent, and a square if also one of its interior angles is right. Theorem Either diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two congruent triangles. // Corollary Both pairs of opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. // Corollary Any pair of adjacent angles in a parallelogram are supplementary. // Corollary If a convex quadrilateral has both pairs of opposite sides congruent, it is a parallelogram. //
5 Corollary If a convex quadrilateral has a pair of opposite sides congruent and parallel, it is a parallelogram. // Corollary The diagonals of a convex quadrilateral bisect each other if and only if it is a parallelogram. // Theorem A parallelogram is a rhombus if and only if its diagonals are perpendicular. // Theorem A parallelogram is a rectangle if and only if its diagonals are congruent. // Theorem A parallelogram is a square if and only if its diagonals are perpendicular and congruent. // A trapezoid is a convex quadrilateral having one pair of opposite sides, called the bases, parallel to each other. The other pair of opposite sides are called its legs. (Note that all parallelograms are trapezoids.) The median of a trapezoid is the segment joining the midpoints of its legs. Theorem [The Midpoint Connector Theorem for Trapezoids] A line parallel to the bases of a trapezoid that bisects one leg bisects the other; conversely, the median of a trapezoid is parallel to its bases. Further, the length of the median is the average of the lengths of the bases. //
Downloaded from
 1 IX Mathematics Chapter 8: Quadrilaterals Chapter Notes Top Definitions 1. A quadrilateral is a closed figure obtained by joining four points (with no three points collinear) in an order. 2. A diagonal
1 IX Mathematics Chapter 8: Quadrilaterals Chapter Notes Top Definitions 1. A quadrilateral is a closed figure obtained by joining four points (with no three points collinear) in an order. 2. A diagonal
Geometry by Jurgensen, Brown and Jurgensen Postulates and Theorems from Chapter 1
 Postulates and Theorems from Chapter 1 Postulate 1: The Ruler Postulate 1. The points on a line can be paired with the real numbers in such a way that any two points can have coordinates 0 and 1. 2. Once
Postulates and Theorems from Chapter 1 Postulate 1: The Ruler Postulate 1. The points on a line can be paired with the real numbers in such a way that any two points can have coordinates 0 and 1. 2. Once
16. DOK 1, I will succeed." In this conditional statement, the underlined portion is
 Geometry Semester 1 REVIEW 1. DOK 1 The point that divides a line segment into two congruent segments. 2. DOK 1 lines have the same slope. 3. DOK 1 If you have two parallel lines and a transversal, then
Geometry Semester 1 REVIEW 1. DOK 1 The point that divides a line segment into two congruent segments. 2. DOK 1 lines have the same slope. 3. DOK 1 If you have two parallel lines and a transversal, then
Axiom A-1: To every angle there corresponds a unique, real number, 0 < < 180.
 Axiom A-1: To every angle there corresponds a unique, real number, 0 < < 180. We denote the measure of ABC by m ABC. (Temporary Definition): A point D lies in the interior of ABC iff there exists a segment
Axiom A-1: To every angle there corresponds a unique, real number, 0 < < 180. We denote the measure of ABC by m ABC. (Temporary Definition): A point D lies in the interior of ABC iff there exists a segment
Geometry. a) Rhombus b) Square c) Trapezium d) Rectangle
 Geometry A polygon is a many sided closed shape. Four sided polygons are called quadrilaterals. Sum of angles in a quadrilateral equals 360. Parallelogram is a quadrilateral where opposite sides are parallel.
Geometry A polygon is a many sided closed shape. Four sided polygons are called quadrilaterals. Sum of angles in a quadrilateral equals 360. Parallelogram is a quadrilateral where opposite sides are parallel.
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 MATH 121 SPRING 2017 - PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Given that point P is the midpoint of both and, it follows that. 2. If, then. 3. In a circle (or congruent
MATH 121 SPRING 2017 - PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Given that point P is the midpoint of both and, it follows that. 2. If, then. 3. In a circle (or congruent
6-1. Angles of Polygons. Lesson 6-1. What You ll Learn. Active Vocabulary
 6-1 Angles of Polygons What You ll Learn Skim Lesson 6-1. Predict two things that you expect to learn based on the headings and figures in the lesson. 1. 2. Lesson 6-1 Active Vocabulary diagonal New Vocabulary
6-1 Angles of Polygons What You ll Learn Skim Lesson 6-1. Predict two things that you expect to learn based on the headings and figures in the lesson. 1. 2. Lesson 6-1 Active Vocabulary diagonal New Vocabulary
1. Take out a piece of notebook paper and make a hot dog fold over from the right side over to the pink line. Foldable
 Four sided polygon 1. Take out a piece of notebook paper and make a hot dog fold over from the right side over to the pink line. Foldable Foldable The fold crease 2. Now, divide the right hand section
Four sided polygon 1. Take out a piece of notebook paper and make a hot dog fold over from the right side over to the pink line. Foldable Foldable The fold crease 2. Now, divide the right hand section
CHAPTER 3. Parallel & Perpendicular lines
 CHAPTER 3 Parallel & Perpendicular lines 3.1- Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Parallel Lines: two lines are parallel if they do not intersect and are coplaner Skew lines: Two lines are skew if they
CHAPTER 3 Parallel & Perpendicular lines 3.1- Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Parallel Lines: two lines are parallel if they do not intersect and are coplaner Skew lines: Two lines are skew if they
Ch. 3 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
 Ch. 3 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Section 3.1 Lines and Angles 1. I CAN identify relationships between figures in space. 2. I CAN identify angles formed by two lines and a transversal. Key Vocabulary:
Ch. 3 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Section 3.1 Lines and Angles 1. I CAN identify relationships between figures in space. 2. I CAN identify angles formed by two lines and a transversal. Key Vocabulary:
Geometry Vocabulary Book
 Geometry Vocabulary Book Units 2-4 Page 1 Unit 2 General Geometry Point Characteristics: Line Characteristics: Plane Characteristics: RELATED POSTULATES: Through any two points there exists exactly one
Geometry Vocabulary Book Units 2-4 Page 1 Unit 2 General Geometry Point Characteristics: Line Characteristics: Plane Characteristics: RELATED POSTULATES: Through any two points there exists exactly one
Step 2: Extend the compass from the chosen endpoint so that the width of the compass is more than half the distance between the two points.
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 1 Description: GEO Topic 1 Test: Tools of Geometry Form: 201 1. A student followed the given
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 1 Description: GEO Topic 1 Test: Tools of Geometry Form: 201 1. A student followed the given
Chapter 2 Review WS Period: Date:
 Geometry Name: Chapter 2 Review WS Period: Date:. A transversal intersects two parallel lines. The measures of a pair of alternate interior angles are 5v and 2w. The measures of a pair of same-side exterior
Geometry Name: Chapter 2 Review WS Period: Date:. A transversal intersects two parallel lines. The measures of a pair of alternate interior angles are 5v and 2w. The measures of a pair of same-side exterior
Title: Quadrilaterals Aren t Just Squares
 Title: Quadrilaterals ren t Just Squares Brief Overview: This is a collection of the first three lessons in a series of seven lessons studying characteristics of quadrilaterals, including trapezoids, parallelograms,
Title: Quadrilaterals ren t Just Squares Brief Overview: This is a collection of the first three lessons in a series of seven lessons studying characteristics of quadrilaterals, including trapezoids, parallelograms,
Date: Period: Quadrilateral Word Problems: Review Sheet
 Name: Quadrilateral Word Problems: Review Sheet Date: Period: Geometry Honors Directions: Please answer the following on a separate sheet of paper. Completing this review sheet will help you to do well
Name: Quadrilateral Word Problems: Review Sheet Date: Period: Geometry Honors Directions: Please answer the following on a separate sheet of paper. Completing this review sheet will help you to do well
Geometry Unit 5 Practice Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: X Geometry Unit 5 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the value of x in the rectangle? Hint: use
Name: Class: Date: ID: X Geometry Unit 5 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the value of x in the rectangle? Hint: use
Honors Geometry Chapter 6 Supplement. Q (4x) (5x)
 Honors Geometry hapter 6 upplement Name: 1. Given: Q m Q = (4x) m Q = (5x) m Q = 40 m Q = 32 Find the value of x, m Q, m Q, m Q Q (4x) (5x) 40 32 2. Given: m = (8x + 20) m = (150 6x) m = (12x + 60) a)
Honors Geometry hapter 6 upplement Name: 1. Given: Q m Q = (4x) m Q = (5x) m Q = 40 m Q = 32 Find the value of x, m Q, m Q, m Q Q (4x) (5x) 40 32 2. Given: m = (8x + 20) m = (150 6x) m = (12x + 60) a)
Name Period GEOMETRY CHAPTER 3 Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Section 3.1 Lines and Angles GOAL 1: Relationship between lines
 Name Period GEOMETRY CHAPTER 3 Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Section 3.1 Lines and Angles GOAL 1: Relationship between lines Two lines are if they are coplanar and do not intersect. Skew lines. Two
Name Period GEOMETRY CHAPTER 3 Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Section 3.1 Lines and Angles GOAL 1: Relationship between lines Two lines are if they are coplanar and do not intersect. Skew lines. Two
Project Maths Geometry Notes
 The areas that you need to study are: Project Maths Geometry Notes (i) Geometry Terms: (ii) Theorems: (iii) Constructions: (iv) Enlargements: Axiom, theorem, proof, corollary, converse, implies The exam
The areas that you need to study are: Project Maths Geometry Notes (i) Geometry Terms: (ii) Theorems: (iii) Constructions: (iv) Enlargements: Axiom, theorem, proof, corollary, converse, implies The exam
E G 2 3. MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland
 MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland Point A point is a location in space. It has no length or width. A point is represented by a dot and is named by writing a capital letter next to the dot.
MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland Point A point is a location in space. It has no length or width. A point is represented by a dot and is named by writing a capital letter next to the dot.
18 Two-Dimensional Shapes
 18 Two-Dimensional Shapes CHAPTER Worksheet 1 Identify the shape. Classifying Polygons 1. I have 3 sides and 3 corners. 2. I have 6 sides and 6 corners. Each figure is made from two shapes. Name the shapes.
18 Two-Dimensional Shapes CHAPTER Worksheet 1 Identify the shape. Classifying Polygons 1. I have 3 sides and 3 corners. 2. I have 6 sides and 6 corners. Each figure is made from two shapes. Name the shapes.
Regents Exam Questions G.G.69: Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane 2
 Regents Exam Questions G.G.69: Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane 2 www.jmap.org Name: G.G.69: Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane 2: Investigate the properties of quadrilaterals in the coordinate
Regents Exam Questions G.G.69: Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane 2 www.jmap.org Name: G.G.69: Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane 2: Investigate the properties of quadrilaterals in the coordinate
Warm-Up Exercises. Find the value of x. 1. ANSWER 65 ANSWER 120
 Warm-Up Exercises Find the value of x. 1. 65 2. 120 Warm-Up Exercises Find the value of x. 3. 70 EXAMPLE Warm-Up 1Exercises Identify quadrilaterals Quadrilateral ABCD has at least one pair of opposite
Warm-Up Exercises Find the value of x. 1. 65 2. 120 Warm-Up Exercises Find the value of x. 3. 70 EXAMPLE Warm-Up 1Exercises Identify quadrilaterals Quadrilateral ABCD has at least one pair of opposite
Geometry - Chapter 6 Review
 Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 6 Review 1. Find the sum of the measures of the angles of the figure. 4. Find the value of x. The diagram is not to scale. A. 1260 B. 900 C. 540 D. 720 2. The sum of the
Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 6 Review 1. Find the sum of the measures of the angles of the figure. 4. Find the value of x. The diagram is not to scale. A. 1260 B. 900 C. 540 D. 720 2. The sum of the
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures. Grade 9 Mathematics
 Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
Lesson 10.1 Skills Practice
 Lesson 10.1 Skills Practice Location, Location, Location! Line Relationships Vocabulary Write the term or terms from the box that best complete each statement. intersecting lines perpendicular lines parallel
Lesson 10.1 Skills Practice Location, Location, Location! Line Relationships Vocabulary Write the term or terms from the box that best complete each statement. intersecting lines perpendicular lines parallel
All in the Family. b. Use your paper tracing to compare the side lengths of the parallelogram. What appears to be true? Summarize your findings below.
 The quadrilateral family is organized according to the number pairs of sides parallel in a particular quadrilateral. Given a quadrilateral, there are three distinct possibilities: both pairs of opposite
The quadrilateral family is organized according to the number pairs of sides parallel in a particular quadrilateral. Given a quadrilateral, there are three distinct possibilities: both pairs of opposite
and Transitional Comprehensive Curriculum. Geometry Unit 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Relationships
 Geometry Unit 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Relationships Time Frame: Approximately three weeks Unit Description This unit demonstrates the basic role played by Euclid s fifth postulate in geometry. Euclid
Geometry Unit 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Relationships Time Frame: Approximately three weeks Unit Description This unit demonstrates the basic role played by Euclid s fifth postulate in geometry. Euclid
Geometry Topic 4 Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Proof
 Geometry Topic 4 Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Proof MAFS.912.G-CO.3.11 In the diagram below, parallelogram has diagonals and that intersect at point. Which expression is NOT always true? A. B. C. D. C
Geometry Topic 4 Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Proof MAFS.912.G-CO.3.11 In the diagram below, parallelogram has diagonals and that intersect at point. Which expression is NOT always true? A. B. C. D. C
Semester A Review Answers. 1. point, line, and plane. 2. one. 3. three. 4. one or No, since AB BC AC 11. AC a. EG FH.
 1. point, line, and plane 2. one 3. three 4. one 5. 18 or 8 6. b 23, c 30 7. No, since C C 8. 8 9. x 20 10. C 470 11. C 12 12. x 10 13. x 25 14. x 25 15. a. EG FH b. EG 43 16. m 2 55 o 17. x 30 18. m 1
1. point, line, and plane 2. one 3. three 4. one 5. 18 or 8 6. b 23, c 30 7. No, since C C 8. 8 9. x 20 10. C 470 11. C 12 12. x 10 13. x 25 14. x 25 15. a. EG FH b. EG 43 16. m 2 55 o 17. x 30 18. m 1
(1) Page 482 #1 20. (2) Page 488 #1 14. (3) Page # (4) Page 495 #1 10. (5) Page #12 30,
 Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 8: Circles Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 482 #1 20 (2) Page 488 #1 14 (3) Page 488 489 #15 26 (4) Page 495 #1 10 (5) Page 495 496 #12 30, 37 39 (6) Page 502 #1 7 (7) Page
Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 8: Circles Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 482 #1 20 (2) Page 488 #1 14 (3) Page 488 489 #15 26 (4) Page 495 #1 10 (5) Page 495 496 #12 30, 37 39 (6) Page 502 #1 7 (7) Page
Unit 6: Quadrilaterals
 Name: Period: Unit 6: Quadrilaterals Geometry Honors Homework Section 6.1: Classifying Quadrilaterals State whether each statement is true or false. Justify your response. 1. All squares are rectangles.
Name: Period: Unit 6: Quadrilaterals Geometry Honors Homework Section 6.1: Classifying Quadrilaterals State whether each statement is true or false. Justify your response. 1. All squares are rectangles.
Geometry Ch 3 Vertical Angles, Linear Pairs, Perpendicular/Parallel Lines 29 Nov 2017
 3.1 Number Operations and Equality Algebraic Postulates of Equality: Reflexive Property: a=a (Any number is equal to itself.) Substitution Property: If a=b, then a can be substituted for b in any expression.
3.1 Number Operations and Equality Algebraic Postulates of Equality: Reflexive Property: a=a (Any number is equal to itself.) Substitution Property: If a=b, then a can be substituted for b in any expression.
6-6 Trapezoids and Kites. CCSS SENSE-MAKING If WXYZ is a kite, find each measure. 25. WP
 CCSS SENSE-MAKING If WXYZ is a kite, find each measure. 25. WP By the Pythagorean Theorem, WP 2 = WX 2 XP 2 = 6 2 4 2 = 20 27. A kite can only have one pair of opposite congruent angles and Let m X = m
CCSS SENSE-MAKING If WXYZ is a kite, find each measure. 25. WP By the Pythagorean Theorem, WP 2 = WX 2 XP 2 = 6 2 4 2 = 20 27. A kite can only have one pair of opposite congruent angles and Let m X = m
Find the coordinates of the midpoint of a segment having the given endpoints.
 G.(2) Coordinate and transformational geometry. The student uses the process skills to understand the connections between algebra and geometry and uses the one- and two-dimensional coordinate systems to
G.(2) Coordinate and transformational geometry. The student uses the process skills to understand the connections between algebra and geometry and uses the one- and two-dimensional coordinate systems to
Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles.
 CONSTRUCTIONS Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles. Introduction to Constructions Constructions: The drawing of various shapes using only a pair of compasses
CONSTRUCTIONS Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles. Introduction to Constructions Constructions: The drawing of various shapes using only a pair of compasses
2.2. Special Angles and Postulates. Key Terms
 And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates. Learning Goals Key Terms In this lesson, you will: Calculate the complement and supplement of an angle. Classify adjacent angles, linear pairs, and
And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates. Learning Goals Key Terms In this lesson, you will: Calculate the complement and supplement of an angle. Classify adjacent angles, linear pairs, and
6-5 P R OV I N G R H O M B U S E S, R E C TA N G L E S, A N D S Q UA R E S
 6-5 P R OV I N G R H O M B U S E S, R E C TA N G L E S, A N D S Q UA R E S Workbook page 261, number 13 Given: ABCD is a rectangle Prove: EDC ECD A D E B C Statements Reasons 1) ABCD is a rectangle 1)
6-5 P R OV I N G R H O M B U S E S, R E C TA N G L E S, A N D S Q UA R E S Workbook page 261, number 13 Given: ABCD is a rectangle Prove: EDC ECD A D E B C Statements Reasons 1) ABCD is a rectangle 1)
Unit 6 Quadrilaterals
 Unit 6 Quadrilaterals ay lasswork ay Homework Monday Properties of a Parallelogram 1 HW 6.1 11/13 Tuesday 11/14 Proving a Parallelogram 2 HW 6.2 Wednesday 11/15 Thursday 11/16 Friday 11/17 Monday 11/20
Unit 6 Quadrilaterals ay lasswork ay Homework Monday Properties of a Parallelogram 1 HW 6.1 11/13 Tuesday 11/14 Proving a Parallelogram 2 HW 6.2 Wednesday 11/15 Thursday 11/16 Friday 11/17 Monday 11/20
Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles.
 CONSTRUCTIONS Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles. Oct 1 8:33 AM Oct 2 7:42 AM 1 Introduction to Constructions Constructions: The drawing of various shapes
CONSTRUCTIONS Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles. Oct 1 8:33 AM Oct 2 7:42 AM 1 Introduction to Constructions Constructions: The drawing of various shapes
9.1 and 9.2 Introduction to Circles
 Date: Secondary Math 2 Vocabulary 9.1 and 9.2 Introduction to Circles Define the following terms and identify them on the circle: Circle: The set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given
Date: Secondary Math 2 Vocabulary 9.1 and 9.2 Introduction to Circles Define the following terms and identify them on the circle: Circle: The set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given
AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School
 AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved AGS Math Algebra 2 Grade
AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved AGS Math Algebra 2 Grade
MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY HONORS. OPTIONS FOR NEXT COURSE Algebra II, Algebra II/Trigonometry, or Algebra, Functions, and Data Analysis
 Parent / Student Course Information MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY HONORS Counselors are available to assist parents and students with course selections and career planning. Parents may arrange to meet with the
Parent / Student Course Information MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY HONORS Counselors are available to assist parents and students with course selections and career planning. Parents may arrange to meet with the
4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and
 4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids using appropriate tools (e.g., ruler, straightedge
4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids using appropriate tools (e.g., ruler, straightedge
(A) Circle (B) Polygon (C) Line segment (D) None of them (A) (B) (C) (D) (A) Understanding Quadrilaterals <1M>
 Understanding Quadrilaterals 1.A simple closed curve made up of only line segments is called a (A) Circle (B) Polygon (C) Line segment (D) None of them 2.In the following figure, which of the polygon
Understanding Quadrilaterals 1.A simple closed curve made up of only line segments is called a (A) Circle (B) Polygon (C) Line segment (D) None of them 2.In the following figure, which of the polygon
Target 5.4: Use angle properties in triangles to determine unknown angle measurements 5.4: Parallel Lines and Triangles
 Unit 5 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Target 5.1: Classify and identify angles formed by parallel lines and transversals 5.1 a Parallel and Perpendicular lines 5.1b Parallel Lines and its Angle Relationships
Unit 5 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Target 5.1: Classify and identify angles formed by parallel lines and transversals 5.1 a Parallel and Perpendicular lines 5.1b Parallel Lines and its Angle Relationships
Geometry Tutor Worksheet 9 Quadrilaterals
 Geometry Tutor Worksheet 9 Quadrilaterals 1 Geometry Tutor - Worksheet 9 - Quadrilaterals 1. Which name best describes quadrilateral DEFG? 2. Which name best describes quadrilateral ABCD? 3. Which name
Geometry Tutor Worksheet 9 Quadrilaterals 1 Geometry Tutor - Worksheet 9 - Quadrilaterals 1. Which name best describes quadrilateral DEFG? 2. Which name best describes quadrilateral ABCD? 3. Which name
8.3 Prove It! A Practice Understanding Task
 15 8.3 Prove It! A Practice Understanding Task In this task you need to use all the things you know about quadrilaterals, distance, and slope to prove that the shapes are parallelograms, rectangles, rhombi,
15 8.3 Prove It! A Practice Understanding Task In this task you need to use all the things you know about quadrilaterals, distance, and slope to prove that the shapes are parallelograms, rectangles, rhombi,
Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards
 Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards WALCH EDUCATION Table of Contents Standards Correlations...................................................... v Introduction..............................................................vii
Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards WALCH EDUCATION Table of Contents Standards Correlations...................................................... v Introduction..............................................................vii
(A) Circle (B) Polygon (C) Line segment (D) None of them
 Understanding Quadrilaterals 1.The angle between the altitudes of a parallelogram, through the same vertex of an obtuse angle of the parallelogram is 60 degree. Find the angles of the parallelogram.
Understanding Quadrilaterals 1.The angle between the altitudes of a parallelogram, through the same vertex of an obtuse angle of the parallelogram is 60 degree. Find the angles of the parallelogram.
Table of Contents. Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x
 Table of Contents Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x...1...1 Set 2: Classifying Triangles and Angle Theorems... 13 Set 3: Corresponding Parts, Transformations, and Proof...
Table of Contents Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x...1...1 Set 2: Classifying Triangles and Angle Theorems... 13 Set 3: Corresponding Parts, Transformations, and Proof...
Secondary 2 Unit 7 Test Study Guide
 Class: Date: Secondary 2 Unit 7 Test Study Guide 2014-2015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement can you use to conclude that
Class: Date: Secondary 2 Unit 7 Test Study Guide 2014-2015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement can you use to conclude that
Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define rectangles and rhombuses based on those attributes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 18 5 5 Lesson 18 Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 18 5 5 Lesson 18 Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
Geometer s Skethchpad 7th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry
 Geometer s Skethchpad 7th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: 2 -- Learning with Geometer s Sketchpad **a story can be added or one could choose to use the activities alone and
Geometer s Skethchpad 7th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: 2 -- Learning with Geometer s Sketchpad **a story can be added or one could choose to use the activities alone and
The Texas Education Agency and the Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board Geometry Module Pre-/Post-Test. U x T'
 Pre-/Post-Test The Texas Education Agency and the Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board Geometry Module Pre-/Post-Test 1. Triangle STU is rotated 180 clockwise to form image STU ' ' '. Determine the
Pre-/Post-Test The Texas Education Agency and the Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board Geometry Module Pre-/Post-Test 1. Triangle STU is rotated 180 clockwise to form image STU ' ' '. Determine the
GEO: Sem 1 Unit 1 Review of Geometry on the Coordinate Plane Section 1.6: Midpoint and Distance in the Coordinate Plane (1)
 GEO: Sem 1 Unit 1 Review of Geometr on the Coordinate Plane Section 1.6: Midpoint and Distance in the Coordinate Plane (1) NAME OJECTIVES: WARM UP Develop and appl the formula for midpoint. Use the Distance
GEO: Sem 1 Unit 1 Review of Geometr on the Coordinate Plane Section 1.6: Midpoint and Distance in the Coordinate Plane (1) NAME OJECTIVES: WARM UP Develop and appl the formula for midpoint. Use the Distance
STUDENT: We made it right now and then we used the end points of the blue and yellow sticks. Then if you connect the dots...
 Tuesday Group Work Part B: STUDENT: We made it right now and then we used the end points of the blue and yellow sticks. Then if you connect the dots... STUDENT: Oh, so it s kind of like making a kite but
Tuesday Group Work Part B: STUDENT: We made it right now and then we used the end points of the blue and yellow sticks. Then if you connect the dots... STUDENT: Oh, so it s kind of like making a kite but
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry
 Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Constructing Angle Bisectors and Parallel Lines
 Name: Date: Period: Constructing Angle Bisectors and Parallel Lines TASK A: 1) Complete the following steps below. a. Draw a circle centered on point P. b. Mark any two points on the circle that are not
Name: Date: Period: Constructing Angle Bisectors and Parallel Lines TASK A: 1) Complete the following steps below. a. Draw a circle centered on point P. b. Mark any two points on the circle that are not
UNIT 14 Loci and NC: Shape, Space and Measures Transformations 3b, 3c, 3d and 3e
 UNIT 14 Loci and NC: Shape, Space and Measures Transformations 3b, 3c, 3d and 3e TOPICS (Text and Practice Books) St Ac Ex Sp 14.1 Drawing and Symmetry - - - 14.2 Scale Drawings - - 14.3 Constructing Triangles
UNIT 14 Loci and NC: Shape, Space and Measures Transformations 3b, 3c, 3d and 3e TOPICS (Text and Practice Books) St Ac Ex Sp 14.1 Drawing and Symmetry - - - 14.2 Scale Drawings - - 14.3 Constructing Triangles
1 st Subject: 2D Geometric Shape Construction and Division
 Joint Beginning and Intermediate Engineering Graphics 2 nd Week 1st Meeting Lecture Notes Instructor: Edward N. Locke Topic: Geometric Construction 1 st Subject: 2D Geometric Shape Construction and Division
Joint Beginning and Intermediate Engineering Graphics 2 nd Week 1st Meeting Lecture Notes Instructor: Edward N. Locke Topic: Geometric Construction 1 st Subject: 2D Geometric Shape Construction and Division
Unit 3. Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. a. n and m. b. p and q. c. n and p. Sep 14 7:54 AM. Sep 14 7:58 AM. Sep 14 8:07 AM.
 3.1 Relationships between lines Unit 3 -- Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Parallel lines lie in the same plane do not intersect Perpendicular lines lie in the same plane intersect to form right angles
3.1 Relationships between lines Unit 3 -- Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Parallel lines lie in the same plane do not intersect Perpendicular lines lie in the same plane intersect to form right angles
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
3. Given the similarity transformation shown below; identify the composition:
 Midterm Multiple Choice Practice 1. Based on the construction below, which statement must be true? 1 1) m ABD m CBD 2 2) m ABD m CBD 3) m ABD m ABC 1 4) m CBD m ABD 2 2. Line segment AB is shown in the
Midterm Multiple Choice Practice 1. Based on the construction below, which statement must be true? 1 1) m ABD m CBD 2 2) m ABD m CBD 3) m ABD m ABC 1 4) m CBD m ABD 2 2. Line segment AB is shown in the
9.5 Properties and Conditions for Kites and Trapezoids
 Name lass ate 9.5 Properties and onditions for Kites and Trapezoids ssential uestion: What are the properties of kites and trapezoids? Resource Locker xplore xploring Properties of Kites kite is a quadrilateral
Name lass ate 9.5 Properties and onditions for Kites and Trapezoids ssential uestion: What are the properties of kites and trapezoids? Resource Locker xplore xploring Properties of Kites kite is a quadrilateral
The Quadrilateral Detective
 The Quadrilateral Detective a Coordinate Geometry Activity An object might certainly LOOK like a square, but how much information do you really need before you can be absolutely sure that it IS a square?
The Quadrilateral Detective a Coordinate Geometry Activity An object might certainly LOOK like a square, but how much information do you really need before you can be absolutely sure that it IS a square?
KCATM Geometry
 Name School KCATM Geometry 9 10 2013 1) Find the minimum perimeter of a rectangle whose area is 169 square meters. a) 42 meters b) 13 meters c) 26 meters d) 52 meters 2) Find the coordinates of the midpoint
Name School KCATM Geometry 9 10 2013 1) Find the minimum perimeter of a rectangle whose area is 169 square meters. a) 42 meters b) 13 meters c) 26 meters d) 52 meters 2) Find the coordinates of the midpoint
Challenges from Ancient Greece
 Challenges from ncient Greece Mathematical goals Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods. Use congruent triangles to justify geometric constructions. Common Core State Standards
Challenges from ncient Greece Mathematical goals Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods. Use congruent triangles to justify geometric constructions. Common Core State Standards
THINGS TO DO WITH A GEOBOARD
 THINGS TO DO WITH A GEOBOARD The following list of suggestions is indicative of exercises and examples that can be worked on the geoboard. Simpler, as well as, more difficult suggestions can easily be
THINGS TO DO WITH A GEOBOARD The following list of suggestions is indicative of exercises and examples that can be worked on the geoboard. Simpler, as well as, more difficult suggestions can easily be
Name. Ms. Nong. Due on: Per: Geometry 2 nd semester Math packet # 2 Standards: 8.0 and 16.0
 Name FRIDAY, FEBRUARY 24 Due on: Per: TH Geometry 2 nd semester Math packet # 2 Standards: 8.0 and 16.0 8.0 Students know, derive, and solve problems involving the perimeter, circumference, area, volume
Name FRIDAY, FEBRUARY 24 Due on: Per: TH Geometry 2 nd semester Math packet # 2 Standards: 8.0 and 16.0 8.0 Students know, derive, and solve problems involving the perimeter, circumference, area, volume
Midsegment of a Trapezoid
 Technology ctivity 6.5 idsegment of a Trapezoid Question What are some properties of the midsegment of a trapezoid? Explore 1 raw. raw a point not on and construct a line parallel to through point. onstruct
Technology ctivity 6.5 idsegment of a Trapezoid Question What are some properties of the midsegment of a trapezoid? Explore 1 raw. raw a point not on and construct a line parallel to through point. onstruct
Geometry 1 FINAL REVIEW 2011
 Geometry 1 FINL RVIW 2011 1) lways, Sometimes, or Never. If you answer sometimes, give an eample for when it is true and an eample for when it is not true. a) rhombus is a square. b) square is a parallelogram.
Geometry 1 FINL RVIW 2011 1) lways, Sometimes, or Never. If you answer sometimes, give an eample for when it is true and an eample for when it is not true. a) rhombus is a square. b) square is a parallelogram.
3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm.
 1 In the diagram below, ABC XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements identify
1 In the diagram below, ABC XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements identify
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Big Ideas Math: A Common Core Curriculum Geometry 2015 Correlated to Common Core State Standards for High School Geometry
 Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
5.3. Area of Polygons and Circles Play Area. My Notes ACTIVITY
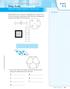 Area of Polygons and Circles SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share ACTIVITY 5.3 Pictured below is an aerial view of a playground. An aerial view is the view from above something. Decide what
Area of Polygons and Circles SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share ACTIVITY 5.3 Pictured below is an aerial view of a playground. An aerial view is the view from above something. Decide what
Objective: Draw kites and squares to clarify their attributes, and define kites and squares based on those attributes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 19 5 5 Lesson 19 Objective: Draw kites and squares to clarify their attributes, and define kites and Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 19 5 5 Lesson 19 Objective: Draw kites and squares to clarify their attributes, and define kites and Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application
Geometric Constructions
 Geometric onstructions (1) opying a segment (a) Using your compass, place the pointer at Point and extend it until reaches Point. Your compass now has the measure of. (b) Place your pointer at, and then
Geometric onstructions (1) opying a segment (a) Using your compass, place the pointer at Point and extend it until reaches Point. Your compass now has the measure of. (b) Place your pointer at, and then
PENNSYLVANIA. List properties, classify, draw, and identify geometric figures in two dimensions.
 Know: Understand: Do: CC.2.3.4.A.1 -- Draw lines and angles and identify these in two-dimensional figures. CC.2.3.4.A.2 -- Classify twodimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. CC.2.3.4.A.3
Know: Understand: Do: CC.2.3.4.A.1 -- Draw lines and angles and identify these in two-dimensional figures. CC.2.3.4.A.2 -- Classify twodimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. CC.2.3.4.A.3
3 Kevin s work for deriving the equation of a circle is shown below.
 June 2016 1. A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation?
June 2016 1. A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation?
Parallel Postulate. Perpendicular Postulate PARALLEL AND SKEW LINES WITH PARALLEL PLANES. Lines m and n are. Lines m and k are. Planes T and U are.
 Unit 6: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Lesson 6.1: Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Lesson 3.1 from textbook Objectives Identify relationships between lines such as parallel and skew. Understand and
Unit 6: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Lesson 6.1: Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Lesson 3.1 from textbook Objectives Identify relationships between lines such as parallel and skew. Understand and
6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms
 Warm Up Justify each statement. 1. 2. Reflex Prop. of Conv. of Alt. Int. s Thm. Evaluate each expression for x = 12 and y = 8.5. 3. 2x + 7 4. 16x 9 31 183 5. (8y + 5) 73 Objective Prove that a given quadrilateral
Warm Up Justify each statement. 1. 2. Reflex Prop. of Conv. of Alt. Int. s Thm. Evaluate each expression for x = 12 and y = 8.5. 3. 2x + 7 4. 16x 9 31 183 5. (8y + 5) 73 Objective Prove that a given quadrilateral
Copying a Line Segment
 Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Do Now: Do Now Slip. Do Now. Lesson 20. Drawing Conclusions. Quiz Tomorrow, Study Blue Sheet. Module 1 Lesson 20 Extra Practice.
 Lesson 20 Drawing Conclusions HW Quiz Tomorrow, Study Blue Sheet Do Now: Do Now Slip Oct 20 1:03 PM Do Now 1. CB is parallel to DE 2.
Lesson 20 Drawing Conclusions HW Quiz Tomorrow, Study Blue Sheet Do Now: Do Now Slip Oct 20 1:03 PM Do Now 1. CB is parallel to DE 2.
11.2 Areas of Trapezoids,
 11. Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Goal p Find areas of other types of quadrilaterals. Your Notes VOCABULARY Height of a trapezoid THEOREM 11.4: AREA OF A TRAPEZOID b 1 The area of a trapezoid
11. Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Goal p Find areas of other types of quadrilaterals. Your Notes VOCABULARY Height of a trapezoid THEOREM 11.4: AREA OF A TRAPEZOID b 1 The area of a trapezoid
Geometry 2001 part 1
 Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
The Formal Proof of a Theorem
 .7 The Formal Proof of a Theorem 5.7 The Formal Proof of a Theorem KY ONPTS Formal Proof of a Theorem onverse of a Theorem Picture Proof (Informal) of a Theorem Recall from Section. that statements that
.7 The Formal Proof of a Theorem 5.7 The Formal Proof of a Theorem KY ONPTS Formal Proof of a Theorem onverse of a Theorem Picture Proof (Informal) of a Theorem Recall from Section. that statements that
6. Which angles in the diagram are congruent to 1? Choose all that apply. 2. m YKZ
 PRYZ is a rhombus. If RK = 5, RY = 13 and m YRZ = 67, find each measure. Quadrilateral GHJK is a rectangle and m 1 = 37. 1. KY 6. Which angles in the diagram are congruent to 1? Choose all that apply.
PRYZ is a rhombus. If RK = 5, RY = 13 and m YRZ = 67, find each measure. Quadrilateral GHJK is a rectangle and m 1 = 37. 1. KY 6. Which angles in the diagram are congruent to 1? Choose all that apply.
FINAL REVIEW. 1) Always, Sometimes, or Never. If you answer sometimes, give an example for when it is true and an example for when it is not true.
 FINL RVIW 1) lways, Sometimes, or Never. If you answer sometimes, give an eample for when it is true and an eample for when it is not true. a) rhombus is a square. b) square is a parallelogram. c) oth
FINL RVIW 1) lways, Sometimes, or Never. If you answer sometimes, give an eample for when it is true and an eample for when it is not true. a) rhombus is a square. b) square is a parallelogram. c) oth
JMG. Review Module 1 Lessons 1-20 for Mid-Module. Prepare for Endof-Unit Assessment. Assessment. Module 1. End-of-Unit Assessment.
 Lesson Plans Lesson Plan WEEK 161 December 5- December 9 Subject to change 2016-2017 Mrs. Whitman 1 st 2 nd Period 3 rd Period 4 th Period 5 th Period 6 th Period H S Mathematics Period Prep Geometry Math
Lesson Plans Lesson Plan WEEK 161 December 5- December 9 Subject to change 2016-2017 Mrs. Whitman 1 st 2 nd Period 3 rd Period 4 th Period 5 th Period 6 th Period H S Mathematics Period Prep Geometry Math
To Explore the Properties of Parallelogram
 Exemplar To Explore the Properties of Parallelogram Objective To explore the properties of parallelogram Dimension Measures, Shape and Space Learning Unit Quadrilaterals Key Stage 3 Materials Required
Exemplar To Explore the Properties of Parallelogram Objective To explore the properties of parallelogram Dimension Measures, Shape and Space Learning Unit Quadrilaterals Key Stage 3 Materials Required
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PATTY PAPER GEOMETRY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : PATTY PAPER GEOMETRY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 patty paper geometry patty paper geometry pdf patty paper geometry Patty Paper Geometry is designed as two books. A PPG Teacher
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PATTY PAPER GEOMETRY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 patty paper geometry patty paper geometry pdf patty paper geometry Patty Paper Geometry is designed as two books. A PPG Teacher
Geometry Benchmark Assessment #1
 Geometry Benchmark Assessment #1 Multiple Choice Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When the net is folded into the rectangular prism shown beside
Geometry Benchmark Assessment #1 Multiple Choice Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When the net is folded into the rectangular prism shown beside
Georgia Department of Education Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Framework Student Edition Analytic Geometry Unit 1
 Analytic Geometry Unit 1 Lunch Lines Mathematical goals Prove vertical angles are congruent. Understand when a transversal is drawn through parallel lines, special angles relationships occur. Prove when
Analytic Geometry Unit 1 Lunch Lines Mathematical goals Prove vertical angles are congruent. Understand when a transversal is drawn through parallel lines, special angles relationships occur. Prove when
7.1 Properties of Parallelograms
 PropertiesofParallelograms20052006.nb 1 7.1 Properties of Parallelograms A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel. Notice that the definition states that both pairs
PropertiesofParallelograms20052006.nb 1 7.1 Properties of Parallelograms A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel. Notice that the definition states that both pairs
0810ge. Geometry Regents Exam y # (x $ 3) 2 % 4 y # 2x $ 5 1) (0,%4) 2) (%4,0) 3) (%4,%3) and (0,5) 4) (%3,%4) and (5,0)
 0810ge 1 In the diagram below, ABC! XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements
0810ge 1 In the diagram below, ABC! XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements
6.3 proving parallelograms day ink.notebook. January 17, Page 20 Page Prove Parallelogram Using Coordinate Geometry.
 6.3 proving parallelograms da 2 2016 ink.notebook Januar 17, 2017 Page 20 Page 21 6.3 Prove Using oordinate Geometr Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes 6.3 Proving s Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson
6.3 proving parallelograms da 2 2016 ink.notebook Januar 17, 2017 Page 20 Page 21 6.3 Prove Using oordinate Geometr Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes 6.3 Proving s Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson
Properties of Special Parallelograms
 Properties of Special Parallelograms Lab Summary: This lab consists of four activities that lead students through the construction of a trapezoid. Students then explore the shapes, making conclusions about
Properties of Special Parallelograms Lab Summary: This lab consists of four activities that lead students through the construction of a trapezoid. Students then explore the shapes, making conclusions about
Objective: Draw trapezoids to clarify their attributes, and define trapezoids based on those attributes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 16 5 5 Lesson 16 Objective: Draw trapezoids to clarify their attributes, and define trapezoids based Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 16 5 5 Lesson 16 Objective: Draw trapezoids to clarify their attributes, and define trapezoids based Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application
Angles with Parallel Lines Topic Index Geometry Index Regents Exam Prep Center
 Angles with Parallel Lines Topic Index Geometry Index Regents Exam Prep Center A transversal is a line that intersects two or more lines (in the same plane). When lines intersect, angles are formed in
Angles with Parallel Lines Topic Index Geometry Index Regents Exam Prep Center A transversal is a line that intersects two or more lines (in the same plane). When lines intersect, angles are formed in
