Counting in multiples Page 8
|
|
|
- Jeremy King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Counting in multiples Page 8 1 a Add four Accept +4 b Add eight Accept +8 c Add fifty Accept a Missing numbers are: 60, 80, 100 b Missing numbers are: 300, 400, 600 c Missing numbers are: 24, 48, 56 d Missing numbers are: 20, 28, 32, , 30, 36, 42 1 a Add six Accept +6 b Add seven Accept +7 c Add twenty-five Accept +25 d Add one thousand Accept +1,000 2 a Missing numbers are: 84, 91 b Missing numbers are: 250, 275, 300 c Missing numbers are: 42, 48, 60, There is a pattern for multiples of 25. The tens and ones always end in (cycle through): 00, 25, 50 and 75. 5,175 ends in will not divide exactly by 7 so repeated adding of 7 will never generate a number that is divisible by is incorrect = 362 If 9 had been added, this would give = 360 The sequence would be correct. 1
2 Working with larger numbers Page 9 1 a < b < c > 2 a 904 b 522 c 299 d , 635, 563, 536, a > b < c > 2 9,934 3 a 7,564, 7,456, 6,864, 6,856, 6,845 b 9,030, 8,320, 7,435, 6,934, 5,932 c 8,953, 8,935, 8,593, 8,395, 8,359 1 a 8,742 The digits must be in order, largest first so they have the greatest place value. b 2,478 The digits must be in order, smallest first so they have the least place value. 2 Both numbers have five thousands, the next most significant digit is the value of the hundreds. In 5,841 the value of the hundreds is eight hundreds. In 5,481 the value of the hundreds is four hundreds. 5,841 > 5, , = 5,994 6, ,100 = 7,884 3, ,000 = 4,581 Only 4,581 has increased by 1,000. Only the thousands digit has increased by 1. 2
3 Place value Page 10 1 a four tens Accept 40 b four ones Accept 4 or four units c four hundred Accept , , a Four tens Accept 40 b Four hundred Accept 400 c Four thousand Accept 4, , ,847 4 a 34 b 97 c 66 1 Both numbers have four thousands, the next most significant digit is the value of the hundreds. In 4,825 the value of the hundreds is eight hundreds. In 4,258 the value of the hundreds is two hundreds. 4,825 > 4,258 2 The first two numbers have five thousands and seven hundreds, the next most significant digit is the value of the tens. In 5,734 the value of the tens is three tens or thirty. In 5,724 the value of the tens is two tens or twenty. 5,734 > 5,724 All three numbers have five thousands, the next most significant digit is the value of the hundreds. In 5,734 the value of the hundreds is seven hundreds. In 5,834 the value of the hundreds is eight hundreds. 5,736 < 5,834 3
4 3 Many possible answers, e.g. 8, , , , , ,953 4
5 Representing numbers Page , , 9 2 4, , ,600 1 a Correct, 3,200 is 32 hundreds. b Incorrect, 3,200 is 320 tens not 32 tens. c Correct, 3,200 is 3,200 ones. d Incorrect, 3,200 is 3,200 ones not 320 ones. 2 Many possible answers, e.g. 7, , , , , ,285 3 Dan has written the significant digits in the order that they have been written, instead of their value. The correct answer should be 8, Accept 215 5
6 Rounding numbers Page 12 1 a 80 b 570 c 5,090 2 a 800 b 3,100 c 8,000 d 2,200 3 a 8,000 b 4,000 c 10,000 d 12,000 1 a 40,900 b 7,000 c 54,900 2 a 9,000 b 63,000 c 40, ,000 1 Mia needs to look at the column to the right of the thousands column. 5,199 rounded to the nearest 1,000 would be 5,000. The 1 in the hundreds column tells you to round down. 2 The smallest number is 6,250. Any smaller number rounded to the nearest hundred would be 6, The largest number is 54, ,500 rounded to the nearest thousand would be 55,000. 6
7 Negative numbers Page 13 1 a 1 b 4 2 a 6 b 0 3 a 4 b 0 c 3 d 8 e 1, 2 f 9, 10 1 a 2, 4 b 10, 12 2 a 8, 10 b 15, o C 4 6 o C 5 4, 2, 0, 3, Addition can be done in any order, but subtraction cannot, so Ben is incorrect. 0 4 = = = = o C 4 6 m Ben dives 3 m from the board to the water and then another 3 m under the water. 3 m + 3 m = 6 m 7
8 Addition Page 14 1 a 630 b a 607 b 1,178 c 1,200 d 1, (rings) a 6,500 b 7,100 2 a 9,207 b 8, ,419 (rings) 4 14,133 1 a 192 b = 1,206 3 a 563 The largest total would be 797, this gives the missing number as 563. b 473 The smallest total would be 707, this gives the missing number as
9 Subtraction Page 15 1 a 190 b a 206 b 459 c 349 d (people) (t-shirts) 1 a 6,700 b 4,600 2 a 4,262 b 3,476 c 3, (pupils) 4 1, (passengers) 1 a 808 b 5, = a 636 The largest answer would be 394, this gives the missing number as 636. b 546 The smallest answer would be 304, this gives the missing number as
10 Checking addition and subtraction Page 16 1 a = 140 b = 70 c = a = 900 b = 700 c a = 236 Accept = 732 b = 818 c = 573 Accept = 293 d = a = 200 b = 1,600 2 a 7, ,000 = 13,000 b 9,000 4,000 = 5,000 3 a The calculation is incorrect. 9,719 5,443 = 4,276 Accept 9,719 4,376 = 5,343 b The calculation is correct. 8,663 1,467 = 7,196 Accept 8,663 7,196 = 1,467 c The calculation is incorrect. 5, ,184 = 8,037 1 Pat has added 8,654 and 3, Use the inverse to find the missing number. 4,000 2,500 = 1,500 The missing number is 1, a The calculation is incorrect. 3, ,491 = 5,828 The correct calculation is 5,728 2,491 = 3,237 b The calculation is incorrect. 8,351 4,736 = 3,615 Accept 8,351 3,625 = 4,726 10
11 The correct calculation is 3, ,736 = 8,361 11
12 Addition and subtraction problems Page (cards) 2 ( ) ( ) (km) 2 ( )3, , ,499 (seats) 1 1,250 and 3, ,500 3 The addition and subtraction values are unchanged and so the answer is not affected. The order is not important. (Unlike 4 3 and 3 4, where the values of the number being subtracted changes.) 4 2, , ,001 = 9,000 12
13 Multiplication and division facts Page
14 a 240 b 2,400 c 2,400 d 4 e Accept any two numbers that multiply to 48, e.g
15 Multiplying mentally Page 19 1 a 1 b 0 c 0 d 11 e 1 2 a 5 b 2 3 a 48 b 17 1 a 20 b 12 c 6 d 96 2 a 16 b 50 c 8, 12 3 a 6 b 6 c 6 d Accept any two numbers that multiply to 24, e.g. 1 24, 2 12, 3 8, 4 6, , or a 7 b 14 c 21 d 28 15
16 a 5 b 50 c 500 d 5,000 e 50,000 5 = 10,000 16
17 Written methods of multiplication Page , , = 1, = 3, = 1,506 so Tom is not correct = 3, is one more eight than so = 1, = 1, = = 2, = 1,440 1,440 2 = 2,880 Doubling 360 three times and multiplying 360 by 8 both give the same answer. 17
18 Multiplication problems Page 21 1 ( ) (kg) (km) 4 a 1 12, 2 6, 3 4 b 1 20, 2 10, ( )35 6 ( ) (minutes) 2 2,100 (ml) 3 40, 6 4 a 1 32, 2 16, 4 8 b 1 48, 2 24, 3 16, 4 12, a 550 (g) b 825 (g) 1 1,175 (counters) (counters) 3 There are different possible answers, e.g. 2 t-shirts and 7 pairs of shorts 4 t-shirts and 4 pairs of shorts 6 t-shirts and 1 pair of shorts. 4 2,400 (ml) 18
19 Hundredths Page a 7, , b a b c 2 a b c 3 a b , Accept , c and d indicated only. 3 a b 10 c 100 d and are the same. 100 Accept diagrams, finding 1 and 10 are the same or of a number or equivalent or simplified fractions as a way of explaining
20 Equivalent fractions Page a 2 b 10 1 a 2 b 8 c 4 d 3 2 6, 12, 10, 18 3 a 21 b 21 1 Accept any three fractions equivalent to 3 4, e.g. 6 8, 9 12, 12 16, a > because 7 3 2, 32 b > because 7 = = and > and > Accept any three fractions equivalent to 2 5, e.g. 4 10, 6 15, 8 20,
21 Adding and subtracting fractions Page 24 1 a b c 2 a b c = = = a b c d = Accept either answer if given alone. e f Max has added the denominators. Any denominator could be used, e.g = 7 = a 4 b 3 3 Yes, Polly is correct. You only add the numerators, the denominators only name the fraction for addition and subtraction. 21
22 Finding fractions Page 25 1 Any 2 sections shaded. 2 Any 2 sections shaded. 3 3 (litres) 4 ( ) (children) (calculations) 6 12 (boys) (counters)
23 Fraction and decimal equivalents Page 26 1 a i b i c i d i e i f i g i h i ii 0.5 ii 0.25 ii 0.75 ii 0.5 ii 0.5 ii 0.1 ii 0.9 ii a b a 0.57 b a 1.3 b , has a whole number, but 1 is a part of one whole is is equivalent to Dan has used 0.4, this is equivalent to is equivalent to. 10 Dan is incorrect. 5 Accept solutions for which the sum of the fractions is equivalent to
24 Rounding decimals Page a 6 b 33 c 100 d 73 e (litres) 3 30 (kg) 1 a 14.5 b or = (metres) 24
25 Comparing decimals Page 28 1 a < b > c < d < 2 a 2.5, 8.8, 15.1 b 12.8, 13.8, 14.8 c 3.56, 35.6, 356 d 29.7, 77.6, a > b > c < 2 a 2.98, 5.67, 6.54 b 19.79, 20.09, a 45.5 kg, 45.7 kg, 46.1 kg b 4.68 m, 4.74 m, 4.76 m m 1 Accept any number >5,61, <5.7, e.g Both numbers have 1 ten, 12.1 has 2 ones, 11.9 has only 1 one must be the larger number. 3 Dan has put 4.5 as the smallest number. 4.5 is the largest number. 4 The number of digits in a number is not important, Gail needs to think about the value of the digits has 1 ten and 3 ones has 1 ten and 2 ones, so is the smaller number. 25
26 Dividing by 10 and 100 Page 29 1 a 0.05 b 0.12 c 0.06 d 0.8 e 0.42 f (litres) Accept 300 (millilitres) 3 ( )0.40 Accept 40(p) 1 a 0.57 b 0.08 c (kg) 3 No, ( )4 100 = ( )0.04 or 4(p) There are no 4p coins. 4 a 10 b 1 c Accept any number greater than 5.6 but less than 6, e.g Accept any number greater than 60 but less than 70, e.g ,001 indicated only. 5 Ayesha is correct = 0.1, = =
27 Decimal problems Page 30 1 a 10.5 b 1.9 c 73.9 d 42.5 e f ( )3.04, ( )3.40, ( )4.03, ( ) ( ) ( )10 1 a b c (m), 2.62 (m), 3 (m), 3.57 (m), 3.75 (m) 3 ( ) a 18.9 (m) b 55 (kg) 1 Accept a reasonable explanation showing an understanding the calculation is incorrectly set out, e.g. The columns have not been used correctly. The decimal points should be in a row. The value of the digits do not match in the columns = 1.5 (m) 3 Answers will vary. Accept any reasonable explanation. 27
28 Comparing measures Page (m) (kg) 3 5,000 (ml) 4 ( ) (m), 7.5 (m), 8 (m) 6 4 (kg), 3.75 (kg), 3.7 (kg) 1 8 (l) 2 ( ) (m), 7.25 (m), 6.75 (m), 6 (m), 5.25 (m) (kg), 11.8 (kg), (kg), 12.5 (kg), 14 (kg) 5 a < b < c > 1 Ali is incorrect. 3,350 (g) is 3.35 (kg) which is not between 3.4 (kg) and 3.5 (kg) or 3.4 (kg) is 3,400 (g) and 3.5 (kg) is 3,500 (g) and 3,350 (g) does not come between them. 2 5 (m) is shorter than 650 (cm) but not for the reason Zak gives. The value of the digits alone is not important, the value must be linked to the units of measure. 3 All the measures must be in the same units, e.g. all metres (m). 3 km = 3,000 (m) 2,500 (m) 2,500 (cm) = 25 (m) When the units are the same use place value to compare the numbers: 3,000 (m) / 3 (km) is the longest. 4 The scales show 500 (g) is heavier than 2 (kg). This is incorrect. 2 (kg) = 2,000 (g) and is heavier than 500 (g) OR 500 (g) is 0.5 (kg) and is lighter than 2 (kg) 28
29 Estimate measures Pages a Bag of sugar 1,000 (g) b Orange 200 (g) c Bag of crisps 30 (g) d Ketchup 500 (g) 2 a Bucket 12 (litres ) b Can 330 (millilitres) c Bottle 500 (millilitres) d Petrol can 5 (litres) 3 Accept any weight, in grams, greater than 2,000 (g) but less than 3,000 (g) (g) 5 80 (litres) 6 2 (m) (kg) (ml) (cm) (cm) 2 1 litre bottle of water 3 The length of a football field 4 A mug 5 > 1 litre 6 < 20 litres 7 > 50 mm 8 > 100 grams 1 Kira is correct. A car is between 4 and 5 metres long metres is about twice this length. 2 Ben s idea is correct. A door is about 2 metres. 6 or 7 rulers would be 180 centimetres to 210 centimetres. 29
30 3 Samir s idea is incorrect. 2 litres is 2,000 millilitres. If Samir fills 40 glasses, each glass is holding 50 millilitres not 500 millilitres. 4 Jenny s idea is incorrect. A car weighs about 1,500 to 2,000 kilograms, much more than the mass of 5 suitcases (100 kg). 5 Count number of paces for the length of the school playground. Multiply the number of paces by the length of one pace. 30
31 12-hour clock Pages a 2:00 a.m. b 5:30 p.m. c 6:45 p.m. d 1:40 a.m. 2 a 8:15 a.m. b 7:05 p.m. c 2:10 p.m. 3 a Hands showing 5:15, minute hand longer than the hour hand. Allow some inaccuracy. b Hands showing 11:30, minute hand longer than the hour hand. Allow some inaccuracy. c Hands showing 11:00, minute hand longer than the hour hand. Allow some inaccuracy. 1 a i twenty past two Accept 20 past 2 ii 2:20 a.m. b i quarter past 6 Accept 1 past 6 4 ii 6:15 p.m. c i twenty to two Accept 20 to 2 ii 1:40 p.m. d i half past eleven Accept 1 past 11 2 ii 11:30 p.m. e i ten past two Accept 10 past 2 ii 2:10 p.m. f i five past nine Accept 5 past 9 ii 9:05 a.m. 2 a quarter past three in the afternoon Accept 1 4 past 3 b ten to eight in the evening Accept 10 to 8 3 a 10:40 a.m. b 6:05 p.m. 1 12:10 p.m. 2 Harry has used a.m. but he should use p.m. for a time in the evening (minutes) 4 a Correct b 9:30 p.m. = half past nine in the morning indicated. The correct time should be 9:30 in the evening. c Correct d 7:50 a.m. = ten to seven in the morning indicated. 31
32 The correct time should be ten to eight in the morning. 5 If the time is 7:70, this would mean 70 minutes past 7. There are only 60 minutes in an hour so the time has moved 10 minutes past 8 o clock. The correct finishing time is 8:10 p.m. 32
33 24-hour time Pages a 07:30 a.m. b 3:15 p.m. c 8:20 p.m. d 02:00 a.m. e 11:55 a.m. 2 a 17:05 b 04:55 c 15:30 d 13:45 e 22:20 1 a i ten past nine Accept 10 past 9 ii 09:10 b i ten past six Accept 10 past 6 ii 18:10 c i half past four Accept 1 past 4 2 ii 16:30 d i five to two Accept 5 to 2 ii 01:55 e i twenty-five to twelve Accept 25 to 12 ii 23:35 f i eight o clock Accept 8 o clock ii 08:00 2 a i quarter to 7 Accept 1 to 7 ii 06:45 4 b i twenty-five past nine Accept 25 past 9 ii 21:25 c i twenty to three Accept 20 to 3 ii 02:40 d i ten to eight Accept 10 to 8 ii 19:50 1 Ben is correct. 14:50 is 2:50 p.m. 2 In 24-hour time, the time 24:15 does not exist as only 24 hours (the length of 1 day) are used. 24:15 should be recorded as 00:15. 3 Bess is incorrect. 35 minutes past 4 means 25 minutes to 5. 16:35 is closer to 5 p.m. than 4 p.m. 4 a Correct b Incorrect 33
34 The correct time is 10:40. c Incorrect 24-hour time uses 4 digits so the correct time is 08:40. d Correct 5 There are a number of possible answers. The digits should total 15, e.g. 23:55 22:36 21:57 34
35 Converting time Page (seconds) (minutes) 3 48 (hours) 4 14 (days) 5 48 (months) (minutes) (seconds) (months) 1 42 (days) (days) 3 30 (seconds) 4 12 (hours) 5 6 (months) (years) 7 12 (months) 8 31 (days) 1 3,600 (seconds) = 52 r 1 There are 52 weeks and 1 day in a year. Accept = 52 r 2 There are 52 weeks and 2 days in a leap year (days) 35
36 Calculating with time Page 39 1 a 45 (minutes) b 40 (minutes) c 1 hour 15 minutes Accept 75 (minutes) 2 a 17:25 b twenty past eight (in the evening) 3 a 10:10 b 1:55 p.m. c ten to twelve in the morning Do not accept ten to twelve in the afternoon. 1 a 1 hour 25 minutes b 1 hour 40 minutes 2 a Twenty-five to nine in the evening b 14:45 3 a 19:55 b Quarter past ten in the morning 4 6:45 a.m. 1 a Accept 5 minutes = 300 seconds or 5 hours = 300 minutes b 5 weeks = 35 days 2 There are only 60 minutes in an hour. Once 60 minutes have passed a new hour is reached. The correct answer is 11:05. 3 Change the units to minutes: 600 seconds = 10 minutes 1 5 of an hour = 12 minutes The missing number of minutes is 11 (minutes). 36
37 Converting units of measure Pages a 20 (mm) b 60 (mm) c 80 (mm) 2 a 3,000 (g) b 6,000 (g) c 8,500 (g) 3 a 2,000 (ml) b 3,000 (ml) c 4,500 (ml) 4 3,000 (metres) 1 a 4 (m) b 5,000 (ml) c 6 (kg) d 10 (cm) e 8,000 (m) 2 1,600 (grams) 3 74 (centimetres) 4 1,650 (millilitres) 5 1,250 (metres) 6 17 cm 1 1,000 (millimetres) 2 No 3 No 80 cm 8 = 640 cm 5 m = 500 cm 640 cm > 500 cm 3 l = 3,000 ml 1 1 l = 1,500 ml 2 1,500 ml ml ml = 3,100 ml 37
38 3,000 ml < 3,100 ml (g) 5 No 5 km = 5,000 m 1,000 m takes 3 minutes, so 5,000 m would take (3 minutes 5) = 15 minutes 15 minutes > 10 minutes 38
39 Calculating with money Page 42 1 a ( )6.82 b ( )6.87 c ( )29.20 d ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) a ( )7.97 b ( )6.79 c An adult ticket to Leeds. 1 There are several possible answers, e.g. 1, 10p, 10p, 10p, 10p, 10p 50p, 50p, 20p, 20p, 5p, 5p 2 ( )105 3 Yes ( ) = ( )15 ( ) = ( )13 ( )15 + ( )13 = ( )28 ( )28 < ( )30 4 There are several possible answers, e.g. ( )20, ( )20, ( )20, ( )10, ( )5, ( )5 ( )20, ( )20, ( )10, ( )10, ( )10, ( )10 39
40 Calculating with measures Page 43 1 a 9.6 (m) b 0.7 (km) c 8.2 (kg) d 14.8 (cm) (kg) (km) (l) (kg) 1 a 86.3 (m) b 43.9 (mm) c 1,000.6 (kg) d (km) (kg) (l) (kg) 1 Nia is correct. 2 l = 2,000 ml 300 ml 6 = 1,800 ml 2,000 ml > 1,800 ml 2 No 0.5 m 10 = 5 m 5 m > 4 m (m) 4 60 cm and 40 cm Accept 0.6 m and 0.4 m 40
41 Perimeter Pages a 22 (cm) b 18 (cm) c 24 (cm) d 34 (cm) e 28 (cm) f 56 (cm) 2 a 28 (cm) b 48 (cm) c 60 (cm) 3 50 (cm) 1 a 26 (cm) b 30 (cm) c 44 (cm) d 60 (cm) e 100 (cm) 2 32 (cm) 3 80 (cm) 4 a 18 (cm) b 20 (cm) c 20 (cm) 1 12 (cm) 2 48 (cm) 3 A length is two widths. The perimeter is made up of 6 widths. 12 (cm) 6 = 2 (cm) 2 (cm) 2 = 4 (cm) 4 Accept 9 (cm) 1 (cm) 8 (cm) 2 (cm) 41
42 7 (cm) 3 (cm) 6 (cm) 4 (cm) 5 (cm) 5 (cm) Accept answers with decimals and fractions if correct. 5 No Accept a counter-example, e.g. A rectangle 4 cm long and 2 cm wide has a perimeter of 12 cm. 12 is an even number. 42
43 Area Pages (cm 2 ) 2 10 (cm 2 ) 3 12 (cm 2 ) 4 12 (cm 2 ) 5 21 (cm 2 ) 6 16 (cm 2 ) 7 13 (cm 2 ) 8 20 (cm 2 ) 9 25 (cm 2 ) (cm 2 ) 1 8 (cm 2 ) 2 16 (cm 2 ) 3 10 (cm 2 ) 4 16 (cm 2 ) 5 12 (cm 2 ) 6 12 (cm 2 ) 7 14 (cm 2 ) 8 13 (cm 2 ) 9 10 (cm 2 ) (cm 2 ) 1 Accept rectangles with these lengths and widths in either order: 12 (cm) 1 (cm) 6 (cm) 2 (cm) 4 (cm) 3 (cm) Do not accept answers using decimals or fractions. 2 5 (cm) 3 27 (cm 2 ) 4 26 (cm 2 ) 5 7 (cm) 43
44 Compare and classify 2-D shapes Pages a and b 2 a and e 3 c and d 1 b and c. 2 scalene triangle obtuse-angled triangle 3 a and d 4 octagon 5 parallelogram, kite 6 square, rectangle 7 a and d 1 It is a square because it has 4 right angles and all sides are equal. The position of a shape does not affect its properties. 2 Yes All obtuse-angled triangles have an angle larger than a right angle. 3 A rhombus is an irregular shape because its angles are not all equal. 4 a always true b sometimes true When a rectangle is a square, its diagonals will cross at right angles. 44
45 Symmetry Pages rectangle A and B trapezium D isosceles triangle G 2 a b c 1 a 2 b 0 c 0 d 1 e 2 2 a rectangle b pentagon c kite d rectangle e triangle (isosceles and acute-angled) 1 No A rectangle only has two lines of symmetry; its diagonals are not lines of symmetry. 2 No If the shape was folded along the dotted line, the two halves would not fit exactly over each other. 3 Sometimes true 4 Sometimes true (equilateral triangles have 3 lines of symmetry)
46 Angles Pages a 4 b 5 c 3 2 A three-quarter turn 3 a Greater than a right angle b Less than a right angle c Less than a right angle d A right angle e Greater than a right angle f Less than a right angle 1 a 2 b 3 c, a, b 4 a and c 5 a and c Yes Two right angles make a straight angle. An obtuse angle is greater than a right angle, but less than a straight angle. 3 Sometimes true Two smaller acute angles may be less than a right angle, but two larger acute angles could be larger than a right angle. 4 Never true Every obtuse angle is greater than a right angle, so two obtuse angles must always be greater than two right angles. 5 No An obtuse angle alone is always greater than a right angle so could not be used to make a right angle. 46
47 Coordinates Pages a A (2, 9) b B (8, 6) c C (3, 4) d D (9, 2) e E (4, 8) 2 a Point F drawn at (9, 8) b Point G drawn at (1, 2) c Point H drawn at (6, 1) d Point I drawn at (5, 6) e Point J drawn at (7, 9) 1 a A (5, 2) b B (3, 4) 2 a Point C drawn at (1, 3) b Point D drawn at (4, 5) 3 (2,4) 4 (4, 2) 5 (2, 3) or (3, 4) or other fractional coordinates 6 (2, 3) 7 Accept any of: (1, 5) (5, 5) Any coordinate with an x-coordinate of 3, except (3, 1). Also accept: (1, 3) (5, 3) 1 (12, 13) 2 (13, 12) 3 (13, 22) and (21, 22) or (13,18) and (21,18) 4 (20, 26) and (23, 26) or (20, 20) and (23, 20) 47
48 5 (14, 14) and (20, 17) 48
49 Translations Pages a 2 right, 2 up b 5 right, 1 down c 2 left, 3 down d 3 left, 4 up e 7 right, 1 up 2 a E to F b F to H c G to E d G to F e H to E 1 a 3 left, 2 down b 7 right, 3 down c 4 left, 1 up d 4 up Accept 0 right, 4 up OR 0 left, 4 up e 7 left, 1 down 2 a d c E a b d 3 The shape will stay in the same position. 1 Ben is incorrect. There is no reason why a shape cannot sit on another. The shape has just moved. 2 Nia has probably looked at the space between the two shapes. Nia should focus on one vertex, not the space between them. 49
50 (The correct translation is 2 right, 2 down.) 3 3 left, 4 up 4 (6, 15) 5 (6, 5) 50
51 Pictograms Pages a 4 (letters) b c d e 10 (letters) Monday and Friday 4 (letters) 8 (letters) 2 School dinners represents 2 children Hot meal Salad Sandwich Pack lunch Home dinner Accept inaccuracies in drawing the symbols. 1 a Ben, Gus, Dev b c 30 (km) 50 (km) 2 a ( )5,000 b Beth and Gary c ( )34,000 1 a 10 (people) b 15 (people) 2 Accept any reasonable answer and explanation, e.g. Symbol = 2 (km) All the distances are even numbers. Symbol = 4 (km) All the distances are multiples of 4. 3 a 20 (symbols) b Max should realise that it s not possible to have half a person. 51
52 4 Sunny days June 15 July 25 August 10 In the pictogram, June shows 3 sun symbols and in the table June shows = 5 1 sun symbol represents 5 sunny days. July: August: 5 sun symbols 5 = 25 days 2 sun symbols 5 = 10 days 52
53 Bar charts Pages a 30 b 25 Accept c 15 Accept d 10 Accept 8 12 e 2 (girls) noon to 3:00 p.m. 2 a 60 (visitors) b 90 (visitors) c 30 (visitors) 3 60 (visitors) 4 30 (visitors) (visitors) 6 equal to 1 Accept any reasonable explanation, e.g. There are fewer visitors in the afternoon, so it may be a good idea. It depends how much it costs to keep the castle open longer. 2 Accept any reasonable explanation, e.g. It s not possible to tell exactly when visitors arrived only the period they arrived in. 3 Yes 53
54 There were 180 visitors for the whole day and 90 arrived between 12 noon to 3:00 p.m. 90 = It is not a fair comparison because it is a longer period of time after 12 noon. 5 Ayesha would be in the bar showing 12 noon to 3:00 p.m. because she arrived between those times. 54
55 Time graphs Pages ( C) 2 15 ( C) 3 20 ( C) 4 10 ( C) 5 The temperature stayed the same (cm) Accept 18 (cm) to 22 (cm) 7 80 (cm) Accept 78 (cm) to 82 (cm) 8 3 (weeks) Accept 19 (days) to 23 (days) 9 7 (weeks) Accept 47 (days) to 51 (days) 10 2 (weeks) Accept 12 (days) to 26 (days) 1 8:20 a.m. Accept 8:20, 08:20, twenty past eight, 20 past 8 Do not accept 8:20 p.m (m) 3 5 (minutes) (m) 5 5 (minutes) (m) (m) 8 5 (minutes) 9 25 (minutes) (minutes) 1 The temperature stayed the same. 2 Between Week 5 and Week 6. The growth slowed down. 3 You cannot tell. The plant may have continued growing after Week 8 as the graph shows it was continuing to grow up to Week 8. 4 The line is steeper. A steep line shows that Ari walked a further distance in the same period of time and so was walking faster. 55
56 5 Ari walked 500 metres in 5 minutes at his fastest. If he walked 700 metres at the same pace it would have taken him 7 minutes. 56
57 Tables Page 64 1 Moto 2 2 (cars) 3 39 (vans) 4 25 (vehicles) 5 7 (cars) 1 22 (children) 2 16 (boys) 3 22 (girls) 4 26 (children) 5 48 (children) 1 True The number of men who visited in the afternoon (p.m.) is is double False The number of children who visited in the morning (a.m.) is is three times False The total number of visitors is
Counting in 4s, 8s, 50s and 100s Page 8
 Counting in 4s, 8s, 50s and 100s Page 8 1 Add 2 2 Add 10 3 Add 3 4 10, 30, 35 5 52, 62, 102 6 31, 51, 61 1 12, 16, 20 2 24, 32, 48 3 300, 400, 600 4 75 5 350 6 14 1 Horizontal row: 12 / Vertical column:
Counting in 4s, 8s, 50s and 100s Page 8 1 Add 2 2 Add 10 3 Add 3 4 10, 30, 35 5 52, 62, 102 6 31, 51, 61 1 12, 16, 20 2 24, 32, 48 3 300, 400, 600 4 75 5 350 6 14 1 Horizontal row: 12 / Vertical column:
Day 1. Mental Arithmetic Questions KS3 MATHEMATICS. 60 X 2 = 120 seconds. 1 pm is 1300 hours So gives 3 hours. Half of 5 is 2.
 Mental Arithmetic Questions. The tally chart shows the number of questions a teacher asked in a lesson. How many questions did the teacher ask? 22 KS MATHEMATICS 0 4 0 Level 4 Answers Day 2. How many seconds
Mental Arithmetic Questions. The tally chart shows the number of questions a teacher asked in a lesson. How many questions did the teacher ask? 22 KS MATHEMATICS 0 4 0 Level 4 Answers Day 2. How many seconds
Properties of Numbers
 Properties of Numbers 1. Write the number twelve thousand and forty-eight in figures. 2. Round two hundred and thirty-five to the nearest ten. 3. Which of these numbers is not a multiple of eight? Fifty-four,
Properties of Numbers 1. Write the number twelve thousand and forty-eight in figures. 2. Round two hundred and thirty-five to the nearest ten. 3. Which of these numbers is not a multiple of eight? Fifty-four,
Year 9 mathematics: holiday revision. 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four?
 DAY 1 ANSWERS Mental questions 1 Multiply seven by seven. 49 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four? 54 9 = 6 6 3 What number should you add to negative three to get the answer five? -3 0 5 8 4 Add two
DAY 1 ANSWERS Mental questions 1 Multiply seven by seven. 49 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four? 54 9 = 6 6 3 What number should you add to negative three to get the answer five? -3 0 5 8 4 Add two
Stage 2 PROMPT sheet. 2/3 Estimate numbers. 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables. 2/4 Order numbers. Count in 10s.
 Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x 2 = 12 7 x 2 = 14 8 x
Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x 2 = 12 7 x 2 = 14 8 x
Stage 2 PROMPT sheet. 2/3 Estimate numbers. 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables. 2/4 Order numbers. 2/2 Place value
 tens units tens units Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x
tens units tens units Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x
Sample Pages. out of 17. out of 15. a $1.15 b $0.85. a 4280 b 2893 c 724. a Which of these are odd? b Which of these are even?
 1:1 out of 15 1:2 out of 17 7 + 8 13 4 12 9 3 3 4 2 9 plus 5. 8 + 6 4 groups of 5. 1 8 + 1 1 1 5 4 12 + 7 9 2 16 + 4 7 4 10 7 17 subtract 7. 11 6 20 minus 12. 6 7 + 2 2 7 9 4 3 Write these numbers on the
1:1 out of 15 1:2 out of 17 7 + 8 13 4 12 9 3 3 4 2 9 plus 5. 8 + 6 4 groups of 5. 1 8 + 1 1 1 5 4 12 + 7 9 2 16 + 4 7 4 10 7 17 subtract 7. 11 6 20 minus 12. 6 7 + 2 2 7 9 4 3 Write these numbers on the
Hyde Community College
 Hyde Community College Numeracy Booklet 1 Introduction What is the purpose of this booklet? This booklet has been produced to give guidance to pupils and parents on how certain common Numeracy topics are
Hyde Community College Numeracy Booklet 1 Introduction What is the purpose of this booklet? This booklet has been produced to give guidance to pupils and parents on how certain common Numeracy topics are
Year 4. Term by Term Objectives. Year 4 Overview. Autumn. Spring Number: Fractions. Summer. Number: Addition and Subtraction.
 Summer Overview Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement:
Summer Overview Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement:
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy
 The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
Test B. Calculator allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. DfE no. KEY STAGE LEVELS
 Ma KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 Mathematics test Test B Calculator allowed First name Last name School DfE no. 2011 For marker s use only Page Marks 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 TOTAL These three children appear
Ma KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 Mathematics test Test B Calculator allowed First name Last name School DfE no. 2011 For marker s use only Page Marks 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 TOTAL These three children appear
Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths. Mark schemes
 Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths Mark schemes Introduction This booklet contains the mark schemes for the higher tiers tests (Tests A and B) and the lower tier test (Test C). The
Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths Mark schemes Introduction This booklet contains the mark schemes for the higher tiers tests (Tests A and B) and the lower tier test (Test C). The
Write down all the factors of 15 Write down all the multiples of 6 between 20 and 40
 8th September Convert 90 millimetres into centimetres Convert 2 centimetres into millimetres Write down all the factors of 15 Write down all the multiples of 6 between 20 and 40 A printer prints 6 pages
8th September Convert 90 millimetres into centimetres Convert 2 centimetres into millimetres Write down all the factors of 15 Write down all the multiples of 6 between 20 and 40 A printer prints 6 pages
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests
 Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests 1 Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests 1 Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Mathematics. Stage 7
 Mathematics Stage 7 V These tables give general guidelines on marking answers that involve number and place value, and units of length, mass, money or duration. If the mark scheme does not specify the
Mathematics Stage 7 V These tables give general guidelines on marking answers that involve number and place value, and units of length, mass, money or duration. If the mark scheme does not specify the
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests
 Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics tests KEY STAGE LEVEL. First name. Middle name. Last name. Date of birth Day Month Year.
 Ma KEY STAGE 2 Mathematics tests LEVEL 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Middle name 2013 Last name Date of birth Day Month Year School name DfE number 1 A box of crisps contains three different
Ma KEY STAGE 2 Mathematics tests LEVEL 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Middle name 2013 Last name Date of birth Day Month Year School name DfE number 1 A box of crisps contains three different
These tests contain questions ranging from Level 2 to Level 4. They get progressively more difficult. Children should have five seconds to
 These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. They get progressively more difficult. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test and ten seconds to answer questions.
These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. They get progressively more difficult. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test and ten seconds to answer questions.
These tests contain questions ranging from Level 2 to Level 3. Children should have five seconds to answer questions 1 3 in each test,
 These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test, ten seconds to answer questions and fifteen seconds to answer questions -.
These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test, ten seconds to answer questions and fifteen seconds to answer questions -.
4 One ticket costs What will four tickets cost? 17.50
 TOP TEN Set X TEST 1 1 Multiply 6.08 by one thousand. 2 Write one quarter as a decimal. 3 35% of a number is 42. What is 70% of the number? 4 One ticket costs 17.50. What will four tickets cost? 17.50
TOP TEN Set X TEST 1 1 Multiply 6.08 by one thousand. 2 Write one quarter as a decimal. 3 35% of a number is 42. What is 70% of the number? 4 One ticket costs 17.50. What will four tickets cost? 17.50
S1/2 Checklist S1/2 Checklist. Whole Numbers. No. Skill Done CfE Code(s) 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting
 Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
These are some times as shown on a digital clock. Draw a circle around the two times that could be the same as the clock.
 GM3 End-of-unit Test 1 a This is the time as shown on a clock. These are some times as shown on a digital clock. Draw a circle around the two times that could be the same as the clock. 12:09 09:00 19:00
GM3 End-of-unit Test 1 a This is the time as shown on a clock. These are some times as shown on a digital clock. Draw a circle around the two times that could be the same as the clock. 12:09 09:00 19:00
Using column addition, keep the decimal points aligned one beneath the other to keep the correct place value of the digits.
 Q1-5. Using column addition, keep the decimal points aligned one beneath the other to keep the correct place value of the digits. Q1. 1. 6 3 8. 2 + 3. 2 5 4 3. 0 5 [1.6 + 38.2 + 3.25 = 43.05] Q2. 0. 1
Q1-5. Using column addition, keep the decimal points aligned one beneath the other to keep the correct place value of the digits. Q1. 1. 6 3 8. 2 + 3. 2 5 4 3. 0 5 [1.6 + 38.2 + 3.25 = 43.05] Q2. 0. 1
ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS TERM 1: 2012 EXEMPLAR MEMORANDUM
 ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS TERM : 0 EXEMPLAR MEMORANDUM GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS TERM : 0 EXEMPLAR MEMORANDUM COUNT FORWARDS AND BACKWARDS IN DECIMALS TO AT LEAST DECIMAL PLACES.. C. C.
ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS TERM : 0 EXEMPLAR MEMORANDUM GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS TERM : 0 EXEMPLAR MEMORANDUM COUNT FORWARDS AND BACKWARDS IN DECIMALS TO AT LEAST DECIMAL PLACES.. C. C.
Percentage means, a 'number over 100'. For example: 16% = 16 5% = 5 12% = 12 35% =
 Q1. [0.2 0.2 = 0.04] The skill you need here is multiplications of decimal numbers. Count the total number of decimal places in the two numbers. Your answer should also have the same number of decimal
Q1. [0.2 0.2 = 0.04] The skill you need here is multiplications of decimal numbers. Count the total number of decimal places in the two numbers. Your answer should also have the same number of decimal
Topic. Easter Intervention. If you have any questions, feel free to
 Easter Intervention Foundation Questions Topic Angles Transformations Multiples, Factors, Primes Indices Algebra Area and Perimeter Factions, Decimals and Percentages Ratio Equations Probability Averages
Easter Intervention Foundation Questions Topic Angles Transformations Multiples, Factors, Primes Indices Algebra Area and Perimeter Factions, Decimals and Percentages Ratio Equations Probability Averages
Mark schemes for Mental mathematics Tests A, B and C
 Ma KEY STAGE LOWER TIER & HIGHER TIERS 004 Mathematics tests Mark schemes for Mental mathematics Tests A, B and C 004 First published in 004 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 004 Reproduction, storage,
Ma KEY STAGE LOWER TIER & HIGHER TIERS 004 Mathematics tests Mark schemes for Mental mathematics Tests A, B and C 004 First published in 004 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 004 Reproduction, storage,
First Name. Last Name. School MATHEMATICS LEVELS 3 5 KEY STAGE TEST A PAGE TOTAL MARKS CALCULATOR NOT ALLOWED
 MATHEMATICS KEY STAGE 2 2003 TEST A LEVELS 3 5 CALCULATOR NOT ALLOWED PAGE 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 TOTAL MARKS First Name Last Name School Instructions You may not use a calculator to answer any questions
MATHEMATICS KEY STAGE 2 2003 TEST A LEVELS 3 5 CALCULATOR NOT ALLOWED PAGE 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 TOTAL MARKS First Name Last Name School Instructions You may not use a calculator to answer any questions
Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers
 LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Grade 04
 Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Reigate Grammar School. 11+ Entrance Examination January 2012 MATHEMATICS
 Reigate Grammar School + Entrance Examination January 0 MATHEMATICS Time allowed: 45 minutes NAME Work through the paper carefully You do not have to finish everything Do not spend too much time on any
Reigate Grammar School + Entrance Examination January 0 MATHEMATICS Time allowed: 45 minutes NAME Work through the paper carefully You do not have to finish everything Do not spend too much time on any
Year 5 Maths Assessment Guidance - NUMBER Working towards expectations. Meeting expectations 1 Entering Year 5
 5.1.a.1 Count forwards and backwards with positive and negative whole numbers, including through zero (^) 5.1.a.2 Count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number to 1 000 000
5.1.a.1 Count forwards and backwards with positive and negative whole numbers, including through zero (^) 5.1.a.2 Count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number to 1 000 000
Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme
 Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme Every student is assigned to a Stage, based on their academic year and assessed study level. Stage 2 students are approximately 8 to 10 years old. The sheets
Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme Every student is assigned to a Stage, based on their academic year and assessed study level. Stage 2 students are approximately 8 to 10 years old. The sheets
First Practice Test 2 Levels 3-5 Calculator allowed
 Mathematics First Practice Test 2 Levels 3-5 Calculator allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need: pen,
Mathematics First Practice Test 2 Levels 3-5 Calculator allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need: pen,
First Name: Last Name: Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator in completing this packet.
 5 Entering 5 th Grade Summer Math Packet First Name: Last Name: 5 th Grade Teacher: I have checked the work completed: Parent Signature Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator
5 Entering 5 th Grade Summer Math Packet First Name: Last Name: 5 th Grade Teacher: I have checked the work completed: Parent Signature Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator
MATHS REVISION GRADE 6. 1.(a) x 1000 = (b) ( 4 x 9 ) = 6. c) 2/9 + 8/9 = (d) What is 2/3 of 78? g) ¼ 3 = (h) =
 MATHS REVISION GRADE 6 NAME 1.(a) 5.9 10 x 1000 = (b) ( 4 x 9 ) = 6 c) 2/9 + 8/9 = (d) What is 2/3 of 78? e) 9/10 2/5 = (f) 5 x ¾ = g) ¼ 3 = (h) 17.39 6.8 = i) 25% of 460 = (j) Place value of 6 in 23.56
MATHS REVISION GRADE 6 NAME 1.(a) 5.9 10 x 1000 = (b) ( 4 x 9 ) = 6 c) 2/9 + 8/9 = (d) What is 2/3 of 78? e) 9/10 2/5 = (f) 5 x ¾ = g) ¼ 3 = (h) 17.39 6.8 = i) 25% of 460 = (j) Place value of 6 in 23.56
w = 17 1st March What fraction of the rectangle is not shaded? In this rectangle,! is shaded purple is shaded green.
 1st March 6 7 2 In this rectangle,! is shaded purple!!! is shaded green. What fraction of the rectangle is not shaded? w = 17 Work out 6w + 7 The volume of the cube and the cuboid are equal. Find the length
1st March 6 7 2 In this rectangle,! is shaded purple!!! is shaded green. What fraction of the rectangle is not shaded? w = 17 Work out 6w + 7 The volume of the cube and the cuboid are equal. Find the length
What must be added to 60 to make one hundred? What is seventy minus forty?
 2.1 1. How many groups of ten can be made out of 100 marbles? 2.2 2. Order these numbers starting with the smallest: 49, 27, 17, 34 2.2 3. Write the number one hundred and nineteen in digits. 2.3 4. Write
2.1 1. How many groups of ten can be made out of 100 marbles? 2.2 2. Order these numbers starting with the smallest: 49, 27, 17, 34 2.2 3. Write the number one hundred and nineteen in digits. 2.3 4. Write
Introduction. It gives you some handy activities that you can do with your child to consolidate key ideas.
 (Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
(Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
What must be added to 30 to make one hundred? =
 2.1 1. How many groups of ten can be made out of 70 marbles? 2.2 2. Order these numbers starting with the smallest: 30, 17, 12, 23 2.2 3. Write the number two hundred and seven in digits. 2.3 4. Write
2.1 1. How many groups of ten can be made out of 70 marbles? 2.2 2. Order these numbers starting with the smallest: 30, 17, 12, 23 2.2 3. Write the number two hundred and seven in digits. 2.3 4. Write
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM MATHEMATICS
 THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 8 January 2016 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 8 January 2016 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
THE ENGLISH SCHOOL ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes
 THE ENGLISH SCHOOL ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS 2014 MATHEMATICS FIRST FORM Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Answer ALL questions. Show all necessary working on the question paper in the spaces provided and
THE ENGLISH SCHOOL ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS 2014 MATHEMATICS FIRST FORM Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Answer ALL questions. Show all necessary working on the question paper in the spaces provided and
8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER. Paper 1. Year 8 mathematics test. Calculator not allowed. First name. Last name. Class. Date YEAR
 Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER Year 8 mathematics test Paper Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the spaces
Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER Year 8 mathematics test Paper Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the spaces
SAN ĠORĠ PRECA COLLEGE PRIMARY SCHOOLS. Half Yearly Exams 2016
 SAN ĠORĠ PRECA COLLEGE PRIMARY SCHOOLS Half Yearly Exams 2016 Total Marks 80 Year 6 MATHS Pupil s Paper Time: 1 hour 15 minutes Name: Class: 1. Work out: a) 115 + 35 = b) 409-268 = c) 7.92 + 2.43 = d)
SAN ĠORĠ PRECA COLLEGE PRIMARY SCHOOLS Half Yearly Exams 2016 Total Marks 80 Year 6 MATHS Pupil s Paper Time: 1 hour 15 minutes Name: Class: 1. Work out: a) 115 + 35 = b) 409-268 = c) 7.92 + 2.43 = d)
A COMPLETE NUMERACY PROGRAMME FOR PRIMARY SCHOOLS 4th Class Satellite Book Answers
 A COMPLETE NUMERACY PROGRAMME FOR PRIMARY SCHOOLS 4th Class Satellite Book Answers Topic 1: Place Value Page 5 1. (a) 500 (b) 100 (c) 900 (d) 100 (e) 100 (f) 700 (g) 8,300 (h) 4,400 (i) 6,800 (j) 1,700
A COMPLETE NUMERACY PROGRAMME FOR PRIMARY SCHOOLS 4th Class Satellite Book Answers Topic 1: Place Value Page 5 1. (a) 500 (b) 100 (c) 900 (d) 100 (e) 100 (f) 700 (g) 8,300 (h) 4,400 (i) 6,800 (j) 1,700
KS3 Revision work Level 4
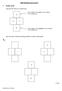 KS3 Revision work Level 4. Number grids Here are the rules for a number grid. 2 This number is the sum of the numbers in the middle row. 0 2 20 This number is the product of the numbers in the middle row.
KS3 Revision work Level 4. Number grids Here are the rules for a number grid. 2 This number is the sum of the numbers in the middle row. 0 2 20 This number is the product of the numbers in the middle row.
Block D: Calculating, measuring and understanding shape Unit 1 10 days
 1 of 7 The National Strategies Primary Key - Italic text signifies objectives which do not appear in the single-age version of this unit but have been added to create a coherent mixed-age unit - Smaller
1 of 7 The National Strategies Primary Key - Italic text signifies objectives which do not appear in the single-age version of this unit but have been added to create a coherent mixed-age unit - Smaller
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM MATHEMATICS
 THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 1 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 17 January 2014 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 1 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 17 January 2014 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
 Key Stage Mathematics TESTS ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES Page 48 of 34 Answers & Mark Schemes About the KS Maths Practice Papers There are three full sets of KS Maths Practice Papers within this book. Each set
Key Stage Mathematics TESTS ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES Page 48 of 34 Answers & Mark Schemes About the KS Maths Practice Papers There are three full sets of KS Maths Practice Papers within this book. Each set
MATHEMATICS TEST SPECIMEN QUESTIONS (calculators not allowed)
 MATHEMATICS TEST SPECIMEN QUESTIONS (calculators not allowed) For questions 1 and 2 use the following information: Input Add 5 Divide by 3 Output 1. Find the output when the input is 13 2. Find the input
MATHEMATICS TEST SPECIMEN QUESTIONS (calculators not allowed) For questions 1 and 2 use the following information: Input Add 5 Divide by 3 Output 1. Find the output when the input is 13 2. Find the input
2. Attempt to answer all questions in the spaces provided in this book.
 ENTRANCE AND SCHOLARSHIP EXAMINATION 2017 MATHEMATICS 1 HOUR CALCULATORS NOT ALLOWED CANDIDATE NAME Instructions to Candidates: 1. Write your name on the line above. 2. Attempt to answer all questions
ENTRANCE AND SCHOLARSHIP EXAMINATION 2017 MATHEMATICS 1 HOUR CALCULATORS NOT ALLOWED CANDIDATE NAME Instructions to Candidates: 1. Write your name on the line above. 2. Attempt to answer all questions
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 3 5 2005 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 3 5 2005 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Paper B Numeracy Paper 11+ Name:... Candidate Number... Seat Number...
 Paper B. 2016 Numeracy Paper 11+ Name:... Candidate Number... Seat Number... This paper has 40 questions, and you have 40 minutes to complete the test. Read the questions carefully. If you cannot answer
Paper B. 2016 Numeracy Paper 11+ Name:... Candidate Number... Seat Number... This paper has 40 questions, and you have 40 minutes to complete the test. Read the questions carefully. If you cannot answer
ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes
 ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS 2017 MATHEMATICS FIRST FORM Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Answer ALL questions. Show all necessary working on the question paper in the spaces provided and write your answers
ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS 2017 MATHEMATICS FIRST FORM Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Answer ALL questions. Show all necessary working on the question paper in the spaces provided and write your answers
Maths Makes Sense. 1 Medium-term plan
 Maths Makes Sense 1 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Copy addition and subtraction Maths Stories with 1-digit, zero, a half and a quarter, e.g. 2 + 1
Maths Makes Sense 1 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Copy addition and subtraction Maths Stories with 1-digit, zero, a half and a quarter, e.g. 2 + 1
What number is represented by the blocks? Look at each four digit number. What's the value of each highlighted digit?
 Numbers and place value to 1000 What number is represented by the blocks? thousands hundreds tens ones Look at each four digit number. What's the value of each highlighted digit? 2 8 9 6 5 3 7 8 7 3 9
Numbers and place value to 1000 What number is represented by the blocks? thousands hundreds tens ones Look at each four digit number. What's the value of each highlighted digit? 2 8 9 6 5 3 7 8 7 3 9
Name. Present School. The London Independent Girls Schools Consortium. Group 1. Mathematics Entrance Examination
 Name. Present School The London Independent Girls Schools Consortium Group 1 Mathematics Entrance Examination 18 th January 2008 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes Write in pencil. Do all your rough working
Name. Present School The London Independent Girls Schools Consortium Group 1 Mathematics Entrance Examination 18 th January 2008 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes Write in pencil. Do all your rough working
Minute Simplify: 12( ) = 3. Circle all of the following equal to : % Cross out the three-dimensional shape.
 Minute 1 1. Simplify: 1( + 7 + 1) =. 7 = 10 10. Circle all of the following equal to : 0. 0% 5 100. 10 = 5 5. Cross out the three-dimensional shape. 6. Each side of the regular pentagon is 5 centimeters.
Minute 1 1. Simplify: 1( + 7 + 1) =. 7 = 10 10. Circle all of the following equal to : 0. 0% 5 100. 10 = 5 5. Cross out the three-dimensional shape. 6. Each side of the regular pentagon is 5 centimeters.
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, mirror, pen, HB pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Primary Curriculum Centre Number Mathematics Year 6 Achievement Test Candidate Number Friday 3 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour Paper
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Primary Curriculum Centre Number Mathematics Year 6 Achievement Test Candidate Number Friday 3 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour Paper
Time. On the first day of Christmas. Memory. Notation
 Hour Minute Second Duration Period Notation 24 hour OR 12 hour clock (am or pm or 12 midnight or 12 noon) On the first day of Time 1 year = 52 weeks = 365 days 1 week = 7 days 1 day = 24 hours 1 hour =
Hour Minute Second Duration Period Notation 24 hour OR 12 hour clock (am or pm or 12 midnight or 12 noon) On the first day of Time 1 year = 52 weeks = 365 days 1 week = 7 days 1 day = 24 hours 1 hour =
Corbettmaths
 1st February 11 11 235 5 A teacher has 380 sweets. She gives 9 children 6 sweets each. How many sweets does the teacher have left? Rob finishes school at half past three. He then walks home and this takes
1st February 11 11 235 5 A teacher has 380 sweets. She gives 9 children 6 sweets each. How many sweets does the teacher have left? Rob finishes school at half past three. He then walks home and this takes
GCSE 4370/03 MATHEMATICS LINEAR PAPER 1 FOUNDATION TIER
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4370/03 MATHEMATICS LINEAR PAPER 1 FOUNDATION TIER A.M. WEDNESDAY, 6 November 2013 1 hour 45 minutes For s use CALCULATORS ARE NOT TO BE USED FOR
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4370/03 MATHEMATICS LINEAR PAPER 1 FOUNDATION TIER A.M. WEDNESDAY, 6 November 2013 1 hour 45 minutes For s use CALCULATORS ARE NOT TO BE USED FOR
TEST 6. 12, 7, 15, 4, 1, 10, Circle all the odd numbers.
 TEST 6. Complete the picture so that it has 7 dots. 2. What is the number shown? 0 5 0. Fill in the missing numbers. 2 + = 4 = (c) + 4 = (d) 4 + = 9 (e) 8 = (f) + 7 = 7 4. Write these numbers in order
TEST 6. Complete the picture so that it has 7 dots. 2. What is the number shown? 0 5 0. Fill in the missing numbers. 2 + = 4 = (c) + 4 = (d) 4 + = 9 (e) 8 = (f) + 7 = 7 4. Write these numbers in order
Mark scheme. Mathematics tests. for Mental mathematics tests A, B and C. National curriculum assessments KEY STAGE 3. satspapers.
 Ma KEY STAGE LOWER TIER & HIGHER TIERS Mathematics tests Mark scheme for Mental mathematics tests A, B and C 2008 National curriculum assessments QCA wishes to make its publications widely accessible.
Ma KEY STAGE LOWER TIER & HIGHER TIERS Mathematics tests Mark scheme for Mental mathematics tests A, B and C 2008 National curriculum assessments QCA wishes to make its publications widely accessible.
50 min. year. Use 2B or HB pencil only. Time available for students to complete test: 50 minutes
 NUMERACY year 5 2016 50 min Time available for students to complete test: 50 minutes Use 2B or HB pencil only Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority, 2016 1 Maria gets 10 cents for every
NUMERACY year 5 2016 50 min Time available for students to complete test: 50 minutes Use 2B or HB pencil only Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority, 2016 1 Maria gets 10 cents for every
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
Triangles, Rectangles, Squares, and Circles
 LESSON Name 2 Teacher Notes: page 27 Triangles, Rectangles, Squares, and Circles Refer students to Circle on page 4 in the Student Reference Guide. Post Reference Chart Circle. Use the compasses from the
LESSON Name 2 Teacher Notes: page 27 Triangles, Rectangles, Squares, and Circles Refer students to Circle on page 4 in the Student Reference Guide. Post Reference Chart Circle. Use the compasses from the
Instructions to Candidates
 DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Department for Curriculum Management and elearning Educational Assessment Unit Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2012 LEVELS 7-8 FORM 1 MATHEMATICS
DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Department for Curriculum Management and elearning Educational Assessment Unit Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2012 LEVELS 7-8 FORM 1 MATHEMATICS
Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring
 Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Alternating chains Children create chains of alternating positive and negative numbers and look at the patterns in their totals. Skill practised:
Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Alternating chains Children create chains of alternating positive and negative numbers and look at the patterns in their totals. Skill practised:
Year 1. Using and applying mathematics. Framework review
 Year 1 Using and applying mathematics Solve problems involving counting, adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the context of numbers, measures or money, for example to pay and give change I am going
Year 1 Using and applying mathematics Solve problems involving counting, adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the context of numbers, measures or money, for example to pay and give change I am going
Paper 2. Calculator allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 2 Calculator allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 2 Calculator allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
Summer Solutions Common Core Mathematics 4. Common Core. Mathematics. Help Pages
 4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
Section 1: Whole Numbers TERM 4
 Grade Play! Mathematics Answer Book 0 Section : Whole Numbers TERM Question Place Value and Value: -digit Numbers. Write down the place value of each underlined digit. a) 0 HTh b) T c) Th d) H e) TTh f)
Grade Play! Mathematics Answer Book 0 Section : Whole Numbers TERM Question Place Value and Value: -digit Numbers. Write down the place value of each underlined digit. a) 0 HTh b) T c) Th d) H e) TTh f)
Representing Square Numbers. Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array.
 1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
Section 1: Whole Numbers
 Grade 6 Play! Mathematics Answer Book 67 Section : Whole Numbers Question Value and Place Value of 7-digit Numbers TERM 2. Study: a) million 000 000 A million has 6 zeros. b) million 00 00 therefore million
Grade 6 Play! Mathematics Answer Book 67 Section : Whole Numbers Question Value and Place Value of 7-digit Numbers TERM 2. Study: a) million 000 000 A million has 6 zeros. b) million 00 00 therefore million
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM MATHEMATICS
 THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 1 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 13 January 2017 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 1 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 13 January 2017 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Year 5. Mathematics A booklet for parents
 Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
Maths SATs practice paper 2: reasoning
 Maths SATs paper 2: reasoning First name... Middle name... Last name... Date of birth Day... Month... Year... School name... www.teachitprimary.co.uk 208 320 Page of 8 Instructions You must not use a calculator
Maths SATs paper 2: reasoning First name... Middle name... Last name... Date of birth Day... Month... Year... School name... www.teachitprimary.co.uk 208 320 Page of 8 Instructions You must not use a calculator
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary. Correlations
 Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
TIME ALLOWED FOR THIS PAPER: Reading time before commencing work: MATERIAL REQUIRED / RECOMMENDED FOR THIS PAPER:
 TIME ALLOWED FOR THIS PAPER: Reading time before commencing work: Working time for this paper: 0 minutes hour & 30 minutes MATERIAL REQUIRED / RECOMMENDED FOR THIS PAPER: To be provided by the supervisor
TIME ALLOWED FOR THIS PAPER: Reading time before commencing work: Working time for this paper: 0 minutes hour & 30 minutes MATERIAL REQUIRED / RECOMMENDED FOR THIS PAPER: To be provided by the supervisor
Mathematics A *P49303RA0128* Pearson Edexcel GCSE P49303RA. Paper 2 (Calculator) Foundation Tier. Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Write your name here Surname Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Other names Candidate Number Foundation Tier Paper
Write your name here Surname Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Other names Candidate Number Foundation Tier Paper
Winslow C of E Combined School. Progression in the 4 Operations & Fun Maths Activities to do at Home.
 Winslow C of E Combined School. Progression in the 4 Operations & Fun Maths Activities to do at Home. Dear Parents, Carers, Please have a look through some of these short, simple maths games and activities
Winslow C of E Combined School. Progression in the 4 Operations & Fun Maths Activities to do at Home. Dear Parents, Carers, Please have a look through some of these short, simple maths games and activities
Name Date Class. Total (A) Total (B) Total (C) Test Total (A+B+C) R (0-9) I y (10-19) I G (20-25) Maths Basic Skills Week 1
 rk bo k,let t r a h Maths Basic Skills Week 1 Name Date Class. 1. What are the next two numbers? 11. Six times a number is forty two. 21. In a sale, there is twenty-five per -19' -15' -11'... '... What
rk bo k,let t r a h Maths Basic Skills Week 1 Name Date Class. 1. What are the next two numbers? 11. Six times a number is forty two. 21. In a sale, there is twenty-five per -19' -15' -11'... '... What
ST NICHOLAS COLLEGE HALF YEARLY PRIMARY EXAMINATIONS. February YEAR 6 Mathematics (Written Paper) TIME: 1 h 15 min.
 ST NICHOLAS COLLEGE HALF YEARLY PRIMARY EXAMINATIONS February 2014 YEAR 6 Mathematics (Written Paper) TIME: 1 h 15 min Name: Class: Total Mark 80 1. Write the value of 6 in each number: a) 6457 = b) 0.6
ST NICHOLAS COLLEGE HALF YEARLY PRIMARY EXAMINATIONS February 2014 YEAR 6 Mathematics (Written Paper) TIME: 1 h 15 min Name: Class: Total Mark 80 1. Write the value of 6 in each number: a) 6457 = b) 0.6
Paper B Numeracy Paper 11+ Candidate Number... This is a multiple-choice test. Please fill in the details on the multiple-choice answer sheet.
 Paper B. 2015 Numeracy Paper 11+ Name... Candidate Number... Seat Number... This is a multiple-choice test. Please fill in the details on the multiple-choice answer sheet. This numeracy paper contains
Paper B. 2015 Numeracy Paper 11+ Name... Candidate Number... Seat Number... This is a multiple-choice test. Please fill in the details on the multiple-choice answer sheet. This numeracy paper contains
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM MATHEMATICS
 THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 6 January 2017 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 6 January 2017 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
Downloaded from satspapers.org MATHEMATICS YEAR 3 LEVELS. TEST 3b. Total marks CALCULATOR NOT ALLOWED. Name. Class. School. Date
 MATHEMATICS YEAR 3 TEST 3b LEVELS 3 4 CALCULATOR NOT ALLOWED Total marks Name Class School Date Vijay Dan Sarah 2 Getting started This shows you where you need to put each answer. Some questions have an
MATHEMATICS YEAR 3 TEST 3b LEVELS 3 4 CALCULATOR NOT ALLOWED Total marks Name Class School Date Vijay Dan Sarah 2 Getting started This shows you where you need to put each answer. Some questions have an
BREATHITT COUNTY SCHOOLS 3 rd Grade Math Curriculum Map Week Standard Key Vocabulary Learning Target Resources Assessment
 Number Operations/Fractions/Algebraic Expressions Week 1 Week 2 3.NBT.1: Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. 3.NBT.2: Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using
Number Operations/Fractions/Algebraic Expressions Week 1 Week 2 3.NBT.1: Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. 3.NBT.2: Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using
Name: Primary 5-a-day Silver. 1st August. 3 bananas cost apples cost How much more does one banana cost than one apple?
 1st August 3 8 + 4 8 80 60 3 bananas cost 0.96 4 apples cost 1.12 How much more does one banana cost than one apple? Here is part of a number line Write missing numbers in the boxes Find the two missing
1st August 3 8 + 4 8 80 60 3 bananas cost 0.96 4 apples cost 1.12 How much more does one banana cost than one apple? Here is part of a number line Write missing numbers in the boxes Find the two missing
PAGE TOTAL MARKS MATHEMATICS KEY STAGE LEVELS 3 5 TEST B BORDERLINE CHECK CALCULATOR ALLOWED. First Name. Last Name.
 MATHEMATICS KEY STAGE 2 2001 TEST B LEVELS 3 5 CALCULATOR ALLOWED PAGE 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 TOTAL BORDERLINE CHECK MARKS First Name Last Name School Instructions You may use a calculator to answer any
MATHEMATICS KEY STAGE 2 2001 TEST B LEVELS 3 5 CALCULATOR ALLOWED PAGE 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 TOTAL BORDERLINE CHECK MARKS First Name Last Name School Instructions You may use a calculator to answer any
Paper B Maths Paper 11+ Candidate Number. Seat Number.. Please put your name in the space provided above.
 Paper B. 2016 Maths Paper 11+ Name Candidate Number. Seat Number.. Please put your name in the space provided above. This maths paper contains 36 questions, which you have 40 minutes to complete. The paper
Paper B. 2016 Maths Paper 11+ Name Candidate Number. Seat Number.. Please put your name in the space provided above. This maths paper contains 36 questions, which you have 40 minutes to complete. The paper
Year 6 Maths Assessment Guidance - NUMBER Meeting expectations 3 Working Within Year 6 4 Secure within Year 6
 6.1.a.1 Calculate intervals across zero (^) 6.1.a.2 Consolidate counting forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number to 1 000 000 (+) 6.1.a.3 Consolidate counting in multiples of
6.1.a.1 Calculate intervals across zero (^) 6.1.a.2 Consolidate counting forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number to 1 000 000 (+) 6.1.a.3 Consolidate counting in multiples of
Class- VI (Mathematics)
 Index Class- VI (Mathematics) 1. Knowing our Numbers 001 2. Whole Numbers 011 3. Playing with Numbers 021 4. Basic Geometrical Ideas 031 5. Understanding Elementary Shapes 035 6. Integers 041 7. Fractions
Index Class- VI (Mathematics) 1. Knowing our Numbers 001 2. Whole Numbers 011 3. Playing with Numbers 021 4. Basic Geometrical Ideas 031 5. Understanding Elementary Shapes 035 6. Integers 041 7. Fractions
8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER. Paper 2. Year 8 mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. Class. Date YEAR
 Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER 2 Year 8 mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the spaces
Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER 2 Year 8 mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the spaces
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 259572_P2 4-6_KS3_Ma.qxd 1/4/04 3:43 PM Page 1 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you
259572_P2 4-6_KS3_Ma.qxd 1/4/04 3:43 PM Page 1 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you
DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET
 DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET This booklet is an optional revision aid for the Summer Exam Name: Maths Teacher: Revision List for Summer Exam Topic Junior Maths Bk 3 Place Value Chapter
DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET This booklet is an optional revision aid for the Summer Exam Name: Maths Teacher: Revision List for Summer Exam Topic Junior Maths Bk 3 Place Value Chapter
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM MATHEMATICS
 THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 11 January 2013 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 11 January 2013 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
ENTRANCE AND SCHOLARSHIP EXAMINATION 2012 MATHEMATICS 1 HOUR CALCULATORS NOT ALLOWED CANDIDATE NAME. Instructions to Candidates:
 ENTRANCE AND SCHOLARSHIP EXAMINATION 2012 MATHEMATICS 1 HOUR CALCULATORS NOT ALLOWED CANDIDATE NAME Instructions to Candidates: 1. Write your name on the line above. 2. Attempt to answer all questions
ENTRANCE AND SCHOLARSHIP EXAMINATION 2012 MATHEMATICS 1 HOUR CALCULATORS NOT ALLOWED CANDIDATE NAME Instructions to Candidates: 1. Write your name on the line above. 2. Attempt to answer all questions
Dulwich College MATHEMATICS ONE HOUR
 Dulwich College ENTRANCE AND SCHOLARSHIP EXAMINATION AT 11+ SPECIMEN PAPER MATHEMATICS ONE HOUR Answer all the questions. Do all your written work on this paper. Calculators must not be used. Numbers in
Dulwich College ENTRANCE AND SCHOLARSHIP EXAMINATION AT 11+ SPECIMEN PAPER MATHEMATICS ONE HOUR Answer all the questions. Do all your written work on this paper. Calculators must not be used. Numbers in
