Deconstructing Prisms
|
|
|
- Arnold Lester
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using Patterns, Write Expressions That Determine the Number of Unit Cubes With Any Given Number of Exposed Faces Based on the work of Linda S. West, Center for Integrative Natural Science and Mathematics Kentucky Center for Mathematics
2 Math Concepts & Standards CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.OA.A.2 Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.6.EE.A.2.A Write expressions that record operations with numbers and with letters standing for numbers. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.6.EE.B.6 Use variables to represent numbers and write expressions when solving a real world or mathematical problem; understand that a variable can represent an unknown number, or, depending on the purpose at hand, any number in a specified set. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.B.6 Solve real world and mathematical problems involving area, volume and surface area of two and three dimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, cubes, and right prisms. Materials Rubik s Cubes sets of 27 cubes (one set for each student or group) Cubes can be borrowed from /lending library/ Handouts for each student In this activity students will: Use the vocabulary of prisms in recognizing patterns Extend patterns Describe the pattern that leads from one size to another Find an explicit rule for each pattern to predict the total number of cubes and/or exposed faces for any size cube (puzzle); recognize equivalent expressions Determine the size of the Rubik s Cube (Puzzle) given the total number of unit cubes or the number of unit cubes with a given number of exposed faces Evaluate expressions Vocabulary prism, regular rectangular prism bases faces, lateral faces unit cube edge corner (vertex, vertices) exposed
3 Rubik's Cube Vocabulary The mathematical term for the Rubik s Cube shown is prism. A prism has two bases and rectangular faces. The top and bottom of a prism are called the bases. What shape are the bases of this prism? The sides of a prism are called lateral faces, or sometimes just faces. The faces of a prisms are always parallelograms. In right prisms, the faces are rectangles. Why? How many lateral faces are there? What determines the number of lateral faces in a prism? If the bases of a prism are regular polygons, the prism is called regular. The Rubik's Cube is a regular rectangular prism. Explain why. The size of a Rubik's Cube is determined by the number of smaller cubes or unit cubes on the edge of the larger cube. An edge is a line segment where exactly 2 faces meet. How many edges are there in the cube above? What is the length of the edge of the cube above? A corner or vertex is the point where exactly 3 faces meet. How many corners or vertices are there in the cube above? Are there any unit cubes in the interior of this cube that can t be seen?
4 Teacher Notes: This page could be classwork after some general instruction to prisms. It reinforces the prism vocabulary using a 2x2x2 Rubik s Cube. It could also be used as the instruction for prism vocabulary. Rubik's Cube Vocabulary The mathematical term for the Rubik s Cube shown is prism. A prism has two bases and rectangular faces. The top and bottom of a prism are called the bases. What shape are the bases of this prism? Square The sides of a prism are called lateral faces, or sometimes just faces. The faces of a prisms are always parallelograms. In right prisms, the faces are rectangles. Why? It is assumed here that students are working with right prisms. Perhaps the student s working definition of a prism at this point is that the bases are parallel and segments connecting the vertices are perpendicular to the bases. Therefore, the lateral faces would have 4 right angles making them rectangles. It is important that students know the term lateral faces because there are times when the term faces will include the bases. This can be confusing even when using context clues. Using the term lateral faces helps to clarify. How many lateral faces are there? 4 If this is being used for instruction, the teacher may also ask. How many lateral faces there would be if the bases were triangular or some other polygon?. What determines the number of lateral faces in a prism? Students should generalize that the number of lateral faces is equal to the number of sides on the base. If the bases of a prism are regular polygons, the prism is called regular. The Rubik's Cube is a regular rectangular prism. Explain why. The base of a Rubik s Cube is a square. A square is a regular polygon because all the sides and angles are congruent. A square is a rectangle. A regular rectangular prism is also called a square prism. If all the faces, including the bases, are squares, the prism is a cube. The size of a Rubik's Cube is determined by the number of smaller cubes or unit cubes on the edge of the larger cube. An edge is a line segment where exactly 2 faces meet. How many edges are there in the cube above? 12 Students may generalize that the number of lateral faces is equal to the number of sides of the base times 3. What is the length of the edge of the cube above? 2 units The teacher may want to reinforce the difference between linear units (units of perimeter), square units (units of area), and cubic units (units of volume). An extension could be made to exponents and the vocabulary of squaring and cubing a number. A corner or vertex is the point where exactly 3 faces meet. How many corners or vertices are there in the cube above? 8 Students may generalize that the number of vertices is equal to the number of sides of the base times 2.
5 Are there any unit cubes in the interior of this cube that can t be seen? No. Students could use smaller unit cubes to prove this. This sets up the work that follows which focuses on the number of exposed faces of the unit cubes which make up the larger cube.
6 Look for patterns in the number of faces that are exposed on the unit cubes. You will be counting the colored sides of each of the unit cubes. To help you write the rule, you may want to look at what you learned on the previous page. Large Cube Edge length of the large cube Number of cubic units 3 faces exposed on unit cubes 2 faces exposed on unit cubes 1 face exposed on unit cubes 0 faces exposed on unit cubes Rules: Is there a way to predict the number of cubes and faces based on the size of the edge of a cube? e Hint: How many squares on 1 edge? (corners) (edges) (center) Hint: How many cubes can t be seen?
7 Teacher Notes: Students may work individually or in pairs to complete the chart. Remind students that they are focusing on the faces of the unit cubes. This will be important as they may confuse edge of the prism with edge pieces which have 2 exposed faces. The teacher may want to have unit cubes available so that students can build the first two or three cubes to see how faces of the unit cubes become hidden in the larger cube. Have students look for generalizations after completing each larger cube so they are working towards the rule throughout the task. Look for patterns in the number of faces that are exposed on the unit cubes. You will be counting the colored sides of each of the unit cubes. To help you write the rule, you may want to look at what you learned on the previous page. Large Cube Edge length of the large cube Number of cubic units 3 faces expose d on unit cubes 2 faces exposed on unit cubes 1 face exposed on unit cubes 0 faces exposed on unit cubes (2 2) 12(0) 0 6(2 2) 2 6(0) 2 6(0) 0 (2 2) 3 (0) (3 2) 12(1) 6 6(3 2) 2 6(1) 2 6(1) 1 (3 2) 3 (1) (4 2) 12(2) 24 6(4 2) 2 6(2) 2 6(4) 8 (4 2) 3 (2) (5 2) 12(3) 54 6(5 2) 2 6(3)2 6(9) 27 (5 2) 3 (3) (6 2) 12(4) 96 6(6 2) 2 6(4) 2 6(16) 64 (6 2) 3 (4) 3 Rules: Is there a way to predict the number of cubes and faces based on the size of the edge of a cube? e Hint: How many squares on 1 edge? e e e e 3 (corners) (edge pieces) 12(e 2) or 2 4(e 2)+4(e 2) or 3 4(e 2) (center pieces) 6(e 2) 2 or (2+4)(e 2) 2 Hint: How many cubes can t be seen? (e 2) 3
8 Teacher Notes: Have students share their rules. Have them explain how they formulated the rules so that they recognize equivalent expressions such as those for edge pieces. Challenge: On the vocabulary page, students may have generalized about the number of corners and edges in a prism. Have students articulate why the 2, 12, and 6 remain constant in the corner, edge and center rules. Let n = number of edges on the base (corners = 2n; edge pieces = 3n or 2n,top & bottom, + n, #edges to connect the bases; center pieces = 2, top & bottom, + n, the number of lateral faces). Have students explain or show how (e 2) 3 is the rule for the number of hidden cubes. Basically, the corner and edge piece faces are removed from each side and they are finding the volume of the remaining cube. The following pages could be used as stations. Students working in small groups could circulate through the stations. Have unit cubes available at each station so students can construct the cubes as needed. Or Each group of students could get a different sheet. Have unit cubes available to each group so students can construct the cubes as needed. After completing their tasks, students share out how they approached the task and how the table worksheet helped them. Or The tasks could be assigned by ability to generalize concepts. Have unit cubes available to all students. Follow up question: What answers are the same no matter which task was completed? Why? All cubes have 8 corners or 8 cubes with 3 exposed faces. All rules were the same, except for the last page which uses a rectangular prism that is not a cube.
9 What if you had a 12 x 12 x 12 Rubik s Cube? Use the patterns in the table to help you answer the questions below. Show or explain how you got your answer to each of the questions. 1) How many smaller unit cubes would make a 12 x 12 x 12 Rubik s Cube? 2) How many unit cubes would have three colored faces showing? 3) How many unit cubes would have only two colored faces exposed? 4) How many unit cubes would have only one face exposed? 5) How many unit cubes would have absolutely no exposed faces? 6) If you would try to build a 12 x 12 x 12 Rubik s Cube, using 3 x 3 x 3 Rubik s Cubes instead of unit cubes, how many would you need?
10 Teacher Notes: The Rubik s Cube shown is not the size under consideration. What if you had a 12 x 12 x 12 Rubik s Cube? Use the patterns in the table to help you answer the questions below. Show or explain how you got your answer to each of the questions. 1) How many smaller unit cubes would make a 12 x 12 x 12 Rubik s Cube? = 1,728 cubic units 2) How many unit cubes would have three colored faces showing? cubes which are the corners 3) How many unit cubes would have only two colored faces exposed? 12 ( e 2) 12 (12 2) 12(10) 120 cubes which are on the edges 4) How many unit cubes would have only one face exposed? 6(e 2) 2 6(12 2) 2 6(10) cubes are in the center of each face, including the bases 5) How many unit cubes would have absolutely no exposed faces? (e 2) 3 (12 2) cubes will be in the interior of the large cube 6) If you would try to build a 12 x 12 x 12 Rubik s Cube, using 3 x 3 x 3 Rubik s Cubes instead of unit cubes, how many would you need? Each 3 x 3 x 3 cube has a volume of or 27 cubic units = 64 cubes
11 In a particular Rubik s Cube, 1000 unit cubes are hidden unit cubes. Use the patterns in the table to help you answer the questions below. Show or explain how you got your answer to each of the questions. 1) What are the dimensions of this Rubik s Cube? 2) How many unit cubes have only one colored face showing? 3) How many unit cubes have only two colored faces exposed? 4) How many unit cubes have three colored faces exposed?
12 Teacher Notes: The Rubik s Cube shown is not the size under consideration. In a particular Rubik s Cube, 1000 unit cubes are hidden unit cubes. Use the patterns in the table to help you answer the questions below. Show or explain how you got your answer to each of the questions. 1) What are the dimensions of this Rubik s Cube? (e 2) 3 = 1000 (e 2) 3 = factors that equal e 2 = 10 Each factor must equal 10. e = 12 Each factor is 2 less than the number of unit cubes on one edge. Older students may have more formal equation solving notation. 2) How many unit cubes have only one colored face showing? 6(e 2) 2 6(12 2) 2 6(10) cubes are in the center of each face, including the bases 3) How many unit cubes have only two colored faces exposed? 12 ( e 2) 12 (12 2) 12(10) 120 cubes which are on the edges 4) How many unit cubes have three colored faces exposed? cubes which are the corners
13 There is a Rubik s Cube of unknown size. It has 864 unit cubes with only one face showing. Show or explain how you got your answers to the following questions. 1) What are the dimensions of this Rubik s Cube? 2) How many unit cubes have no faces showing? 3) How many unit cubes have only two colored faces showing? 4) How many unit cubes have three colored faces exposed?
14 Teacher Notes: The Rubik s Cube shown is not the size under consideration. There is a Rubik s Cube of unknown size. It has 864 unit cubes with only one face showing. Show or explain how you got your answers to the following questions. 1) What are the dimensions of this Rubik s Cube? 6(e 2) 2 = 864 6(e 2) 2 = 6 (144) What times 6 = 864? 6(e 2) 2 = 6 (12 12) What number times itself is 144? e 2 = 12 Each factor is 2 less than the edge length. e = 14 units on each edge Older students may have more formal equation solving notation. 2) How many unit cubes have no faces showing? (e 2) 3 (14 2) 3 (12) cubic units are hidden 3) How many unit cubes have only two colored faces showing? 12 ( e 2) 12 (14 2) 12(12) 144 cubes are on the edges 4) How many unit cubes have three colored faces exposed? cubes which are the corners
15 There is another Rubik s Cube of unknown size. It has 132 unit cubes with only two faces exposed. Show or explain how you got your answers to the following questions. 1) What are the dimensions of this Rubik s Cube? 2) How many unit cubes have no exposed faces? 3) How many unit cubes have only one face exposed? 4) How many unit cubes have three faces exposed?
16 Teacher Notes: The Rubik s Cube shown is not the size under consideration. There is another Rubik s Cube of unknown size. It has 132 unit cubes with only two faces exposed. Show or explain how you got your answers to the following questions. 1) What are the dimensions of this Rubik s Cube? 12 ( e 2) = (e 2) = 12 (11) What number times 12 = 132? e 2 = 11 The factor is 2 less than the edge length. e = 13 units on each edge 2) How many unit cubes have no exposed faces? (e 2) 3 (13 2) cubic units are in the interior of the larger cube 3) How many unit cubes have only one face exposed? 6(e 2) 2 6(13 2) 2 6(11) 2 6(121) 726 unit cubes are on the edges 4) How many unit cubes have three faces exposed? cubes which are the corners
17 You have a Rubik s Cube with edges of length e. Show or explain how you got your answers to the following questions. 1) If the Rubik s Cube consists of 125 unit cubes, what is the value of e? 2) If the Rubik s Cube has 343 unit cubes that have no faces exposed, what is the value of e? 3) If the Rubik s Cube has 120 unit cubes that have only two faces showing, what is the value of e? 4) If the Rubik s Cube has 486 unit cubes that have only one exposed face, what is the value of e? 5) If the Rubik s Cube has 8 unit cubes with 3 exposed faces, what is the value of e?
18 Teacher Notes: The Rubik s Cube shown is not the size under consideration. You have a Rubik s Cube with edges of length e. Show or explain how you got your answers to the following questions. 1) If the Rubik s Cube consists of 125 unit cubes, what is the value of e? 125 = e = e = 5 cubes on each edge 2) If the Rubik s Cube has 343 unit cubes that have no faces exposed, what is the value of e? (e 2) 3 = 343 (e 2) 3 = What number used as a factor 3 times has a product of 343? e 2 = 7 Each factor is 2 less than the edge length. e = 9 units on each edge 3) If the Rubik s Cube has 120 unit cubes that have only two faces showing, what is the value of e? 12 (e 2) = (e 2) = 12 (10) What number times 12 = 120? e 2 = 10 Each factor is 2 less than the edge length. e = 12 units on each edge 4) If the Rubik s Cube has 486 unit cubes that have only one exposed face, what is the value of e? 6(e 2) 2 = 486 6(e 2) 2 = 6 81 What number times 6 = 486? 6(e 2) 2 = What number times itself = 81? e 2 = 9 Each factor is 2 less than the edge length. e = 11 units on each edge 5) If the Rubik s Cube has 8 unit cubes with 3 exposed faces, what is the value of e? All Rubik s Cubes have 8 corners with 3 exposed faces because the base of the cubes is a square. There is no way to determine a single value for e.
19 6) How many of the unit cubes have exactly two faces exposed? Deconstructing Prisms This puzzle pictured is not your typical Rubik s Cube because it is not a cube. 1) Why is this puzzle not a cube? 2) What is a geometric term we could use for this puzzle? 3) What are its dimensions? 4) How many unit cubes does the puzzle contain? Show or explain how you got your answer. 5) How many of the unit cubes have three faces showing?
20 Deconstructing Prisms 7) How many of the unit cubes have only one exposed face? 8) How many of the unit cubes have no exposed faces? Challenge: Write the rules for rectangular prisms of any size using variables. How many variables will you need? Define each of the variables.
21 Teacher Notes: This puzzle pictured is not your typical Rubik s Cube because it is not a cube. 1) Why is this puzzle not a cube? All of the faces are not squares. The bases are squares, but the lateral faces are rectangles. All the faces of a cube are squares. 2) What is a geometric term we could use for this puzzle? Rectangular prism, regular rectangular prism (The bases are squares, regular polygons.) 3) What are its dimensions? 4 x 4 x 5 4) How many unit cubes does the puzzle contain? Show or explain how you got your answer. 4 x 4 x 5 = 80 cubic units 5) How many of the unit cubes have only three faces showing? Show or explain how you got your answer. 8 All rectangular prisms have 8 corners with 3 exposed faces because the bases are rectangles. 6) How many of the unit cubes have exactly two faces exposed? Show or explain how you got your answer. 28. Each base has e 2 or 2 edge pieces on each side. That makes 8 edge pieces per base for a total of 16 edge pieces. The edges connecting the bases have a length of 5. There are e 2 or 3 edge pieces on each of these edges for a total of 12 edges pieces = 28 edge pieces with only two exposed faces in the prism. 7) How many of the unit cubes have only one exposed face? The cubes with one exposed face are in the center of each face of the prism. For the bases, that would be 2(e 2) 2. 2(4 2) 2 = 2(2) 2 or 8 cubes on the bases. Each lateral face would have (x 2)(y 2) cubes with 1 exposed face. So, for the 4 lateral faces there would be 4(4 2)(5 2) = or 24 cubes with 1 exposed face = 32 unit cubes with one exposed face. 8) How many of the unit cubes have no exposed faces? The hidden prism inside has dimensions of 3 x 2 x 2. Therefore, there are 12 unit cubes with no exposed faces.
22 Teacher Notes: Challenge: Write the rules for rectangular prisms of any size using variables. How many variables will you need? Define each of the variables. Since prisms are 3 dimensional, there might be three variables. Some traditional choices are l, w, h or x, y, z. For this example, e represents the length of the base edge and h represents the height of the prism. Volume: e e h 3 exposed faces: 2 e 2 exposed faces: 2 4(e 2) + 4(h 2) 1 exposed face: 2 (e 2) 2 + 4(h 2)(e 2) 0 exposed faces: (h 2)(e 2) Some students might be challenged to write the rules for any rectangular prism using 3 variables.
Lesson 1 Pre-Visit Ballpark Figures Part 1
 Lesson 1 Pre-Visit Ballpark Figures Part 1 Objective: Students will be able to: Estimate, measure, and calculate length, perimeter, and area of various rectangles. Time Requirement: 1 class period, longer
Lesson 1 Pre-Visit Ballpark Figures Part 1 Objective: Students will be able to: Estimate, measure, and calculate length, perimeter, and area of various rectangles. Time Requirement: 1 class period, longer
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Cross Sections of Three-Dimensional Figures
 Domain 4 Lesson 22 Cross Sections of Three-Dimensional Figures Common Core Standard: 7.G.3 Getting the Idea A three-dimensional figure (also called a solid figure) has length, width, and height. It is
Domain 4 Lesson 22 Cross Sections of Three-Dimensional Figures Common Core Standard: 7.G.3 Getting the Idea A three-dimensional figure (also called a solid figure) has length, width, and height. It is
Period: Date Lesson 2: Common 3-Dimensional Shapes and Their Cross- Sections
 : Common 3-Dimensional Shapes and Their Cross- Sections Learning Target: I can understand the definitions of a general prism and a cylinder and the distinction between a cross-section and a slice. Warm
: Common 3-Dimensional Shapes and Their Cross- Sections Learning Target: I can understand the definitions of a general prism and a cylinder and the distinction between a cross-section and a slice. Warm
Making a 2x2 Rubik s Cube
 Making a 2x2 Rubik s Cube Common Core: Objectives: Solve real- world and mathematical problems involving area, volume and surface area of two- and three- dimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals,
Making a 2x2 Rubik s Cube Common Core: Objectives: Solve real- world and mathematical problems involving area, volume and surface area of two- and three- dimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals,
Engineering & Construction: Build a Rubik s Cube (2x2)
 Engineering & Construction: Build a Rubik s Cube (2x2) Middle School In this lesson, students will build a functional 2x2 Rubik s Cube out of paper. Common Core Standards: CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.MD.C.3 Recognize
Engineering & Construction: Build a Rubik s Cube (2x2) Middle School In this lesson, students will build a functional 2x2 Rubik s Cube out of paper. Common Core Standards: CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.MD.C.3 Recognize
GRADE 3 TEKS ALIGNMENT CHART
 GRADE 3 TEKS ALIGNMENT CHART TEKS 3.2.A compose and decompose numbers up to,000 as the sum of so many ten thousands, so many thousands, so many hundreds, so many tens, and so many ones using objects, pictorial
GRADE 3 TEKS ALIGNMENT CHART TEKS 3.2.A compose and decompose numbers up to,000 as the sum of so many ten thousands, so many thousands, so many hundreds, so many tens, and so many ones using objects, pictorial
4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and
 4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids using appropriate tools (e.g., ruler, straightedge
4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids using appropriate tools (e.g., ruler, straightedge
Student Teacher School. Mathematics Assesslet. Geometry
 Student Teacher School 6GRADE Mathematics Assesslet Geometry All items contained in this assesslet are the property of the. Items may be used for formative purposes by the customer within their school
Student Teacher School 6GRADE Mathematics Assesslet Geometry All items contained in this assesslet are the property of the. Items may be used for formative purposes by the customer within their school
Middle School Making a 2x2 Rubik s Cube
 Middle School Making a 2x2 Rubik s Cube Texas Essential Knowledge & Skills (TEKS) Math 7.9A Expressions, equations, and relationships Objectives: 1) Students will learn how a 3x3 Rubik s Cube can be modified
Middle School Making a 2x2 Rubik s Cube Texas Essential Knowledge & Skills (TEKS) Math 7.9A Expressions, equations, and relationships Objectives: 1) Students will learn how a 3x3 Rubik s Cube can be modified
5.3. Area of Polygons and Circles Play Area. My Notes ACTIVITY
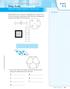 Area of Polygons and Circles SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share ACTIVITY 5.3 Pictured below is an aerial view of a playground. An aerial view is the view from above something. Decide what
Area of Polygons and Circles SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share ACTIVITY 5.3 Pictured below is an aerial view of a playground. An aerial view is the view from above something. Decide what
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets
 Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Middle School Geometry. Session 2
 Middle School Geometry Session 2 Topic Activity Name Page Number Related SOL Spatial Square It 52 6.10, 6.13, Relationships 7.7, 8.11 Tangrams Soma Cubes Activity Sheets Square It Pick Up the Toothpicks
Middle School Geometry Session 2 Topic Activity Name Page Number Related SOL Spatial Square It 52 6.10, 6.13, Relationships 7.7, 8.11 Tangrams Soma Cubes Activity Sheets Square It Pick Up the Toothpicks
18 Two-Dimensional Shapes
 18 Two-Dimensional Shapes CHAPTER Worksheet 1 Identify the shape. Classifying Polygons 1. I have 3 sides and 3 corners. 2. I have 6 sides and 6 corners. Each figure is made from two shapes. Name the shapes.
18 Two-Dimensional Shapes CHAPTER Worksheet 1 Identify the shape. Classifying Polygons 1. I have 3 sides and 3 corners. 2. I have 6 sides and 6 corners. Each figure is made from two shapes. Name the shapes.
QaD Teacher Support Materials
 QaD Teacher Support Materials Focus: Develop skills at interpreting geometric diagrams and using them to solve problems. Instructions Remember to download the Weekly Class Report and use it to help plan
QaD Teacher Support Materials Focus: Develop skills at interpreting geometric diagrams and using them to solve problems. Instructions Remember to download the Weekly Class Report and use it to help plan
Mary Rosenberg. Author
 Editor Lorin E. Klistoff, M.A. Managing Editor Karen Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Cover Artist Barb Lorseyedi Art Manager Kevin Barnes Art Director CJae Froshay Imaging James Edward Grace Rosa C. See Publisher
Editor Lorin E. Klistoff, M.A. Managing Editor Karen Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Cover Artist Barb Lorseyedi Art Manager Kevin Barnes Art Director CJae Froshay Imaging James Edward Grace Rosa C. See Publisher
AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School
 AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved AGS Math Algebra 2 Grade
AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved AGS Math Algebra 2 Grade
Robert Smith. Author. Editor Gisela Lee, M.A. Managing Editor Karen Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed.
 Editor Gisela Lee, M.A. Managing Editor Karen Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Cover Artist Barb Lorseyedi Art Coordinator Kevin Barnes Art Director CJae Froshay Imaging Alfred
Editor Gisela Lee, M.A. Managing Editor Karen Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Cover Artist Barb Lorseyedi Art Coordinator Kevin Barnes Art Director CJae Froshay Imaging Alfred
Revised Elko County School District 2 nd Grade Math Learning Targets
 Elko County School District 2 nd Grade Math Learning Targets Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Elko County School District 2 nd Grade Math Learning Targets Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define rectangles and rhombuses based on those attributes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 18 5 5 Lesson 18 Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 18 5 5 Lesson 18 Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
Grade 7 Mathematics Item Specifications Florida Standards Assessments
 Assessment Limit MAFS7.G.1 Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including
Assessment Limit MAFS7.G.1 Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including
Geometry. a) Rhombus b) Square c) Trapezium d) Rectangle
 Geometry A polygon is a many sided closed shape. Four sided polygons are called quadrilaterals. Sum of angles in a quadrilateral equals 360. Parallelogram is a quadrilateral where opposite sides are parallel.
Geometry A polygon is a many sided closed shape. Four sided polygons are called quadrilaterals. Sum of angles in a quadrilateral equals 360. Parallelogram is a quadrilateral where opposite sides are parallel.
Dream Home Academic Lesson Plan
 Academic Lesson Plan PREPARATION INFORMATION lesson summary This lesson reviews the geometric concepts of area and perimeter while reinforcing the Second Step concept of handling emotions by staying calm.
Academic Lesson Plan PREPARATION INFORMATION lesson summary This lesson reviews the geometric concepts of area and perimeter while reinforcing the Second Step concept of handling emotions by staying calm.
Can You Cut It? Slicing Three-Dimensional Figures
 Name: Period: Can You Cut It? Slicing Three-Dimensional Figures Lesson Activity 1. The Cube Using modeling clay or play-doh, each student creates a model of a cube. With your group, predict the type of
Name: Period: Can You Cut It? Slicing Three-Dimensional Figures Lesson Activity 1. The Cube Using modeling clay or play-doh, each student creates a model of a cube. With your group, predict the type of
Course: Math Grade: 7. Unit Plan: Geometry. Length of Unit:
 Course: Math Grade: 7 Unit Plan: Geometry Length of Unit: Enduring Understanding(s): Geometry is found in the visual world in two and three dimension. We use geometry daily in problem solving. Essential
Course: Math Grade: 7 Unit Plan: Geometry Length of Unit: Enduring Understanding(s): Geometry is found in the visual world in two and three dimension. We use geometry daily in problem solving. Essential
Please bring a laptop or tablet next week! Upcoming Assignment Measurement Investigations Patterns & Algebraic Thinking Investigations Break A Few
 Please bring a laptop or tablet next week! Upcoming Assignment Measurement Investigations Patterns & Algebraic Thinking Investigations Break A Few More Investigations Literature Circles Final Lesson Plan
Please bring a laptop or tablet next week! Upcoming Assignment Measurement Investigations Patterns & Algebraic Thinking Investigations Break A Few More Investigations Literature Circles Final Lesson Plan
use properties and relationships in geometry.
 The learner will understand and 3 use properties and relationships in geometry. 3.01 Using three-dimensional figures: a) Identify, describe, and draw from various views (top, side, front, corner). A. Going
The learner will understand and 3 use properties and relationships in geometry. 3.01 Using three-dimensional figures: a) Identify, describe, and draw from various views (top, side, front, corner). A. Going
Honors Geometry Summer Math Packet
 Honors Geometry Summer Math Packet Dear students, The problems in this packet will give you a chance to practice geometry-related skills from Grades 6 and 7. Do your best to complete each problem so that
Honors Geometry Summer Math Packet Dear students, The problems in this packet will give you a chance to practice geometry-related skills from Grades 6 and 7. Do your best to complete each problem so that
Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4. Common Core State Standards Math - Content Standards
 Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4 The task challenges a student to demonstrate understanding of concepts of 2-dimensional shapes and ir properties. A student must be able to use characteristics,
Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4 The task challenges a student to demonstrate understanding of concepts of 2-dimensional shapes and ir properties. A student must be able to use characteristics,
When entering fourth grade this is what is expected that your child should already know.
 Summer Math Reinforcement Packet Students Entering into 4th Grade THIRD GRADE GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS IN MATHMATICS When entering fourth grade this is what is expected that your child should already know.
Summer Math Reinforcement Packet Students Entering into 4th Grade THIRD GRADE GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS IN MATHMATICS When entering fourth grade this is what is expected that your child should already know.
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD. We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential
 Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
21st Century Learning Skills
 Contents: Lesson Focus & Standards Lesson Content Review.. Vocabulary.... Math Content Trivia.. ¼ Turn Practice... Memory Game... p. 1-2 p. 3-9 p. 10-11 p. 11 p. 12 p. 12 p. 13-15 p. 16-17 21st Century
Contents: Lesson Focus & Standards Lesson Content Review.. Vocabulary.... Math Content Trivia.. ¼ Turn Practice... Memory Game... p. 1-2 p. 3-9 p. 10-11 p. 11 p. 12 p. 12 p. 13-15 p. 16-17 21st Century
Math + 4 (Red) SEMESTER 1. { Pg. 1 } Unit 1: Whole Number Sense. Unit 2: Whole Number Operations. Unit 3: Applications of Operations
 Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
UNIT 2: RATIONAL NUMBER CONCEPTS WEEK 5: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 2: RATIONAL NUMBER CONCEPTS WEEK 5: Student Packet 5.1 Fractions: Parts and Wholes Identify the whole and its parts. Find and compare areas of different shapes. Identify congruent
Name Period Date UNIT 2: RATIONAL NUMBER CONCEPTS WEEK 5: Student Packet 5.1 Fractions: Parts and Wholes Identify the whole and its parts. Find and compare areas of different shapes. Identify congruent
Lesson 5: Area of Composite Shape Subject: Math Unit: Area Time needed: 60 minutes Grade: 6 th Date: 2 nd
 Lesson 5: Area of Composite Shape Subject: Math Unit: Area Time needed: 60 minutes Grade: 6 th Date: 2 nd Materials, Texts Needed, or advanced preparation: Lap tops or computer with Geogebra if possible
Lesson 5: Area of Composite Shape Subject: Math Unit: Area Time needed: 60 minutes Grade: 6 th Date: 2 nd Materials, Texts Needed, or advanced preparation: Lap tops or computer with Geogebra if possible
2016 Summer Break Packet for Students Entering Geometry Common Core
 2016 Summer Break Packet for Students Entering Geometry Common Core Name: Note to the Student: In middle school, you worked with a variety of geometric measures, such as: length, area, volume, angle, surface
2016 Summer Break Packet for Students Entering Geometry Common Core Name: Note to the Student: In middle school, you worked with a variety of geometric measures, such as: length, area, volume, angle, surface
Standard 4.G.1 4.G.2 5.G.3 5.G.4 4.MD.5
 Draw and identify lines and angles, as well as classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles (Standards 4.G.1 3). Standard 4.G.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute,
Draw and identify lines and angles, as well as classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles (Standards 4.G.1 3). Standard 4.G.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute,
MEA 501 LESSON _NOTES Period. CRS SKILL LEVEL DESCRIPTION Level 1 ALL students must MEA 301 Compute the perimeter of polygons when all
 MEA 501 LESSON _NOTES Period Name CRS SKILL LEVEL DESCRIPTION Level 1 ALL students must MEA 301 Compute the perimeter of polygons when all attain mastery at this level side lengths are given MEA 302 Compute
MEA 501 LESSON _NOTES Period Name CRS SKILL LEVEL DESCRIPTION Level 1 ALL students must MEA 301 Compute the perimeter of polygons when all attain mastery at this level side lengths are given MEA 302 Compute
Grades 6 8 Innoventure Components That Meet Common Core Mathematics Standards
 Grades 6 8 Innoventure Components That Meet Common Core Mathematics Standards Strand Ratios and Relationships The Number System Expressions and Equations Anchor Standard Understand ratio concepts and use
Grades 6 8 Innoventure Components That Meet Common Core Mathematics Standards Strand Ratios and Relationships The Number System Expressions and Equations Anchor Standard Understand ratio concepts and use
Enhanced Instructional Transition Guide
 Geometry: Coordinate Plane, Graphing Transformations, and Perspectives (9 days) Possible Lesson 01 (6 days) Possible Lesson 02 (3 days) POSSIBLE LESSON 02 (3 days) This lesson is one approach to teaching
Geometry: Coordinate Plane, Graphing Transformations, and Perspectives (9 days) Possible Lesson 01 (6 days) Possible Lesson 02 (3 days) POSSIBLE LESSON 02 (3 days) This lesson is one approach to teaching
NUMBERS & OPERATIONS. 1. Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers and number systems.
 7 th GRADE GLE S NUMBERS & OPERATIONS 1. Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers and number systems. A) Read, write and compare numbers (MA 5 1.10) DOK 1 * compare
7 th GRADE GLE S NUMBERS & OPERATIONS 1. Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers and number systems. A) Read, write and compare numbers (MA 5 1.10) DOK 1 * compare
Grade 6. Prentice Hall. Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units Alaska Standards and Grade Level Expectations. Grade 6
 Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units 2004 Grade 6 C O R R E L A T E D T O Expectations Grade 6 Content Standard A: Mathematical facts, concepts, principles, and theories Numeration: Understand
Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units 2004 Grade 6 C O R R E L A T E D T O Expectations Grade 6 Content Standard A: Mathematical facts, concepts, principles, and theories Numeration: Understand
All About That Base... and Height
 All About That Base... and Height Area of Triangles and Quadrilaterals 2 WARM UP Write 3 different expressions to describe the total area of this rectangle. LEARNING GOALS State and compare the attributes
All About That Base... and Height Area of Triangles and Quadrilaterals 2 WARM UP Write 3 different expressions to describe the total area of this rectangle. LEARNING GOALS State and compare the attributes
Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions.
 Student Outcomes Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions. Lesson Notes It is recommended that students have access to a calculator as they work
Student Outcomes Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions. Lesson Notes It is recommended that students have access to a calculator as they work
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII. Mathematics Laboratory
 LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook
 Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook Almost everything you need to know for 7 th grade math Plus a little about 6 th grade math And a little about 8 th grade math 1 Table of Contents by Outcome Outcome Topic Page
Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook Almost everything you need to know for 7 th grade math Plus a little about 6 th grade math And a little about 8 th grade math 1 Table of Contents by Outcome Outcome Topic Page
INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT
 INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT TABLE OF CONTENTS Format & Background Information...3-6 Learning Experience 1- Getting Started...6-7 Learning Experience 2 - Cube and Rectangular Prisms...8 Learning Experience
INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT TABLE OF CONTENTS Format & Background Information...3-6 Learning Experience 1- Getting Started...6-7 Learning Experience 2 - Cube and Rectangular Prisms...8 Learning Experience
Before How does the painting compare to the original figure? What do you expect will be true of the painted figure if it is painted to scale?
 Dilations LAUNCH (7 MIN) Before How does the painting compare to the original figure? What do you expect will be true of the painted figure if it is painted to scale? During What is the relationship between
Dilations LAUNCH (7 MIN) Before How does the painting compare to the original figure? What do you expect will be true of the painted figure if it is painted to scale? During What is the relationship between
7 th grade Math Standards Priority Standard (Bold) Supporting Standard (Regular)
 7 th grade Math Standards Priority Standard (Bold) Supporting Standard (Regular) Unit #1 7.NS.1 Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers;
7 th grade Math Standards Priority Standard (Bold) Supporting Standard (Regular) Unit #1 7.NS.1 Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers;
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures. Grade 9 Mathematics
 Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
Summer Solutions Problem Solving Level 4. Level 4. Problem Solving. Help Pages
 Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12. Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the. Externally set task 2017
 Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12 Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the Externally set task 2017 This document is an extract from the Mathematics Essentials General Course Year 12 syllabus,
Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12 Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the Externally set task 2017 This document is an extract from the Mathematics Essentials General Course Year 12 syllabus,
Standard Indicator The Logic Behind the Formula
 Standard Indicator 5.5.1 The Logic Behind the Formula Purpose Students will understand the formulas for the area of a triangle, parallelogram, and trapezoid by comparing them to the area of a related rectangle
Standard Indicator 5.5.1 The Logic Behind the Formula Purpose Students will understand the formulas for the area of a triangle, parallelogram, and trapezoid by comparing them to the area of a related rectangle
Grade 4 + DIGITAL. EL Strategies. DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3. Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print
 Standards PLUS Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print Grade 4 SAMPLER Mathematics EL Strategies DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3 15-20 Minute Lessons Assessments Consistent with CA Testing Technology
Standards PLUS Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print Grade 4 SAMPLER Mathematics EL Strategies DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3 15-20 Minute Lessons Assessments Consistent with CA Testing Technology
Simple Solutions Mathematics. Level 2. Help Pages & Who Knows?
 Simple Solutions Mathematics Level 2, 2nd semester Level 2 & Who Knows? 139 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Addition When you combine numbers, you add. The sign + means add. The answer to an addition
Simple Solutions Mathematics Level 2, 2nd semester Level 2 & Who Knows? 139 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Addition When you combine numbers, you add. The sign + means add. The answer to an addition
E G 2 3. MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland
 MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland Point A point is a location in space. It has no length or width. A point is represented by a dot and is named by writing a capital letter next to the dot.
MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland Point A point is a location in space. It has no length or width. A point is represented by a dot and is named by writing a capital letter next to the dot.
1 Version 2.0. Related Below-Grade and Above-Grade Standards for Purposes of Planning for Vertical Scaling:
 Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Geometry Target E [a]: Draw, construct,
Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Geometry Target E [a]: Draw, construct,
Lesson 1 Introductory Geometry: Measurement
 Lesson 1 Introductory Geometry: Measurement National Standards Instructional programs for Geometry grades 5 th and 6 th should enable all students to: understand relationships among the angles, side lengths,
Lesson 1 Introductory Geometry: Measurement National Standards Instructional programs for Geometry grades 5 th and 6 th should enable all students to: understand relationships among the angles, side lengths,
Big Ideas Math: A Common Core Curriculum Geometry 2015 Correlated to Common Core State Standards for High School Geometry
 Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 6th Grade Unit 8
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 8 Unit 8 Geometry and Measurement MATH 608 Geometry and Measurement INTRODUCTION 3 1. PLANE FIGURES 5 PERIMETER 5 AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS 11 AREA OF TRIANGLES 17 AREA OF
MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 8 Unit 8 Geometry and Measurement MATH 608 Geometry and Measurement INTRODUCTION 3 1. PLANE FIGURES 5 PERIMETER 5 AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS 11 AREA OF TRIANGLES 17 AREA OF
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Grade 04
 Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers
 LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
SESSION THREE AREA MEASUREMENT AND FORMULAS
 SESSION THREE AREA MEASUREMENT AND FORMULAS Outcomes Understand the concept of area of a figure Be able to find the area of a rectangle and understand the formula base times height Be able to find the
SESSION THREE AREA MEASUREMENT AND FORMULAS Outcomes Understand the concept of area of a figure Be able to find the area of a rectangle and understand the formula base times height Be able to find the
A. 100 B. 110 C. 115 D. 145 E. 210
 Practice Quiz Polygons Area Perimeter Volume 1. Two angles of a hexagon measure 140 each. The other four angles are equal in measure. What is the measure of each of the other four equal angles, in degrees?
Practice Quiz Polygons Area Perimeter Volume 1. Two angles of a hexagon measure 140 each. The other four angles are equal in measure. What is the measure of each of the other four equal angles, in degrees?
UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Using Origami to Engage, Promote Geometry Understanding, and Foster a Growth Mindset
 Using Origami to Engage, Promote Geometry Understanding, and Foster a Growth Mindset Session Day/Time: Friday, May 6, 2016, at 9:30 11:00 a.m. Location: YC Huber Evans Presenter: Shelly Grothaus, Nature
Using Origami to Engage, Promote Geometry Understanding, and Foster a Growth Mindset Session Day/Time: Friday, May 6, 2016, at 9:30 11:00 a.m. Location: YC Huber Evans Presenter: Shelly Grothaus, Nature
6-1. Angles of Polygons. Lesson 6-1. What You ll Learn. Active Vocabulary
 6-1 Angles of Polygons What You ll Learn Skim Lesson 6-1. Predict two things that you expect to learn based on the headings and figures in the lesson. 1. 2. Lesson 6-1 Active Vocabulary diagonal New Vocabulary
6-1 Angles of Polygons What You ll Learn Skim Lesson 6-1. Predict two things that you expect to learn based on the headings and figures in the lesson. 1. 2. Lesson 6-1 Active Vocabulary diagonal New Vocabulary
Modeling a Rubik s Cube in 3D
 Modeling a Rubik s Cube in 3D Robert Kaucic Math 198, Fall 2015 1 Abstract Rubik s Cubes are a classic example of a three dimensional puzzle thoroughly based in mathematics. In the trigonometry and geometry
Modeling a Rubik s Cube in 3D Robert Kaucic Math 198, Fall 2015 1 Abstract Rubik s Cubes are a classic example of a three dimensional puzzle thoroughly based in mathematics. In the trigonometry and geometry
Copying a Line Segment
 Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
SOL Review April Class work-nallari Math 8 Measurement & Geometry SOL -CAT Questions 13 SOL 8.6a, 8.7a-b, 8.8a-b,8.9,8.10a-b&8.
 SOL Review April 18-22 Class work-nallari Math 8 Measurement & Geometry SOL -CAT Questions 13 SOL 8.6a, 8.7a-b, 8.8a-b,8.9,8.10a-b&8.11 Nallari Math 8 1 SOL8.6a 1.Lines l, m, and n intersect at the same
SOL Review April 18-22 Class work-nallari Math 8 Measurement & Geometry SOL -CAT Questions 13 SOL 8.6a, 8.7a-b, 8.8a-b,8.9,8.10a-b&8.11 Nallari Math 8 1 SOL8.6a 1.Lines l, m, and n intersect at the same
Downloaded from
 1 IX Mathematics Chapter 8: Quadrilaterals Chapter Notes Top Definitions 1. A quadrilateral is a closed figure obtained by joining four points (with no three points collinear) in an order. 2. A diagonal
1 IX Mathematics Chapter 8: Quadrilaterals Chapter Notes Top Definitions 1. A quadrilateral is a closed figure obtained by joining four points (with no three points collinear) in an order. 2. A diagonal
POST TEST KEY. Math in a Cultural Context *
 POST TEST KEY Building a : The Geometry of Prisms A 6 th grade module in Math in a Cultural Context * UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA FAIRBANKS Student Name: POST TEST KEY Grade: Teacher: School: Location of School:
POST TEST KEY Building a : The Geometry of Prisms A 6 th grade module in Math in a Cultural Context * UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA FAIRBANKS Student Name: POST TEST KEY Grade: Teacher: School: Location of School:
Decide how many topics you wish to revise at a time (let s say 10)
 1 Minute Maths for the Higher Exam (grades B, C and D topics*) Too fast for a first-time use but... brilliant for topics you have already understood and want to quickly revise. for the Foundation Exam
1 Minute Maths for the Higher Exam (grades B, C and D topics*) Too fast for a first-time use but... brilliant for topics you have already understood and want to quickly revise. for the Foundation Exam
Class : VI - Mathematics
 O. P. JINDAL SCHOOL, RAIGARH (CG) 496 001 Phone : 07762-227042, 227293, (Extn. 227001-49801, 02, 04, 06); Fax : 07762-262613; e-mail: opjsraigarh@jspl.com; website : www.opjsrgh.in Class : VI - Mathematics
O. P. JINDAL SCHOOL, RAIGARH (CG) 496 001 Phone : 07762-227042, 227293, (Extn. 227001-49801, 02, 04, 06); Fax : 07762-262613; e-mail: opjsraigarh@jspl.com; website : www.opjsrgh.in Class : VI - Mathematics
Objective. Materials. Find the lengths of diagonal geoboard segments. Find the perimeter of squares, rectangles, triangles, and other polygons.
 . Objective To find the perimeter of a variety of shapes (polygons) Activity 6 Materials TI-73 Student Activity pages (pp. 68 71) Walking the Fence Line In this activity you will Find the lengths of diagonal
. Objective To find the perimeter of a variety of shapes (polygons) Activity 6 Materials TI-73 Student Activity pages (pp. 68 71) Walking the Fence Line In this activity you will Find the lengths of diagonal
Geometry 2001 part 1
 Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
8.3 Prove It! A Practice Understanding Task
 15 8.3 Prove It! A Practice Understanding Task In this task you need to use all the things you know about quadrilaterals, distance, and slope to prove that the shapes are parallelograms, rectangles, rhombi,
15 8.3 Prove It! A Practice Understanding Task In this task you need to use all the things you know about quadrilaterals, distance, and slope to prove that the shapes are parallelograms, rectangles, rhombi,
AW Math 10 UNIT 6 SIMILARITY OF FIGURES
 AW Math 10 UNIT 6 SIMILARITY OF FIGURES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Review Proportional Reasoning Cross Multiply and Divide 2 Similar Figures Similar Figures 3 4 Determining Sides in Similar
AW Math 10 UNIT 6 SIMILARITY OF FIGURES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Review Proportional Reasoning Cross Multiply and Divide 2 Similar Figures Similar Figures 3 4 Determining Sides in Similar
The Pythagorean Theorem and Right Triangles
 The Pythagorean Theorem and Right Triangles Student Probe Triangle ABC is a right triangle, with right angle C. If the length of and the length of, find the length of. Answer: the length of, since and
The Pythagorean Theorem and Right Triangles Student Probe Triangle ABC is a right triangle, with right angle C. If the length of and the length of, find the length of. Answer: the length of, since and
Understand Plane Sections of Prisms and Pyramids
 Lesson 25 Understand Plane Sections of Prisms and Pyramids Name: Prerequisite: How do you identify shapes according to their properties? Study the example showing how to identify shapes by using their
Lesson 25 Understand Plane Sections of Prisms and Pyramids Name: Prerequisite: How do you identify shapes according to their properties? Study the example showing how to identify shapes by using their
UNIT 6 SIMILARITY OF FIGURES
 UNIT 6 SIMILARITY OF FIGURES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete Complete the vocabulary words on Vocabulary the attached handout with information from the booklet or text. 1 Review Proportional
UNIT 6 SIMILARITY OF FIGURES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete Complete the vocabulary words on Vocabulary the attached handout with information from the booklet or text. 1 Review Proportional
Connected Mathematics 2, 6th Grade Units 2006 Correlated to: Nebraska Mathematics Academic Standards (By the End of Grade 8)
 8.1 Numeration/Number Sense 8.1.1 By the end of eighth grade, students will recognize natural numbers whole numbers, integers, and rational numbers. SE: Bits and Pieces I: 5 11, 12 18, 19 27, 28 34, 35
8.1 Numeration/Number Sense 8.1.1 By the end of eighth grade, students will recognize natural numbers whole numbers, integers, and rational numbers. SE: Bits and Pieces I: 5 11, 12 18, 19 27, 28 34, 35
Measuring and Drawing Angles and Triangles
 NME DTE Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles Measuring an angle 30 arm origin base line 0 180 0 If the arms are too short to reach the protractor scale, lengthen them. Step 1: lace the origin of the
NME DTE Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles Measuring an angle 30 arm origin base line 0 180 0 If the arms are too short to reach the protractor scale, lengthen them. Step 1: lace the origin of the
HPS Scope Sequence Last Revised June SUBJECT: Math GRADE: 7. Michigan Standard (GLCE) Code & Language. What this Standard means:
 Number and Numeration MA.7.NS.1 (Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical
Number and Numeration MA.7.NS.1 (Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical
Mathematics Background
 For a more robust teacher experience, please visit Teacher Place at mathdashboard.com/cmp3 The Measurement Process While this Unit does not focus on the global aspects of what it means to measure, it does
For a more robust teacher experience, please visit Teacher Place at mathdashboard.com/cmp3 The Measurement Process While this Unit does not focus on the global aspects of what it means to measure, it does
Target 5.4: Use angle properties in triangles to determine unknown angle measurements 5.4: Parallel Lines and Triangles
 Unit 5 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Target 5.1: Classify and identify angles formed by parallel lines and transversals 5.1 a Parallel and Perpendicular lines 5.1b Parallel Lines and its Angle Relationships
Unit 5 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Target 5.1: Classify and identify angles formed by parallel lines and transversals 5.1 a Parallel and Perpendicular lines 5.1b Parallel Lines and its Angle Relationships
English 1 st Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14
 English 1 st Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State
English 1 st Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State
Developing geometric thinking. A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9
 Developing geometric thinking A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9 Developing geometric thinking ii Contents Van Hiele: Developing Geometric Thinking... 1 Sorting objects using Geostacks...
Developing geometric thinking A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9 Developing geometric thinking ii Contents Van Hiele: Developing Geometric Thinking... 1 Sorting objects using Geostacks...
An Overview of Mathematics 4
 An Overview of Mathematics 4 Number (N) read, write, represent, and describe whole numbers to 10 000 using concrete materials, pictures, expressions (e.g., 400 + 7), words, place-value charts, and symbols
An Overview of Mathematics 4 Number (N) read, write, represent, and describe whole numbers to 10 000 using concrete materials, pictures, expressions (e.g., 400 + 7), words, place-value charts, and symbols
activity sheet 1 AREA AND PERIMETER Name Area in Square Units Ratio of Perimeter to Area (P/A) Ratio in Decimal Form 1 Figure Number
 activity sheet 1 AREA AND PERIMETER 1. Use 12 tiles. Keeping in mind that each tile is a square unit, make as many different rectangles with the tiles as possible, each with an area of 12 square units.
activity sheet 1 AREA AND PERIMETER 1. Use 12 tiles. Keeping in mind that each tile is a square unit, make as many different rectangles with the tiles as possible, each with an area of 12 square units.
TenMarks Curriculum Alignment Guide: EngageNY/Eureka Math, Grade 7
 EngageNY Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic A: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Understand equivalent ratios, rate, and unit rate related to a Understand proportional
EngageNY Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic A: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Understand equivalent ratios, rate, and unit rate related to a Understand proportional
The Grade 6 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that students should
 The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
Grade 1 Unit Unit Title Lesson Day
 1 of 4 1-3 1.MD.1 Order three objects by length; compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using a third object. SMP5 Use appropriate tools SMP6 Attend to precision. Order three objects by length.
1 of 4 1-3 1.MD.1 Order three objects by length; compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using a third object. SMP5 Use appropriate tools SMP6 Attend to precision. Order three objects by length.
First Grade Saxon Math Curriculum Guide Key Standards Addressed in Section
 Sections and Lessons First Grade Saxon Math Curriculum Guide MAP September 15 26, 2014 Section 1: Lessons 1-10 Making Sets of Tens & Ones with Concrete Objects, Numerals, Comparing Numbers, Using Graphs
Sections and Lessons First Grade Saxon Math Curriculum Guide MAP September 15 26, 2014 Section 1: Lessons 1-10 Making Sets of Tens & Ones with Concrete Objects, Numerals, Comparing Numbers, Using Graphs
K-PREP. Kentucky Performance Rating For Educational Progress
 GRADE 5 K-PREP Kentucky Performance Rating For Educational Progress EVERY CHILD MATH SAMPLE ITEMS PROFICIENT & PREPARED FOR S U C C E S S Spring 2012 Developed for the Kentucky Department of Education
GRADE 5 K-PREP Kentucky Performance Rating For Educational Progress EVERY CHILD MATH SAMPLE ITEMS PROFICIENT & PREPARED FOR S U C C E S S Spring 2012 Developed for the Kentucky Department of Education
Summer Solutions Common Core Mathematics 4. Common Core. Mathematics. Help Pages
 4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
Name Date Class Practice A. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see.
 Practice A Geometric Patterns Identify a possible pattern. Use the pattern to draw the next figure. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see. 6. Use squares to create a geometric
Practice A Geometric Patterns Identify a possible pattern. Use the pattern to draw the next figure. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see. 6. Use squares to create a geometric
Date Learning Target/s Classwork Homework Self-Assess Your Learning Mon, Mar. 21
 Filling and Wrapping: Three-Dimensional Measurement Name: Per: Investigation 1: Building Smart Boxes: Rectangular Prisms Date Learning Target/s Classwork Homework Self-Assess Your Learning Mon, Mar. 21
Filling and Wrapping: Three-Dimensional Measurement Name: Per: Investigation 1: Building Smart Boxes: Rectangular Prisms Date Learning Target/s Classwork Homework Self-Assess Your Learning Mon, Mar. 21
4th Grade Mathematics Mathematics CC
 Course Description In Grade 4, instructional time should focus on five critical areas: (1) attaining fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing understanding of dividing to find quotients
Course Description In Grade 4, instructional time should focus on five critical areas: (1) attaining fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing understanding of dividing to find quotients
