Year 3. Term by Term Objectives. Year 3 Overview. Spring Autumn. Summer. Number: Place Value
|
|
|
- Reginald Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Year 3 Autumn
2 Term by Term Objectives Year 3 Year 3 Overview Spring Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Multiplication and Division Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement Measurement Number: Fractions Consolidation Summer Number: Fractions Geometry: Property of shapes Measurement Statistics Consolidation
3 Term by Term Objectives Year 3 Year Group Y3 Term Autumn Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Number place value Identify, represent and estimate numbers using different representations. Find 10 or 100 more or less than a given number; recognise the place value of each digit in a three digit number (hundreds, tens, ones). Compare and order numbers up to 1000 Read and write numbers up to 1000 in numerals and in words. Solve number problems and practical problems involving these ideas. Count from 0 in multiples of 50 and 100 Number addition and subtraction Add and subtract numbers mentally, including: a three-digit number and ones; a three-digit number and tens; a three digit number and hundreds. Add and subtract numbers with up to three digits, using formal written methods of columnar addition and subtraction. Estimate the answer to a calculation and use inverse operations to check answers. Solve problems, including missing number problems, using number facts, place value, and more complex addition and subtraction. Number multiplication and division Recall and use multiplication and division facts for the 3, 4 and 8 multiplication tables. Calculate mathematical statements for multiplication and division within the multiplication tables and write them using the multiplication (x), division ( ) and equals (=) signs. Solve problems involving multiplication and division, using materials, arrays, repeated addition, mental methods, and multiplication and division facts, including problems in context. Show that multiplication of two numbers can be done in any order (commutative) and division of one number by another cannot. Measurement Measure, compare, add and subtract: lengths (m/cm/mm). Solve problems, including missing number problems, using number facts, place value, and more complex addition and subtraction. Measure the perimeter of simple 2D shapes. Continue to measure using the appropriate tools and units, progressing to using a wider range of measures, including comparing and using mixed and simple equivalents of mixed units.
4 Place Value National Curriculum Count from 0 in multiples of 50 and 100 Continue the pattern, 50, 100, 150, , 200, 300, 400 Fill in the missing numbers Count in 10s from 0. Whenever you get to a multiple of 50 say Fizz, when you get to multiples of 100 say Buzz. If it is a multiple of both say Fizzbuzz. Circle the odd one out. 100, 150, 200, 215, 300 Explain your answer. True or False. If I count in 100 s from 0, all the numbers will be even. Convince me. Always, sometimes, never All multiples of 50 are multiples of 100 therefore all multiples of 100 are multiples of 50. Use the number cards to make a sequence. Can you make more than one sequence? Hannah and Zara are counting. One of them is counting in 50 s, one of them is counting in 100 s. When they say a number that the other person has said they clap. From their claps (x) can you work out who is saying which pattern? H X X Z X X Al s money is arranged in stacks. Each stack contains 50p. How much money does Al have?
5 Place Value National Curriculum Find 10 or 100 more or less than a given number. Find 10 more and less than the following numbers: 23, 65, , 192, 374 What is 100 more or less than these numbers? 283, 591, 1392, 2901, 1892 Fill in the missing numbers: 10 less Starting 10 number more Emily has made the number: Write down the number that is 10 less than 305. Now write down the number that is 10 less than this new number. Explain what is happening to the number each time. What comes next? = = =506 True or False When I add 100 to any number, I only need to change the hundreds digit. 10 more than my number is 100 less than 320. What is my number? Using number cards 0-9 can you make the answers to the questions below: 10 less than 8 + 7: 10 more than 3 x 10: 100 less than 336: 100 more than 691: 10 less than 3 x 6: I think of a number. I add 10 and then take away 100. My answer is 350. What was my number?
6 Place Value National Curriculum Recognise the place value of each digit in a three digit number (hundreds, tens, ones). Write the value of each underlined digit. 318, 92, is made of ten and hundreds, ones. Find the value of in each of these statements. = = = Explain the value of 4 in the following numbers: 546, 473, is made of 5 hundreds, 4 tens and 3 ones. It is also made of 54 tens and 3 ones. It is also made of 543 ones. Can you express 627 in the same way? What is the same about these numbers and what is different? Henry thought of a number. He thought of a two-digit number less than 50. The sum of its digits was 12. Their difference was 4. What number did Henry think of? Use the clues to find the missing digits: The hundreds digit is double the tens digit. The tens digit is 5 less than 2 x 8. The ones digit is 2 less than the hundreds digit. Claire, Libby and Katie are holding three digit numbers. Claire and Libby have given clues below: Claire- My number has the smallest amount of ones. Libby- The tens in my number are 2 less Claire and Katie s added together Can you work out which number is which?
7 Place Value National Curriculum Compare and order numbers up to 1000 Harry puts the following numbers in order. 345, 278, 301, 287, 368. Which number would be third? Using 3 counters, like shown in the place value grid below, make all the numbers possible. Order from smallest to largest. 100s 10s 1s Here are three digit cards. Write all the three digit numbers that you can make and order them from smallest to largest Write the following numbers from largest to smallest. Explain how you ordered them. 445, 378, 601, 387, 468 Put one digit in each box to make the list of numbers in order from smallest to largest True or False: You must look at the highest place value column first when ordering any numbers. In pairs, each child has to make a 3 digit number. They pick a 0-9 number card and decide where to write the number. Do this until they have created a 3 digit number. In each game they change the criteria they have to meet to win. Eg Make the smallest number. Make the largest number. Make a number between 300 and 500. I am thinking of a number. My number is between 300 and 500. The digits add up to 14. The difference between the largest and the smallest digit is 2. What could my number be? Order all the possible numbers from smallest to largest. Deena has ordered 5 numbers. The largest number is 845, the smallest number is 800. The other numbers all have digit totals of 12. What could the other numbers be?
8 Place Value National Curriculum Read and write numbers up to 1000 in numerals and in words. Fill in the blanks Numbers in words Four hundred and two Three hundred and sixty six Numerals What number is represented by the Base 10? Write it in numerals and words. What number is represented in the place value grid? 100s 10s 1s Using the same number of counters, how many different numbers can you make? Convince me you have found them all. Tim was asked to write the number four hundred and forty. He wrote Do you agree with Tim? Explain why. Hannah has written the number five hundred and thirteen as 530. Explain the mistake that Hannah has made. Match the number in words to the number in numerals. Fill in the missing numbers. Four hundred 4 and sixty two Four hundred and twenty six Six hundred and forty two Two hundred and sixty four There are 3 cards with a digit on each. Find every 3 digit number that could be made from the cards. Write out the largest, smallest and middle number in words children were on time for school this morning. Write this number in words. Five hundred and seventy people went to the school fair. Write this number in numerals. Work out the missing word: A number between 450 and 460. Four hundred and six. Repeat this with different clues and numbers.
9 National Curriculum Covered above Covered above Covered above Place Value Solve number problems and practical problems involving these ideas.
10 National Curriculum What number is represented in each set? Place 725 on each of the number lines below Using four counters and the place value grid below, how many different numbers can you make? Eg s 10s 1s Place Value Identify, represent and estimate numbers up to 1000 using different representations. Use place value counters or base 10 to represent the following numbers 382, 560, 905 Show 450 on the number line. Alice says The number in the place value grid is the largest number you can make with 8 counters. Do you agree? Prove your answer. 100s 10s 1s Simon was making a three digit number using place value counters. He has dropped three of his counters on the floor. What could his number be? If the number on the number line is 780, what could the start and end point of the number line be? Henry has one counter and a place value grid. He says he can make a one, two, three and four digit number. Is he correct? Show this on a place value grid.
11 Addition and Subtraction National Curriculum Add and subtract numbers mentally, including: a three-digit number and ones; a three-digit number and tens; a three digit number and hundreds. Calculate: Calculate: Fill in the missing numbers Start Add Add Add Are these number sentences true or false? = = = 706 Justify your answers. Always, Sometimes, Never When you add 7 to a number ending in 8 your answer ends with 5. Explain your answer. Which questions are easy, which are hard? = = = = Why are some easy and some hard? Explain your reasons. Always, Sometimes, Never - 2 odd numbers add up to make an even number. - 3 odd numbers add up to make an even number. - Adding 8 to a number ending in 2 makes a multiple of 10. Three pandas ate 25 bamboo sticks. Each of them ate a different odd number of bamboo sticks. How many bamboo sticks did they each eat? Find as many ways as you can to do it. A magician is performing a card trick. He has eight cards with the digits 1-8 on them. He chooses four cards and the numbers on them add up to 20. How many different combinations could he have chosen?
12 Addition and Subtraction National Curriculum Add and subtract numbers with up to three digits, using formal written methods of columnar addition and subtraction. Use the grid to solve the calculation below Write down three numbers that add up to make = 247 Write down a different set of numbers that add up to 247. Harry has 357 stickers, John has 263. How many do they have altogether? If Harry gives John 83 stickers, how many do they have each now? Find the missing numbers in the addition Dan saved 342 in his bank account. He spent 282. Does the subtraction below show how much he has left? Explain your answer Find the errors in the calculations and correct them to find the right answer. Calculation Error Correct solution The answer to the addition is 201. All the digits used are either 1 or 9. Fill in the boxes. 201 = + + Can this be done more than one way? Convince me. Roll a 1-6 die, fill in each of the boxes and try to make the smallest total possible. Repeat and try to find different answers. Could you have placed the digits in a different place to make a lower total? + Molly went swimming every day for 5 days. She swam 80 lengths during the 5 days. Each day she swam 4 less lengths than the day before, how many lengths did she swim each day?
13 Addition and Subtraction National Curriculum Estimate the answer to a calculation and use inverse operations to check answers. Make an estimate: Which of the following number sentences have an answer between 50 and 60? = 79 Use a subtraction to check the answer to the addition. Hannah has baked 45 cakes for a bun sale. She sells 18 cakes. How many does she have left? Double check your answer by using an addition. Niamh estimates the answer to as shown: Do you agree with Niamh? Explain your answer. Leonie says = 333 because = 300, 50 20= 30, 6 3= 3 so = 333 Do you agree with her answer? Prove your answer by using an addition calculation. Colin says If I add two numbers together I can check my answer by taking them away afterwards. So to check 3 + 4, I can do 4-3. Is he right? Explain Colin s thinking. Is it magic? Think of a number. Multiply it by 5. Double it. Add 2. Subtract 2. Halve it. Divide it by 5. Have you got back to your original number? Is this magic? Can you work out what has happened? Using the idea above (Is it magic?). Create your own set of instructions where you think of a number and end up back at the original number. I think of a number. I divide by 2 and add 98. My answer is 100. What was my number?
14 Addition and Subtraction National Curriculum Solve problems, including missing number problems, using number facts, place value, and more complex addition and subtraction. Covered above Covered above Covered above
15 Multiplication and Division National Curriculum Recall and use multiplication and division facts for the 3, 4 and 8 multiplication tables. Calculate: 3 x 4 = 4 x 7 = 8 x 3= If I know 3 x 8= 24. What other multiplication and division facts do I know? Fill in the gaps 3 x = 24 = x 4 = 8 x Tom says I can use my 4 times table to help me work out my 8 times table. Is he correct? Convince me. What pair of numbers could be written in the boxes? X = 24 Start this rhythm, clap, clap, click, clap, clap, click. Carry on the rhythm, what will you be doing on the 15 th beat? How do you know? What will you be doing on the20th beat? Explain and prove your answer. A group of aliens live on Planet Xert. Tinions have three legs, Quinions have four legs. The group has 22 legs altogether. How many Tinions and Quinions might there be? Is there more than one solution? Sally has baked some buns. She counted her buns in 4 s and had 3 left over. She counted them in fives and had four left over. How many buns has Sally got? Can you sort the cards below so that they would follow round in a loop? The number at the top is the answer, then follow the instruction at the bottom to get the next answer X2 X2 +1 X X6 X2
16 Multiplication and Division National Curriculum Calculate mathematical statements for multiplication and division within the multiplication tables and write them using the multiplication (x), division ( ) and equals (=) signs. Cards come in packs of 4. How many packs do I need to buy to get 32 cards? Show your working in a number sentence. Use the three numbers below to make 4 multiplication and division sentences Harry bought 5 bags of sweets. There are 8 sweets in each. How many sweets are there altogether? Show your answer in a number sentence. Andy says I can use my three times table to work out Explain what Andy could do to work out this calculation. Which of the problems below can be solved using 8 2? -There are 2 bags of sweets with 8 sweets in each. How many altogether? -A rollercoaster carriage holds 2 people, how many carriages are needed for 8 people? -I have 8 crayons and share them out so people have 2 crayons each. How many people did I share them between? -I have 8 buns and I give two to my brother. How many do I have left? Explain your reasoning. You are asked to work out 54 x 3. Would you need to know 3 x 5 to solve it? Convince me. Holly bought a chocolate bar costing 55p. She paid using 8 coins which were either 5p s or 10p s. How many different ways could she have paid? Write down the multiplication sentences you have used to solve the problem. Use the numbers 1-8 to fill in the circles below. Solve the problem and write down all the steps you went through in number sentences: I think of a number, I divide my number by 3, add 4 and times by 2. My answer is 20. What number did I start with?
17 National Curriculum Fluency Reasoning Problem Solving Covered above Covered above Covered above Multiplication and Division Solve problems involving multiplication and division, using materials, arrays, repeated addition, mental methods, and multiplication and division facts, including problems in context.
18 National Curriculum Fluency Reasoning Problem Solving Multiplication and Division Show that multiplication of two numbers can be done in any order (commutative) and division of one number by another cannot. Write multiplication sentences for the bars below Fill in the gaps: X 4 = 48 4 x = 48 Use the numbers 4, 6 and 24 to fill the number sentences below: x = = x = = What is the relationship between these calculations? 4 x 5 7 x 3 5 x 4 3 x 7 True or False? 3 x 4 = 6 x 2 2 x 6 = 4 x 3 Explain your reasoning. Can you write multiplication and division sentences to describe this rectangle? What do you notice about the number sentences? Play a game of Go Fish, there are sets of four cards that the children have to try and collect. Each set will look like the one below. 3 x 4 4 x As players collect cards they must ask each otherdo you have 3 x 4 or do you have an array showing 3 x 4 or do you have a bar model showing 3 x 4. The language they are using will therefore model their understanding of the commutative law. Using the same cards as above plus some division cards. Children need to match cards that show a linking division and multiplication fact. There will be some red herrings within the pack ie 4 12=3
19 Measurement National Curriculum Measure, compare, add and subtract: lengths (m/cm/mm). How long is the pencil? Find the length from A B, find the length from B-C. Which is longer? How much longer? Insert < and > into the number sentences. 13cm 1m 140mm 90cm If I have 3m of ribbon and cut it into 50cm lengths, how many lengths can I cut? Convince me. Abigail s ruler has broken. How could she still use it to measure things? Harry is measuring the length of this pencil. Explain what he is doing wrong. A coach is three times as long as a car. A train is 6.5m longer than a coach. The train is 36.5m long. How long is the car? Which of the following statements could be true? Check them and correct the false ones by using measuring equipment. - A chair is about 120mm tall. - A sensible portion of pasta is about 40m. - A ruler is about 300mm long. The length of a swimming pool is 50m, Miss Jones swims 200m every morning. How many lengths is this?
20 Measurement National Curriculum Measure the perimeter of simple 2D shapes. What is the perimeter of the rectangle? 4cm 2cm A square has sides of 3cm. What is the perimeter of the square? Measure the perimeter of the triangle. A square has sides that are in whole cm. Which of the following measurements could be its perimeter? 18cm, 8cm, 25cm, 24cm Explain your thinking. Tick the correct statement about the shapes below. Shape A B Shape - Shape A has a bigger perimeter than shape B. - Shape B has a bigger perimeter than shape A. - Shape A has the same perimeter as shape B. Explain how you know. This shape is made from identical squares. The perimeter of the whole shape is 24cm. Find the perimeter of the central square. Explain how you found the solution. How many different rectangles can you draw with a perimeter of 20cm? A rectangle has sides where the length is double the width. If the perimeter is 12cm, what are the length and the width of the rectangle?
21 National Curriculum Covered above and practically Covered above and practically Covered above and practically Measurement Continue to measure using the appropriate tools and units, progressing to using a wider range of measures, including comparing and using mixed and simple equivalents of mixed units.
Released January Years 3/4. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area
 Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
Released October Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 4: Multiplication & Division
 Released October 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Multiply and divide numbers mentally drawing upon known facts. Multiples Factors Common factors Prime numbers
Released October 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Multiply and divide numbers mentally drawing upon known facts. Multiples Factors Common factors Prime numbers
Updated December Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 4: Multiplication & Division
 Updated December 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Year 5 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Multiples Notes and Guidance Building on their times tables knowledge,
Updated December 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Year 5 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Multiples Notes and Guidance Building on their times tables knowledge,
Year 1. Place Value. Term by Term Objectives. All students Fluency Reasoning Problem Solving. National Curriculum Statement
 National Curriculum Place Value Given a number, identify one more or one less. 9 2 Fill in the missing numbers. Is 1 less than Is 1 more than How many fingers if I put one down? I roll the number that
National Curriculum Place Value Given a number, identify one more or one less. 9 2 Fill in the missing numbers. Is 1 less than Is 1 more than How many fingers if I put one down? I roll the number that
Released November /2. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 4: Measurement - Money
 Released November 2017 1/2 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Measurement - Money Year 1/2 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 1 Year 2 Recognising coins Recognising notes Counting
Released November 2017 1/2 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Measurement - Money Year 1/2 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 1 Year 2 Recognising coins Recognising notes Counting
What must be added to 30 to make one hundred? =
 2.1 1. How many groups of ten can be made out of 70 marbles? 2.2 2. Order these numbers starting with the smallest: 30, 17, 12, 23 2.2 3. Write the number two hundred and seven in digits. 2.3 4. Write
2.1 1. How many groups of ten can be made out of 70 marbles? 2.2 2. Order these numbers starting with the smallest: 30, 17, 12, 23 2.2 3. Write the number two hundred and seven in digits. 2.3 4. Write
Count in multiples of 6, 7, and Find 1000 more or less than a given number.
 Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers Order numbers Round
Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers Order numbers Round
Updated October 2017
 Updated October 2017 Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers
Updated October 2017 Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers
There are 5 people upstairs on the bus, there are 4 people downstairs. How many altogether? Write a number sentence to show this.
 National Curriculum Fluency Reasoning Problem Solving Read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition (+), subtraction (-) and equals (=) signs. There are 5 people upstairs on the
National Curriculum Fluency Reasoning Problem Solving Read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition (+), subtraction (-) and equals (=) signs. There are 5 people upstairs on the
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 E Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Thousands 1 Hundreds Tens 1 Units Name Series E Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Contents Topic 1 Looking at whole numbers (pp. 1 8) reading
E Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Thousands 1 Hundreds Tens 1 Units Name Series E Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Contents Topic 1 Looking at whole numbers (pp. 1 8) reading
Please make sure that you print this resource at 100% so that all measurements are correct. To do this, follow the relevant steps below.
 Please make sure that you print this resource at 00% so that all measurements are correct. To do this, follow the relevant steps below. Adobe Reader or Adobe Acrobat Adobe Reader is a free PDF viewer,
Please make sure that you print this resource at 00% so that all measurements are correct. To do this, follow the relevant steps below. Adobe Reader or Adobe Acrobat Adobe Reader is a free PDF viewer,
Year 1. Mastery Overview Autumn
 Mastery Overview Autumn SOL Overview As well as providing term by term overviews for the new as a Maths Hub we are aiming to support primary schools by providing more detailed Schemes of Learning, which
Mastery Overview Autumn SOL Overview As well as providing term by term overviews for the new as a Maths Hub we are aiming to support primary schools by providing more detailed Schemes of Learning, which
Multiplication and Division
 Series D Student My name Multiplication and Division Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning
Series D Student My name Multiplication and Division Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning
What must be added to 60 to make one hundred? What is seventy minus forty?
 2.1 1. How many groups of ten can be made out of 100 marbles? 2.2 2. Order these numbers starting with the smallest: 49, 27, 17, 34 2.2 3. Write the number one hundred and nineteen in digits. 2.3 4. Write
2.1 1. How many groups of ten can be made out of 100 marbles? 2.2 2. Order these numbers starting with the smallest: 49, 27, 17, 34 2.2 3. Write the number one hundred and nineteen in digits. 2.3 4. Write
Year 4. Term by Term Objectives. Year 4 Overview. Autumn. Spring Number: Fractions. Summer. Number: Addition and Subtraction.
 Summer Overview Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement:
Summer Overview Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement:
Meet the Characters 3. Yearly Overview 4. Block 1 Number: Multiplication and Division 5. Block 2 Measurement: Money 25. Block 3 Statistics 37
 1 Meet the Characters 3 Yearly Overview 4 Spring Blocks Block 1 Number: Multiplication and Division 5 Block 2 Measurement: Money 25 Block 3 Statistics 37 Block 4 Measurement: Length and Perimeter 45 Block
1 Meet the Characters 3 Yearly Overview 4 Spring Blocks Block 1 Number: Multiplication and Division 5 Block 2 Measurement: Money 25 Block 3 Statistics 37 Block 4 Measurement: Length and Perimeter 45 Block
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests
 Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests 1 Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests 1 Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8. satspapers.org
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
MEP Y9 Practice Book A. This section deals with the revision of place value. Remember that we write decimal numbers in the form:
 2 Basic Operations 2.1 Place Value This section deals with the revision of place value. Remember that we write decimal numbers in the form: Thousands Hundreds Tens Units Tenths Hundredths Thousandths Example
2 Basic Operations 2.1 Place Value This section deals with the revision of place value. Remember that we write decimal numbers in the form: Thousands Hundreds Tens Units Tenths Hundredths Thousandths Example
MATH NUMBER SENSE 3 Performance Objective Task Analysis Benchmarks/Assessment Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers.
 Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers. 1. Count, read, and write whole numbers to 10,000. Count to 10,000 Which numbers are whole numbers? Whole number 0, 15.3, 4/5, 8, 25 1/2 Count
Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers. 1. Count, read, and write whole numbers to 10,000. Count to 10,000 Which numbers are whole numbers? Whole number 0, 15.3, 4/5, 8, 25 1/2 Count
Year 1. Using and applying mathematics. Framework review
 Year 1 Using and applying mathematics Solve problems involving counting, adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the context of numbers, measures or money, for example to pay and give change I am going
Year 1 Using and applying mathematics Solve problems involving counting, adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the context of numbers, measures or money, for example to pay and give change I am going
Use repeated addition to find the total number of fingers. Find the total of each group by using repeated addition. Multiplication and Division
 Introducing multiplication groups of 5 Use repeated addition to find the total number of fingers. 5 + 5 + 5 = 5 groups of 5 is equal to 5. Find the total of each group by using repeated addition. a How
Introducing multiplication groups of 5 Use repeated addition to find the total number of fingers. 5 + 5 + 5 = 5 groups of 5 is equal to 5. Find the total of each group by using repeated addition. a How
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
We are packing 22 balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) 3 balls in each box b) 5 balls in each box
 MEP Book We are packing balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) balls in each box b) balls in each box Write each as a multiplication and addition, then as a division. = + = +
MEP Book We are packing balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) balls in each box b) balls in each box Write each as a multiplication and addition, then as a division. = + = +
Day 1. Mental Arithmetic Questions KS3 MATHEMATICS. 60 X 2 = 120 seconds. 1 pm is 1300 hours So gives 3 hours. Half of 5 is 2.
 Mental Arithmetic Questions. The tally chart shows the number of questions a teacher asked in a lesson. How many questions did the teacher ask? 22 KS MATHEMATICS 0 4 0 Level 4 Answers Day 2. How many seconds
Mental Arithmetic Questions. The tally chart shows the number of questions a teacher asked in a lesson. How many questions did the teacher ask? 22 KS MATHEMATICS 0 4 0 Level 4 Answers Day 2. How many seconds
Multiplication and Division
 D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Introducing multiplication (pp. 1 7) groups of 5 5 times table 10 times table multiplying any number by 10 multiplying numbers by 0 and 1 Date completed Topic
D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Introducing multiplication (pp. 1 7) groups of 5 5 times table 10 times table multiplying any number by 10 multiplying numbers by 0 and 1 Date completed Topic
7 + Entrance Examination Sample Paper Mathematics. Total marks: 84 Time allowed: 1hour
 7 + Entrance Examination Sample Paper Mathematics Total marks: 84 Time allowed: 1hour Information for parents: This sample paper has been created for children who are embarking on the 7+ exam. We recommend
7 + Entrance Examination Sample Paper Mathematics Total marks: 84 Time allowed: 1hour Information for parents: This sample paper has been created for children who are embarking on the 7+ exam. We recommend
Coin Combinations. Crayons. 1. Mark the coins you need to buy an eraser. 2. Mark the coins you need to buy a box of crayons. $0.70.
 HOME LINK 8 1 Coin Combinations 88 89 Family Note In the next lesson, we will extend our work with money to include dollars. In preparation for this, we have been practicing counting coins. If your child
HOME LINK 8 1 Coin Combinations 88 89 Family Note In the next lesson, we will extend our work with money to include dollars. In preparation for this, we have been practicing counting coins. If your child
MATHEMATICS. Y4 Counting and Understanding Number 4207 Use decimal notation. Order decimal fractions. Equipment
 MATHEMATICS Y4 Counting and Understanding Number 4207 Use decimal notation. Order decimal fractions. Paper, pencil, ruler Calculator Equipment Maths Go Go Go 4207 Use decimal notation Order decimal fractions
MATHEMATICS Y4 Counting and Understanding Number 4207 Use decimal notation. Order decimal fractions. Paper, pencil, ruler Calculator Equipment Maths Go Go Go 4207 Use decimal notation Order decimal fractions
E CA AC EA AA AM AP E CA AC EA AA AM AP E CA AC EA AA AM AP E CA AC EA AA AM AP E CA AC EA AA AM AP E CA AC EA AA AM AP
 1 The role of this book. School wide assessment resource instructions. Contents page Pg3 Pg3 E CA AC EA AA AM AP I am learning my addition and subtraction facts to five. Pg4, 5 I am learning my doubles
1 The role of this book. School wide assessment resource instructions. Contents page Pg3 Pg3 E CA AC EA AA AM AP I am learning my addition and subtraction facts to five. Pg4, 5 I am learning my doubles
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM MATHEMATICS
 THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 1 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 18 January 2013 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 1 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 18 January 2013 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
Name. Present School. The London Independent Girls Schools Consortium. Group 1. Mathematics Entrance Examination
 Name. Present School The London Independent Girls Schools Consortium Group 1 Mathematics Entrance Examination 18 th January 2008 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes Write in pencil. Do all your rough working
Name. Present School The London Independent Girls Schools Consortium Group 1 Mathematics Entrance Examination 18 th January 2008 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes Write in pencil. Do all your rough working
We are packing 22 balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) 3 balls in each box b) 5 balls in each box
 1 We are packing balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) balls in each box b) balls in each box E.g: E.g: Write each as a multiplication and addition, then as a division. = 7
1 We are packing balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) balls in each box b) balls in each box E.g: E.g: Write each as a multiplication and addition, then as a division. = 7
Answers Solving mathematical problems
 Solving mathematical problems 1 in the middle (p.8) Many answers are possible, for example: 10, 11, 1, 13, 14 (on in steps of 1) 14, 13, 1, 11, 10 (back in steps of 1) 8, 10, 1, 14, 16 (on in steps of
Solving mathematical problems 1 in the middle (p.8) Many answers are possible, for example: 10, 11, 1, 13, 14 (on in steps of 1) 14, 13, 1, 11, 10 (back in steps of 1) 8, 10, 1, 14, 16 (on in steps of
Write down all the factors of 15 Write down all the multiples of 6 between 20 and 40
 8th September Convert 90 millimetres into centimetres Convert 2 centimetres into millimetres Write down all the factors of 15 Write down all the multiples of 6 between 20 and 40 A printer prints 6 pages
8th September Convert 90 millimetres into centimetres Convert 2 centimetres into millimetres Write down all the factors of 15 Write down all the multiples of 6 between 20 and 40 A printer prints 6 pages
Updated October 2017
 Updated October 2017 Count objects to 100 and read and write numbers in numerals and words Represent numbers to 100 Tens and ones with a part whole model Tens and ones using addition Use a place alue chart
Updated October 2017 Count objects to 100 and read and write numbers in numerals and words Represent numbers to 100 Tens and ones with a part whole model Tens and ones using addition Use a place alue chart
MATHEMATICS MARKS PAGE TOTAL KEY STAGE LEVELS 3 5 TEST A CALCULATOR NOT ALLOWED. First Name. Last Name.
 MATHEMATICS KEY STAGE 2 2001 TEST A LEVELS 3 5 CALCULATOR NOT ALLOWED PAGE 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 TOTAL MARKS First Name Last Name School Instructions You may not use a calculator to answer any questions
MATHEMATICS KEY STAGE 2 2001 TEST A LEVELS 3 5 CALCULATOR NOT ALLOWED PAGE 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 TOTAL MARKS First Name Last Name School Instructions You may not use a calculator to answer any questions
Year 5. Mathematics A booklet for parents
 Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
These tests contain questions ranging from Level 2 to Level 3. Children should have five seconds to answer questions 1 3 in each test,
 These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test, ten seconds to answer questions and fifteen seconds to answer questions -.
These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test, ten seconds to answer questions and fifteen seconds to answer questions -.
Test A. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. DCSF no. KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5
 Ma KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 Mathematics test Test A Calculator not allowed First name Last name School DCSF no. 2010 For marker s use only Page 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 TOTAL Marks These three children appear
Ma KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 Mathematics test Test A Calculator not allowed First name Last name School DCSF no. 2010 For marker s use only Page 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 TOTAL Marks These three children appear
Multiplication and Division
 F Student Book Name Series F Contents Topic Mental multiplication strategies (p. - 0) doubling strategy multiply by 0s, 00s and 000s split strategy compensation strategy factors and multiples Date completed
F Student Book Name Series F Contents Topic Mental multiplication strategies (p. - 0) doubling strategy multiply by 0s, 00s and 000s split strategy compensation strategy factors and multiples Date completed
Enhancing their play with topic based mathematics and role play. For example,
 Overview The ability to calculate mentally lies at the heart of the mathematics taught at primary school. During Key Stage 1, emphasis will be placed upon developing mental calculations. Written recordings
Overview The ability to calculate mentally lies at the heart of the mathematics taught at primary school. During Key Stage 1, emphasis will be placed upon developing mental calculations. Written recordings
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests
 Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Released November /5. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 4: Length & Perimeter
 Released November 2017 4/5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Length & Perimeter Year 4/5 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 4 Year 5 Kilometres Perimeter on a grid Perimeter
Released November 2017 4/5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Length & Perimeter Year 4/5 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 4 Year 5 Kilometres Perimeter on a grid Perimeter
SERIES Addition and Subtraction
 D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
Important Words in Mathematics
 1 P a g e Important Words in Mathematics... 2 Numbers... 3 Number Words... 4 EVEN OR ODD... 5 PLACE VALUE... 6 PLACE VALUE... 7 VALUE... 8 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 9 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 10
1 P a g e Important Words in Mathematics... 2 Numbers... 3 Number Words... 4 EVEN OR ODD... 5 PLACE VALUE... 6 PLACE VALUE... 7 VALUE... 8 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 9 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 10
Second Practice Test 1 Level 5-7
 Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Level 5-7 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Level 5-7 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
SERIES Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 F Teacher Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Name Contents Series F Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Section Looking Answers at whole (pp. ) numbers (pp. 8) read looking
F Teacher Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Name Contents Series F Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Section Looking Answers at whole (pp. ) numbers (pp. 8) read looking
THE SULTAN S SCHOOL HELPING YOUR CHILD WITH MATHS AT HOME
 HELPING YOUR CHILD WITH MATHS AT HOME Your child has taken home a letter which explains the main things that your child has or will be learning in maths. Have a look through this letter so you can get
HELPING YOUR CHILD WITH MATHS AT HOME Your child has taken home a letter which explains the main things that your child has or will be learning in maths. Have a look through this letter so you can get
Focus on Mathematics
 Focus on Mathematics Year 4 Pre-Learning Tasks Number Pre-learning tasks are used at the start of each new topic in Maths. The children are grouped after the pre-learning task is marked to ensure the work
Focus on Mathematics Year 4 Pre-Learning Tasks Number Pre-learning tasks are used at the start of each new topic in Maths. The children are grouped after the pre-learning task is marked to ensure the work
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM MATHEMATICS
 THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 8 January 2016 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 8 January 2016 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
Grade 3 NAPLAN preparation pack:
 Grade 3 NAPLAN preparation pack: Below is a guide with example questions to use with students preparing for NAPLAN for three weeks prior to the test. By this stage students are expected to have spent a
Grade 3 NAPLAN preparation pack: Below is a guide with example questions to use with students preparing for NAPLAN for three weeks prior to the test. By this stage students are expected to have spent a
Chapter 2: Numeration Systems
 Chapter 2: Numeration Systems 8. In base ten, 215.687 is exactly ones, exactly tens, exactly hundreds, and exactly thousands; also, 3421 is exactly tenths and exactly hundredths. In base ten, 215.687 is
Chapter 2: Numeration Systems 8. In base ten, 215.687 is exactly ones, exactly tens, exactly hundreds, and exactly thousands; also, 3421 is exactly tenths and exactly hundredths. In base ten, 215.687 is
b) 12 - = 6 d) 9 - = 3 e) 11 - = 8 f) 10 - = 7
 Level 7 Card 1 a) Using the number chart count by 2s from 10 to 30. Use counters for these equations: b) + 2 = 6 c) 2 + 6 = d) 2 + = 6 e) 12 = + 6 f) + 5 = 8 g) 9 = + 4 h) 7 + = 11 Level 7 Card 2 a) Using
Level 7 Card 1 a) Using the number chart count by 2s from 10 to 30. Use counters for these equations: b) + 2 = 6 c) 2 + 6 = d) 2 + = 6 e) 12 = + 6 f) + 5 = 8 g) 9 = + 4 h) 7 + = 11 Level 7 Card 2 a) Using
MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT
 MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT By Kerry Dalton Using manipulatives from Early Years Foundation Stage to Year 6 10 minutes per day, in addition to the daily mathematics lesson Covers Early Years Foundation Stage
MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT By Kerry Dalton Using manipulatives from Early Years Foundation Stage to Year 6 10 minutes per day, in addition to the daily mathematics lesson Covers Early Years Foundation Stage
7 + Entrance Examination
 7 + Entrance Examination Paper 7 Numeracy / Maths Total marks: 84 Time allowed: 1 hour Full name. Answer the questions below. Don t forget to show your working. 1a. Grandma likes to knit mittens. Today
7 + Entrance Examination Paper 7 Numeracy / Maths Total marks: 84 Time allowed: 1 hour Full name. Answer the questions below. Don t forget to show your working. 1a. Grandma likes to knit mittens. Today
Dear Parents,
 Dear Parents, This packet of math activities was created to help your child engage with and become excited about Math over the summer months. All projects in this packet are based upon the Connecticut
Dear Parents, This packet of math activities was created to help your child engage with and become excited about Math over the summer months. All projects in this packet are based upon the Connecticut
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7. satspapers.org
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Test B. Calculator allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. DfE no. KEY STAGE LEVELS
 Ma KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 Mathematics test Test B Calculator allowed First name Last name School DfE no. 2011 For marker s use only Page Marks 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 TOTAL These three children appear
Ma KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 Mathematics test Test B Calculator allowed First name Last name School DfE no. 2011 For marker s use only Page Marks 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 TOTAL These three children appear
First Name: Last Name: Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator in completing this packet.
 5 Entering 5 th Grade Summer Math Packet First Name: Last Name: 5 th Grade Teacher: I have checked the work completed: Parent Signature Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator
5 Entering 5 th Grade Summer Math Packet First Name: Last Name: 5 th Grade Teacher: I have checked the work completed: Parent Signature Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator
Year 1 Spring Term Week 5 to 7 Number: Place Value (within 50)
 1 Numbers to 50 Tens and ones Represent numbers to 50 One more one less Compare objects within 50 Compare numbers within 50 Order numbers within 50 Count in 2s Count in 5s Count to 50 forwards and backwards,
1 Numbers to 50 Tens and ones Represent numbers to 50 One more one less Compare objects within 50 Compare numbers within 50 Order numbers within 50 Count in 2s Count in 5s Count to 50 forwards and backwards,
KEY STAGE 1 NUMERACY PRESENTATION PLACE VALUE & THE NUMBER SYSTEM.
 KEY STAGE 1 NUMERACY PRESENTATION PLACE VALUE & THE NUMBER SYSTEM. LOOKING AT THE NUMBER SYSTEM. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Our number
KEY STAGE 1 NUMERACY PRESENTATION PLACE VALUE & THE NUMBER SYSTEM. LOOKING AT THE NUMBER SYSTEM. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Our number
Numeracy Warm Up. Introduction
 Numeracy Warm Up Introduction Numeracy Warm Up is a set of numeracy exercises that can be used for starters, main lessons and plenaries. It is aimed at Numeracy lessons covering National Curriculum Levels
Numeracy Warm Up Introduction Numeracy Warm Up is a set of numeracy exercises that can be used for starters, main lessons and plenaries. It is aimed at Numeracy lessons covering National Curriculum Levels
SAMPLE BOOKLET Published July 2015
 National curriculum tests Key stage 1 Mathematics Paper 2: reasoning First name Middle name Last name SAMPLE BOOKLET Published July 2015 This sample test indicates how the national curriculum will be assessed
National curriculum tests Key stage 1 Mathematics Paper 2: reasoning First name Middle name Last name SAMPLE BOOKLET Published July 2015 This sample test indicates how the national curriculum will be assessed
4 + 3 = 7 10= Starting at the bigger number and counting on. Progression in Calculations
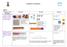 Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together as a group or in a bar.
Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together as a group or in a bar.
Mathematics Test B 3 5 TEST. Calculator allowed. Name. Date YEAR LEVELS. Total marks
 Ma YEAR 5 LEVELS 3 5 TEST B Mathematics Test B Calculator allowed Name Date Total marks Instructions You may use a calculator to answer any questions in this test. Work as quickly and as carefully as
Ma YEAR 5 LEVELS 3 5 TEST B Mathematics Test B Calculator allowed Name Date Total marks Instructions You may use a calculator to answer any questions in this test. Work as quickly and as carefully as
Paper 1. Mathematics test. Calculator not allowed KEY STAGE TIERS. First name. Last name. School
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIERS 5 7 2006 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIERS 5 7 2006 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of
7 + Entrance Examination Sample Paper Mathematics Total Marks: 71 Time allowed: 1 hour
 7 + Entrance Examination Sample Paper Mathematics Total Marks: 71 Time allowed: 1 hour Information for parents: This sample paper has been created for children who are embarking on the 7+ exam. We recommend
7 + Entrance Examination Sample Paper Mathematics Total Marks: 71 Time allowed: 1 hour Information for parents: This sample paper has been created for children who are embarking on the 7+ exam. We recommend
Whole Numbers. Whole Numbers. Curriculum Ready.
 Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
Section 1: Whole Numbers
 Grade 6 Play! Mathematics Answer Book 67 Section : Whole Numbers Question Value and Place Value of 7-digit Numbers TERM 2. Study: a) million 000 000 A million has 6 zeros. b) million 00 00 therefore million
Grade 6 Play! Mathematics Answer Book 67 Section : Whole Numbers Question Value and Place Value of 7-digit Numbers TERM 2. Study: a) million 000 000 A million has 6 zeros. b) million 00 00 therefore million
Paper 1. Mathematics test. Calculator not allowed KEY STAGE TIERS. First name. Last name. School
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIERS 4 6 2006 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIERS 4 6 2006 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of
These tests contain questions ranging from Level 2 to Level 4. They get progressively more difficult. Children should have five seconds to
 These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. They get progressively more difficult. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test and ten seconds to answer questions.
These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. They get progressively more difficult. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test and ten seconds to answer questions.
Operation Target. Round Number Sentence Target How Close? Building Fluency: creating equations and the use of parentheses.
 Operations and Algebraic Thinking 5. OA.1 2 Operation Target Building Fluency: creating equations and the use of parentheses. Materials: digit cards (0-9) and a recording sheet per player Number of Players:
Operations and Algebraic Thinking 5. OA.1 2 Operation Target Building Fluency: creating equations and the use of parentheses. Materials: digit cards (0-9) and a recording sheet per player Number of Players:
Unit 1. Activity 1. Whole numbers. 1. Copy and complete each number pattern.
 1 2 Unit 1 Whole numbers Activity 1 1. Copy and complete each number pattern. 2 671 2 680 2 689 13 450 13 650 14 450 25 125 25 000 24 875 124 300 126 300 128 300 180 500 180 000 179 500 2. Write these
1 2 Unit 1 Whole numbers Activity 1 1. Copy and complete each number pattern. 2 671 2 680 2 689 13 450 13 650 14 450 25 125 25 000 24 875 124 300 126 300 128 300 180 500 180 000 179 500 2. Write these
This book belongs to
 This book belongs to This book was made for your convenience. It is available for printing from the website. It contains all of the printables from Easy Peasy's Math 4 course. The instructions for each
This book belongs to This book was made for your convenience. It is available for printing from the website. It contains all of the printables from Easy Peasy's Math 4 course. The instructions for each
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy
 The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
1 Summer Math Booklet
 Summer Math Booklet 1 2 How Many Combinations? Sarah has 68. What different combinations of dimes and pennies could she have to equal 68? Try to find all the possible combinations. Write an equation for
Summer Math Booklet 1 2 How Many Combinations? Sarah has 68. What different combinations of dimes and pennies could she have to equal 68? Try to find all the possible combinations. Write an equation for
 I Write the Number Names 223-89 - 605-1000 - 812-437 - 893-910 - II 115-844 - Fill in the blanks 6 X 7 = 2 X 9 = 7 X 8 = 7 X 5 = 3 X10 = 6 X 7 = 5 X 5 = 3 X 6 = 6 X 3 = 7 X 7 = 3 X 9 = 5 X 8 = III Write
I Write the Number Names 223-89 - 605-1000 - 812-437 - 893-910 - II 115-844 - Fill in the blanks 6 X 7 = 2 X 9 = 7 X 8 = 7 X 5 = 3 X10 = 6 X 7 = 5 X 5 = 3 X 6 = 6 X 3 = 7 X 7 = 3 X 9 = 5 X 8 = III Write
Mental Calculation Policy 2014
 Mental Calculation Policy 2014 RECEPTION Children count reliably with numbers from one to 20 and place them in order. Children can say which number is one more or one less than a given number up to 20
Mental Calculation Policy 2014 RECEPTION Children count reliably with numbers from one to 20 and place them in order. Children can say which number is one more or one less than a given number up to 20
Key Stage 2. Mathematics. National Curriculum Baseline Test. Paper 3: reasoning. First name. Middle name. Last name. Date of Birth Day Month Year
 National Curriculum Baseline Test Key Stage 2 Mathematics Paper 3: reasoning First name Middle name Last name Date of Birth Day Month Year School name Page 1 of 22 Explore Learning 2017, not to be reproduced.
National Curriculum Baseline Test Key Stage 2 Mathematics Paper 3: reasoning First name Middle name Last name Date of Birth Day Month Year School name Page 1 of 22 Explore Learning 2017, not to be reproduced.
Read and write numbers to at least 100 in numerals and in words. Recognise the place value of each digit in a two digit number (tens, ones)
 Count objects to 100 and read and write numbers in numerals and words Represent numbers to 100 Tens and ones with a part whole model Tens and ones using addition Use a place alue chart Compare objects
Count objects to 100 and read and write numbers in numerals and words Represent numbers to 100 Tens and ones with a part whole model Tens and ones using addition Use a place alue chart Compare objects
WITHINGTON GIRLS SCHOOL
 Name Candidate Number Room Number WITHINGTON GIRLS SCHOOL ENTRANCE EXAMINATION 07 MATHEMATICS PAPER TIME: 40 MINUTES Some questions paper involve new ideas, but there are examples to guide you and help
Name Candidate Number Room Number WITHINGTON GIRLS SCHOOL ENTRANCE EXAMINATION 07 MATHEMATICS PAPER TIME: 40 MINUTES Some questions paper involve new ideas, but there are examples to guide you and help
First Practice Test 2 Levels 3-5 Calculator allowed
 Mathematics First Practice Test 2 Levels 3-5 Calculator allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need: pen,
Mathematics First Practice Test 2 Levels 3-5 Calculator allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need: pen,
Use a pencil. No calculators or protractors or rulers are allowed.
 Name: Age: Yrs Mths Group Number: Use a pencil. No calculators or protractors or rulers are allowed. There are 18 questions. Answer all of them if you can. Show all your working in the spaces provided
Name: Age: Yrs Mths Group Number: Use a pencil. No calculators or protractors or rulers are allowed. There are 18 questions. Answer all of them if you can. Show all your working in the spaces provided
Patterns in Multiplication and Division
 UNIT 3 1 STUDENT BOOK LESSO N Patterns in Multiplication and Division Quick Review Here are some strategies to help you multiply and divide. Skip count up or down from a known fact to multiply. To find
UNIT 3 1 STUDENT BOOK LESSO N Patterns in Multiplication and Division Quick Review Here are some strategies to help you multiply and divide. Skip count up or down from a known fact to multiply. To find
Pupil s Book. Maths 5A rd Edition 2O% OFF. Dr Fong Ho Kheong Gan Kee Soon Chelvi Ramakrishnan
 Pupil s Book 0.2 Maths 5A 3rd Edition 2O% OFF Dr Fong Ho Kheong Gan Kee Soon Chelvi Ramakrishnan APPROVED BY MINIS OF EDUCATION for use from 207 202 Preface My Pals Are Here! Maths (3rd Edition) is a comprehensive,
Pupil s Book 0.2 Maths 5A 3rd Edition 2O% OFF Dr Fong Ho Kheong Gan Kee Soon Chelvi Ramakrishnan APPROVED BY MINIS OF EDUCATION for use from 207 202 Preface My Pals Are Here! Maths (3rd Edition) is a comprehensive,
E D C B A MS2.1. Correctly calculates the perimeter of most of the drawn shapes. Shapes are similarly drawn. Records lengths using cm.
 Stage 2 - Assessment Measurement Outcomes: MS2.1 Estimates, measures, compares and records lengths, distances and perimeters in metres, cm and mm MS2.2 Estimates, measures, compares and records the areas
Stage 2 - Assessment Measurement Outcomes: MS2.1 Estimates, measures, compares and records lengths, distances and perimeters in metres, cm and mm MS2.2 Estimates, measures, compares and records the areas
Year 9 mathematics: holiday revision. 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four?
 DAY 1 ANSWERS Mental questions 1 Multiply seven by seven. 49 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four? 54 9 = 6 6 3 What number should you add to negative three to get the answer five? -3 0 5 8 4 Add two
DAY 1 ANSWERS Mental questions 1 Multiply seven by seven. 49 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four? 54 9 = 6 6 3 What number should you add to negative three to get the answer five? -3 0 5 8 4 Add two
Essentials. Week by. Week. Fraction Action Bill, Rasheed, and Juan own a hobby shop. Probability Pizzazz
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Bill, Rasheed, and Juan own a hobby shop. Juan owns of the shop. Rasheed owns twice as much as Bill. What fraction of the shop does Bill own? Andy and Fran are playing
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Bill, Rasheed, and Juan own a hobby shop. Juan owns of the shop. Rasheed owns twice as much as Bill. What fraction of the shop does Bill own? Andy and Fran are playing
Essentials. Week by. Week. Investigations. Let s Write Write a story about. Seeing Math $ $ $ $ What Do You Think? Patterns, Patterns, Patterns
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 21 Let s Write Write a story about 1 2 Seeing Math What Do You Think? Suppose you hit the target with three darts. How could you score 15? Is there more
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 21 Let s Write Write a story about 1 2 Seeing Math What Do You Think? Suppose you hit the target with three darts. How could you score 15? Is there more
DIVISION THE BOOK OF SAMPLE ACTIVITY. your source of inspiration JAMES BURNETT CALVIN IRONS ALLAN TURTON
 THE BOOK OF DIVISION SAMPLE ACTIVITY JAMES BURNETT CALVIN IRONS ALLAN TURTON T 1300 674 461 info@origo.com.au www.origo.com.au your source of inspiration Eights Facts Introduce 1 Draw a simple diagram
THE BOOK OF DIVISION SAMPLE ACTIVITY JAMES BURNETT CALVIN IRONS ALLAN TURTON T 1300 674 461 info@origo.com.au www.origo.com.au your source of inspiration Eights Facts Introduce 1 Draw a simple diagram
NEW ENGLAND COMMON ASSESSMENT PROGRAM
 NEW ENGLAND COMMON ASSESSMENT PROGRAM Released Items Support Materials 2013 Grade 4 Mathematics N&O 3.1 Demonstrates conceptual understanding of rational numbers with respect to: whole numbers from 0 to
NEW ENGLAND COMMON ASSESSMENT PROGRAM Released Items Support Materials 2013 Grade 4 Mathematics N&O 3.1 Demonstrates conceptual understanding of rational numbers with respect to: whole numbers from 0 to
4 + 3 = 7 10= model. Starting at the bigger number and counting on
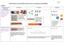 South Wilford C of E Endowed Primary School - Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partpart whole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes
South Wilford C of E Endowed Primary School - Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partpart whole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes
 OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION 1325 Lower Ferry Rd, Ewing NJ 08618 Don Wahlers, District Supervisor for Curriculum & Instruction Phone 609-538-9800 Ext. 3148 Fax 609-882-8172 S.T.E.M. K-6 www.ewing.k12.nj.us
OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION 1325 Lower Ferry Rd, Ewing NJ 08618 Don Wahlers, District Supervisor for Curriculum & Instruction Phone 609-538-9800 Ext. 3148 Fax 609-882-8172 S.T.E.M. K-6 www.ewing.k12.nj.us
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT
 Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Math Made Easy! Parents Workshop Primary 1 and st January 2015
 Math Made Easy! Parents Workshop Primary 1 and 2 31 st January 2015 Some useful reminders Example 1 Amy has 10 stickers. Lisa has 7 more stickers than Amy. How many stickers do the two children have altogether?
Math Made Easy! Parents Workshop Primary 1 and 2 31 st January 2015 Some useful reminders Example 1 Amy has 10 stickers. Lisa has 7 more stickers than Amy. How many stickers do the two children have altogether?
Multiplication and Division
 Series Student Multiplication and Division My name E Copyright 009 P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from P Learning
Series Student Multiplication and Division My name E Copyright 009 P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from P Learning
3. What must be added to seven hundred thirty to make one thousand?
 MENTAL PAPER --- YEAR 6--- HALF YEARLY For the following group of questions, you have 5 seconds to work out each answer and write it down. Għal dawn il-mistoqsijiet li ġejjin, għandek 5 sekondi biex taħdem
MENTAL PAPER --- YEAR 6--- HALF YEARLY For the following group of questions, you have 5 seconds to work out each answer and write it down. Għal dawn il-mistoqsijiet li ġejjin, għandek 5 sekondi biex taħdem
Meaningful Ways to Develop Math Facts
 NCTM 206 San Francisco, California Meaningful Ways to Develop Math Facts -5 Sandra Niemiera Elizabeth Cape mathtrailblazer@uic.edu 2 4 5 6 7 Game Analysis Tool of Game Math Involved in the Game This game
NCTM 206 San Francisco, California Meaningful Ways to Develop Math Facts -5 Sandra Niemiera Elizabeth Cape mathtrailblazer@uic.edu 2 4 5 6 7 Game Analysis Tool of Game Math Involved in the Game This game
Year 5 Maths Assessment Guidance - NUMBER Working towards expectations. Meeting expectations 1 Entering Year 5
 5.1.a.1 Count forwards and backwards with positive and negative whole numbers, including through zero (^) 5.1.a.2 Count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number to 1 000 000
5.1.a.1 Count forwards and backwards with positive and negative whole numbers, including through zero (^) 5.1.a.2 Count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number to 1 000 000
