Relations Cultural Activity and Environment Resources on Cultural Model
|
|
|
- Ariel Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Relations Cultural Activity and Environment Resources on Cultural Model Takuya Anbe and Minetada Osano The University of Aizu Aizu-Wakamatsu, Fukushima, , Japan Abstract: - The importance of the research of social problems is increasing recently, in proportion to frequency of occurrence of ethnic and religious conflict and problems of environment. Using computer simulation is one of the ways to solve these serious problems to make peaceful future. We devised a model of the human society as Artificial Culture by using a concept of memes. A model of artificial culture used the multi-agent system to model the migration of humans, and used the artificial chemistry to model the network of cultural activity and economy and is confirmed by the clustering and dividing of group were made by cultural difference and the running out of the resources and extinction of society caused by irreversible process of cultural production. The polarization of culture and activity are simulated by behaviors of each agent. Those results of the experiment are insightful. Key-Words: - Artificial Culture, Artificial chemistry, Environment Resources, Human Agent 1. Introduction There are various social problems in the world which are caused by polarization of wealth based on culture and resources. We must solve these problems for world peace. Hence, there are various studies to solve various problems in the world. However, the variety and range of human activity are increasing day by day, therefore it is difficult for us to analyze the future of the human society and its culture. Since the computer science provides broad solutions today, using computer simulation is one of better solutions for analyzing social problem. Robert Axelrod provides some important suggestion for study of human society in computer science[1]. He devised the model of local assimilation and global polarization caused by imitation of adjacent actors. His model is suitable to describe the spread of culture, such as ideology, technology or fashion. The model of cultural imitation was devised by Richard Dawkins[2]. A meme which he defined as replicator represents a minimum unit of imitation. The meme can evolve in the similar way to the genetic evolution. However, there are two differences in the effect on the population. First, the meme has wider range of propagation and faster speed of replication. The gene can replicate only in the individual reproduction. On the other hand, the meme can replicate in the communication between humans. Superb idea, such as arts or technology, can spread to all over the world. On the other hand, genes need human to survive and prosper, because they are sharing the destiny with human. The interaction of cultural elements and resources can be explained as artificial chemistry. Stuart Kauffman argues that the network of economy and technology is auto-catalytic system[3]. He explains that products and services build the network of complements and substitutes. Geographical issues are also important for the argument of culture. Attributes of culture depend on both humans and location. Jared Diamond discussed the reason why the progress of civilization is so polarized between the Eurasian Continent and the African Continent [4]. He concluded that there are following major reasons: inequality of resource distribution, difference of easiness of cultural propagation and population density and size of the land. We developed the simulation program using model and carried out the experiment in several situation, including the polarization of cultural activity. Our model of human behavior consists of 'movement' and 'production' ultimately. The model
2 of human is designed as an agent who can move and produce. The agent can also evaluate its local environment. In our model, culture is represented by memes. The memes spread in the society of the agents via imitation, and affect the process of evaluation and production. To implement the production by meme the agents have, we used artificial chemistry. In this paper, our objective is to analysis our results of getting the universal model of culture and human society, especially enabled to describe polarization of culture and activity, under the effects of cultural interaction and evolution. 2. The Concepts of Artificial Culture 2.1. Chemical Reactions of Artificial Chemistry Chemical reactions among a pool of molecules show us insightful behaviors. The artificial chemistry describes universal model of chemical reactions. In the artificial chemistry, structures of symbols represent virtual molecules. The virtual molecules are in a pool and react each other. The system of the artificial chemistry consists of three elements as below. Molecules: A set of elements in the system. The set contains all elements which react. Operations: Interactions between molecules, such as bonding, decomposition or catalysis. Dynamics: Handling method of molecules which specifies how the molecules are selected for reaction, or how the new molecules are put in. Artificial chemistries are used for various studies, such as chemistry, ecosystem and even economic system. Definition of the virtual molecules is important for these studies. In ecosystem, each molecule represents individuals or populations. On the other hand, each molecule represents products and services in economic system Representation of Artificial Culture Since a meme is defined as a unit of culture, culture is represented as a set of memes. Thus, the combination of memes yields cultural differences in spite of sharing some memes. This representation is useful to describe the spread of culture, because we can handle memes as portable element The Application to Cultural Production We modeled cultural production of human beings as chemical reaction. The reason why we can regard the production as chemical reaction is that cultures always convert some resources into other resources in the local environment. For example, the meme of farming converts a wild grassy plain and seeds of grains into a farm. In this case, the wild plain and the seeds are reactants and the farm is product. The production uses a pair of reactant and catalyst to generate a new resource as product (Fig. 1). The meme uses its pattern matching of reactants and catalysts to select the reactant and catalyst. Fig.1: Cultural Production that is using Catalyst The production replaces the reactant with its product. The reactant which has been used in the production is removed. The use of memes yields new resources and niches for other cultural production. This process builds the network of resources conversion and catalysis. Since the Post's production system represents such chemical reaction, we can represent the cultural production by using the system. Some of the memes increase opportunity of use of themselves because their products become their catalysts via the network. The network which especially contains self-helping memes is called auto-catalytic system. Fig. 2 shows the flow of the resources on the network of auto-catalytic process between two humans. In this Fig., Resource A and B exist initially. Then the two humans produce resource C and D, and they work as catalysis of each other. Thus, the production of them is accelerated. Stuart Kauffman states that the network of culture, especially of technology and
3 economy is developing by auto-catalysis of complements and substitutions. If the range of interaction increases, the number decreases. If the geographical area increases over a certain threshold, the number decreases. Fig. 2: Auto-Catalytic System of Production The complements are mutually needed elements such as the relations of screw and screwdriver or cars and gas stations. The substitutions are competing elements such as the relations of nails and screws or railways and airlines. In this network, existing products and services will make new niches for new products and services in the relations of complements and substitutions. The network repeats such an expansion and diversifying Geographical Dynamic Imitations among Adjacent Actors Mutual imitations between individuals or subgroups make a cultural assimilation. However, some differences remain for long time and divide a group into several subgroups. Robert Axelrod modeled the spread of culture by multi-agent system. In this model, a success rate of a cultural imitation is in proportion to cultural similarity. He carried out the experiment of this model and the result yields local assimilation and global polarization in the model world. In the Fig. 3, the left diagram shows that the imitations that are represented as arrow symbols expand the regions which share a uniform culture. The right figure shows that the model world is finally The number of stable subgroups shows following features. If the number of cultural feature increases, the number decreases. If the number of variation in each cultural feature increases, the number increases. Fig. 3: Propagation process of culture (Left) and Polarization (Right) 3. Model of Artificial Cultural Society We built the model of artificial cultural society which consists of human agents, memes and resources. We expect that this model builds the auto-catalytic cultural network in the model world. Our model can describe various situations among the humans, cultures and resources Human Agents A human agent represents a minimum unit of human activity, thus each agent represent not one person but one family or one band. The behavior of this agent consists of three elements: evaluation, migration and cultural production Evaluation of Resources The human agent evaluates the environment for survival and breeding. In this process, the human agent firstly obtains a list of accessible resources which is near than the preset Manhattan distance. Once the list of resources is obtained, the agent evaluates each resource in the list and scores by its decision making process. The evaluated resources are stored temporary in the memory for migration and cultural production Migration In order to settle in a suitable position for its cultural production, the human agent migrates from one place to another in the model world. A suitable position for the human agent means a good place for cultural production by a set of memes which the human has. The human agent decides the migration vector according to the scores and locations of all
4 resources. The human agent migrates along the vector m when the agent succeeded to decide to migrate. However, because of the viscosity of group, the agent can not always succeed to migrate. Each human agent has viscosity of group to repress excessive migration. Excessive migration makes the human impossible to adapt to local environment and to maintain the group and cultural imitation among the group. On the other side, insufficient migration yields danger when the environment changes or other groups invade. Hence, the construction of cultural society requires a proper Cultural Production A cultural production yields profit or loss for the human agent. This process practices chemical reaction of a reactant resource and catalyst resource to generate a new resource as product. The reactant and catalyst are selected from the list of accessible resources which is obtained in the evaluation process. The product resource will be put at the place where the agent exists. Each meme defines the reaction rule and pattern matching for selection of reactants and catalysts. Therefore, a set of meme influences a cultural production of each human Cultural Similarity Model of Memes As discussed above, a set of memes represents a culture. We used set theory to handle culture in order to obtain a cultural similarity. We assume that there are n memes in the universal set of memes U: Mi: Score that is based on memes. A culture among humans is represented as a subset of U. When we assume there are two culture: Culture A and B which are represented as two sets CA and CB respectively, we can define four types of relations between them. 1. Equal: Culture A and B share all elements of them. 2. Inclusion: Culture A includes all elements of Culture B. In this case, a cultural similarity of them is equal to 1, because there is no collision in both cultures. 3. Overlap: Culture A and B share some elements of them, but other elements are different and yield cultural conflicts. 4. Complete Difference: Culture A and B share no elements. This yields severe cultural conflicts, thus they cannot imitate each other. In order to implement cultural propagation via imitation, we must obtain cultural similarity among humans and human groups Cultural Production The human agent can do cultural production by its memes. The agent selects the meme and the accessible resource for chemical reaction. After the reaction, the agent puts new resource where reactant existed. In our model, the system scores the cultural activities in order to evaluate the fitness of the agents. The agent produces its child when its fitness score crosses the upper threshold. On the other hand, when the fitness score crosses the lower threshold, the agent dies. The reason why such a complicated mechanism exists is that the profit of humans and the profit of memes are different. Therefore, evaluation must be separated Evolution of Memes In our model, a function of the meme evolution is omitted, because the evolution is too complicated to implement. We predefined limited memes which contains initial set of memes, instead of evolution Resources The resource represents a feature of environment. Natural, artificial, material and immaterial resources are indiscriminate. Even the agents' presence is also handled as resource. Hence, the cultural production is not the plain production but the creation which has infinite possibility Environment In the simulation program, we defined the whole environment as limited torus two-dimensional space. And we distribute the initial set of natural resources and human agents on the environment. The simulation program updates the state of the model world in each iteration. The environment space is divided into mosaic tile, and each mosaic cell means minimum unit of area and resource storage. The resources are distributed on the space and stored in each cell. The agent exploits the resources for the cultural activity.
5 4. Simulation Result on relating between Population and Resource We developed the simulation program in order to verify this model. The properties of simulation environment are given with optional value on each parameter of ChildRearingCost, ReproduceThreshold, MemePoolCapacity, MemeVariety and MemeLength. In the simulation, we obtained some interesting results among the interaction and propagation of culture and human Two Patterns of History There are two patterns of history of model world: decline and prosperity. Both patterns have shown different patterns among society Decline Pattern First we found the decline pattern in the experiment. The each parameter are given as 10, 50, 3, 10, 6 and the set of meme from Meme ID(0) to Meme D(9) are also given with character form set as 000 -> 000. Result of this simulation is that an initial population grew larger and became diversified through the history in the model world. However, once they reached their peak of prosperity, the decline began. Fig. 4 and Fig. 5 show the dynamics among society in 1000 iterations on our simulation. In Fig. 4, the population reaches the first peak after 330 iterations, then they begin decline. At the same time, variety of resources shown in Fig. 5 slowed down its growth. In iterations from 600 to 700, population has been maintained by cultural conflict and mixture. Fig. 6 shows cultural stress that a human agent gains from amount of cultural difference among surrounding others. Fig. 5: Variety of Resources (1000 iterations) Fig. 6: Cultural Stress (1000 iterations) Prosperity Pattern Second, we found the prospering pattern in the other experiment. The each parameter are given as 10, 50, 3, 10, 5 and the set of meme from Meme ID(0) to Meme ID(9) are also given with other deference character form set to declined pattern sets. The growth of population and the growth of variety of resources did not slow down but accelerated until the memory usage became full at iteration 370. However, both the population of human agents and the variety of resource became extremely large when the simulation terminated by 'out of memory'. Fig. 7: Variety of Resources (370 iterations) Fig. 4: Population of Human Agents (1000 iterations) Fig. 7 and Fig. 8 show the variety of resources and the cultural stress in the prospering pattern in 370 iterations on our simulation. The first peak in Fig. 8 shows the same shape as the decline pattern
6 because this is common pattern while the society is growing. The increase of stress is in proportion to the population of humans. Fig. 8: Cultural Stress (370 iterations) 4.2. Meaning of Cultural Stress and Prosperity In two patterns of history, we found the relations between cultural stress and growth of population. Cultural variety yields the variety of resources, cultural productions and even growth of population of humans. Comparing to decline pattern, both the population of humans and the variety of resources are larger when even at iteration 300 (Fig. 5, Fig. 7). The most important difference in above two Fig.s is the variety of resources. In decline pattern, we found the maximum variety of resource is up to 183. On the other hand, this pattern showed over 120,000 at last. When this property is low, the model world has uniform culture. On the other hand, when this property is high, the model world is polarized. We found that the higher rate of increase of population yields higher cultural stress among the model world Geographical Condition Fig. 9: Geographical Distribution of Cultural Stress We found that the culturally assimilated group was formed especially in the edge of population (Fig. 9). This phenomenon is yielded from accessibility of other agents. Inner agents are surrounded by other agents constantly, so that they cannot maintain same memes. On the other side, outer agents have some neighboring agent, but other side is open. This subtle difference grows through a number of iterations. At last, outer agents make small group. 5. Conclusion In this paper, we focused on model the society that contains memetics and geography. The result of experiment gave us following property of society: the growth of population makes cultural stress, and the cultural group is born at isolated area. We also handled memetics as tool to define cultural production of human beings. We combined memetics and artificial chemistry to express auto-catalytic process of cultural production. The result showed two patterns of history of society, prosperity and decline. In decline pattern, we found a dead-lock in auto-catalytic process that makes the growth of resource variety stop. Evaluation of production also influences the result. If the highly valued production is yielded from one meme, uniform culture will conquer the model world. If not, such culture will disappear soon, as shown in the result of our experiment. Memetics is still arguable, but we focused on not individual meme but a combination of memes, and succeeded to model the abstract society. We need to improve this model and program to obtain more fine comprehensive results on society. References [1] Robert Axelrod, The Complexity of Cooperation, Princeton University Press, [2] Richard Dawkins, THE SELFISH GENE New Edition, Oxford University Press, [3] Stuart Kauffman, AT HOME IN THE UNIVERSE : THE SEARCH FOR LAWS OFSELFORGANIZATION AND COMPLEXITY, Oxford University Press, [4] Jared Diamond, "GUNS, GERMS AND STEEL: The Fates of Human Societies," W. W. Norton & Company, 1999.
What is a Meme? Brent Silby 1. What is a Meme? By BRENT SILBY. Department of Philosophy University of Canterbury Copyright Brent Silby 2000
 What is a Meme? Brent Silby 1 What is a Meme? By BRENT SILBY Department of Philosophy University of Canterbury Copyright Brent Silby 2000 Memetics is rapidly becoming a discipline in its own right. Many
What is a Meme? Brent Silby 1 What is a Meme? By BRENT SILBY Department of Philosophy University of Canterbury Copyright Brent Silby 2000 Memetics is rapidly becoming a discipline in its own right. Many
NonZero. By Robert Wright. Pantheon; 435 pages; $ In the theory of games, a non-zero-sum game is a situation in which one participant s
 Explaining it all Life's a game NonZero. By Robert Wright. Pantheon; 435 pages; $27.50. Reviewed by Mark Greenberg, The Economist, July 13, 2000 In the theory of games, a non-zero-sum game is a situation
Explaining it all Life's a game NonZero. By Robert Wright. Pantheon; 435 pages; $27.50. Reviewed by Mark Greenberg, The Economist, July 13, 2000 In the theory of games, a non-zero-sum game is a situation
The Study of Knowledge Innovation Based on Enterprise Knowledge Ecosystem
 The Study of Knowledge Innovation Based on Enterprise Knowledge Ecosystem Mingkui Huo 1 1 School of Economics and Management, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China Correspondence:
The Study of Knowledge Innovation Based on Enterprise Knowledge Ecosystem Mingkui Huo 1 1 School of Economics and Management, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China Correspondence:
SOCI 360. SociAL Movements. Community Change. sociology.morrisville.edu. Professor Kurt Reymers, Ph.D. And
 SOCI 360 SociAL Movements And Community Change Professor Kurt Reymers, Ph.D. sociology.morrisville.edu Cultural ideas are a deliberative and potent means of reinforcing social norms, roles and institutions.
SOCI 360 SociAL Movements And Community Change Professor Kurt Reymers, Ph.D. sociology.morrisville.edu Cultural ideas are a deliberative and potent means of reinforcing social norms, roles and institutions.
Information Evolution in Social Networks
 Presentation for INFO I-501: Introduction to Informatics; Fall 2017 Jayati Dev PhD Student Security Informatics Information Evolution in Social Networks Lada A. Adamic, Thomas M. Lento, Eytan Adar, Pauling
Presentation for INFO I-501: Introduction to Informatics; Fall 2017 Jayati Dev PhD Student Security Informatics Information Evolution in Social Networks Lada A. Adamic, Thomas M. Lento, Eytan Adar, Pauling
N = R * f p n e f l f i f c L
 Music: Human Human League Astronomy 230 This class (Lecture 22): Jake O'Keefe Brandon Eckardt Kevin Quinn Next Class: Evolution of World View Ken Sampson # of advanced civilizations we can contact in our
Music: Human Human League Astronomy 230 This class (Lecture 22): Jake O'Keefe Brandon Eckardt Kevin Quinn Next Class: Evolution of World View Ken Sampson # of advanced civilizations we can contact in our
The International School of Athens
 The International School of Athens Programme of Inquiry - KDG Senses help us to learn about the world around us Form, Function, Responsibility Health, appreciation The importance of our senses What we
The International School of Athens Programme of Inquiry - KDG Senses help us to learn about the world around us Form, Function, Responsibility Health, appreciation The importance of our senses What we
FreeCiv Learner: A Machine Learning Project Utilizing Genetic Algorithms
 FreeCiv Learner: A Machine Learning Project Utilizing Genetic Algorithms Felix Arnold, Bryan Horvat, Albert Sacks Department of Computer Science Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30318 farnold3@gatech.edu
FreeCiv Learner: A Machine Learning Project Utilizing Genetic Algorithms Felix Arnold, Bryan Horvat, Albert Sacks Department of Computer Science Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30318 farnold3@gatech.edu
Technologists and economists both think about the future sometimes, but they each have blind spots.
 The Economics of Brain Simulations By Robin Hanson, April 20, 2006. Introduction Technologists and economists both think about the future sometimes, but they each have blind spots. Technologists think
The Economics of Brain Simulations By Robin Hanson, April 20, 2006. Introduction Technologists and economists both think about the future sometimes, but they each have blind spots. Technologists think
Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical Thinking Skills
 AP World History 2015-2016 Nacogdoches High School Nacogdoches Independent School District Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical
AP World History 2015-2016 Nacogdoches High School Nacogdoches Independent School District Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical
Scenario Development Process
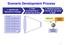 Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Presented by Jeremy Lent
 Presented by Jeremy Lent Increasing numbers of component parts Source: Cynthia Stokes Brown, The Meaning of Big History, Philosophically Speaking, Origins VI 1, January 2016 Interact with increased flows
Presented by Jeremy Lent Increasing numbers of component parts Source: Cynthia Stokes Brown, The Meaning of Big History, Philosophically Speaking, Origins VI 1, January 2016 Interact with increased flows
Chapter 3: Complex systems and the structure of Emergence. Hamzah Asyrani Sulaiman
 Chapter 3: Complex systems and the structure of Emergence Hamzah Asyrani Sulaiman In this chapter, we will explore the relationship between emergence, the structure of game mechanics, and gameplay in more
Chapter 3: Complex systems and the structure of Emergence Hamzah Asyrani Sulaiman In this chapter, we will explore the relationship between emergence, the structure of game mechanics, and gameplay in more
Table of Contents SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY AND PROCESS UNDERSTANDING HOW TO MANAGE LEARNING ACTIVITIES TO ENSURE THE SAFETY OF ALL STUDENTS...
 Table of Contents DOMAIN I. COMPETENCY 1.0 SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY AND PROCESS UNDERSTANDING HOW TO MANAGE LEARNING ACTIVITIES TO ENSURE THE SAFETY OF ALL STUDENTS...1 Skill 1.1 Skill 1.2 Skill 1.3 Understands
Table of Contents DOMAIN I. COMPETENCY 1.0 SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY AND PROCESS UNDERSTANDING HOW TO MANAGE LEARNING ACTIVITIES TO ENSURE THE SAFETY OF ALL STUDENTS...1 Skill 1.1 Skill 1.2 Skill 1.3 Understands
Achieving Desirable Gameplay Objectives by Niched Evolution of Game Parameters
 Achieving Desirable Gameplay Objectives by Niched Evolution of Game Parameters Scott Watson, Andrew Vardy, Wolfgang Banzhaf Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland St John s.
Achieving Desirable Gameplay Objectives by Niched Evolution of Game Parameters Scott Watson, Andrew Vardy, Wolfgang Banzhaf Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland St John s.
Cooperative Behavior Acquisition in A Multiple Mobile Robot Environment by Co-evolution
 Cooperative Behavior Acquisition in A Multiple Mobile Robot Environment by Co-evolution Eiji Uchibe, Masateru Nakamura, Minoru Asada Dept. of Adaptive Machine Systems, Graduate School of Eng., Osaka University,
Cooperative Behavior Acquisition in A Multiple Mobile Robot Environment by Co-evolution Eiji Uchibe, Masateru Nakamura, Minoru Asada Dept. of Adaptive Machine Systems, Graduate School of Eng., Osaka University,
Martha Holmes and Michael Gunton. Rupert Barrington, Adam Chapman, Patrick Morris and Ted Oakes
 E X T R A O R D I N A R Y A N I M A L S, E X T R E M E B E H A V I O U R Martha Holmes and Michael Gunton Rupert Barrington, Adam Chapman, Patrick Morris and Ted Oakes Introduction 8 Location map 14 3
E X T R A O R D I N A R Y A N I M A L S, E X T R E M E B E H A V I O U R Martha Holmes and Michael Gunton Rupert Barrington, Adam Chapman, Patrick Morris and Ted Oakes Introduction 8 Location map 14 3
Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved
 Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved 6-15-2017 Learner Objective: Students will be able to independently use their learning to develop the ability to make informed decisions
Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved 6-15-2017 Learner Objective: Students will be able to independently use their learning to develop the ability to make informed decisions
Foundation. Central Idea: People s awareness of their characteristics, abilities and interests shape who they are and how they learn.
 Foundation Who we are An inquiry into the nature of the self; beliefs and values; personal, mental, social and spiritual health; human relationships including families, friends, communities and cultures;
Foundation Who we are An inquiry into the nature of the self; beliefs and values; personal, mental, social and spiritual health; human relationships including families, friends, communities and cultures;
A crude look at the whole curiosity, innovation, complexity. Helga Nowotny 4-6 March 2013 Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
 A crude look at the whole curiosity, innovation, complexity Helga Nowotny 4-6 March 2013 Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Where is society? A crude look at the whole: where is human society?
A crude look at the whole curiosity, innovation, complexity Helga Nowotny 4-6 March 2013 Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Where is society? A crude look at the whole: where is human society?
PYP Programme of Inquiry
 IB PYP Application for Authorization PYP Programme of Inquiry Where We Are in Place and Time descriptors that the planner teaches. Kindergarten nature of the self; beliefs and values; personal, physical,
IB PYP Application for Authorization PYP Programme of Inquiry Where We Are in Place and Time descriptors that the planner teaches. Kindergarten nature of the self; beliefs and values; personal, physical,
Core Content for Social Studies Assessment
 Core Content for Social Studies Assessment Middle School Version 4.1 August 2006 Kentucky Department or Education Kentucky Department of Education 1 Introduction Core Content for Social Studies Assessment
Core Content for Social Studies Assessment Middle School Version 4.1 August 2006 Kentucky Department or Education Kentucky Department of Education 1 Introduction Core Content for Social Studies Assessment
Converting Motion between Different Types of Humanoid Robots Using Genetic Algorithms
 Converting Motion between Different Types of Humanoid Robots Using Genetic Algorithms Mari Nishiyama and Hitoshi Iba Abstract The imitation between different types of robots remains an unsolved task for
Converting Motion between Different Types of Humanoid Robots Using Genetic Algorithms Mari Nishiyama and Hitoshi Iba Abstract The imitation between different types of robots remains an unsolved task for
Evolving CAM-Brain to control a mobile robot
 Applied Mathematics and Computation 111 (2000) 147±162 www.elsevier.nl/locate/amc Evolving CAM-Brain to control a mobile robot Sung-Bae Cho *, Geum-Beom Song Department of Computer Science, Yonsei University,
Applied Mathematics and Computation 111 (2000) 147±162 www.elsevier.nl/locate/amc Evolving CAM-Brain to control a mobile robot Sung-Bae Cho *, Geum-Beom Song Department of Computer Science, Yonsei University,
Image Analysis of Granular Mixtures: Using Neural Networks Aided by Heuristics
 Image Analysis of Granular Mixtures: Using Neural Networks Aided by Heuristics Justin Eldridge The Ohio State University In order to gain a deeper understanding of how individual grain configurations affect
Image Analysis of Granular Mixtures: Using Neural Networks Aided by Heuristics Justin Eldridge The Ohio State University In order to gain a deeper understanding of how individual grain configurations affect
1.1 Students know how to use maps, globes, and other geographic tools to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective.
 Prentice Hall World Geography: Building a Global Perspective 2005 Colorado Model Academic Standards for Social Studies: Geography (Grades 9-12) GEOGRAPHY STANDARD 1: Students know how to use and construct
Prentice Hall World Geography: Building a Global Perspective 2005 Colorado Model Academic Standards for Social Studies: Geography (Grades 9-12) GEOGRAPHY STANDARD 1: Students know how to use and construct
GUNS, GERMS, AND STEEL Jared Diamond
 Preface Questions: (9-11) GUNS, GERMS, AND STEEL Jared Diamond 1. What is the prime question motivating 2. According to Diamond, the roots of Diamond s book? What is the obvious western Eurasian dominance
Preface Questions: (9-11) GUNS, GERMS, AND STEEL Jared Diamond 1. What is the prime question motivating 2. According to Diamond, the roots of Diamond s book? What is the obvious western Eurasian dominance
Multi-Robot Coordination. Chapter 11
 Multi-Robot Coordination Chapter 11 Objectives To understand some of the problems being studied with multiple robots To understand the challenges involved with coordinating robots To investigate a simple
Multi-Robot Coordination Chapter 11 Objectives To understand some of the problems being studied with multiple robots To understand the challenges involved with coordinating robots To investigate a simple
CPS331 Lecture: Genetic Algorithms last revised October 28, 2016
 CPS331 Lecture: Genetic Algorithms last revised October 28, 2016 Objectives: 1. To explain the basic ideas of GA/GP: evolution of a population; fitness, crossover, mutation Materials: 1. Genetic NIM learner
CPS331 Lecture: Genetic Algorithms last revised October 28, 2016 Objectives: 1. To explain the basic ideas of GA/GP: evolution of a population; fitness, crossover, mutation Materials: 1. Genetic NIM learner
Lecture 10: Memetic Algorithms - I. An Introduction to Meta-Heuristics, Produced by Qiangfu Zhao (Since 2012), All rights reserved
 Lecture 10: Memetic Algorithms - I Lec10/1 Contents Definition of memetic algorithms Definition of memetic evolution Hybrids that are not memetic algorithms 1 st order memetic algorithms 2 nd order memetic
Lecture 10: Memetic Algorithms - I Lec10/1 Contents Definition of memetic algorithms Definition of memetic evolution Hybrids that are not memetic algorithms 1 st order memetic algorithms 2 nd order memetic
(Beijing, China,25 May2017)
 Remarks by the Secretary General of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), Dr. Fang Liu, to the First Session of the 2017 China Civil Aviation Development Forum: New Opportunities for Aviation
Remarks by the Secretary General of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), Dr. Fang Liu, to the First Session of the 2017 China Civil Aviation Development Forum: New Opportunities for Aviation
Next Factor in Drake Equation: f c!
 Cultural Evolution Next Factor in Drake Equation: f c f c : fraction of planets with intelligent life that develop a technological phase, during which there is a capability for and interest in interstellar
Cultural Evolution Next Factor in Drake Equation: f c f c : fraction of planets with intelligent life that develop a technological phase, during which there is a capability for and interest in interstellar
AHMEDABAD INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL PROGRAMME OF INQUIRY Grade K1 How the world works
 Grade K1 nature Family and Friends Relationships with family and friends contribute to shaping our identity All About Materials Materials are used to build and create ways 100 Languages People use different
Grade K1 nature Family and Friends Relationships with family and friends contribute to shaping our identity All About Materials Materials are used to build and create ways 100 Languages People use different
Optimization of Tile Sets for DNA Self- Assembly
 Optimization of Tile Sets for DNA Self- Assembly Joel Gawarecki Department of Computer Science Simpson College Indianola, IA 50125 joel.gawarecki@my.simpson.edu Adam Smith Department of Computer Science
Optimization of Tile Sets for DNA Self- Assembly Joel Gawarecki Department of Computer Science Simpson College Indianola, IA 50125 joel.gawarecki@my.simpson.edu Adam Smith Department of Computer Science
SOCI 101 Principles of Social Organizations
 SOCI 101 Principles of Social Organizations Session 8 SOCIETY, SOCIAL INTERACTION AND SOCIAL STRUCTURE Lecturer: Dr. Dan-Bright S. Dzorgbo, UG Contact Information: ddzorgbo@ug.edu.gh College of Education
SOCI 101 Principles of Social Organizations Session 8 SOCIETY, SOCIAL INTERACTION AND SOCIAL STRUCTURE Lecturer: Dr. Dan-Bright S. Dzorgbo, UG Contact Information: ddzorgbo@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Carl Mosk Economics 328, Fall Economic History of the Pacific Rim [13967] Course Outline and Reading List
![Carl Mosk Economics 328, Fall Economic History of the Pacific Rim [13967] Course Outline and Reading List Carl Mosk Economics 328, Fall Economic History of the Pacific Rim [13967] Course Outline and Reading List](/thumbs/86/93078241.jpg) Department of Economics University of Victoria Carl Mosk Economics 328, Fall 2011 Economic History of the Pacific Rim [13967] Course Outline and Reading List [I] Introduction This is a course dealing with
Department of Economics University of Victoria Carl Mosk Economics 328, Fall 2011 Economic History of the Pacific Rim [13967] Course Outline and Reading List [I] Introduction This is a course dealing with
Unified Growth Theory and Comparative Economic Development. Oded Galor. AEA Continuing Education Program
 Unified Growth Theory and Comparative Economic Development Oded Galor AEA Continuing Education Program Lecture II AEA 2014 Unified Growth Theory and Comparative Economic Development Oded Galor AEA Continuing
Unified Growth Theory and Comparative Economic Development Oded Galor AEA Continuing Education Program Lecture II AEA 2014 Unified Growth Theory and Comparative Economic Development Oded Galor AEA Continuing
Smart Automatic Level Control For improved repeater integration in CDMA and WCDMA networks
 Smart Automatic Level Control For improved repeater integration in CDMA and WCDMA networks The most important thing will build is trust Smart Automatic Level Control (SALC) Abstract The incorporation of
Smart Automatic Level Control For improved repeater integration in CDMA and WCDMA networks The most important thing will build is trust Smart Automatic Level Control (SALC) Abstract The incorporation of
ty of solutions to the societal needs and problems. This perspective links the knowledge-base of the society with its problem-suite and may help
 SUMMARY Technological change is a central topic in the field of economics and management of innovation. This thesis proposes to combine the socio-technical and technoeconomic perspectives of technological
SUMMARY Technological change is a central topic in the field of economics and management of innovation. This thesis proposes to combine the socio-technical and technoeconomic perspectives of technological
Digital Media and Legal Narrative, Three Teaching Ideas: Non linearity Memes Emergence
 Digital Media and Legal Narrative, Three Teaching Ideas: Non linearity Memes Emergence Professor Lucy Jewel Applied Legal Storytelling Conference July 9, 2011 Non Linear Approaches to Narrative Digital
Digital Media and Legal Narrative, Three Teaching Ideas: Non linearity Memes Emergence Professor Lucy Jewel Applied Legal Storytelling Conference July 9, 2011 Non Linear Approaches to Narrative Digital
IB/Primary Years Programme: Programme of Inquiry Marshpoint Elementary School, Savannah, Georgia. How we express ourselves.
 K self; beliefs and values; personal, physical, mental, social and spiritual health; human relationships including families, friends, communities, and cultures; rights and responsibilities; what it means
K self; beliefs and values; personal, physical, mental, social and spiritual health; human relationships including families, friends, communities, and cultures; rights and responsibilities; what it means
Sequential Dynamical System Game of Life
 Sequential Dynamical System Game of Life Mi Yu March 2, 2015 We have been studied sequential dynamical system for nearly 7 weeks now. We also studied the game of life. We know that in the game of life,
Sequential Dynamical System Game of Life Mi Yu March 2, 2015 We have been studied sequential dynamical system for nearly 7 weeks now. We also studied the game of life. We know that in the game of life,
Innovation and Inclusive Growth in Emerging Economies. Poh Kam Wong Professor, NUS Business School Director, NUS Entrepreneurship Centre
 Innovation and Inclusive Growth in Emerging Economies Poh Kam Wong Professor, NUS Business School Director, NUS Entrepreneurship Centre Outline Innovation and Inclusive Growth in the context of Emerging
Innovation and Inclusive Growth in Emerging Economies Poh Kam Wong Professor, NUS Business School Director, NUS Entrepreneurship Centre Outline Innovation and Inclusive Growth in the context of Emerging
Creating a Poker Playing Program Using Evolutionary Computation
 Creating a Poker Playing Program Using Evolutionary Computation Simon Olsen and Rob LeGrand, Ph.D. Abstract Artificial intelligence is a rapidly expanding technology. We are surrounded by technology that
Creating a Poker Playing Program Using Evolutionary Computation Simon Olsen and Rob LeGrand, Ph.D. Abstract Artificial intelligence is a rapidly expanding technology. We are surrounded by technology that
Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing: Fuzzy Sets. Chapter 1 of Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing by Jang, Sun and Mizutani
 Chapter 1 of Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing by Jang, Sun and Mizutani Outline Introduction Soft Computing (SC) vs. Conventional Artificial Intelligence (AI) Neuro-Fuzzy (NF) and SC Characteristics 2 Introduction
Chapter 1 of Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing by Jang, Sun and Mizutani Outline Introduction Soft Computing (SC) vs. Conventional Artificial Intelligence (AI) Neuro-Fuzzy (NF) and SC Characteristics 2 Introduction
Syllabus Science for Teachers ST 589 Semiconductors for Teachers
 Syllabus Science for Teachers ST 589 Semiconductors for Teachers Two Credit Hours Prerequisites: ST 526-Survey of Physics, and ST 550-Math for Teachers, or passing scores on their placement tests, or consent
Syllabus Science for Teachers ST 589 Semiconductors for Teachers Two Credit Hours Prerequisites: ST 526-Survey of Physics, and ST 550-Math for Teachers, or passing scores on their placement tests, or consent
Econ 911 Midterm Exam. Greg Dow February 27, Please answer all questions (they have equal weight).
 Econ 911 Midterm Exam Greg Dow February 27, 2013 Please answer all questions (they have equal weight). 1. Consider the Upper Paleolithic economy and the modern Canadian economy. What are the main ways
Econ 911 Midterm Exam Greg Dow February 27, 2013 Please answer all questions (they have equal weight). 1. Consider the Upper Paleolithic economy and the modern Canadian economy. What are the main ways
UDIS Programme of Inquiry
 UDIS Programme of Inquiry This is the school s programme of inquiry. These units are used at every level of the school from Preschool to Year 6. For both K1/K2, Y1/2 and Y3/4 each set of classes shares
UDIS Programme of Inquiry This is the school s programme of inquiry. These units are used at every level of the school from Preschool to Year 6. For both K1/K2, Y1/2 and Y3/4 each set of classes shares
POPULAT A ION DYNAMICS
 POPULATION DYNAMICS POPULATIONS Population members of one species living and reproducing in the same region at the same time. Community a number of different populations living together in the one area.
POPULATION DYNAMICS POPULATIONS Population members of one species living and reproducing in the same region at the same time. Community a number of different populations living together in the one area.
Footscray Primary School Whole School Programme of Inquiry 2017
 Footscray Primary School Whole School Programme of Inquiry 2017 Foundation nature People s awareness of their characteristics, abilities and interests shape who they are and how they learn. Physical, social
Footscray Primary School Whole School Programme of Inquiry 2017 Foundation nature People s awareness of their characteristics, abilities and interests shape who they are and how they learn. Physical, social
Evolution of Technology:
 Evolution of Technology Brent Silby 1 Evolution of Technology: Exposing the Myth of Creative Design By BRENT SILBY Department of Philosophy, University of Canterbury, New Zealand Copyright Brent Silby
Evolution of Technology Brent Silby 1 Evolution of Technology: Exposing the Myth of Creative Design By BRENT SILBY Department of Philosophy, University of Canterbury, New Zealand Copyright Brent Silby
Relation Formation by Medium Properties: A Multiagent Simulation
 Relation Formation by Medium Properties: A Multiagent Simulation Hitoshi YAMAMOTO Science University of Tokyo Isamu OKADA Soka University Makoto IGARASHI Fuji Research Institute Toshizumi OHTA University
Relation Formation by Medium Properties: A Multiagent Simulation Hitoshi YAMAMOTO Science University of Tokyo Isamu OKADA Soka University Makoto IGARASHI Fuji Research Institute Toshizumi OHTA University
LAPPING FOR MIRROR-LIKE FINISH ON CYLINDRICAL INNER AND END SURFACES USING THE LATHE WITH LINEAR MOTOR
 Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, 1 lapping, linear motor lathe, mirror-like surface, high quality and productivity Aung Lwin MOE 1 Ikuo TANABE Tetsuro IYAMA 3 Fumiaki NASU LAPPING FOR MIRROR-LIKE
Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, 1 lapping, linear motor lathe, mirror-like surface, high quality and productivity Aung Lwin MOE 1 Ikuo TANABE Tetsuro IYAMA 3 Fumiaki NASU LAPPING FOR MIRROR-LIKE
Primary Years Programme - Programme of Inquiry
 Primary Years Programme - Programme of Inquiry nature of the ways in which we natural world and K 1 People are indedpendent in different ways. People are unique People can do things independently People
Primary Years Programme - Programme of Inquiry nature of the ways in which we natural world and K 1 People are indedpendent in different ways. People are unique People can do things independently People
Chapter 1: Introduction to Neuro-Fuzzy (NF) and Soft Computing (SC)
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Neuro-Fuzzy (NF) and Soft Computing (SC) Introduction (1.1) SC Constituants and Conventional Artificial Intelligence (AI) (1.2) NF and SC Characteristics (1.3) Jyh-Shing Roger
Chapter 1: Introduction to Neuro-Fuzzy (NF) and Soft Computing (SC) Introduction (1.1) SC Constituants and Conventional Artificial Intelligence (AI) (1.2) NF and SC Characteristics (1.3) Jyh-Shing Roger
Evolution of Sensor Suites for Complex Environments
 Evolution of Sensor Suites for Complex Environments Annie S. Wu, Ayse S. Yilmaz, and John C. Sciortino, Jr. Abstract We present a genetic algorithm (GA) based decision tool for the design and configuration
Evolution of Sensor Suites for Complex Environments Annie S. Wu, Ayse S. Yilmaz, and John C. Sciortino, Jr. Abstract We present a genetic algorithm (GA) based decision tool for the design and configuration
Machine Learning in Iterated Prisoner s Dilemma using Evolutionary Algorithms
 ITERATED PRISONER S DILEMMA 1 Machine Learning in Iterated Prisoner s Dilemma using Evolutionary Algorithms Department of Computer Science and Engineering. ITERATED PRISONER S DILEMMA 2 OUTLINE: 1. Description
ITERATED PRISONER S DILEMMA 1 Machine Learning in Iterated Prisoner s Dilemma using Evolutionary Algorithms Department of Computer Science and Engineering. ITERATED PRISONER S DILEMMA 2 OUTLINE: 1. Description
Responsibility in Wealth
 Responsibility in Wealth The Kaiser Partner Special Report Series Issue #1/June 2012 With great wealth comes great responsibility. Introduction At Kaiser Partner, we understand that the world is changing
Responsibility in Wealth The Kaiser Partner Special Report Series Issue #1/June 2012 With great wealth comes great responsibility. Introduction At Kaiser Partner, we understand that the world is changing
The Global in the social science and humanities
 The Global in the social science and humanities Well, I hope Dave and I did not throw too much at you in the first day of class! My objective on the first day was to introduce some basic themes that we
The Global in the social science and humanities Well, I hope Dave and I did not throw too much at you in the first day of class! My objective on the first day was to introduce some basic themes that we
AIM: WHAT WAS THE IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION?
 *COMMON CORE TASK* 10/07/13 AIM: WHAT WAS THE IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? Do Now: Collect Comparative Essays Hand out Common Core Task Common Core Task Did the benefits of the Industrial Revolution
*COMMON CORE TASK* 10/07/13 AIM: WHAT WAS THE IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? Do Now: Collect Comparative Essays Hand out Common Core Task Common Core Task Did the benefits of the Industrial Revolution
From the foundation of innovation to the future of innovation
 From the foundation of innovation to the future of innovation Once upon a time, firms used to compete mainly on products... Product portfolio matrixes for product diversification strategies The competitive
From the foundation of innovation to the future of innovation Once upon a time, firms used to compete mainly on products... Product portfolio matrixes for product diversification strategies The competitive
DBE and the eeconomy Arturo di Corinto Neil Rathbone
 DBE and the eeconomy Arturo di Corinto Neil Rathbone Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are the backbone of the European economy. Accounting for 99% of enterprises, Europe s 19 million SMEs are
DBE and the eeconomy Arturo di Corinto Neil Rathbone Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are the backbone of the European economy. Accounting for 99% of enterprises, Europe s 19 million SMEs are
Summer Assignment. Welcome to AP World History!
 Summer Assignment Welcome to AP World History! You have elected to participate in a college-level world history course that will broaden your understanding of the world, as well as prepare you to take
Summer Assignment Welcome to AP World History! You have elected to participate in a college-level world history course that will broaden your understanding of the world, as well as prepare you to take
The Medium is the Message is the Content: Meaning, Media, Communication and Information in Biosemiosis and Human Symbolic Communication
 1 The Medium is the Message is the Content: Meaning, Media, Communication and Information in Biosemiosis and Human Symbolic Communication Robert K. Logan logan@physics.utoronto.ca We wish to distinguish
1 The Medium is the Message is the Content: Meaning, Media, Communication and Information in Biosemiosis and Human Symbolic Communication Robert K. Logan logan@physics.utoronto.ca We wish to distinguish
A comparison of a genetic algorithm and a depth first search algorithm applied to Japanese nonograms
 A comparison of a genetic algorithm and a depth first search algorithm applied to Japanese nonograms Wouter Wiggers Faculty of EECMS, University of Twente w.a.wiggers@student.utwente.nl ABSTRACT In this
A comparison of a genetic algorithm and a depth first search algorithm applied to Japanese nonograms Wouter Wiggers Faculty of EECMS, University of Twente w.a.wiggers@student.utwente.nl ABSTRACT In this
Wright-Fisher Process. (as applied to costly signaling)
 Wright-Fisher Process (as applied to costly signaling) 1 Today: 1) new model of evolution/learning (Wright-Fisher) 2) evolution/learning costly signaling (We will come back to evidence for costly signaling
Wright-Fisher Process (as applied to costly signaling) 1 Today: 1) new model of evolution/learning (Wright-Fisher) 2) evolution/learning costly signaling (We will come back to evidence for costly signaling
Enacting Transformative Innovation Policy: A Comparative Study
 Enacting Transformative Innovation Policy: A Comparative Study Johan Schot - Director Science Policy Research Unit - SPRU University of Sussex @Johan_Schot Transformative Innovation Policy Consortium Aim
Enacting Transformative Innovation Policy: A Comparative Study Johan Schot - Director Science Policy Research Unit - SPRU University of Sussex @Johan_Schot Transformative Innovation Policy Consortium Aim
Planning Activity. Theme 1
 Planning Activity Theme 1 This document provides an example of a plan for one topic within Theme 1. This resource goes into more detail than is required in the specification but it provides some background
Planning Activity Theme 1 This document provides an example of a plan for one topic within Theme 1. This resource goes into more detail than is required in the specification but it provides some background
An Agent-Based Architecture for Large Virtual Landscapes. Bruno Fanini
 An Agent-Based Architecture for Large Virtual Landscapes Bruno Fanini Introduction Context: Large reconstructed landscapes, huge DataSets (eg. Large ancient cities, territories, etc..) Virtual World Realism
An Agent-Based Architecture for Large Virtual Landscapes Bruno Fanini Introduction Context: Large reconstructed landscapes, huge DataSets (eg. Large ancient cities, territories, etc..) Virtual World Realism
ENHANCED HUMAN-AGENT INTERACTION: AUGMENTING INTERACTION MODELS WITH EMBODIED AGENTS BY SERAFIN BENTO. MASTER OF SCIENCE in INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 BY SERAFIN BENTO MASTER OF SCIENCE in INFORMATION SYSTEMS Edmonton, Alberta September, 2015 ABSTRACT The popularity of software agents demands for more comprehensive HAI design processes. The outcome of
BY SERAFIN BENTO MASTER OF SCIENCE in INFORMATION SYSTEMS Edmonton, Alberta September, 2015 ABSTRACT The popularity of software agents demands for more comprehensive HAI design processes. The outcome of
Global Intelligence. Neil Manvar Isaac Zafuta Word Count: 1997 Group p207.
 Global Intelligence Neil Manvar ndmanvar@ucdavis.edu Isaac Zafuta idzafuta@ucdavis.edu Word Count: 1997 Group p207 November 29, 2011 In George B. Dyson s Darwin Among the Machines: the Evolution of Global
Global Intelligence Neil Manvar ndmanvar@ucdavis.edu Isaac Zafuta idzafuta@ucdavis.edu Word Count: 1997 Group p207 November 29, 2011 In George B. Dyson s Darwin Among the Machines: the Evolution of Global
Supplemental Lab. EXTINCTION GAME
 Extinction Game 1 Supplemental Lab. EXTINCTION GAME Refer to the Extinction: The Game of Ecology (S.P. Hubbell, Sinauer Associates, Inc.) manual for more details. A. Introduction The Extinction board game
Extinction Game 1 Supplemental Lab. EXTINCTION GAME Refer to the Extinction: The Game of Ecology (S.P. Hubbell, Sinauer Associates, Inc.) manual for more details. A. Introduction The Extinction board game
Environmental Science: Your World, Your Turn 2011
 A Correlation of To the Milwaukee Public School Learning Targets for Science & Wisconsin Academic Model Content and Performance Standards INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how Science meets the Milwaukee
A Correlation of To the Milwaukee Public School Learning Targets for Science & Wisconsin Academic Model Content and Performance Standards INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how Science meets the Milwaukee
Mehrdad Amirghasemi a* Reza Zamani a
 The roles of evolutionary computation, fitness landscape, constructive methods and local searches in the development of adaptive systems for infrastructure planning Mehrdad Amirghasemi a* Reza Zamani a
The roles of evolutionary computation, fitness landscape, constructive methods and local searches in the development of adaptive systems for infrastructure planning Mehrdad Amirghasemi a* Reza Zamani a
Andrew Danziger December 5, 2011 HIS 480 Dr. Jones West Chester s Second First Radio Station WCOJ established itself in West Chester in 1950 as West C
 Andrew Danziger December 5, 2011 HIS 480 Dr. Jones West Chester s Second First Radio Station WCOJ established itself in West Chester in 1950 as West Chester s first radio station, but in 1963 WCHE was
Andrew Danziger December 5, 2011 HIS 480 Dr. Jones West Chester s Second First Radio Station WCOJ established itself in West Chester in 1950 as West Chester s first radio station, but in 1963 WCHE was
Concepts and Challenges
 Concepts and Challenges LIFE Science Globe Fearon Correlated to Pennsylvania Department of Education Academic Standards for Science and Technology Grade 7 3.1 Unifying Themes A. Explain the parts of a
Concepts and Challenges LIFE Science Globe Fearon Correlated to Pennsylvania Department of Education Academic Standards for Science and Technology Grade 7 3.1 Unifying Themes A. Explain the parts of a
An Idea for a Project A Universe for the Evolution of Consciousness
 An Idea for a Project A Universe for the Evolution of Consciousness J. D. Horton May 28, 2010 To the reader. This document is mainly for myself. It is for the most part a record of some of my musings over
An Idea for a Project A Universe for the Evolution of Consciousness J. D. Horton May 28, 2010 To the reader. This document is mainly for myself. It is for the most part a record of some of my musings over
Statement by Ms. Shamika N. Sirimanne Director Division on Technology and Logistics and Head CSTD Secretariat
 Presentation of the Report of the Secretary-General on Progress made in the implementation of and follow-up to the outcomes of the World Summit of the Information Society at the regional and international
Presentation of the Report of the Secretary-General on Progress made in the implementation of and follow-up to the outcomes of the World Summit of the Information Society at the regional and international
Social Studies: RESOURCES
 Social Studies Key Themes: Grade 8 To be productive members of society, students must be critical consumers of information they read, hear, and observe and communicate effectively about their ideas. They
Social Studies Key Themes: Grade 8 To be productive members of society, students must be critical consumers of information they read, hear, and observe and communicate effectively about their ideas. They
STRANDS KEY CONCEPTS BENCHMARKS GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS. Grade 8 Science Assessment Structure
 Grade 8 Science Assessment Structure The grade 8 LEAP test continues to assess Louisiana s science benchmarks. The design of the test remains the same as in previous administrations. The purpose of this
Grade 8 Science Assessment Structure The grade 8 LEAP test continues to assess Louisiana s science benchmarks. The design of the test remains the same as in previous administrations. The purpose of this
Handout 6 Enhancement and Human Development David W. Agler, Last Updated: 4/12/2014
 1. Introduction This handout is based on pp.35-52 in chapter 2 ( Enhancement and Human Development ) of Allen Buchanan s 2011 book Beyond Humanity? The Ethics of Biomedical Enhancement. This chapter focuses
1. Introduction This handout is based on pp.35-52 in chapter 2 ( Enhancement and Human Development ) of Allen Buchanan s 2011 book Beyond Humanity? The Ethics of Biomedical Enhancement. This chapter focuses
Towards a World in Common Strategy. #WorldInCommon
 Towards a World in Common 2018-2022 Strategy #WorldInCommon Our vision A World in Common AFD Group has a mission to help construct a world in common, a world that preserves and protects five important
Towards a World in Common 2018-2022 Strategy #WorldInCommon Our vision A World in Common AFD Group has a mission to help construct a world in common, a world that preserves and protects five important
Developing the Model
 Team # 9866 Page 1 of 10 Radio Riot Introduction In this paper we present our solution to the 2011 MCM problem B. The problem pertains to finding the minimum number of very high frequency (VHF) radio repeaters
Team # 9866 Page 1 of 10 Radio Riot Introduction In this paper we present our solution to the 2011 MCM problem B. The problem pertains to finding the minimum number of very high frequency (VHF) radio repeaters
Co-evolutionary of technologies, institutions and business strategies for a low carbon future
 Co-evolutionary of technologies, institutions and business strategies for a low carbon future Dr Timothy J Foxon Sustainability Research Institute, University of Leeds, Leeds, U.K. Complexity economics
Co-evolutionary of technologies, institutions and business strategies for a low carbon future Dr Timothy J Foxon Sustainability Research Institute, University of Leeds, Leeds, U.K. Complexity economics
AP World History SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP World History SCORING GUIDELINES Long Essay Question 2 In the period 1950 to 2001, scientific and technological innovations led to advances in communication, transportation, and industry that transformed
AP World History SCORING GUIDELINES Long Essay Question 2 In the period 1950 to 2001, scientific and technological innovations led to advances in communication, transportation, and industry that transformed
Summer Assignment. Due August 29, 2011
 Summer Assignment Welcome to AP World History! You have elected to participate in a college-level world history course that will broaden your understanding of the world, as well as prepare you to take
Summer Assignment Welcome to AP World History! You have elected to participate in a college-level world history course that will broaden your understanding of the world, as well as prepare you to take
BLUE ECONOMY DISCOURSES
 BLUE ECONOMY DISCOURSES Are we speaking the same language? Prof Lyn Snodgrass CMR April 2017. What do we mean by discourses, and Why are they important? What are these discourses? Verbal and written communication,
BLUE ECONOMY DISCOURSES Are we speaking the same language? Prof Lyn Snodgrass CMR April 2017. What do we mean by discourses, and Why are they important? What are these discourses? Verbal and written communication,
A Note on General Adaptation in Populations of Painting Robots
 A Note on General Adaptation in Populations of Painting Robots Dan Ashlock Mathematics Department Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa 511 danwell@iastate.edu Elizabeth Blankenship Computer Science Department
A Note on General Adaptation in Populations of Painting Robots Dan Ashlock Mathematics Department Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa 511 danwell@iastate.edu Elizabeth Blankenship Computer Science Department
Central Idea: People s beliefs influence their behaviour. Key concepts: perspective; reflection. Related concepts: diversity; perception
 Who we are An inquiry into the nature of the self; beliefs and values; personal, physical, mental, social and spiritual health; human relationships including families, friends, communities, and cultures;
Who we are An inquiry into the nature of the self; beliefs and values; personal, physical, mental, social and spiritual health; human relationships including families, friends, communities, and cultures;
The Behavior Evolving Model and Application of Virtual Robots
 The Behavior Evolving Model and Application of Virtual Robots Suchul Hwang Kyungdal Cho V. Scott Gordon Inha Tech. College Inha Tech College CSUS, Sacramento 253 Yonghyundong Namku 253 Yonghyundong Namku
The Behavior Evolving Model and Application of Virtual Robots Suchul Hwang Kyungdal Cho V. Scott Gordon Inha Tech. College Inha Tech College CSUS, Sacramento 253 Yonghyundong Namku 253 Yonghyundong Namku
Next Factor in Drake Equation: f c! Cultural Evolution! What is Cultural Evolution?! Example!
 Next Factor in Drake Equation: f c! Cultural Evolution! f c : fraction of planets with intelligent life that develop a technological phase, during which there is a capability for and interest in interstellar
Next Factor in Drake Equation: f c! Cultural Evolution! f c : fraction of planets with intelligent life that develop a technological phase, during which there is a capability for and interest in interstellar
CNC Thermal Compensation Based on Mind Evolutionary Algorithm Optimized BP Neural Network
 World Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2016, 4, 38-44 Published Online February 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjet.2016.41004 CNC Thermal Compensation
World Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2016, 4, 38-44 Published Online February 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjet.2016.41004 CNC Thermal Compensation
Module 2 WAVE PROPAGATION (Lectures 7 to 9)
 Module 2 WAVE PROPAGATION (Lectures 7 to 9) Lecture 9 Topics 2.4 WAVES IN A LAYERED BODY 2.4.1 One-dimensional case: material boundary in an infinite rod 2.4.2 Three dimensional case: inclined waves 2.5
Module 2 WAVE PROPAGATION (Lectures 7 to 9) Lecture 9 Topics 2.4 WAVES IN A LAYERED BODY 2.4.1 One-dimensional case: material boundary in an infinite rod 2.4.2 Three dimensional case: inclined waves 2.5
An Inquiry into Who We Are WWAIPAT How We Express Ourselves How the World Works How We Organize Ourselves
 PK Date: Key An Inquiry into Who We Are WWAIPAT How We Express How the World Works How We Organize September October November nature of the self; beliefs and values; personal, physical, mental, social,
PK Date: Key An Inquiry into Who We Are WWAIPAT How We Express How the World Works How We Organize September October November nature of the self; beliefs and values; personal, physical, mental, social,
Where we are in place & time
 Where we are in place & time How we express Pre School 3 5 years old nature of the self; mental, social and spiritual health; including families, friends, communities, and cultures; rights and responsibilities;
Where we are in place & time How we express Pre School 3 5 years old nature of the self; mental, social and spiritual health; including families, friends, communities, and cultures; rights and responsibilities;
Design and Development of an Optimized Fuzzy Proportional-Integral-Derivative Controller using Genetic Algorithm
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CONTROL, AUTOMATION, COMMUNICATION AND ENERGY CONSERVATION 2009, KEC/INCACEC/708 Design and Development of an Optimized Fuzzy Proportional-Integral-Derivative Controller using
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CONTROL, AUTOMATION, COMMUNICATION AND ENERGY CONSERVATION 2009, KEC/INCACEC/708 Design and Development of an Optimized Fuzzy Proportional-Integral-Derivative Controller using
Key Concept 6.1 Science and the Environment
 Key Concept 6.1 Science and the Environment Rapid advances in science altered the understanding of the universe and the natural world and led to the development of new technologies. These changes enabled
Key Concept 6.1 Science and the Environment Rapid advances in science altered the understanding of the universe and the natural world and led to the development of new technologies. These changes enabled
Generating Interesting Patterns in Conway s Game of Life Through a Genetic Algorithm
 Generating Interesting Patterns in Conway s Game of Life Through a Genetic Algorithm Hector Alfaro University of Central Florida Orlando, FL hector@hectorsector.com Francisco Mendoza University of Central
Generating Interesting Patterns in Conway s Game of Life Through a Genetic Algorithm Hector Alfaro University of Central Florida Orlando, FL hector@hectorsector.com Francisco Mendoza University of Central
CBSE Sample Paper-01 (Unsolved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SCIENCE (Theory) Class X. Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90
 General Instructions: CBSE Sample Paper-01 (Unsolved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SCIENCE (Theory) Class X Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90 a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper comprises
General Instructions: CBSE Sample Paper-01 (Unsolved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SCIENCE (Theory) Class X Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90 a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper comprises
New Hampshire College and Career Ready Standards Science Grade: 1 - Adopted: 2006
 Main Criteria: New Hampshire College and Career Ready Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 1 Correlation Options: Show Correlated New Hampshire College and Career Ready
Main Criteria: New Hampshire College and Career Ready Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 1 Correlation Options: Show Correlated New Hampshire College and Career Ready
